Development of Pretreatment Strategies for the Fractionation of Hazelnut Shells in the Scope of Biorefinery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Autohydrolysis of Hazelnut Shells
2.3. Delignification Pretreatments
- Alkaline-organosolv pretreatments of HS and AS were carried out in an autoclave at 121 °C or 135 °C for 60 min, in media with equal amounts of ethanol and alkaline solutions, containing 2–8 wt% NaOH with respect to the total solution.
- Acid-catalyzed organosolv treatments of HS and AS were performed in the Parr reactor indicated above. The media contained a mixture of ethanol/aqueous H2SO4 (60/40 w/w), where the amount of H2SO4 corresponded 1 g H2SO4/100 g substrate. The reaction media were kept at 160–180 °C for 60–120 min.
2.4. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
2.5. Analytical Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Autohydrolysis and Composition of HS and AS
3.2. Delignification Treatments
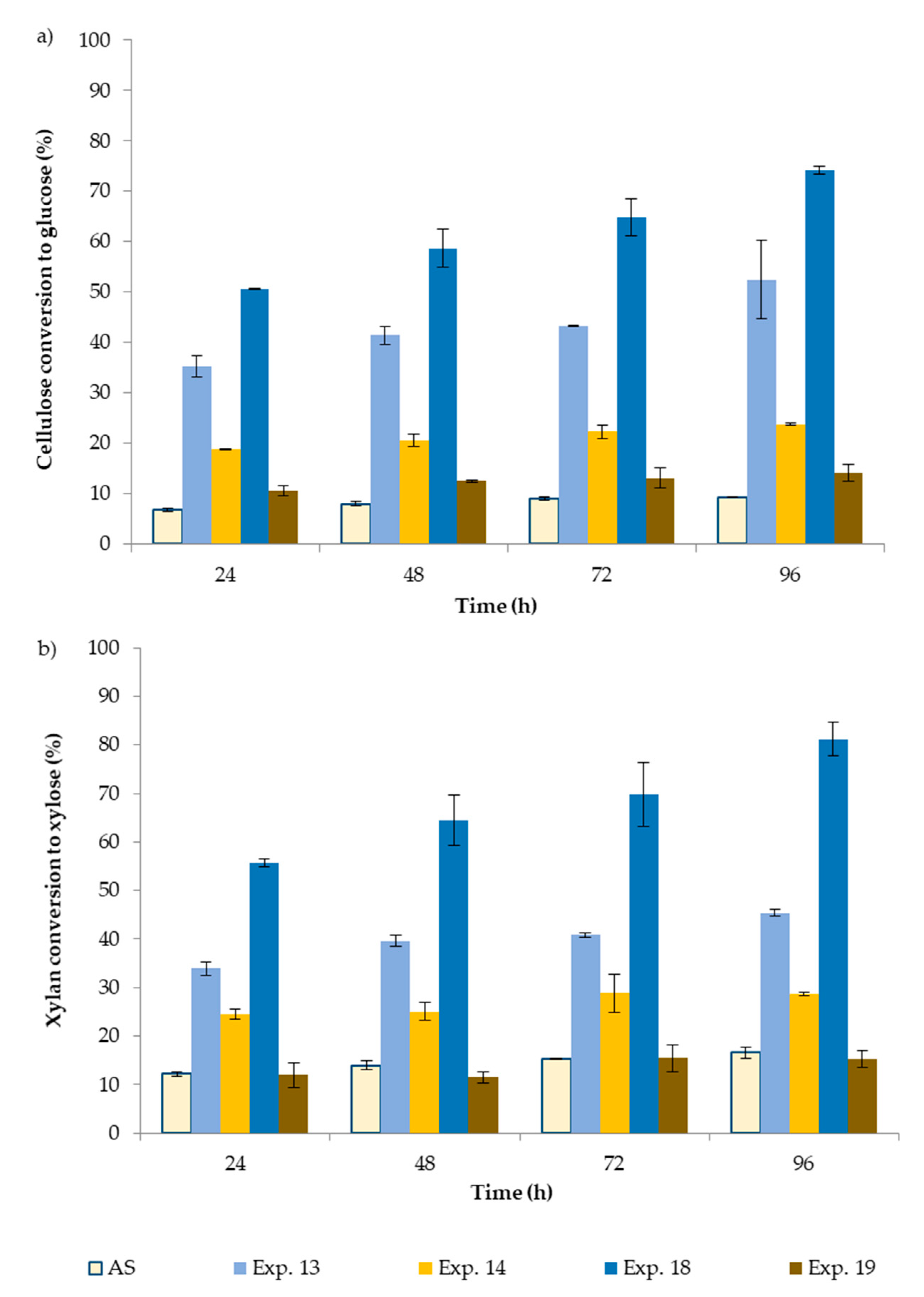
3.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romaní, A.; Garrote, G.; López, F.; Parajó, J.C. Eucalyptus globulus Wood fractionation by autohydrolysis and organosolv delignification. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5896–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Iqbal, T.; Khan, M.J. Recent advances in the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for fuels and value-added products. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 20, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubando, A.T.; Feliz, C.B.; Chen, W.-H. Biorefineries in circular bioeconomy: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Bhardwaj, N.; Agrawal, K.; Chaturvedi, V.; Verma, P. Current perspective on pretreatment technologies using lignocellulosic biomass: An emerging biorefinery concept. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 199, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönson, L.J.; Martín, C. Pretreatment of lignocellulose: Formation of inhibitory by-products and strategies for minimizing their effects. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galbe, M.; Wallberg, O. Pretreatment for biorefineries: A review of common methods for the efficient utilisation of lignocellulosic materials. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Jagtap, S.S.; Bedekar, A.A.; Bhatia, R.K.; Patel, A.K.; Pant, D.; Banu, J.R.; Rao, C.V.; Kim, Y.-G.; Yang, Y.-H. Recent developments in pretreatment technologies on lignocellulosic biomass: Effect of key parameters, technological improvements, and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachapur, V.L.; Kaur Brar, S.; Le Bihan, Y. Integrated wood biorefinery: Improvements and tailor-made two-step strategies on hydrolysis techniques. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aachary, A.A.; Prapulla, S.G. Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) as an emerging prebiotic: Microbial synthesis, utilization, structural characterization, bioactive properties and applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, S.; Moure, A.; Parajó, J.C. Pretreatment of hazelnut shells as a key strategy for the solubilization and valorization of hemicelluloses into bioactive compounds. Agronomy 2020, 10, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bionod, P.; Sindhu, R.; Gnansounou, E.; Ahuwalia, V. Bioconversion of pentose sugars to value added chemicals and fuels: Recent trends, challenges and possibilities. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-Medina, J.; López-Cremades, F.J.; Olivares-Carrillo, P. Organosolv extraction of lignin from hydrolyzed almond shells and application of the δ-value theory. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8252–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelin, M.; Liebentritt, S.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A. Lignin from an integrated process consisting of liquid hot water and ethanol organosolv: Physicochemical and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moniz, P.; Lino, J.; Duarte, L.C.; Roseiro, L.B.; Boeriu, C.G.; Pereira, H.; Carvalheiro, F. Fractionation of hemicelluloses and lignin from rice straw by combining autohydrolysis and optimised mild organosolv delignification. Bioresources 2015, 10, 2626–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romaní, A.; Larramendi, A.; Yáñez, R.; Cancela, A.; Sánchez, A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Domingues, L. Valorization of Eucalyptus nitens bark by organosolv pretreatment for the production of advanced biofuels. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 132, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robles, E.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.; Barbosa, A.M.; Gordobil, O.; Carreño, N.L.V.; Labidi, J. Production of cellulose nanoparticles from blue agave waste treated with environmentally friendly processes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnaouri, A.; Asimakopoulou, G.; Kalogiannis, K.G.; Lappas, A.; Topakas, E. Efficient D-lactic acid production by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus through conversion of organosolv pretreated lignocellulosic biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 140, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Sun, S.; Cao, X.; Sun, R. Effect of hydrothermal pretreatment on the structural changes of alkaline ethanol lignin from wheat straw. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossberg, C.; Bremer, M.; Machill, S.; Koenig, S.; Kerns, G.; Boeriu, C.; Windeisen, E.; Fischer, S. Separation and characterisation of sulphur-free lignin form different agricultural residues. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 73, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoşgün, E.Z.; Bozan, B. Effect of different types of thermochemical pretreatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis and the composition of hazelnut shells. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 3739–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Hazelnut Production. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/visualize (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Yuan, B.; Lu, M.; Eskridge, K.M.; Isom, L.D.; Hanna, M.A. Extraction, identification and quantification of antioxidant phenolics from hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) shells. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Armada, L.; Rivas, S.; González, B.; Moure, A. Extraction of phenolic compounds from hazelnut shells by green processes. J. Food Eng. 2019, 255, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Oils from hazelnut shell and hazelnut kernel husk for biodiesel production. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. 2008, 30, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surek, E.; Buyukkileci, A.O. Production of xylooligosaccharides by autohydrolysis of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) shell. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 174, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydinli, B.; Caglar, A. The investigation of the effects of two different polymers and three catalysts on pyrolysis of hazelnut shell. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çöpür, Y.; Tozluoglu, A.; Özkan, M. Evaluating pretreatment techniques for converting hazelnut husks to bioethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzuner, S.; Sharma-Shivappa, R.R.; Cekmecelioglu, D. Bioconversion of alkali pretreated hazelnut shells to fermentable sugars for generation of high value products. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoşgün, E.Z.; Berikten, D.; Kivanç, M.; Bozan, B. Ethanol production from hazelnut shells through enzymatic saccharification and fermentation by low-temperature alkali pretreatment. Fuel 2017, 196, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.F.; Hong, J.; Hu, J.; Saddler, J.N.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, S. Accesory enzymes influence cellulase hydrolysis of the model substrate and the realistic lignocellulosic biomass. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2015, 79, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TAPPI Method T 264 cm-07. Preparation of wood for chemical analysis. Available online: https://imisrise.tappi.org/TAPPI/Products/01/T/0104T264.aspx (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- TAPPI Method T 211 om-07. Ash in wood, pulp, paper and paperboard: Combustion at 525 °C. Available online: https://imisrise.tappi.org/TAPPI/Products/01/T/0104T211.aspx (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- TAPPI Method T 249 cm-00. Carbohydrate composition of extractive free wood and wood pulp by gas–liquid chromatography. Available online: https://imisrise.tappi.org/TAPPI/Products/01/T/0104T249.aspx (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Fernández-Rodríguez, J.; Erdocia, X.; Sánchez, C.; González Alriols, M.; Labidi, J. Lignin depolymerization for phenolic monomers production by sustainable processes. J. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dagnino, E.P.; Felissia, F.E.; Chamorro, E.; Area, M.C. Optimization of the soda-ethanol delignification stage for a rice husk biorefinery. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 97, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnino, E.P.; Felissia, F.E.; Chamorro, E.; Area, M.C. Studies on lignin extraction from rice husk by a soda-ethanol treatment: Kinetics, separation, and characterization of products. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 129, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanci, K.; Buyukkileci, A.O. Comparision of liquid hot water, very dilute acid and alkali treatments for enhancing enzymatic digestibility of hazelnut tree pruning residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa, L.; González, E.; Ruiz, E.; Romero, I.; Cara, C.; Felissia, F.; Castro, E. Preliminary evaluation of organosolv pre-treatment of sugar cane bagasse for glucose production: Application of 2³ experimental design. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, L.; González, E.; Cara, C.; González, M.; Castro, E.; Mussatto, S.I. The effect of organosolv pretreatment variables on enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obama, P.; Ricochon, G.; Muniglia, L.; Brosse, N. Combination of enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol organosolv pretreatments: Effect on lignin structures, delignification yields and cellulose-to-glucose conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijgen, W.J.J.; Smit, A.T.; de Wild, P.J.; den Uil, H. Fractionation of wheat straw by prehydrolysis, organosolv delignification and enzymatic hydrolysis for production of sugars and lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Hage, R.; Chrusciel, L.; Desharnais, L.; Brosse, N. Effect of autohydrolysis of Miscanthus x giganteus on lignin structure and organosolv delignification. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9321–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallac, B.B.; Sannigrahi, P.; Pu, Y.; Ray, M.; Murphy, R.J.; Ragauskas, A.J. Effect of ethanol organosolv pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis of Buddleja davidii Stem Biomass. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Pan, X. Correlation between lignin physicochemical properties and inhibition to enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Delignification Method | Experiment | Substrate and Operational Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Alkaline (NaOH-water) | 1 | HS 121 °C 60 min, 2% NaOH |
| 2 | AS 121 °C 60 min, 2% NaOH | |
| 3 | HS 121 °C 60 min, 4% NaOH | |
| 4 | AS 121 °C 60 min, 4% NaOH | |
| 5 | HS 121 °C 60 min, 8% NaOH | |
| 6 | AS 121 °C 60 min, 8% NaOH | |
| Alkaline-organosolv (ethanol-aqueous NaOH) | 7 | HS 121 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/aqueous NaOH, 2% total solution |
| 8 | AS 121 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/aqueous NaOH, 2% total solution | |
| 9 | HS 121 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/aqueous NaOH, 4% total solution | |
| 10 | AS 121 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/aqueous NaOH, 4% total solution | |
| 11 | HS 121 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/aqueous NaOH, 8% total solution | |
| 12 | AS 121 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/aqueous NaOH, 8% total solution | |
| 13 | HS 135 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/ aqueous NaOH, 4% total solution | |
| 14 | AS 135 °C 60 min, 50/50 ethanol/aqueous NaOH, 4% total solution | |
| Organosolv (ethanol-water) | 15 | HS 200 °C 60 min, 55/45 ethanol/water |
| 16 | AS 200 °C 60 min, 55/45 ethanol/water | |
| 17 | AS 200 °C 120 min, 55/45 ethanol/water | |
| Acid-catalyzed organosolv (ethanol/aqueous H2SO4) | 18 | HS 180 °C 60 min, 60/40 ethanol/aqueous H2SO4, |
| 19 | AS 180 °C 60 min, 60/40 ethanol/aqueous H2SO4, | |
| 20 | AS 180 °C 120 min, 60/40 ethanol/aqueous H2SO4, | |
| 21 | HS 160 °C 120 min, 60/40 ethanol/aqueous H2SO4, | |
| 22 | AS 160 °C 120 min, 60/40 ethanol/aqueous H2SO4, |
| Component | HS (g/100 g of dry HS) | AS (g/100 g of AS) |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | 24.2 ± 0.1 | 38.7 ± 0.2 |
| Xylan | 23.2 ± 0.1 | 7.5 ± 0.2 |
| Arabinan | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Acetyl groups | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| Klason lignin | 38.5 ± 0.6 | 49.7 ± 0.7 |
| Acid Soluble Lignin (ASL) | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| Other components | 8.0 | 1.80 |
| Experiment | Solid Yield (%) | Lignin Removal (%) | Cellulose Removal (%) | Hemicellulose Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91.7 | 7.2 | 10.0 | 26.6 |
| 2 | 81.8 | 12.7 | 22.5 | 74.7 |
| 3 | 88.0 | 15.7 | 9.0 | 38.8 |
| 4 | 78.1 | 20.7 | 22.3 | 76.7 |
| 5 | 76.1 | 19.2 | 7.4 | 47.8 |
| 6 | 76.9 | 24.3 | 20.3 | 79.2 |
| 7 | 86.8 | 11.3 | 11.5 | 27.5 |
| 8 | 82.3 | 17.2 | 20.0 | 70.6 |
| 9 | 82.4 | 18.0 | 10.9 | 42.5 |
| 10 | 88.0 | 22.4 | 13.8 | 62.2 |
| 11 | 82.7 | 18.9 | 10.3 | 52.4 |
| 12 | 85.5 | 29.1 | 24.9 | 69.1 |
| 13 | 73.5 | 21.2 | 11.0 | 49.2 |
| 14 | 75.8 | 26.6 | 16.2 | 70.1 |
| 15 | 53.6 | 53.3 | 0.0 | 67.5 |
| 16 | 76.8 | 35.2 | 2.6 | 42.0 |
| 17 | 75.8 | 32.8 | 5.2 | 51.0 |
| 18 | 46.2 | 65.3 | 0.0 | 76.0 |
| 19 | 64.9 | 47.9 | 7.1 | 87.7 |
| 20 | 57.9 | 50.5 | 17.3 | 93.2 |
| 21 | 61.4 | 47.9 | 0.0 | 56.2 |
| 22 | 73.2 | 37.2 | 5.6 | 62.1 |
| Raw Material | Reagents | T (°C) | Time | LSR | % Deligni-fication | Pre-Processing | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazelnut shell | NaOH 4% (w/v) | 121 | 60 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 32 | Steam explosion, 5 min, 198–200 °C | [27] |
| NaOH 4% (w/v) | 121 | 90 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 42.5 | Steam explosion, 5 min, 198–200 °C | [27] | |
| H2O2 4% (w/v) | 121 | 30 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 36 | Steam explosion, 5 min, 198–200 °C | [27] | |
| NaBH4 4% (w/v) | 121 | 60 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 48 | Steam explosion, 5 min, 198–200 °C | [27] | |
| NaOH 5% (w/v) | 121 | 60 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 19.7 | - | [28] | |
| NaOH 2.25% | 120 | 60 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 60 | - | [20] | |
| NaOH 2.25% | 200 | 60 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 73.28 | - | [20] | |
| Almond shell | Ethanol 70/30 (v/v) | 200 | 90 min | 6/1 | 10.8 | Autohydrolysis, 180 °C, 30 min, LSR 8/1 | [34] |
| NaOH 7.5 wt.% | 121 | 90 min | 6/1 | 18.4 | Autohydrolysis. 180 °C, 30 min, LSR 8/1 | [34] | |
| Rice husks | Ethanol 54/46, NaOH 8% (w/w on solid) | 160 | 60 min | 10/1 | 90.1 | Acid, 0.3% H2SO4 (w/v), 152 °C, 33 min | [35] |
| Ethanol 54/46, NaOH 8% (w/w on solid) | 160 | 100 min | 10/1 | 91.47 | Acid, 0.3% H2SO4 (w/v), 152 °C, 33 min | [36] | |
| Hazelnut tree prunings | NaOH 2% | 121 | 60 min | 10/1 | 30.7 | - | [37] |
| NaOH 2% | 121 | 60 min | 10/1 | 51.2 | Hydrothermal, 190 °C, 45 min, LSR 10/1 (v/w) | [37] | |
| Olive tree pruning | Ethanol 70/30 (v/v) | 200 | 90 min | 6/1 | 31.2 | Autohydrolysis, 180 °C, 30 min, LSR 8/1 | [34] |
| NaOH 7.5 wt.% | 121 | 90 min | 6/1 | 14.6 | Autohydrolysis, 180 °C, 30 min, LSR 8/1 | [34] | |
| Sugarcane bagasse | Ethanol 50/50 (v/v), NaOH 1.5% on dry fiber (w/w) | 175 | 60 min | 5/1 (v/w) | 44.3 | - | [38] |
| Ethanol 30/70 (v/v), NaOH 3% on dry fiber (w/w) | 195 | 60 min | 7/1 (w/w) | 17.1 | Acid, 0.2 M H2SO4, LSR 5/1 (w/w), 40 min, 120 °C | [39] | |
| Miscanthus biomass | Ethanol 80/20 (v/v), H2SO4 1% (w/w, based on solid) | 170 | 60 min | 8/1 | 84 | - | [40] |
| Ethanol 80/20 (v/v), H2SO4 1% (w/w, on solid) | 170 | 60 min | 8/1 | 88.5 | Autohydrolysis. LSR 9/1. 150 °C, 8h | [40] | |
| Eucalyptus globulus | Ethanol 60:40 (w/w) | 180–200 | 60 min | 8/1 (w/w) | 81 | Autohydrolysis. LSR 8/1 (w/w), Severity) 3.65–3.94 | [1] |
| Eucalyptus nitens bark | Ethanol 52-65% | 192–200 | 60–86 min | 8/1 (w/w) | 49–52 | - | [15] |
| Wheat straw | Ethanol 60/40 (w/w) | 200 | 60 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 67 | - | [41] |
| Ethanol 60/40 (w/w) | 200 | 60 min | 10/1 (v/w) | 64.3 | Acid, LSR 7.5/1 (v/w), 160 °C, 30 min | [41] |
| Substrate for Enzymatic Hydrolysis | Delignified HS (from exp. 13) | Delignified AS (from exp. 14) | Delignified HS (from exp. 18) | Delignified AS (from exp. 19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid composition (g/100 g of delignified solid) | ||||
| Cellulose | 29.3 ± 0.5 | 42.8 ± 0.7 | 54.0 ± 1.2 | 55.4 ± 1.9 |
| Xylan | 19.3 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 0.1 | 11.9 ± 0.9 | 1.7 ± 0.3 |
| Arabinan | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Acetyl groups | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| Klason lignin | 41.5 ± 3.5 | 48.3 ± 2.5 | 29.0 ± 0.7 | 40.1 ± 1.2 |
| Acid soluble lignin (ASL) | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.0 |
| Other | 8.7 | 4.7 | 2.5 | 2.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López, L.; Rivas, S.; Moure, A.; Vila, C.; Parajó, J.C. Development of Pretreatment Strategies for the Fractionation of Hazelnut Shells in the Scope of Biorefinery. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101568
López L, Rivas S, Moure A, Vila C, Parajó JC. Development of Pretreatment Strategies for the Fractionation of Hazelnut Shells in the Scope of Biorefinery. Agronomy. 2020; 10(10):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101568
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez, Laura, Sandra Rivas, Andrés Moure, Carlos Vila, and Juan Carlos Parajó. 2020. "Development of Pretreatment Strategies for the Fractionation of Hazelnut Shells in the Scope of Biorefinery" Agronomy 10, no. 10: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101568
APA StyleLópez, L., Rivas, S., Moure, A., Vila, C., & Parajó, J. C. (2020). Development of Pretreatment Strategies for the Fractionation of Hazelnut Shells in the Scope of Biorefinery. Agronomy, 10(10), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101568





