Finsler Geometry Modeling of Phase Separation in Multi-Component Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Two-Component Surface Model
2.1. Continuous Surface Model
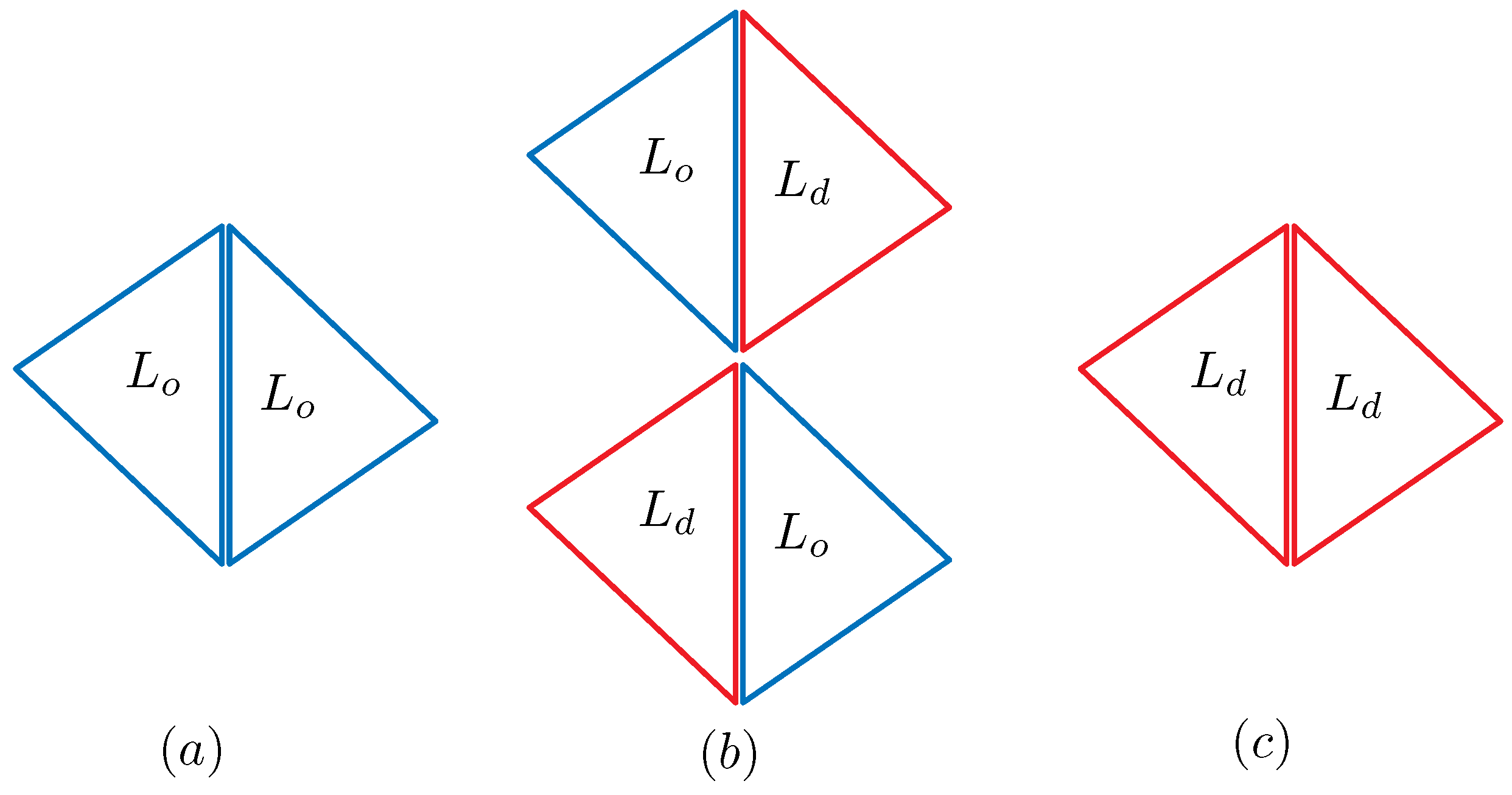
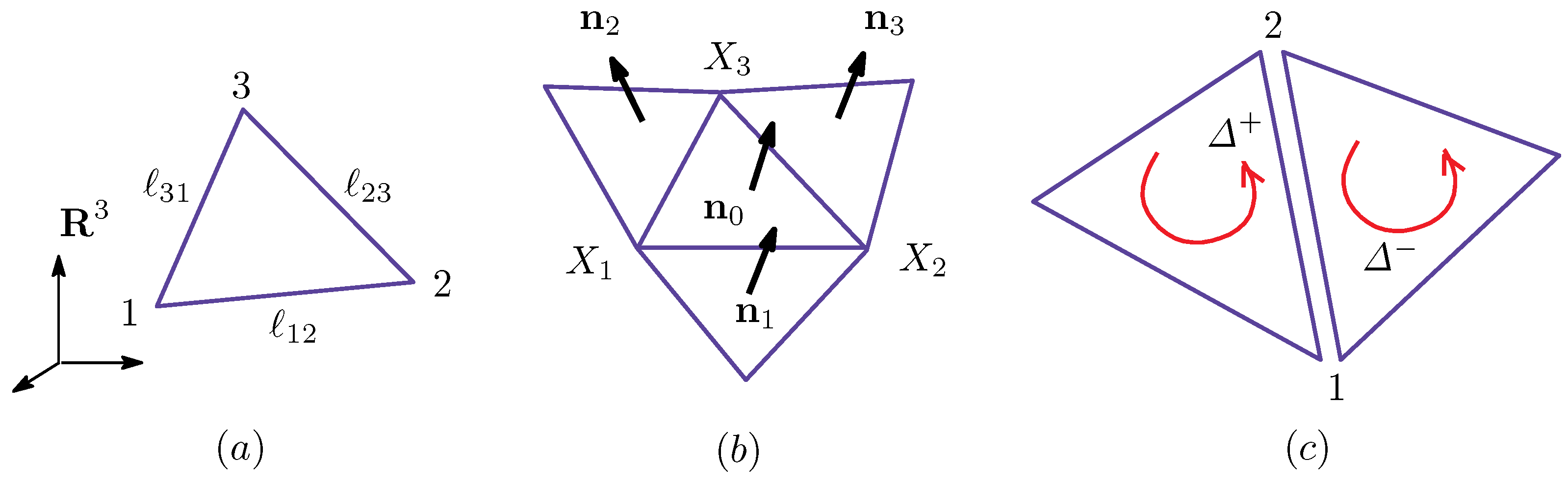
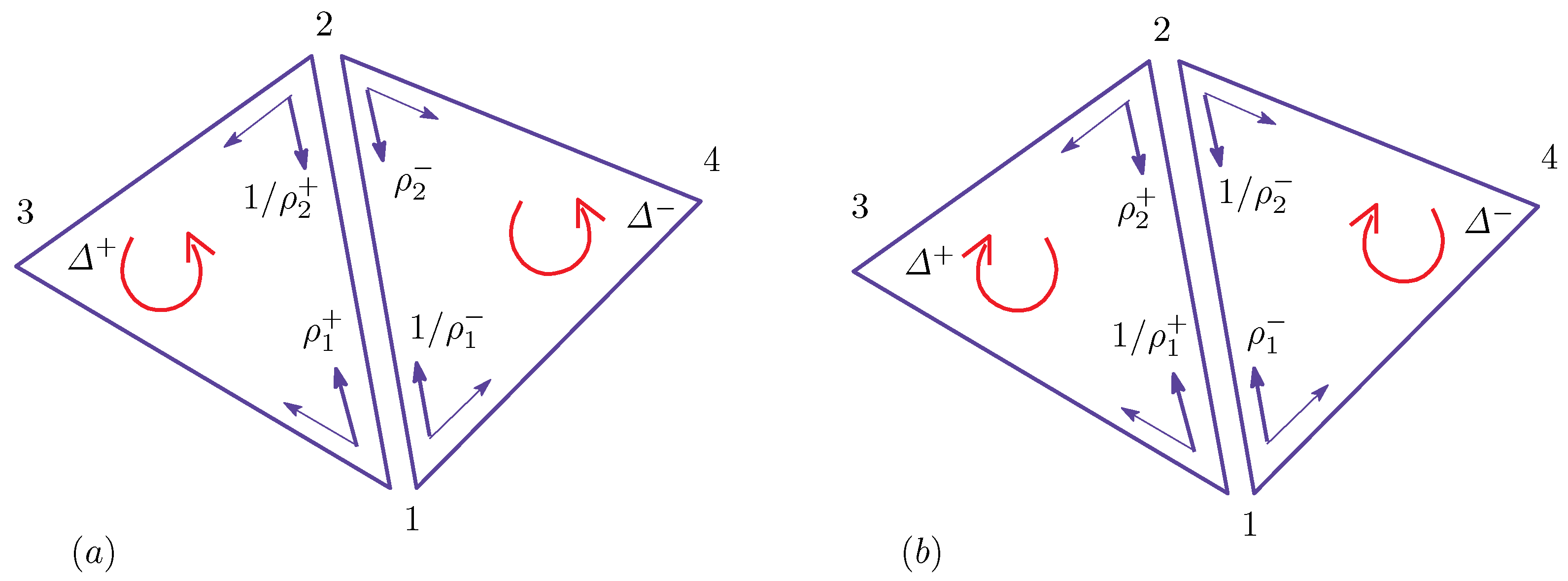
2.2. Discrete Model
3. Monte Carlo Technique
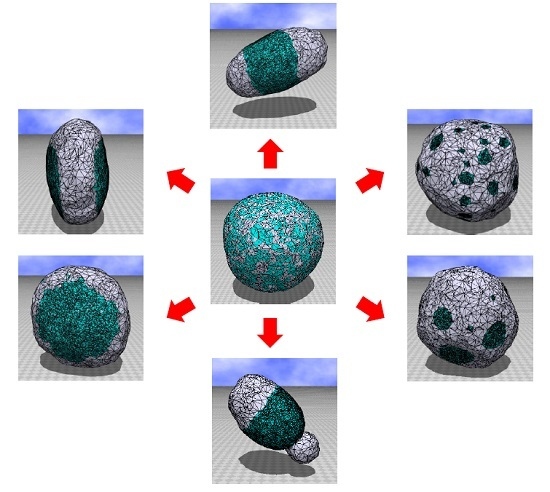
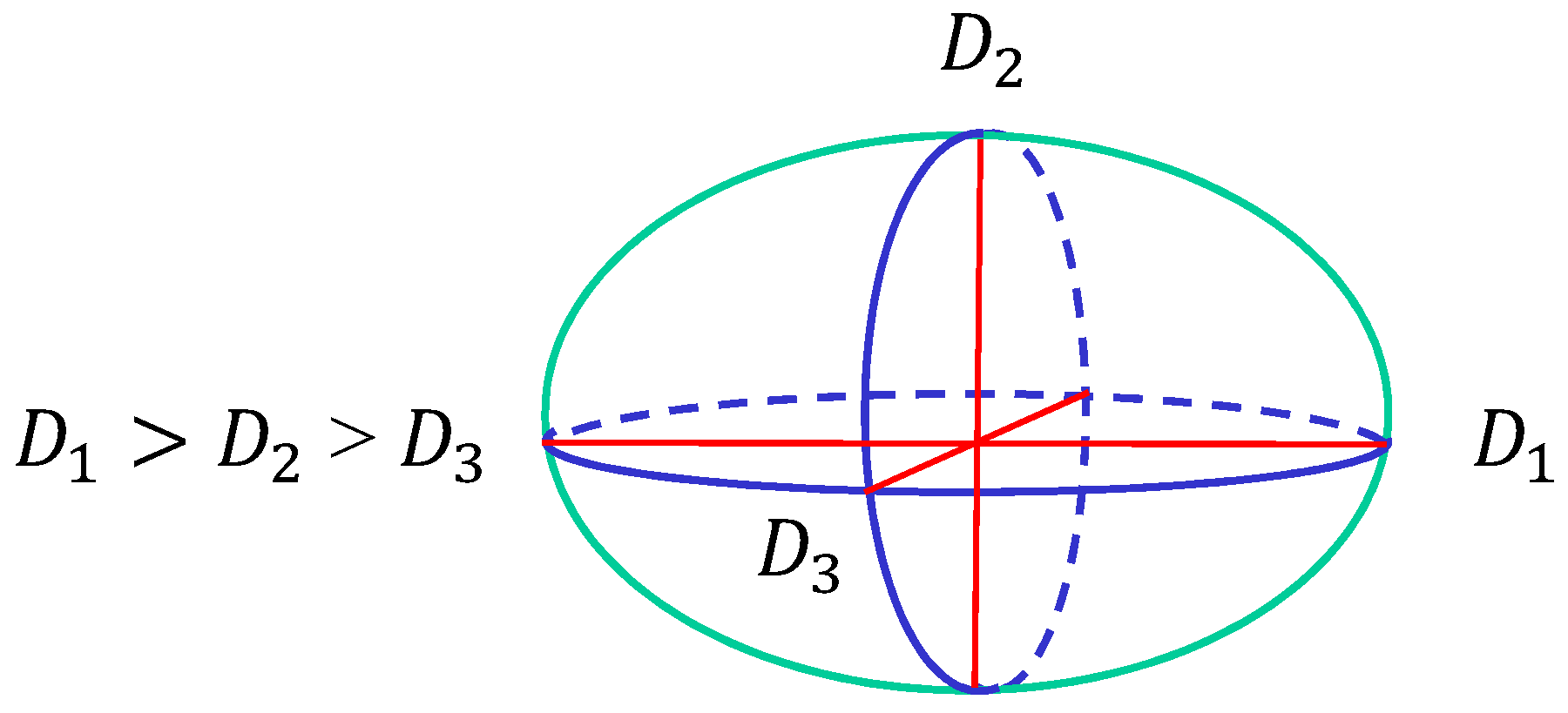
4. Simulation Results
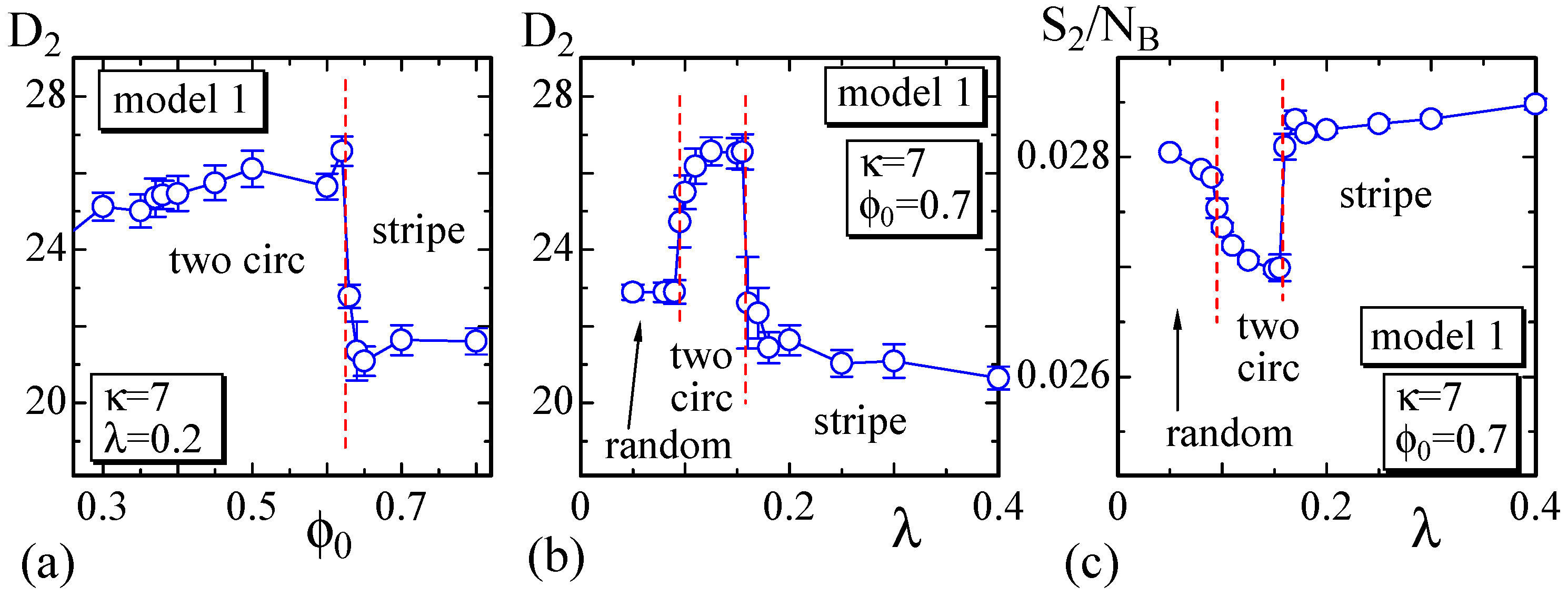
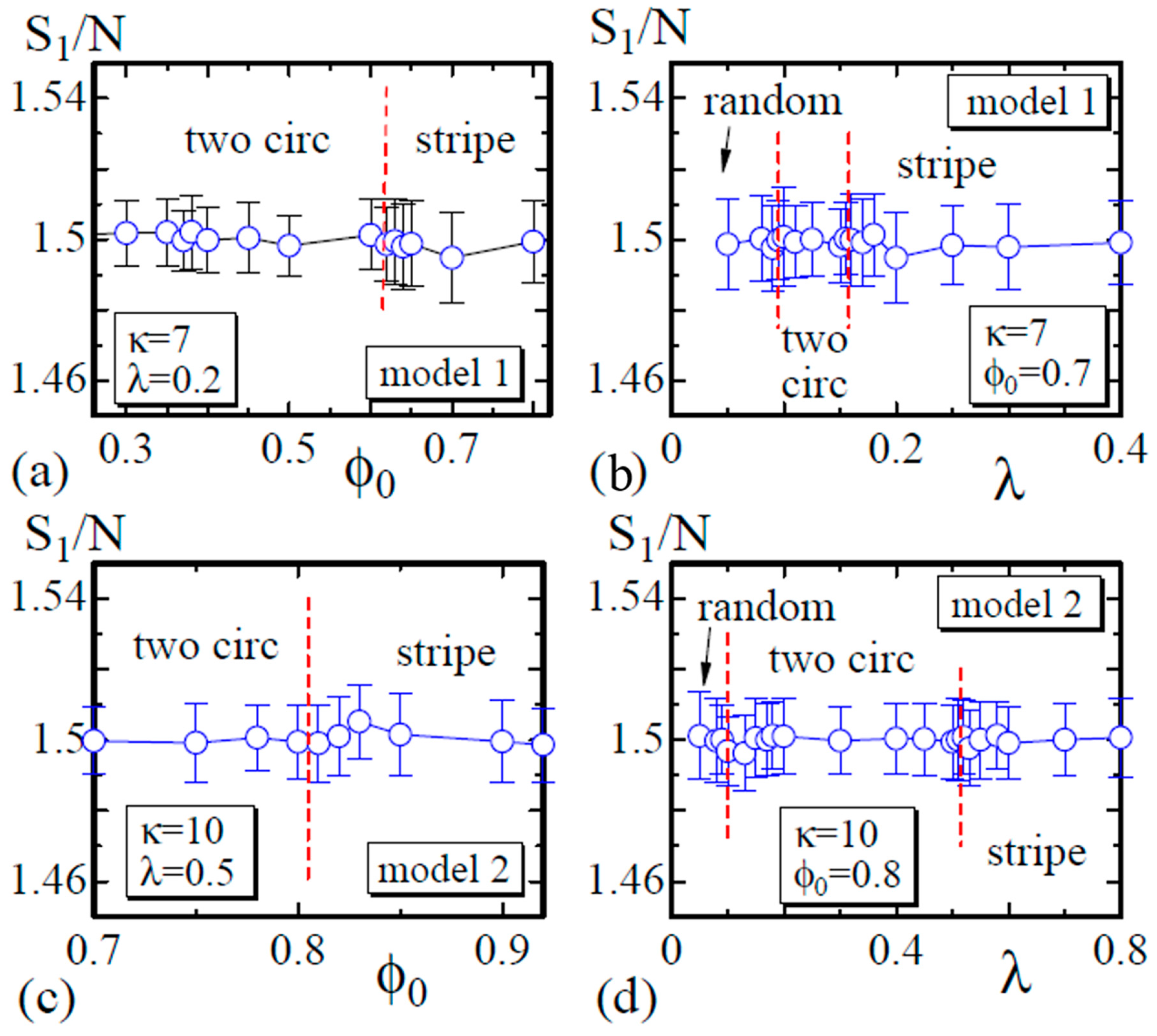
4.1. Model 1
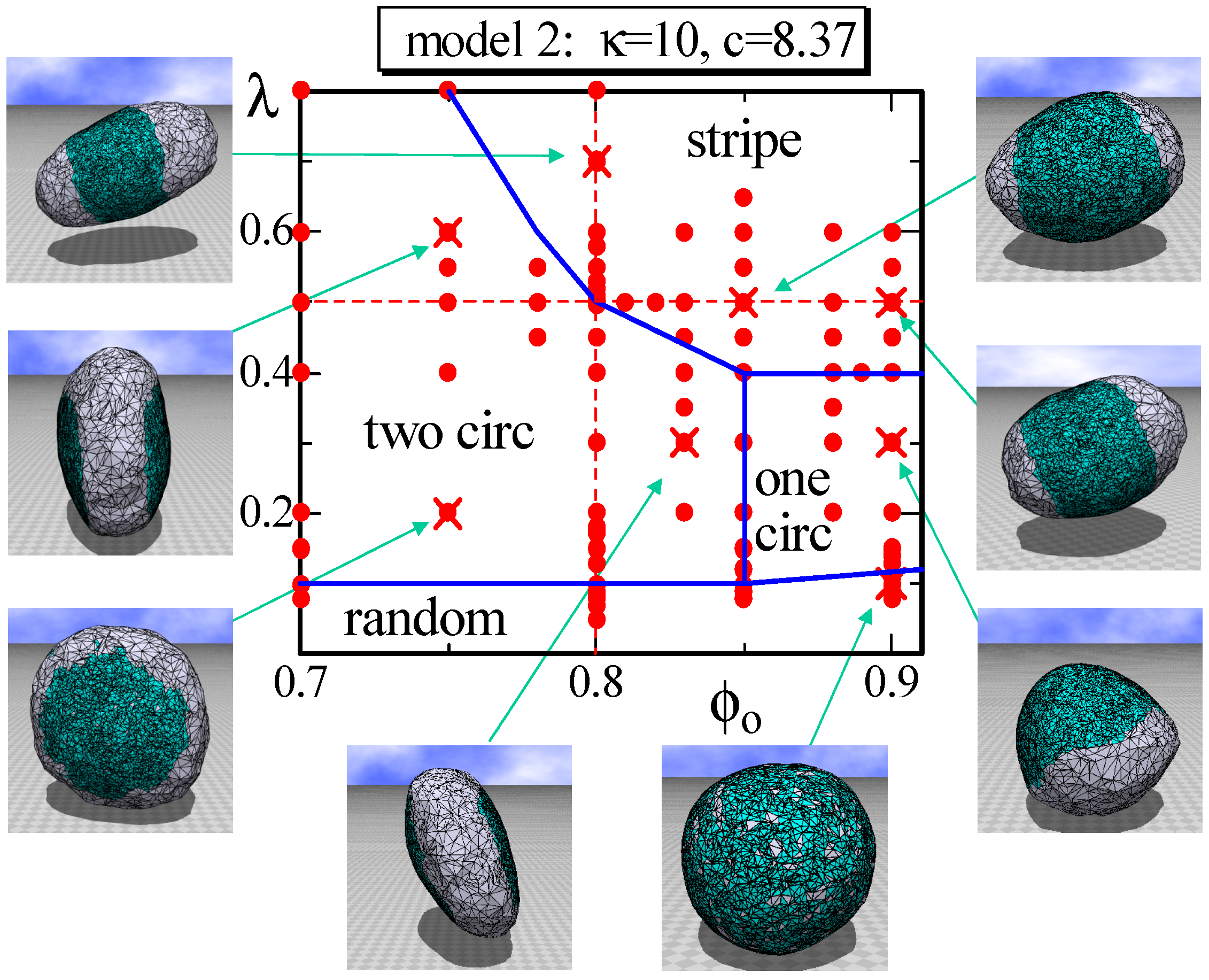
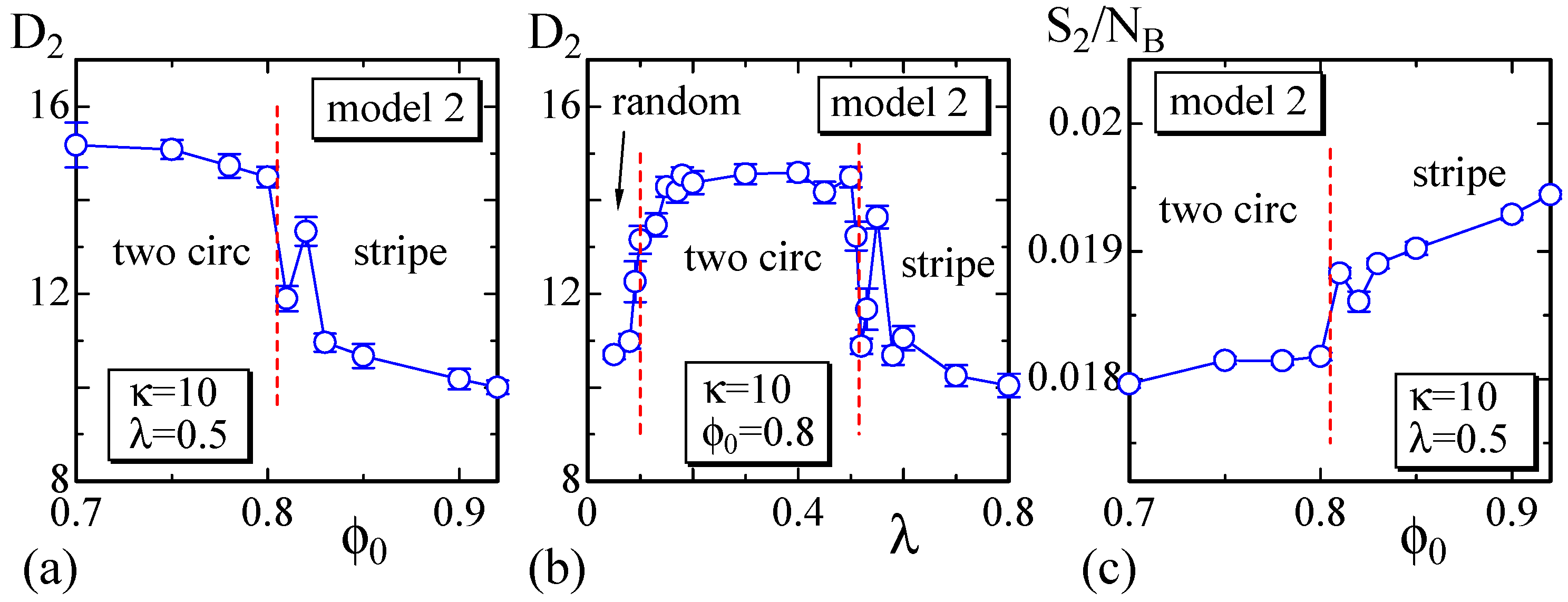
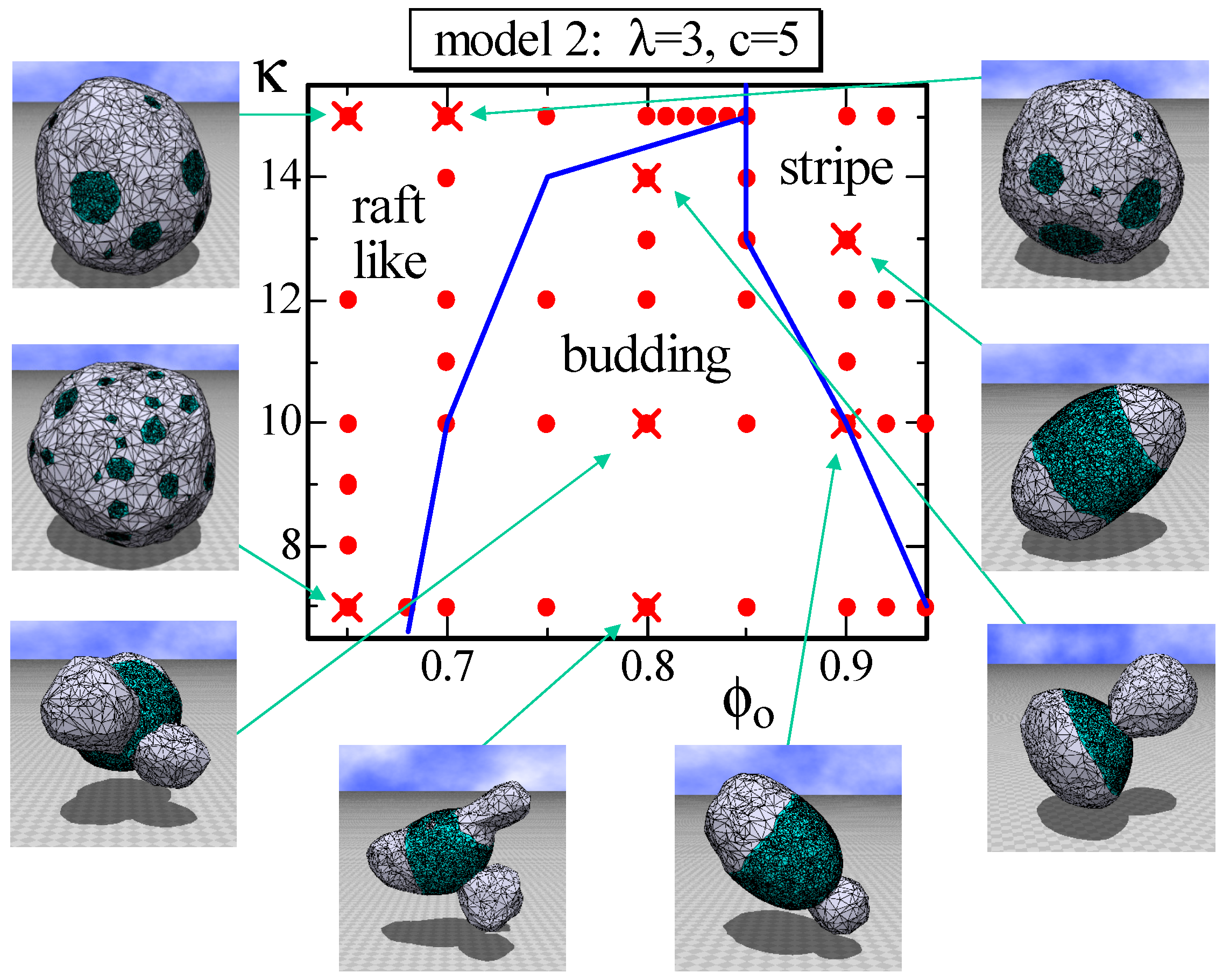
4.2. Model 2
5. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MC | Monte Carlo |
| MCS | Monte Carlo sweep |
Liquid-ordered | |
Liquid-disordered | |
| DOPC | Dioleoylphosphatidylcholine |
| DPPC | Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine |
| HP | Helfrich and Polyakov |
| FG | Finsler geometry |
Appendix A Finsler Geometry Modeling
Appendix A.1. Discrete Surface Model
Appendix A.2. Finsler Geometry Model
References
- Veatch, S.L.; Keller, S.L. Miscibility phase diagrams of giant vesicles containing sphingomyelin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, M.; Imai, M.; Taniguchi, T. Shape deformation of ternary vesicles coupled with phase separation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, M.; Imai, M.; Taniguchi, T. Periodic modulation of tubular vesicles induced by phase separation. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutlederer, E.; Gruhn, T.; Lipowsky, R. Polymorphism of vesicles with multi-domain patterns. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3303–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jülicher, P.; Lipowsky, R. Domain-induced budding of vesicles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 2964–2967. [Google Scholar]
- Jülicher, P.; Lipowsky, R. Shape transformations of vesicles with intramembrane domains. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 53, 2670–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Jug, G. Theory of the thermal magnetocapacitance of multicomponent silicate glasses at low temperature. Philos. Mag. 2004, 84, 3599–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A.M. Fine structure of strings. Nucl. Phys. B 1986, 268, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, W. Elastic properties of lipid bilayers: Theory and possible experiments. Z. Naturforsch 1973, 28c, 693–703. [Google Scholar]
- Koibuchi, H.; Sekino, H. Monte Carlo studies of a Finsler geometric surface model. Physica A 2014, 393, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M. Keiryou Bibun Kikagaku (in Japanese); Shokabo: Tokyo, Japan, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, D.; Chern, S.-S.; Shen, Z. An Introduction to Riemann-Finsler Geometry, GTM 200; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, M.; Edwards, S.F. The Theory of Polymer Dynamics; Oxford University Press: New York, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- David, F. Geometry and field theory of random surfaces and membranes. In Statistical Mechanics of Membranes and Surfaces, 2nd ed.; Nelson, D., Piran, T., Weinberg, S., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2004; pp. 149–209. [Google Scholar]
- Paczuski, M.; Kardar, M.; Nelson, D.R. Landau theory of the crumpling transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 60, 2638–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantor, Y.; Nelson, D.R. Phase transitions in flexible polymeric surfaces. Phys. Rev. A 1987, 36, 4020–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peliti, L.; Leibler, S. Effects of thermal fluctuations on systems with small surface tension. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 54, 1690–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, F.; Guitter, E. Crumpling transition in elastic membranes: Renormalization group treatment. Europhys. Lett. 1988, 5, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D. The statistical mechanics of membranes and interfaces. In Statistical Mechanics of Membranes and Surfaces, 2nd ed.; Nelson, D., Piran, T., Weinberg, S., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2004; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bowick, M.; Travesset, A. The statistical mechanics of membranes. Phys. Rep. 2001, 344, 255–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, K.J. Polymerized Membranes, a Review. In Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena 19; Domb, C., Lebowitz, J.L., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2000; pp. 253–498. [Google Scholar]
- Gompper, G.; Kroll, D.M. Triangulated-surface models of fluctuating membranes. In Statistical Mechanics of Membranes and Surfaces, 2nd ed.; Nelson, D., Piran, T., Weinberg, S., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2004; pp. 359–426. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgӓrtner, A.; Ho, J.-S. Crumpling of fluid vesicles. Phys. Rev. A 1990, 41, 5747(R)–5750(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.-S.; Baumgӓrtner, A. Simulations of fluid self-avoiding membranes. Europhys. Lett. 1990, 12, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, S.M. Extrinsic curvature in dynamically triangulated random surfaces. Phys. Lett. B 1989, 220, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, S.M.; Kogut, J.B.; Renken, R.L. Numerical study of field theories coupled to 2D quantum gravity. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 1992, 25, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambjӧrn, J.; Irbӓck, A.; Jurkiewicz, J.; Petersson, B. The theory of dynamical random surfaces with extrinsic curvature. Nucl. Phys. B 1993, 393, 571–600. [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi, H. Membrane simulation models from nanometer to micrometer scale. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheater, J.F. Random surfaces: From polymer membranes to strings. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1994, 27, 3323–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Rosenbluth, A.W.; Rosenbluth, M.N.; Teller, A.H. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.P. Finite-size behavior of the Ising square lattice. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 2997–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kownacki, J.-P.; Diep, H.T. First-order transition of tethered membranes in three-dimensional space. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kownacki, J.-P.; Mouhanna, D. Crumpling transition and flat phase of polymerized phantom membranes. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essafi, K.; Kownacki, J.-P.; Mouhanna, D. First-order phase transitions in polymerized phantom membranes. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuerno, R.; Caballero, R.G.; Gordillo-Guerrero, A.; Monroy, P.; Ruiz-Lorenzo, J.J. Universal behavior of crystalline membranes: Crumpling transition and Poisson ratio of the flat phase. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Model 1 | 1 | ||
| Model 2 |
| λ | κ | c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 7 | 5 | ||
| Model 2 | 10 | 8.37 | ||
| Model 2 | 3 | 5 |
| c | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 5 | 2.6 | 1.8 | 1 |
| Model 2 | 8.37 | 4.24 | 2.62 | 1 |
| Model 2 | 5 | 2.6 | 1.8 | 1 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Usui, S.; Koibuchi, H. Finsler Geometry Modeling of Phase Separation in Multi-Component Membranes. Polymers 2016, 8, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080284
Usui S, Koibuchi H. Finsler Geometry Modeling of Phase Separation in Multi-Component Membranes. Polymers. 2016; 8(8):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080284
Chicago/Turabian StyleUsui, Satoshi, and Hiroshi Koibuchi. 2016. "Finsler Geometry Modeling of Phase Separation in Multi-Component Membranes" Polymers 8, no. 8: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080284
APA StyleUsui, S., & Koibuchi, H. (2016). Finsler Geometry Modeling of Phase Separation in Multi-Component Membranes. Polymers, 8(8), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8080284






