Carbon Dioxide Efflux of Bare Soil as a Function of Soil Temperature and Moisture Content under Weather Conditions of Warm, Temperate, Dry Climate Zone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
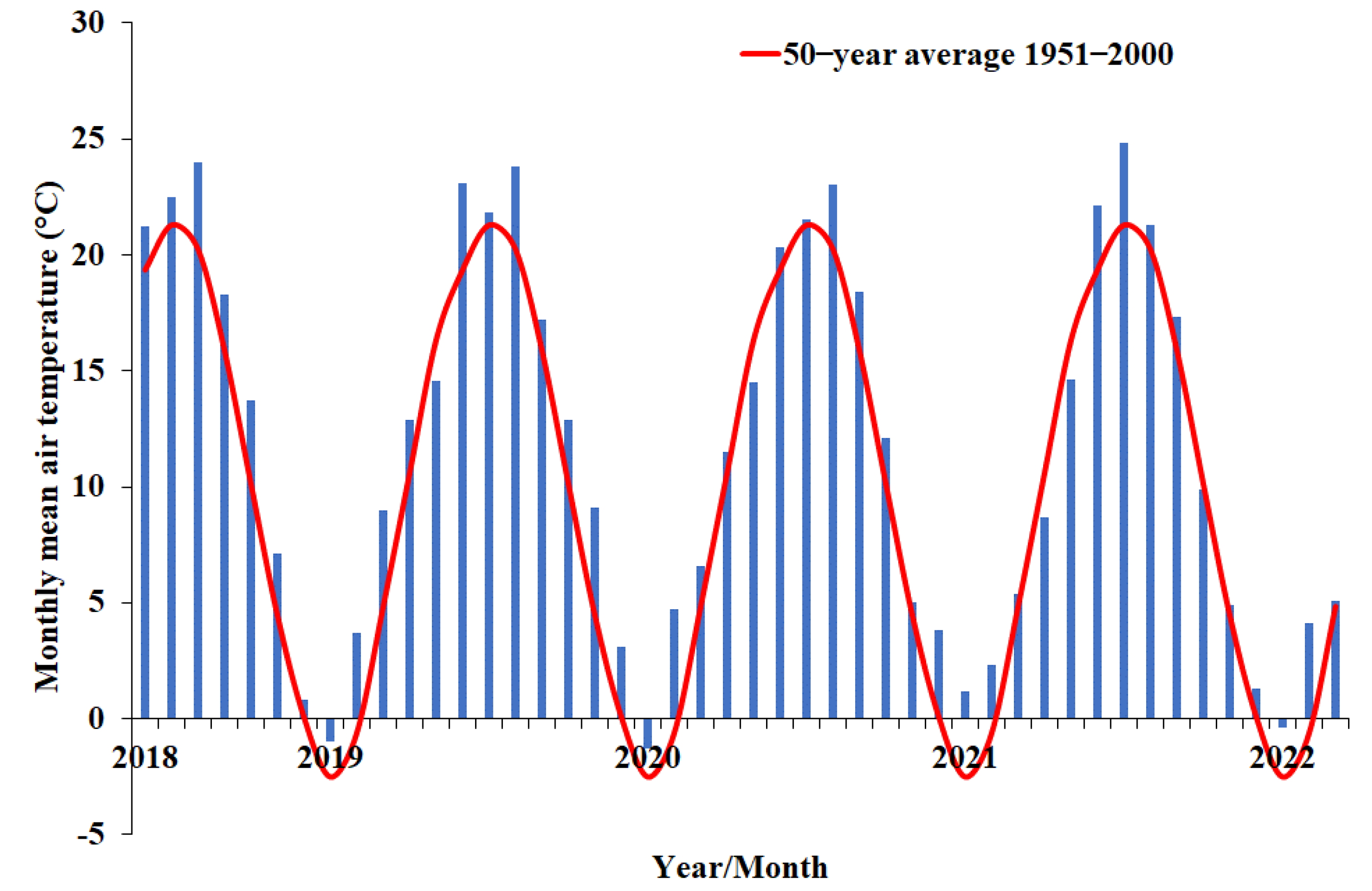
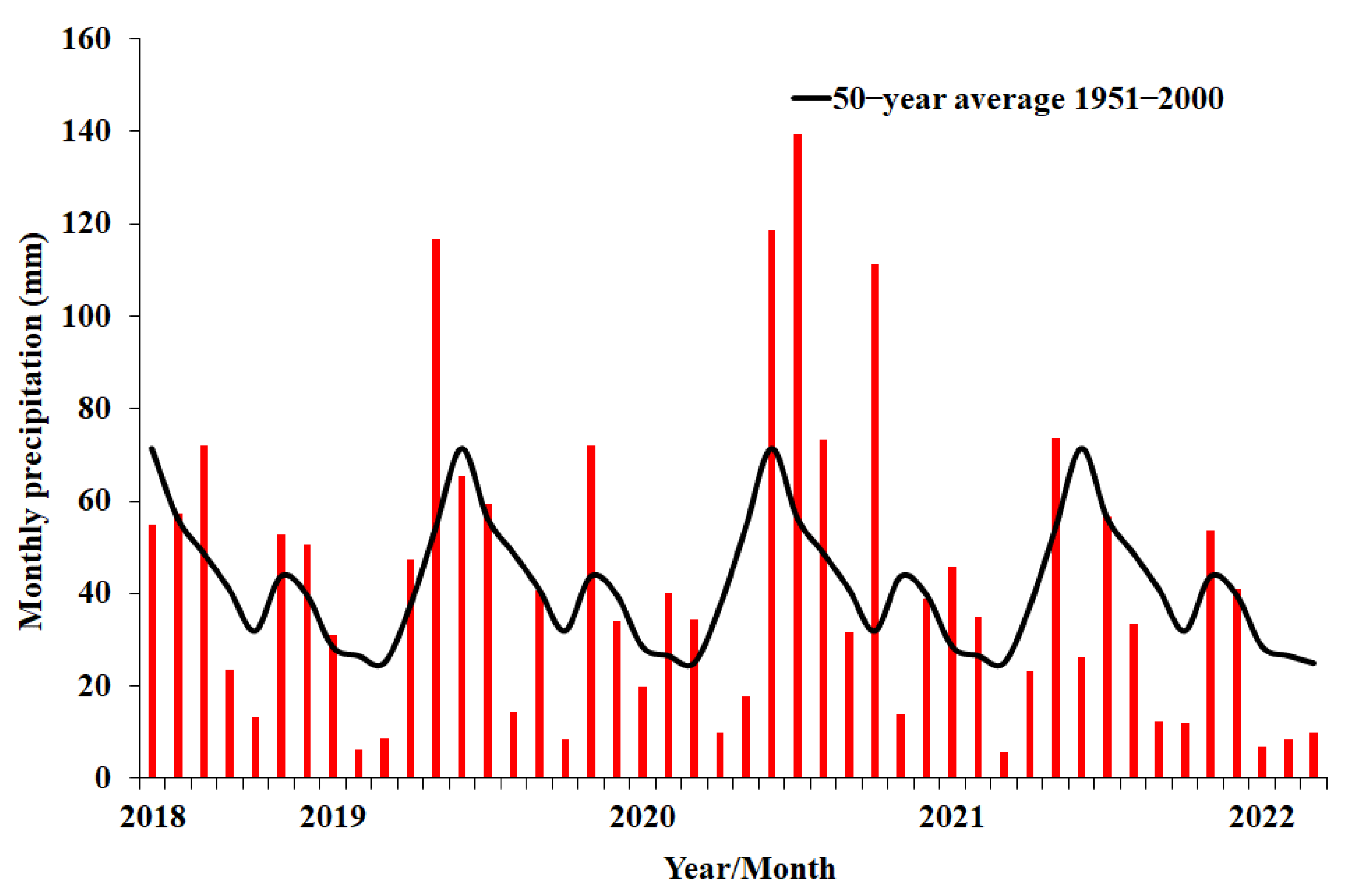
2.1. Experimental Site and Measurement Techniques
2.2. Model Calculations
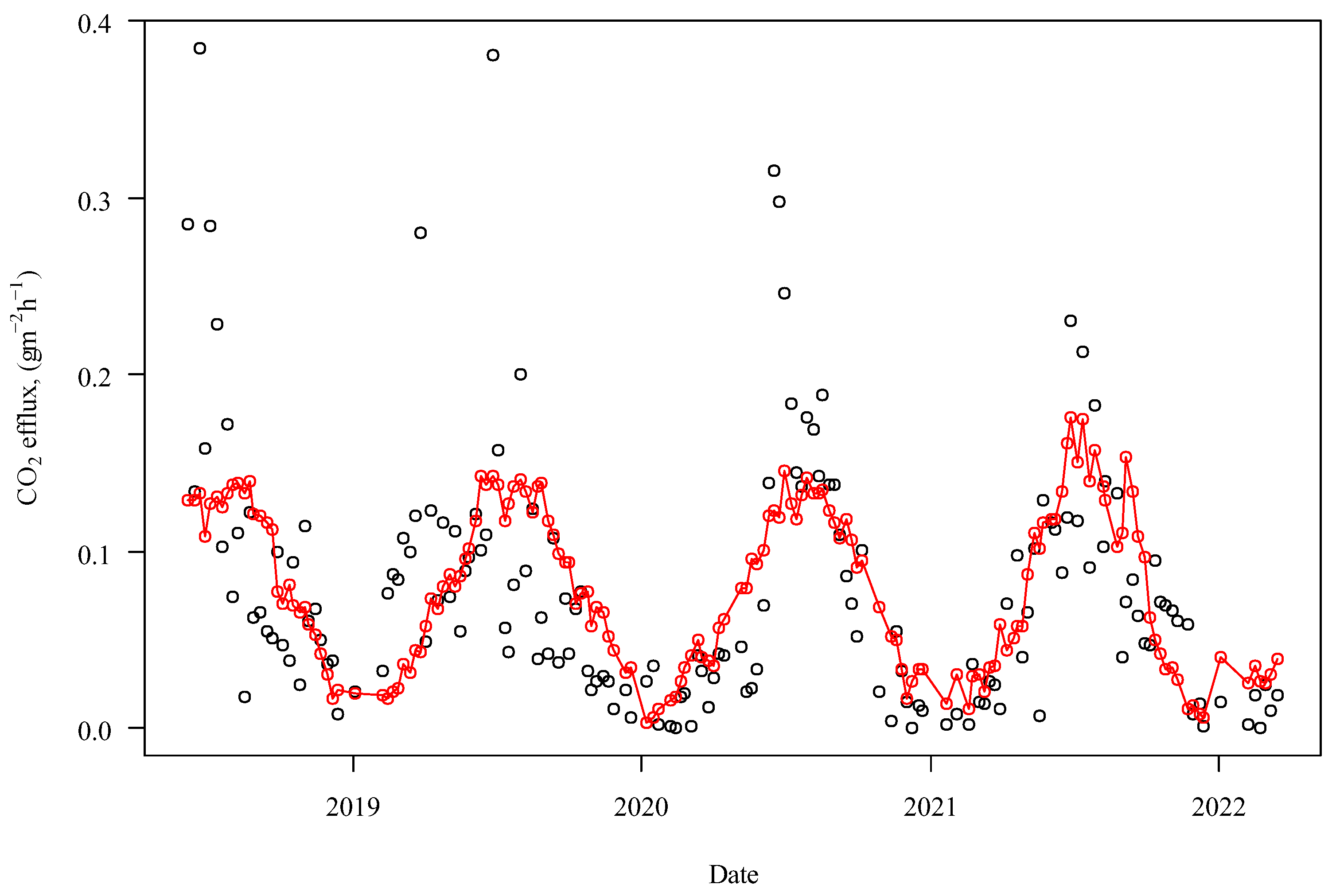
3. Results
3.1. Linear Model for the Description of CO2 Efflux as a Function of Soil Temperature
3.2. Quadratic Exponential Model for the Description of CO2 Efflux as a Function of Soil Temperature
3.3. Exponential Model for the Description of CO2 Efflux as a Function of Soil Temperature
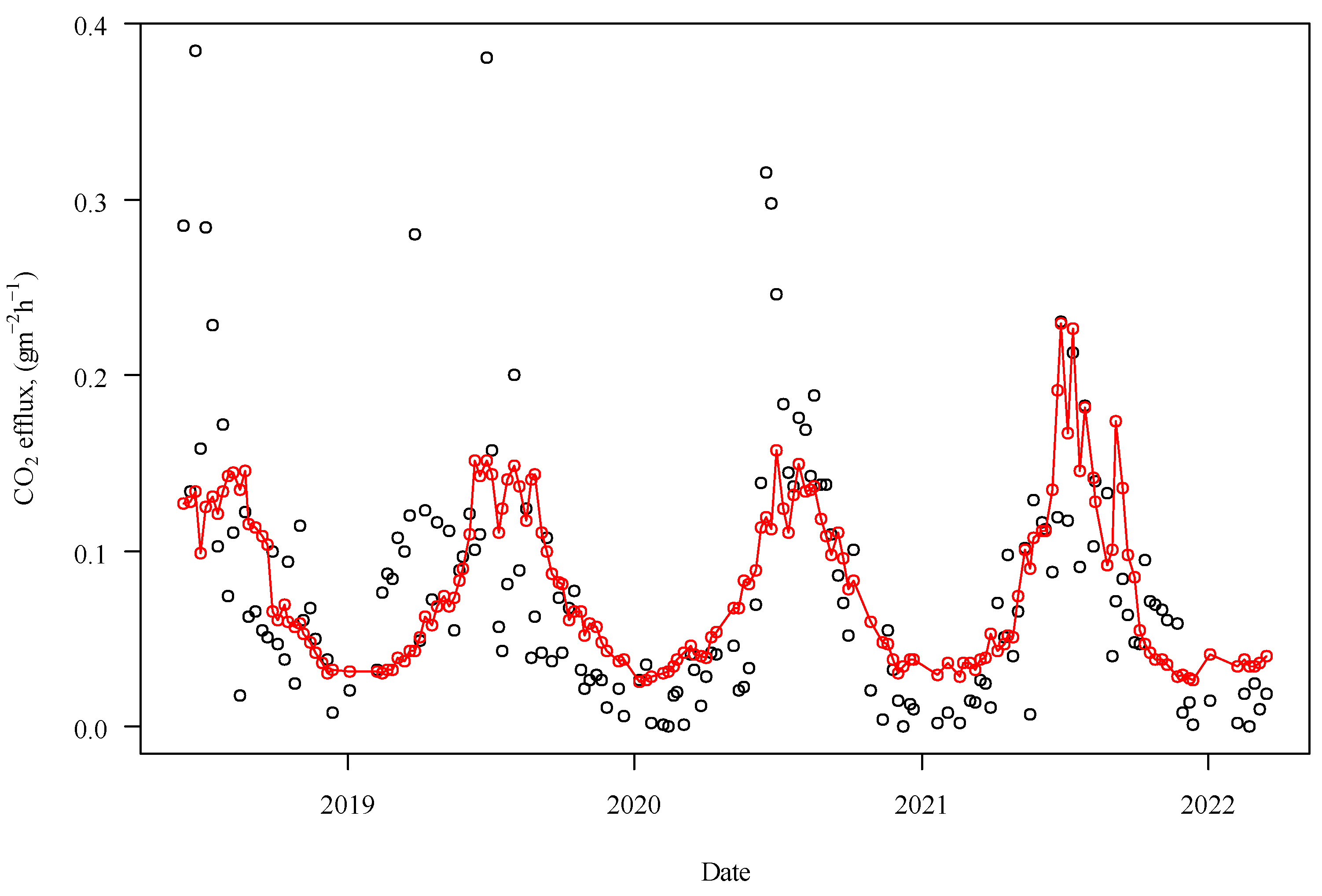
3.4. Combined Exponential and Powered Model for the Description of CO2 Efflux as a Function of Air Temperature and Soil Moisture Content
3.5. Extended Exponential Model for the Description of CO2 Efflux as a Function of Air Temperature and Soil Moisture Content
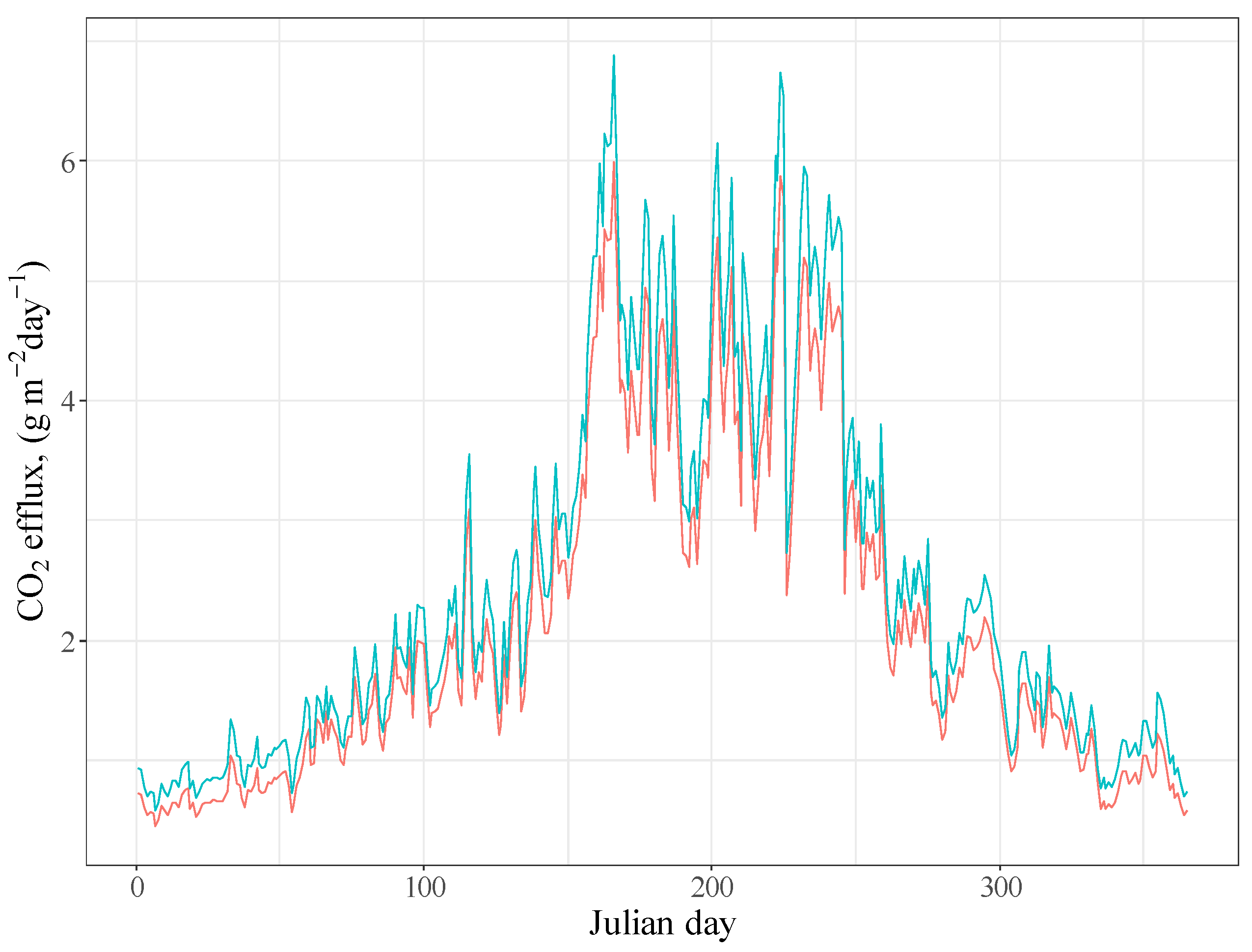
3.6. CO2 Efflux Predictions of Bare Soil for the Year 2050
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bunt, J.S.; Rovira, A.D. Oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide evolution of heat-sterilized soil. Nature 1954, 173, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Sources of CO2 efflux from soil and review of partitioning methods. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 3, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Potter, C.S. Global patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Nemergut, D.R.; Schmidt, S.K.; Townsend, A.R. Increases in soil respiration following labile carbon additions linked to rapid shifts in soil microbial community composition. Biogeochemistry 2007, 82, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Hui, D.; Chu, G.; Han, X.; Zhang, Q. Rain-induced changes in soil CO2 flux and microbial community composition in a tropical forest of China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lundquist, E.J.; Scow, K.M.; Jackson, L.E.; Uesugi, S.L.; Johnson, C.R. Rapid response of soil microbial communities from conventional, low input, and organic farming systems to a wet/dry cycle. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 12, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, F.T.; Cortina, J. Small-scale spatial variation in soil CO2 efflux in a Mediterranean semiarid steppe. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 3, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhu, K.; Auffret, M.; Dungait, J.; Hopkins, D.W.; Prosser, J.I.; Singh, B.K.; Subke, J.A.; Wookey, P.A.; Ågren, G.I.; Sebastià, M.T.; et al. Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration rates enhanced by microbial community response. Nature 2014, 513, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, Y.; Kimura, S.D.; Yamada, H.; Hirose, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Kusa, K.; Hatano, R. Effects of environmental factors on temporal variation in annual carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions from an unfertilized bare field on Gray Lowland soil in Mikasa, Hokkaido, Japan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, C.J.R.; Sánchez-Cañete, E.P.; Serrano-Ortiz, P.; López-Ballesteros, A.; Domingo, F.; Kowalski, A.S.; Oyonarte, C. From microhabitat to ecosystem: Identifying the biophysical factors controlling soil CO2 dynamics in a karst shrubland. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Y.; Yan, M.J.; Zhang, J.G.; Guan, J.H.; Du, S. Soil CO2 emissions from five different types of land use on the semiarid Loess Plateau of China, with emphasis on the contribution of winter soil respiration. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-J.; Yan, J.-X.; Yue, X.-F.; Wang, M.-B. Significance of soil temperature and moisture for soil respiration in a Chinese mountain area. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, R.; Campiglia, E.; Di Tizio, A.; Marinari, S. Soil carbon dioxide emission and carbon content as affected by conventional and organic cropping systems in Mediterranean environment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Ding, G. Response of soil respiration and Q10 to temperature and moisture in naturally regenerated and bare lands based on an 11-year observation period. Catena 2022, 208, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Scala, N., Jr.; Panosso, A.R.; Pereira, G.T. Modelling short-term temporal changes of bare soil CO2 emissions in a tropical agrosystem by using meteorological data. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 24, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.; Taylor, J.A. On the temperature dependence of soil respiration. Funct. Ecol. 1994, 8, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Kuang, X.; Sauer, T.J.; Heitman, J.L.; Horton, R. Bare soil carbon dioxide fluxes with time and depth determined by high-resolution gradient-based measurements and surface chambers. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zsembeli, J.; Tuba, G.; Juhász, C.; Nagy, I. CO2 measurements in a soil tillage experiment. Cereal Res. Comm. 2005, 33, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, A.M. Microbial decomposition (respiration) of litter in eucalypt forests of South-Western Australia: An empirical model based on laboratory incubations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Cubasch, U. Projections of Future Climate Change. Report Chapter 9, The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; pp. 1–58. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/TAR-09.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- French, S.; Levy-Booth, D.; Samarajeewa, A.; Shannon, K.E.; Smith, J.; Trevors, J.T. Elevated temperatures and carbon dioxide concentrations: Effects on selected microbial activities in temperate agricultural soils. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillion, S.S.; Roy, J.; Abrams, M. Assessing the impact of elevated CO2 on soil microbial activity in a Mediterranean model ecosystem. Plant Soil 1995, 187, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakadai, T.; Yokozawa, M.; Ikeda, H.; Koizumi, H. Diurnal changes of carbon dioxide flux from bare soil in agricultural field in Japan. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 19, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radicetti, E.; Osipitan, O.A.; Langeroodi, A.R.S.; Marinari, S.; Mancinelli, R. CO2 flux and C balance due to the replacement of bare soil with agro-ecological service crops in Mediterranean environment. Agriculture 2019, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, H.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Xu, L.; Li, M.; Zheng, S.; He, N. Soil moisture affects the rapid response of microbes to labile organic C addition. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 857185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
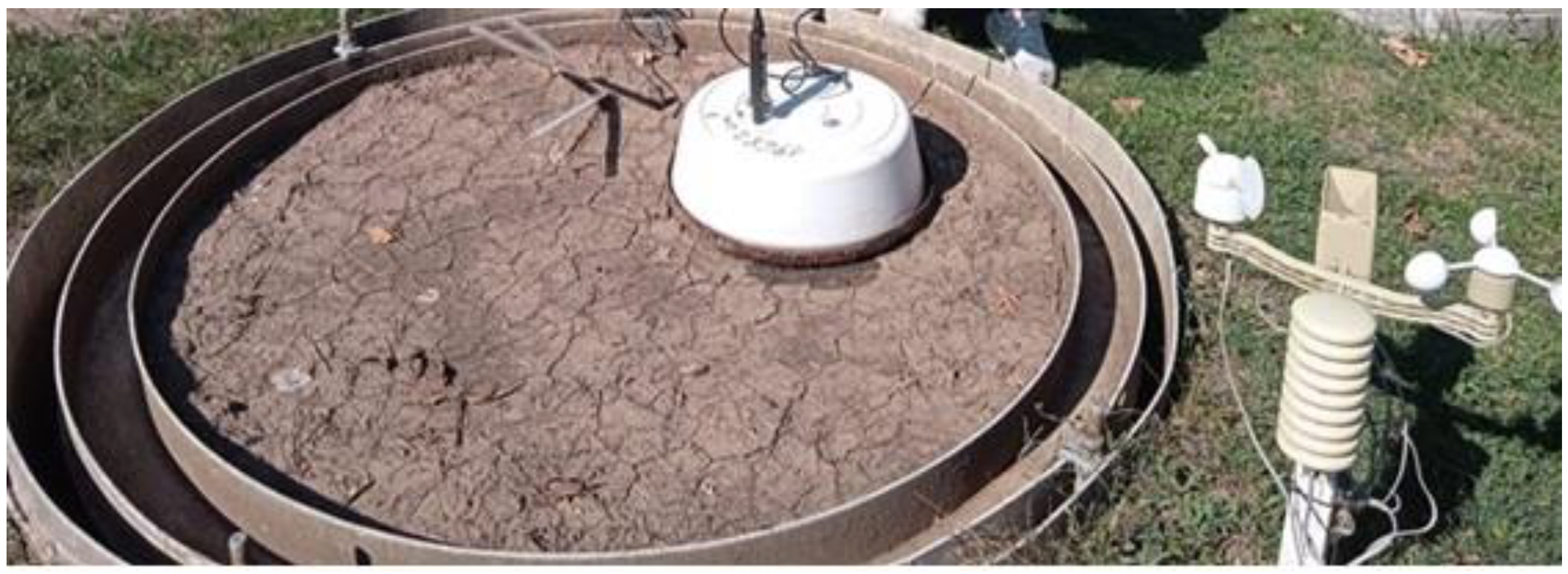


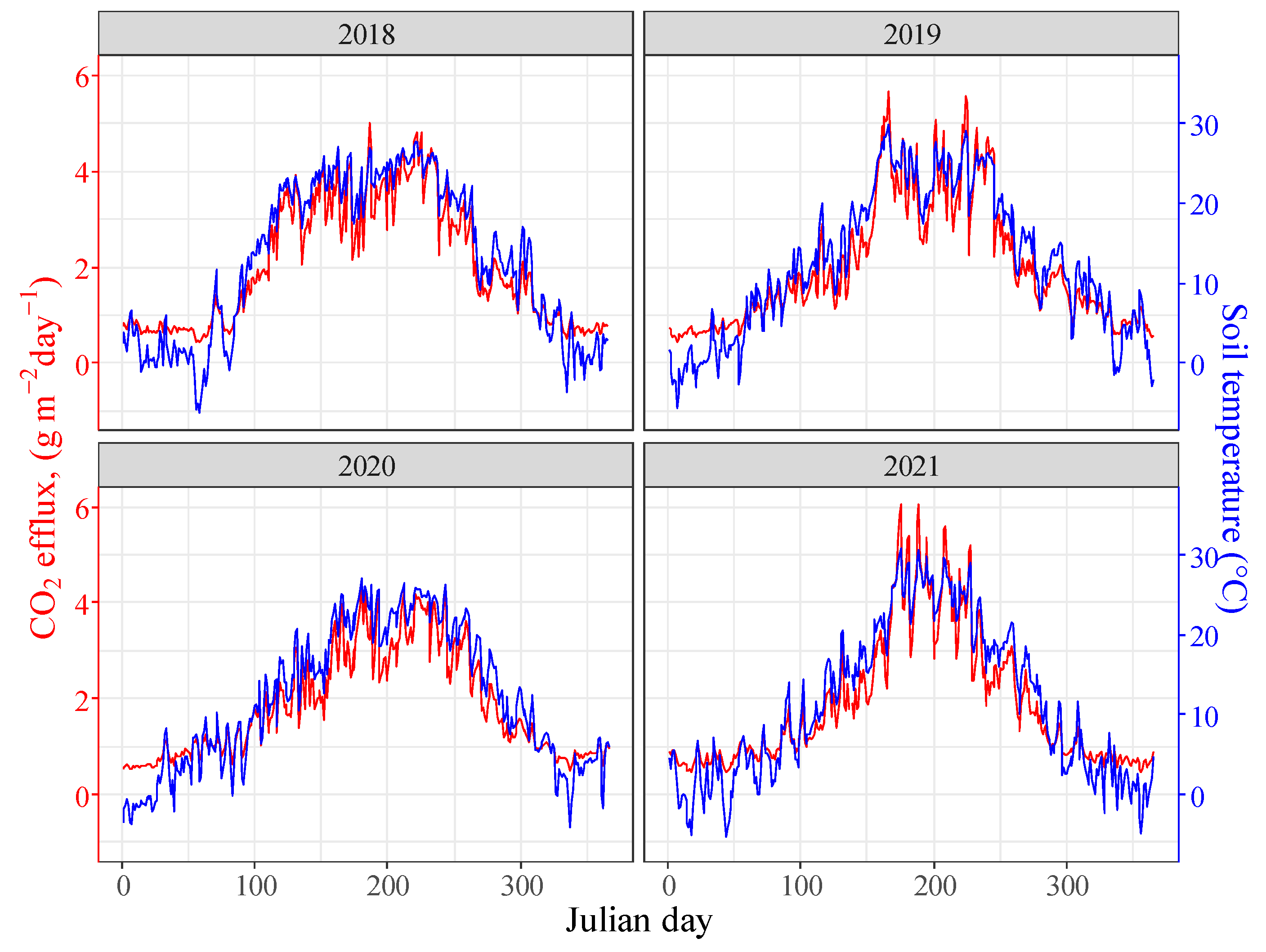
| Depth cm | pH (KCl) | Salt Cont. m/m% | CaCO3 % | Organic Matter m/m% | NO3-N mg/kg | P2O5 mg/kg | K2O mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 5.21 | 0.02 | <0.05 | 3.22 | 9.7 | 86 | 338 |
| 20–40 | 5.27 | 0.02 | 1.09 | 3.17 | 18.5 | 40 | 299 |
| 40–60 | 6.14 | 0.02 | 10.88 | 2.68 | 8.5 | 33 | 245 |
| Particle size distribution (%) | |||||||
| Depth cm | >0.25 mm | 0.25–0.05 | 0.05–0.02 | 0.02–0.01 | 0.01–0.005 | 0.005–0.002 | <0.002 mm |
| 0–20 | 0.5 | 6.4 | 11.4 | 15.4 | 13.6 | 11.5 | 41.2 |
| 20–40 | 0.2 | 5.8 | 7.2 | 16.3 | 14.1 | 10.6 | 45.9 |
| 40–60 | 0.1 | 3.5 | 9.0 | 13.4 | 16.0 | 11.0 | 47.0 |
| Coefficient | Estimate | Standard Error | t Value | Pr (>|t|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.005875 | 0.008419 | 0.698 | 0.48615 |
| Soil temperature | 0.005320 | 0.000515 | 10.330 | <20−16 *** |
| Constant | Estimate | Standard Error | t Value | Pr (>|t|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.0285905 | 0.0049207 | 5.810 | 3.08 × 10−8 *** |
| b | 0.0511563 | 0.0143776 | 3.558 | 0.000487 *** |
| c | 0.0004216 | 0.0003250 | 1.297 | 0.196298 |
| Constant | Estimate | Standard Error | t Value | Pr (>|t|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.026743 | 0.004583 | 5.835 | 2.70 × 10−8 *** |
| b | 0.067437 | 0.007491 | 9.002 | 4.63 × 10−16 *** |
| Constant | Estimate | Standard Error | t Value | Pr (>|t|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.018790 | 0.006062 | 3.100 | 0.00227 ** |
| b | 0.065668 | 0.007499 | 8.757 | 2.15 × 10−15 *** |
| c | 0.157738 | 0.121944 | 1.294 | 0.198 |
| Constant | Estimate | Standard Error | t Value | Pr (>|t|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.023405 | 0.004573 | 5.118 | 8.40 × 10−7 *** |
| b | 0.066250 | 0.007460 | 8.881 | 1.01 × 10−15 *** |
| c | 0.012325 | 0.009166 | 1.3453 | 0.181 |
| Model | R2 | RSE | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear 1 | 0.37 | 0.058 | −964.89 |
| Quadratic exponential 2 | 0.41 | 0.057 | −973.19 |
| Exponential 3 | 0.40 | 0.057 | −973.28 |
| Combined exponential and powered 4 | 0.41 | 0.057 | −973.06 |
| Extended exponential 5 | 0.41 | 0.057 | −973.02 |
| Season | Temperature Increase °C y−1 ± SE × z95% | Estimated Change until 2050 Compared to 2019 °C ± SE × z95% |
|---|---|---|
| winter | 0.069 ± 0.060 | 2.139 ± 1.860 |
| spring | 0.063 ± 0.033 | 1.953 ± 1.023 |
| summer | 0.059 ± 0.033 | 1.829 ±1.023 |
| autumn | 0.069 ± 0.037 | 2.139 ± 1.147 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juhász, C.; Huzsvai, L.; Kovács, E.; Kovács, G.; Tuba, G.; Sinka, L.; Zsembeli, J. Carbon Dioxide Efflux of Bare Soil as a Function of Soil Temperature and Moisture Content under Weather Conditions of Warm, Temperate, Dry Climate Zone. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123050
Juhász C, Huzsvai L, Kovács E, Kovács G, Tuba G, Sinka L, Zsembeli J. Carbon Dioxide Efflux of Bare Soil as a Function of Soil Temperature and Moisture Content under Weather Conditions of Warm, Temperate, Dry Climate Zone. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123050
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuhász, Csaba, László Huzsvai, Elza Kovács, Györgyi Kovács, Géza Tuba, Lúcia Sinka, and József Zsembeli. 2022. "Carbon Dioxide Efflux of Bare Soil as a Function of Soil Temperature and Moisture Content under Weather Conditions of Warm, Temperate, Dry Climate Zone" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123050
APA StyleJuhász, C., Huzsvai, L., Kovács, E., Kovács, G., Tuba, G., Sinka, L., & Zsembeli, J. (2022). Carbon Dioxide Efflux of Bare Soil as a Function of Soil Temperature and Moisture Content under Weather Conditions of Warm, Temperate, Dry Climate Zone. Agronomy, 12(12), 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123050







