Protein-Repellence PES Membranes Using Bio-grafting of Ortho-aminophenol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Enzyme Activity (Assay)
2.3. Model Membrane Preparation
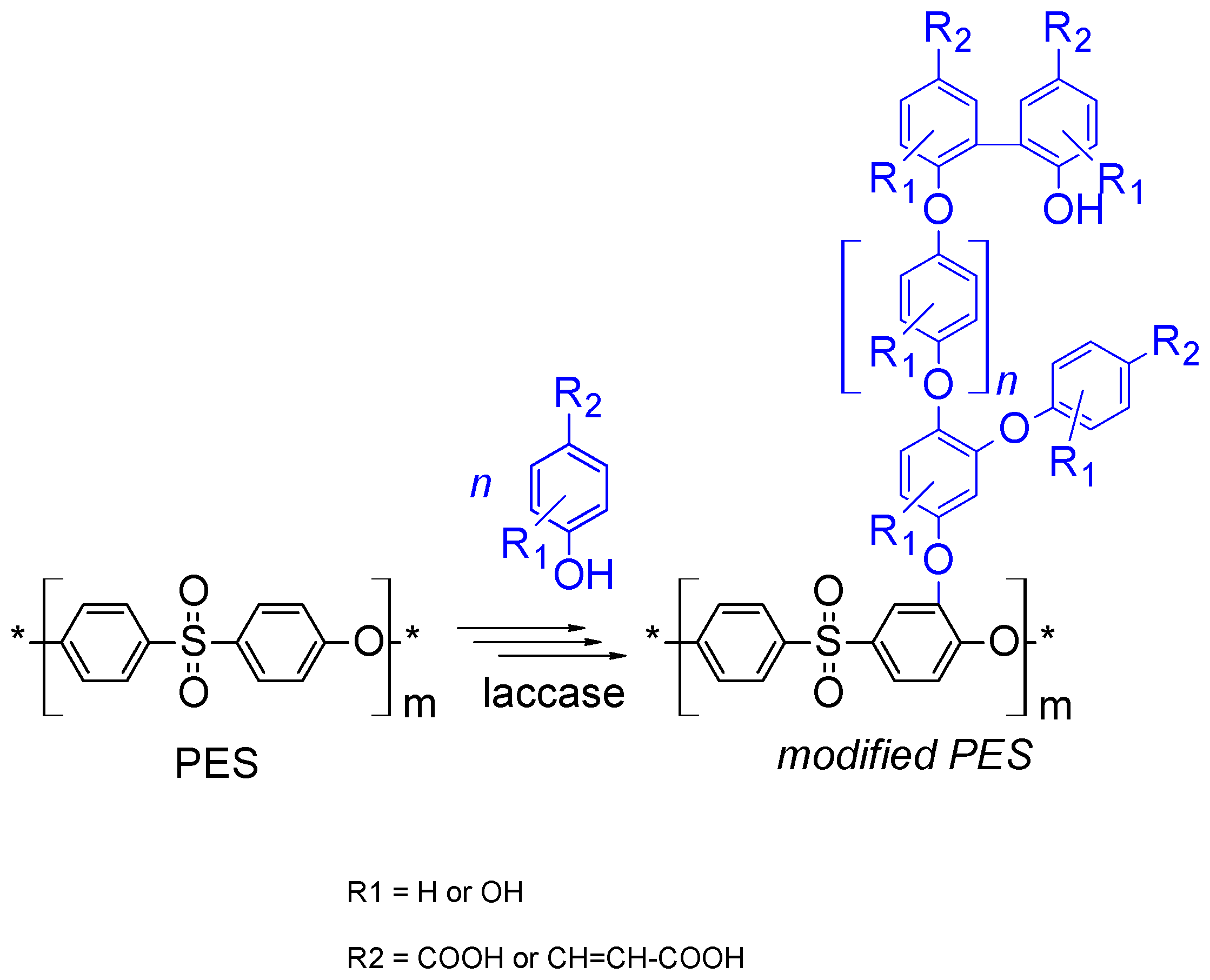
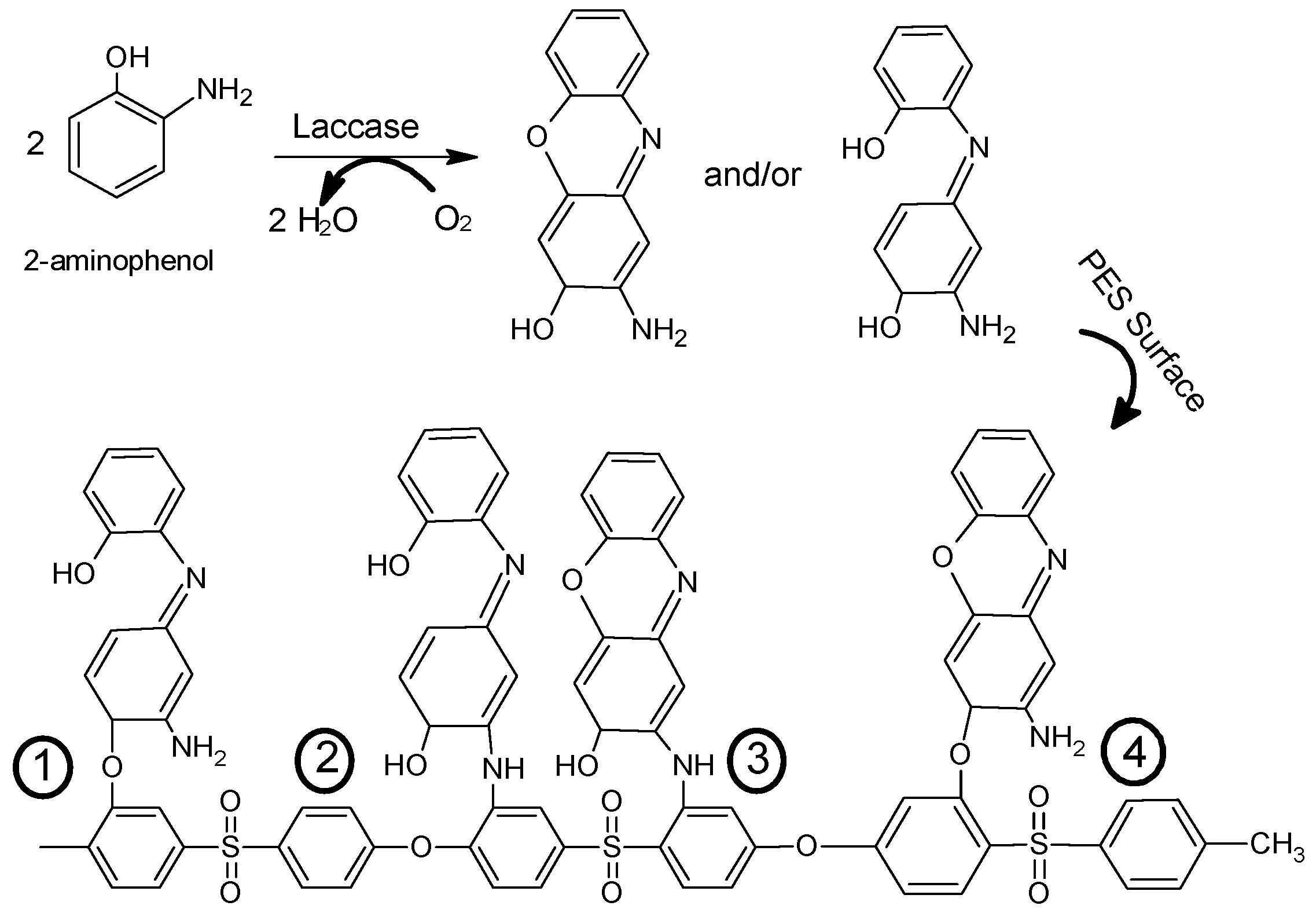
2.4. Membrane (Surface) Modification
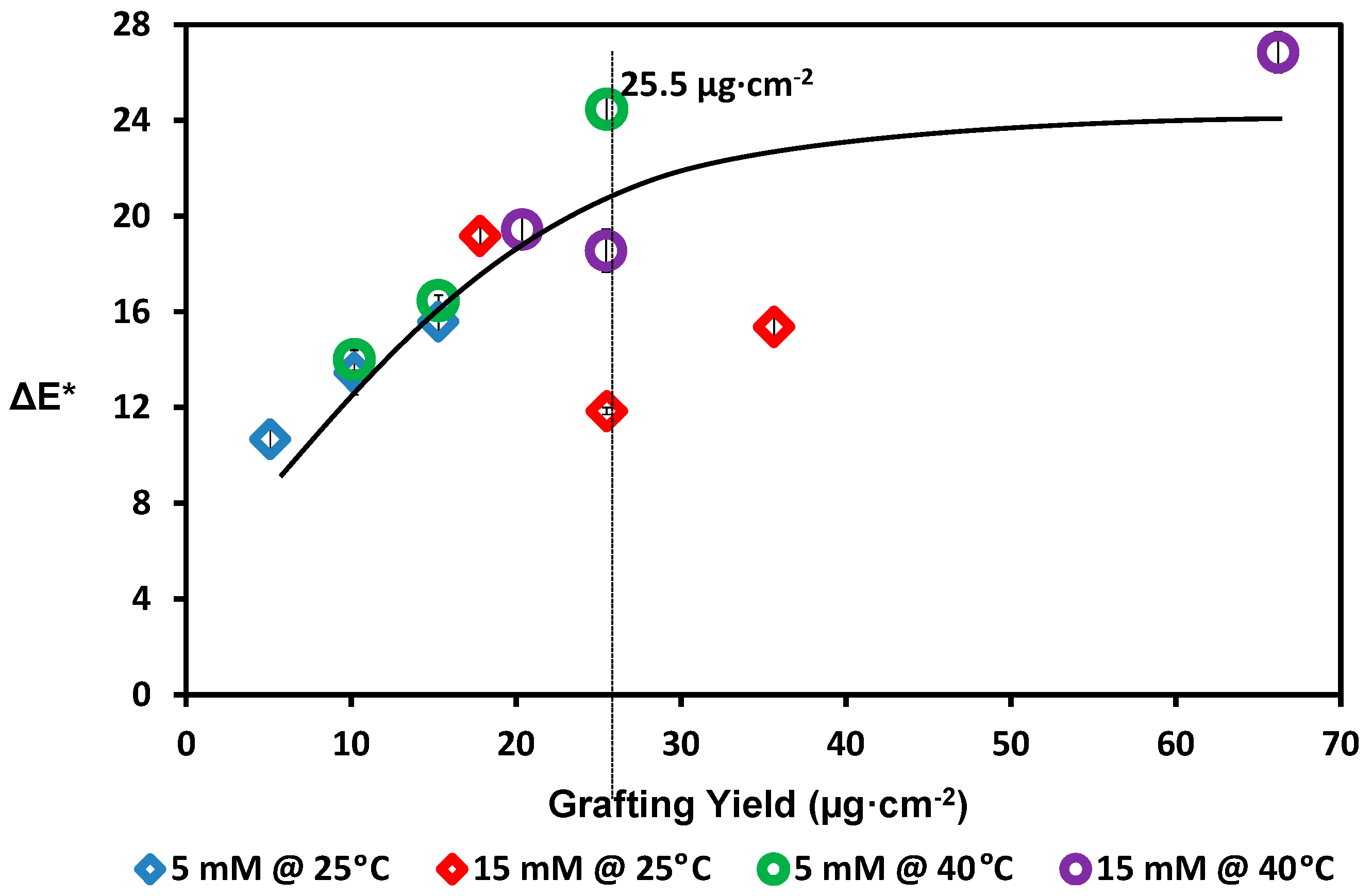
2.5. Membrane Color Change
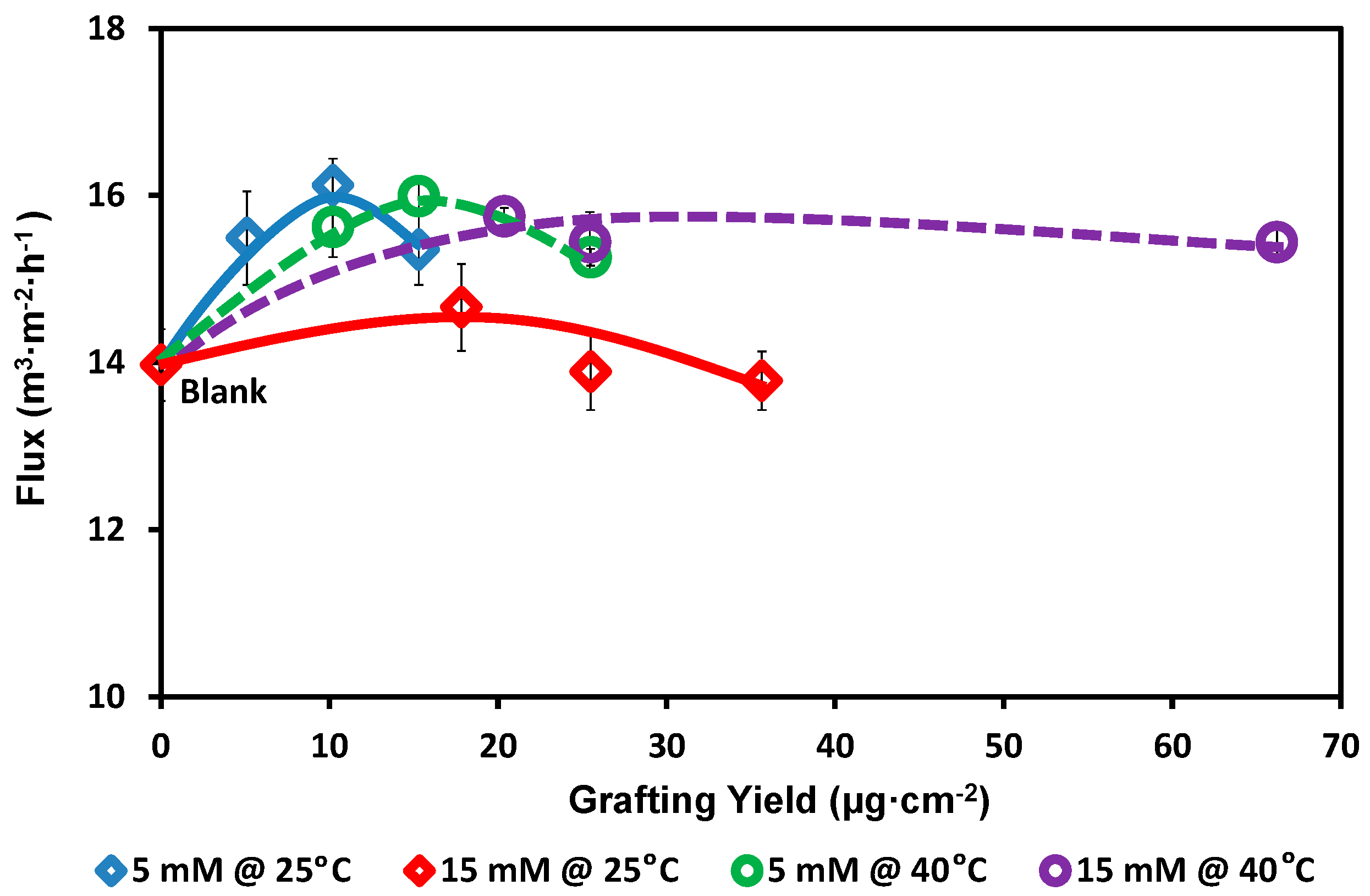
2.6. Pure Water Flux
2.7. The Added Modifier per Unit Membrane Surface Area (Grafting Yield)
2.8. Protein Repellence
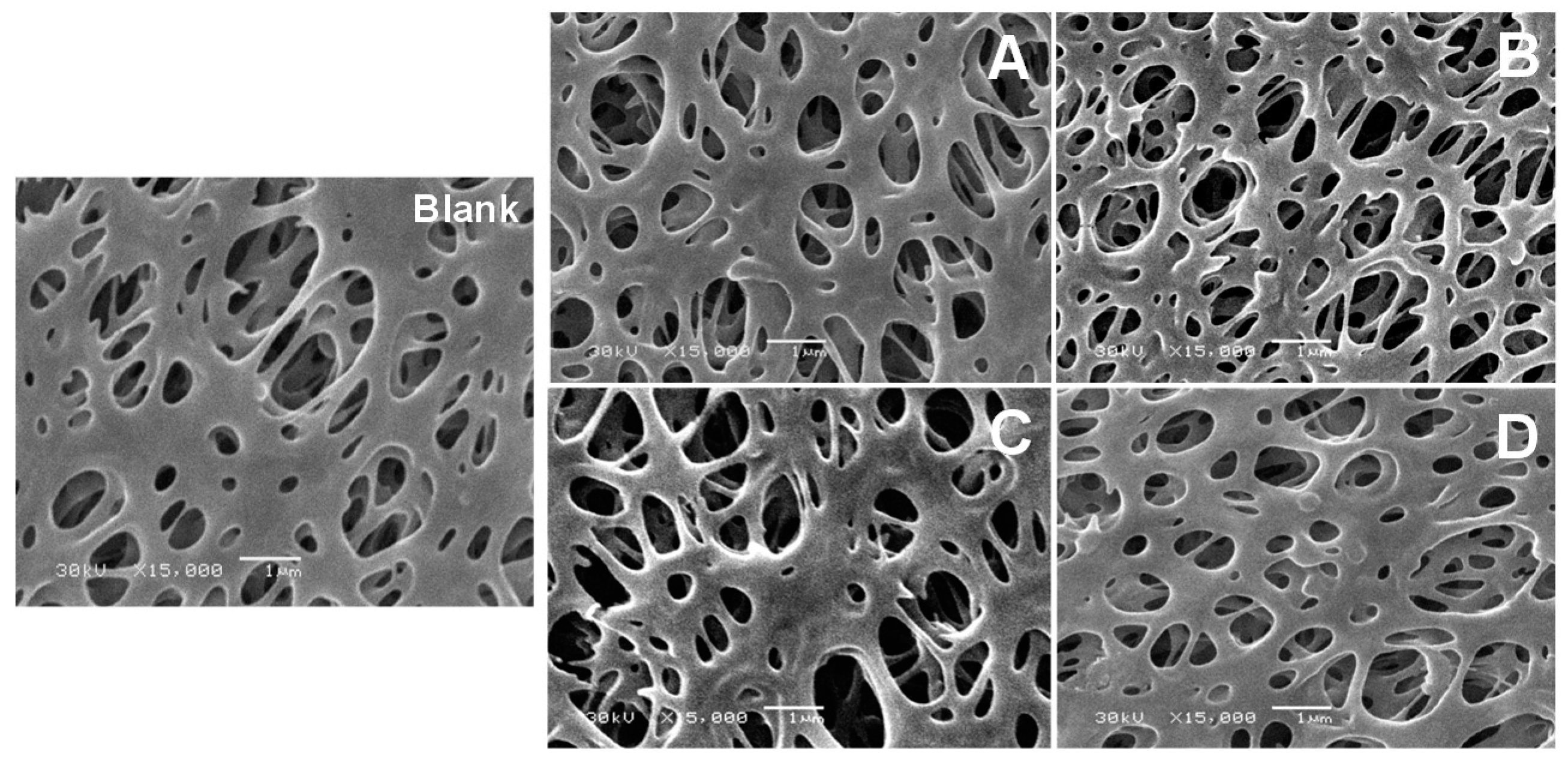
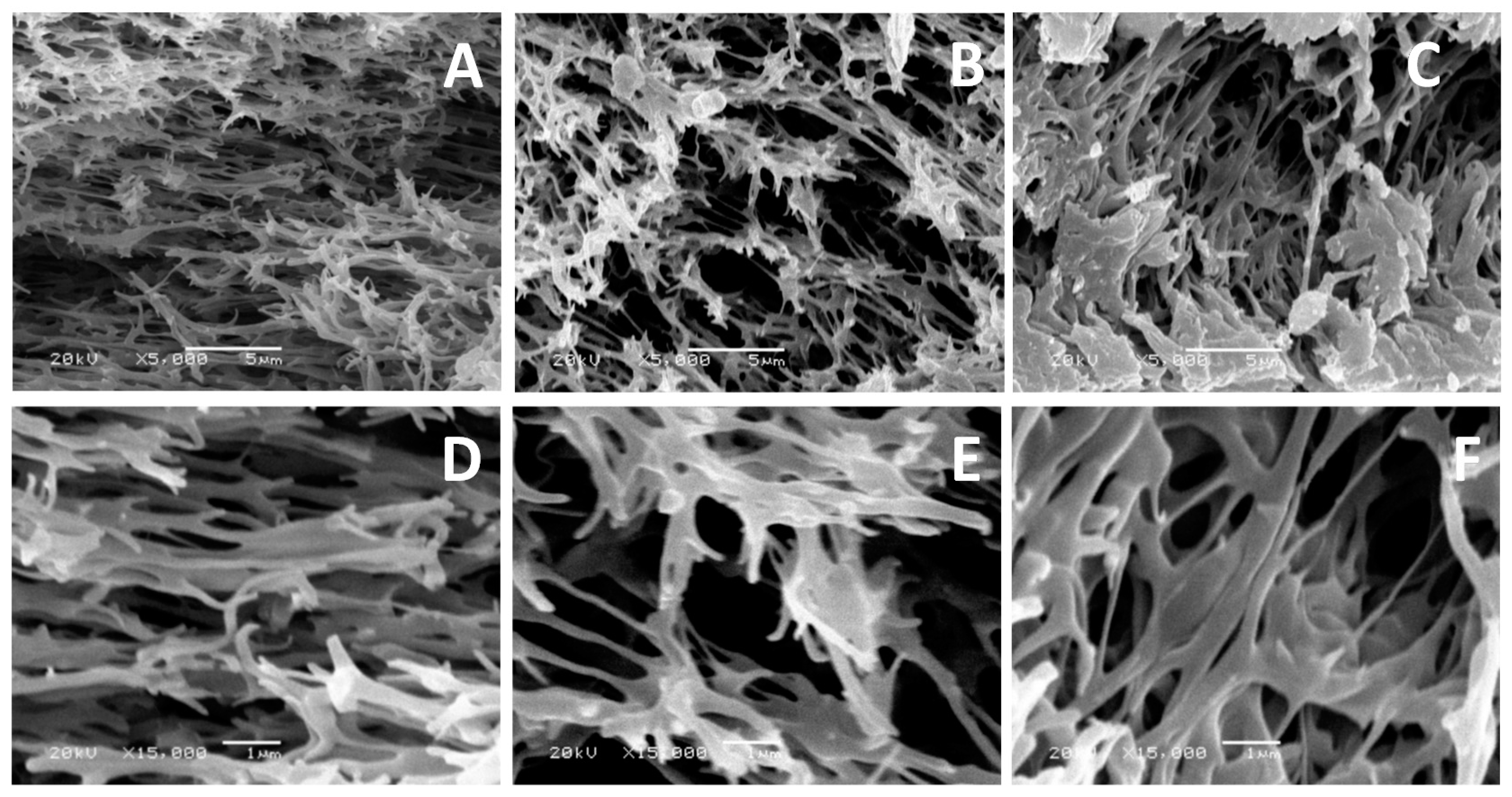
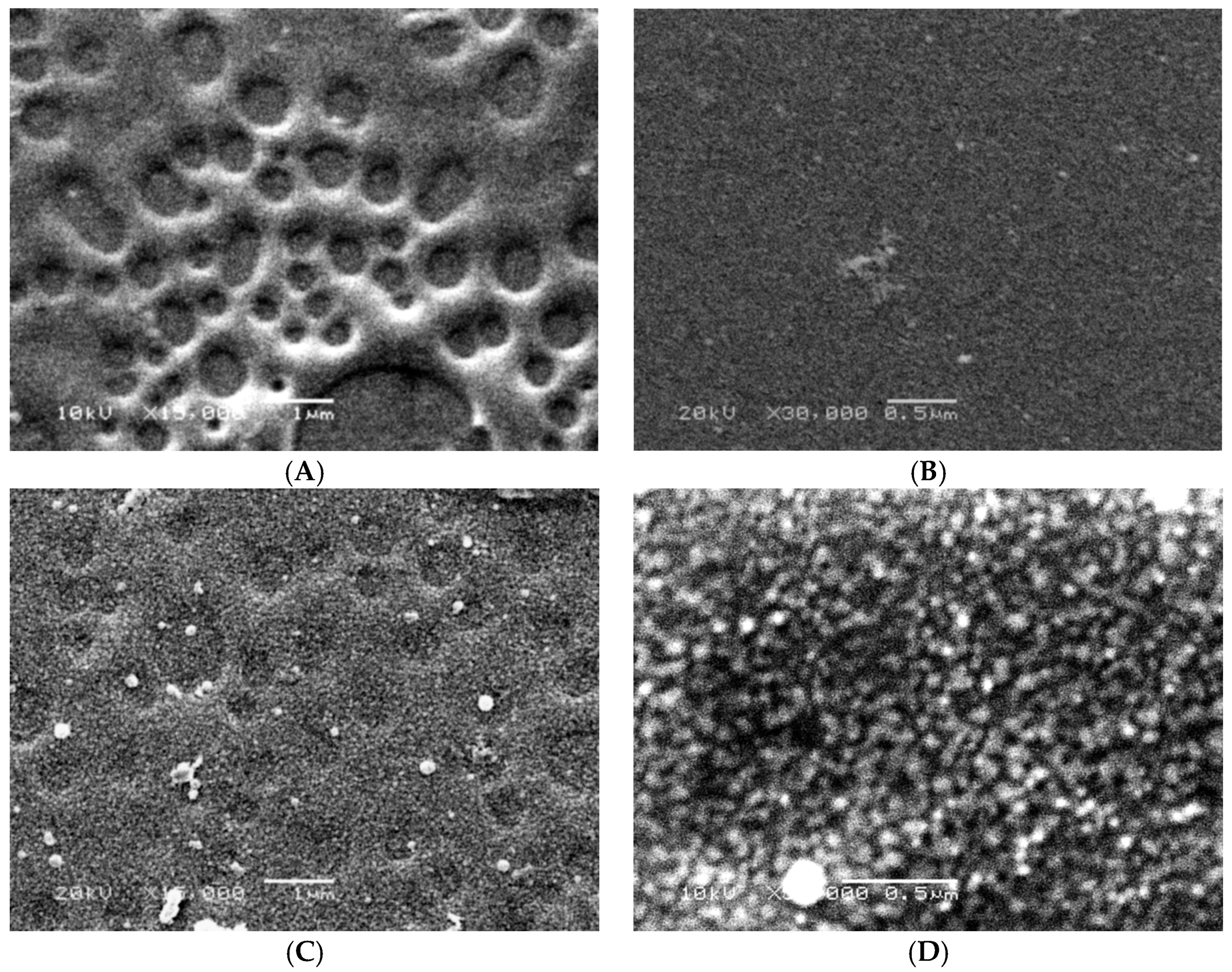
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
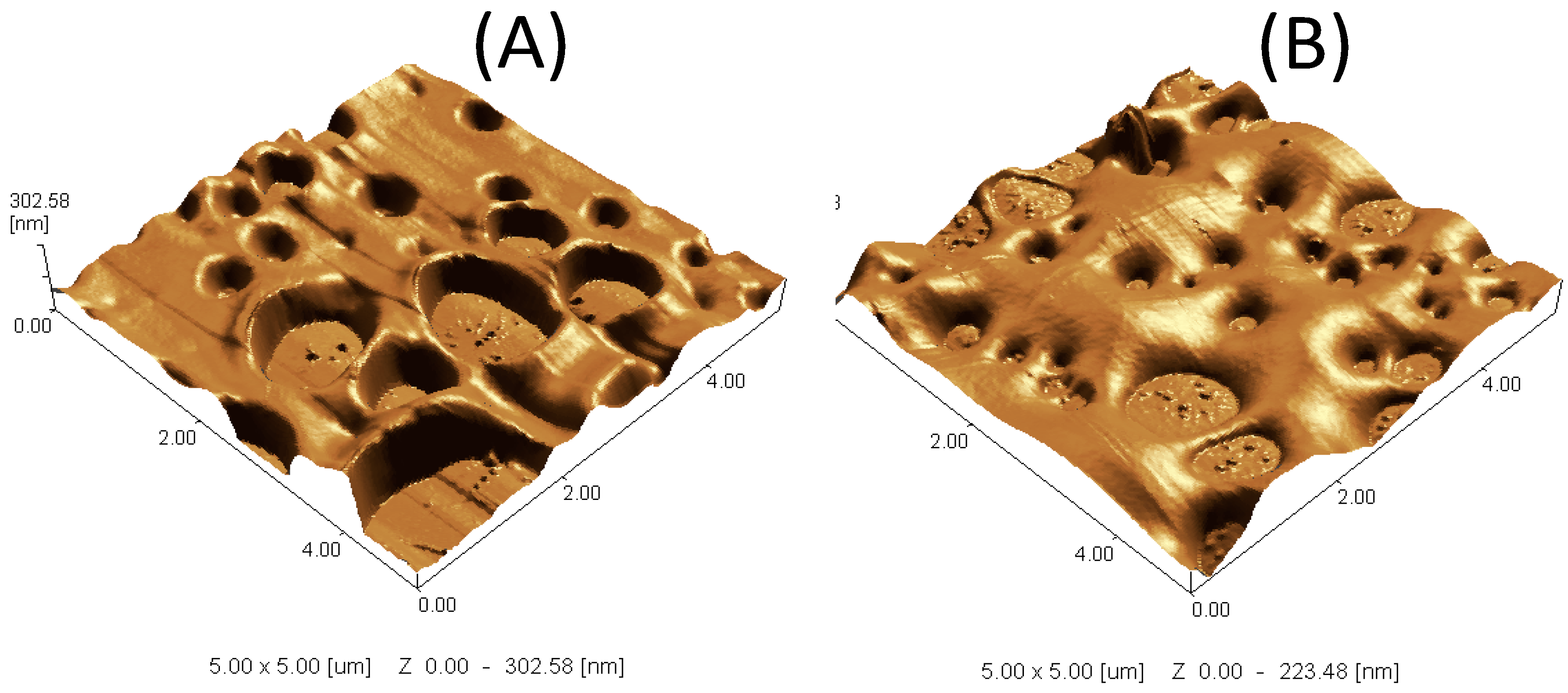
2.10. Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM)
2.11. Static Water Contact Angle
2.12. Membrane Tensile Strength
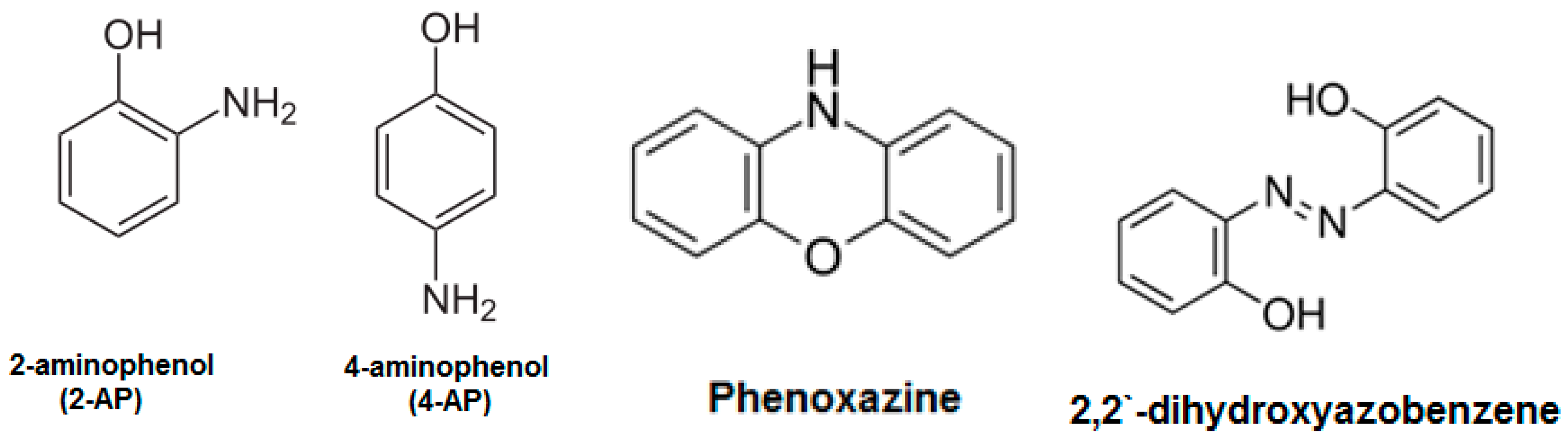
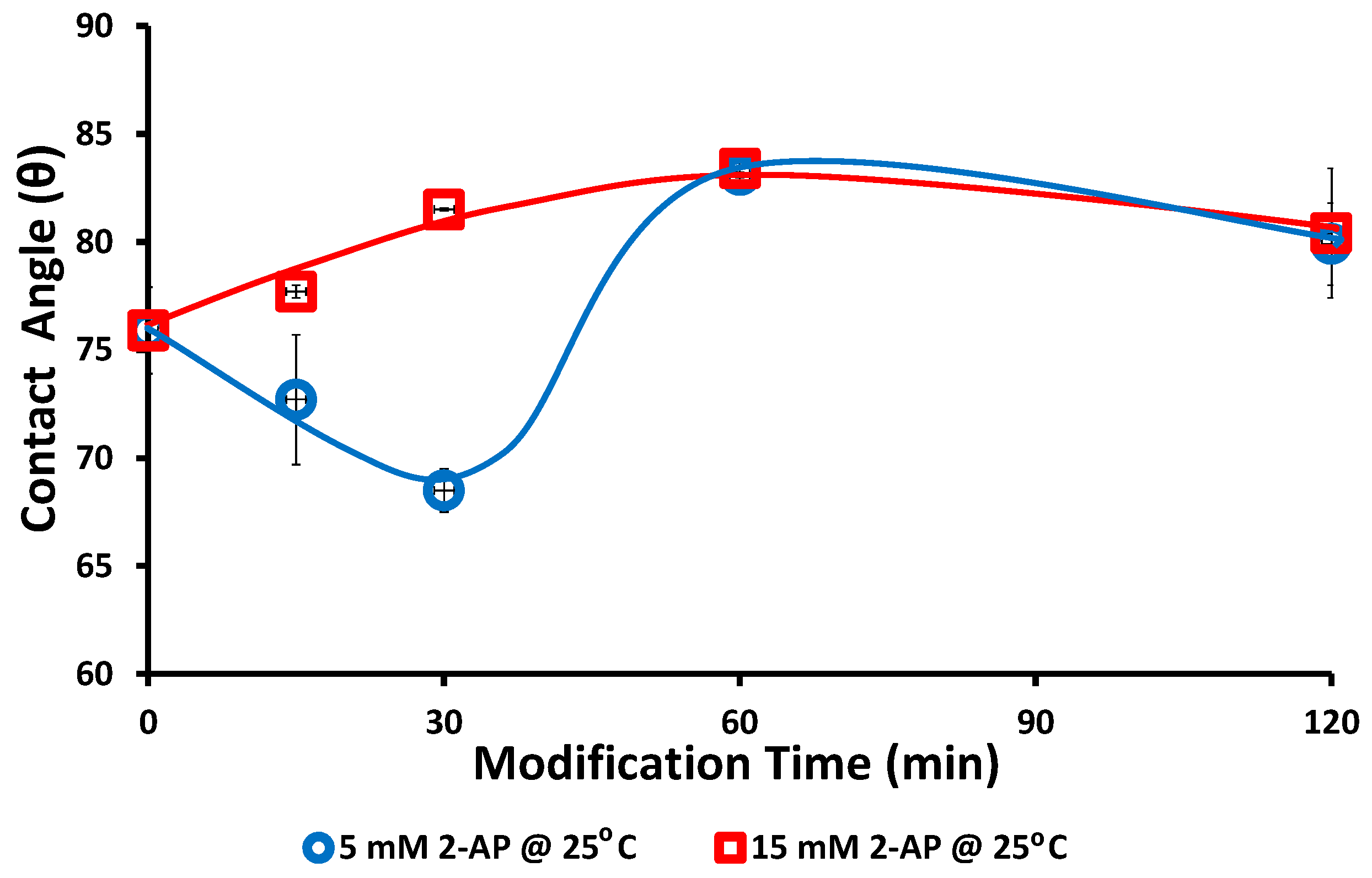
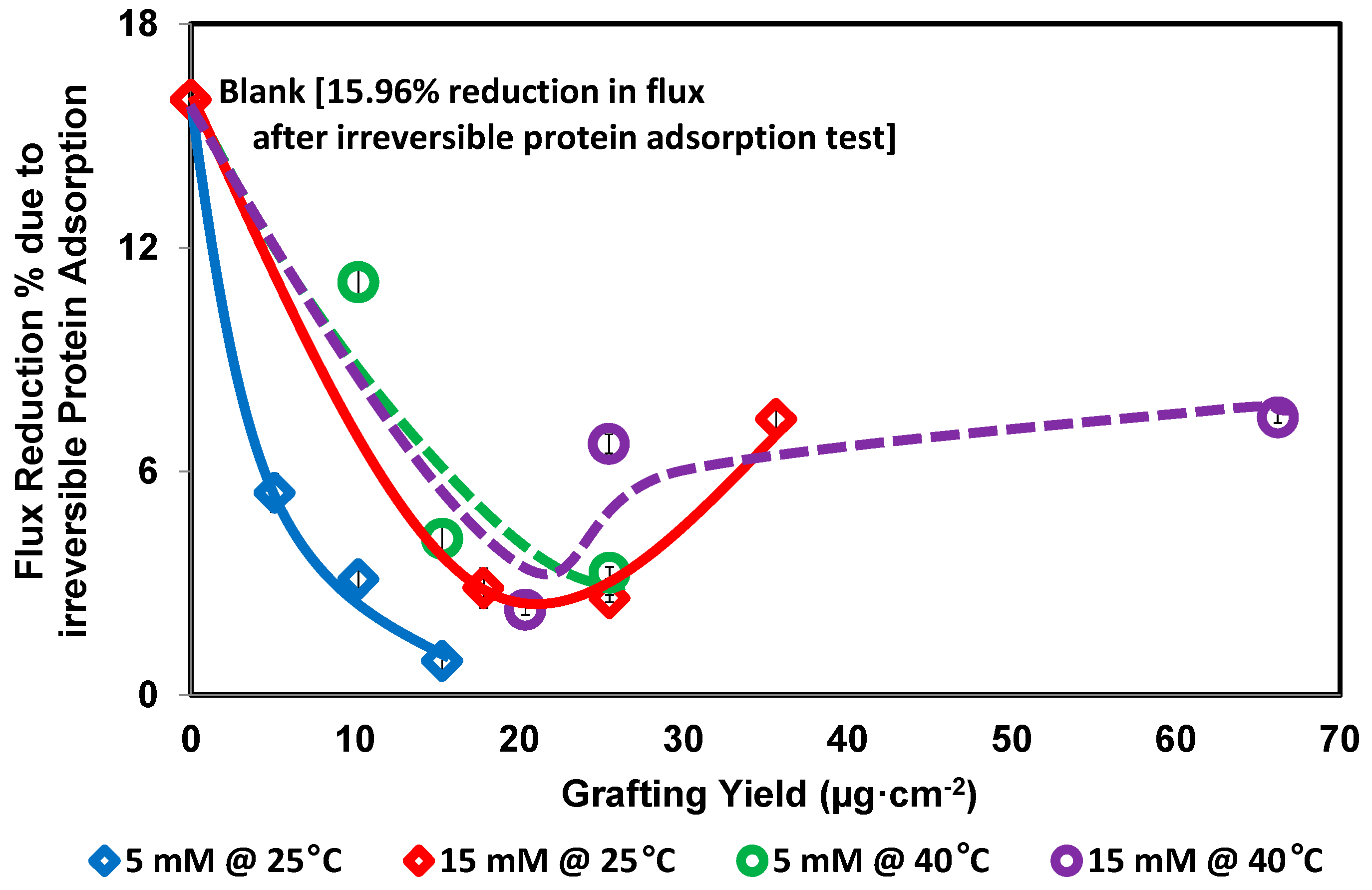
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakatsuka, S.; Ase, T.; Miyano, T. High flux ultrafiltration for drinking water production. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2001, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Hilal, N.; Ogunbiyi, O.O.; Miles, N.J.; Nigmatullin, R. Methods employed for control of fouling in MF and UF membranes: A comprehensive review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 1957–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiantsios, S.G.; Karabelas, A.J. The effect of colloid stability on membrane fouling. Desalination 1998, 118, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Elimelech, M. Colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis membranes: Measurements and fouling mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3654–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonné, P.A.C.; Hofman, J.A.M.H.; van der Hoek, J.P. Scaling control of RO membranes and direct treatment of surface water. Desalination 2000, 132, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahachaiyunta, P.; Koo, T.; Sheikholeslami, R. Effect of several inorganic species on silica fouling in RO membranes. Desalination 2002, 144, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, M.K.H.; Fane, A.G.; Rogers, P.L. Fouling of microfiltration membranes by broth-free antifoam agents. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 56, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagiwa, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Onodera, M.; Ohkawa, A. Antifoam fouling and its reduction by surfactant precoat treatment of polysulfone ultrafiltration. Biotechnol. Tech. 1994, 8, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanemaaijer, J.H.; Robbertsen, T.; van den Boomgaard, T.; Gunnink, J.W. Fouling of ultrafiltration membranes. The role of protein adsorption and salt precipitation. J. Membr. Sci. 1989, 40, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio, L.; Ho, C.-C.; Prádanos, P.; Hernández, A.; Zydney, A.L. Fouling with protein mixtures in microfiltration: BSA-Lysozyme and BSA-Pepsin. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 22, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Schaule, G. Biofouling on membranes—A microbiological approach. Desalination 1988, 70, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, H.; Ishida, K.; Rodriguez, G.; Safarik, J.; Knoell, T.; Bold, R. Biofouling of membranes: Membrane preparation, characterization, and analysis of bacterial adhesion. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 310, 463–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, T.; Moghadam, M.K.; Madaeni, S.S. Hydrodynamic factors affecting flux and fouling during reverse osmosis of seawater. Desalination 2002, 151, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueptow, R.M.; Lee, S. Control of scale formation in reverse osmosis by membrane rotation. Desalination 2003, 155, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Frappart, M.; Massé, A.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Pruvost, J.; Jaouen, P. Influence of hydrodynamics in tangential and dynamic ultrafiltration systems for microalgae separation. Desalination 2011, 265, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Surface modifications for antifouling membranes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2448–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, X.; Kobayashi, T.; Fujii, N. Ultrasound-associated cleaning of polymeric membranes for water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1999, 15, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereschenko, L.A.; Prummel, H.; Euverink, G.J.W.; Stams, A.J.M. Effect of conventional chemical treatment on the microbial population in a biofouling layer of reverse osmosis systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundström, I. Surface physics and biological phenomena. Phys. Scr. 1983, 1983, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.-L.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Tang, W.; Pu, C.-S. Hydrophilic modification of poly(ethersulfone) ultrafiltration membrane surface by self-assembly of TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 249, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, N. PES surface modification using green chemistry: New generation of antifouling membranes. Membranes 2016, 6, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Xiaohua, Z.; Childress, A.E.; Seungkwan, H. Role of membrane surface morphology in colloidal fouling of cellulose acetate and composite aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 127, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misdan, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Hilal, N. Recent advances in the development of (bio)fouling resistant thin film composite membranes for desalination. Desalination 2016, 380, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronis, S.; Berntsson, K.; Gold, J.; Gatenholm, P. Design and microstructuring of PDMS surfaces for improved marine biofouling resistance. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2000, 11, 1051–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richert, L.; Vetrone, F.; Yi, J.-H.; Zalzal, S.F.; Wuest, J.D.; Rosei, F.; Nanci, A. Surface nanopatterning to control cell growth. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirtcliffe, N.J.; McHale, G.; Newton, M.I.; Chabrol, G.; Perry, C.C. Dual-scale roughness produces unusually water-repellent surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruf, S.H.; Wang, L.; Greenberg, A.R.; Pellegrino, J.; Ding, Y. Use of nanoimprinted surface patterns to mitigate colloidal deposition on ultrafiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 428, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruf, S.H.; Rickman, M.; Wang, L.; Mersch IV, J.; Greenberg, A.R.; Pellegrino, J.; Ding, Y. Influence of sub-micron surface patterns on the deposition of modelproteins during active filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelaar, L.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Barsema, J.N.; Nijdam, W.; Bolhuis-Versteeg, L.A.M.; van Rijn, C.J.M.; Wessling, M. Phase separation micromolding: A new generic approach for microstructuring various materials. Small 2005, 1, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelaar, L.; Jonathan, N.B.; van Rijn, C.J.M.; Wietze, N.; Matthias, M. Phase separation micromolding—PsuM. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Arias, J.; Garcés, P.; Morallán, E.; Barbero, C.; Vázquez, J.L. Spectroelectrochemical study of the oxidation of aminophenols on platinum electrodes in acid medium. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 565, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Shan, X.; Tao, Y.; Xue, H. Synthesis of poly(o-phenylenediamine-co-o-aminophenol) via electrochemical copolymerization and its electrical properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, B.N.; Kumara Swamy, B.E.; Pandurangachar, M.; Sathisha, T.V.; Sherigara, B.S. Electrochemical investigation of 4-aminophenol at CTAB modified carbon paste electrode: A cyclic voltammetric technique. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2011, 3, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, J.; Oelßner, W.; Kaden, H.; Schumer, F.; Hennig, H. Voltammetric and spectroelectrochemical studies on 4-aminophenol at gold electrodes in aqueous and organic media. Electrochim. Acta. 2003, 48, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, B.; Cheng, L. Investigation on redox mechanism of p-aminophenol in non-aqueous media by FT-IR spectroelectrochemistry. Electrochim. Acta. 2013, 91, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, G.; JayaKumar, D.; Gopalswamy, M.; Santhi, R.J. Synthesis, characterization and biological applications of conducting poly(p-aminophenol) and its nanocompound. Der Pharm. Chem. 2011, 3, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nady, N.; El-Shazly, A.H. Laccase-catalyzed modification of PES membranes using amine-bearing modifiers. Desalin. Water Treatm. 2015, 55, 2996–3002. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, C. Electropolymerization of m-aminophenol on expanded graphite and its electrochemical properties. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 2301–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackowska, K.; Bukowska, J.; Kudelski, A. Electro-oxidation of o-aminophenol studied by cyclic voltammetry and surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). J. Electroanal. Chem. 1993, 350, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherf, U. Ladder-type materials. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałys, B.; Marzec, M.; Rogalski, J. Poly-o-aminophenol as a laccase mediator and influence of the enzyme on the polymer electrodeposition. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 80, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nady, N.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Zuilhof, H.; Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Boom, R.M.; Schroën, K. Modification methods for poly(arylsulfone) membranes: A mini-review focusing on surface modification. Desalination 2011, 275, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.; Staples, R.C. Laccase: New functions for an old enzyme. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, S. Laccases: Blue enzymes for green chemistry. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witayakran, S.; Ragauskas, A.J. Synthetic applications of laccase in green chemistry. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, N.; Schroën, K.; Franssen, M.C.R.; van Lagen, B.; Murali, S.; Boom, R.M.; Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Zuilhof, H. Mild and highly flexible enzyme-catalyzed modification of poly(ethersulfone) membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nady, N.; Schroën, K.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Boom, R.M.; Zuilhof, H. Laccase-catalyzed modification of PES membranes with 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and gallic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, N.; Schroën, K.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Fokkink, R.; Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Zuilhof, H.; Boom, E.M. Enzyme-catalyzed modification of PES surfaces: Reduction in adsorption of BSA, dextrin and tannin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 378, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Veen, S.; Nady, N.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Zuilhof, H.; Boom, R.M.; Abee, T.; Schroen, K. Listeria monocytogenes repellence by enzymatically modified PES surfaces. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41576–41582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, N.; El-Shazly, A.H. Antifouling PES membranes using bio-catalyzed surface modification. In Proceedings of the 2014 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research, Busan, Korea, 24–28 August 2014.
- Singh, G.; Capalash, N.; Goel, R.; Sharma, P. A pH-stable laccase from alkali-tolerant γ-proteobacterium JB: Purification, characterization and indigo carmine degradation. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 4, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid Sarmadi, A.; Ying, T.H.; Denes, F. Surface modification of polypropylene fabrics by acrylonitrile cold plasma. Text. Res. J. 1993, 63, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattsa, B.; Ade, H. NEXAFS imaging of synthetic organic materials. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, R.; Muniglia, L.; Rovel, B.; Girardin, M. Phenolic colorants obtained by enzymatic synthesis using a fungal laccase in a hydro-organic biphasic system. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Schmitt, S.K.; Choi, J.W.; Krutty, J.D.; Gopalan, P. From self-assembled monolayers to coatings: Advances in the synthesis and nanobio applications of polymer brushes. Polymers 2015, 7, 1346–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.A.; Voelcker, N.H.; Thissen, H.; Griesser, H.J. Stimuli-responsive interfaces and systems for the control of protein–surface and cell–surface interactions. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1827–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, E.P.K.; Wagemaker, M.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van Well, A.A. Structure of mono disperse and bimodal brushes. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 9041–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormidontova, E.E. Role of competitive PEO-water and water-water hydrogen bonding in aqueous solution PEO behavior. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ismail, A.F. Fouling control on microfiltration/ultrafiltration membranes: Effects of morphology, hydrophilicity, and charge. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernobai, V.A. The effects of monomer structure on initiation rate and kp/kt1/2 in homopolymerization. Polym. Sci. U.S.S.R. 1968, 10, 1986–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.C.; Waring, R.H. Aminophenols. In Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, R.; Finn, A.; Helbig, R.; Braun, H.-G.; Neinhuis, C.; Fischer, W.-J.; Werner, C. Biologically inspired omniphobic surfaces by reverse imprint lithography. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Parak, W.J. Surface modification, functionalization and bioconjugation of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 1333–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexeev, A.; Uspal, W.E.; Balazs, A.C. Harnessing Janus Nanoparticles to Create Controllable Pores in Membranes. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nady, N.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Soliman, H.M.A.; Kandil, S.H. Protein-Repellence PES Membranes Using Bio-grafting of Ortho-aminophenol. Polymers 2016, 8, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080306
Nady N, El-Shazly AH, Soliman HMA, Kandil SH. Protein-Repellence PES Membranes Using Bio-grafting of Ortho-aminophenol. Polymers. 2016; 8(8):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080306
Chicago/Turabian StyleNady, Norhan, Ahmed H. El-Shazly, Hesham M. A. Soliman, and Sherif H. Kandil. 2016. "Protein-Repellence PES Membranes Using Bio-grafting of Ortho-aminophenol" Polymers 8, no. 8: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080306
APA StyleNady, N., El-Shazly, A. H., Soliman, H. M. A., & Kandil, S. H. (2016). Protein-Repellence PES Membranes Using Bio-grafting of Ortho-aminophenol. Polymers, 8(8), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080306






