Bermudagrass Responses and Tolerance to Salt Stress by the Physiological, Molecular Mechanisms and Proteomic Perspectives of Salinity Adaptation
Abstract
1. Introduction
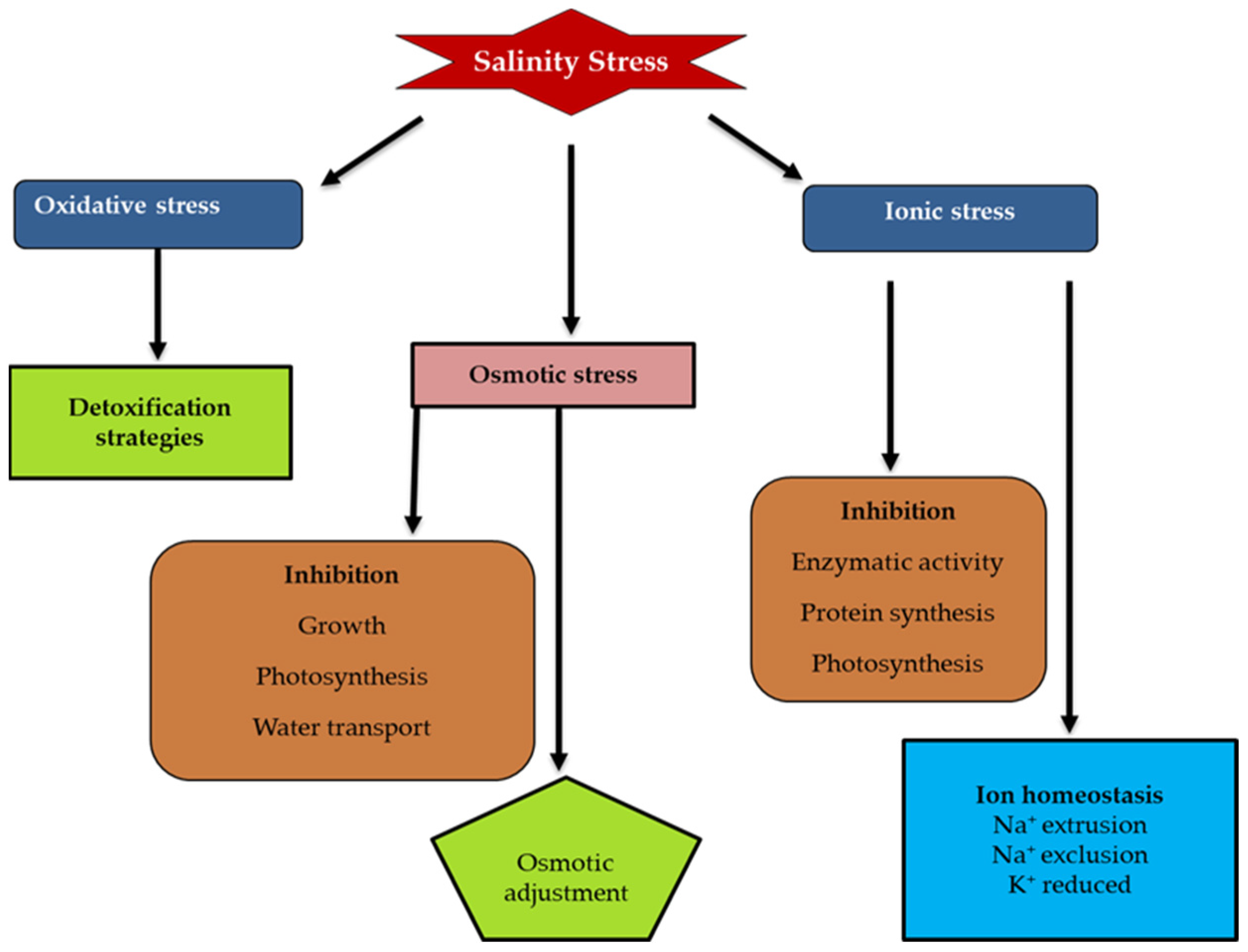
2. Effects of Salt Stress on Bermudagrass
3. Salt-Stress Responses in Bermudagrass
4. Morphological Responses

5. Anatomical Responses
6. Physiological and Metabolic Responses
7. Biochemical Responses
7.1. Antioxidant Enzyme System
7.2. Osmolytes
8. Molecular and Proteomic Responses
| Serial No | Gene Involved | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CdWRKY50 | Antioxidant activation, Cell membrane damage | [67] |
| 2 | COR, LEA, POD-1 | Protect plant from damage under salt stress | [78] |
| 3 | CdSOD1, CdPOD1, CdPOD2, CdCAT2 | Antioxidant activation, Oxidative stress | [79] |
| 4 | psbA1, psbB1, psbP, psbY, ECA4, RAN1, MHX1 | Ion-homeostasis, photosynthesis-related | [80] |
| 5 | BeDREB1, BeDREB2 | Role in signal transduction against salt stress | [81] |
| 6 | Cdt-NY-YC1 | Osmotic stress, ion leakage | [82] |
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| POD | Peroxide dismutase |
| APX | Ascorbate peroxidase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| DHAR | Dehydroascorbate reductase |
| PPO | Polyphenol oxidase |
| GPOX | Glutathione peroxidase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| SOS | Salt overly sensitive |
| NDPK | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase |
| LEA | Late embryogenesis abundant |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| Put | Putrescine |
| Spd | Spermidine |
| Spm | Spermine |
| CBF | C-repeat binding factors |
| TF | Transcription factors |
| COR | Cold-regulated |
References
- Hussain, S.; Shaukat, M.; Ashraf, M.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, J. Salinity Stress in Arid and Semi-Arid Climates: Effects and Management in Field Crops. Clim. Change Agric. 2019, 13, 197–222. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil processes affecting crop production in salt-affected soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, P.; Grazia, M.; Pontecorvo, G.; Fuggi, A.; Woodrow, P. Salinity Stress and Salt Tolerance. Abiotic Stress Plants Mech. Adapt. 2011, 1, 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X. Impacts of de-icing salt pollution on urban road greenspace: A case study of Beijing. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; DaCosta, M.; Jiang, Y. Research Advances in Mechanisms of Turfgrass Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses: From Physiology to Molecular Biology. CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2014, 33, 141–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, K.B.; Pessarakli, M. Salinity tolerance and salt gland excretion efficiency of bermudagrass turf cultivars. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 2571–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal Uddin, M.; Juraimi, A.S.; Ismail, M.R.; Othman, R.; Rahim, A.A. Relative salinity tolerance of warm season turfgrass species. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 309. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zong, J.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Effects of low nitrogen nutrition on plant growth characteristics and nitrogen accumulation in Chinese natural bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.) germplasm resources. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2018, 64, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, P. Regulation of plant responses to salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Pandey, V.C.; Singh, R.P. Cynodon dactylon: An efficient perennial grass to revegetate sodic lands. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Moss, J.Q.; Martin, D.L.; Su, K.; Dunn, B.L.; Wu, Y. Evaluating the salinity tolerance of clonal-type bermudagrass cultivars and an experimental selection. HortScience 2017, 52, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Moss, J.Q.; Martin, D.L.; Wu, Y. The salinity tolerance of seeded-type common bermudagrass cultivars and experimental selections. Horttechnology 2018, 28, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Fu, J. Growth response and gene expression in antioxidant-related enzymes in two bermudagrass genotypes differing in salt tolerance. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2012, 137, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, H.; Guo, A.; Liu, J. Growth responses and ion regulation of four warm season turfgrasses to long-term salinity stress. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zong, J.; Chen, Y.; Chu, X.; Liu, J. Variation in the salt-tolerance of 13 genotypes of hybrid bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. × C. transvaalensis Burtt-Davy] and its relationship with shoot Na+, K+, and Cl− ion concentrations. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudeck, A.E.; Singh, S.; Giordano, C.E.; Nell, T.A.; McConnell, D.B. Effects of Sodium Chloride on Cynodon Turfgrasses 1. Agron. J. 1983, 75, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunt, O.R.; Youngner, V.B.; Oertli, J.J. Salinity Tolerance of Five Turfgrass Varieties. Agron. J. 1961, 53, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertli, J.J.; Kohl, H.C. Some considerations about the tolerance of various plant species to excessive supplies of boron. Soil Sci. 1961, 92, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngner, V.B.; Lunt, O.R. Salinity Effects on Roots and Tops of Bermudagrass. Grass Forage Sci. 1967, 22, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.M.; Dietz, K.J. Salinity and crop yield. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tari, I.; Laskay, G.; Takács, Z.; Poór, P. Response of sorghum to abiotic stresses: A review. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2013, 199, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of Plant Responses and Adaptation to Soil Salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zong, J.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Guo, A.; Liu, J. Growth response and ion homeostasis in two bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance under salinity stress. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 65, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerson, R.C.; Youngner, V.B. Responses of Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) to Salinity. Agron. J. 1975, 67, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netondo, G.W.; Onyango, J.C.; Beck, E. Sorghum and salinity: I. Response of growth, water relations, and ion accumulation to NaCl salinity. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chakraborty, U. Role of sodium ion transporters and osmotic adjustments in stress alleviation of Cynodon dactylon under NaCl treatment: A parallel investigation with rice. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puyang, X.; An, M.; Xu, L.; Han, L.; Zhang, X. Protective effect of exogenous spermidine on ion and polyamine metabolism in Kentucky bluegrass under salinity stress. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 57, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, K.B.; Murdoch, C.L. Growth Responses, Ion Relations, and Osmotic Adaptations of Eleven C 4 Turfgrasses to Salinity. Agron. J. 1990, 85, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Bhaduri, D.; Meena, H.N.; Kalariya, K. External potassium (K+) application improves salinity tolerance by promoting Na+ exclusion, K+ accumulation and osmotic adjustment in contrasting peanut cultivars. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keisham, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhatla, S.C. Mechanisms of sodium transport in plants—Progresses and challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, N.; Hameed, M.; Wahid, A.; Arshad, M.; Aqeel Ahmad, M.S. Patterns of ion excretion and survival in two stoloniferous arid zone grasses. Physiol. Plant. 2009, 135, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Tabassum, J.; Fakhar, A.Z.; Sharif, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Ju, L.; Fotopoulos, V.; Siddique, K.H.; Singh, R.K.; et al. Smart reprograming of plants against salinity stress using modern biotechnological tools. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 12, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessarakli, M.; Touchane, H. Growth responses of bermudagrass and seashore paspalum under various levels of sodium chloride stress. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2006, 4, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Shahba, M.A. Erratum to Comparative Responses of Bermudagrass and Seashore Paspalum Cultivars Commonly Used in Egypt to Combat Salinity Stress. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2013, 51, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizhani, S.; Salehi, H. Physio-morphological and structural changes in common bermudagrass and Kentucky bluegrass during salt stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.; Singh, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salinity induced physiological and biochemical changes in plants: An omic approach towards salt stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, M.; Ashraf, M.; Naz, N.; Nawaz, T.; Batool, R.; Sajid Aqeel Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, F.; Hussain, M. Anatomical adaptations of Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. from the salt range (Pakistan) to salinity stress. II. leaf anatomy. Pak. J. Bot. 2013, 45, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, M.; Younis, A.; Riaz, A.; Hameed, M.; Nawaz, T.; Qasim, M. Growth response of some cultivars of bermuda grass (Cyanodon dactylon L.) to salt stress. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, R.K.; Sodani, R.; Chauhan, J.; Sharma, M.K.; Yashu, B.R. Physiological Adaptation and Tolerance Mechanism of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Multiple Abiotic Stresses. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 2017, 5, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.Y.; Akhtar, K.; Sarwar, G.; Ashraf, M. Evaluation of arid and semi-arid ecotypes of guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) for salinity (NaCl) tolerance. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 52, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, A.A.; Shahid, M.; Al-Maskri, A. Genetic diversity in the Batini barley landrace from Oman: II. Response to salinity stress. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A review on plant responses to salt stress and their mechanisms of salt resistance. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanin, M.; Ebel, C.; Ngom, M.; Laplaze, L.; Masmoudi, K. New insights on plant salt tolerance mechanisms and their potential use for breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.Q.; Chan, Z. Physiological and metabolomic responses of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) to alkali stress. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawazish, S.; Hameed, M.; Naurin, S. Leaf anatomical adaptations of Cenchrus ciliaris L. from the salt range, Pakistan against drought stress. Pak. J. Bot. 2006, 38, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, T.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Chan, Z. Contrasting changes caused by drought and submergence stresses in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon). Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Raihan, M.R.H.; Masud, A.A.C.; Rahman, K.; Nowroz, F.; Rahman, M.; Nahar, K.; Fujita, M. Regulation of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under salinity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Chan, Z. Contrasting proteomic and metabolomic responses of bermudagrass to drought and salt stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Amee, M.; Liu, D.; Chen, L. Salt-induced damage is alleviated by short-term pre-cold treatment in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon). Plants 2019, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Huang, B. Up-regulation of lipid metabolism and glycine betaine synthesis are associated with choline-induced salt tolerance in halophytic seashore paspalum. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Hu, T.; Zhang, X.; Pang, H.; Fu, J. Exogenous glycine betaine Ameliorates the adverse effect of salt stress on perennial ryegrass. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2012, 137, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Luo, H.J.; Fu, J.M. Toxic effect of NaCl on ion metabolism, antioxidative enzymes and gene expression of perennial ryegrass. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusvuran, S.; Kiran, S.; Ellialtioglu, S.S. Antioxidant enzyme activities and abiotic stress tolerance relationship in vegetable crops. Abiotic Biot. Stress Plants-Recent Adv. Future Perspect. 2016, 21, 481–506. [Google Scholar]
- Iwaniuk, P.; Lozowicka, B. Biochemical compounds and stress markers in lettuce upon exposure to pathogenic Botrytis cinerea and fungicides inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation. Planta 2022, 255, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Wang, F.; Luo, B.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Shabala, L.; Ahmed, H.A.I.; Deng, S.; Zhang, H.; Song, P.; et al. Antioxidant enzymatic activity and osmotic adjustment as components of the drought tolerance mechanism in Carex duriuscula. Plants 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abogadallah, G.M. Insights into the significance of antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal. behavior. 2010, 5, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Lou, Y.; Amombo, E.; Fu, J. Metabolic acclimation of source and sink tissues to salinity stress in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon). Physiol. Plant. 2015, 155, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, A.; Regalado, A.; Rodrigues, D.; Costa, J.M.; Blumwald, E.; Chaves, M.M.; Gerós, H. Polyols in grape berry: Transport and metabolic adjustments as a physiological strategy for water-deficit stress tolerance in grapevine. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 66, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, A.; Gitau, M.M.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.; Fu, J. Insights into the MicroRNA-regulated response of bermudagrass to cold and salt stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 145, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zong, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J. Genetic variation of salinity tolerance in Chinese natural bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.) germplasm resources. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2014, 64, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Peng, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Pang, C.; Fan, Z.; Wang, J. In vitro selection of salinity tolerant variants from triploid bermudagrass (Cynodon transvaalensis x C. dactylon) and their physiological responses to salt and drought stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahba, M.A. Interaction effects of salinity and mowing on performance and physiology of bermudagrass cultivars. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 2620–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ye, T.; Chan, Z. Comparative proteomic and physiological analyses reveal the protective effect of exogenous polyamines in the bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) response to salt and drought stresses. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4951–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, S.; Ye, N.; Jiang, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J. WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 59, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Ringler, P.; Shen, Q.J. WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Amee, M.; Chen, L. Bermudagrass CdWRKY50 gene negatively regulates plants’ response to salt stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 188, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fu, Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, W.; Yu, D. Arabidopsis thaliana WRKY25, WRKY26, and WRKY33 coordinate induction of plant thermotolerance. Planta 2011, 233, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Yu, D. Transcription factor WRKY75 interacts with DELLA proteins to affect flowering. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Horvath, E.; Bela, K.; Holinka, B.; Riyazuddin, R.; Galle, A.; Hajnal, A.; Hurton, A.; Feher, A.; Csiszar, J. The Arabidopsis Glutathione Transferases, Atgstf8 and Atgstu19 Are Involved in the Maintenance of Root Redox Homeostasis Affecting Meristem Size and Salt Stress Sensitivity. Plant Sci. 2019, 283, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.; Lee, B.; Choi, G.; Shin, D.; Theertha Prasad, D.; Lee, O.; Kwak, S.S.; Hoon Kim, D.; Nam, J.; Bahk, J.; et al. NDP kinase 2 interacts with two oxidative stress-activated MAPKs to regulate cellular redox state and enhances multiple stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verslues, P.E.; Batelli, G.; Grillo, S.; Agius, F.; Kim, Y.-S.; Zhu, J.; Agarwal, M.; Katiyar-Agarwal, S.; Zhu, J.-K. Interaction of SOS2 with Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase 2 and Catalases Reveals a Point of Connection between Salt Stress and H2O2 Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7771–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.D.; Choi, Y.I.; Park, S.C.; Yun, D.J.; Noh, E.W.; Lee, H.S.; Kwak, S.S. Transgenic poplar expressing Arabidopsis NDPK2 enhances growth as well as oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ye, T.; Chen, F.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, Z. Manipulation of arginase expression modulates abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis: Effect on arginine metabolism and ROS accumulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.T.; Chan, Z.L. In vivo role of Arabidopsis arginase in arginine metabolism and abiotic stress response. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e24138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tavladoraki, P.; Cona, A.; Federico, R.; Tempera, G.; Viceconte, N.; Saccoccio, S.; Battaglia, V.; Toninello, A.; Agostinelli, E. Polyamine catabolism: Target for antiproliferative therapies in animals and stress tolerance strategies in plants. Amino Acids. 2012, 42, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, A.; Wang, W.; Fan, S.; Xu, X.; Yin, Y.; Erick, A.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Fu, J. Comprehensive transcriptional analysis reveals salt stress-regulated key pathways, hub genes and time-specific responsive gene categories in common bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.) roots. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Hu, Z.; Bi, A.; Fan, J.; Gitau, M.M.; Amombo, E.; Chen, L.; Fu, J. Photosynthesis, antioxidant system and gene expression of bermudagrass in response to low temperature and salt stress. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ren, J.; Zhu, W.; Amombo, E.; Fu, J.; Chen, L. Antioxidant responses and gene expression in bermudagrass under cold stress. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 139, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S. Cloning and functional identification of stress-resistant BeDREB genes from Bermuda grass. Front. Biol. China 2006, 1, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuo, C.; Lu, S.; Guo, Z. Overexpression of a NF-YC transcription factor from bermudagrass confers tolerance to drought and salinity in transgenic rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y. Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in environmental stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, M.; Fan, J.-B.; Zhang, J.-X.; Zhang, C.-J.; Sun, S.-N.; Gan, L.; Yan, X.-B. Bermudagrass Responses and Tolerance to Salt Stress by the Physiological, Molecular Mechanisms and Proteomic Perspectives of Salinity Adaptation. Agronomy 2023, 13, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010174
Noor M, Fan J-B, Zhang J-X, Zhang C-J, Sun S-N, Gan L, Yan X-B. Bermudagrass Responses and Tolerance to Salt Stress by the Physiological, Molecular Mechanisms and Proteomic Perspectives of Salinity Adaptation. Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010174
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Maryam, Ji-Biao Fan, Jing-Xue Zhang, Chuan-Jie Zhang, Sheng-Nan Sun, Lu Gan, and Xue-Bing Yan. 2023. "Bermudagrass Responses and Tolerance to Salt Stress by the Physiological, Molecular Mechanisms and Proteomic Perspectives of Salinity Adaptation" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010174
APA StyleNoor, M., Fan, J.-B., Zhang, J.-X., Zhang, C.-J., Sun, S.-N., Gan, L., & Yan, X.-B. (2023). Bermudagrass Responses and Tolerance to Salt Stress by the Physiological, Molecular Mechanisms and Proteomic Perspectives of Salinity Adaptation. Agronomy, 13(1), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010174