Baseline Sensitivity to and Succinate Dehydrogenase Activity and Molecular Docking of Fluxapyroxad and SYP-32497 in Rice Sheath Blight (Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA) in China
Abstract
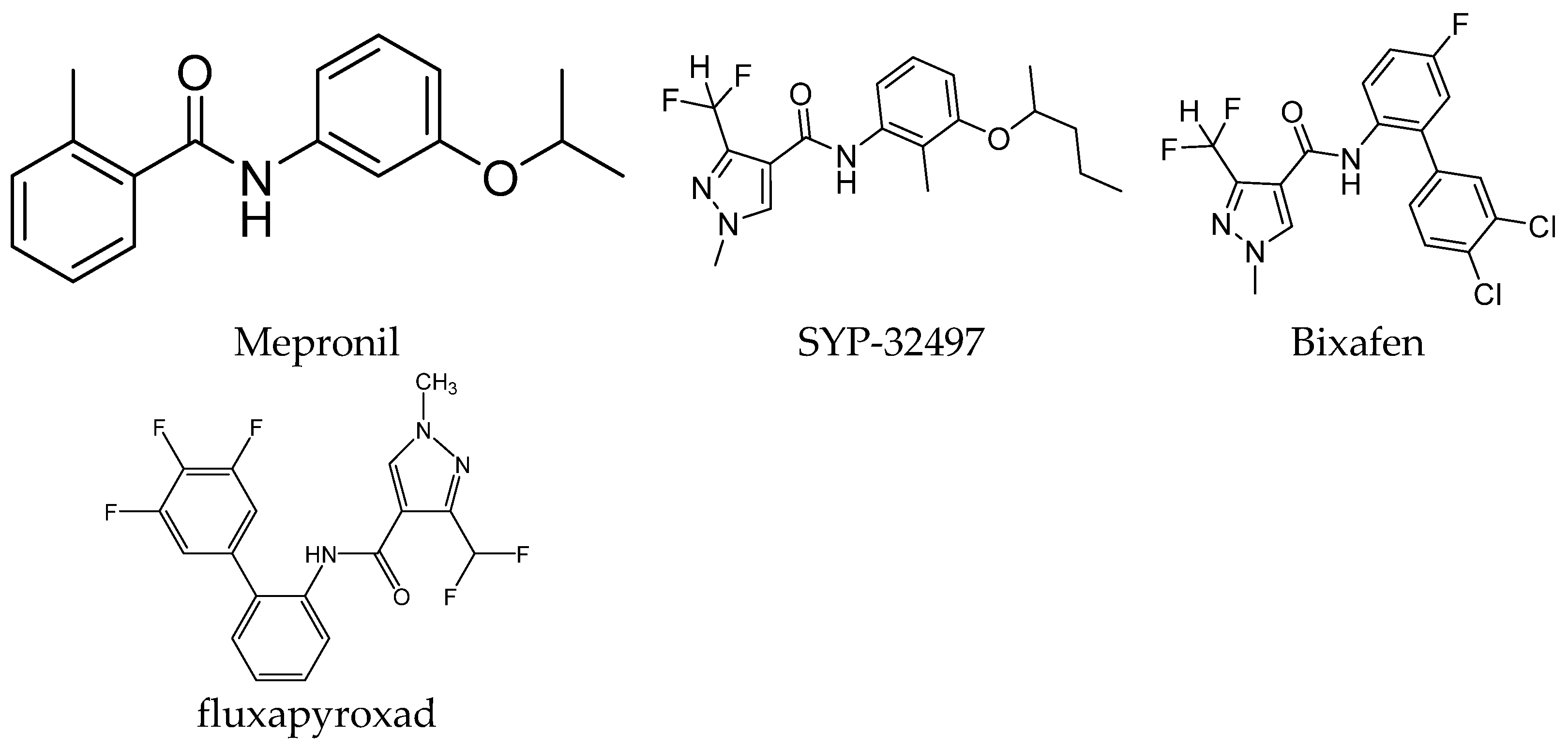
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains
2.2. Fungicides
2.3. Sensitivity of R. solani to SYP-32497 and Fluxapyroxad
2.4. Determination of Enzyme Efficiency
2.5. Molecular Docking
2.6. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Sensitivity of R. solani to SYP-32497 and Fluxapyroxad
3.2. Determination of Enzyme Efficiency
3.3. Molecular Docking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pareja, L.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Cesio, V.; Heinzen, H. Analytical methods for pesticide residues in rice. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 270–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Shu, B.S.; Sethuraman, V.; Zhong, G.H. Design, synthesis, fungicidal property and QSAR studies of novel beta-carbolines containing urea, benzoylthiourea and benzoylurea for the control of rice sheath blight. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moliszewska, E.; Nabrdalik, M.; Ziembik, Z. Rhizoctonia solani AG 11 isolated for the first time from sugar beet in Poland. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mazumdar, P.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Babu, S. Sheath blight of rice: A review and identification of priorities for future research. Planta 2019, 250, 1387–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, M.; Pujol, M.; Metraux, J.-P.; Gonzalez-Garcia, V.; Bolton, M.D.; Borrás-Hidalgo, O. Tobacco leaf spot and root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Mubeen, M.; Sohail, M.A.; Solanki, M.K.; Hussain, B.; Nosheen, S.; Kashyap, B.K.; Zhou, L.; Fang, X. Root rot a silent alfalfa killer in China: Distribution, fungal, and oomycete pathogens, impact of climatic factors and its management. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 961794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Jha, G. Identification and functional analysis of AG1-IA specific genes of Rhizoctonia solani. Curr. Genet. 2014, 60, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, A.; Lin, R.; Zhang, D.; Qin, P.; Xu, L.; Ai, P.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the rice sheath blight pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Shah, F.; Yao, F.; Peng, S. Sheath blight reduces stem breaking resistance and increases lodging susceptibility of rice plants. Field Crops Res. 2012, 128, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suharti, W.S.; Nose, A.; Zheng, S.H. Metabolomic study of two rice lines infected by Rhizoctonia solani in negative ion mode by CE/TOF-MS. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 206, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Ma, X.Y.; Feng, Z.; Ma, Z.H. Characterization of sensitivity of Rhizoctonia solani, causing rice sheath blight, to mepronil and boscalid. Crop Prot. 2009, 28, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Pozza, E.; Dando, I.; Pacchiana, R.; Liboi, E.; Scupoli, M.T.; Donadelli, M.; Palmieri, M. Regulation of succinate dehydrogenase and role of succinate in cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, B.; Berry, E.A.; Zhu, X.L.; Yang, W.C.; Yang, G.F. The assembly of succinate dehydrogenase: A key enzyme in bioenergetics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4023–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.J. Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)-deficient neoplasia. Histopathology 2018, 72, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.-Y.; Zhao, B.; Fan, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.-M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Kalinina, T.A.; Glukhareva, T.V. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Succinate Dehydrogenase Inhibitor Derivatives as Potent Fungicide Candidates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13185–13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.P.; Luo, J.; Li, B.X.; Song, Y.F.; Mu, W.; Liu, F. Bioactivity, physiological characteristics and efficacy of the SDHI fungicide pydiflumetofen against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 160, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Hayashi, K.; Okada, R.; Wari, D.; Ogawara, T. Resistance to succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors in field isolates of Podosphaera xanthii on cucumber: Monitoring, cross-resistance patterns and molecular characterization. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 169, 104646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, J.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Dong, B.; Qiao, K. Synergistic Effect of Combined Application of a New Fungicide Fluopimomide with a Biocontrol Agent Bacillus methylotrophicus TA-1 for Management of Gray Mold in Tomato. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Wand, G.; Wu, S.-S.; Shan, Z.-G.; Li, B. Synthesis and Fungicidal Activity of SYP-32497. Agrochemicals 2020, 59, 871–872. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, W.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Ni, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X. Sensitivity determination and resistance risk assessment of Rhizoctonia solani to SDHI fungicide thifluzamide. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2017, 170, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, A.-F.; Gao, T.-C. Sensitivity of Rhizoctonia solani causing rice sheath blight to fluxapyroxad in China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 140, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Matsuyama, N. Trials of direct detection and identification of Rhizoctonia solani, AG1 and AG2 subgroups using specifically primed PCR analysis. Mycoscience 2002, 43, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hederstedt, L.; Rutberg, L. Succinate Dehydrogenase—A Comparative Review. Microbiol. Rev. 1981, 45, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhu, F.; Sun, B.; Xie, X.; Chai, A.; Li, B. Two adjacent mutations in the conserved domain of SdhB confer various resistance phenotypes to fluopyram in Corynespora cassiicola. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3980–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; He, L.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. The relationship between features enabling SDHI fungicide binding to the Sc-Sdh complex and its inhibitory activity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Cui, P.; Bai, H.; Wei, S.; Li, S. Late-Stage C-H Functionalization of Nicotinamides for the Expedient Discovery of Novel Antifungal Leads. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11901–11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, H.; Shaw, M.W.; Mehenni-Ciz, J.; Spink, J.; Kildea, S. Detection of Zymoseptoria tritici SDHI-insensitive field isolates carrying the SdhC-H152R and SdhD-R47W substitutions. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 2203–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Cui, J.H.; Tian, B.H.; Cao, S.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, H.G. Resistance risk assessment for Fusarium graminearum to pydiflumetofen, a new succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardas, G.A.; Veloukas, T.; Koutita, O.; Karaoglanidis, G.S. Multiple resistance of Botrytis cinerea from kiwifruit to SDHIs, QoIs and fungicides of other chemical groups. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Ishii, H.; Stammler, G.; Koch, A.; Ogawara, T.; Tomita, Y.; Fountaine, J.M.; Ushio, S.; Seko, T.; Kobori, S. Distribution and molecular characterization of Corynespora cassiicola isolates resistant to boscalid. Plant Pathol. 2010, 59, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhou, J.; Pu, T.; Zhang, A.; Gao, X.; Tao, K.; Hou, T. Synthesis of novel fenfuram-diarylether hybrids as potent succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 73, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Y.; Li, W.K.; Meiler, J.; Zheng, Q.C.; Zhang, H.X. Insight on mutation-induced resistance to anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor ceritinib from molecular dynamics simulations. Biopolymers 2019, 110, e23257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierotzki, H.; Scalliet, G. A review of current knowledge of resistance aspects for the next-generation succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor fungicides. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Qu, X.P.; Wang, J.X.; Zhou, M.G. Effects of a novel SDHI fungicide pyraziflumid on the biology of the plant pathogenic fungi Bipolaris maydis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 149, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraaije, B.A.; Bayon, C.; Atkins, S.; Cools, H.J.; Lucas, J.A.; Fraaije, M.W. Risk assessment studies on succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors, the new weapons in the battle to control Septoria leaf blotch in wheat. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.; Mu, W.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Liu, X. Heterokaryotic state of a point mutation (H249Y) in SDHB protein drives the evolution of thifluzamide resistance in Rhizoctonia solani. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Xu, L.; Zeng, R.; Gao, P.; Song, Z.; Dai, F. Baseline sensitivity of Rhizoctonia solani to four DMI fungicides. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022, 62, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Gao, L.; Han, C.; Wu, X. Molecular Mechanisms Associated with the Resistance of Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 Isolates to the Succinate Dehydrogenase Inhibitor Thifluzamide. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.; Gai, X.; Sun, Y.; He, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Gao, Z. Transcriptomic evidence for involvement of reactive oxygen species in Rhizoctonia solani AG1 IA sclerotia maturation. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Region, Province | Coordinates | Number of Isolates and Code | SYP–32497 EC50 (μg mL−1) | Fluxapyroxad EC50 (μg mL−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | Range | Mean | |||
| Hefei, Anhui Province | E117.22 N31.82 | 3 HF | 0.00794–0.01976 | 0.01528 ± 0.00641 | 0.07680–0.10490 | 0.09367 ± 0.01487 |
| Tiaozhou, Anhui Province | E117.54 N32.93 | 12 TZ | 0.00085–0.01483 | 0.00426 ± 0.00423 | 0.04210–0.10140 | 0.06721 ± 0.02037 |
| Fengyang, Anhui Province | E117.82 N32.85 | 17 FY | 0.00079–0.00974 | 0.00268 ± 0.00239 | 0.00093–0.00804 | 0.04547 ± 0.02469 |
| Jixi, Heilongjiang Province | E132.40 N45.91 | 14 JX | 0.00105–0.00945 | 0.00397 ± 0.00244 | 0.03220–0.08680 | 0.06606 ± 0.01623 |
| Jiamusi, Heilongjiang Province | E130.89 N47.04 | 4 JMS | 0.00156–0.01745 | 0.01155 ± 0.00694 | 0.08070–0.12540 | 0.10015 ± 0.01856 |
| Haerbin, Heilongjiang Province | E127.03 N45.49 | 15 HEB | 0.00202–0.01073 | 0.00502 ± 0.00276 | 0.03500–0.09490 | 0.06315 ± 0.01663 |
| Xinyang, Henan Province | E114.21 N32.12 | 8 XY | 0.00149–0.01493 | 0.00870 ± 0.00398 | 0.05340–0.09670 | 0.08115 ± 0.01437 |
| Yanghe, Henan Province | E113.74 N32.44 | 4 YH | 0.00413–0.00769 | 0.00663 ± 0.00169 | 0.03780–0.12570 | 0.09825 ± 0.04064 |
| Xiaochang, Hubei Province | E113.97 N31.39 | 4 XC | 0.00555–0.01837 | 0.01446 ± 0.00606 | 0.09120–0.11120 | 0.09888 ± 0.00864 |
| Songzi, Hubei Province | E111.88 N30.18 | 3 SC | 0.00371–0.00775 | 0.00514 ± 0.00226 | 0.03850–0.07180 | 0.05050 ± 0.01850 |
| Yizhou, Hunan Province | E112.32 N28.93 | 13 YZ | 0.00125–0.01315 | 0.00535 ± 0.00343 | 0.03690–0.12400 | 0.08252 ± 0.02572 |
| Miluo, Hunan Province | E113.09 N28.89 | 2 ML | 0.00258–0.00585 | 0.00422 ± 0.00231 | 0.04980–0.06110 | 0.05545 ± 0.00799 |
| Inner Mongolia | E123.28 N46.71 | 9 XAM | 0.00445–0.01692 | 0.00952 ± 0.00454 | 0.05230–0.09480 | 0.07062 ± 0.01571 |
| Yancheng, Jiangsu Province | E119.89 N33.43 | 18 YCH | 0.00171–0.01871 | 0.00907 ± 0.00572 | 0.05160–0.12970 | 0.08518 ± 0.02194 |
| Nanjing, Jiangsu Province | E118.89 N32.04 | 11 NJ | 0.00093–0.00804 | 0.00452 ± 0.00231 | 0.03310–0.09510 | 0.05313 ± 0.01919 |
| Nanchang, Jiangxi Province | E115.64 N28.45 | 7 NC | 0.00082–0.00422 | 0.00241 ± 0.00120 | 0.02740–0.07090 | 0.04783 ± 0.01431 |
| Yichun, Jiangxi Province | E115.19 N28.02 | 2 YC | 0.01215–0.01228 | 0.01222 ± 0.00009 | 0.03770–0.05590 | 0.04680 ± 0.01287 |
| Gaoan, Jiangxi Province | E115.14 N28.47 | 9 GA | 0.00178–0.01723 | 0.00637 ± 0.00449 | 0.04060–0.07760 | 0.06131 ± 0.01275 |
| Xinjian, Jiangxi Province | E115.85 N28.69 | 5 XJ | 0.00273–0.01106 | 0.00655 ± 0.00354 | 0.04240–0.08890 | 0.06684 ± 0.02044 |
| Fuzhou, Jiangxi Province | E116.37 N28.01 | 7 FZ | 0.00192–0.01836 | 0.01115 ± 0.00705 | 0.01590–0.12780 | 0.07637 ± 0.04073 |
| Shuangliao, Jilin Province | E123.41 N43.52 | 12 SL | 0.00299–0.01957 | 0.00802 ± 0.00445 | 0.05010–0.11330 | 0.07340 ± 0.01824 |
| Changyi, Jilin Province | E126.40 N44.14 | 21 CY | 0.00155–0.01715 | 0.00820 ± 0.00489 | 0.05050–0.12540 | 0.07559 ± 0.02047 |
| Panshi, Jilin Province | E126.07 N42.95 | 9 PS | 0.00175–0.01419 | 0.00779 ± 0.00519 | 0.04260–0.10990 | 0.08222 ± 0.02303 |
| Gongzhuling, Jilin Province | E124.75 N43.46 | 9 GZL | 0.00132–0.01901 | 0.00959 ± 0.00529 | 0.03660–0.09760 | 0.07673 ± 0.01920 |
| Shenyang, Liaoning Province | E123.55 N41.97 | 10 SY | 0.00323–0.01746 | 0.00865 ± 0.00473 | 0.04540–0.10520 | 0.07091 ± 0.01844 |
| Fushun, Liaoning Province | E124.98 N41.75 | 4 FS | 0.00171–0.01309 | 0.00714 ± 0.00468 | 0.04620–0.08440 | 0.05838 ± 0.01781 |
| Tieling, Liaoning Province | E123.88 N42.32 | 33 TL | 0.00096–0.01716 | 0.00701 ± 0.00535 | 0.01680–0.09590 | 0.04333 ± 0.01932 |
| Xinmin, Liaoning Province | E122.90 N41.89 | 9 XM | 0.00100–0.00911 | 0.00491 ± 0.00260 | 0.02480–0.07980 | 0.05912 ± 0.01825 |
| Dandong, Liaoning Province | E123.9 N39.86 | 11 DD | 0.00330–0.01243 | 0.00665 ± 0.00329 | 0.03730–0.08500 | 0.05799 ± 0.01403 |
| Liaoyang, Liaoning Province | E123.10 N41.43 | 8 LY | 0.00085–0.00813 | 0.00409 ± 0.00269 | 0.03270–0.07080 | 0.05218 ± 0.01405 |
| Dalian, Liaoning Province | E122.84 N39.74 | 4 DL | 0.00252–0.00360 | 0.00286 ± 0.00051 | 0.04370–0.06100 | 0.05153 ± 0.00784 |
| Panjin, Liaoning Province | E122.19 N40.98 | 2 PJ | 0.00149–0.00190 | 0.00170 ± 0.00029 | 0.03890–0.05630 | 0.04760 ± 0.01230 |
| Yingkou, Liaoning Province | E122.19 N40.82 | 7 YK | 0.00275–0.01756 | 0.00720 ± 0.00583 | 0.03940–0.12970 | 0.07489 ± 0.02904 |
| Benxi, Liaoning Province | E125.30 N41.21 | 2 BX | 0.00256–0.00263 | 0.00260 ± 0.00005 | 0.04940–0.05770 | 0.05355 ± 0.00587 |
| Anshan, Liaoning Province | E122.73 N40.98 | 5 AS | 0.00587–0.00938 | 0.00714 ± 0.00146 | 0.05260–0.09040 | 0.07180 ± 0.01432 |
| Qingshen, Sichuan Province | E103.84 N29.83 | 2 QS | 0.00622–0.00765 | 0.00694 ± 0.00101 | 0.06780–0.09240 | 0.08010 ± 0.01739 |
| Tianjin | E117.61 N39.41 | 11 TJ | 0.00397–0.01586 | 0.00825 ± 0.00380 | 0.04350–0.10330 | 0.06325 ± 0.01933 |
| Jinhua, Zhejiang Province | E119.49 N29.07 | 16 JH | 0.00225–0.01810 | 0.00860 ± 0.00454 | 0.01680–0.12360 | 0.08876 ± 0.02787 |
| Jiaxing, Zhejiang Province | E120.75 N30.75 | 18 JXI | 0.00079–0.01222 | 0.00311 ± 0.00251 | 0.02–0.06840 | 0.03958 ± 0.01264 |
| Fungicides | Binding Free Energy (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|
| GB | PB | |
| SYP-32497 | −45.9022 | −36.8614 |
| Fluxapyroxad | −23.7088 | −19.2052 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, P.; Deng, Y.; Wang, T.; Qi, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, L.; Ji, M. Baseline Sensitivity to and Succinate Dehydrogenase Activity and Molecular Docking of Fluxapyroxad and SYP-32497 in Rice Sheath Blight (Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA) in China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123075
Zhao P, Deng Y, Wang T, Qi Z, Du Y, Liu L, Ji M. Baseline Sensitivity to and Succinate Dehydrogenase Activity and Molecular Docking of Fluxapyroxad and SYP-32497 in Rice Sheath Blight (Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA) in China. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123075
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ping, Yunyan Deng, Tao Wang, Zhiqiu Qi, Ying Du, Liru Liu, and Mingshan Ji. 2022. "Baseline Sensitivity to and Succinate Dehydrogenase Activity and Molecular Docking of Fluxapyroxad and SYP-32497 in Rice Sheath Blight (Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA) in China" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123075
APA StyleZhao, P., Deng, Y., Wang, T., Qi, Z., Du, Y., Liu, L., & Ji, M. (2022). Baseline Sensitivity to and Succinate Dehydrogenase Activity and Molecular Docking of Fluxapyroxad and SYP-32497 in Rice Sheath Blight (Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA) in China. Agronomy, 12(12), 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123075






