Combination of GIS and Multivariate Analysis to Assess the Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in Some Arid Zones
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1-
- Assessing the studied soil properties [pH, soil salinity (EC), %clay, soil organic matter content (%SOM)] and total concentrations of As, Co, Cu, Ni, V, and Zn for soil profiles in order to improve the understanding of the environmental impacts in that region and their causes.
- 2-
- Utilizing contamination indices such as the geo-accumulation index (I-geo), contamination factor (CF), Improved Nemerow’s Pollution Index (Pn), and Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI) to evaluate the risk of contamination for six heavy metals in different layers of soil profiles.
- 3-
- Using PCA and cluster analysis to uncover relationships among variables to improve estimations for the variables under study and determine the sources of heavy metals within the study area.
2. Materials and Methods
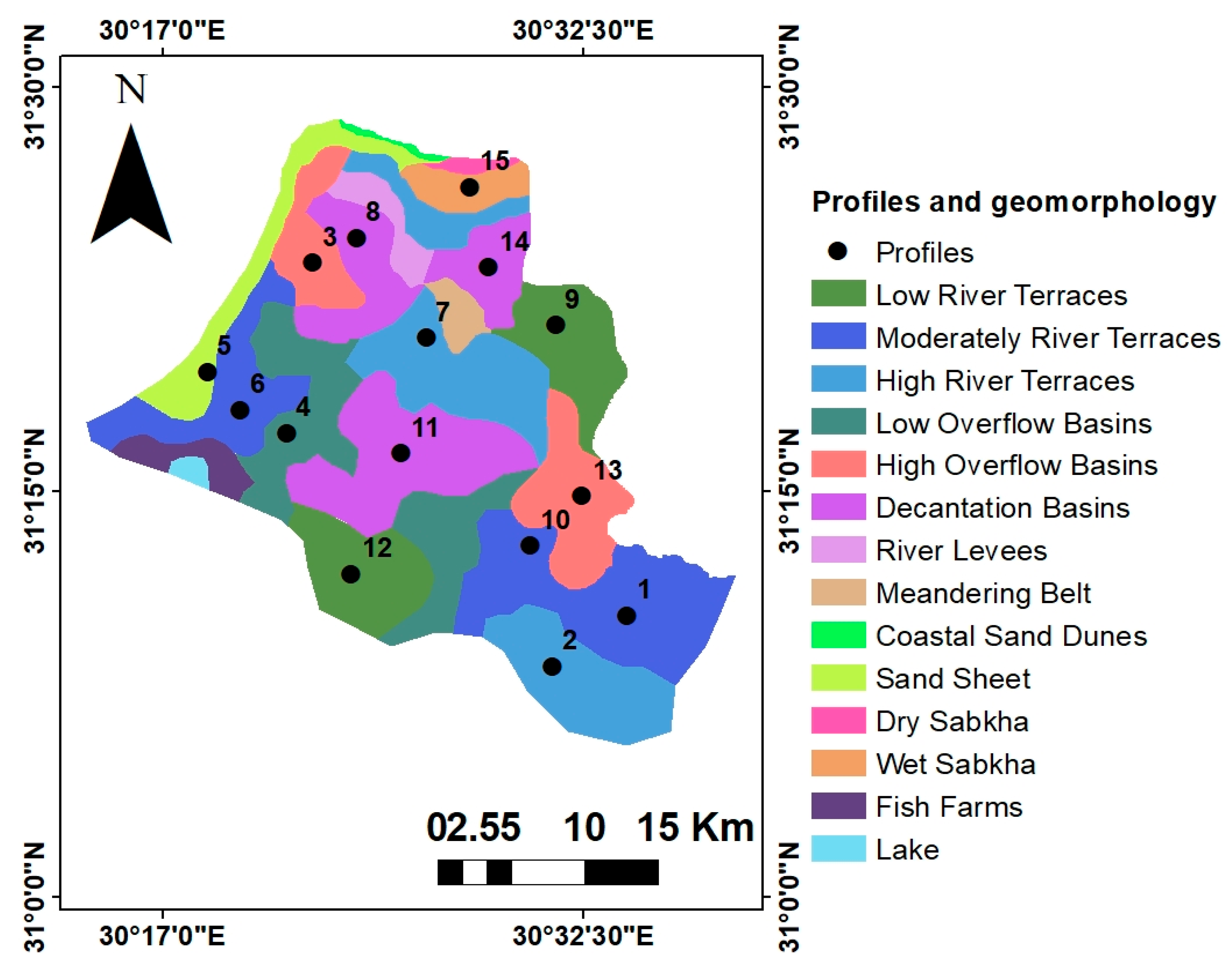
2.1. The Research Region
2.2. Analysis of Collected Samples
2.3. Contamination Indices
2.3.1. Geo-Accumulation Index (I-Geo)
2.3.2. Improved Nemerow’s Pollution Index (Pn)
2.3.3. Contamination Factor (CF)
- = measured heavy metal’s total concentration
- = The background value of each metal.
2.3.4. Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI)
- = potential ecological risk,
- = the toxic response factor for heavy metal, and
- = the contamination factor, as mentioned above.
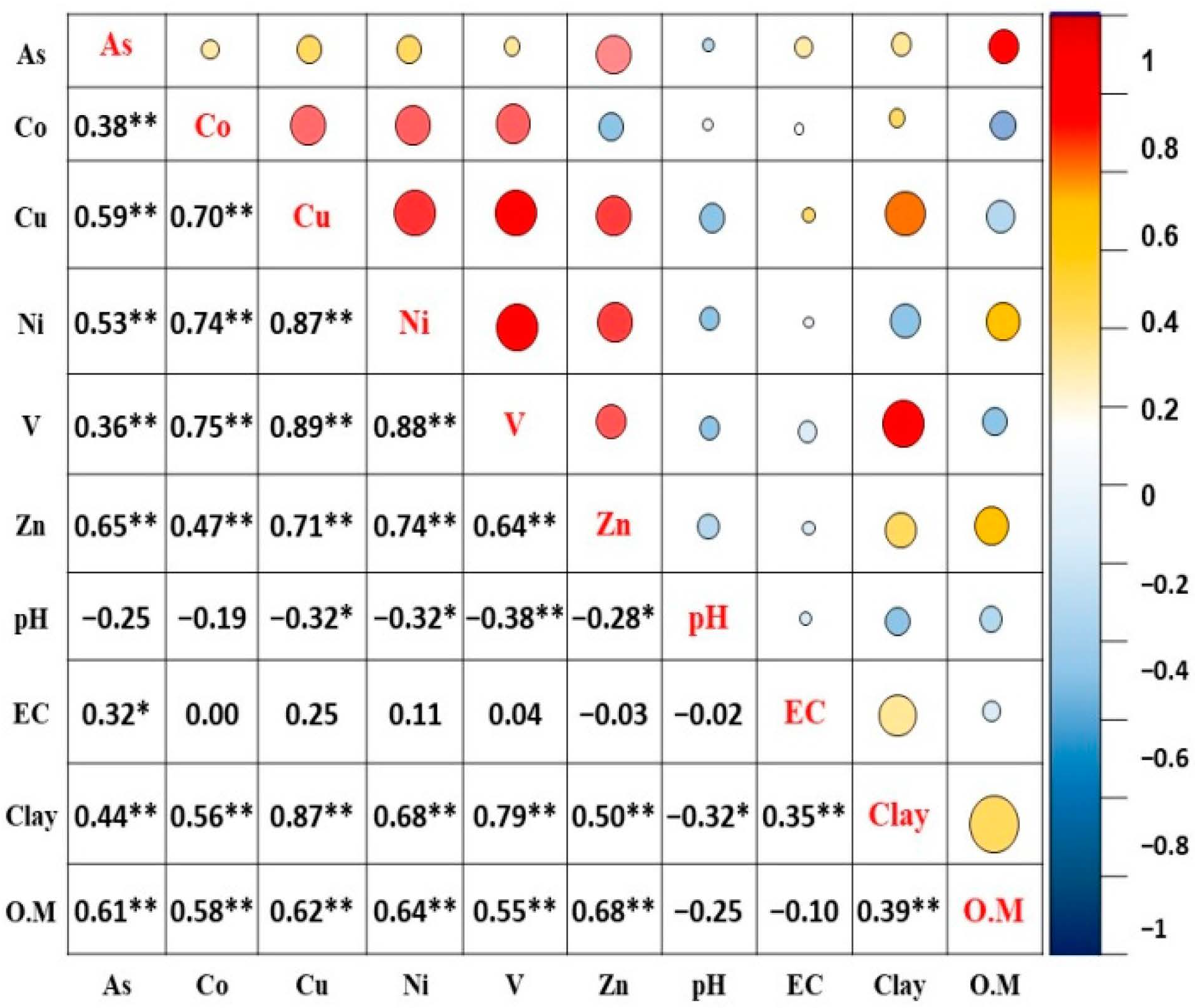
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Utilizing IDW to Map Soil Properties and Heavy Metal Concentrations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Some Soil Properties and Heavy Metal Concentrations of the Investigated Area
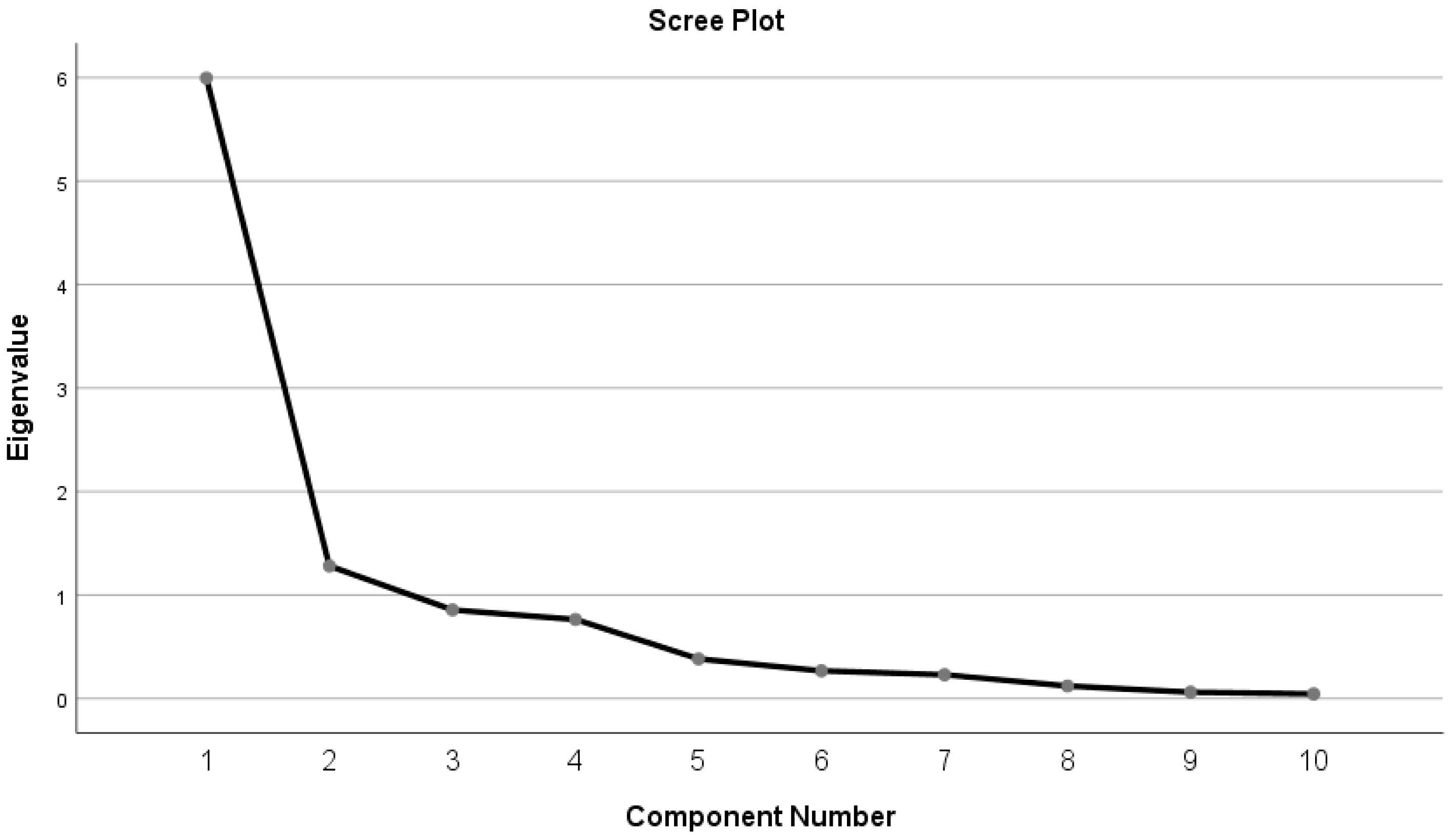
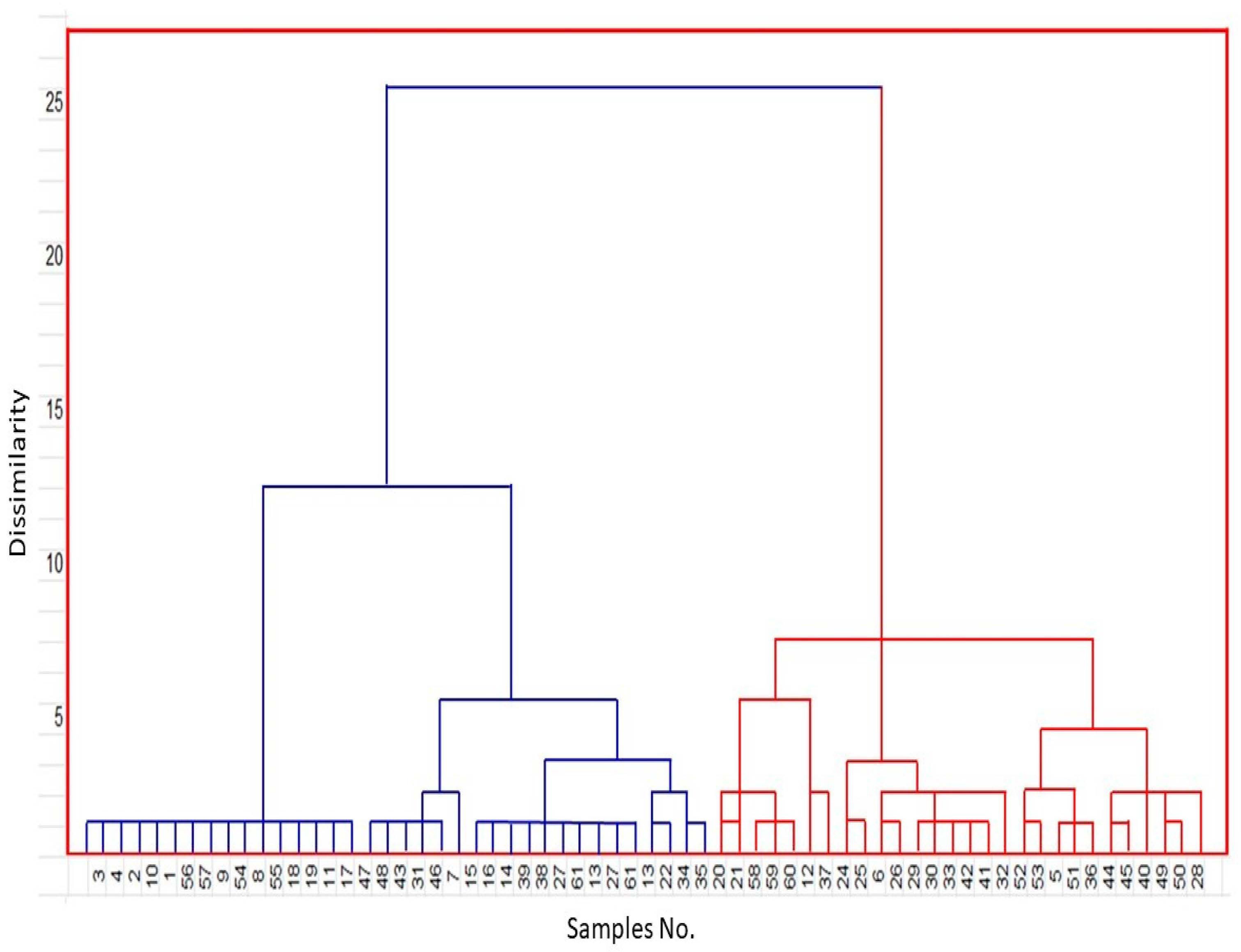
3.2. Principal Component and Cluster Analysis
3.3. The Spatial Distribution of the Mean Soil Properties and Heavy Metal Weight
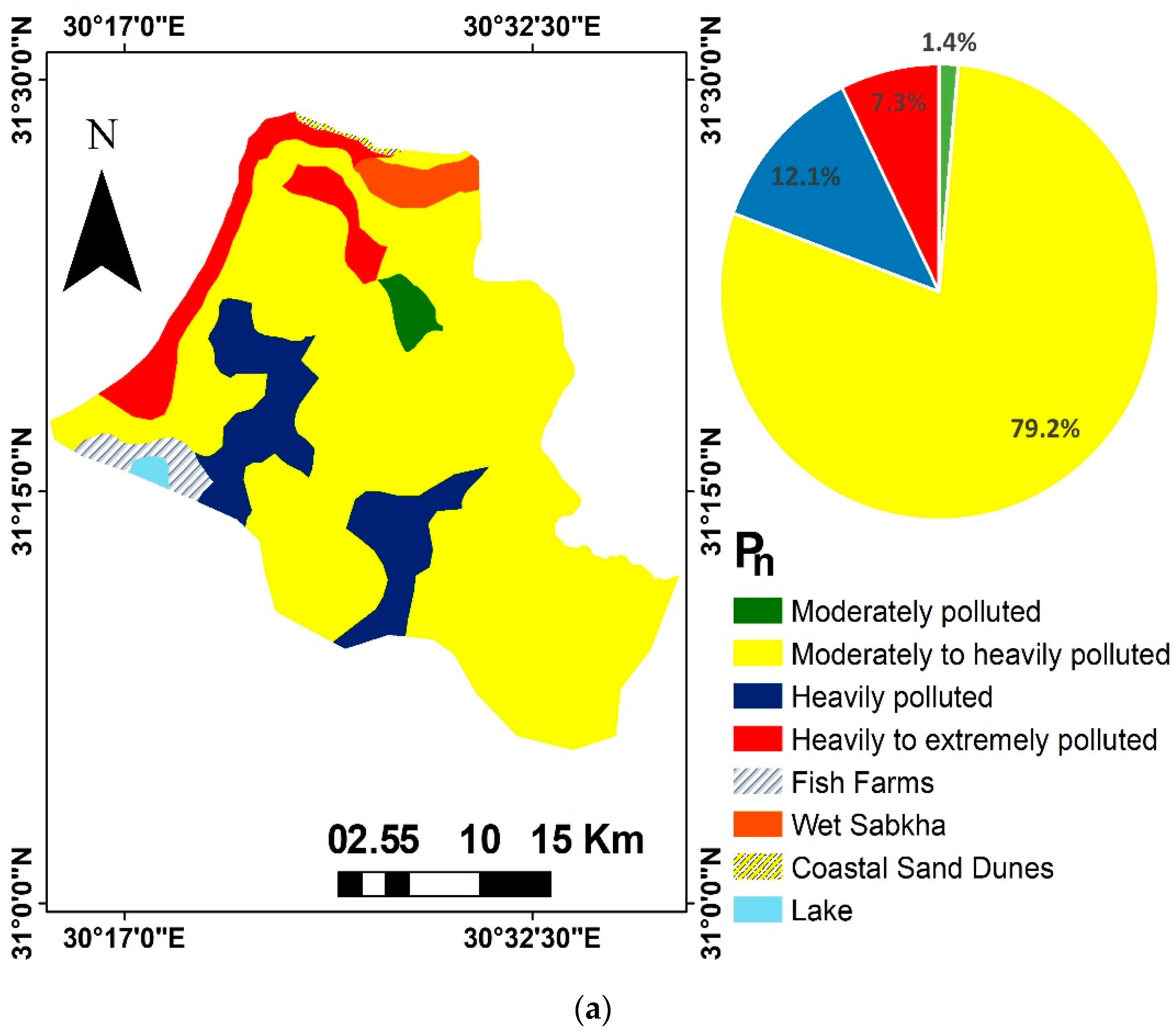
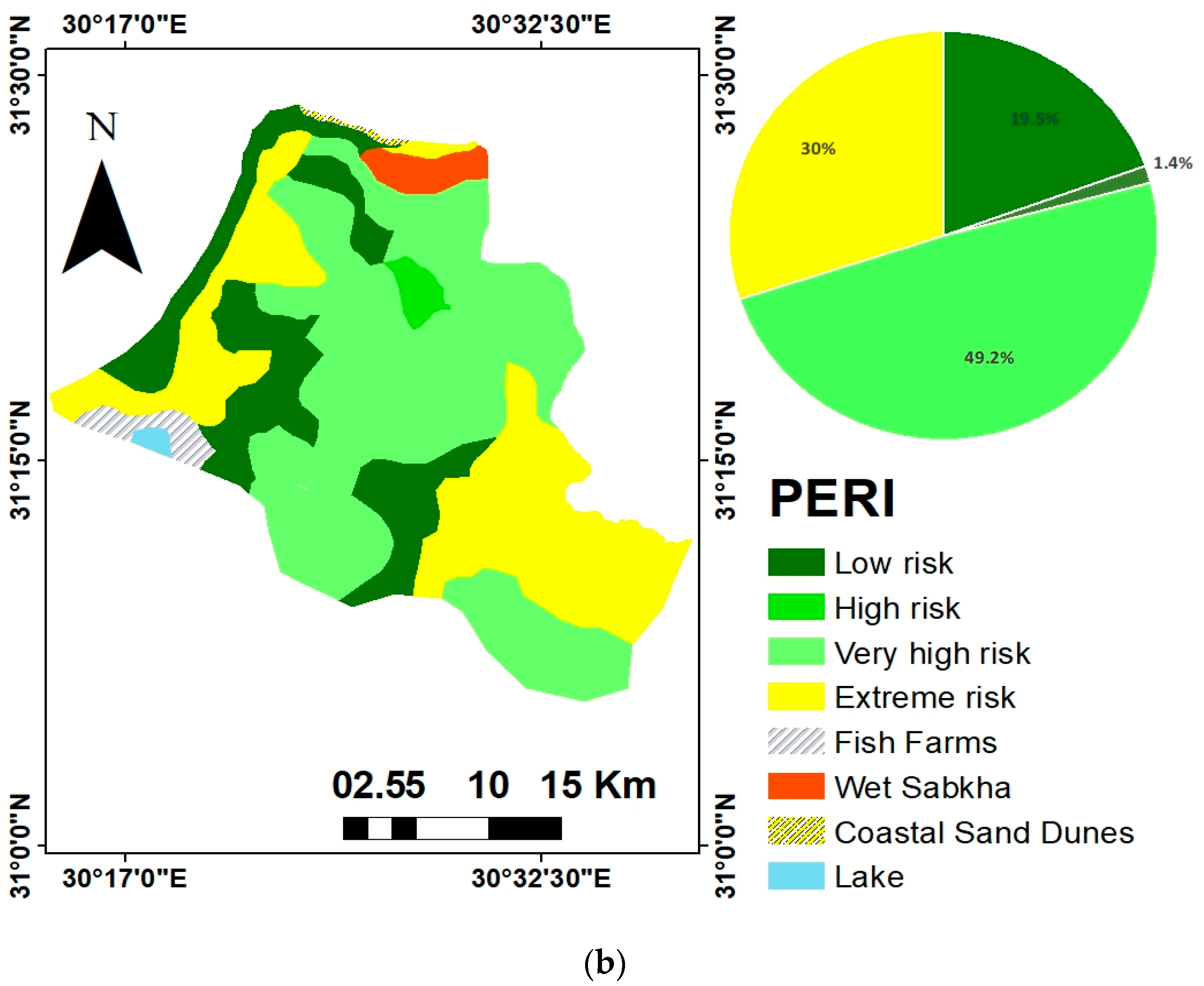
3.4. Contamination Hazards Indices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Sun, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Cheng, J. Soil physiochemical properties and landscape patterns control trace metal contamination at the urban-rural interface in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, R. Accumulation Characteristics and Pollution Evaluation of Soil Heavy Metals in Different Land Use Types: Study on the Whole Region of Tianjin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, F.A.; Ishaq, M.; Khan, S.; Ihsanullah, I.; Ahmad, I.; Shakirullah, M. A comparative study of human health risks via consumption of food crops grown on wastewater irrigated soil (Peshawar) and relatively clean water irrigated soil (lower Dir). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Khatita, A.M. Assessment of Soil and Sediment Contamination in the Middle Nile Delta area (Egypt)-Geo-Environmental Study Using Combined Sedimentological, Geophysical and Geochemical Methods; Alexander-Universität Erlangen Nürnberg zur Erlangung: Erlangen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, A.; Kitamura, Y.; Shimizu, K.; El Hassan, W.A.; Fujimaki, H. Quantitative analysis of reusing agricultural water to compensate for water supply deficiencies in the Nile Delta irrigation network. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abowaly, M.E.; Belal, A.-A.A.; Abd Elkhalek, E.E.; Elsayed, S.; Abou Samra, R.M.; Alshammari, A.S.; Moghanm, F.S.; Shaltout, K.H.; Alamri, S.A.M.; Eid, E.M. Assessment of Soil Pollution Levels in North Nile Delta, by Integrating Contamination Indices, GIS, and Multivariate Modeling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, H.; Sha, Q.; Li, X.; Jia, G.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, J. Environmental Controls to Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Vary at Multiple Scales in a Highly Urbanizing Region in Southern China. Sensors 2022, 22, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, J. Effects of landscape heterogeneity on the elevated trace metal concentrations in agricultural soils at multiple scales in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamghar, A.; Jaime Gomez-Hernandez, J. Factorial kriging of a geochemical dataset for heavy-metal spatial-variability characterization. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Hao, S. Spatial variation of soil quality and pollution assessment of heavy metals in cultivated soils of Henan Province, China. Chem. Spec. Bioavail. 2014, 26, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmannova, D.H.; Pavlovsky, J.; Chovanec, P. Heavy metal Contaminations of Urban soils in Ostrava, Czech Republic: Assessment of Metal Pollution and using Principal Component Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 683–696. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, P.H.; Berg, L.R.; Johnson, G.B. Environment, 2nd ed.; Saunders College Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, F.; Fakhruddin, A.N.M.; Imam, M.D.T.; Khan, N.; Abdullah, A.T.M.; Khan, T.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, M.N. Assessment of roadside surface water quality of Savar, Dhaka, Bangladesh using GIS and multivariate statistical techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3511–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, T.-B.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Guo, Q.-J.; Song, B.; Zhou, X.-Y. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: Accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C. Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, M.S.; El Baroudy, A.A.; Fullen, M.A.; El-Beshbeshy, T.R.; Ali, R.R.; Elhalim, A.; Guerra, A.J.T.; Jorge, M.C.O. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the middle Nile delta of Egypt. Int. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 4, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z. Hazard of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil and its ecological risk assessment method. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 781, 32052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Guo, M.; Xiao, L.; Huang, W. Space-time quantitative source apportionment of soil heavy metal con- centration increments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, M.; Christakos, G. Beyond mere pollution source identification: Determination of land covers emitting soil heavy metals by combining PCA/APCS, GeoDetector and GIS analysis. CATENA 2020, 185, 104297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.K.; Abd-Elmabod, S.K.; Aldosari, A.A.; Elrys, A.S.; Mohamed, E.S. Multivariate Analysis for Assessing Irrigation Water Quality: A Case Study of the Bahr Mouise Canal, Eastern Nile Delta. Water 2020, 12, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climatological Normal for Egypt. The Normal for Beheira Governorate from 1960–2011; Ministry of Civil Aviation, Meteorological Authority: Cairo, Egypt, 2011.
- Shaltout, K.H.; Galal, T.M.; El-Komi, T.M. Evaluation of the nutrient status of some hydrophytes in the water courses of Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Bot. 2009, 36, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molle, F.; Gaafar, I.; El-Agha, D.E.; Rap, E. The Nile delta’s water and salt balances and implications for management. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Behairy, R.A.; El Baroudy, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Kheir, A.M.S.; Shokr, M.S. Modelling and assessment of irrigation water quality index using GIS in semi-arid region for sustainable agriculture. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Behairy, R.A. Using New Techniques for Studying Land Resources in Some Areas of North West Nile Delta, Egypt. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, Tanta University, Cairo, Egypt, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Guidelines for Soil Profile Description, 3rd ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, USDA-NRCS, 11th ed.; U.S. Government Print Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- El Behairy, R.A.; El Baroudy, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Mohamed, E.S.; Kucher, D.E.; Shokr, M.S. Assessment of Soil Capability and Crop Suitability Using Integrated Multivariate and GIS Approaches toward Agricultural Sustainability. Land 2022, 11, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.W. Soil pH and Soil Acidity. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3, Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America Book Series, No. 5; Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D. Salinity: Electrical Conductivity and Total Dissolved Solids. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3, Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America Book Series, No. 5; Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 417–435. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, B. Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC). In Soils and Sediments; Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, D.L. Soil Science Methods & Applications; Library of Congress Cataloging Publication Data: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L.; Keeney, D. Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Khanam, D.; Adyel, T.; Islam, M.S.; Mohammad Ahsan, A.; Akbor, M.A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil around Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ), Bangladesh: Implication of seasonal variation and indices. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shao, C.; Ju, M. Heavy metal contamination assessment and partition for industrial and mining gathering areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 7286–7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. J. Geol. 1979, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Harikumar, P.S.; Jisha, T.S. Distribution pattern of trace metal pollutants in the sediments of an urban wetlands in the southwest coast of India. Int. J. Eng. 2010, 2, 840–850. [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Min, X.; Liao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Men, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, J. Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: Distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, K.; Morgan, G. SPSS for Intermediate Statistics; Use and Interpretation; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA; London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperato, M.; Adamo, P.; Naimo, D.; Arienzo, M.; Stanzione, D.; Violante, P. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, D.; Zhang, C.; Carton, O.T. Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines area, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.L.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Cheung, S.C.N.; Thornton, I. Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, D.W.; Peck, T.R. Field soil sampling density for variable rate fertilization. J. Prod. Agric. 1995, 8, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, R.; Fleischer, S.; Smilowitz, Z. Map generation in high value horticultural integrated pest management: Appropriate interpolation methods for site-specific pest management of Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1995, 88, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR (United States Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). Toxicological Profile for Arsenic; US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; p. 428.
- ATSDR (United States Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). Toxicological Profile for Cobalt; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; p. 486.
- Fishel, F.M. Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Copper-based Pesticides; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2014; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cempel, M.; Nikel, G. Nickel: A review of its sources and environmental toxicology. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Jia, Y.; Gou, M.; Zeyer, J. Toxicity of vanadium in soil on soybean at different growth stages. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartjes, F.A. Introduction to contaminated site management. In Dealing with Contaminated Sites; Swatrjes, F., Ed.; Springer Science+Business Media B.V.: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA). National Environmental Management, Waste Act, 2008; National Norms and Standards for the Remediation of Contaminated Land and Soil Quality in the Republic of South Africa. Government Gazette, No. 36447; DEA: Pretoria, South Africa, 2013.
- Ostovari, Y.; Ghorbani-Dashtaki, S.; Bahrami, H.; Abbasi, M.; Dematte, A.; Arthur, E.; Panagos, P. Towards prediction of soil erodibility, SOM and CaCO3 using laboratory Vis-NIR spectra: A case study in a semi-arid region of Iran. Geoderma 2018, 314, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, A.A.; Mohamed, E.S. Mapping soil salinity in the East Nile Delta using several methodological approaches of salinity assessment. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hendawy, E.; Belal, A.A.; Mohamed, E.S.; Elfadaly, A.; Murgante, B.; Aldosari, A.A.; Lasaponara, R. The Prediction and Assessment of the Impacts of Soil Sealing on Agricultural Land in the North Nile Delta (Egypt) Using Satellite Data and GIS Modeling. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, A.A.; Mohamed, W.S.; Sayed, S.E.-E.; Kucher, D.E.; Mohamed, E.S. Assessment of Soil Contamination Using GIS and Multi-Variate Analysis: A Case Study in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiong, B.; Yang, M. Relationships among Heavy Metals and Organic Matter in Sediment Cores from Lake Nanhu, an Urban Lake in Wuhan, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2010, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.R.; Talabani, M.J.A. Heavy Metals Distribution and Their Correlation with Clay Size Fraction in Stream Sediments of the Lesser Zab River at Northeastern Iraq. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2018, 6, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhou, H.; Qi, Z. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution with Principal Component Analysis and Geoaccumulation Index. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergen, I.; Harmanescu, M. Application of principal component analysis in the pollution assessment with heavy metals of vegetable food chain in the old mining areas. Chem. Central J. 2012, 6, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres-Neto, P.R.; Jackson, D.A.; Somers, K.M. How many principal components? Stopping rules for determining the number of non-trivial axes revisited. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2005, 49, 974–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. The Application of Electronic Computers to Factor Analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelbaya, M.M.A.; El-Azeim, M.M.A.; Menesi, A.M.; El-Mageed, M.M.A. Heavy Metals and Microbial Activity in Alluvial Soils Affected by Different Land-Uses. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2021, 12, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azeim, M.A.; Mohamed, W.; Hammam, A. Soil Physiochemical Properties in Relation to Heavy Metals Status of Agricultural Soils in El-Minia Governorate, Egypt. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2016, 7, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils: A Review of Sources, Chemistry, Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgrath, S.P. Nickel in Heavy Metals in Soils, 2nd ed.; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Blackie Academic & Professional: London, UK, 1995; 371p. [Google Scholar]
- Parth, V.; Murthy, N.N.; Saxena, P.R. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil around hazardous waste disposal sites in Hyderabad City (India): Natural and anthropogenic implications. J. Environ. Res. Manag. 2011, 2, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Senesi, G.S.; Baldassarre, G.; Senesi, N.; Radina, B. Trace element input into soils by anthropogenic activities and implications for human health. Chemosphere 1999, 39, 343–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wei, D.P.; Zhu, Y.G. An inventory of heavy metal inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Smith, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carlton-Smith, C.; Chambers, B.J. An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, W.; Yang, M.; Wang, X. Environmental Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Coastal Cities of Estuarine Bay—A Case Study of Hangzhou Bay, China. Toxics 2020, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, J.; Baran, A. Pollution indices and biotests as useful tools for the evaluation of the degree of soil contamination by trace elements. J Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.K.; Pu, J.C. Mineral materials as feasible amendments to stabilize heavy metals in polluted urban soils. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2011, 23, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeigwe, T.K.; Eze, P.N.; Teboh, J.M.; Stietiya, M.H. Application, chemistry, and environmental implications of contaminant-immobilization amendments on agricultural soil and water quality. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Xu, Z. Remediation of Alkaline Soil with Heavy Metal Contamination Using Tourmaline as a Novel Amendment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


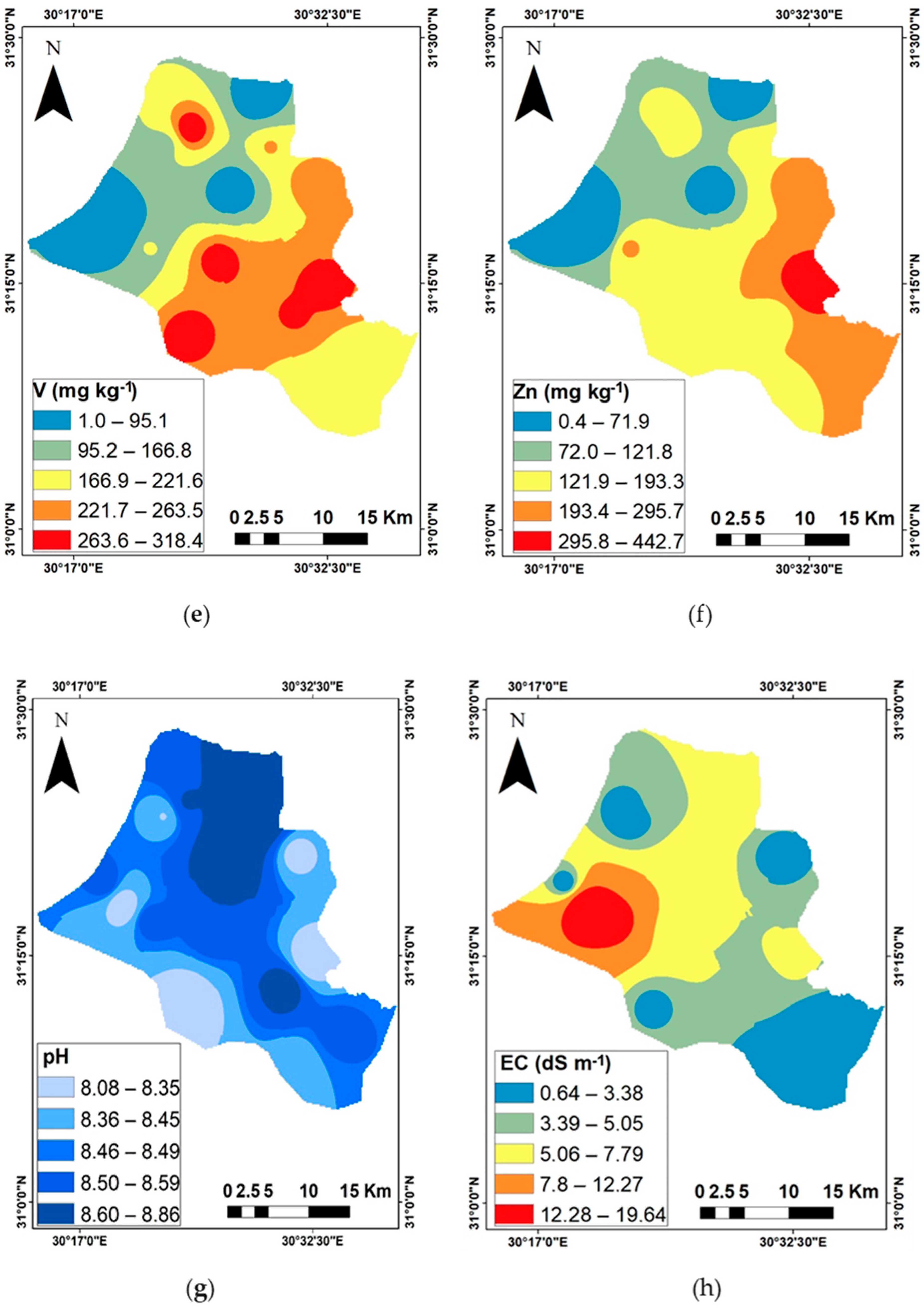
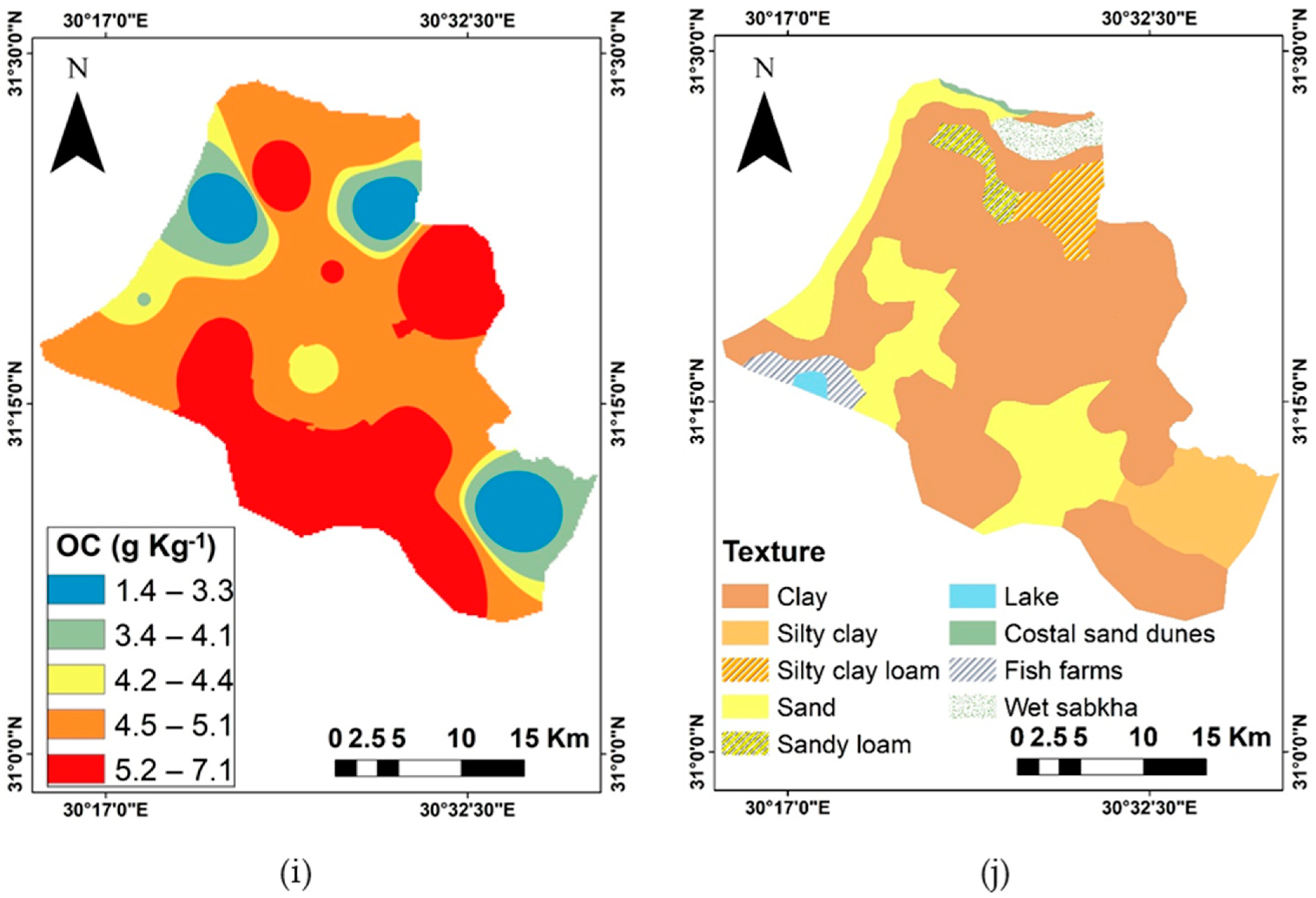
| Statistical Parameters | pH | EC | Clay | OC | As | Co | Cu | Ni | V | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:2.5 | dS m−1 | % | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||||||
| Min. | 7.97 | 0.55 | 1.38 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 1.05 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 1.01 | 0.01 |
| Max. | 8.90 | 23.20 | 83.59 | 12.30 | 121.20 | 59.94 | 80.80 | 195.43 | 377.50 | 399.27 |
| Mean | 8.47 | 5.55 | 45.43 | 5.26 | 25.52 | 17.39 | 37.80 | 70.29 | 170.95 | 149.27 |
| St. Dev. | 0.28 | 5.75 | 27.02 | 3.61 | 25.97 | 13.33 | 24.98 | 54.60 | 123.84 | 144.02 |
| Skewness | −0.06 | 1.76 | −0.71 | 0.44 | 1.52 | 0.61 | −0.61 | 0.17 | −0.18 | 0.37 |
| Kurtosis | −1.17 | 2.52 | −1.07 | −1.19 | 2.87 | 0.26 | −1.09 | −0.90 | −1.27 | −1.41 |
| Background values (Wedepohl, 1995) [34]. | 2 | 11.6 | 14.3 | 18.6 | 53 | 52 | ||||
| Recommended concentration based on the Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA, 2013) [55]. | 5.8 | 300 | 16 | 91 | 150 | 240 | ||||
| KMO and Bartlett’s Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.851 | |
| Bartlet’s Test of Sphericity | Chi-Square (Approx. value) | 496.844 |
| Degree of freedom (DF) | 45 | |
| p-value | 0.0001 | |
| PCs Parameters | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | 5.99 | 1.28 |
| Variability (%) | 59.95 | 12.81 |
| Cumulative (%) | 59.95 | 72.76 |
| Component Matrix | ||
| Indicator | PC1 | PC2 |
| As | 0.71 | 0.28 |
| Co | 0.79 | −0.19 |
| Cu | 0.96 | 0.11 |
| Ni | 0.93 | −0.09 |
| V | 0.93 | −0.12 |
| Zn | 0.84 | −0.20 |
| pH | −0.44 | −0.03 |
| EC | 0.18 | 0.95 |
| Clay | 0.83 | 0.32 |
| O.M | 0.78 | −0.30 |
| Pollution Level | Areas of Pn Index | |
|---|---|---|
| (Km2) | (%) | |
| Moderately polluted | 10.32 | 1.36 |
| Moderately to heavily polluted | 600.4 | 79.19 |
| Heavily polluted | 92.01 | 12.14 |
| Heavily to extremely polluted | 55.43 | 7.31 |
| Contamination Classes | Areas of PER Index | |
|---|---|---|
| (Km2) | (%) | |
| Low risk | 147.44 | 19.45 |
| High risk | 10.32 | 1.36 |
| Very high risk | 372.79 | 49.17 |
| Extreme risk | 227.61 | 30.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Behairy, R.A.; El Baroudy, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Mohamed, E.S.; Rebouh, N.Y.; Shokr, M.S. Combination of GIS and Multivariate Analysis to Assess the Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in Some Arid Zones. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112871
El Behairy RA, El Baroudy AA, Ibrahim MM, Mohamed ES, Rebouh NY, Shokr MS. Combination of GIS and Multivariate Analysis to Assess the Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in Some Arid Zones. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112871
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Behairy, Radwa A., Ahmed A. El Baroudy, Mahmoud M. Ibrahim, Elsayed Said Mohamed, Nazih Y. Rebouh, and Mohamed S. Shokr. 2022. "Combination of GIS and Multivariate Analysis to Assess the Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in Some Arid Zones" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112871
APA StyleEl Behairy, R. A., El Baroudy, A. A., Ibrahim, M. M., Mohamed, E. S., Rebouh, N. Y., & Shokr, M. S. (2022). Combination of GIS and Multivariate Analysis to Assess the Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in Some Arid Zones. Agronomy, 12(11), 2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112871











