Short-Term Effect of Biochar on Microbial Biomass, Respiration and Enzymatic Activities in Wastewater Irrigated Soils in Urban Agroecosystems of the West African Savannah
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Site Description
2.2. Analysis of Soil Chemical Parameters
2.3. Assessment of Soil Respiration, Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Treatment Effects on Soil Chemical Parameters
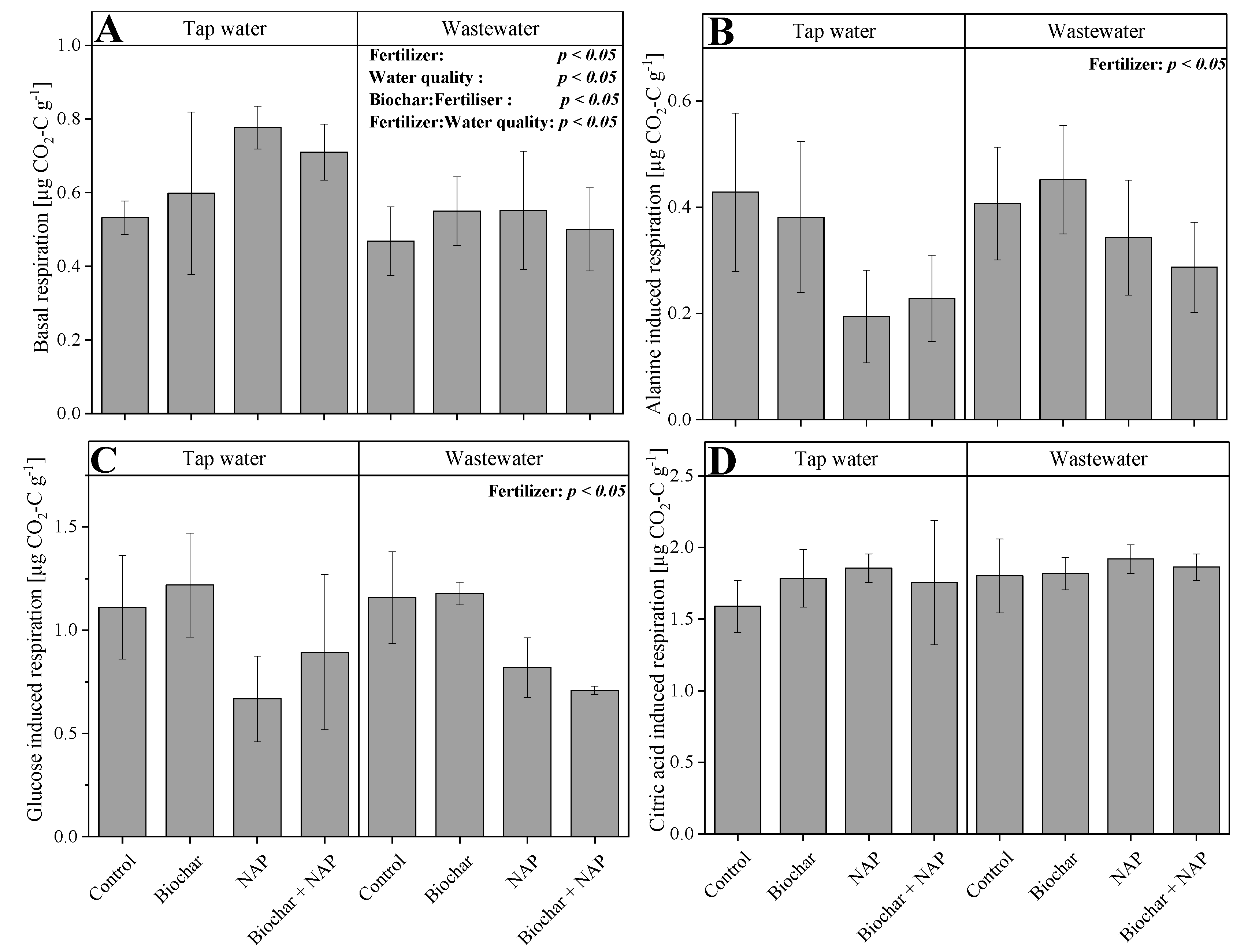
3.2. Substrate Induced Microbial Respiration
3.3. Microbial Biomass Carbon and Metabolic Quotients
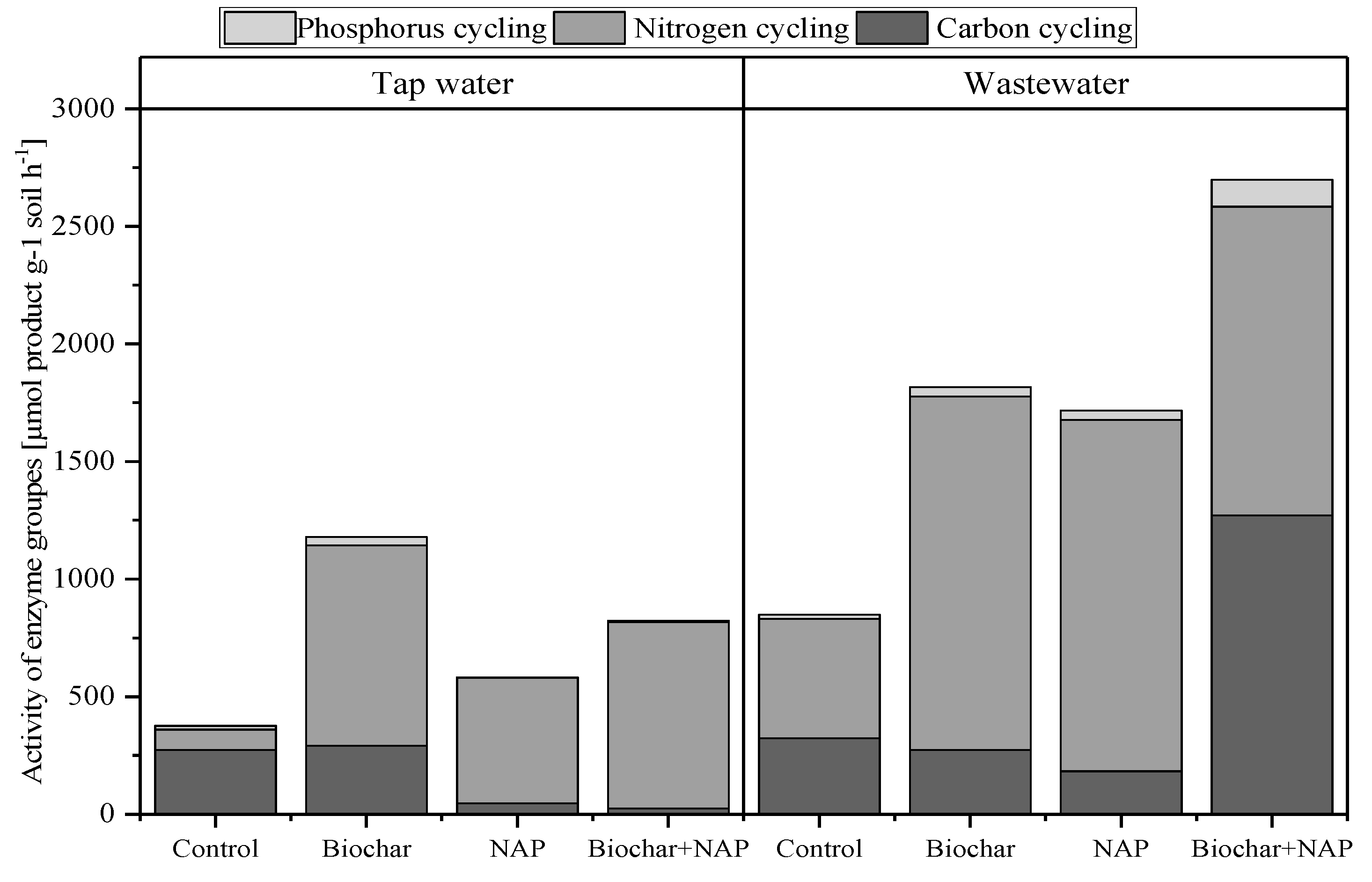
3.4. Enzyme Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Chemical Parameters
4.2. Basal and Substrate Induced Microbial Respiration
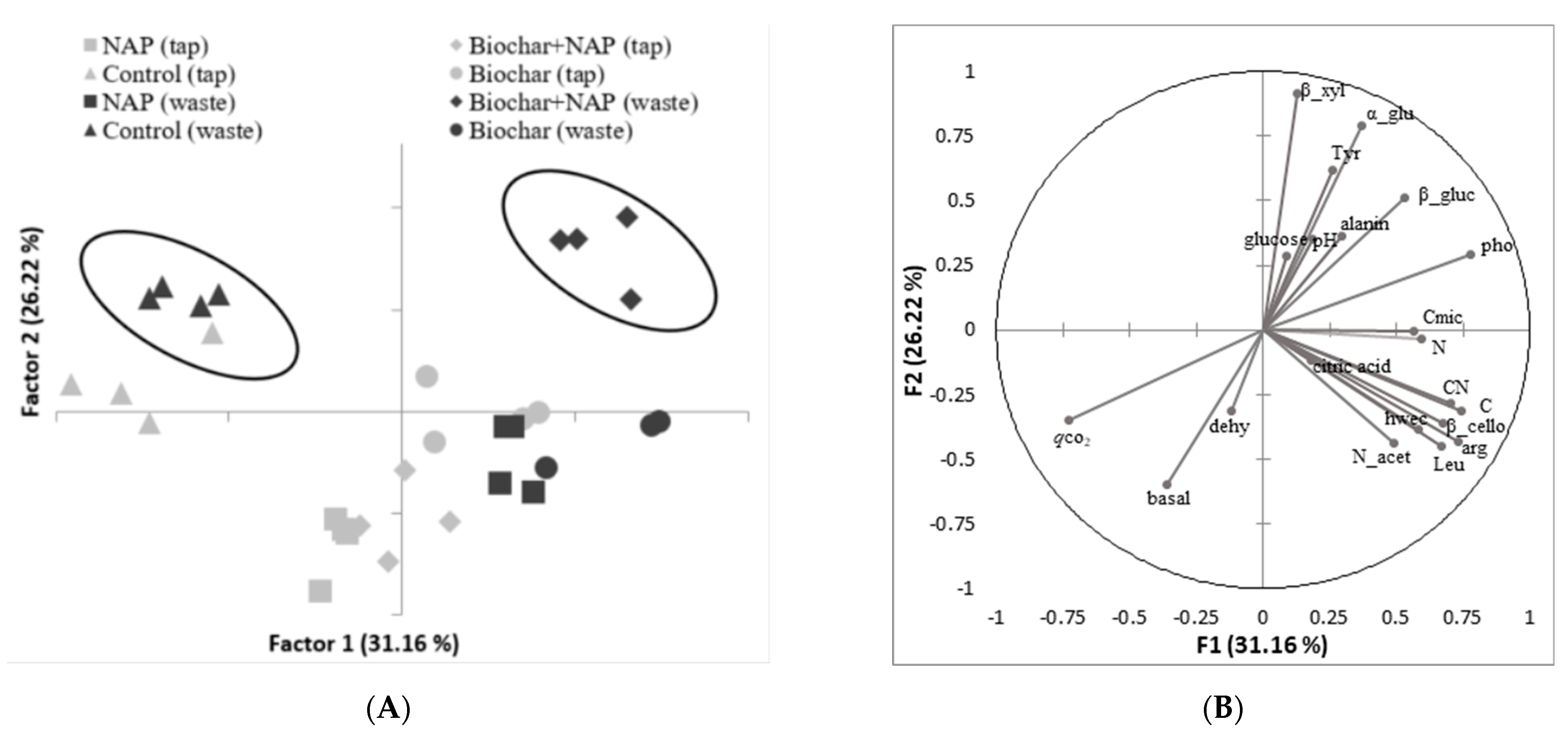
4.3. Microbial Biomass Carbon and Metabolic Quotients
4.4. Enzyme Activities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drechsel, P. Informal Irrigation in Urban West Africa. An Overview; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006; ISBN 978-92-9090-642-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cofie, O.O.; Veenhuizen, V.R.; Drechsel, P. Contribution of urban and peri-urban agriculture to food security in Sub- Saharan Africa. In Proceedings of the Africa Day of the 3rd WWF, Kyoto, Japan, 17 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel, P.; Keraita, B. Irrigated Urban Vegetable Production in Ghana: Characteristics, Benefits and Risk Mitigation, 2nd ed.; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2014; ISBN 9789290907985. [Google Scholar]
- Häring, V.; Manka’abusi, D.; Akoto-Danso, E.K.; Werner, S.; Atiah, K.; Steiner, C.; Lompo, D.J.P.; Adiku, S.; Buerkert, A.; Marschner, B. Effects of biochar, waste water irrigation and fertilization on soil properties in West African urban agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S.; Akoto-Danso, E.K.; Manka’abusi, D.; Steiner, C.; Haering, V.; Nyarko, G.; Buerkert, A.; Marschner, B. Nutrient balances with wastewater irrigation and biochar application in urban agriculture of Northern Ghana. Nutri. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 115, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bationo, A.; Buerkert, A. Soil organic carbon management for sustainable land use in Sudano-Sahelian West Africa. Nutri. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 61, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jueschke, E.; Marschner, B.; Tarchitzky, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on the dissolved and soil organic carbon in Israeli soils. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, J.K.; Langer, T.; Siebe, C.; Stahr, K. Effects of long-term waste water irrigation on soil organic matter, soil microbial biomass and its activities in central Mexico. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, S.; Chen, Y.; El-Nahhal, Y.; Hadar, Y.; Jung, R.; Safi, J.; Safi, M.; Tarchitzky, J.; Marschner, B. Small scale stratification of microbial activity parameters in Mediterranean soils under freshwater and treated wastewater irrigation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, L.; Frankenberger, W.T.; Chang, A.C. Soil enzyme activities of long-term reclaimed wastewater-irrigated soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, S36–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Abalos, D.; Prodana, M.; Bastos, A.C.; van Groenigen, J.W.; Hungate, B.A.; Verheijen, F. Biochar boosts tropical but not temperate crop yields. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 53001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Fu, S.; Méndez, A.; Gascó, G. Interactive effects of biochar and the earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus on plant productivity and soil enzyme activities. J. Soils Sediment. 2014, 14, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammirato, C.; Miltner, A.; Kaestner, M. Effects of wood char and activated carbon on the hydrolysis of cellobiose by β-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.R.; Gao, B.; Ahn, M.-Y. Positive and negative carbon mineralization priming effects among a variety of biochar-amended soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 978-92-5-108369-7. [Google Scholar]
- Akoto-Danso, E.K.; Manka’abusi, D.; Steiner, C.; Werner, S.; Häring, V.; Nyarko, G.; Marschner, B.; Drechsel, P.; Buerkert, A. Agronomic effects of biochar and wastewater irrigation in urban crop production of Tamale, northern Ghana. Nutri. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 115, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asirifi, I.; Werner, S.; Kaetzl, K.; Saba, C.; Felix, K.; Abagale, K.; Philip Amoah, P.; Marschner, B. Impact of biochar application on pathogen and heavy metal pollutions in West African urban agricultural production systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2021. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J.; Francis, G.S. Changes in microbial biomass C, soil carbohydrate composition and aggregate stability induced by growth of selected crop and forage species under field conditions. J. Soil Sci. 1993, 44, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.D.; Chapman, S.J.; Cameron, C.M.; Davidson, M.S.; Potts, J.M. A rapid microtiter plate method to measure carbon dioxide evolved from carbon substrate amendments so as to determine the physiological profiles of soil microbial communities by using whole soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Joergensen, R.G.; Pommerening, B.; Chaussod, R.; Brookes, P.C. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction—an automated procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P. Dehydrogenase activity in soil: A comparison between the TTC and INT assay under their optimum conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.-C.; Wood, M.; Jarvis, S. A microplate fluorimetric assay for the study of enzyme diversity in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Development Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2008.
- Siebe, C.; Chapela, M.; Cayetano-Salazar, M.; Prado, B.; Siemens, J. Effects of more than 100 years of irrigation with Mexico City’s wastewater in the Mezquital Valley (Mexico). In Safe Use of Wastewater in Agriculture: Good Practice Examples; Hettiarachchi, H., Ardakanian, R., Eds.; UNU-FLORES: Dresden, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-944863-31-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, K.; Minhas, P.S.; Yadav, R.K. Long-term impact of wastewater irrigation and nutrient rates II. Nutrient balance, nitrate leaching and soil properties under peri-urban cropping systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 156, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikcioglu, H.H. Short-term effects of irrigation with treated domestic wastewater on microbiological activity of a Vertic xerofluvent soil under Mediterranean conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 102, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitkötter, J.; Marschner, B. Interactive effects of biochar ageing in soils related to feedstock, pyrolysis temperature, and historic charcoal production. Geoderma 2015, 245, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ding, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Bolan, N.; Xie, Z. Biochar suppressed the decomposition of organic carbon in a cultivated sandy loam soil: A negative priming effect. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körschens, M.; Weigel, A.; Schulz, E. Turnover of soil organic matter (SOM) and long-term balances—tools for evaluating sustainable productivity of soils. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenkd. 1998, 161, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Nazaries, L.; Singh, B.K.; Singh, B.P. Microbial mechanisms of carbon priming effects revealed during the interaction of crop residue and nutrient inputs in contrasting soils. Global Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2775–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Minchin, T.; Kimber, S.; van Zwieten, L.; Gilbert, J.; Munroe, P.; Joseph, S.; Thomas, T. Comparative analysis of the microbial communities in agricultural soil amended with enhanced biochars or traditional fertilisers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnankambary, Z.; Ilstedt, U.; Nyberg, G.; Hien, V.; Malmer, A. Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of soil microbial respiration in two tropical agroforestry parklands in the south-Sudanese zone of Burkina Faso: The effects of tree canopy and fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, S.; Porto, M.; Belligno, A.; Bufo, S.A.; Mazzatura, A.; Scopa, A. Influence of irrigation with lagooned urban wastewater on chemical and microbiological soil parameters in a citrus orchard under Mediterranean condition. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 285, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y. Biochar stability in soil: Meta-analysis of decomposition and priming effects. GCB Bioenerg. 2016, 8, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Aoki, M.; Kitayama, K. Biodegradation of low molecular weight organic acids in rhizosphere soils from a tropical montane rain forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 47, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason-Jones, K.; Schmücker, N.; Kuzyakov, Y. Contrasting effects of organic and mineral nitrogen challenge the N-Mining Hypothesis for soil organic matter priming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Rousk, J.; Edwards-Jones, G.; DeLuca, T.H.; Murphy, D.V. Biochar-mediated changes in soil quality and plant growth in a three year field trial. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 45, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Sohi, S.P.; Thies, J.E.; O’Neill, B.; Trujillo, L.; Gaunt, J.; Solomon, D.; Grossman, J.; Neves, E.G.; et al. Black carbon affects the cycling of non-black carbon in soil. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, S.E.; Fermanich, K.J.; Dornbush, M.E. Effect of Charcoal Quantity on Microbial Biomass and Activity in Temperate Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; de Neve, S.; Jegajeevagan, K.; Yildiz, G.; Buchan, D.; Funkuin, Y.N.; Prins, W.; Bouckaert, L.; Sleutel, S. Short-term CO2 and N2O emissions and microbial properties of biochar amended sandy loam soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, D.N.; Gleeson, D.B.; Solaiman, Z.M.; Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V. Decreased soil microbial biomass and nitrogen mineralisation with Eucalyptus biochar addition to a coarse textured soil. Plant Soil 2012, 354, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.-H.; Domsch, K.H. Application of eco-physiological quotients (qCO2 and qD) on microbial biomasses from soils of different cropping histories. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Bian, R.; Cheng, K.; Jinwei, Z. Biochar decreased microbial metabolic quotient and shifted community composition four years after a single incorporation in a slightly acid rice paddy from southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnock, D.D.; Lehmann, J.; Kuyper, T.W.; Rillig, M.C. Mycorrhizal responses to biochar in soil—concepts and mechanisms. Plant Soil 2007, 300, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M. Microbial respiration per unit microbial biomass depends on litter layer carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, Z.; Kanazawa, S.; Berthelin, J. Characterization of effects of a long-term wastewater irrigation on soil quality by microbiological and biochemical parameters. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 1999, 162, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemanowicz, J. Activity of selected enzymes as markers of ecotoxicity in technogenic salinization soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 13014–13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, V.; Stott, D.; Cruz, J.; Curi, N. Tillage impacts on soil biological activity and aggregation in a Brazilian Cerrado Oxisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, R. Biochar amendment effects on the activities of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus hydrolytic enzymes: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22990–23001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Tang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhang, R. Effects of amendment of different biochars on soil enzyme activities related to carbon mineralisation. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Sun, K.; Ji, L.; He, Q.; Han, L. The effects of different biochars on microbial quantity, microbial community shift, enzyme activity, and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Geoderma 2018, 328, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnock, D.D.; Mummey, D.L.; McBride, B.; Major, J.; Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C. Influences of non-herbaceous biochar on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal abundances in roots and soils: Results from growth-chamber and field experiments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, B.; Alaei, S.; Bengtson, P.; Bodé, S.; Boeckx, P.; Schnecker, J.; Mayerhofer, W.; Rütting, T. Short-term carbon input increases microbial nitrogen demand, but not microbial nitrogen mining, in a set of boreal forest soils. Biogeochemistry 2017, 136, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.R.; Condron, L.M.; Clough, T.J.; Fiers, M.; Stewart, A.; Hill, R.A.; Sherlock, R.R. Biochar induced soil microbial community change: Implications for biogeochemical cycling of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebender, U. Effect of Mineral N Fertilizers—N form, Amount and Way of Application—on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Croplands; Cuvillier Verlag: Göttingen, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3954047659. [Google Scholar]
- Moeskops, B.; Sukristiyonubowo; Buchan, D.; Sleutel, S.; Herawaty, L.; Husen, E.; Saraswati, R.; Setyorini, D.; de Neve, S. Soil microbial communities and activities under intensive organic and conventional vegetable farming in West Java, Indonesia. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, S.; Sánchez, L.E.; Alvarez, J.; Valverde, A.; Galindo, P.; Igual, J.M.; Peix, A.; Santa-Regina, I. Correlation among soil enzyme activities under different forest system management practices. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Jia, Z.; Wang, S.; Chang, S.X.; Startsev, A. Contrasting effects of wheat straw and its biochar on greenhouse gas emissions and enzyme activities in a Chernozemic soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brtnicky, M.; Dokulilova, T.; Holatko, J.; Pecina, V.; Kintl, A.; Latal, O.; Vyhnanek, T.; Prichystalova, J.; Datta, R. Long-Term Effects of Biochar-Based Organic Amendments on Soil Microbial Parameters. Agronomy 2019, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, M.; Etesami, H.; Alikhani, H.A. Effect of different biochars amendment on soil biological indicators in a calcareous soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14752–14761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sial, T.A.; Lan, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kumbhar, F.; Memon, M.; Lashari, M.S.; Shah, A.N. Effects of Different Biochars on Wheat Growth Parameters, Yield and Soil Fertility Status in a Silty Clay Loam Soil. Molecules 2019, 24, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaine, M.; Obrike, R.; Clark, J.M.; Shaw, L.J. Biochar Alteration of the Sorption of Substrates and Products in Soil Enzyme Assays. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, V.L.; Fansler, S.J.; Smith, J.L.; Bolton, H. Reconciling apparent variability in effects of biochar amendment on soil enzyme activities by assay optimization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| A. | Initial Properties | B. | Irrigation Water Inputs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Unit | Soil | Biochar | Parameter | Unit | Wastewater | Tap Water |
| Sand | % | 45.7 | – | NO3-N | mgL−1 | 0.16 | 0.27 |
| Silt | % | 48.40 | – | NH4-N | mgL−1 | 35.54 | 0.04 |
| Clay | % | 5.90 | – | PO4-P | mgL−1 | 8.13 | 0.05 |
| CEC | mmolc kg–1 | 36.10 | pH | - | 7.37 | 7.56 | |
| pH | 5.10 | 9.1 | EC | µS cm−1 | 546.31 | 97.51 | |
| SOC | % | 0.41 | K | mgL−1 | 4.46 | 1.16 | |
| Bulk density | g cm−3 | 1.42 | Al | mgL−1 | 0.055 | 0.05 | |
| Carbon | % | 0.40 | 42.4 | Fe | mgL−1 | 0.47 | 0.68 |
| Nitrogen | % | 0.04 | 0.6 | Zn | mgL−1 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| Avail. phosphorus | mg kg–1 | 7.70 | nd | Cu | mgL−1 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Total phosphorus | mg kg–1 | 110.9 | 861.3 | Mn | mgL−1 | 0.33 | 0.03 |
| Potassium | mg kg–1 | 38.9 | 977.1 | Pb | mgL−1 | 1.82 | nd |
| BET | m2 g–1 | – | 62.9 | Ni | mgL−1 | 0.1 | nd |
| Volatile matter | % | – | 23.2 | Cd | mgL−1 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ash content | % | – | 45.2 | As | mgL−1 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| H/C (molar ratio) | – | 0.05 | Ba | mgL−1 | 0.05 | 0.07 | |
| O/C (molar ratio) | – | 0.27 | Mo | mgL−1 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| Water Quality | Soil Treatment | C | N | C: N | p | pH | HWEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [g kg−1] ±SD | [g kg−1] ±SD | - | [g kg−1] ±SD | [-] ±SD | [g kg−1] ±SD | ||
| Tap water irrigation | Control | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 7.94 ± 0.57 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 5.2 ± 0.24 | 166.49 ± 10.9 |
| Biochar | 6.9 ± 0.8 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 15.81 ± 2.27 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 5.23 ± 0.32 | 210.2 ± 7.95 | |
| NAP | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 8.94 ± 0.64 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 4.51 ± 0.16 | 191.69 ± 4.23 | |
| NAP/Biochar | 8 ± 2 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 12.92 ± 1.21 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 4.54 ± 0.18 | 212.37 ± 16.75 | |
| Wastewater irrigation | Control | 3.5 ± 1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 8.26 ± 0.64 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 5.04 ± 0.19 | 173.08 ± 7.16 |
| Biochar | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 16.39 ± 1.67 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 5.25 ± 0.25 | 218.1 ± 2.19 | |
| NAP | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 0.5± 0.1 | 9.33 ± 1.02 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 4.67 ± 0.12 | 197.94 ± 8.44 | |
| NAP/Biochar | 8.3 ± 0.9 | 0.5± 0.0 | 13.62 ± 1.34 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 4.58 ± 0.07 | 223.43 ± 4.0 | |
| Transformation | log | log | log | ||||
| p values (MANOVA) | |||||||
| Block | |||||||
| Biochar | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | ||||
| Fertilizer | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
| Water Quality | <0.05 | ||||||
| Sig. Interactions (p ≤ 0.05) | BC:Fert | BC:Fert BC:Watqu | BC:Fert | ||||
| α-Glucosidase | β-Xylosidase | β-Glucosidase | β-Cellobiosidase | N-Acetyl-β-Glucosaminidase | acid Phosphatase | Leucine-Aminopeptidase | Tyrosine-Aminopeptidase | Arginine-Aminopeptidase | Dehydrogenase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µmol product g−1 soil h−1] ± SD | |||||||||||
| Tap water irrigation | Control | 16.98 ± 10.98 | 19.00 ± 1.54 | 235.60 ± 39.5 | 1.66 ± 0.47 | 6.74 ± 1.89 | 15.95 ± 2.18 | 3.42 ± 1.58 | 44.50 ± 15.02 | 38.72 ± 8.84 | 15.03 ± 2.96 |
| Biochar | 15.11 ± 7.31 | 13.76 ± 1.41 | 132.84 ± 28.77 | 130.18 ± 22.72 | 60.86 ± 60.01 | 34.32 ± 9.28 | 140.52 ± 30.41 | 84.86 ± 9.07 | 426.92 ± 510.04 | 14.58 ± 3.32 | |
| NAP | 6.42 ± 2.87 | 8.04 ± 3.06 | 2.10 ± 1.98 | 29.44 ± 6.00 | 15.99 ± 3.55 | 1.63 ± 0.06 | 24.60 ± 5.45 | 13.42 ± 4.33 | 496.91 ± 270.09 | 15..50 ± 2.98 | |
| NAP + Biochar | 8.28 ± 2.88 | 8.13 ± 1.84 | 3.43 ± 2.67 | 4.53 ± 2.76 | 14.53 ± 6.98 | 5.68 ± 6.91 | 38.69 ± 7.54 | 47.06 ± 9.75 | 706.57 ± 96.40 | 18.21 ± 2.86 | |
| Waste water irrigation | Control | 33.85 ± 6.41 | 25.58 ± 2.73 | 254.07 ± 54.42 | 9.31 ± 7.67 | 10.23 ± 4.16 | 17.39 ± 4.89 | 6.29 ± 0.99 | 179.16 ± 86.57 | 322.66 ± 351.08 | 16.50 ± 1.93 |
| Biochar | 14.96 ± 2.36 | 12.11 ± 3.25 | 101.55 ± 9.69 | 144.82 ± 37.61 | 134.02 ± 38.36 | 39.05 ± 2.26 | 227.28 ± 23.50 | 80.86 ± 11.48 | 1657.55 ± 857. | 18.50 ± 2.76 | |
| NAP | 11.68 ± 5.28 | 10.11 ± 2.20 | 95.78 ± 5.41 | 65.88 ± 51.77 | 119.59 ± 14.03 | 38.73 ± 2.20 | 208.80 ± 17.67 | 68.78 ± 3.60 | 1216.10 ± 194.27 | 14.18 ± 2.28 | |
| NAP + Biochar | 36.97 ± 17.77 | 19.95 ± 2.52 | 1180.33 ± 26.78 | 33.75 ± 9.44 | 8.91 ± 2.26 | 114.97 ± 3.37 | 92.50 ± 4.29 | 108.78 ± 9.28 | 1111.36 ± 28.80 | 12.04 ± 2.17 | |
| Transformation | log | sqrt | log | log | sqrt | sqrt | |||||
| p values from MANOVA | |||||||||||
| Block | <0.05 | ||||||||||
| Biochar (BC) | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||||
| Fertilizer (Fert) | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||||||
| Water quality (Watqu) | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
| Sig. Interactions (p ≤ 0.05) | Bc:Fert BC:Fert:Watqu | BC:Fert Fert:Watqu BC:Fert:Watqu | BC:Fert BC:Watqu Fert:Watqu BC:Fert:Watqu | BC:Fert BC:Fert:Watqu | BC:Fert BC:Fert:Watqu | BC:Fert BC:Watqu Fert:Watqu BC:Fert:Watqu | BC:Fert BC:Watqu Fert:Watqu BC:Fert:Watqu | BC:Fert BC:Watqu Fert:Watqu BC:Fert:Watqu | Fert: Watqu | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asirifi, I.; Werner, S.; Heinze, S.; Saba, C.K.S.; Lawson, I.Y.D.; Marschner, B. Short-Term Effect of Biochar on Microbial Biomass, Respiration and Enzymatic Activities in Wastewater Irrigated Soils in Urban Agroecosystems of the West African Savannah. Agronomy 2021, 11, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020271
Asirifi I, Werner S, Heinze S, Saba CKS, Lawson IYD, Marschner B. Short-Term Effect of Biochar on Microbial Biomass, Respiration and Enzymatic Activities in Wastewater Irrigated Soils in Urban Agroecosystems of the West African Savannah. Agronomy. 2021; 11(2):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020271
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsirifi, Isaac, Steffen Werner, Stefanie Heinze, Courage K. S. Saba, Innocent Y. D. Lawson, and Bernd Marschner. 2021. "Short-Term Effect of Biochar on Microbial Biomass, Respiration and Enzymatic Activities in Wastewater Irrigated Soils in Urban Agroecosystems of the West African Savannah" Agronomy 11, no. 2: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020271
APA StyleAsirifi, I., Werner, S., Heinze, S., Saba, C. K. S., Lawson, I. Y. D., & Marschner, B. (2021). Short-Term Effect of Biochar on Microbial Biomass, Respiration and Enzymatic Activities in Wastewater Irrigated Soils in Urban Agroecosystems of the West African Savannah. Agronomy, 11(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020271







