Genetic Variation for Biomass Yield and Predicted Genetic Gain in Lowland Switchgrass “Kanlow”
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Half-Sib Families
2.2. Field Evaluation
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Feedstock Composition Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Variance Components
2.5.2. Comparison of Mean Performance of Traits
2.5.3. Narrow Sense Heritability
2.5.4. Phenotypic and Genetic Correlation
2.5.5. Predicted per Cycle Genetic Gain
3. Results
3.1. Variance Components of Biomass Yield and Morphological and Quality Traits
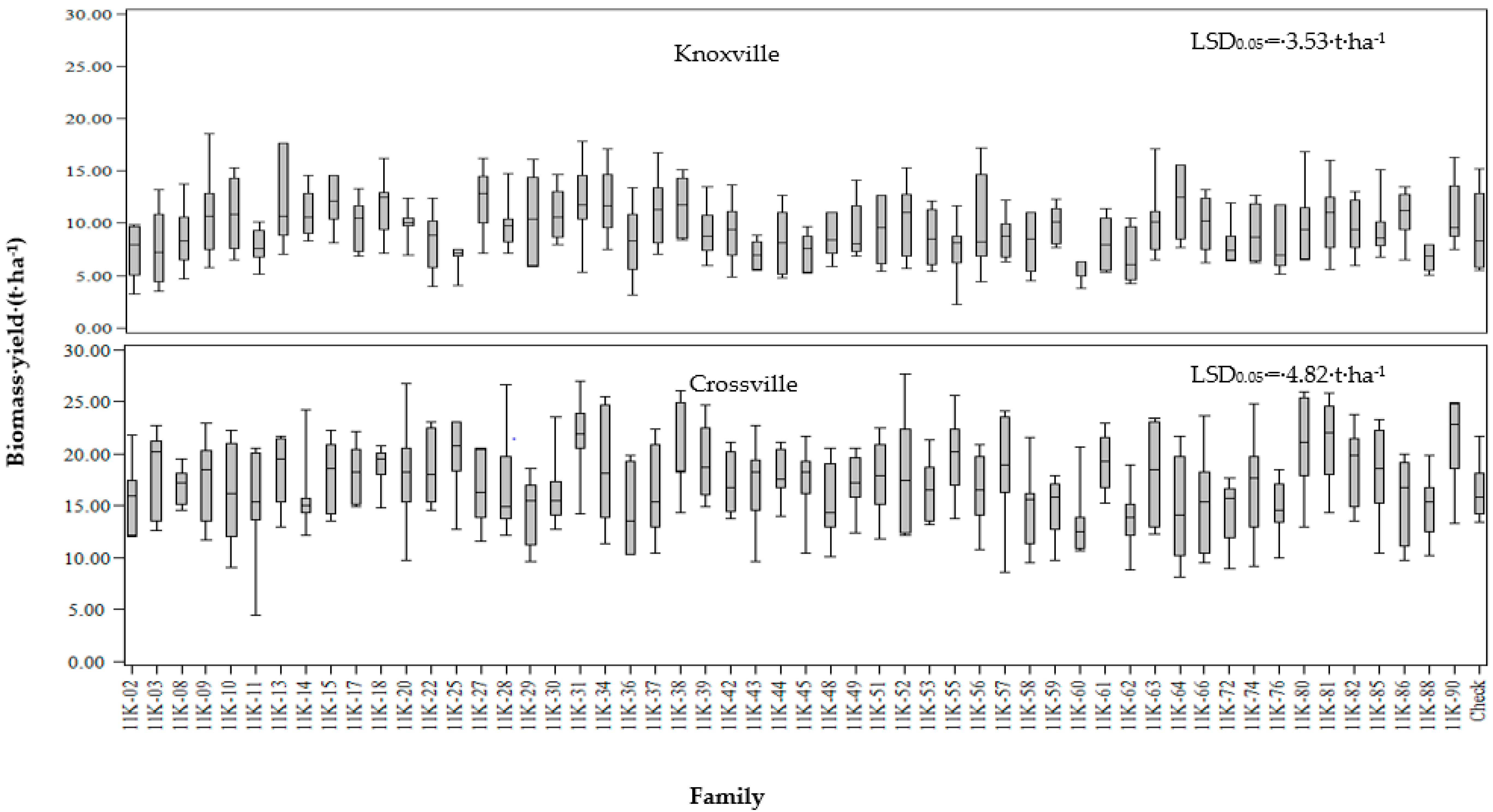
3.2. Summary Statistics of Biomass Yield and Morphological and Quality Traits
3.3. Efficiency of Phenotypic Selection
3.4. Heritability
3.5. Genetic and Phenotypic Correlation
3.6. Predicted per Cycle Genetic Gain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogel, K.P.; Brejda, J.J.; Walters, D.T.; Buxton, D.R. Switchgrass biomass production in the midwest USA: Harvest and nitrogen management. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Vogel, K.P.; Harrison, M. Switchgrass germplasm resources. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 2463–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, S.B.; Kszos, L.A. Development of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) as a bioenergy feedstock in the United States. Biomass Bioenergy 2005, 28, 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclaughlin, S.; Bouton, J.; Bransby, D.; Conger, B.; Ocumpaugh, W.; Parrish, D.; Taliaferro, C.; Vogel, K.; Wullschleger, S. Developing switchgrass as a bioenergy Crop. In Perspectives on New Crops and New Uses; Janick, J., Ed.; ASHS Press: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1999; pp. 282–299. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. A USDA Regional Roadmap to Meeting the Biofuels Goals of the Renewable Fuels Standard by 2022; USDA Biofuels Strategic Production Report, 2010. Available online: https://www.usda.gov/sites/default/files/documents/USDA_Biofuels_Report_6232010.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- Martínez-Reyna, J.M.; Vogel, K.P. Incompatibility systems in switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D. Ecotypic Variation among switchgrass populations from the northern USA. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultquist, S.J.; Vogel, K.P.; Lee, D.J.; Arumuganathan, K.; Kaeppler, S. Chloroplast DNA and nuclear DNA content variations among cultivars of switchgrass, Panicum virgatum L. Crop Sci. 1996, 36, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.P. Switchgrass. In Warm-Season (C4) Grasses; Moser, L.E., Burson, B.L., Sollenberger, L.E., Eds.; ASA, CSSA, and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2004; pp. 561–588. [Google Scholar]
- Brunken, J.; Estes, J.R. Cytological and morphological variation in Panicum virgatum L. Southwest. Nat. 1975, 19, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.L. An analysis of variation between upland and lowland switchgrass, Panicum virgatum L., in Central Oklahoma. Ecology 1966, 47, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.D.; Vogel, K.P. Chromosome Numbers of released cultivars of switchgrass, indiangrass, big bluestem, and sand bluestem. Crop Sci. 1982, 22, 1082–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultquist, S.J.; Vogel, K.P.; Lee, D.J.; Arumuganathan, K.; Kaeppler, S. DNA content and chloroplast DNA polymorphisms among switchgrasses from remnant midwestern prairies. Crop Sci. 1997, 37, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zalapa, J.; Jakubowski, A.R.; Price, D.L.; Acharya, A.; Wei, Y.; Brummer, E.C.; Kaeppler, S.M.; Casler, M.D. Natural hybrids and gene flow between upland and lowland switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 2626–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.F.; Sarath, G.; Edme, S.; Casler, M.D.; Mitchell, R.B.; Tobias, C.M.; Hale, A.L.; Sattler, S.E.; Knoll, J.E. Dedicated herbaceous biomass feedstock genetics and development. Bioenergy Res. 2016, 9, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.L. Analysis of variation in Panicum virgatum. J. Agric. Res. 1944, 69, 327–353. [Google Scholar]
- Anex, R.P.; Lynd, L.R.; Laser, M.S.; Heggenstaller, A.H.; Liebman, M. Potential for enhanced nutrient cycling through coupling of agricultural and bioenergy systems. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.P.; Pedersen, J.F. Breeding systems for cross-pollinated perennial grasses. In Plant Breeding Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Casler, M.D. Heterosis and reciprocal-cross effects in tetraploid switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 2063–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, H.S.; Nayak, S.; Dalid, C.O.; Sykes, V.R. Biomass Yield heterosis in lowland switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.P.; Mitchell, R.B. Heterosis in switchgrass: Biomass yield in swards. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Reyna, J.M.; Vogel, K.P. Heterosis in switchgrass: Spaced plants. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaoui, A.M.; Boerma, H.R.; Bouton, J.H. Genetic variation and heritability of phosphorus uptake in Alamo switchgrass grown in high phosphorus soils. Field Crops Res. 2005, 93, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D. Changes in mean and genetic variance during two cycles of within-family selection in switchgrass. Bioenergy Res. 2010, 3, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D. Switchgrass breeding, genetics, and genomics. In Switchgrass: A Valuable Biomass Crop for Energy; Monti, A., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 29–53. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, K.P.; Hopkins, A.A.; Moore, K.J.; Johnson, K.D.; Carlson, I.T. Registration of “Shawnee” switchgrass. Crop Sci. 1996, 36, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.K.; Fuentes, R.G.; Taliaferro, C.M. Genetic variability and trait relationships in switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose IV, L.W.; Das, M.K.; Taliaferro, C.M. Estimation of genetic variability and heritability for biofuel feedstock yield in several populations of switchgrass. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2008, 152, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, H.S.; Saha, M.C.; Mascia, P.N.; Fasoula, V.A.; Bouton, J.H. Variation among half-sib families and heritability for biomass yield and other traits in lowland switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, V.R.; Allen, F.L.; DeSantis, A.C.; Saxton, A.M.; Bhandari, H.S.; West, D.R.; Hughes, E.W.; Bobbitt, M.E.; Benelli, V.G. Efficiency of spaced-plant selection in improving sward biomass and ethanol yield in switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalid, C.O.; Saxton, A.M.; Allen, F.L.; Pantalone, V.; Nayak, S.; Bhandari, H.S. Genetic variation and expected per cycle biomass yield gain in lowland switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbert, L.E.; Timothy, D.H.; Burns, J.C.; Rawlings, J.O.; Moll, R.H. Estimates of genetic parameters in switchgrass. Crop Sci. 1983, 23, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godshalk, E.B.; Mcclure, W.F.; Burns, J.C.; Timothy, D.H.; Fisher, D.S. Heritability of cell wall carbohydrates in switchgrass. Crop Sci. 1988, 28, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahufer, M.Z.; Casler, M.D. Application of the Smith-Hazel selection index for improving biomass yield and quality of switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmé, S.; Mitchell, R.; Sarath, G. Genetic parameters and prediction of breeding values in switchgrass bred for bioenergy. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.A.; Vogel, K.P.; Moore, K.J.; Johnson, K.D.; Carlson, I.T. Genotype effects and genotype by environment interactions for traits of elite switchgrass populations. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Boe, A.R. Cultivar x environment interactions in switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 2229–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.A.; Vogel, K.P.; Moore, K.J.; Johnson, K.D.; Carlson, I.T. Genotypic variability and genotype × environment interactions among switchgrass accessions from the midwestern USA. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Vogel, K.P.; Taliaferro, C.M.; Wynia, R.L. Latitudinal adaptation of switchgrass populations. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Vogel, K.P. Selection for biomass yield in upland, lowland, and hybrid switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Release Brochure for Kanlow Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, Manhattan PMC, Manhattan, KS. Published: May 2011. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_PLANTMATERIALS/publications/kspmcrb10373.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Eberhart, S.A.; Newell, L.C. Variation in domestic collections of switchgrass, Panicum virgatum L. Agron. J. 1959, 51, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.B. Estimating genotypic correlations and their standard errors using multivariate restricted maximum likelihood estimation with SAS Proc MIXED. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.A.; Williams, J.C.; Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E. Estimates of genotypic and environmental variances and covariances in upland cotton and their implications in selection. Agron. J. 1958, 50, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Sleper, D.A. Theory and application of half-sib matings in forage grass breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1983, 64, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, H.S.; Fasoula, V.A.; Bouton, J.H. Space-plant versus sward-plot evaluation of half-sib families to select parents for synthetic cultivars with superior biomass yield in lowland switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hallauer, A.R.; Carena, M.J.; Filho, J.B.M. Quantitative Genetics in Maize Breeding; Springer Science + Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, H.S.; Saha, M.C.; Fasoula, V.A.; Bouton, J.H. Estimation of genetic parameters for biomass yield in lowland switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Brummer, E.C. Theoretical expected genetic gains for among-and-within-family selection methods in perennial forage crops. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Centers for Environmental Information. Climate Data Online. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cdo-web (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Sarath, G.; Baird, L.; Mitchell, R. Senescence, dormancy and tillering in perennial C4 Grasses. Plant Sci. 2014, 217, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, D.; Yu, C.; Deng, Q.; Dzantor, E.K.; Zhou, S.; Dennis, S.; Sauve, R.; Johnson, T.L.; Fay, P.A.; Shen, W.; et al. Effects of precipitation changes on switchgrass photosynthesis, growth, and Biomass: A mesocosm experiment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casler, M.D.; Stendal, C.A.; Kapich, L.; Vogel, K.P. Genetic diversity, plant adaptation regions, and gene pools for switchgrass. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Caligari, P.; Campos, H. Plant Breeding, 2nd ed.; Wiley Blackwell: West Sussex, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, D.S.; Mackay, T.F.C. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 4th ed.; Longman Press: Essex, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Casler, M.D. Phenotypic recurrent selection methodology for reducing fiber concentration in smooth bromegrass. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.W. Recurrent restricted phenotypic selection increases forage yields of pensacola bahiagrass. Crop Sci. 1974, 14, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sources | Df | Knoxville | Crossville | Combined |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -------------------Variance Component------------------- | ||||
| KHS | 53 | 1.67 ** | 2.26 ** | 0.96 * |
| Rep †/Rep [Location] | 2 (4) ‡ | 0.04 | 1.77 | 0.90 |
| KHS × Location | 53 | - | - | 0.99 * |
| KHS × Year | 53 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.30 |
| KHS × Rep/Rep [Location] | 106 (212) ‡ | 1.43 ** | 2.85 ** | 2.14 *** |
| KHS × Year × Location | 53 | - | - | - |
| KHS × Year × Rep [Location] | 108 (216) ‡ | 1.68 *** | 5.02 *** | 3.28 *** |
| Plant [KHS] § | df | 28.44 *** | 45.53 *** | 37.24 *** |
| --------------Test of Fixed Effects (F-Values)-------------- | ||||
| Year | 1 | 379.32 *** | 357.64 *** | 612.52 *** |
| Location | 1 | - | - | 87.56 ** |
| Location × Year | 1 | - | - | 10.01 ** |
| Sources | PH | TA | ST | CL | HC | LG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -------------------Variance component------------------- | ||||||
| KHS | 5.39 | 0.04 | - | 0.01 | 0.14 * | 0.06 ** |
| Rep †/Rep [Location] | 26.25 | 0.88 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| KHS × Location | - | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | - | - |
| KHS × Year | 33.09 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.06 | - | - |
| KHS × Rep/Rep [Location] | 86.98 * | 0.13 ** | 0.05 ** | - | - | 0.01 |
| KHS × Year × Location | 11.25 | 0.01 | - | - | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| KHS × Year × Rep [Location] | 192.08 *** | 0.33 *** | 0.11 *** | 0.18 *** | 0.61 *** | 0.26 *** |
| Plant [KHS] § | 485.28 *** | 1.43 *** | 0.48 *** | 0.95 *** | 1.56 *** | 0.29 *** |
| --------------Test of fixed effects (F-values)-------------- | ||||||
| Year | 44.07 *** | 0.08 | 139.08 *** | 225.35 *** | 88.62 *** | 17.88 *** |
| Location | 1.04 | 0.35 | 10.13 | 186.42 ** | 52.42 * | 278.91 ** |
| Location × Year | 192.42 *** | 0.30 | 215.93 *** | 283.69 *** | 68.50 *** | 235.90 *** |
| Trait † | BMY | PH | ST | TA | CL | HC | LG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -------------------------------------- Knoxville -------------------------------------- | |||||||
| KHS Mean | 9.5 | 240.2 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 45.5 | 32.9 | 6.9 |
| KHS Minimum | 2.2 | 175.8 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 42.3 | 29.1 | 5.6 |
| KHS Maximum | 18.5 | 305.0 | 4.8 | 5.7 | 49.2 | 41.9 | 8.9 |
| Kanlow check | 9.3 | 249.7 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 45.4 | 32.5 | 6.9 |
| LSD0.05 | 3.5 | 48.5 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 1.2 |
| CV% | 34.5 | 11.9 | 17.5 | 22.2 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 11.9 |
| -------------------------------------- Crossville -------------------------------------- | |||||||
| KHS Mean | 17.3 | 245.6 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 43.5 | 34.6 | 5.4 |
| KHS Minimum | 4.4 | 209.2 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 41.6 | 31.6 | 4.1 |
| KHS Maximum | 30.4 | 293.6 | 5.0 | 6.9 | 45.9 | 37.2 | 6.7 |
| Kanlow check | 16.5 | 237.9 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 42.9 | 35.6 | 5.1 |
| LSD0.05 | 4.8 | 22.1 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 1.1 |
| CV% | 25.5 | 5.6 | 18.1 | 26.9 | 1.9 | 3.9 | 12.1 |
| -------------------------------------- Combined -------------------------------------- | |||||||
| KHS Mean | 13.4 | 242.8 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 44.6 | 33.7 | 6.3 |
| KHS Minimum | 9.6 | 226.0 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 43.9 | 32.6 | 5.6 |
| KHS Maximum | 16.9 | 262.0 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 45.4 | 35.1 | 6.9 |
| Kanlow check | 12.9 | 243.8 | 3.2 | 3.8 | 44.3 | 33.9 | 6.1 |
| LSD0.05 | 4.4 | 25.6 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
| CV% | 41.1 | 9.3 | 21.2 | 27.4 | 3.7 | 4.6 | 16.9 |
| Parameter | Biomass Yield | Hemi-Cellulose | Lignin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.84 | 0.56 | 0.24 | |
| 39.49 | 1.76 | 0.36 | |
| h2 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.66 |
| Trait | Biomass Yield | Plant Height | Stem Thickness | Tillering Ability | Cellulose | Hemicellulose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height (rg) | 0.54 *** (±0.26) | |||||
| (rp) | 0.27 *** (±0.06) | |||||
| Stem thickness (rg) | 0.75 *** (±0.17) | 0.67 *** (±0.27) | ||||
| (rp) | 0.31 *** (±0.06) | 0.29 *** (±0.05) | ||||
| Tillering ability (rg) | 0.07 (±0.26) | −0.77 *** (±0.33) | −0.56 *** (±0.27) | |||
| (rp) | 0.19 ** (±0.05) | −0.04 (±0.06) | −0.01 (±0.06) | |||
| Cellulose (rg) | 0.39 *** (±0.28) | 0.90 *** (±0.42) | 0.98 *** (±0.33) | −0.19 ** (±0.37) | ||
| (rp) | 0.16 ** (±0.05) | 0.14 * (±0.05) | 0.11 (±0.06) | 0.07 (±0.05) | ||
| Hemicellulose(rg) | −0.17 ** (±0.29) | −0.25 *** (±0.38) | −0.39 *** (±0.31) | −0.24 *** (±0.34) | −0.54 *** (±0.30) | |
| (rp) | −0.08 (±0.05) | −0.17 ** (±0.06) | −0.09 (±0.06) | −0.02 (±0.05) | −0.45 *** (±0.05) | |
| Lignin (rg) | 0.44 *** (±0.20) | 0.78 *** (±0.27) | 0.66 *** (±0.20) | 0.01 (±0.26) | 0.66 *** (±0.20) | −0.88 *** (±0.17) |
| (rp) | 0.15 * (±0.06) | 0.17 ** (±0.06) | 0.13 * (±0.06) | 0.16 ** (±0.06) | 0.60 *** (±0.04) | −0.51 *** (±0.04) |
| Selection Intensity | PC § | ∆G | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass Yield (t ha−1) | Hemicellulose (% Dry Matter) | Lignin (% Dry Matter) | ||
| 10% | 1 | 1.10 (8.2) | 0.74 (2.2) | 0.94 (15.5) |
| 2 | 2.21 (16.5) | 1.49 (4.4) | 1.89 (30.9) | |
| 15% | 1 | 0.97 (7.3) | 0.65 (1.9) | 0.83 (13.6) |
| 2 | 1.95 (14.6) | 1.31 (3.9) | 1.66 (27.2) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nayak, S.; Bhandari, H.; Sams, C.; Sykes, V.; Hilafu, H.; Dalid, C.; Senseman, S.; Pantalone, V. Genetic Variation for Biomass Yield and Predicted Genetic Gain in Lowland Switchgrass “Kanlow”. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121845
Nayak S, Bhandari H, Sams C, Sykes V, Hilafu H, Dalid C, Senseman S, Pantalone V. Genetic Variation for Biomass Yield and Predicted Genetic Gain in Lowland Switchgrass “Kanlow”. Agronomy. 2020; 10(12):1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121845
Chicago/Turabian StyleNayak, Santosh, Hem Bhandari, Carl Sams, Virginia Sykes, Haileab Hilafu, Cheryl Dalid, Scott Senseman, and Vince Pantalone. 2020. "Genetic Variation for Biomass Yield and Predicted Genetic Gain in Lowland Switchgrass “Kanlow”" Agronomy 10, no. 12: 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121845
APA StyleNayak, S., Bhandari, H., Sams, C., Sykes, V., Hilafu, H., Dalid, C., Senseman, S., & Pantalone, V. (2020). Genetic Variation for Biomass Yield and Predicted Genetic Gain in Lowland Switchgrass “Kanlow”. Agronomy, 10(12), 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10121845





