Abstract
In 2003, a glyphosate-resistant plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) population located in the Robertson district of South Africa was subjected to different glyphosate dosages and the highest dosage (7200 g a.e. ha−1) gave no acceptable levels of control. Here we reconfirm resistance and investigate the mechanism of glyphosate resistance. Dose-response curves indicated that the glyphosate dosage rate causing 50% survival (LD50) for the resistant (R) biotype is 43 times greater than for the susceptible (S) biotype, i.e., 43-fold resistant to glyphosate. Investigation into the molecular mechanism of plantago showed shikimate accumulation of the R biotype was lower than that of the S biotype. The reported 31P and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra show rapid glyphosate translocation into the young untreated leaves of the S biotype. No glyphosate translocation was observed in the R biotype. A point mutation in the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) gene, resulting in an amino acid substitution was also observed, indicating two unique glyphosate resistance mechanisms within the R biotype. The rapid evolution of glyphosate-resistant weeds threatens the usage of the world’s most important herbicide (glyphosate), which is essential in world food production and further limits grower options for weed control. New weed management strategies will be necessary to combat plantago R biotypes.
1. Introduction
Glyphosate [N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine] is by far the world’s most important herbicide, due to its versatility and affordability [1,2,3].
Glyphosate resistant weed species have become very common and they threaten glyphosate-based weed management strategies. This is because glyphosate is the world’s most important herbicide, and is used worldwide to control a broad spectrum of weeds in various cropping systems. Consequently, high selection pressure from glyphosate abuse has led to the evolution of resistance to glyphosate in weeds [3,4,5,6,7]. Glyphosate resistance was first reported in 1996 in an apple orchard. Since the development of glyphosate, more than 71 different countries have reported glyphosate resistance in more than 52 weed species, and the number of glyphosate resistant weed species is expected to increase [3,7]. Although weeds can be destructive in various situations, the ones that have a major economic impact are those in glyphosate-resistant crops. Moreover, glyphosate is widely used to control weeds that are already resistant to other herbicides. Because of this, glyphosate resistant weeds pose a serious threat to sustainable weed management in agronomic crops. This has been exacerbated by the fact that no new site of action has been introduced in the last three decades [3]. Glyphosate is absorbed by the plant, and is then translocated symplastically via the phloem from mature (source) to the young meristematic cells (sink) of the plant [8]. It then enters the chloroplast where the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) enzyme is located [5,8]. Glyphosate then inhibits the EPSPS in the plant cell chloroplasts, which results in accumulation of shikimic acid. The EPSPS enzyme is essential for the shikimate pathway, responsible for the synthesis of three amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan). Inhibition of the biosynthesis of these essential aromatic amino acids results in cell death [5,8].
Resistance to glyphosate in certain R weed biotypes has been studied extensively and various mechanisms have been identified as the reason for resistance: amplified EPSPS, substitution of EPSPS amino acid, multiple gene copying, and reduced translocation through glyphosate sequestration [9]. Limited leaf absorption of glyphosate has been shown to grant low level glyphosate resistance [6,9,10,11,12]. Mutation of EPSPS (target site) and reduced translocation (nontarget site) have all been implicated in conferring glyphosate resistance, particularly the latter has been suggested to be the major mechanism [13,14]. Carbon-13 (13C NMR) and phosphorus-31 (31P NMR) nuclear magnetic resonance are essential tools for the chemist to observe most organic and inorganic compounds; the translocation of glyphosate in leaves can also be monitored by NMR [15,16].
Plantago belongs to the Plantaginaceae family and is a wind pollinated herb [17]. Plantago is characterized by small leaves and consists of upright circular arrangement of leaves produced from the base [18]. Plantago flowers throughout the year, but mostly in the summer [18], and is well-distributed around the world, mostly in mesic or moist habitats across various soil types [17]. In certain countries, plantago is grown for forage purposes [19]. Plantago is resistant to drought, pests, and diseases, and has been reported to be a reservoir of economical important viruses and vectors. [20]. Weeds belonging to the Plantaginaceae family have been reported as the world worst weeds [3,17]. Plantago is a very destructive weed and occurs in vineyards, orchards, sidewalks, and cropping fields [21], due to the fact that it has a high reproductive output [22]. Plantago appears to have been neutralized or indigenous in many parts of the world [18]. Fruit growers in South Africa observed consistent failure in controlling plantago with glyphosate in an area of more than 5000 hectares (12,355 acres). This is understandable since the weed species has long been reported as being glyphosate resistant [7]. However, the mechanisms endowing resistance to plantago R biotypes have never been documented [7]. We hypothesize that failure to control plantago R biotypes is due to persistent selection of glyphosate resistant genotypes within the population, and that the ability of the R biotypes to survive after glyphosate exposure is conferred by one or more resistance mechanisms. Therefore, the aim of our study was (a) to reconfirm glyphosate resistance in a putative R biotype and (b) to determine what mechanism(s) are responsible for resistance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dose Response Trial
Seed from a susceptible (S) plantago biotype NW (S) and from a putatively resistant R2 (R) plantago biotype located in the Robertson district of South Africa was collected in 2018 and used in the current study (Table 1). The growers in the Robertson area usually apply glyphosate and paraquat in rotation to control weeds. Plants from the resulting F2 generation were germinated in sand and also used for subsequent experiments. After germination, the seedlings were transplanted in small plastic pots filled with coarse gravel. The seedlings were placed in a glasshouse and irrigated with a standard Steiner nutrient solution [23]. Glasshouse was set at 20/25 °C, (12/12 h night/day) photoperiod, and 1500 mmol m−2 s−1 PAR. At the 2–3 leaf stage, the plants were subjected to glyphosate (Roundup® Turbo, 450 g a.e. L−1 Bayer Crop Science (Pty) LtD, Isando, South Africa) applications in a dose response trial using a custom built, cabinet pneumatic sprayer equipped with a flat fan nozzle (Stellenbosch University, Department of Engineering) delivering herbicide at 108 L ha −1 at 200 kPa, with a speed of 1 m s −1. Glyphosate was applied at dosage rates of 0, 270, 540, 1080, 2160, 4320, 8640, and 17,280 g a.e. ha−1. Water delivery rate was 100 L ha−1. The dose response trial was a 2 × 8 factorial arranged in a completely randomized block design (CRBD), replicated six times. Evaluation took place 42 days after herbicide application, when survival rate and dry mass were determined. Plants were recorded as alive or dead if they exhibited clear or lack of regrowth 42 days after herbicide application.

Table 1.
Localities where resistant (R) and susceptible (S) plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) biotypes were collected.
2.2. Shikimic Acid Analysis
High shikimate accumulation in leaves is an indicator of susceptible EPSPS enzyme and the reverse is true for R biotypes [5]. To document this, resistant and susceptible plantago biotypes sprayed with glyphosate at 2160, 4320, 8640, and 17,280 g a.e. ha−1 were harvested after one week. Leaf tissue of treated and control plants were collected from each biotype. The plants were harvested and dried at 70 °C. This was due to very high shikimate accumulation after six [24] and seven days (168 h) [25], as reported in literature. The plants were then ground to a fine powder using a milling machine (Peter Rassloff Instruments and Services Pty (Ltd.), Cape Town, South Africa). One mL of 70% methanol (MeOH) was added to ca. 10 mg of each sample. The samples were vortexed and extracted in the oven at 60 °C for three hours. Subsequently, 250 µL of each sample was transferred into a two mL vial and completely dried under a gentle stream of nitrogen. The dried samples were derivatized with 100 µL of acetonitrile (ACN) and 50 µL N, O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) at 80 °C for one hour. The samples were vortexed and transferred to an insert (positioned in a vial) and injected with a 10:1 split ratio into a GC–MS instrument (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) [26].
Gas Chromatograph Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS)
Separation was performed on a gas chromatograph (6890 N, Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). coupled to an Agilent Technologies Inc. inert XL EI/CI Mass Selective Detector (MSD) (5975, Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The GC–MS system was coupled to a CTC Analytics PAL autosampler. Separation of sugars was performed on a ZB-Semivolatile (30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm film thickness) Zebron 7HG-G027-11-GGA capillary column. Helium was used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The injector temperature was maintained at 250 °C. One µL of the sample was injected in 10:1 split ratio. The oven temperature was programmed as follows: 100 °C for two minutes and then increased to 320 °C at a flow rate of 20 °C per minute. The mass selective detector (MSD) was operated in a full scan mode and the source and quad temperatures were maintained at 240 and 150 °C, respectively. The transfer line temperature was maintained at 250 °C. The mass spectrometer was operated under electron impact (EI) mode at an ionization energy of 70 eV, scanning from 35 to 600 m/z. Shikimic acid determination using GC–MS was carried out at the Central Analytical Facilities (CAF) specialized laboratories as per [26], but the method was modified substantially.
2.3. 31P and 13C NMR
Small concentrations of glyphosate in plant cells can be determined by using 31P and 13C NMR procedures (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) [15,27]. Specifically, for this study, due to the easy sample preparation, the translocation of glyphosate in leaves was monitored by solid state NMR [27,28,29]. Comparison of glyphosate translocation in resistant and susceptible plantago biotypes dried leaf tissue was evaluated using both 31P CP MAS and 13C CP MAS NMR after the application of 13C2-labeled glyphosate at CAF specialized laboratories.
Twelve resistant and susceptible plantago biotypes grown in small plastic pots in coarse gravel placed were used. A drop of 13C2 enriched glyphosate made up in commercial formulation of four times the recommended rate (540 g a.e. ha−1) [15]. Roundup® Turbo was applied at the middle of a mature fully expanded leaf [2]. After two days, plants were harvested and sectioned into exposed (treated) leaf and protected (untreated) leaves. The untreated leaves were milled using a milling machine, then vacuum-dried immediately before being subjected to solid state 31P and 13C NMR spectrometry [30]. The 13C2-enriched glyphosate was chosen because of the low natural abundance and receptivity of the 13C isotope. The spectra were acquired using an Agilent VNMRS (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) 500 MHz two-channel solid state NMR spectrometer using 4 mm zirconia rotors spinning at 10,000 Hz, utilizing a 4 mm T3 HX MAS probe. All cross-polarization (CP) magic angle spinning (MAS) spectra were recorded with the latest VnmrJ 4.2 (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) instrument software at ambient temperature with optimized high-power proton decoupling; a relaxation delay of 2 s and 35,587 scans were collected to obtain sufficient signal-to-noise. Both experiments employed were sensitivity-enhanced cross-polarization experiments where the magnetization is transferred from the most NMR sensitive 1H nucleus to either the 31P or 13C nuclei utilizing a 2 us proton excitation pulse width and 2 ms contact time, and a 20 ms acquisition time. The probe was fine-tuned to 1H, 31P, or 31C for each sample.
2.4. EPSPS cDNA Sequencing
RNA was extracted using the NucleoSpin® RNA Plant Kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany). The RNA samples were quantified and assessed for quality using the Bioanalyzer RNA 6000 Nano Assay (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and cDNA was synthesized from 200 ng RNA for each of the samples and extracted using the SuperScript™ VILO™ cDNA synthesis kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The EPSPS gene was amplified with 20 ng first-strand synthesized cDNA, using 10 pmol of each of the sense 5′-GATGTCGAGGAAGACAAAGC-3′ and antisense 5′-CCTTCCAGAAGAGTTACGTG-3′ primers in a final reaction volume of 25 uL, containing 200 µM of each dNTP and one-unit Platinum™ II Taq Hot-Start DNA Polymerase (ThermoFisher Scientific). The cDNA for the samples were amplified using standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) conditions at an annealing temperature of 58 °C to yield a fragment of 795 bp. The resulting PCR fragment was purified with 1.8× volume Agencourt AMPure XP Reagent (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). Direct cycle sequencing was performed on the purified PCR fragment using standard protocols (DNA sequencing Unit, Central Analytical Facilities, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch). DNA sequences from each of the plants were aligned to the partial plantago 5-enol-pyruvylshikimate-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) coding sequence (Genbank accession number: AY545665.1). For the multiple sequence alignment, the reference and alternative alleles were separated using the online analysis software Poly Peak Parser (http://yosttools.genetics.utah.edu/PolyPeakParser/) (accessed on 7 June 2019) [31]. Six independent RNA extractions from each biotype were analyzed and the sequence results were aligned and compared. Sequencing was conducted at CAF specialized laboratories.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All of the experiments had six individual replicates, but each experiment was repeated twice. Nonsignificant differences were detected between repeated experiments; therefore, data from the two experiments were pooled and used for subsequent analysis. For the NMR studies, Mestrenova version 11.02 was employed (Mestrelab research 2020, Santiago de Compostela, Spain).
The herbicide dosage rate causing 50% reduction in survival rate % (SR) (LD50) or growth reduction (GR50) was calculated for each biotype by a log–logistic model using STATISTICA 2019 software version 13.6 (TIBCO SOFTWARE Inc., 2019, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
Data sets were fitted to the log–logistic model:
where C = lower limit, D = upper limit, b = slope, and I50 = dosage rate yielding 50% response [32].
y = C + D − C/1 + exp (b (log(x) − log (I50))),
3. Results
3.1. Dose Response Trial
The dose response trial established 0% survival of a known plantago S biotype at less than half the recommended glyphosate dosage rate (130 g a.e. ha−1). On the contrary, putative R biotype was markedly less affected; 5775 g a.e. ha−1 was needed to achieve LD50 (Table 2 and Figure 1). The resistance index (RI) of 43 for the R biotype in response to glyphosate applications was noted (Table 2). The putative resistant R2 (R) biotype was therefore confirmed to be resistant to glyphosate. Glyphosate rate causing 50% reduction of growth for the R biotype was found to be 784 g a.e. ha−1, fivefold greater than the S biotype (134 g a.e. ha−1) (Table 2 and Figure 2).

Table 2.
Parameter estimates and associated model statistics for log–logistic response curves of resistant (R) and susceptible (S) plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) biotypes in response to glyphosate.
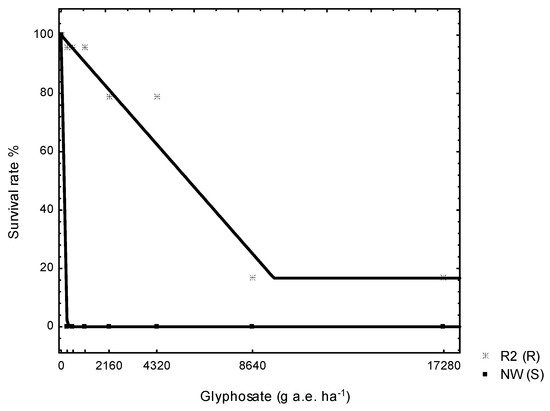
Figure 1.
Percentage survival rates of susceptible NW (S) and putative resistant R2 (R) plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) biotypes, 42 days after application of different glyphosate dosages rates.
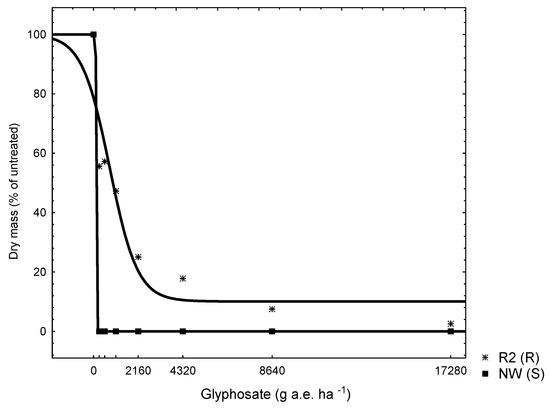
Figure 2.
Dry mass of susceptible NW (S) and putative resistant R2 (R) plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) seedlings, 42 days after application of different glyphosate dosages rates.
3.2. Shikimic Acid
The highest glyphosate dosage resulted in 93% S biotype shikimate accumulation compared to 36% accumulation by the R biotype. Accumulation of shikimate occurs at higher concentrations in S biotypes. Much larger glyphosate dosages are required before the same accumulation is seen in R biotypes (Figure 3).
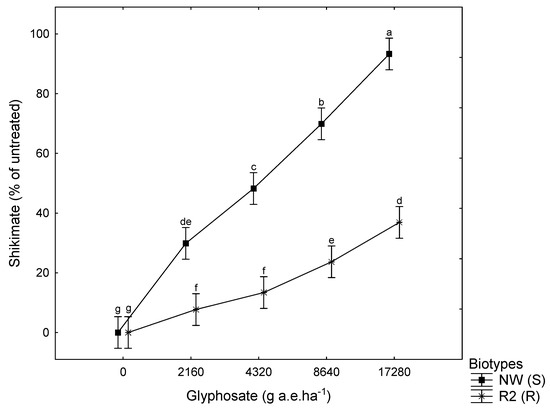
Figure 3.
Shikimate accumulation in susceptible NW (S) and putative resistant R2 (R) plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) after application at various glyphosate dosages rates. Means indicated by different letters differed significantly at p ≤ 0.05 according to Fishers LSD. Means are pooled from two experiments. Vertical bars denote ± standard error of the mean.
3.3. Relationship between Shikimate, Survival Rate, and Dry Mass
There was a significant and negative correlation between shikimate and the dose response results for the R biotype, specifically, survival rate and dry mass (Table 3). Therefore, lower shikimate implies higher survival rate and dry mass in the R biotype. For the S biotype, due to low or lack of variance, correlation was not feasible.

Table 3.
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients between survival rate, dry mass, and shikimate of the plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) R biotype.
3.4. Glyphosate Translocation Using 31P and 13C NMR
The 31P CP MAS NMR spectra from the untreated leaf of the S biotype gave a glyphosate signal at 13 ppm, at the same chemical shift as the (standard) C2-labeled glyphosate and both relative to a H3PO4 (aq) reference standard (Figure 4). Similarly, for 13C NMR, the untreated leaf of the R biotype gave no glyphosate signal. A small glyphosate signal was observed for the S biotype, which was established at 50 ppm by using a 13C2-labeled glyphosate standard (Figure 5).
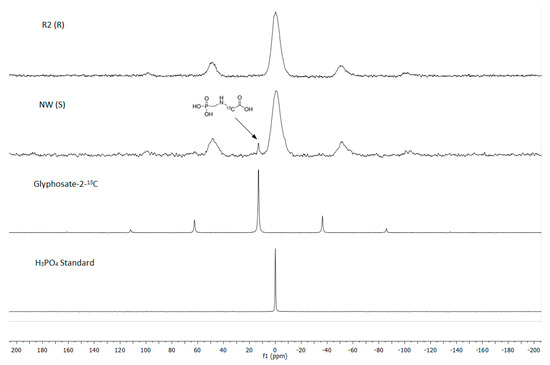
Figure 4.
The 31P NMR spectra obtained from untreated NW (S)/R2 (R) biotypes plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) dried leaf tissue, 48 h after glyphosate application on the treated leaves. Arrow indicates glyphosate signal approximately at 13 ppm identical to the glyphosate-2-13C (99% atom) standard’s chemical shift. All 31P spectra are referenced against orthophosphoric acid set at 0 ppm.
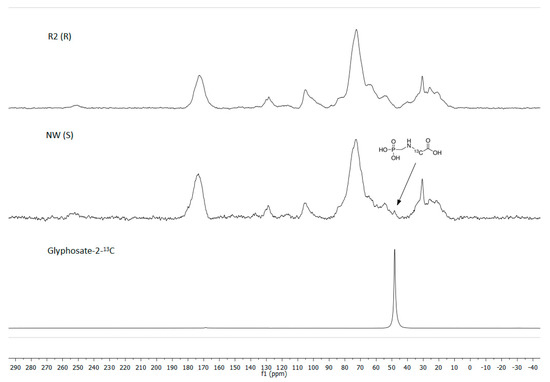
Figure 5.
The 13C NMR spectra obtained from untreated NW (S)/R2 (R) biotypes plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) dried leaf tissue, 48 h after glyphosate application on the treated leaves. Arrow indicates glyphosate signal at approximately 50 ppm identical to the glyphosate-2-13C (99% atom) standard’s chemical shift.
3.5. EPSPS cDNA Sequencing
To identify DNA variants in resistant and susceptible plantago biotypes, the partial coding sequence of the EPSPS gene was PCR amplified and sequenced (Figure 6 and Figure 7). A nucleotide variant, resulting in a predicted Proline (Pro) to Serine (Ser) substitution at position 106 of the amino acid sequence of EPSPS [31], was identified in the R biotype (Figure 6). The reference and alternative alleles were included in the multiple sequence alignment against the plantago EPSPS gene reference sequence (Figure 7). A Cytosine to Adenine transition was observed in the resistant biotype (Figure 6) and in the susceptible alternative allele (Figure 7). Cytosine to Thymine transition DNA variant, predicted to result in a substitution of a Proline at position 106 with a Serine, is denoted by the red arrow (Figure 6 and Figure 7).
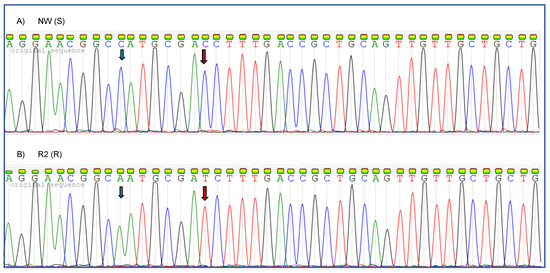
Figure 6.
Electropherograms depicting 41 bp of EPSPS for (A) susceptible NW (S) and (B) resistant R2 (R) plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) biotypes in the sense direction. Cytosine to Adenine transition DNA variant shown by the blue arrow. The red arrow denotes the position of the DNA variant in EPSPS of plantago, which substitutes a dCTP with a dTTP in the resistant phenotype.
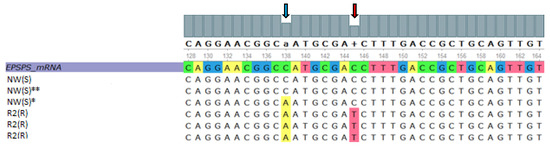
Figure 7.
Multiple nucleotide sequence alignment of resistant and susceptible plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) biotypes against the EPSPS partial reference coding sequence of plantago. Two DNA variants are highlighted in the image: (1) Cytosine to Adenine transition DNA variant shown by the blue arrow and (2) Cytosine to Thymine transition DNA variant, predicted to result in a substitution of a Proline at position 106 with a Serine, denoted by the red arrow. The asterisk (‡) indicates the alternative allele and double asterisk (‡‡) indicates the reference allele.
A partial alignment of the EPSPS amino acid sequence was performed for eleven Eudicots against the partial plantago reference sequence (GenBank accession number: AAT45242.1) (Figure 8). The alignment shows conservation of the Proline amino acid at position 106 (Figure 8). Included in this alignment is the Arabidopsis thaliana and Eleusine indica EPSPS sequences presented by [31]. The only amino acid change shown in the multiple sequence alignment for EPSPS at position 106 of the amino acid sequence was that of the plantago R biotype (Figure 8).
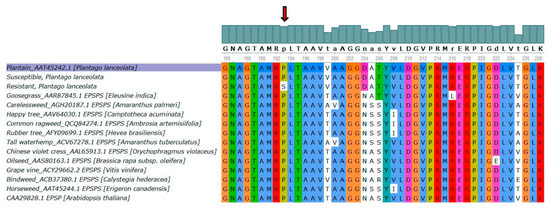
Figure 8.
Multiple alignment of eleven Eudicots EPSPS amino acid sequences, the EPSPS Arabidopsis thaliana, and EPSPS Eleusine indica amino acid sequences, as described by [31], against that of plantago (Plantago lanceolata L.) EPSPS resistant and susceptible biotypes. Highlighted amino acids indicate similarities against the plantago reference sequence. The predicted nonsynonymous variant in the resistant plantago biotype is shown with a red arrow and results in the substitution of a Proline to a Serine at position 106 (Pro-106-Ser), as described by [31].
4. Discussion
The R2 biotype exhibited a high level of resistance, viz., R/S ratios of greater than 40 to glyphosate. These results are similar to Tehranchian et al. [33], but greater than those reported by Yu et al. [2], who reported an R/S ratio of 14 in a ryegrass population after glyphosate application, which is three times less resistant than plantago. These shows that glyphosate resistant weeds are increasing exponentially and becoming virulent [3]. Unfortunately, no recent studies have reported on plantago resistance to glyphosate for a direct comparison. There are currently more than 52 weed species resistant to glyphosate in more than 73 countries. This is likely to be an undercount since there may have been some reports that have not yet been reported [3,7].
The shikimate accumulation observed in the NW (S) biotype after glyphosate application serves as an indicator for susceptible EPSPS enzyme because the shikimate pathway is blocked [34]. Shikimate accumulation occurs in higher concentrations in S biotypes, relative to the R biotypes. This was also reported by several other authors [5,11,25,33,34]. The differences in shikimate accumulation is in line with dose response curve results, where the R biotype showed 43-fold less sensitivity to glyphosate compared to the S biotype. In addition, the survival rate and dry mass of the R biotype was found to be negatively correlated to shikimic accumulation. Accumulation of shikimic acid has been reported to be related to glyphosate dosages [35]. Lack of shikimate in the R biotypes could be because glyphosate does not reach the target sites due to sequestration or due to the (observed) mutations on the EPSPS enzyme [5,8,15,34].
Glyphosate moves through the phloem from high concentration (treated leaves) to lower concentration (untreated leaves) [36]. The observed 31P CP MAS NMR spectra from the S biotype were corroborated by other authors who reported glyphosate signal at approximately 12 ppm [28]. Slight shift differences may be attributed to electron shielding differences between the crystalline and amorphous glyphosate used as the standard. Previous studies using 14C-labeled glyphosate have shown that just after one day of application, about 35% of the glyphosate was translocated from the exposed leaf to the protected leaf [37]. This movement appears to be very quick in S biotypes compared to R biotypes, or perhaps absent in R biotypes [2] since no glyphosate signal was observed for the untreated leaf of the R biotype. This means glyphosate remained at the site of application in the R biotype, even after 48 h following glyphosate application. If there was any translocation, it was below the level of 31P CP MAS NMR detection. Similarly, the observed 13C NMR low glyphosate signal chemical shift was corroborated by [29]. The reason for a small signal is due to 13C low absolute receptivity/natural abundance relative to 31P, based on NMR frequency table. The R biotype gave no glyphosate signal. Reduced glyphosate translocation allows R biotypes to survive glyphosate applications by reducing the amount of glyphosate that moves from the treated leaves to the meristems [34]; this was certainly the case in plantago R biotypes.
In this study, a substitution of GCC to GCA was observed in the resistant biotype and in the susceptible alternative allele. However, the substitution did not result in amino acid changes. Silent mutations are plentiful in literature [2,5]. In contrast, Pro substitutes Ser; these point mutations very likely grants the resistance to glyphosate, together with the reduced translocation mechanism. This target-site resistance is usually accompanied by a nontarget site resistance mechanism [38]. Conversely, no other studies have reported on the mechanism of glyphosate resistance in plantago.
It was expected, however, that mutations of Pro-106-Ser would also occur in plantago, since it has been documented in other glyphosate resistant weed species [39]. Proline to Serine substitution at position 106 has been shown to cause glyphosate resistance EPSPS in bacteria (Escherichia coli) and weed species (Eleusine indica), among others [2,31]. Some other weed species have been found to possess TIPS, which is the double mutation of Thr-102-Ile and Pro-106-Ser, and grants a very high level of resistance [5]. Most recently, the so-called TAP-IVS triple mutation (Thr-102 + Ala-103 + Pro-106) was documented in Amaranthus hybridus [40].
In contrast to the aforementioned weed species, windmill grass (Chloris elata) R biotypes displayed no Pro-106-Ser substitution at any of the sequence position or any other amino acid substitutions (target site resistance), but showed differences in herbicide translocation (nontarget site resistance). This was the case in [12]. In this study, there were no mutations at the Pro106 codon in the gene encoding (EPSPS); however, the biotypes showed differences in translocation with the S biotype, showing higher glyphosate absorption into the leaf compared to the R biotype. In our study, mutation in the EPSPS enzyme of plantago was observed, pointing to target site resistance. However, the 31P and 13C NMR spectra showed reduced glyphosate translocation in the R biotype, implying a nontarget site resistance (presumably due to glyphosate sequestration). Worldwide, many species resistant to glyphosate are known [7]. However, this is the first report on the mechanism of glyphosate resistance in plantago.
5. Conclusions
Conclusively, 31P NMR remains the preferred method to detect glyphosate even when 13C enriched glyphosate is employed. The results unambiguously show the first evidence of glyphosate resistance mechanisms in plantago. Glyphosate resistance in this R biotype is due to a Proline to Serine substitution at amino acid position 106 of the EPSPS gene, and reduced glyphosate translocation to young leaves. This R biotype displayed a total of two mechanisms endowing glyphosate resistance, suggesting the presence of multiple mechanisms that confer glyphosate resistance in these R biotypes. This is very disturbing as it threatens the world’s most important weed control resource (glyphosate). To preserve this essential herbicide resource, growers must be weaned of their total dependence on glyphosate. Herbicide rotation should be encouraged and other urgent alternative nonchemical control management strategies will also be necessary to combat resistant plantago. These results provide a basis for growers and industry to immediately amend how they perceive and control weeds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.N., P.J.P. and E.P.; methodology, V.N., D.J.B., A.V. and A.L.; validation, V.N., D.J.B., A.V. and A.L.; formal analysis, V.N., A.V. and D.J.B.; investigation, V.N., A.V. and A.L.; resources, P.J.P., E.P., A.V. and D.J.B.; data curation, V.N.; writing—original draft preparation, V.N.; writing—review and editing, V.N., P.J.P., E.P., D.J.B., A.V. and A.L.; supervision, P.J.P. and E.P.; project administration, P.J.P.; funding acquisition, P.J.P. and E.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Syngenta (UK) and partially by the Southern African Weed Science Society (SAWSS).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Central Analytical Facilities (CAF) and Seipati Tenyane are greatly acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A once in-a-century herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Cairns, A.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate, paraquat and ACCase multiple herbicide resistance evolved in a Lolium rigidum biotype. Planta 2007, 225, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heap, I.; Duke, S.O. Overview of glyphosate–resistant weeds worldwide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, M.J.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate-resistant rigid ryegrass (Lolium rigidum) populations in the Western Australian Grain Belt. Weed Technol. 2010, 24, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wei, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Mutations and amplification of EPSPS gene confer resistance to glyphosate in goosegrass (Eleusine indica). Planta 2015, 242, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Garcia, J.G.; Palma-Bautista, C.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; De Prado, R.; Menendez, J. The First Case of Glyphosate Resistance in Johnsongrass (Sorghum halepense (L.) Pers.) in Europe. Plants 2020, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds. Available online: http://www.weedscience.com (accessed on 24 March 2021).
- Ge, X.; d’Avignon, D.A.; Ackerman, J.J.; Collavo, A.; Sattin, M.; Ostrander, E.L.; Hall, E.; Sammons, R.D.; Preston, C. Vacuolar glyphosate-sequestration correlates with glyphosate resistance in ryegrass (Lolium spp.) from Australia, South America, and Europe: A 31P NMR investigation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, M.L.; Hanson, B.D. Reduced translocation is involved in resistance to glyphosate and paraquat in Conyza bonariensis and Conyza canadensis from California. Weed Res. 2017, 57, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Aiub, M.M.; Blabi, M.C.; Distefano, A.J.; Fernández, L.; Hopp, E.; Yu, Q.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate resistance in perennial Sorghum halepense (Johnsongrass), endowed by reduced glyphosate translocation and leaf uptake. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandula, V.K.; Ray, J.D.; Ribeiro, D.N.; Pan, R.Z.; Reddy, K.N. Glyphosate resistance in tall waterhemp (Amaranthus tuberculatus) from Mississippi is due to both altered target-site and nontarget-site mechanisms. Weed Sci. 2013, 61, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunharo, C.; Patterson, E.L.; Carrijo, D.R.; de Melo, M.S.C.; Nicolai, M.; Gaines, T.A.; Nissen, S.J.; Christoffoleti, P.J. Confirmation and mechanism of glyphosate resistance in tall windmill grass (Chloris elata) from Brazil. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelin, A.M.; Lorraine-Colwill, D.F.; Preston, C. Glyphosate resistance in four different populations of Lolium rigidium is associated with reduced translocation of glyphosate to meristematic zones. Weed Res. 2004, 44, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, S.B.; Preston, C. Evolved glyphosate resistance in plants: Biochemical and genetic basis of resistance. Weed Technol. 2006, 20, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; d’Avignon, D.A.; Ackerman, J.J.; Sammons, R.D. Rapid vacuolar sequestration: The horseweed glyphosate resistance mechanism. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oromi-Farrús, M.; Minguell, J.P.; Oromi, N.; Canela-Garayoa, R. A reliable method for quantification of phosphonates and their impurities by 31P NMR. Anal. Lett. 2013, 46, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meudt, H.M. A taxonomic revision of native New Zealand Plantago (Plantaginaceae). N. Z. J. Bot. 2012, 50, 101–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glen, H.F. FSA contributions 12: Plantaginaceae. Bothalia 1998, 28, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, L.M.; Kenyon, P.R.; Morris, S.T.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Kemp, P.D. Morphological and physiological responses of plantain (Plantago lanceolata) and Chicory (Cichorium intybus) to water stress and defoliation frequency. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2015, 202, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J. Plantago as a host of economically important viruses. Adv. Virus Res. 1982, 27, 103–138. [Google Scholar]
- Bromilow, C. Problem Plants of South Africa; Briza Publications: Pretoria, South Africa, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Van Groenendael, J.M. Life history characteristics of two ecotypes of Plantago lanceolata L. Acta Bot. Neerl. 1986, 35, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.A. A universal method for preparing nutrient solutions of a certain desired composition. Plant Soil 1961, 15, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, J.M.; Duke, S.O.; Lydon, J. Glyphosate effects on shikimate pathway products in leaves and flowers of velvetleaf. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Torralva, F.; Rojano-Delgado, A.M.; Luque de Castro, M.D.; Mülleder, N.; de Padro, R. Two non-target mechanisms are involved in glyphosate-resistant horseweed (Conyza canadensis L. Cronq.) biotypes. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of (–)-Shikimic acid in chinese star anise by GC–MS with selected ion monitoring. Chromatographia 2008, 69, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gout, E.; Bligny, R.; Genix, P.; Tissut, M.; Douce, R. Effect of glyphosate on plant cell metabolism. 31P and 13C NMR studies. Biochemie 1992, 74, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.M.; Schaefer, J. Solid-State NMR determination of intra- and intermolecular 31P-13C distances for shikimate 3-Phosphate and [l-13C] glyphosate bound to enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2868–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, G.S.; Schaefer, J.; Stejskal, E.O.; McKay, R.A. Solid-state NMR determination of glyphosate metabolism in a Pseudomonas sp. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 5899–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, G.D.; Snape, C.E.; Jarvis, M.C. Comparison of leaf and stem cell-wall components in barley straw by solid-state 13C NMR. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherekhloo, J.; Fernández-Moreno, P.T.; Alcántara-de la Cruz, R.; Sánchez-González, E.; Cruz-Hipolito, H.E.; Domínguez-Valenzuela, J.A.; De Prado, R. Pro-106-Ser mutation and EPSPS overexpression acting together simultaneously in glyphosate-resistant goosegrass (Eleusine indica). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucheri, T.; Pieterse, P.J.; Reinhardt, C.F.; Kleinert, A. Responses of Lolium spp. to glufosinate ammonium application at different temperatures. Weed Res. 2020, 60, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehranchian, P.; Nandula, V.; Jugulam, M.; Putta, K.; Jasieniuk, M. Multiple resistance to glyphosate, paraquat and ACCase-inhibiting herbicides in italian ryegrass populations from California: Confirmation and mechanisms of resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J. Investigation into the Molecular and Biochemical Mechanisms of Resistance in Two Biotypes of Glyphosate Resistant Giant Ragweed. Master’s Thesis, The University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Harring, T.; Streibig, J.C.; Husted, S. Accumulation of shikimic acid: A technique for screening glyphosate efficacy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4406–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougler, J.; Geiger, D.R. Carbon partitioning and herbicide transport in glyphosate-treated sugarbeet (Beta vulgaris). Weed Sci. 1984, 32, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.C.C.; Tran, M.; Chiu, T.; Sammons, R.D.; Heck, G.R.; CaJacob, C.A. Investigations into glyphosate-resistant horseweed (Conyza canadensis): Retention, uptake, translocation and metabolism. Weed Sci. 2004, 52, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammons, R.D.; Gaines, T.A. Glyphosate resistance: State of knowledge. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.P.; Tranel, P.J. Target-site mutations conferring herbicide resistance. Plants 2019, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, V.E.; Larran, A.S.; Palmieri, V.E.; Martinatto, A.K.; Alvarez, C.E.; Tuesca, D.; Permingeat, H.A. novel triple amino acid substitution in the EPSPS found in a high-level glyphosate-resistant Amaranthus hybridus population from Argentina. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).