Nitrous Oxide Emission and Grain Yield in Chinese Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Rotation: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yields
3.2. N2O Emissions
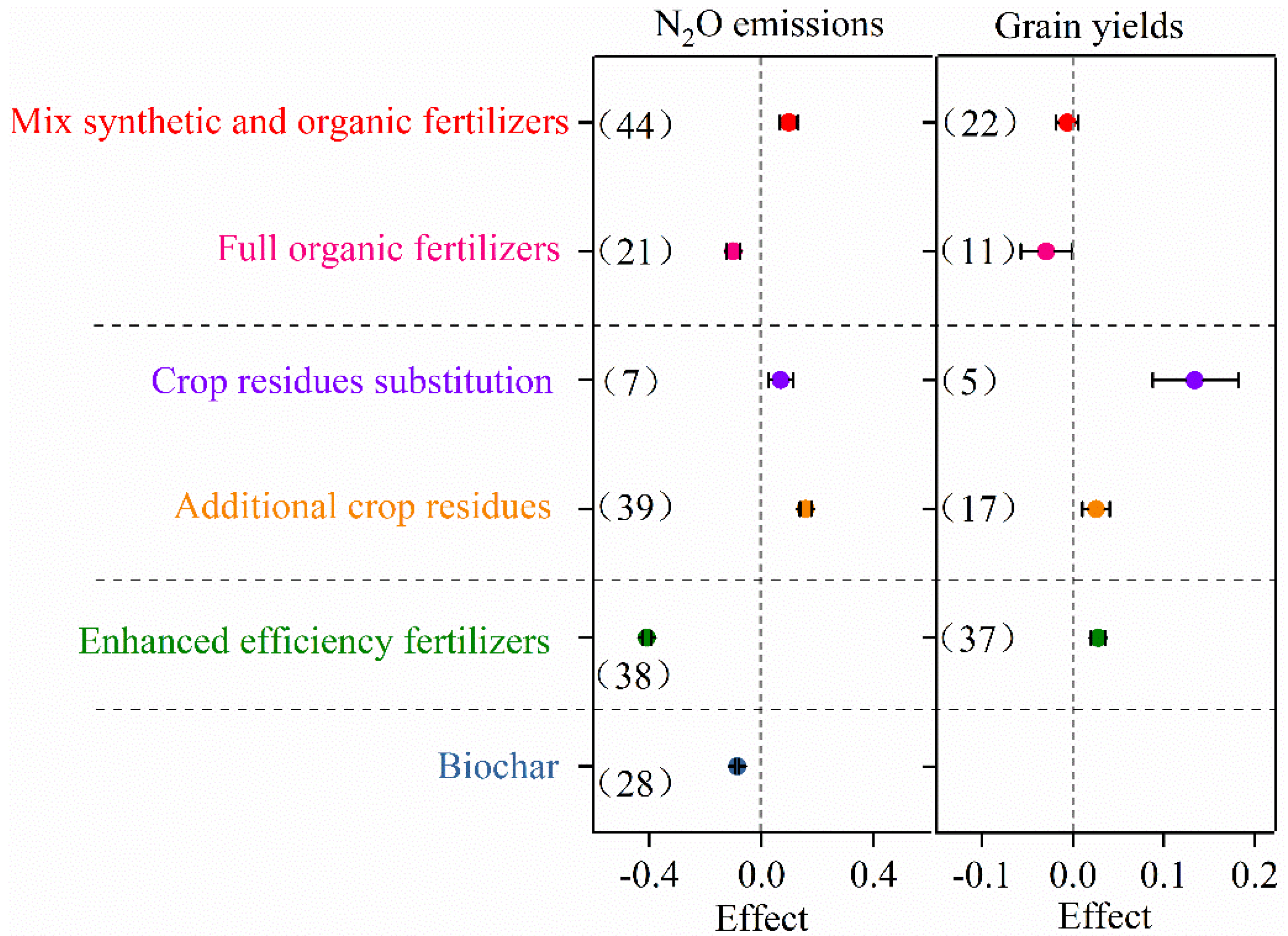
3.3. Effects of Mitigation Strategies
4. Discussion
4.1. Optimal N Input Rate and Maximum Grain Yield
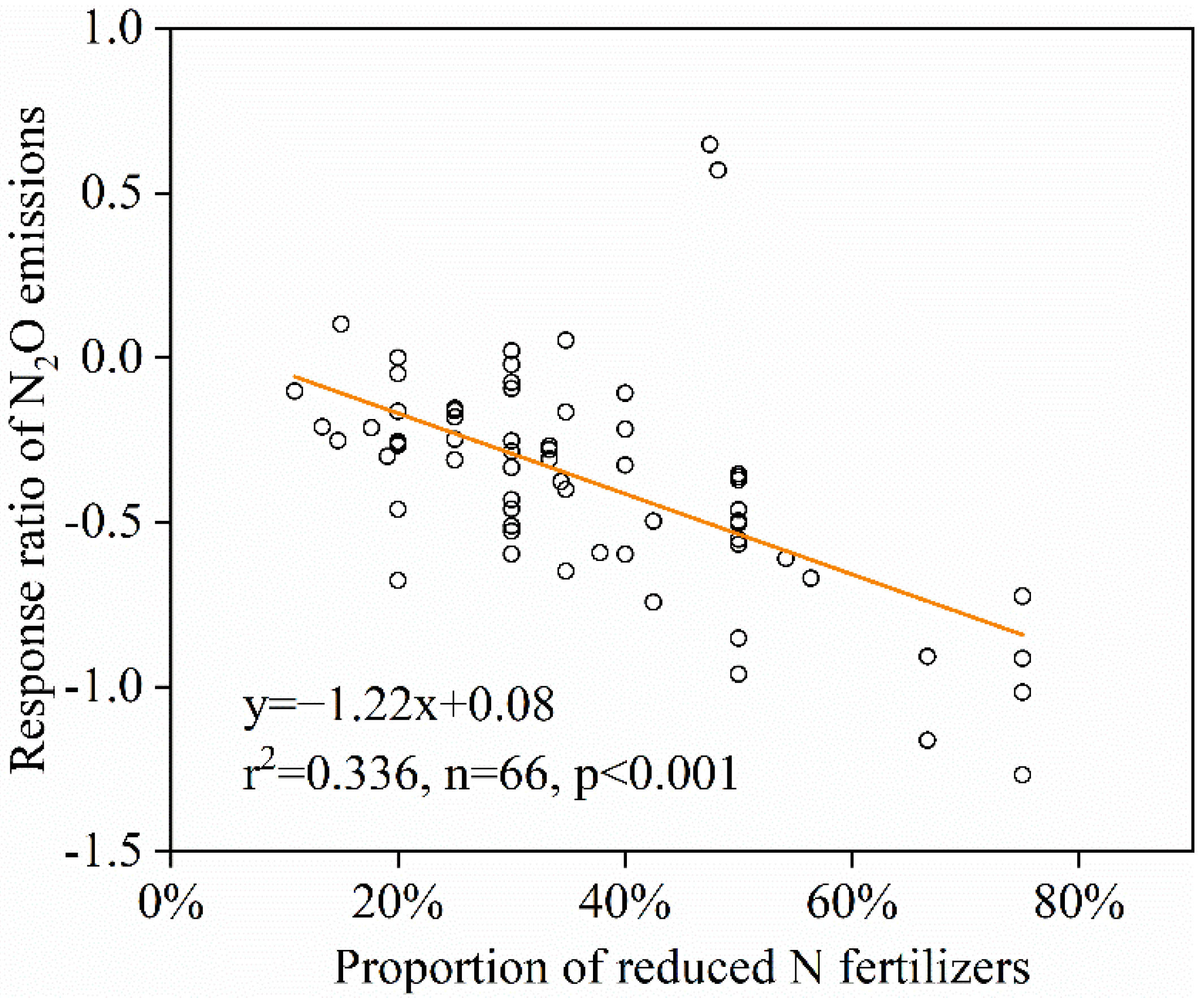
4.2. Variations in N2O Emissions
4.3. N2O Mitigation Strategies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Paustian, K.; Lehmann, J.; Ogle, S.; Reay, D.; Robertson, G.P.; Smith, P. Climate-Smart Soils. Nature 2016, 532, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New Technologies Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Nitrogenous Fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Soils: How Well Do We Understand the Processes and Their Controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Dong, Y.; Xiong, Z. Biochar Mitigated Yield-Scaled N2O and NO Emissions and Ensured Vegetable Quality and Soil Fertility: A 3-Year Greenhouse Field Observation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Han, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zou, J. Emissions of Greenhouse Gases and NO from Rice Fields and a Peach Orchard as Affected by N Input and Land-Use Conversion. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Guo, H.; Xiang, H. The Utility of a Boundary Line Approach for Simulating Denitrification and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from a Regosol under Summer Maize-Winter Wheat Crop Rotation in Southwest China. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 20, e00252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Nicoullaud, B.; Rochette, P.; Pennock, D.J.; Hénault, C.; Cellier, P.; Richard, G. Effect of Topography on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Winter Wheat Fields in Central France. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3149–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Nicoullaud, B.; Rochette, P.; Grossel, A.; Hénault, C.; Cellier, P.; Richard, G. A Regional Experiment Suggests That Soil Texture Is a Major Control of N2O Emissions from Tile-Drained Winter Wheat Fields during the Fertilization Period. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 60, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Khan, A.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B.; Gu, J. Effect of Organic Amendments on Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions from Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Cropping Systems in Northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31933–31945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangjin, D.; Wu, X.; Bai, H.; Gu, J. A Meta-Analysis of Management Practices for Simultaneously Mitigating N2O and NO Emissions from Agricultural Soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Yuan, M.; Liu, J.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qu, D.; Yang, X. Trade-off between Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotations: Implications of a 25-Year Fertilization Experiment in Northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Liu, M.; Ju, X.; Gao, B.; Su, F.; Chen, X.; Rees, R.M. Nitrous Oxide Emissions Increase Exponentially When Optimum Nitrogen Fertilizer Rates Are Exceeded in the North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12504–12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Yang, H.; Huang, C.; Ju, X. Effect of Fertilizer N Rates and Straw Management on Yield-Scaled Nitrous Oxide Emissions in a Maize-Wheat Double Cropping System. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Zheng, X.; Cui, F.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, J.; Xu, Y. Two-Year Simultaneous Records of N2O and NO Fluxes from a Farmed Cropland in the Northern China Plain with a Reduced Nitrogen Addition Rate by One-Third. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 178, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, A.; Rahaman, M.A.; Yang, Z. Inhibited Effect of Biochar Application on N2O Emissions Is Amount and Time-Dependent by Regulating Denitrification in a Wheat-Maize Rotation System in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Niu, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z.; He, T.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Ding, W. Four-Year Continuous Residual Effects of Biochar Application to a Sandy Loam Soil on Crop Yield and N2O and NO Emissions under Maize-Wheat Rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Yao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, C. Characteristics of Annual Nitrous and Nitric Oxide Emissions from Major Cereal Crops in the North China Plain under Alternative Fertilizer Management. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 207, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Di, H.J.; Yu, H.; Zhu, A.; Ding, W. No-Tillage Did Not Increase Organic Carbon Storage but Stimulated N2O Emissions in an Intensively Cultivated Sandy Loam Soil: A Negative Climate Effect. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wu, D.; Bol, R.; Wu, W.; Meng, F. Conservation Farming Practices in Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Cropping Reduce GHG Emissions and Maintain High Yields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 272, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, T.M.; Sapkota, T.B.; Eagle, A.J.; Kantar, M.B.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Majumdar, K. Meta-Analysis of Yield and Nitrous Oxide Outcomes for Nitrogen Management in Agriculture. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F. Benefits and Trade-Offs of Replacing Synthetic Fertilizers by Animal Manures in Crop Production in China: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Lakshmanan, P.; Zhang, F. Global Direct Nitrous Oxide Emissions from the Bioenergy Crop Sugarcane (Saccharum spp. Inter-Specific Hybrids). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Wu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Xu, H. Nitrogen Use Efficiency, Crop Water Productivity and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Chinese Greenhouse Vegetables: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Nie, H.; Guo, H.; Xu, H.; Gunnathorn, T. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Fruit Orchards: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing Environmental Risk by Improving N Management in Intensive Chinese Agricultural Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.K.; Su, F.; Ju, X.T.; Gao, B.; Oenema, O.; Christie, P.; Huang, B.X.; Jiang, R.F.; Zhang, F.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from a Wheat–Maize Double Cropping System with Different Nitrogen Fertilization Regimes. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Bai, H.; Tian, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Gu, J. A Three-Year Measurement Reveals That Partial Conversion from Synthetic Fertilizer to Dairy Manure Increases Cumulative Nitric Oxide Emissions from a Long-Term Experimental Cropland. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 221, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Ding, W.; Cai, Z. Long-Term Application of Organic Manure and Nitrogen Fertilizer on N2O Emissions, Soil Quality and Crop Production in a Sandy Loam Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Xiang, H.; Kuang, F.; Hao, Y.; Qu, D.; Zhu, B. Simulating Denitrification and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Subtropical Maize-Winter Wheat Rotations in Southwestern China Using NOEv2 Model. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Pan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Ju, X.; Wei, H.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Full Straw Incorporation into a Calcareous Soil Increased N2O Emission despite More N2O Being Reduced to N2 in the Winter Crop Season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 335, 108007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F. Direct Emission of Nitrous Oxide from Agricultural Soils. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems. 1996, 46, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R. Quantile Regression; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, G.; Carpenter, J.R.; Rücker, G. Meta-Analysis with R; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Yue, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. In-Season Root-Zone N Management for Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emission and Reactive N Losses in Intensive Wheat Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6015–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Ye, Y.L.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L. Determining the Optimal Nitrogen Rate for Summer Maize in China by Integrating Agronomic, Economic, and Environmental Aspects. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 3031–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme; Eggleston, H.S., Buendia, L., Miwa, K., Ngara, T., Tanabe, K., Eds.; IGES: Kanagawa, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, W. Background Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Croplands in China in the Year 2000. Plant Soil 2009, 320, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquist, B.A.; Anders, M.M.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.A.; Chaney, R.L.; Nalley, L.L.; da Rosa, E.F.F.; van Kessel, C. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Water Use, and Grain Arsenic Levels in Rice Systems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, A.; Zhu, S.; Xiong, Z. Assessing Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Mitigation Potentials from Intensive Vegetable Ecosystems in China: Meta-analysis. J. Afro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 707–714, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X. Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Controlling Factors of Tea Plantations in China. J. Afro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 315–325, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhu, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, J. Regulatory Effects of Soil Properties on Background N2O Emissions from Agricultural Soils in China. Plant Soil 2007, 295, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Quayle, W.; Scheer, C.; Rowlings, D.; Baldock, J. Effect of Soil Texture and Wheat Plants on N2O Fluxes: A Lysimeter Study. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.; Rochette, P.; Whalen, J.K.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Bertrand, N. Global Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors from Agricultural Soils after Addition of Organic Amendments: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaine, N.; Clough, T.J.; Beare, M.H.; Thomas, S.M.; Meenken, E.D.; Ross, J.G. Changes in Relative Gas Diffusivity Explain Soil Nitrous Oxide Flux Dynamics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Brüggemann, N.; Dannenmann, M.; Wang, Y.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Sustaining Crop Productivity While Reducing Environmental Nitrogen Losses in the Subtropical Wheat-Maize Cropping Systems: A Comprehensive Case Study of Nitrogen Cycling and Balance. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ding, W.; Luo, J. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Chinese Maize–Wheat Rotation Systems: A 3-Year Field Measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 65, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Fan, J.; Liu, D. Effect of Long-Term Compost and Inorganic Fertilizer Application on Background N2O and Fertilizer-Induced N2O Emissions from an Intensively Cultivated Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, M.; Xu, M.; Liang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wei, G.; Tian, X. Effects of Long-Term Straw Return on Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Sequestration Rate in North China Upland Crops: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2686–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; van Zwieten, L.; Singh, B.P.; Jeffery, S.; Roig, A.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Biochar’s Role in Mitigating Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Suter, H.; Mosier, A.R.; Chen, D. Using Nitrification Inhibitors to Mitigate Agricultural N2O Emission: A Double-Edged Sword? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A Quantitative Review of the Effects of Biochar Application to Soils on Crop Productivity Using Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bah, H.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhu, B. Characterizing Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Global warming Potential of Wheat-Maize Cropping Systems in Response to Organic Amendments in Eutric Regosols, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. Evaluation of Agricultural and Environmental Performance of Combination of Organic Sources and Chemical Fertilizer on Cropping Systems; Chinese Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2016; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chang, N. Study on the Response of Main Crops Yield and Soil Carbon Sequestration and Greenhouse Gas Emission under Different Fertilization Practices to Future Climate Change in Bohai Rim; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2020; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, H.; Liu, J.; Si, B.; Zhang, A.; Chen, J.; Cheng, G.; Sun, B.; Pi, X.; et al. Effects of Straw and Plastic Film Mulching on Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Loess Plateau, China: A Field Study of 2 Consecutive Wheat-Maize Rotation Cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Cai, Y.; Cai, Z.; Yagi, K.; Zheng, X. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from an Intensively Cultivated Maize-Wheat Rotation Soil in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Ju, X.; Su, F.; Meng, Q.; Oenema, O.; Christie, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Nitrous Oxide and Methane Emissions from Optimized and Alternative Cereal Cropping Systems on the North China Plain: A Two-Year Field Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J. N2O Emission from the Agricultural Soil under the Supply of Nitrogen and Water in Wheat-Maize Rotation System; Henan Agricultural University: Zhengzhou, China, 2017; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Li, J.; Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Ouyang, Z. Lowering Carbon Footprint of Wheat-Maize Cropping System in North China Plain: Through Microbial Fertilizer Application with Adaptive Tillage. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Feng, H. Effects of Biodegradable Plastic Film Mulching on Greenhouse Gas Emissions under Wheat-Maize Rotation System in the Guanzhong Plain. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 2788–2801, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, X. Effects of Agricultura Practices on Soil Carbon Stocks and Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Chinese Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2018; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, J.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Gu, J. Effectsof Long-Term Organic Amendments on Soil N2O Emissions from Winter Wheat-Maize Cropping Systems in the Guanzhong Plain. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2586–2593, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Gao, B.; Christie, P.; Ju, X. Net Global Warming Potential and Greenhouse Gas Intensity in a Double-Cropping Cereal Rotation as Affected by Nitrogen and Straw Management. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7897–7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Effects of Inhibitors and Controlled Release Fertilizers on N2O and NO Emissions from Fluvo-aquic Soil in the Old Course of Yellow River; Northwest Normal University: Lanzhou, China, 2020; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, B. Effect of Different Manures Combined with Chemical Fertilizer on Yields of Crops and Gaseous N loss in Farmland. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2019, 25, 1835–1846, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. Optimal Fertilization Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Wheat-Maize Cropping System; Shandong Agricultural University: Taian, China, 2013; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Effect of Irrigation Amount and Film Mulching on Carbon Sequestration in Wheat-Naize Rotation System; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2017; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. A Study on Biochar Application Affecting Soil Fertility and Nitrous Oxide Emission in Fluvio-Aquatic Soil of North China; Henan Agricultural University: Zhengzhou, China, 2018; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.; Zhang, J.; He, Z.; An, M.; Yang, X.; Gu, J. Effect of Long-Term Dairy Manure Amendment on N2O and NO Emissions from Summer Maize-Winter Wheat Cropping Systems. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 885–892, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Müller, C.; Zaman, M.M.; Kim, D.; Yu, H.; Ding, W. Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions Were Effectively Reduced by Biochar Amendment of Sandy Loam Soil under Maize—Wheat Rotation in the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C.; Oenema, O.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, W. Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions in a Winter Wheat-Summer Corn Double-Cropping System. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, W.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Wang, D. Integrated Management Practices Significantly Affect N2O Emissions and Wheat-Maize Production at Field Scale in the North China Plain. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2013, 95, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Hui, R.; Sui, T.; Yang, L.; Du, W.; Dong, Z. A 4-Year Field Measurement of N2O Emissions from a Maize-Wheat Rotation System as Influenced by Partial Organic Substitution for Synthetic Fertilizer. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y. Effects of Long-Term Straw Return on N2O and NO Emissions from Wheat-Maize Rotation System in Purplish Soil; Inner Mongolia University: Hohhot, China, 2021; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H. Effect of Organic Fertilizer and Inorganic Fertilizer Application on N2O and NO Emissions from Fluvo-Aquic Soil in the North China Plain; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2020; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, D.; Wu, W.; Lal, R.; Meng, F. Effects of Optimized N Fertilization on Greenhouse Gas Emission and Crop Production in the North China Plain. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 205, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; He, K. Effect of N Fertilizer Types on N2O and NO Emissions under Drip Fertigation from an Agricultural Field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P. Effect of Nitrification Inhibitors on Mitigating N2O and NO Emissions from an Agricultural Field under Drip Fertigation in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhao, K.; Wu, X.; Bai, H.; Yang, X.; Gu, J. Effects of Stalk Incorporation on Soil Carbon Sequestration, Nitrous Oxide Emissions, and Global Warming Potential of a Winter wheat-Summer Maize Field in Guanzhong Plain. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 569–576, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Laraib, I.; Shang, M.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Chu, Q. Irrigation-Induced Hydrothermal Variation Affects Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Crop Production. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Dynamic Analysis and Nitrogen Application Simulation on N2O Emission from Wheat-Maize Farmland in Huang-Huai-Hai Region; Shandong Agricultural University: Taian, China, 2019; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Study on Warming Potential and Nitrogen Balance of Long-term Conservation Tillage Farmland and Microbial Processes of N2O Emissions; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2021; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. Effects of Dicyandiamide Combined with Nitrogen Fertilizer on N2O Emission and Economic Benefit in Winter Wheat and Summer Maize Rotation System. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1999–2006, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Han, X.; Meng, F.; Wu, W.; Zhou, M.; Brüggemann, N.; Bol, R. Potential Dual Effect of Nitrification Inhibitor 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate on Nitrifier Denitrification in the Mitigation of Peak N2O Emission Events in North China Plain Cropping Systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhu, B. Effects of Fertilization Regimes on N2O and NO Emissions from Agro-Ecosystems of Purplish Soil. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. Environ. 2018, 26, 203–213, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Yan, G.; Zheng, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Straw Return Reduces Yield-Scaled N2O plus NO Emissions from Annual Winter Wheat-Based Cropping Systems in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Wang, X.; Du, H.; Shen, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, K.; Li, W. N2O and CO2 Emissions, Nitrogen Use Efficiency under Biogas Slurry Irrigation: A Field Study of Two Consecutive Wheat-Maize Rotation Cycles in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Effects of Water and Fertilizer Supply on Soil N2O Emissions in Maize-Wheat Rotation System; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2017; (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, F.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Xiao, G.; Wu, W. Optimized Fertigation Maintains High Yield and Mitigates N2O and NO Emissions in an Intensified Wheat–Maize Cropping System. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, G.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Wu, W.; Meng, F. Mitigation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions through Optimized Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization in Intensively Managed Wheat–Maize Production. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Maize-Wheat Field during 4 Successive Years in the North China Plain. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Ke, Y.; Zhu, B. Effects of Afforestation on Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions in a Subtropical Montane Agricultural Landscape: A 3-Year Field Experiment. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 266–267, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Brüggemann, N.; Bergmann, J.; Wang, Y.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. N2O and CH4 Emissions, and NO3− Leaching on a Crop-Yield Basis from a Subtropical Rain-Fed Wheat-Maize Rotation in Response to Different Types of Nitrogen Fertilizer. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Wang, T.; Bergmann, J.; Brüggemann, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Kuang, F. Nitrate Leaching, Direct and Indirect Nitrous Oxide Fluxes from Sloping Cropland in the Purple Soil Area, Southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Zheng, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Nitrate Leaching from a Rain-Fed Wheat-Maize Rotation in the Sichuan Basin, China. Plant Soil 2013, 362, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Mu, Y. The Influence of Straw Returning on N2O Emissions from a Maize-Wheat Field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
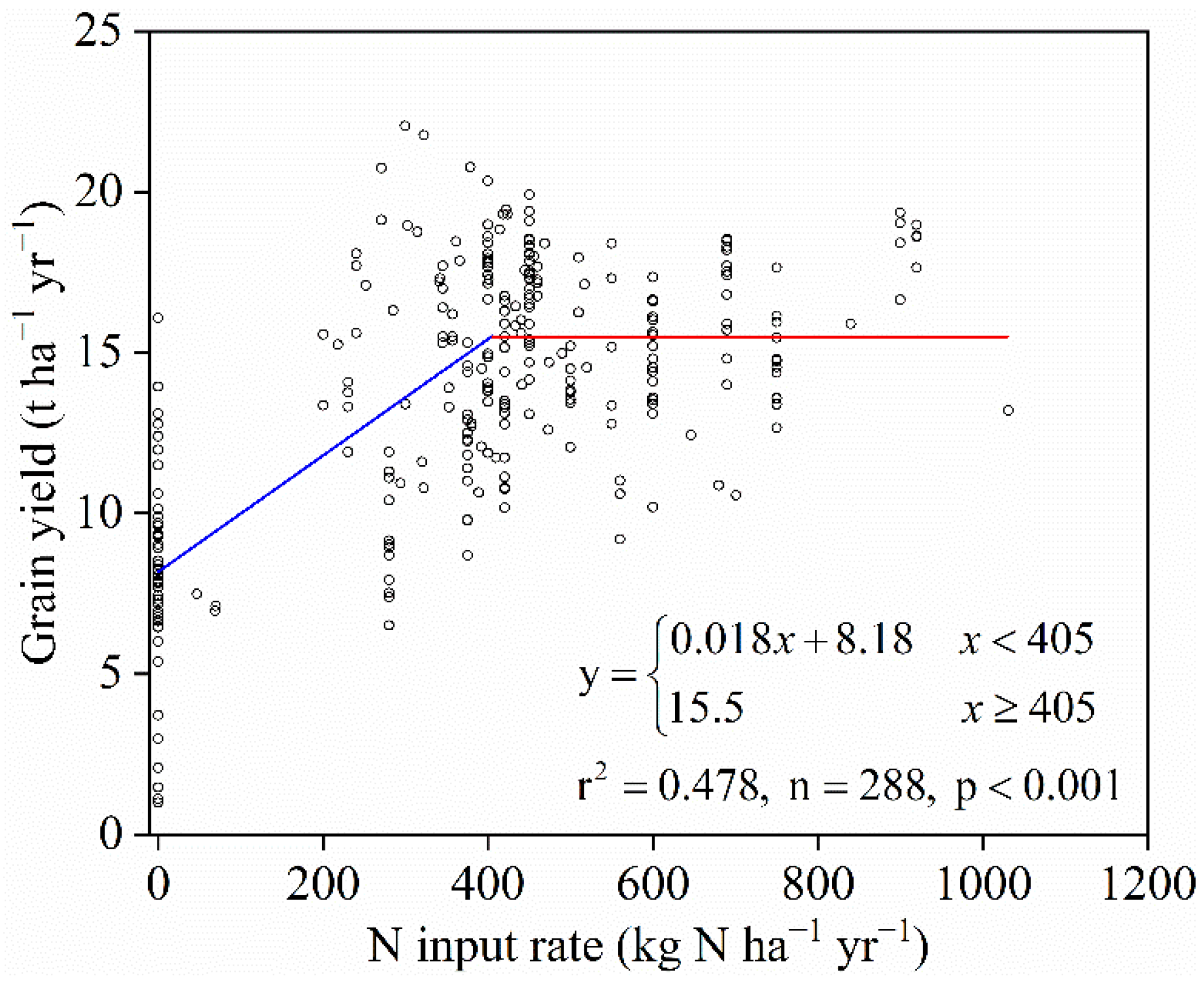
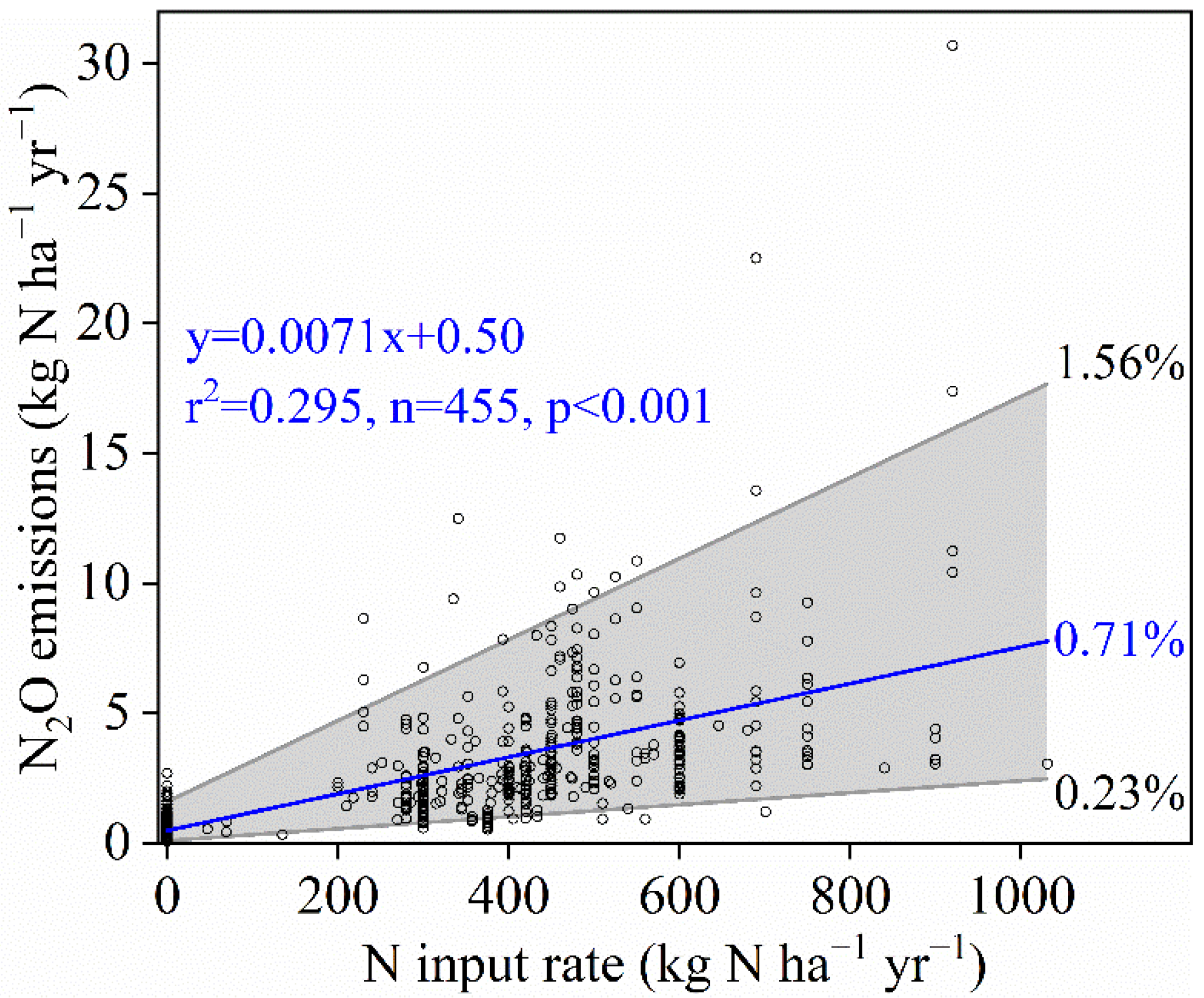
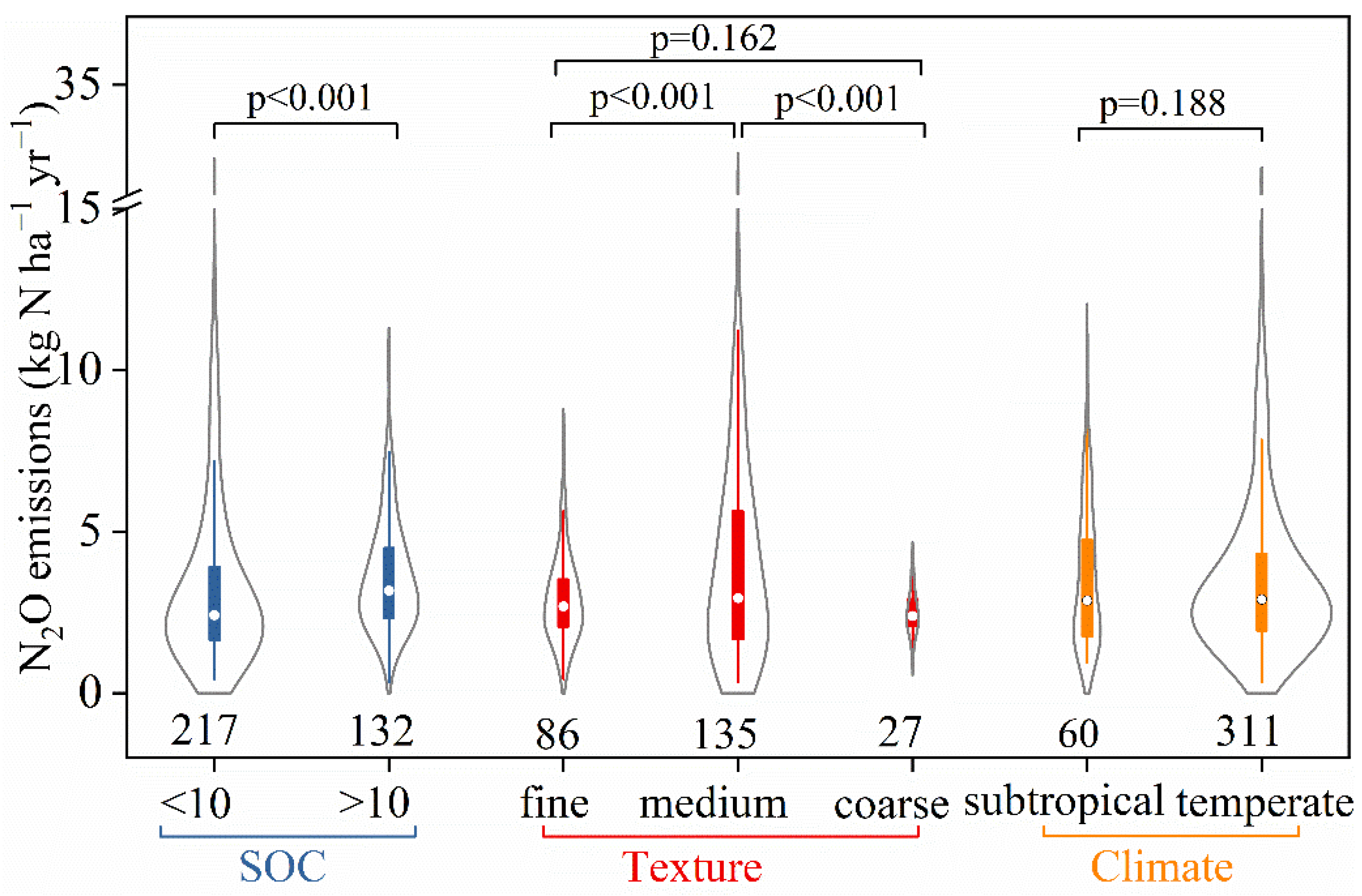
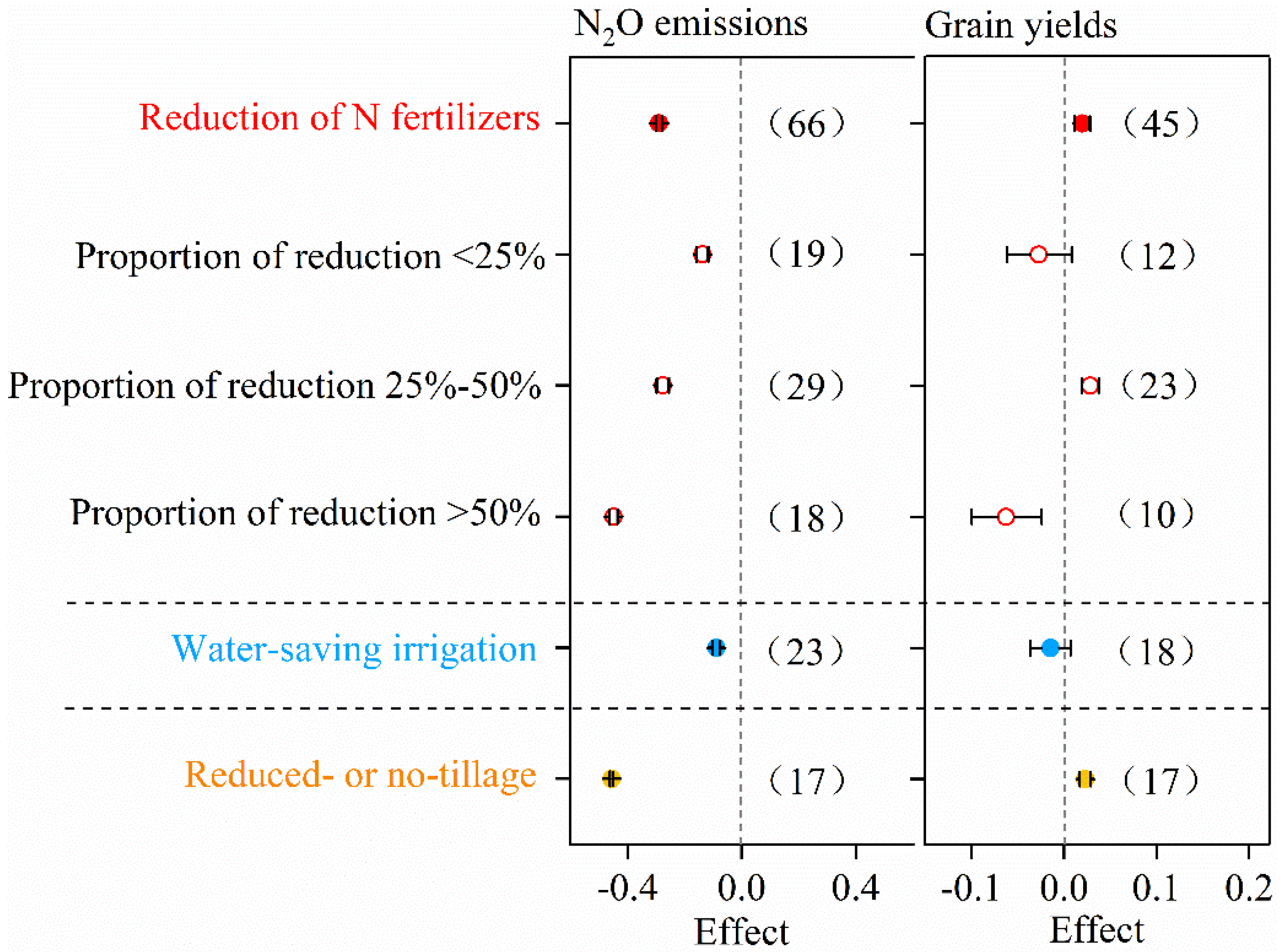
| Region. | Crop | Optimal N Input | Maximum Grain Yield | Model | n | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg N ha−1 yr−1/season−1 | t ha−1 yr−1/season−1 | |||||
| China | winter wheat–summer maize | 405 | 15.5 | linear-plateau | 288 | This study |
| North China Plain | winter wheat | 129 | 6.6 | linear-plateau | 59 | [35] |
| North China Plain | summer maize | 289 | 8.5 | quadratic | 101 | [36] |
| North China Plain | winter wheat–summer maize | 314 | 14.4 | linear-plateau | 37 | [10] |
| Asia | wheat | 315 | 6.3 | quadratic | n.a. | [21] |
| Asia | maize | 313 | 8.3 | quadratic | n.a. | [21] |
| Region | Crop | N2O Emissions | Emission Coefficient | Background Emission | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg N ha−1 yr−1/season−1 | % | kg N ha−1 yr−1/season−1 | |||
| China | winter wheat–summer maize | 0.3–30.7 | 0.71 | 0.50 | This study |
| world | upland crops | 0.89–8.0 | 1.25 | 1.0 | [32] |
| world | maize | 0.1–11.5 | 1.06 | 1.15 | [39] |
| world | wheat | 0.1–9.3 | 1.21 | 0.59 | [39] |
| world | sugarcane | 0.03–9.56 | 1.21 | 0.93 | [23] |
| world | fruit orchard | −0.12–26.0 | 1.36 | 0.73 | [25] |
| China | vegetable | 0.03–48.4 | 0.8 | 16.9 | [40] |
| China | greenhouse vegetable | 0.2–41.8 | 0.95 | 0.78 | [24] |
| China | tea plantation | 1.19–32.7 | 1.8 | 1.70 | [41] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, C.; Wu, X.; Bai, H.; Gu, J. Nitrous Oxide Emission and Grain Yield in Chinese Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Rotation: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102305
Yao C, Wu X, Bai H, Gu J. Nitrous Oxide Emission and Grain Yield in Chinese Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Rotation: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy. 2022; 12(10):2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102305
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Chengcheng, Xiongwei Wu, He Bai, and Jiangxin Gu. 2022. "Nitrous Oxide Emission and Grain Yield in Chinese Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Rotation: A Meta-Analysis" Agronomy 12, no. 10: 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102305
APA StyleYao, C., Wu, X., Bai, H., & Gu, J. (2022). Nitrous Oxide Emission and Grain Yield in Chinese Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Rotation: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy, 12(10), 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102305







