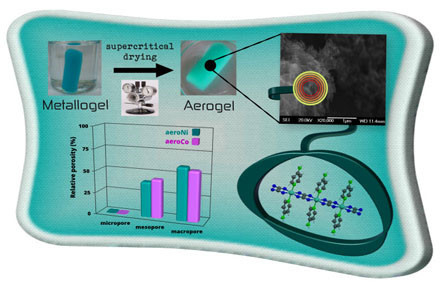
Aerogels of 1D Coordination Polymers: From a Non-Porous Metal-Organic Crystal Structure to a Highly Porous Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Metal-Organic Gels, Xerogels and Aerogels
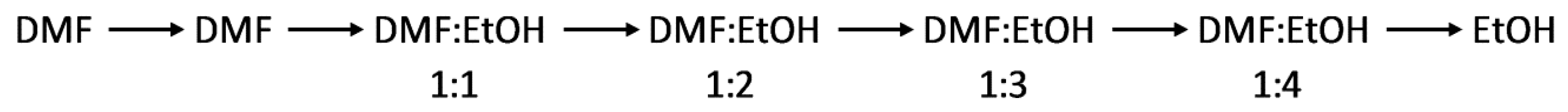
2.2. Physical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
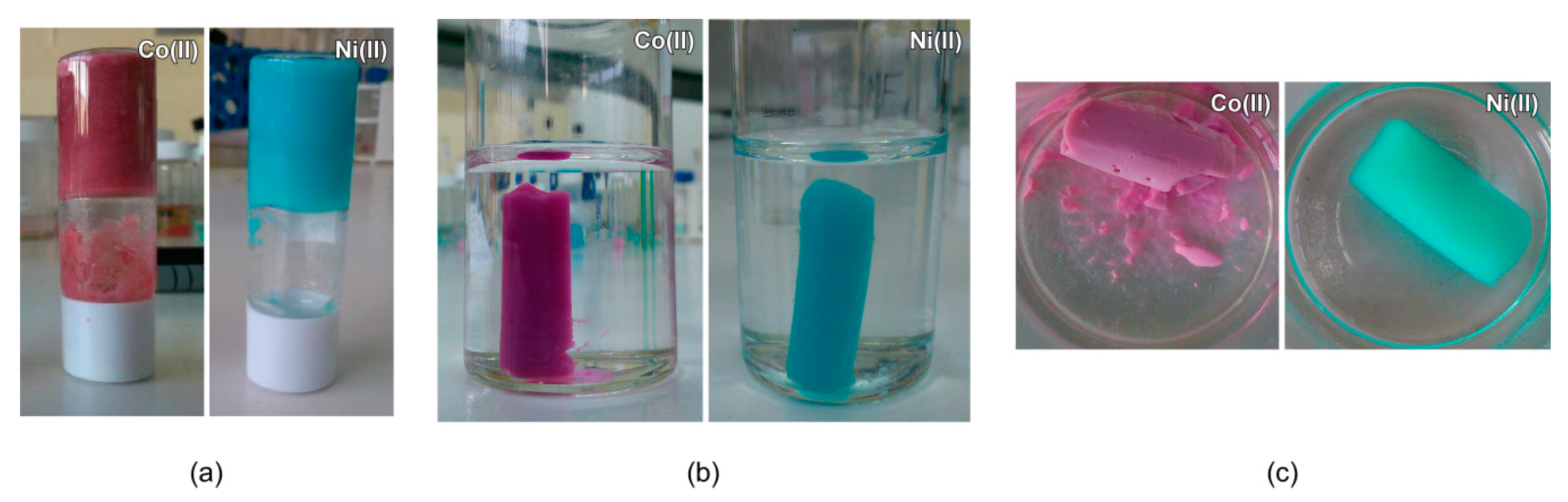
3.1. Gelation and Appearance of Gels, Xerogel and Aerogel
| Sample | Shrinkage (%) | Density (g·cm−3) |
|---|---|---|
| aeroCo | 57.0 | 0.311 |
| xeroCo | 92.5 | 1.783 |
| aeroNi | <0.1 | 0.082 |
| xeroNi | 93.6 | 1.281 |
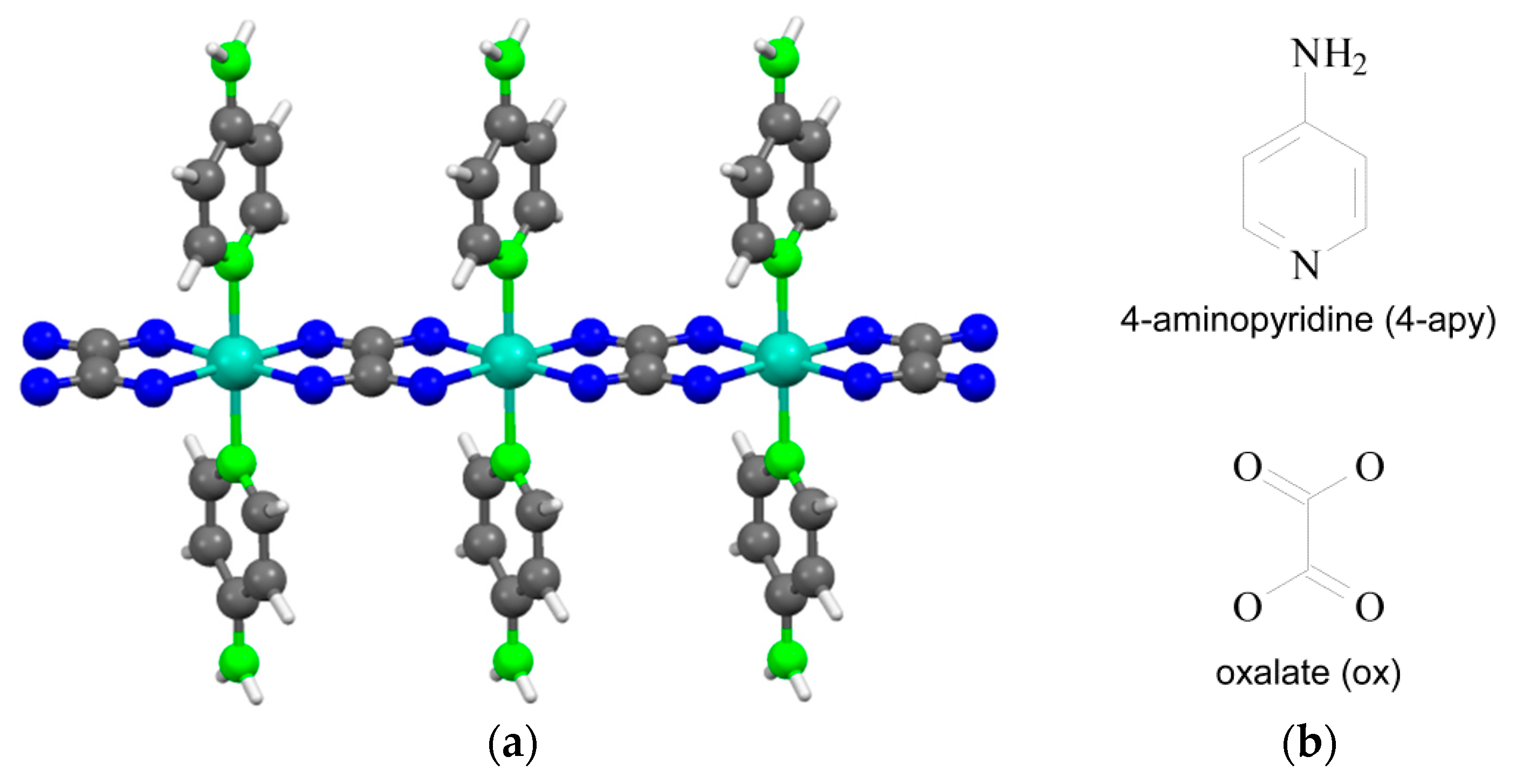
3.2. Chemical Analysis and Molecular Structure
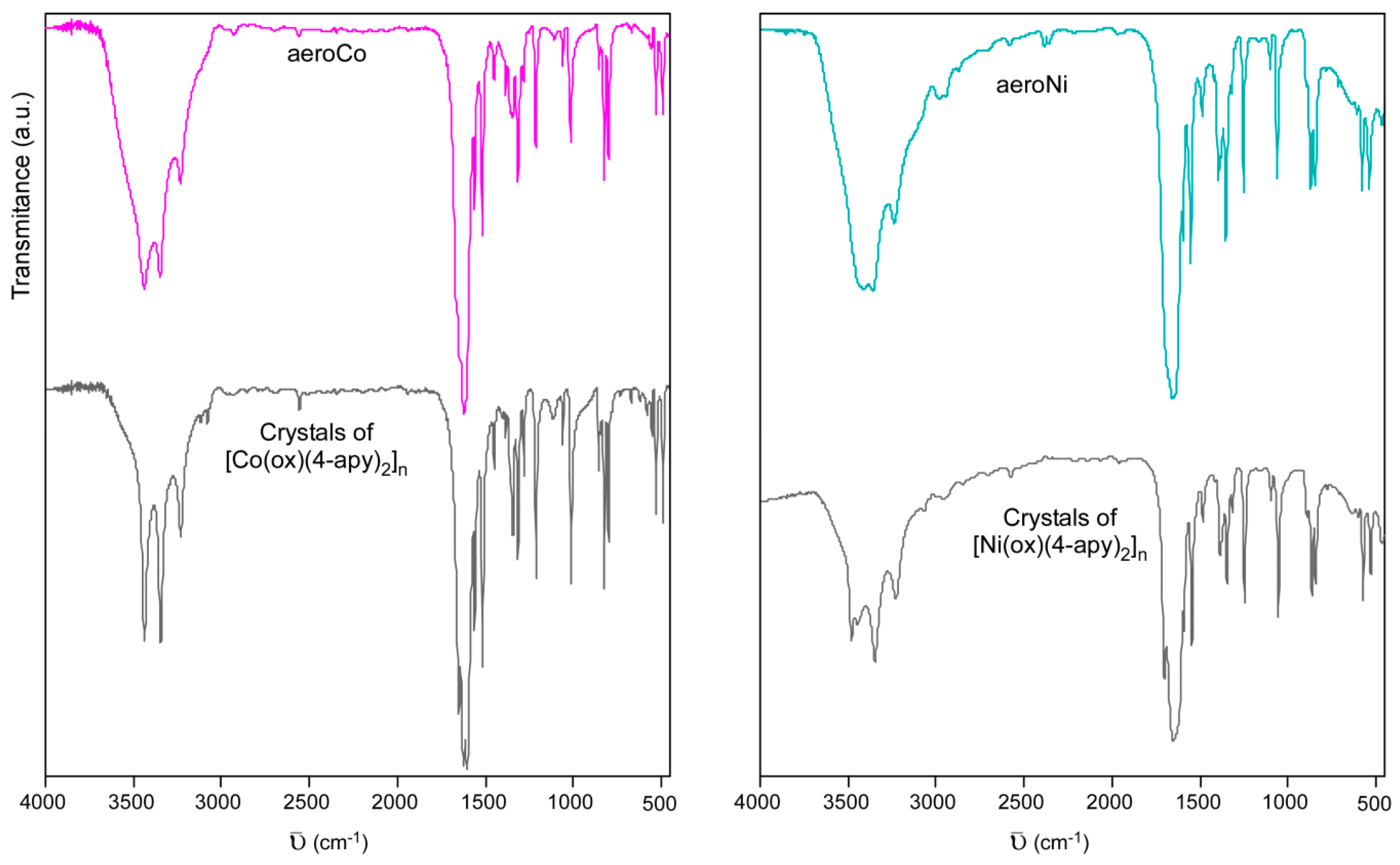
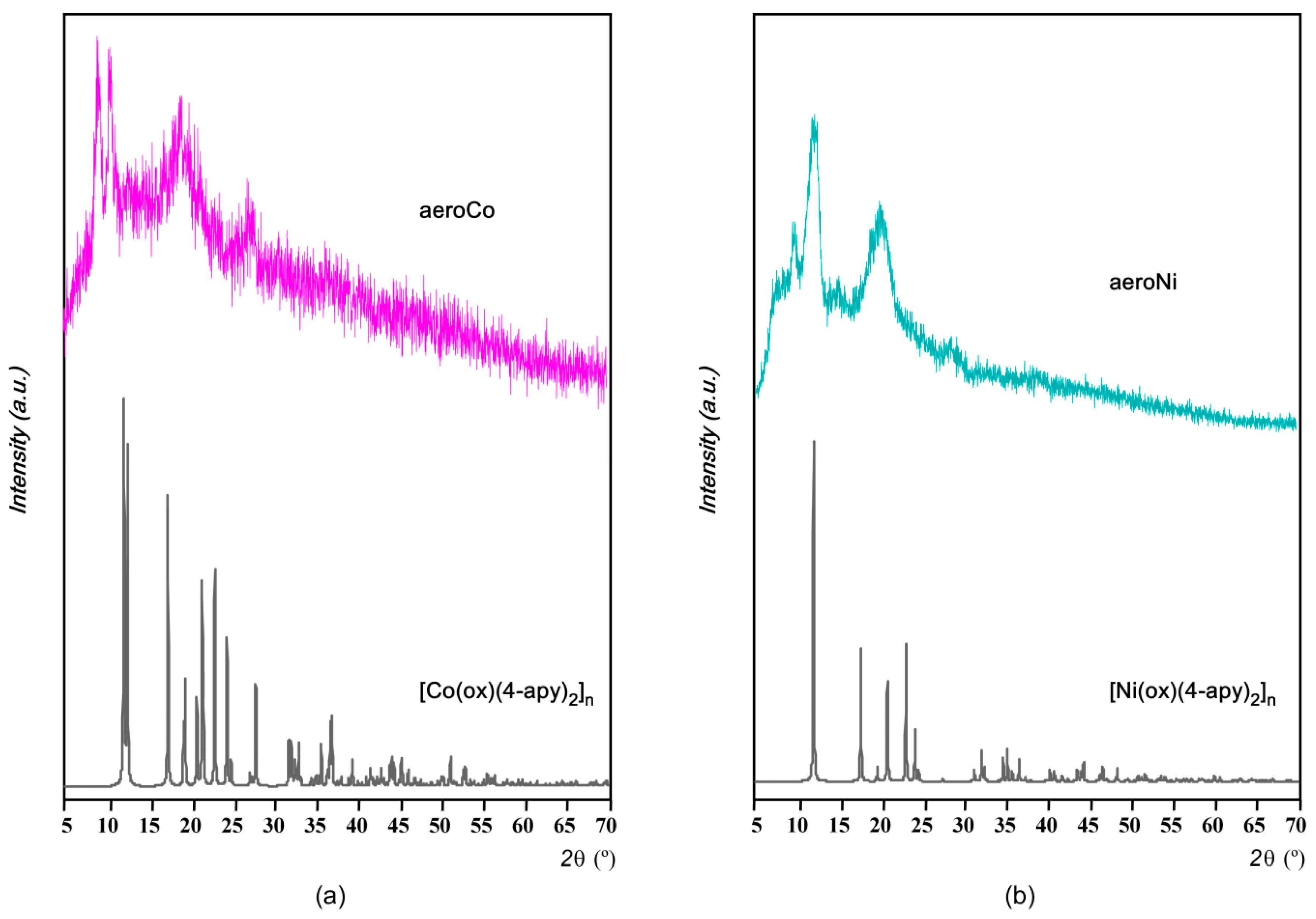
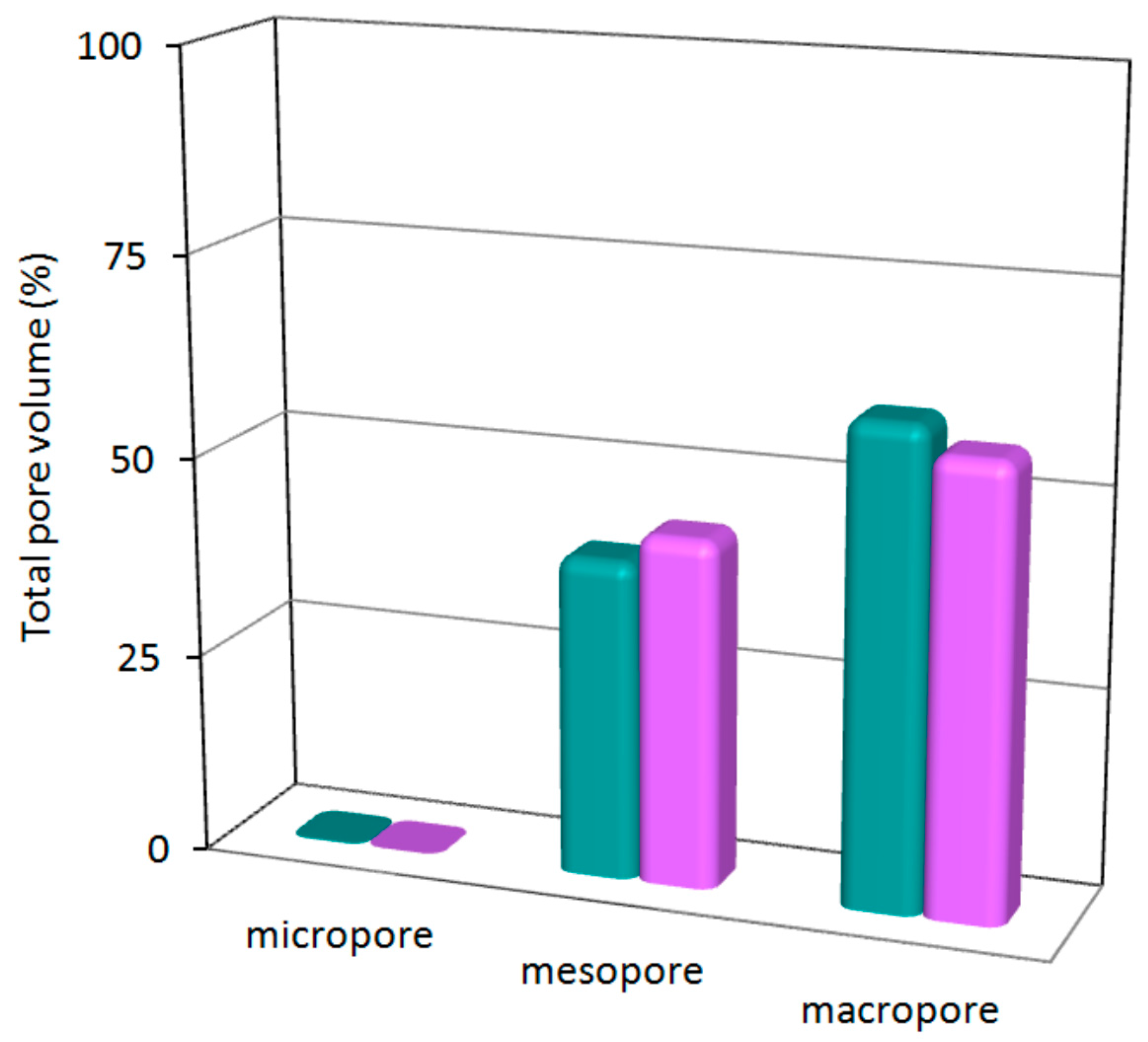
3.3. Microstructural Characterization

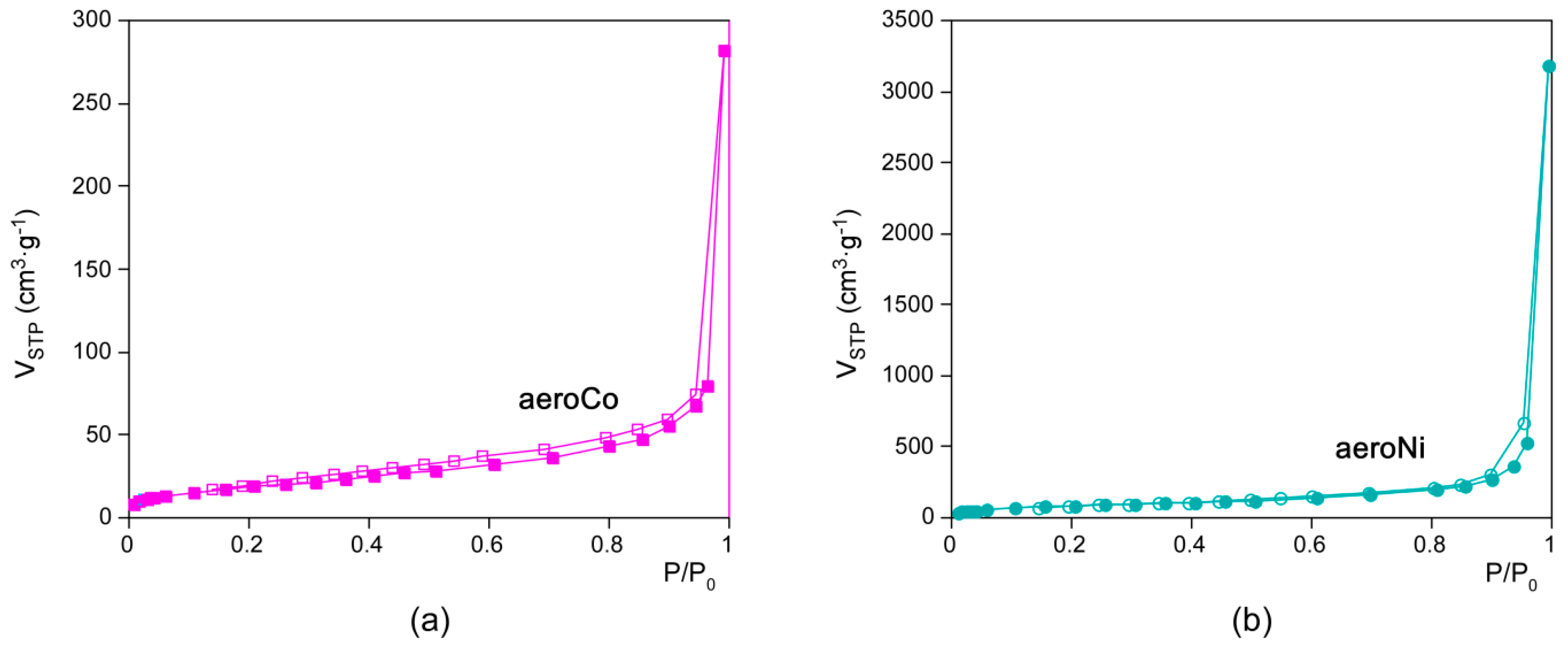
| Sample | aeroCo | aeroNi |
|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2·g−1) | 68.3 | 311.2 |
| Smicro (m2·g−1) | 0.0 | 33.0 |
| Smeso/macro (m2·g−1) | 68.3 | 278.2 |
| VT (cm3·g−1) | 0.44 | 4.93 |
| Vmicro (cm3·g−1) | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| Vmeso/macro (cm3·g−1) | 0.43 | 4.92 |
| Dpore (nm) | 37 | 32 |
| Porosity (%) | 14 | 40 |
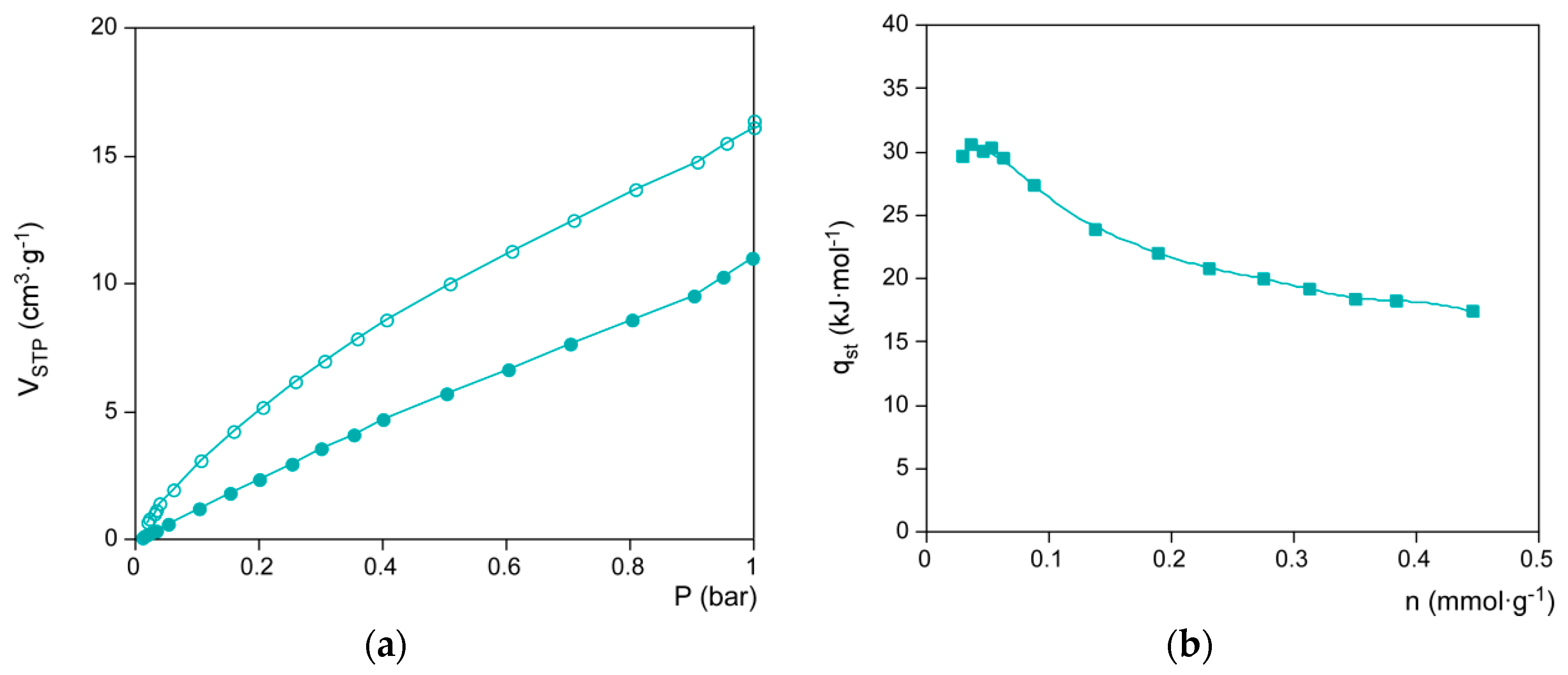
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rösler, C.; Fischer, R.A. Metal-organic frameworks as hosts for nanoparticles. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-C.; Kitagawa, S. Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5415–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Moler, D.B.; Li, H.; Chen, B.; Reineke, T.M.; O’keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Modular Chemistry: Secondary building units as a basis for the design of highly porous and robust metal-organic carboxylate frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Bosch, M.; Gentle, T.; Zhou, H.-C. Rational design of metal–organic frameworks with anticipated porosities and functionalities. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 4069–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, J.R.; Wang, K.; Han, T.; Tong, M.; Li, L.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. An in situ self-assembly template strategy for the preparation of hierarchical-pore metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Z.; Han, B.; Sang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, G. Highly mesoporous metal-organic framework assembled in a switchable solvent. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.R.; Yuan, D.Q.; Sculley, J.; Lu, W.-G.; Zhou, H.-C. A novel MOF with mesoporous cages for kinetic trapping of hydrogen. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 254–256. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-S.; Ma, S.; Sun, D.; Parkin, S.; Zhou, H.-C. A mesoporous metal-organic framework with permanent porosity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16474–16475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Mesoporous metal-organic framework materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1677–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lofgreen, J.E.; Ozin, G.A. Towards functionality and utility of periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Small 2010, 6, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhao, D.; Margolese, D.I.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Generalized syntheses of large-pore mesoporous metal oxides with semicrystalline frameworks. Nature 1998, 396, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao, D. On the controllable soft-templating approach to mesoporous silicates. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2821–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.M.; Jeon, H.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Heterogeneity within order in crystals of a porous metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11920–11923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.-G.; Xu, T.; Li, Z.-Q.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Tian, X.-Y.; Zhang, L.D. Hierarchically micro- and mesoporous metal-organic frameworks with tunable porosity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9487–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górka, J.; Fulvio, P.F.; Pikus, S.; Jaroniec, M. Mesoporous metal organic framework-boehmite and silica composites. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6798–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, X.-D.; Hoang, V.-T.; Kaliaguine, S. Mil-53(Al) mesostructured metal-organic frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 141, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, X.; MacLachlan, M.J. Coordination chemistry: New routes to mesostructured materials. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6552–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Zhao, D.; Timmons, D.J.; Zhou, H.-C. A stepwise transition from microporosity to mesoporosity in metal-organic frameworks by thermal treatment. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Yáñez, S.; Beobide, G.; Castillo, O.; Cepeda, J.; Fröba, M.; Hoffman, F.; Luque, A.; Román, P. Improving the performance of a poorly adsorbing porous material: Template mediated addition of microporosity to a crystalline submicroporous MOF. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 907–909. [Google Scholar]
- Aegerter, M.A.; Leventis, N.; Koebel, M.M. Aerogels Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xiang, S.; Cao, S.; Zhang, J.; Ouyang, G.; Chen, L.; Su, C.-Y. A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohe, M.R.; Rose, M.; Kaskel, S. Metal-organic framework (MOF) aerogels with high micro- and macroporosity. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6056–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X.; Cui, H.; Shi, J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Su, C.-Y.; James, S.L. Porous organic-inorganic hybrid aerogels based on Cr3+/Fe3+ and bridging carboxylates. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.-P.; Su, C.-Y. Porous organic-inorganic hybrid aerogels based on bridging acetylacetonate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 187, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, C.-Y. Metal-organic gels. From discrete metallogelators to coordination polymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 1373–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Schön, E.-M.; Cativiela, C.; Díaz, D.D.; Banerjee, R. Proton-conducting supramolecular metallogels from the lowest molecular weight assembler ligand: A quote for simplicity. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 9562–9568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, O.; Luque, A.; Roman, P.; Lloret, F.; Julve, M. Syntheses, crystal structures, and magnetic properties of one-dimensional oxalate-bridged Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes with n-aminopyridine (n = 2–4) as terminal ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 5526–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercury 3.0 from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC). Available online: http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/mercury/ (accessed on 17 December 2015).
- Farha, O.K.; Eryazici, I.; Jeong, N.C.; Hauser, B.G.; Wilmer, C.E.; Sarjeant, A.A.; Snurr, R.Q.; Nguyen, S.T.; Yazaydın, A.O.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials with ultrahigh surface areas: Is the sky the limit? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15016–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, R. Adsorptive separation of CO2/CH4/CO gas mixtures at high pressures. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 156, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.L.; Monson, P.A. Adsorption in porous materials at high pressure: Theory and experiment. Langmuir 2002, 18, 10261–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, P.L.; Bourrelly, S.; Serre, C.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Hamon, L.; Weireld, G.D.; Chang, J.-S.; Hog, D.-Y.; Hwang, Y.K.; et al. High uptakes of CO2 and CH4 in mesoporous metal-organic frameworks MIL-100 and MIL-101. Langmuir 2008, 24, 7245–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, J.A.; Sumida, K.; Herm, Z.R.; Krishna, R.; Long, J.R. Evaluating metal-organic frameworks for post-combustion carbon dioxide capture via temperature swing adsorption. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3030–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Ahnfeldt, T.; Stock, N. New functionalized flexible Al-MIL-53-X (X = -Cl, -Br, -CH3, -NO2, -(OH)2) solids: Syntheses, characterization, sorption, and breathing. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 9518–9526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, J.A.; Miller, S.R.; Warrender, S.J.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Lightfoot, P.; Wright, P.A. The first route to large pore metal phoshonates. Chem. Commun. 2006, 3305–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caskey, S.R.; Wong-Foy, A.G.; Matzger, A.J. Dramatic tuning of carbon dioxide uptake via metal substitution in a coordination polymer with cylindrical pores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10870–10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grajciar, L.; Wiersum, A.D.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Chang, J.-S.; Nachtigall, P. Understanding CO2 adsorption in CuBTC MOF: Comparing combined DFT-ab initio calculations with microcalorimetry experiments. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17925–17933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Li.; Liu, H.; Lin, M.; Li, S.; Ouyang, G.; Chen, L.; Su, C.-Y. Highly porous aerogels based on imine chemistry: Syntheses and sorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10990–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzis, K.D.; Mavrandonakis, A.; Koppler, W.; Froudakis, G.E. Ab initio study of the interactions between CO2 and N-containing organic heterocycles. ChemPhysChem 2009, 10, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Yáñez, S.; Beobide, G.; Castillo, O.; Fischer, M.; Hoffmann, F.; Fröba, M.; Cepeda, J.; Luque, A. Gas adsorption properties and selectivity in CuII/adeninato/carboxylato metal-biomolecule frameworks. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.L.; Vittal, J.J. One-dimensional coordination polymers: Complexity and diversity in structures, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 688–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angulo-Ibáñez, A.; Beobide, G.; Castillo, O.; Luque, A.; Pérez-Yáñez, S.; Vallejo-Sánchez, D. Aerogels of 1D Coordination Polymers: From a Non-Porous Metal-Organic Crystal Structure to a Highly Porous Material. Polymers 2016, 8, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8010016
Angulo-Ibáñez A, Beobide G, Castillo O, Luque A, Pérez-Yáñez S, Vallejo-Sánchez D. Aerogels of 1D Coordination Polymers: From a Non-Porous Metal-Organic Crystal Structure to a Highly Porous Material. Polymers. 2016; 8(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngulo-Ibáñez, Adrián, Garikoitz Beobide, Oscar Castillo, Antonio Luque, Sonia Pérez-Yáñez, and Daniel Vallejo-Sánchez. 2016. "Aerogels of 1D Coordination Polymers: From a Non-Porous Metal-Organic Crystal Structure to a Highly Porous Material" Polymers 8, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8010016
APA StyleAngulo-Ibáñez, A., Beobide, G., Castillo, O., Luque, A., Pérez-Yáñez, S., & Vallejo-Sánchez, D. (2016). Aerogels of 1D Coordination Polymers: From a Non-Porous Metal-Organic Crystal Structure to a Highly Porous Material. Polymers, 8(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8010016