Interactive Effects of Inorganic–Organic Compounds on Passivation of Cadmium in Weakly Alkaline Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil and Amendments
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Interactions between Inorganic and Organic Components of Compound Amendments in Passivation of Cd
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
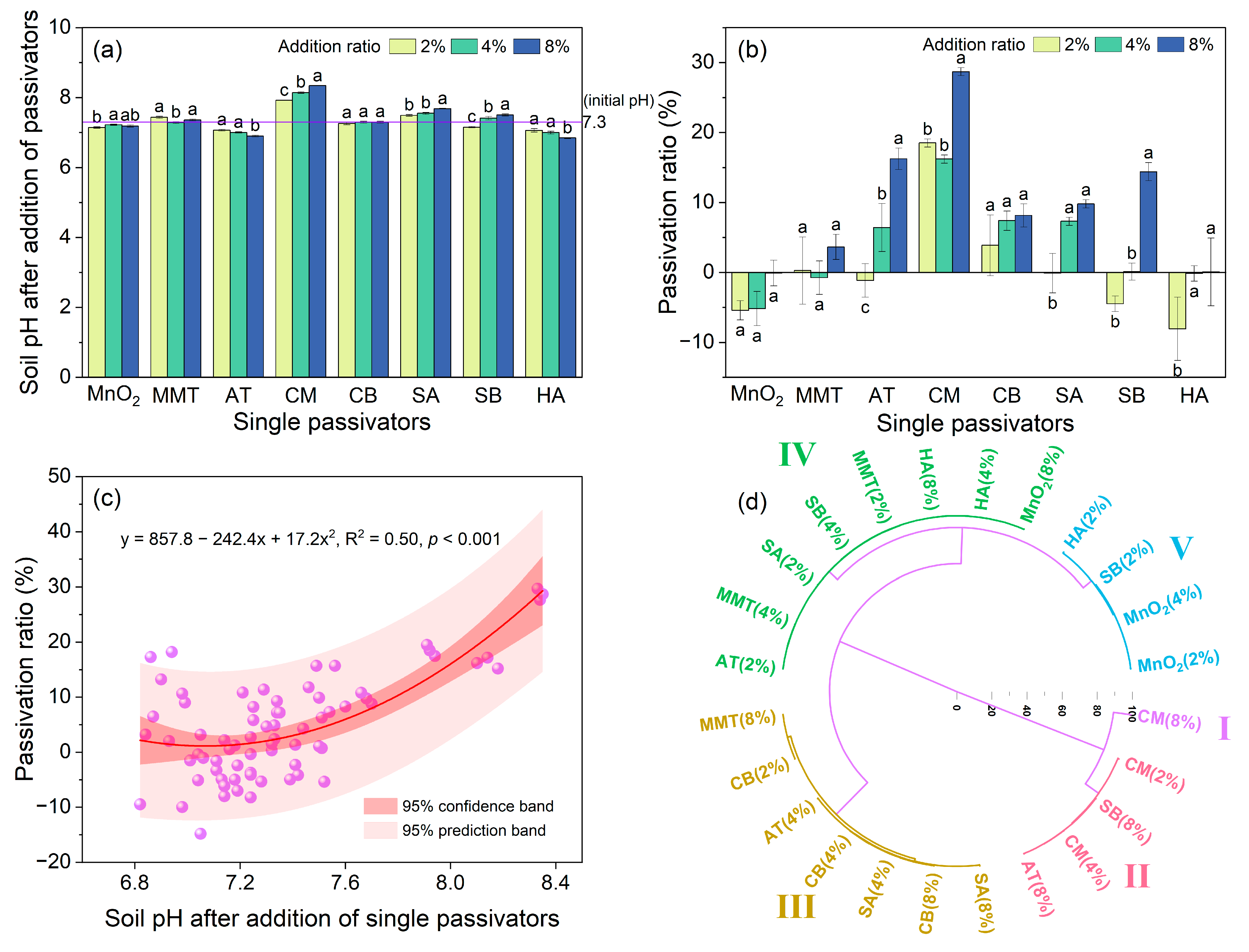
3.1. Effects of Single Amendments on Soil pH and Cd Availability
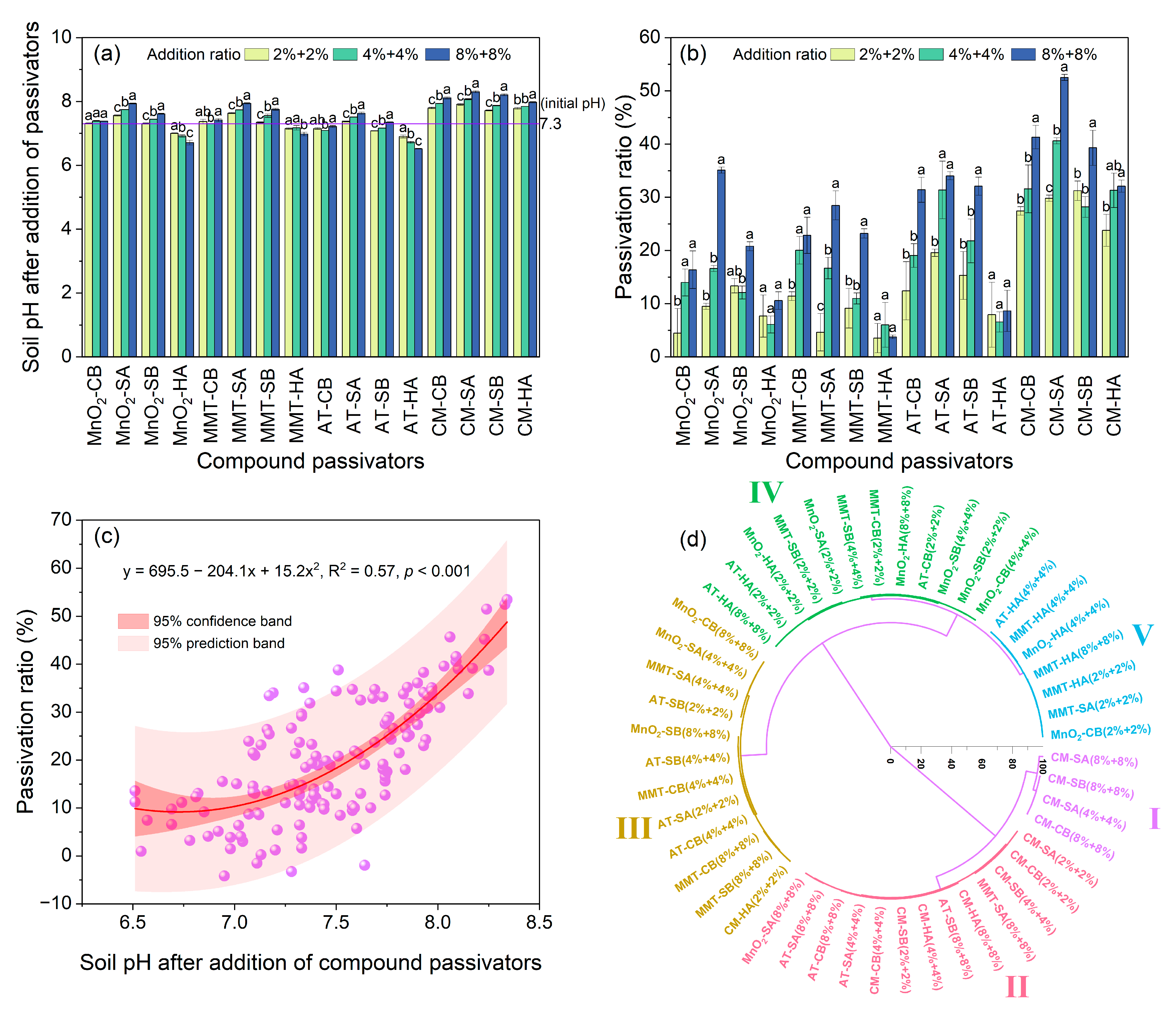
3.2. Effects of Inorganic–Organic Compound Amendments on Soil pH and Cd Availability
3.3. Interactions between Inorganic and Organic Components of Compound Amendments in Passivation of Cd
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Hu, R.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Lei, M.; Guo, G.; Shi, H.; Liao, X.; Chen, T. Challenges and opportunities for improving the environmental quality of cadmium-contaminated soil in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.Q.; Liu, L.J.; Ling, Q.; Cai, Y.W.; Yu, S.J.; Wang, S.Q.; Fu, D.; Hu, B.W.; Wang, X.K. Biochar for the removal of contaminants from soil and water: A review. Biochar 2022, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrelli, D.; Duri, L.G.; Fiorentino, N.; Cozzolino, E.; Fagnano, M.; Adamo, P. Potentially Toxic Element Availability and Risk Assessment of Cadmium Dietary Exposure after Repeated Croppings of Brassica juncea in a Contaminated Agricultural Soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, S.; Ni, W.; He, C.; Yang, Z. Agricultural Strategies to Reduce Cadmium Accumulation in Crops for Food Safety. Agriculture 2023, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.L.; Zhang, H.Z.F.; Hao, S.N.; Wang, L.Y.; Xu, W.X.; Mi, M.; Luo, Y.M.; He, Z.Y. Cadmium contamination in food crops: Risk assessment and control in smart age. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 1643–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, W.; Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, L. Effects of exogenous additives on wheat Cd accumulation, soil Cd availability and physicochemical properties in Cd-contaminated agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, X.; Duan, W.; Xie, M.; Dong, X. Heavy metal stabilization remediation in polluted soils with stabilizing materials: A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 4127–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Ma, Y.B.; Li, J.M.; Tahir, N.; Hussain, B. Effective Amendments on Cadmium, Arsenic, Chromium and Lead Contaminated Paddy Soil for Rice Safety. Agronomy 2020, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Sohail, M.I.; Cao, X.; Hussain, B.; Aziz, M.Z.; Usman, M.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X. An explanation of soil amendments to reduce cadmium phytoavailability and transfer to food chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattha, M.U.; Arif, W.; Khan, I.; Soufan, W.; Chattha, M.B.; Hassan, M.U.; Ullah, N.; El Sabagh, A.; Qari, S.H. Mitigation of Cadmium Induced Oxidative Stress by Using Organic Amendments to Improve the Growth and Yield of Mash Beans [Vigna mungo (L.)]. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.W.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.N.; Dilinuer, Y.; Pasang, L.; Lu, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, H.M.; Li, Z. Combination of Biochar and Phosphorus Solubilizing Bacteria to Improve the Stable Form of Toxic Metal Minerals and Microbial Abundance in Lead/Cadmium-Contaminated Soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Tian, Q.; Hou, R.; Wang, S. Combing phosphorus-modified hydrochar and zeolite prepared from coal gangue for highly effective immobilization of heavy metals in coal-mining contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrhman, F.; Gao, J.; Ali, U.; Wan, N.; Hu, H. Assessment of goethite-combined/modified biochar for cadmium and arsenic remediation in alkaline paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 40745–40754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, C.; Shen, K. Effects of biochars combined with ferrous sulfate and pig manure on the bioavailability of Cd and potential phytotoxicity for wheat in an alkaline contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Kang, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Lou, Y.; et al. Effects of a novel Cd passivation approach on soil Cd availability, plant uptake, and microbial activity in weakly alkaline soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dian, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Jiang, M. Solidification/stabilization of soil heavy metals by alkaline industrial wastes: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, B.; Jiao, L.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Sun, H. Preparation of ball-milled phosphorus-loaded biochar and its highly effective remediation for Cd- and Pb-contaminated alkaline soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xu, Y.; Sun, G.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, L. Application of ferromanganese functionalized biochar simultaneously reduces Cd and Pb uptake of wheat in contaminated alkaline soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Yang, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ma, J.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Jin, G.; Jia, J.; Zhong, B.; et al. Mitigation of Cd accumulation in rice with water management and calcium-magnesium phosphate fertilizer in field environment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Qiu, G. Remediation of cadmium-polluted weakly alkaline dryland soils using iron and manganese oxides for immobilized wheat uptake. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Hussain, B.; Usman, M.; Lin, Q.; Rashid, M.S.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E. Organic soil additives for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soils and their impact on the soil-plant system: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lu, T.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Qiu, G. Combined remediation effects of biochar, zeolite and humus on Cd-contaminated weakly alkaline soils in wheat farmland. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Ye, J.; Zhang, G.; Cai, Y. Simultaneous in-situ remediation and fertilization of Cd-contaminated weak-alkaline farmland for wheat production. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ren, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; He, Q.; Han, Z.; Meng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Factors regulating interaction among inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus species, plant uptake, and relevant cycling genes in a weakly alkaline soil treated with biochar and inorganic fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, N. Effect of crop residue ashes on sorption behavior of herbicides used in the succeeding crop in Indian soils. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skripkina, T.; Belokozenko, M.; Shatskaya, S.; Tikhova, V.; Lomovskiy, I. Concentrating rare earth elements in brown coal humic acids by mechanochemical treatment. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36016–36022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Fu, P.; Li, Z.; Ma, W. The evaluation of in-site remediation feasibility of Cd-contaminated soils with the addition of typical silicate wastes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, N.; Wen, J.; Liu, J.; Jiku, M.A.S.; Wu, C.; Su, S. The performance and mechanism of cadmium availability mitigation by biochars differ among soils with different pH: Hints for the reasonable choice of passivators. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Huang, Z. Effects of composite environmental materials on the passivation and biochemical effectiveness of Pb and Cd in soil: Analyses at the ex-planta of the Pak-choi root and leave. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Khan, Z.S.; Hafeez, M.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, K.; Asrar, M.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Ali, S. Foliar exposure of zinc oxide nanoparticles improved the growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and decreased cadmium concentration in grains under simultaneous Cd and water deficient stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.S.; Rizwan, M.; Hafeez, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Khalid, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Sarwar, M.A. Effects of silicon nanoparticles on growth and physiology of wheat in cadmium contaminated soil under different soil moisture levels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 4958–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatrice, A.; Varco, J.J.; Dygert, A.; Atsar, F.S.; Solomon, S.; Thirumalai, R.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T. Lead immobilization in simulated polluted soil by Douglas fir biochar-supported phosphate. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Jia, H. Crayfish shell biochar for the mitigation of Pb contaminated water and soil: Characteristics, mechanisms, and applications. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, P.; Mi, S.; Ali, A.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Guan, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Effects of crop straw and its derived biochar on the mobility and bioavailability in Cd and Zn in two smelter-contaminated alkaline soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Luo, D.; Yu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, G. Soil pH changes in a small catchment on the Chinese Loess Plateau after long-term vegetation rehabilitation. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.; Saeed, S.; Zhang, B.; Luo, M. The difference of soil properties between pure and mixed Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) plantations depends on tree species. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, Y. Changes in and evaluation of surface soil quality in Populus × xiaohei shelterbelts in midwestern Heilongjiang province, China. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Yu, H.; Chu, H.; Hu, M.; Xu, T.; Xu, X.; He, Z. The potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals using self-organizing map. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Moghaddam, V.; Latifi, P.; Darrudi, R.; Ghaleh Askari, S.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Marufi, N.; Javan, S. Heavy metal contaminated soil, water, and vegetables in northeastern Iran: Potential health risk factors. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, R.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liang, X.; Shen, L.; Li, B.; Ma, C.; Wang, N.; Yao, C.; et al. The use of mercapto-modified palygorskite prevents the bioaccumulation of cadmium in wheat. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 125917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X. Quantitative evaluation of the synergistic effect of biochar and plants on immobilization of Pb. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ye, M.; Tang, Z.; Jiao, T.; Song, X.; Pei, Y.; Liu, H. Using cluster analysis for understanding spatial and temporal patterns and controlling factors of groundwater geochemistry in a regional aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Lai, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, L. Phosphorus fertilization regimes and rates alter Cd extractability in rhizospheric soils and uptake in maize (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Ye, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z. A combined passivator of zeolite and calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer: Passivation behavior and mechanism for Cd (II) in composting. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodygin, E.D.; Alekseev, I.I.; Vasilevich, R.S.; Abakumov, E.V. Complexation of lead and cadmium ions with humic acids from arctic peat soils. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Ou, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, B.; Li, Y.; Bao, M. Additive grain-size: An innovative perspective to investigate the transformation among heavy metal and phosphorus fractions during aerobic composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Gao, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, X.; Fan, B.; Chen, Q. A meta-analysis of heavy metal bioavailability response to biochar aging: Importance of soil and biochar properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Fu, Q.; Hu, H.; Huang, Q. Mineralization of organic matter during the immobilization of heavy metals in polluted soil treated with minerals. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, W.; Xie, F. Removal of Cadmium(II) by hydrated manganese dioxide: Behaviour and mechanism at different pH. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 3544–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Yao, J.; Knudsen, T.S.; Liu, J.L.; Zhu, X.Z.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Liu, B. Performance and mechanisms for Cd(II) and As(III) simultaneous adsorption by goethite-loaded montmorillonite in aqueous solution and soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Adeel, M.; Chen, Q. Effects of magnesium ferrite biochar on the cadmium passivation in acidic soil and bioavailability for packoi (Brassica chinensis L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Wang, J.; Abbas, T.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, M.; Tahir, M.; Wu, D.; Di, H. Immobilization of exchangeable Cd in soil using mixed amendment and its effect on soil microbial communities under paddy upland rotation system. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.Q.; Zheng, S.Q.; Xiao, R.; Guo, Y. Effects of organic-inorganic amendments on the cadmium fraction in soil and its accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 13762–13772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Nie, N.; Liu, K.; Li, Q.; Cui, H.; Du, H. Analog soil organo–ferrihydrite composites as suitable amendments for cadmium and arsenic stabilization in co-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Wang, B.; Cui, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Sun, X.; Feng, Y. Clay-hydrochar composites return to cadmium contaminated paddy soil: Reduced Cd accumulation in rice seed and affected soil microbiome. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Wei, W.; Xu, C.; Meng, Y.; Bai, W.; Yang, W.; Lin, A. Manganese-modified biochar for highly efficient sorption of cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 9126–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.D.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.Q. Optimization and Modelling of Cd(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution with Composite Adsorbent Prepared from Alternanthera philoxeroides Biochar and Bentonite by Response Surface Methodology. Bioresources 2020, 15, 9413–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Du, Q.; Yang, F. Preparation of montmorillonite modified biochar with various temperatures and their mechanism for Zn ion removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 121692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, H.; Dong, M.; Zhang, Y. Stabilization of lead and cadmium in soil by sulfur-iron functionalized biochar: Performance, mechanisms and microbial community evolution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Synergistic mechanism and application of microbially induced carbonate precipitation (MICP) and inorganic additives for passivation of heavy metals in copper-nickel tailings. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Luo, H.Y.; Tie, B.Q.; Li, D.Y.; Liu, S.T.; Lei, M.; Du, H.H. The long-term effectiveness of ferromanganese biochar in soil Cd stabilization and reduction of Cd bioaccumulation in rice. Biochar 2021, 3, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.T.; Zhou, H.; Tang, S.F.; Zeng, P.; Gu, J.F.; Liao, B.H. Enhancing Cd(II) adsorption on rice straw biochar by modification of iron and manganese oxides. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, N.; Ahmed, T.; Noman, M.; Shahid, M.; Nazir, M.M.; Ali, L.; Alnusaire, T.S.; Li, B.; Schulin, R.; Wang, G. Iron oxide nanoparticles ameliorated the cadmium and salinity stresses in wheat plants, facilitating photosynthetic pigments and restricting cadmium uptake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Ouyang, X.; Weng, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Enhanced cadmium removal by biochar and iron oxides composite: Material interactions and pore structure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Ding, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, G.; Wang, X. Stability of immobilization remediation of several amendments on cadmium contaminated soils as affected by simulated soil acidification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, L.; Liu, J.; Deng, J.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Chen, Y. Earthworm-mediated nitrification and gut digestive processes facilitate the remobilization of biochar-immobilized heavy metals. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Li, W.-L.; Li, Q.-S.; Wang, L.-L.; He, T.; Wang, F.-P.; Xu, Z.-M. Nitrogen fertilizer management affects remobilization of the immobilized cadmium in soil and its accumulation in crop tissues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 31640–31652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, A.; Li, T.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Immobilization of Cd and Pb in a contaminated acidic soil amended with hydroxyapatite, bentonite, and biochar. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Amendments | pH | Cd Content (mg·kg−1) | Grain Size (mm) | Specific Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Total Organic Carbon (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manganese dioxide (MnO2) | 5.51 | 0.12 | <0.15 | 46.53 | ND 1 |
| Montmorillonite (MMT) | 6.50 | 0.05 | <0.15 | 39.62 | ND 1 |
| Attapulgite (AT) | 6.34 | 0.08 | <0.15 | 136.23 | ND 1 |
| Calcium–magnesium–phosphate fertilizer (CM) | 9.79 | 0.11 | <0.15 | ND 1 | ND 1 |
| Cow manure biochar (CB) | 6.85 | 0.17 | <0.15 | 4.79 | 34.5 |
| Straw ash (SA) | 9.52 | 0.15 | <0.15 | 1.47 | 18.2 |
| Straw biochar (SB) | 10.21 | 0.15 | <0.15 | 15.84 | 26.3 |
| Humic acid (HA) | 5.12 | 0.13 | <0.15 | 0.71 | 50.9 |
| Amendments 1 | Addition Ratio 2 | Cost 3 | Amendments 1 | Addition Ratio 2 | Cost 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnO2 | 2%, 4%, 8% | 4.32–17.26 | MMT-CB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 10.85–43.40 |
| MMT | 2%, 4%, 8% | 4.99–19.98 | MMT-SA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 6.23–24.91 |
| AT | 2%, 4%, 8% | 4.93–19.73 | MMT-SB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 11.16–44.64 |
| CM | 2%, 4%, 8% | 4.81–19.24 | MMT-HA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 10.05–40.20 |
| CB | 2%, 4%, 8% | 5.86–23.43 | AT-CB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 10.79–43.16 |
| SA | 2%, 4%, 8% | 1.23–4.93 | AT-SA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 6.17–24.66 |
| SB | 2%, 4%, 8% | 6.17–24.66 | AT-SB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 11.10–44.39 |
| HA | 2%, 4%, 8% | 5.06–20.22 | AT-HA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 9.99–39.95 |
| MnO2-CB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 10.17–40.69 | CM-CB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 10.67–42.66 |
| MnO2-SA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 5.55–22.19 | CM-SA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 6.04–24.17 |
| MnO2-SB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 10.48–41.92 | CM-SB | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 10.97–43.90 |
| MnO2-HA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 9.37–37.48 | CM-HA | 2% + 2%, 4% + 4%, 8% + 8% | 9.86–39.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, F.; Huang, Q.; Liu, L.; Fan, G.; Shi, G.; Lu, X.; Gao, Y. Interactive Effects of Inorganic–Organic Compounds on Passivation of Cadmium in Weakly Alkaline Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102647
Tong F, Huang Q, Liu L, Fan G, Shi G, Lu X, Gao Y. Interactive Effects of Inorganic–Organic Compounds on Passivation of Cadmium in Weakly Alkaline Soil. Agronomy. 2023; 13(10):2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102647
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Fei, Qin Huang, Lizhu Liu, Guangping Fan, Gaoling Shi, Xin Lu, and Yan Gao. 2023. "Interactive Effects of Inorganic–Organic Compounds on Passivation of Cadmium in Weakly Alkaline Soil" Agronomy 13, no. 10: 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102647
APA StyleTong, F., Huang, Q., Liu, L., Fan, G., Shi, G., Lu, X., & Gao, Y. (2023). Interactive Effects of Inorganic–Organic Compounds on Passivation of Cadmium in Weakly Alkaline Soil. Agronomy, 13(10), 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102647






