Interactive Effects of Light and Nitrogen on Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Growth and Soil Enzyme Activity in an Underground Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Plant Biomass and Chlorophyll Content Index
2.3. Measurements of Soil Enzyme Activities
2.4. Theories Description
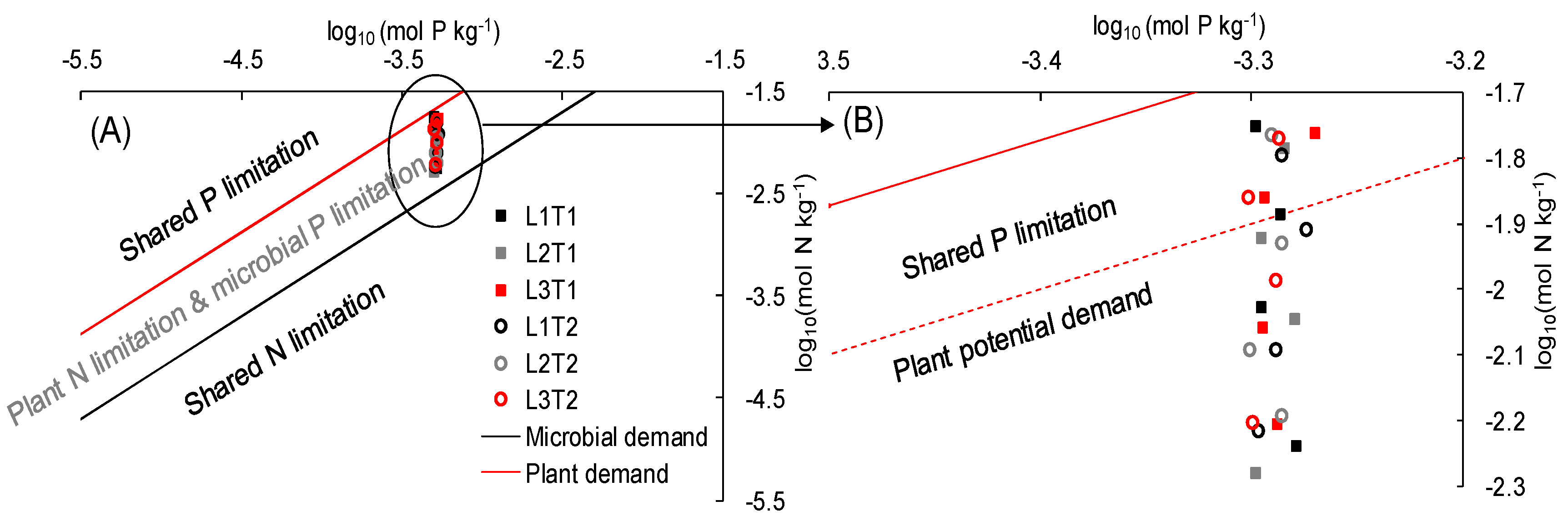
2.4.1. Toxic Effect Theory
2.4.2. Plant-Microbe Interaction Framework
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
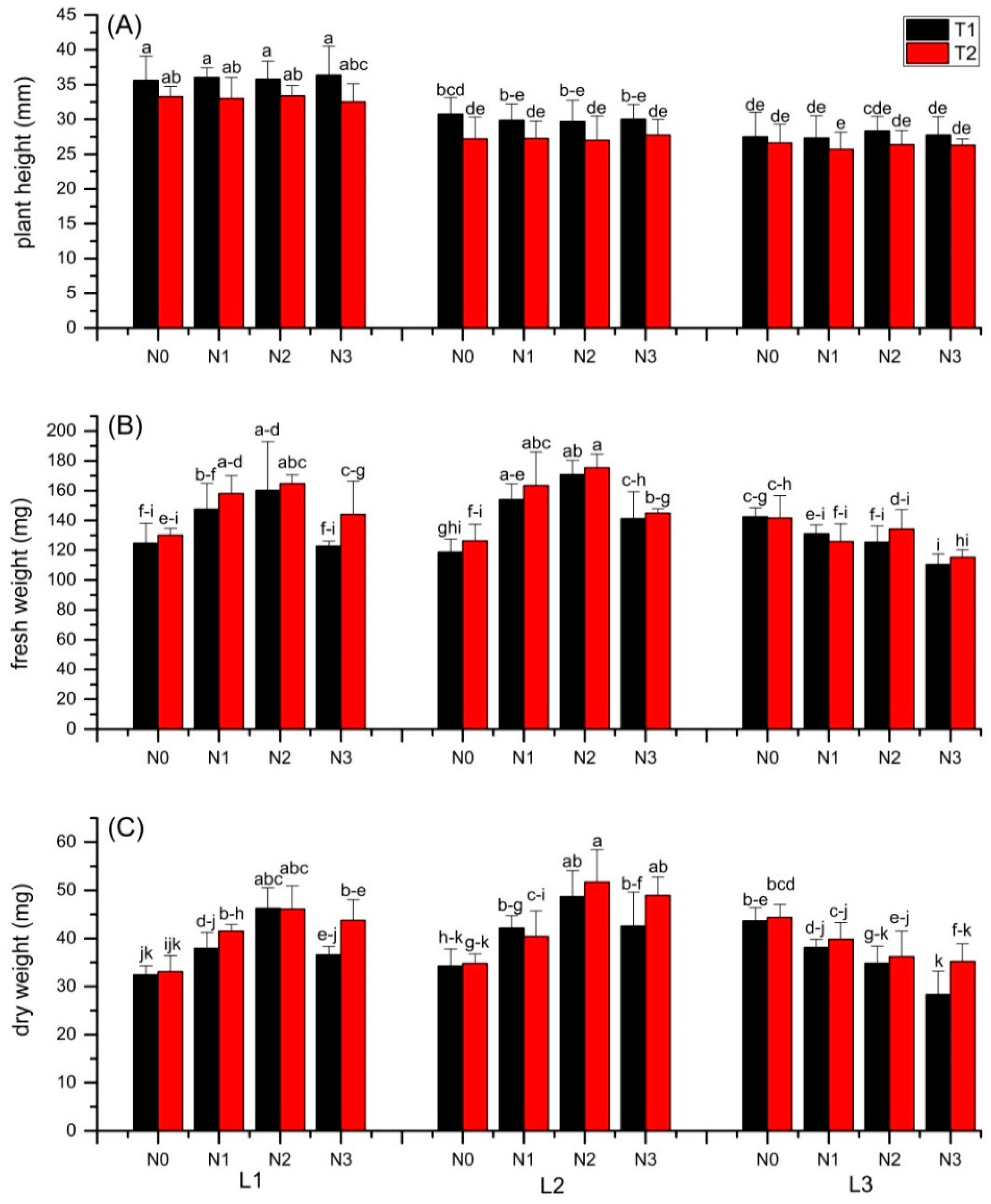
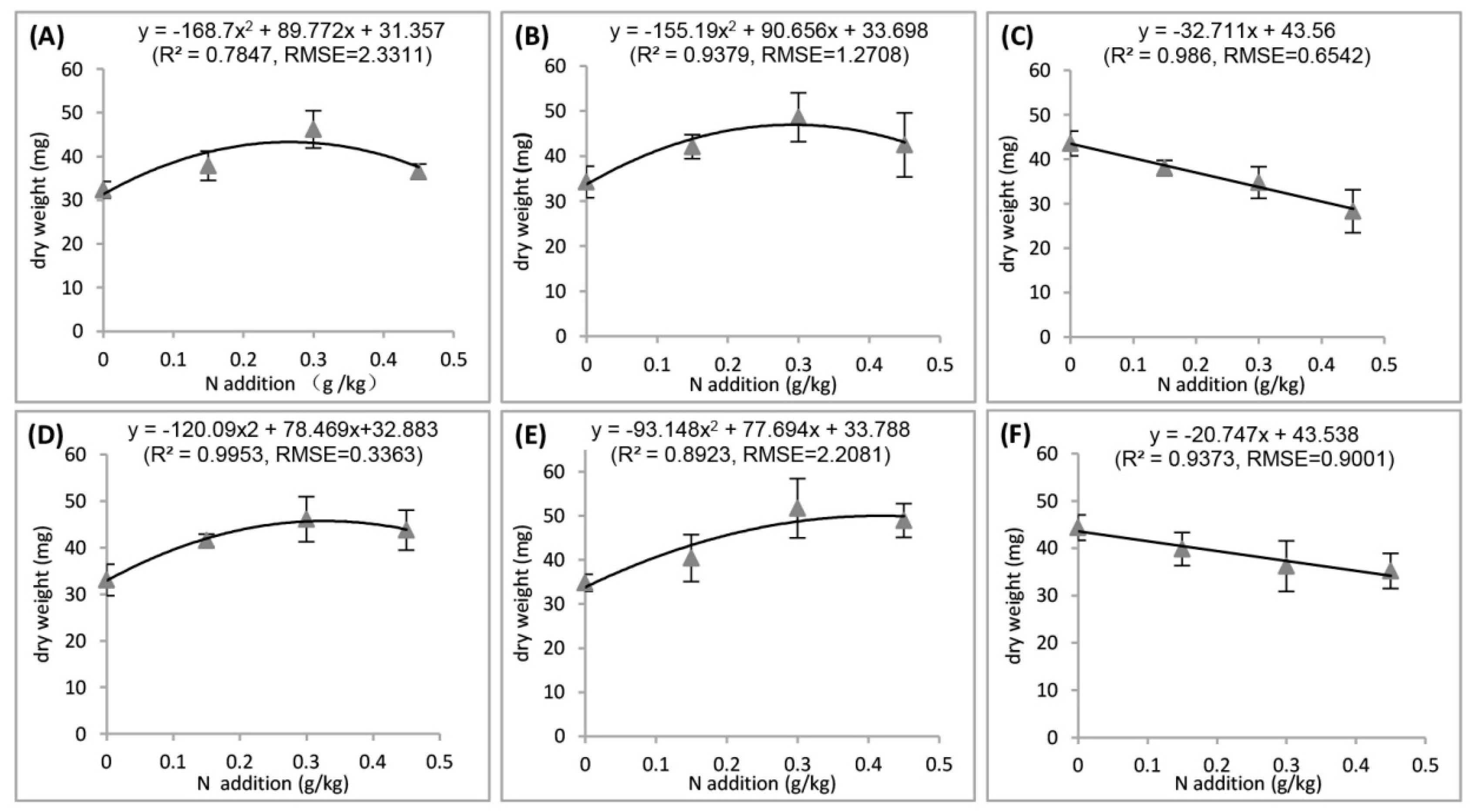
3.1. Plant Growth and Yield
3.2. Chlorophyll Content Index
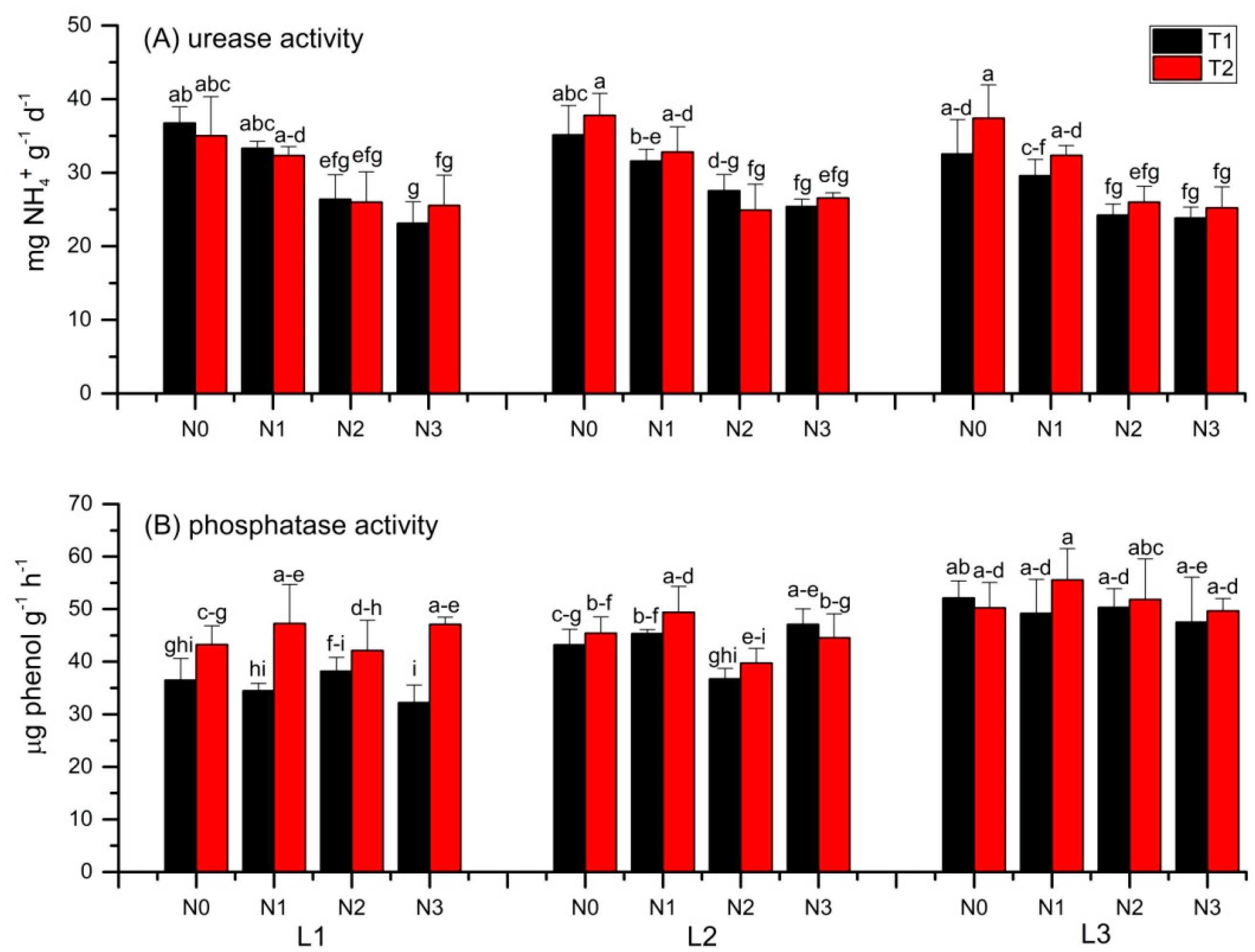
3.3. Soil Urease and Phosphatase Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Light or N
4.2. Interactive Effects of Light and N
4.2.1. Toxic Effect of N
4.2.2. Plant-Microbe Interaction Effect of N
4.3. Urease and Phosphatase Activity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.F. History, advancements, and perspective of biological research in deep-underground laboratories: A brief review. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 207–214. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P.; Gao, M.Z.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.H. The subversive idea and its key technical prospect on underground ecological city and ecosystem. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Liao, Z.; Zhu, J. A case study of development and utilization of urban underground space in Shenzhen and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 107, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.M. Interaction effects of light intensity and nitrogen concentration on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and quality of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. Var. youmaicai). Sci. Hortic. 2017, 214, 51–57. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagnari, F.; Galieni, A.; Pisante, M. Shading and nitrogen management affect quality, safety and yield of greenhouse-grown leaf lettuce. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 192, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, V.; Hellín, P.; Fenoll, J.; Flores, P. Interaction of nitrogen and shading on tomato yield and quality. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 255, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Hao, D.Y.; Su, Y.H. Effects of light and nitrogen interaction on carbon-nitrogen metabolism of Arabidopsis thaliana col-0 and mutant CS3721512. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2018, 41, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.-J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Shen, S.-H.; Jing, Y.-X. Effects of rhizobia inoculation and nitrogen fertilization on photosynthetic physiology of soybean. Photosynthetica 2006, 44, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, P. A plant-microbe interaction framework explaining nutrient effects on primary production. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1588–1596. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusewell, S. High nitrogen: Phosphorus ratios reduce nutrient retention and second-year growth of wetland sedges. New Phytol. 2005, 166, 537–550. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venterink, H.O.; Gusewell, S. Competitive interactions between two meadow grasses under nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 877–886. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, W.A.; Tabatabai, W.A. Significance and Potential Use of Soil Enzymes; Soil Microbial Ecology. Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 95–127. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, R.G.; Deforest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, I.; Evans, J.R. Effects of Light and Nitrogen Nutrition on the Organization of the Photosynthetic Apparatus in Spinach. Plant Cell Physiol. 1988, 29, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, G.J.; Rodriguez, D.; O’Leary, G. Measuring and predicting canopy nitrogen nutrition in wheat using a spectral index—The canopy chlorophyll content index (CCCI). Field Crop. Res. 2010, 116, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, J.M.; Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development. ISME J. 2014, 8, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil enzymes. In Soil Science Society of America, Book Series; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar]
- Klose, S.; Tabatabai, M. Urease activity of microbial biomass in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, P.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Interactive effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer on yield, nitrogen uptake, and recovery of two successive Chinese cabbage crops as assessed using 15N isotope. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 215, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinsakir, K.; Karaca, C.; Ozkan, C.F.; Dinc, N.; Buyuktas, D.; Isik, M. Excess nitrogen exceeds the european standards in lettuce grown under greenhouse conditions. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, U.; Ydin, H.R. Nitrogen fertilization reduces Sphagnum production in bog communities. New Phytol. 2000, 147, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, E.; Bobbink, R.; Smolders, A.; Van Der Ven, P.; Lamers, L.; Roelofs, J. Interactive effects of low pH and high ammonium levels responsible for the decline of Cirsium dissectum (L.) Hill. Plant Ecol. 2003, 165, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, S. Effects of atmospheric ammonia (NH3) on terrestrial vegetation: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 179–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhuang, K.; Chen, Y.; Xu, F.; Hu, Z.; Shen, Z. Effects of excess ammoniacal nitrogen (NH4+-N) on pigments, photosynthetic rates, chloroplast ultrastructure, proteomics, formation of reactive oxygen species and enzymatic activity in submerged plant Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 226, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, R.; Ariz, I.; Cruz, C.; Moran, J.F. Review: Mechanisms of ammonium toxicity and the quest for tolerance. Plant Sci. 2016, 248, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Valdivia, M.D.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; Lamsfus, C.; Cruz, C.; Martins-Loução, M.A.; Moran, J.F. Nitrogen nutrition and antioxidant metabolism in ammonium-tolerant and -sensitive plants. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Duigan, S.P.; Berlyn, G.P. An evaluation of noninvasive methods to estimate foliar chlorophyll content. New Phytol. 2002, 153, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Raza, M.A.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Bin Khalid, M.H.; Du, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, X.; Song, C.; Yu, L.; et al. The Influence of Light Intensity and Leaf Movement on Photosynthesis Characteristics and Carbon Balance of Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-X.; Xu, Z.-G.; Liu, X.-Y.; Tang, C.-M.; Wang, L.-W.; Han, X.-L. Effects of light intensity on the growth and leaf development of young tomato plants grown under a combination of red and blue light. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 153, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K.A. Shade avoidance. New Phytol. 2010, 179, 930–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommers, C.M.; Visser, E.J.; Onge, K.R.S.; Voesenek, L.A.; Pierik, R. Shade tolerance: When growing tall is not an option. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares, F.; Niinemets, U. Shade Tolerance, a Key Plant Feature of Complex Nature and Consequences. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, T.; Falcioni, R.; Tanaka, F.A.O.; Cardoso, K.A.K.; Souza, L.; Benedito, E.; Nanni, M.; Bonato, C.M.; Antunes, W.C. Nitrogen-improved photosynthesis quantum yield is driven by increased thylakoid density, enhancing green light absorption. Plant Sci. 2019, 278, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hong, X.; Hu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, D.; Cheng, K.; An, B.; et al. Impaired Magnesium Protoporphyrin IX Methyltransferase (ChlM) Impedes Chlorophyll Synthesis and Plant Growth in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuraba, Y.; Yanagisawa, S. Light signalling-induced regulation of nutrient acquisition and utilisation in plants. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 83, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotelli, N.J.; Ellison, A.M. Nitrogen deposition and extinction risk in the northern pitcher plant, sarracenia purpurea. Ecology 2002, 83, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.A.; Caporn, S.J.M.; Johnson, D.; Morecroft, M.D.; Lee, J.A. The interactions between plant growth, vegetation structure and soil processes in semi-natural acidic and calcareous grasslands receiving long-term inputs of simulated pollutant nitrogen deposition. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Rengel, Z.; Liu, W.-G.; Yang, W. Light intensity influence maize adaptation to low P stress by altering root morphology. Plant Soil 2019, 447, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P.; Crowley, D.; Rengel, Z. Rhizosphere interactions between microorganisms and plants govern iron and phosphorus acquisition along the root axis—model and research methods. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, N.; Smith, A.; Freedman, R.; Burns, R. Soil urease: Activity, stability and kinetic properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1976, 8, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooshammer, M.; Wanek, W.; Hämmerle, I.; Fuchslueger, L.; Hofhansl, F.; Knoltsch, A.; Schnecker, J.; Takriti, M.; Watzka, M.; Wild, B.; et al. Adjustment of microbial nitrogen use efficiency to carbon:nitrogen imbalances regulates soil nitrogen cycling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olander, L.P.; Vitousek, P.M. Regulation of soil phosphatase and chitinase activity by N and P availability. Biogeochem. 2000, 49, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Nitrogen addition aggravates microbial carbon limitation: Evidence from ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Geoderma 2018, 329, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdig, M.; Schleuss, P.-M.; Weig, A.R.; Guhr, A.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Crawley, M.J.; Kirkman, K.P.; Seabloom, E.W.; Wragg, P.D.; et al. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions Alter the Abundance of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria and Phosphatase Activity in Grassland Soils. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playsted, C.W.S.; Johnston, M.E.; Ramage, C.M.; Edwards, D.G.; Cawthray, G.R.; Lambers, H. Functional significance of dauciform roots: Exudation of carboxylates and acid phosphatase under phosphorus deficiency in Caustis blakei (Cyperaceae). New Phytol. 2006, 170, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannipieri, P.; Giagnoni, L.; Landi, L.; Renella, G. Role of Phosphatase Enzymes in Soil. Soil Biol. 2011, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, S.; Tabatabai, M.A. Urease activity of microbial biomass in soils as affected by cropping systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Photoperiod (T) | PPFD (L) | Nitrogen Supply (N) |
|---|---|---|
| T1: 12-h light,12-h dark | L1: 200 μmol m−2 s−1 L2: 300 μmol m−2 s−1 L3: 400 μmol m−2 s−1 | N0: 0 g N kg−1 |
| N1: 0.15 g N kg−1 | ||
| T2:16-h light, 8-h dark | N2: 0.3 g N kg−1 | |
| N3: 0.45 g N kg−1 |
| Soil Bulk Density | Field Capacity | pH | Electrical Conductivity | Organic Carbon | Total N Content | Total P Content | Total K Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.12 g/cm3 | 40.72% | 6.58 | 219 μS/cm | 27.69 g kg−1 | 1.90 g kg−1 | 0.62 g kg−1 | 14.03 g kg−1 |
| Treatment | Plant Height | Fresh Weight | Dry Weight | CCI | Urease Activity | Phosphatase Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | <0.0001 | 0.0392 | 0.0085 | 0.0299 | n.s. | <0.0001 |
| L | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0263 | n.s. | <0.0001 |
| N | n.s. | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | n.s. |
| TL | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | 0.0039 |
| TN | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| LN | n.s. | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| TLN | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| L1 | L2 | L3 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 | N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 | ||
| T1 | N (mg kg−1) | 80.7(±11.5) | 131.1(±16.9) | 182.5(±26.8) | 248.3(±17.2) | 73.3(±7.0) | 126.5(±8.7) | 167.5(±16.5) | 230.1(±19.4) | 87.2(±26.5) | 122.7(±11.7) | 193.7(±14.9) | 243.1(±25.2) |
| P (mg kg−1) | 16.3(±0.7) | 15.7(±0.7) | 16.0(±0.7) | 15.6(±0.1) | 15.6(±0.5) | 16.3(±0.3) | 15.7(±0.4) | 16.1(±0.9) | 16.0(±0.8) | 15.7(±0.4) | 15.8(±1.0) | 16.6(±0.9) | |
| N/PSOIL | 11.0(±1.5) | 18.5(±2.6) | 25.2(±5.0) | 35.3(±2.6) | 10.4(±1.2) | 17.2(±1.5) | 23.6(±2.8) | 31.6(±2.4) | 12.1(±4.4) | 17.3(±2.0) | 27.2(±2.4) | 32.4(±5.0) | |
| T2 | N (mg kg−1) | 85.4(±21.8) | 113.4(±9.1) | 173.1(±8.7) | 225.4(±33.7) | 90.1(±18.5) | 113.4(±21.8) | 165.7(±29.5) | 242.2(±12.7) | 88.2(±7.9) | 145.1(±8.0) | 194.6(±23.9) | 238.6(±13.0) |
| P (mg kg−1) | 15.6(±0.6) | 15.9(±0.4) | 16.5(±1.6) | 16.1(±0.4) | 16.0(±0.6) | 15.5(±0.3) | 16.0(±0.2) | 15.9(±0.5) | 15.5(±0.6) | 15.9(±0.5) | 15.5(±0.6) | 16.0(±0.2) | |
| N/PSOIL | 12.1(±2.8) | 15.8(±1.7) | 23.3(±2.1) | 31.1(±3.9) | 12.4(±2.5) | 16.2(±3.0) | 22.9(±3.9) | 33.8(±2.8) | 12.6(±1.5) | 20.2(±0.7) | 27.9(±2.3) | 33.0(±2.2) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Liu, C.; Tan, X.; Tan, B.; He, Y.; Li, N. Interactive Effects of Light and Nitrogen on Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Growth and Soil Enzyme Activity in an Underground Environment. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111772
Li S, Liu C, Tan X, Tan B, He Y, Li N. Interactive Effects of Light and Nitrogen on Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Growth and Soil Enzyme Activity in an Underground Environment. Agronomy. 2020; 10(11):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111772
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Songsong, Chao Liu, Xiao Tan, Bo Tan, Yuxin He, and Naiwen Li. 2020. "Interactive Effects of Light and Nitrogen on Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Growth and Soil Enzyme Activity in an Underground Environment" Agronomy 10, no. 11: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111772
APA StyleLi, S., Liu, C., Tan, X., Tan, B., He, Y., & Li, N. (2020). Interactive Effects of Light and Nitrogen on Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Growth and Soil Enzyme Activity in an Underground Environment. Agronomy, 10(11), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111772









