Identification and Validation a Major QTL from “Sea Rice 86” Seedlings Conferred Salt Tolerance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Phenotype Measurements
2.3. DNA-BSA Analysis
2.4. Genotype Identification and QTL Analysis
2.5. Measurements of Agronomic Traits
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
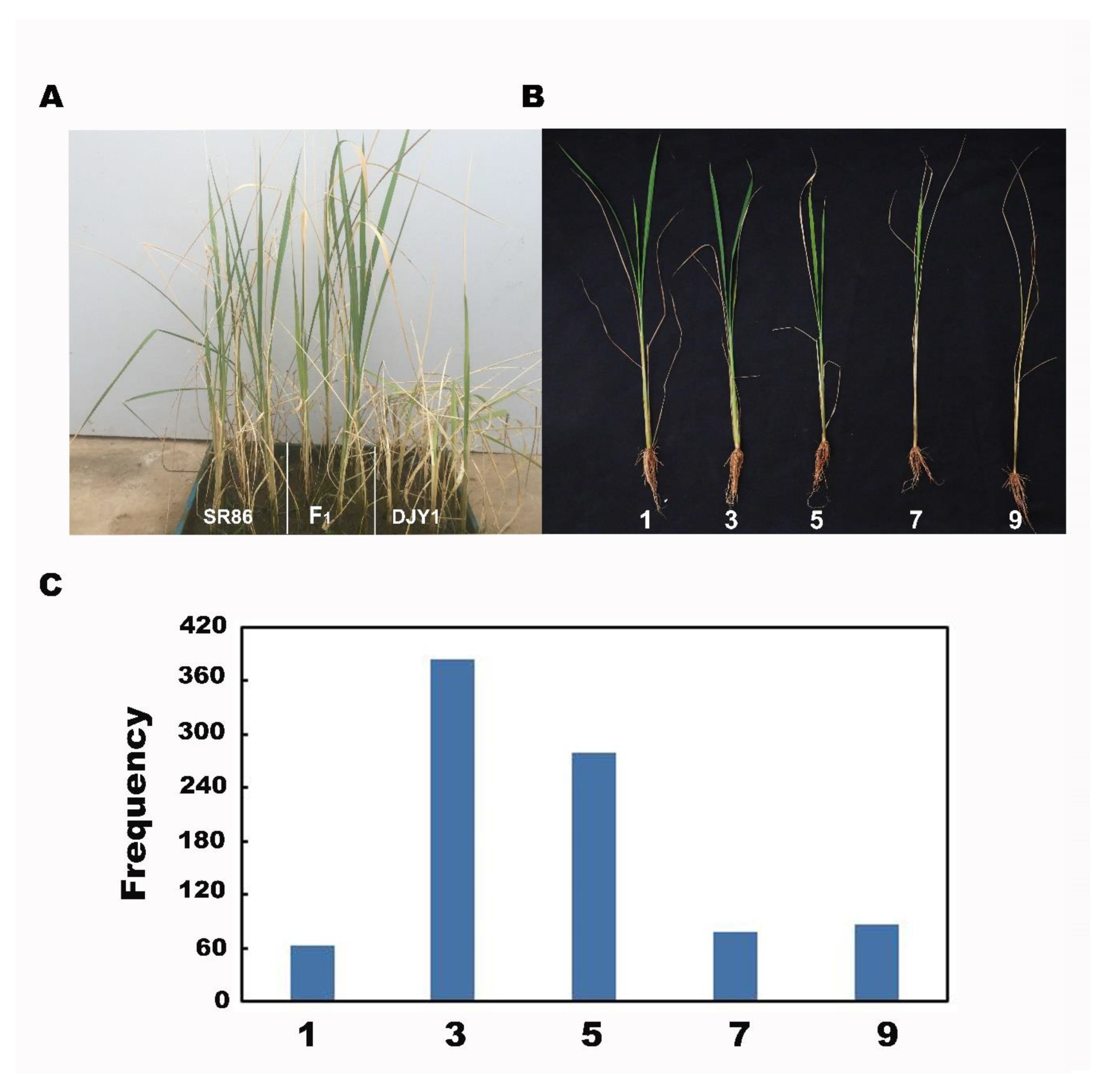
3.1. Phenotypes and Genetics Analysis of Salt Tolerance in SR86
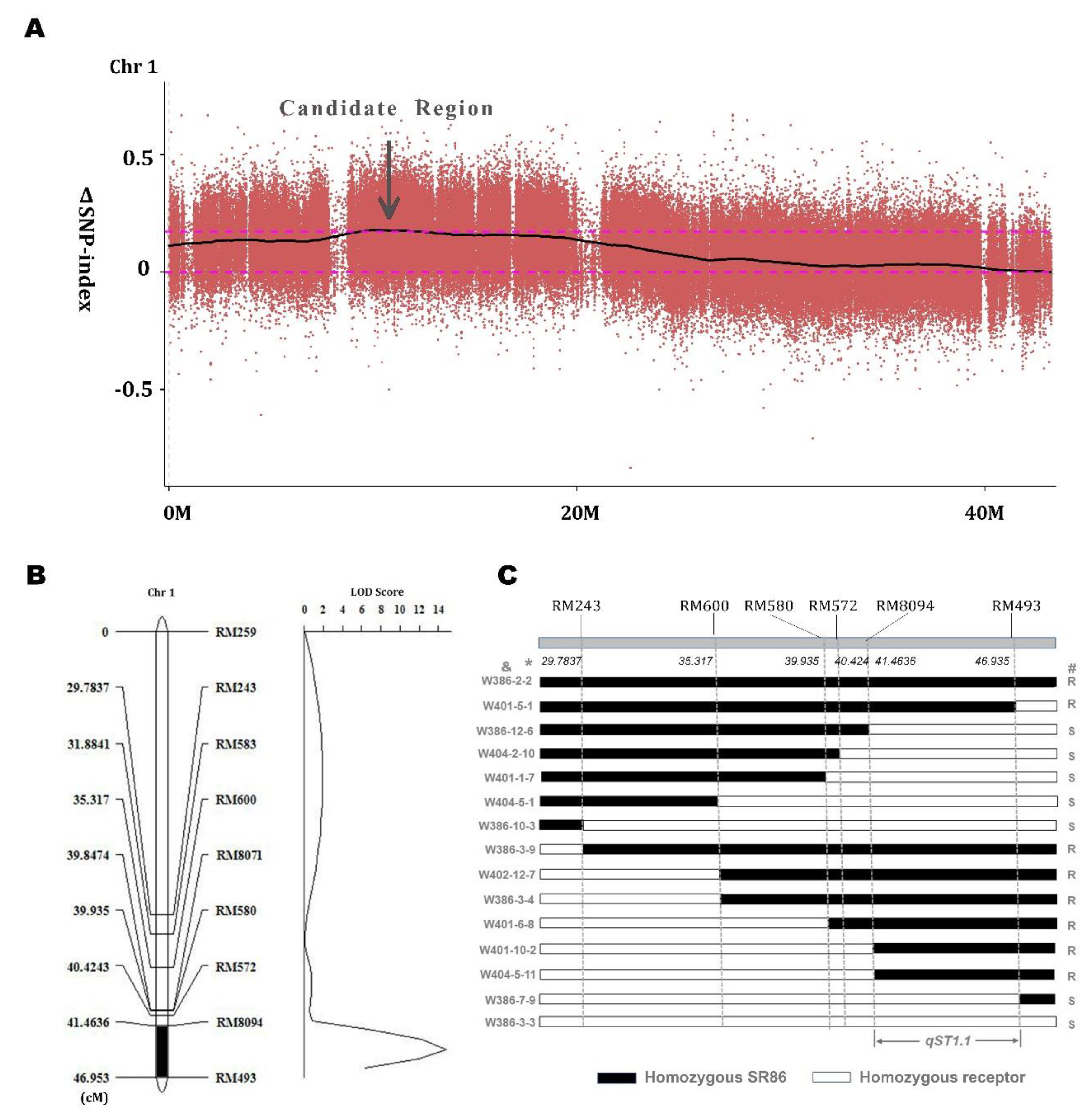
3.2. A New Potential QTL (qST1.1) Involved in the Salt Tolerance of SR86
3.3. qST1.1 Validation by Substitution Experiments and Introgression Line T22
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munns, R.; Gilliham, M. Salinity tolerance of crops-what is the cost? New Phytol. 2015, 208, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, F.; Li, W.; Wang, F.; Zhong, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, J. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals molecular response to salinity stress of salt-tolerant and sensitive genotypes of indica rice at seedling stage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.C.; Lin, T.C.; Kieber, J.; Tsai, Y.C. Response regulators 9 and 10 negatively regulate salinity tolerance in rice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 60, 2549–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radanielson, A.M.; Gaydon, D.S.; Li, T.; Angeles, O.; Roth, C.H. Modeling salinity effect on rice growth and grain yield with ORYZA v3 and APSIM-Oryza. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 100, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Yeo, A.R. Variability in the resistance of sodium chloride salinity within rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. New Phytol. 1981, 88, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, K.; Rabiei, B.; Sabouri, H.; Sabouri, A. Mapping QTLs for traits related to salinity tolerance at seedling stage of rice (Oryza sativa L.): An agrigenomics study of an Iranian rice population. OMICS 2013, 17, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M.; Horie, T. Genomics, Physiology, and molecular breeding approaches for improving salt tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2017, 68, 405–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formentin, E.; Sudiro, C.; Perin, G.; Riccadonna, S.; Barizza, E.; Baldoni, E.; Lavezzo, E.; Stevanato, P.; Sacchi, G.A.; Fontana, P.; et al. Transcriptome and cell physiological analyses in different rice cultivars provide new insights into adaptive and salinity stress responses. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Zhong, H.; Gong, Z.; Fang, X.; Sun, T.; Deng, X.; Li, Y. Meta-analysis of salt stress transcriptome responses in different rice genotypes at the seedling stage. Plants 2019, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, V.R.R.; Ontoy, J.; Linscombe, S.; Subudhi, P.K. Genetic dissection of seedling stage salinity tolerance in rice using introgression lines of a salt tolerant landrace Nona Bokra. J. Hered. 2017, 108, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorio, G.B. Tagging Salinity Tolerance Genes in Rice Using Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP). Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Philippines, Los Banos, Philippines, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, M.; De Ocampo, M.; Egdane, J.; Rahman, M.A.; Sajise, A.G.; Adorada, D.L.; Tumimbang-Raiz, E.; Blumwald, E.; ISeraj, Z.; Singh, R.K.; et al. Characterizing the Saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice. Rice 2010, 3, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; He, P.; Qian, Q.; Shen, L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, S. Identification of salt-tolerance QTL in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chinese Sci. Bullet. 1999, 44, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.X.; Zhu, M.Z.; Yano, M.; Gao, J.P.; Liang, Z.W.; Su, W.A.; Hu, X.H.; Ren, Z.; Chao, D.Y. QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gao, J.-P.; Li, L.-G.; Cai, X.-L.; Huang, W.; Chao, D.-Y.; Zhu, M.-Z.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Luan, S.; Lin, H.-X. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Cha, Y.S.; Yun, D.W.; Lee, M.C.; Ko, J.C.; Lee, S.K.; Eun, M.Y. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance at the seedling stage in rice. Mol. Cells 2006, 21, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Sabouri, H.; Rezai, A.M.; Moumeni, A.; Kavousi, A.; Katouzi, M.; Sabouri, A. QTLs mapping of physiological traits related to salt tolerance in young rice seedlings. Biol. Plantarum. 2009, 53, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Tan, L.; Liu, F.; Cai, H.; Sun, C. Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with salt tolerance at seedling stage from Oryza rufipogon. J. Genet. Genom. 2011, 38, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimhani, D.; Gregorio, G.B.; Kottearachchi, N.; Samarasinghe, W. SNP-based discovery of salinity-tolerant QTLs in a bi-parental population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Genet. Genomics. 2016, 291, 2081–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, T.B.; Linscombe, S.; Subudhi, P.K. Molecular dissection of seedling salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a high-density GBS-based SNP linkage map. Rice 2016, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.A.; Molla, K.A.; Henry, R.J.; Bhat, K.V.; Mondal, T.K. Advances in understanding salt tolerance in rice. Theor Appl Genet. 2019, 132, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Cheng, Y.; Han, S.; Van Handel, B.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Xie, X. Whole genome sequencing and comparative transcriptome analysis of a novel seawater adapted, salt-resistant rice cultivar-sea rice 86. BMC Genomics. 2017, 18, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H. Salt Tolerance Evalution, Gene Discovery and Germplasm Innovation of Water-Saving and Drought Resistant Rice Core Resources. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong agricultural university, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCouch, S.R.; Teytelman, L.; Xu, Y.; Lobos, K.B.; Clare, K.; Walton, M.; Fu, B.; Maghirang, R.; Li, Z.-K.; Xing, Y.; et al. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res. 2002, 9, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.A.; Borgohain, M.J.; Kritika, K.; Talukdar, A.; Pani, D.R.; Mondal, T.K. Assessment of genetic diversity of Saltol QTL among the rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2016, 22, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimpong, I.K.; Manneh, B.; Sock, M.; Diaw, F.; Amoah, N.K.A.; Ismail, A.M.; Gregorio, G.B.; Singh, R.K.; Wopereis, M. Improving salt tolerance of lowland rice cultivar ‘Rassi’ through marker-aided backcross breeding in West Africa. Plant. Sci. 2016, 242, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.; Buu, B.C. Enhancing and stabilizing the productivity of salt-affected areas by incorporating genes for tolerance of abiotic stresses in rice. Omonrice 2011, 18, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Isah, T. Stress and defense responses in plant secondary metabolites production. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Baek, K.H. Physiological and biochemical perspectives of non-salt tolerant plants during bacterial interaction against soil salinity. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 116, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, P.; Dvorak, J.; Mackill, D.; Deal, K.; Gregorio, G. RLFP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Philipp. Agric. Sci. 2002, 85, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, B.D.; Kumar, A.; Maurya, S.; Krishnan, S.G.; Vinod, K.K.; Pal Singh, M.; Ellur, R.K.; Bhowmick, K.; Singh, A.K. Marker-assisted introgression of Saltol QTL enhances seedling stage salt tolerance in the rice variety “Pusa Basmati 1”. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 2018, 8319879. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.C.; Cheng, W.H.; Hong, C.Y.; Chang, Y.S.; Chang, M.C. The transcription factor OsbHLH035 mediates seed germination and enables seedling recovery from salt stress through ABA-dependent and ABA-independent pathways, respectively. Rice 2018, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; He, Y. Genome-wide investigation of WRKY gene family in pineapple: Evolution and expression profiles during development and stress. BMC Genomics. 2018, 19, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifikalhor, M.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Shomali, A.; Azad, N.; Hassani, B.; Lastochkina, O.; Li, T. Calcium signaling and salt tolerance are diversely entwined in plants. Plant. Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1665455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.; Wu, X.; Dong, L. Na+/K+ Balance and transport regulatory mechanisms in weedy and cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) under salt stress. BMC Plant. Biol. 2018, 18, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Liao, K.; Du, H.; Xu, Y.; Song, H.; Li, X.; Xiong, L. A stress-responsive NAC transcription factor SNAC3 confers heat and drought tolerance through modulation of reactive oxygen species in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6803–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Iqbal, W.; Bangash, A.; Rehman, S.U.; Imran, Q.M.; Rha, E.S. Constitutive expression of OSC3H33, OSC3H50 and OSC3H37 genes in rice under salt stress. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 4003–4009. [Google Scholar]
- Nutan, K.K.; Kushwaha, H.R.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Transcription dynamics of Saltol QTL localized genes encoding transcription factors, reveals their differential regulation in contrasting genotypes of rice. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2017, 17, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, M.; Baldoni, E.; Formentin, E.; Milc, J.; Frugis, G.; Schiavo, F.L.; Genga, A.; Francia, E. A Meta-analysis of comparative transcriptomic data reveals a set of key genes involved in the tolerance to abiotic stresses in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, C.; Iriti, M.; Bracale, M.; Locatelli, F.; Faoro, F.; Croce, P.; Pirona, R.; Di Maro, A.; Coraggio, I.; Genga, A. The ectopic expression of the rice Osmyb4 gene in Arabidopsis increases tolerance to abiotic, environmental and biotic stresses. Physiol. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2006, 69, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Dhawan, M.; Sharma, I.; Pati, P.K. Interdependency of reactive oxygen species generating and scavenging system in salt sensitive and salt tolerant cultivars of rice. BMC Plant. Biol. 2016, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Kaur, N.; Pati, P.K. Reactive oxygen species dynamics in roots of salt sensitive and salt tolerant cultivars of rice. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 550, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
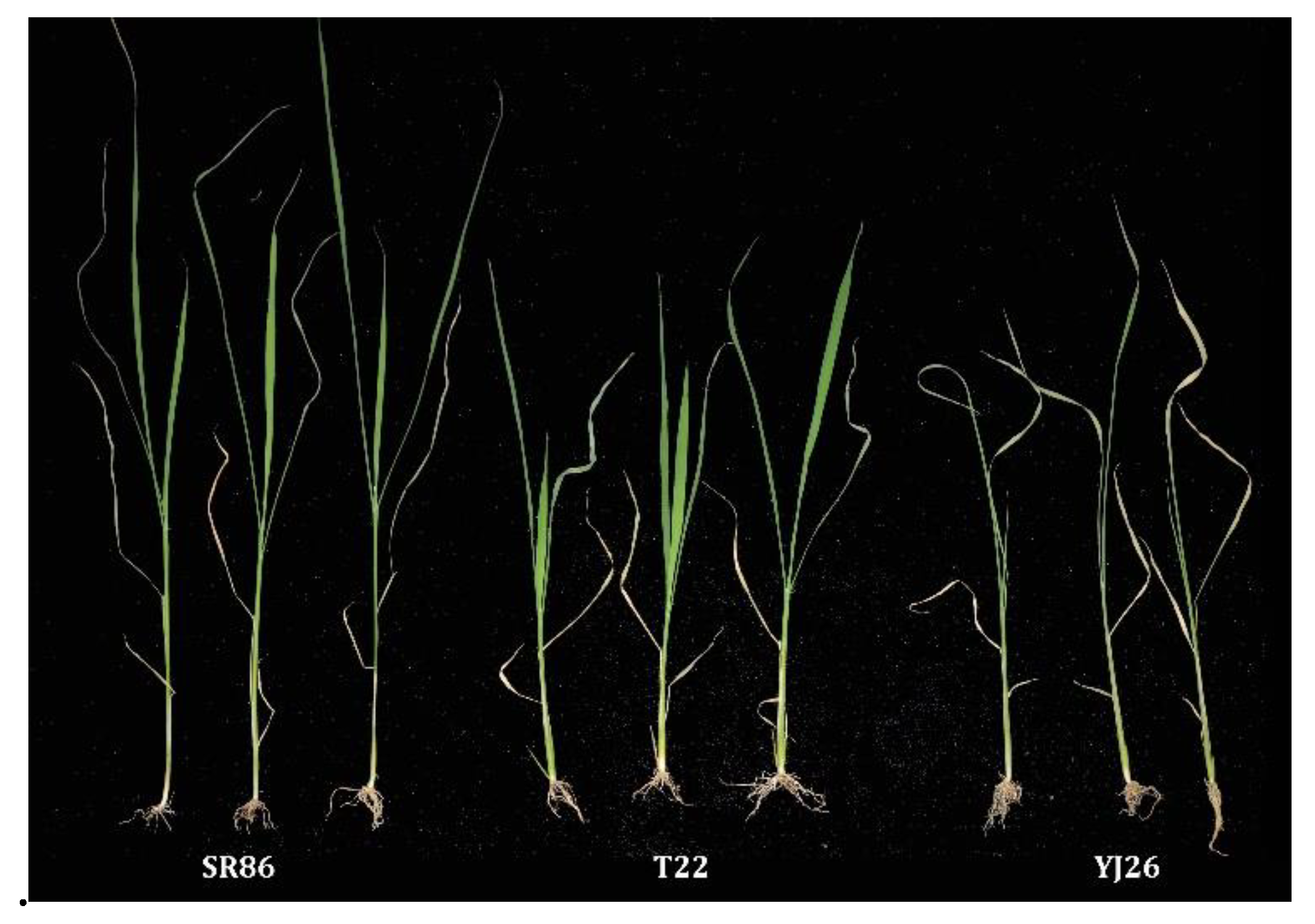

| Soil Conditions (8 d) | Hydroponic Conditions (4 d) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variety/NaCl Concentration (%) | 0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 |
| SR86 | 1 | 1–3 | 1–3 | 1–3 | 1–3 | 3–5 | 1 | 3–5 | 5–7 | 7–9 | 9 |
| DJY1 | 1 | 1–3 | 5–7 | 7–9 | 9 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7–9 | 9 |
| YJ26 | 1 | 1–3 | 5–7 | 7–9 | 9 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7–9 | 9 |
| YJ29 | 1 | 1–3 | 5–7 | 7–9 | 9 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7–9 | 9 |
| YJ32 | 1 | 1–3 | 5–7 | 7–9 | 9 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7–9 | 9 |
| Chromosome ID | Start | End | Size (Mb) | Gene Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr1 | 9,459,487 | 12,134,056 | 2.67 | 432 |
| Chr1 | 12,211,515 | 12,244,801 | 0.03 | 5 |
| Total | - | - | 2.70 | 437 |
| Traits | SR86 | T22 | YJ26 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height (cm) | 163.22 ± 6.10 | 100.52 ± 3.44 * | 95.56 ± 5.63 |
| Number of filled grains per panicle | 71.07 ± 15.74 | 110.70 ± 8.90 ** | 83.33 ± 22.32 |
| Seed setting rate | 0.74 ± 0.10 | 0.77 ± 0.04 ** | 0.86 ± 0.04 |
| Effective tiller | 11.78 ± 2.33 | 10.11 ± 1.21 | 8.77 ± 2.33 |
| 1000-grain weight (g) | 25.59 ± 0.85 | 26.77 ± 0.72 ** | 28.44 ± 0.52 |
| Panicle length (cm) | 22.68 ± 0.75 | 23.50 ± 0.90 * | 17.60 ± 0 .93 |
| Primary branching | 9.82 ± 0.16 | 10.3 1± 0.63 * | 8.96 ± 0.54 |
| Secondary branching | 27.00 ± 2.75 | 26.33 ± 3.05 ** | 18.05 ± 2.56 |
| Grain length (mm) | 7.19 ± 0.24 | 7.81 ± 0.07 ** | 7.12 ± 0.05 |
| Grain width (mm) | 2.76 ± 0.08 | 2.83 ± 0.36 ** | 3.07 ± 0.06 |
| Grain length-to-width ratio | 2.64 ± 0.50 | 2.82 ± 0.03 ** | 2.36 ± 0.05 |
| Grain yield per plant (g) | 22.21 ± 6.51 | 29.32 ± 3.03 ** | 19.88 ± 2.43 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Yu, D.; Xu, P. Identification and Validation a Major QTL from “Sea Rice 86” Seedlings Conferred Salt Tolerance. Agronomy 2020, 10, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030410
Wu F, Yang J, Yu D, Xu P. Identification and Validation a Major QTL from “Sea Rice 86” Seedlings Conferred Salt Tolerance. Agronomy. 2020; 10(3):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030410
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Fengling, Jun Yang, Diqiu Yu, and Peng Xu. 2020. "Identification and Validation a Major QTL from “Sea Rice 86” Seedlings Conferred Salt Tolerance" Agronomy 10, no. 3: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030410
APA StyleWu, F., Yang, J., Yu, D., & Xu, P. (2020). Identification and Validation a Major QTL from “Sea Rice 86” Seedlings Conferred Salt Tolerance. Agronomy, 10(3), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030410




