Comparison Between Ultrasound and High-Pressure Homogenization for Encapsulation of β-Carotene in CNF-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
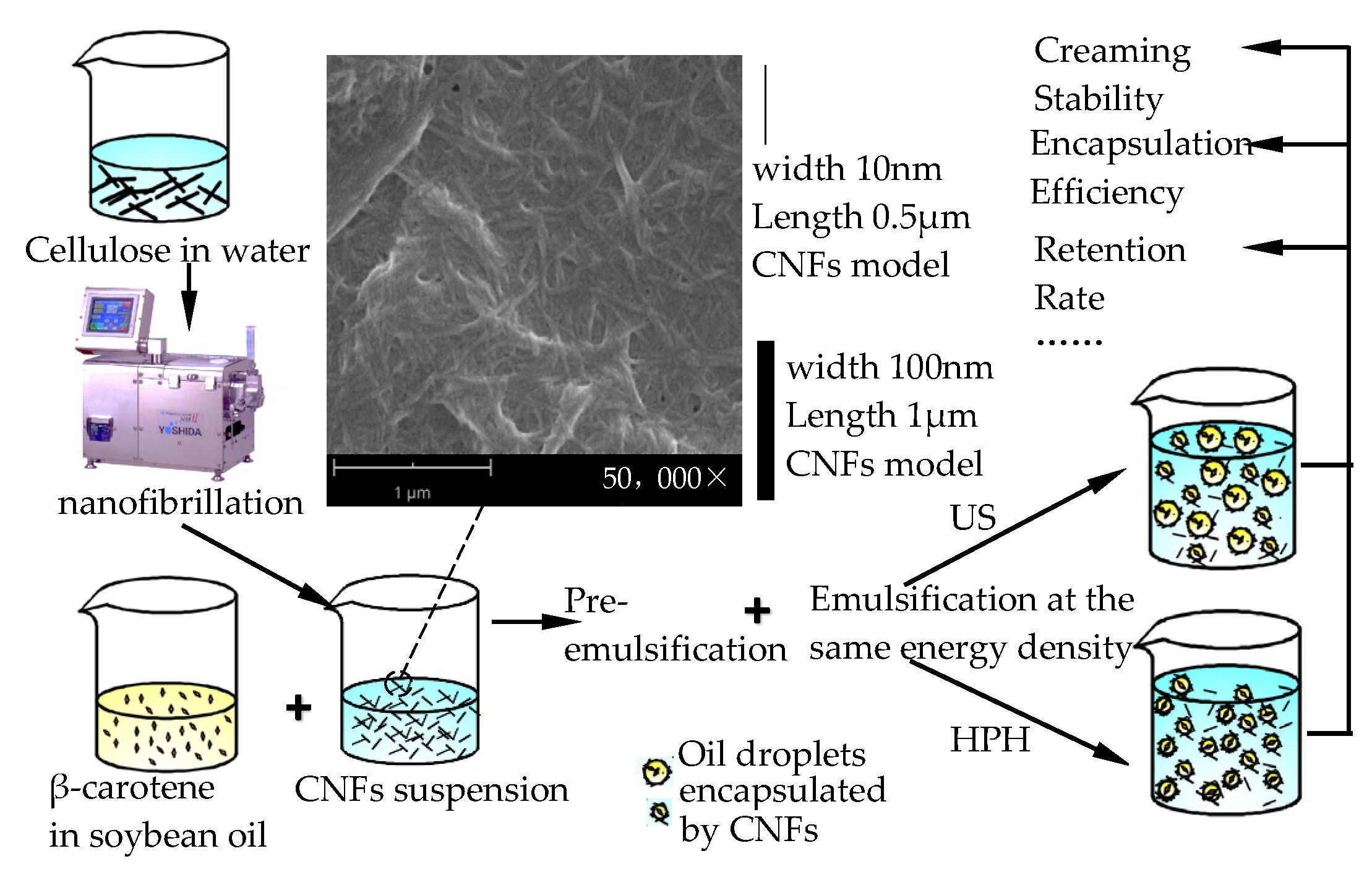
2.2.1. Preparation for Cellulose Nanofibrils (CNFs) Suspension
2.2.2. Fabrication of β-Carotene-Loaded CNF-stabilized Pickering Emulsions
2.3. Characterization
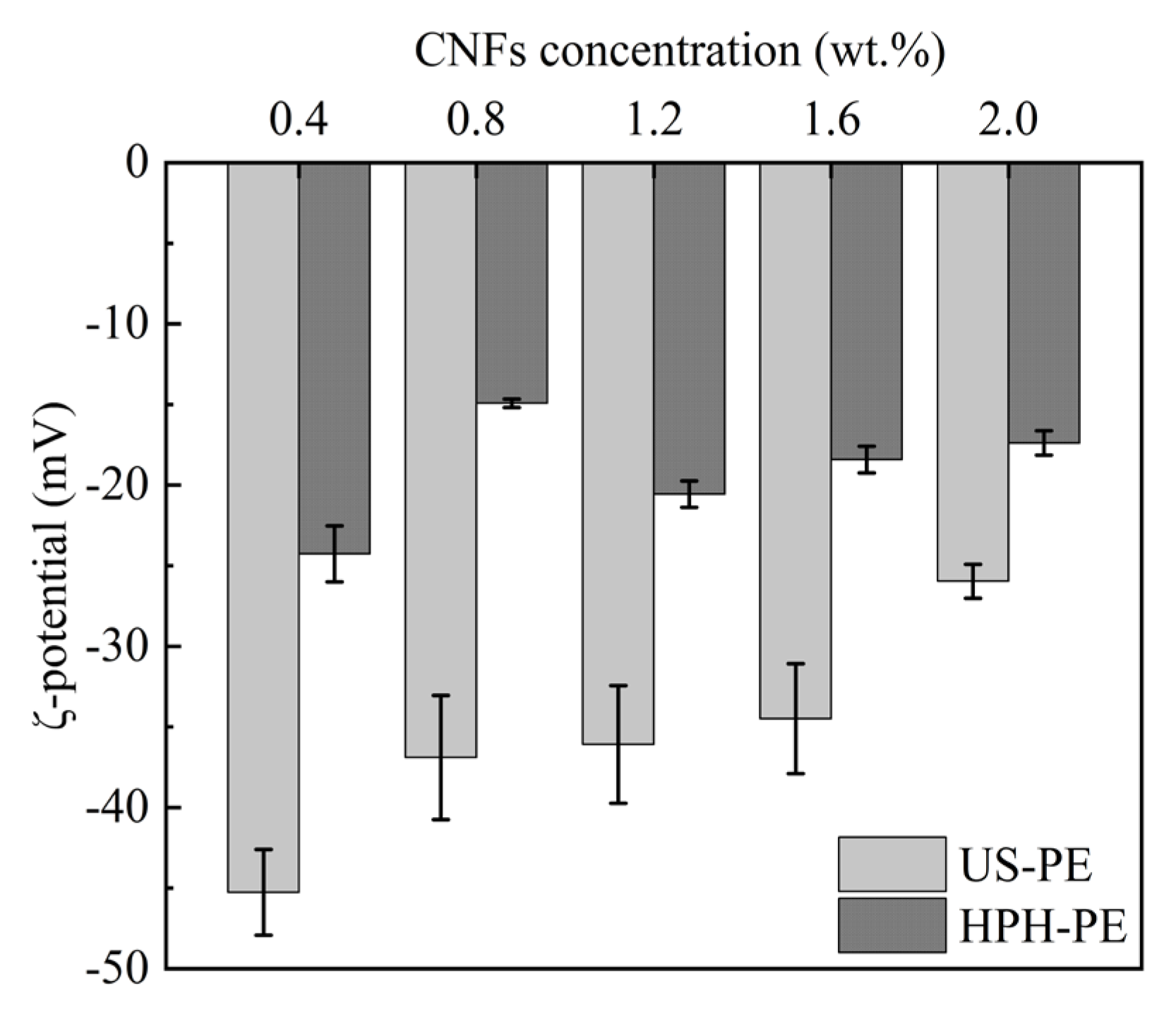
2.3.1. Particle Size and ζ-Potential Measurements
2.3.2. Optical Microscopy
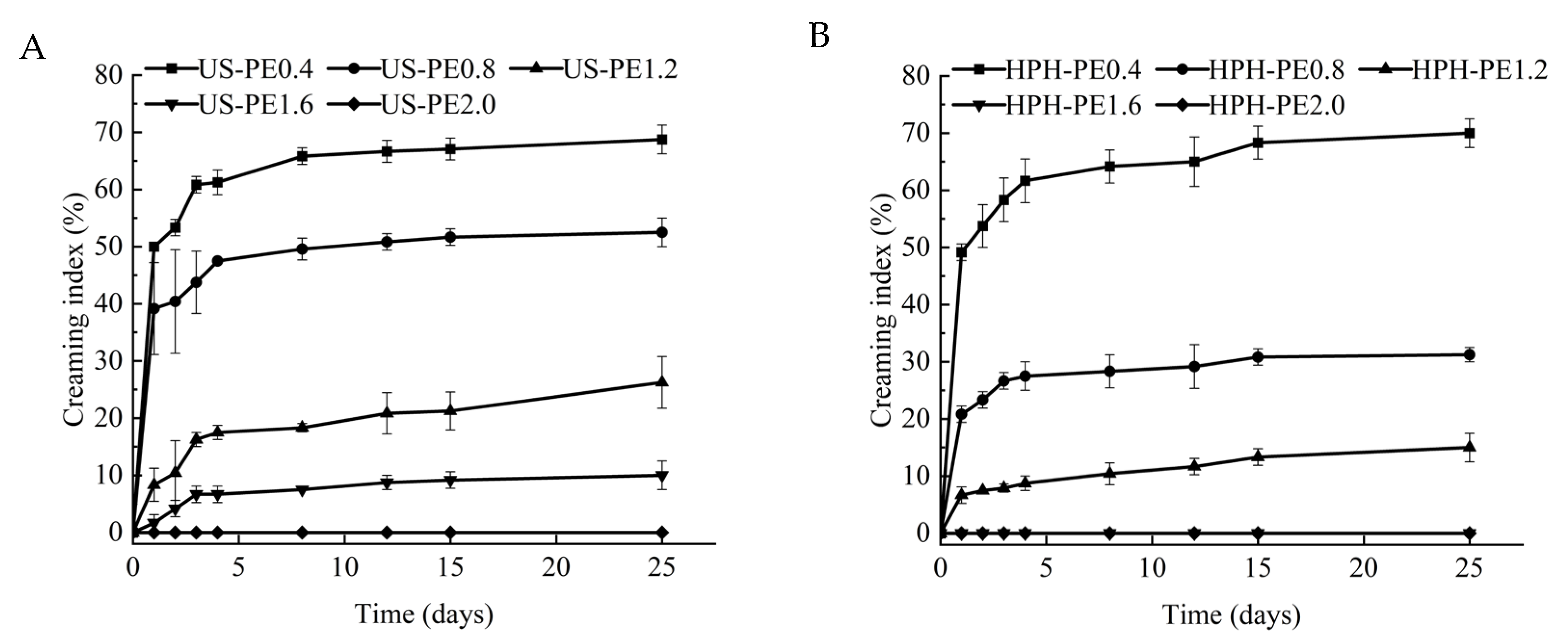
2.3.3. Creaming Stability
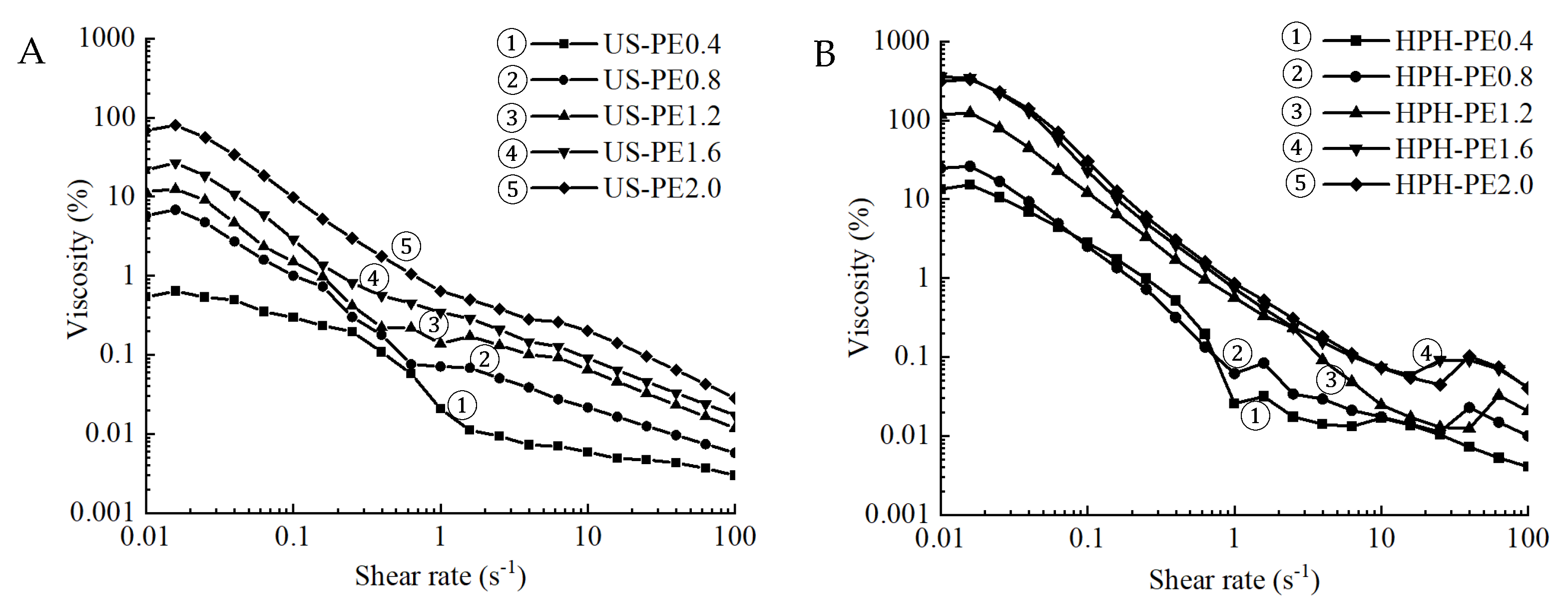
2.3.4. Rheological Characterization
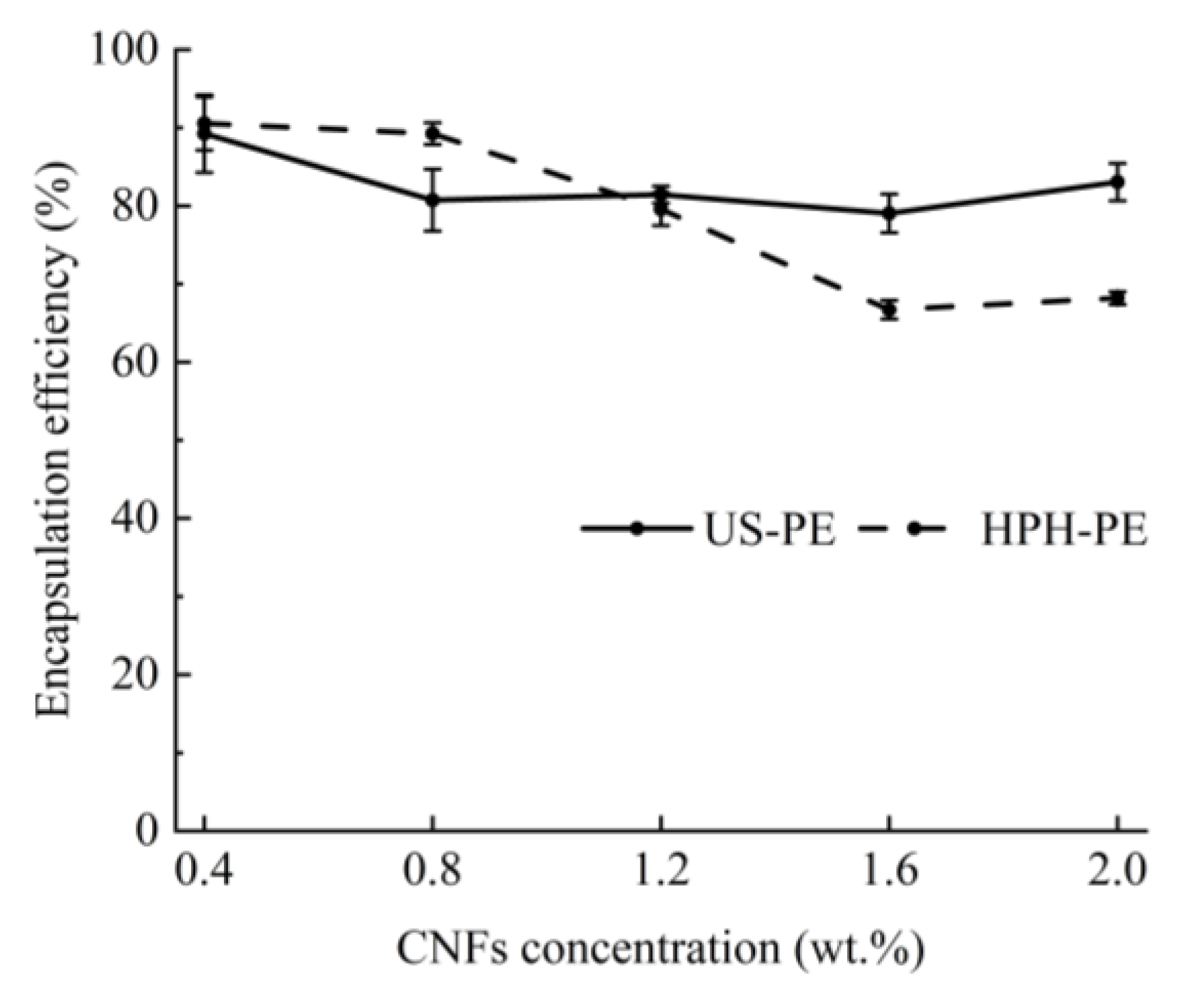
2.3.5. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) of β-Carotene
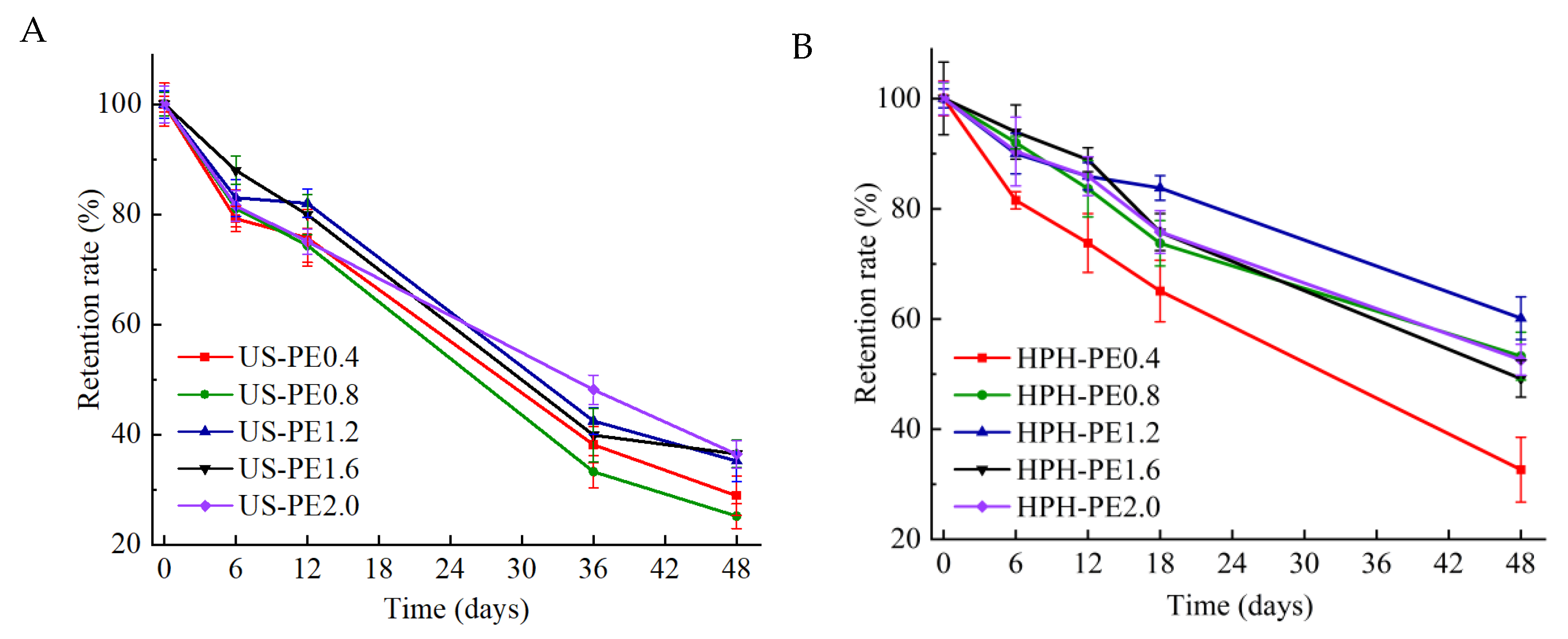
2.3.6. Retention Rate (RR) of β-Carotene During Storage
2.3.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
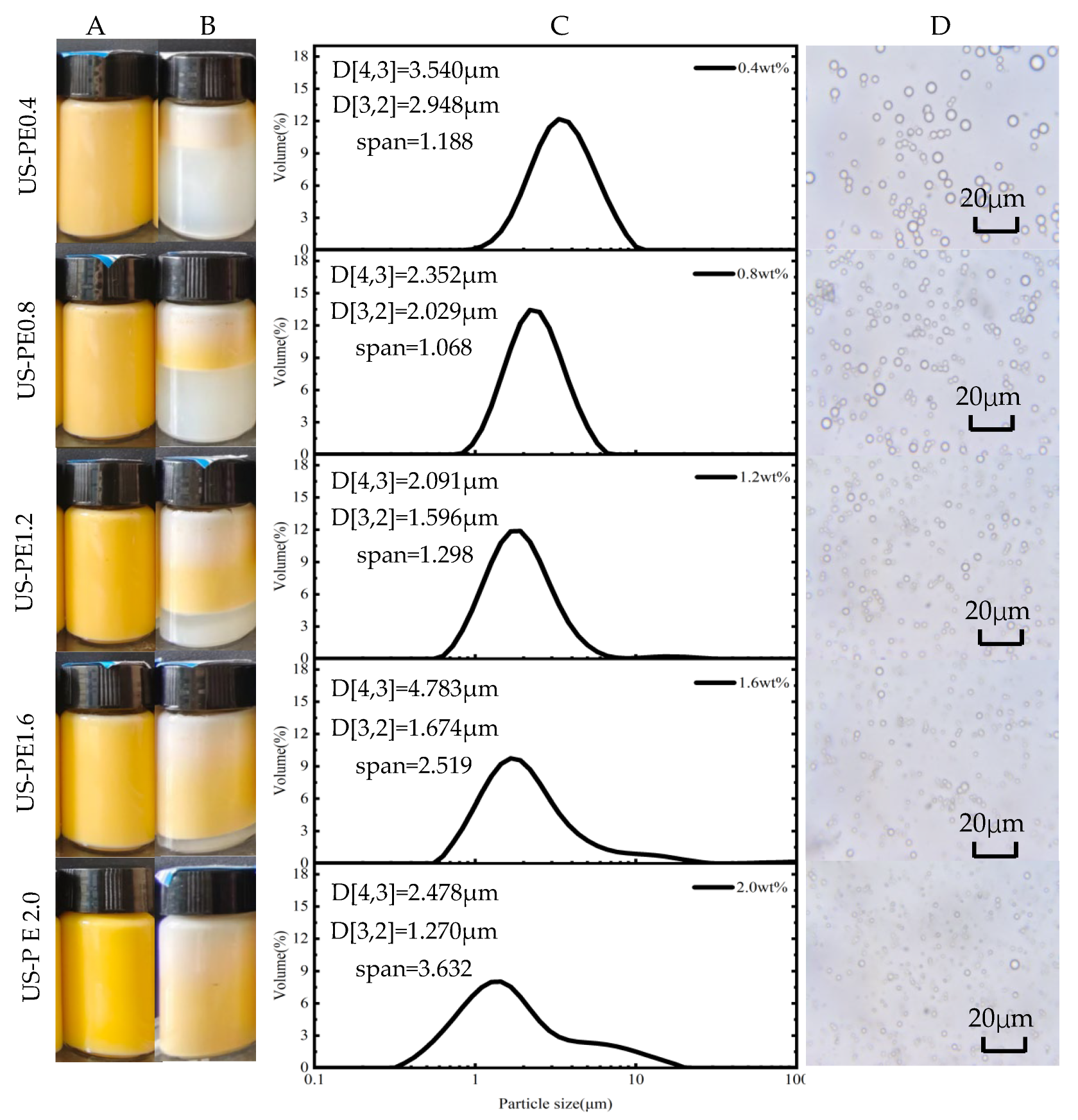
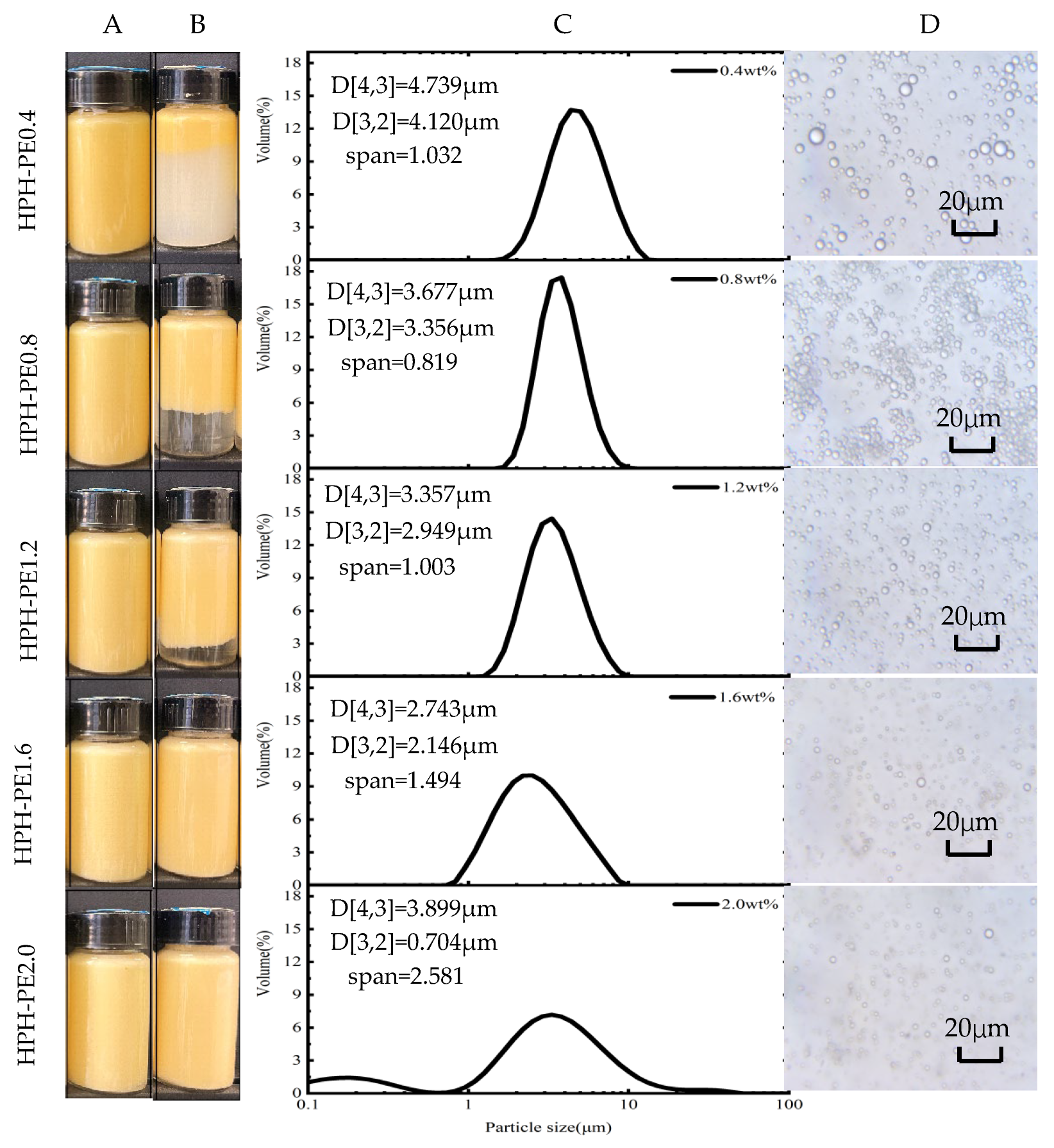
3.1. Formation of c CNF-stabilized Pickering Emulsions
3.2. Characterization of β-Carotene-Loaded CNF-stabilized Pickering Emulsions
3.3. Rheological Properties
3.4. Encapsulation Efficiency of β-Carotene
3.5. Storage Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNFs | Cellulose nanofibrils |
| PE | Pickering emulsions |
| HPH | High-pressure homogenization |
| HPH-PE | High-pressure homogenization prepared Pickering emulsions |
| US | Ultrasound |
| US-PE | Ultrasound-prepared Pickering emulsions |
References
- Jin, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.Y.; Guo, Z.Z.; Li, J.S.; Zhao, Q.S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Comparison of protein hydrolysates against their native counterparts in terms of structural and antioxidant properties, and when used as emulsifiers for curcumin nanoemulsions. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10205–10218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Miao, M.; Cui, S.W.; Jiang, B.; Jin, Z.Y.; Li, X.F. Characterisations of oil-in-water Pickering emulsion stabilized hydrophobic phytoglycogen nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.M.; Si, C.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, B. Cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, Y.; Bolzinger, M.A. Emulsions stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, H.D.; Jang, Y.J. Delivery systems designed to enhance stability and suitability of lipophilic bioactive compounds in food processing: A review. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Roos, Y.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Miao, S. Food emulsions as delivery systems for flavor compounds: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3173–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshani, R.; Tavakolian, M.; Ven, T. Natural emulgel from dialdehyde cellulose for lipophilic drug delivery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4487–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan-Thi, H.; Durand, P.; Prost, M.; Prost, E.; Waché, Y. Effect of heat processing on the antioxidant and prooxidant activities of β-carotene from natural and synthetic origins on red blood cells. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Adin, S.N.; Panda, B.P.; Mujeeb, M. β-Carotene-production methods, biosynthesis from Phaffia rhodozyma, factors affecting its production during fermentation, pharmacological properties: A review. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar]
- De, V.P.; Faas, M.M.; Spasojevic, M.; Sikkema, J. Encapsulation for preservation of functionality and targeted delivery of bioactive food components. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Deng, S.; Mcclements, D.J.; Zhou, L.; Zou, L.Q.; Yi, J.; Liu, C.M.; Liu, W. Encapsulation of β-carotene in wheat gluten nanoparticle-xanthan gum -stabilized Pickering emulsions: Enhancement of carotenoid stability and bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.J.; McClements, D.J.; Sang, S.Y.; Wang, J.P.; Jiao, A.Q.; Jin, Z.Y.; Qiu, C. Encapsulation and protection of β-carotene in Pickering emulsions stabilized by chitosan-phytic acid-cyclodextrin nanoparticles. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Mackie, A.; Zhang, M.K.; Dai, L.; Liu, J.F.; Mao, L.K.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y.X. Co-encapsulation of curcumin and β-carotene in Pickering emulsions stabilized by complex nanoparticles: Effects of microfluidization and thermal treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernice, Q.Q.L.; Chong, W.T.; Thilakarathna, R.C.N.; Tong, S.C.; Tang, T.K.; Phuah, E.K. Palm-based nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) in carotenoid encapsulation and its incorporation into margarine-like reduced fat spread as fat replacer. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 5031–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, D.; Mackie, A.; Yang, S.F.; Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.X. Stability, Interfacial Structure, and Gastrointestinal Digestion of β-Carotene-Loaded Pickering Emulsions Co-stabilized by Particles, a Biopolymer, and a Surfactant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances on cellulose nanocrystals for Pickering emulsions: Development and challenge. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.D.; Zhang, F.F.; Chen, M.L.; Liu, F.; Zheng, B.; Miao, W.H.; Gao, H.M.; Zhou, R.S. Cellulose nanofibrils-stabilized food-grade Pickering emulsions: Clarifying surface charge’s contribution and advancing stabilization mechanism understanding. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, N.; Kawamura, I. Pickering emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanofibers obtained from agricultural and food waste. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 78, 101931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Laguerre, M.; Sprakel, J.; Schroën, K.; Berton-Carabin, C.C. Pickering particles as interfacial reservoirs of antioxidants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 575, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q. Fabrication of milled cellulose particles-stabilized Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lin, Q.; Chen, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, K.; Pang, B.; Xu, T.; Si, C. Microencapsulated phase change material through cellulose nanofibrils stabilized Pickering emulsion templating. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanda, P.; Budiari, S.; Amelia, A. Characteristics of Pickering emulsion stabilized by cellulose nanofibrils in different oil phase polarity. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 2973, 020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.S.; Silva, D.J.; Rosa, D.S. Nonlinear viscoelasticity of Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil Pickering emulsion stabilized with cellulose nanofibrils. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 406, 125058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.K.; Gomes, M.T.M.S.; Hubinger, M.D.; Cunha, R.L.; Meireles, M.A.A. Ultrasound-assisted formation of annatto seed oil emulsions stabilized by biopolymers. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 47, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, C.; Dreher, J.; Helgason, T.; Tadros, T. Investigation of emulsifying properties and emulsion stability of plant and milk proteins using interfacial tension and interfacial elasticity. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Lin, J.; Du, H.; Pang, B. Sustainable production of cellulose nanofibrils from Kraft pulp for the stabilization of oil-in-water Pickering emulsions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 185, 115123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.; Chen, Q.; Huan, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Long, B. High internal phase Pickering emulsions via complexation of cellulose nanofibrils and nanochitin: Enhanced interfacial adsorption and structured aqueous network. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Joyner, H.S. Effect of formulation on structure-function relationships of concentrated emulsions: Rheological, tribological, and microstructural characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitri, I.; Mitbumrung, W.; Akanitkul, P.; Rungraung, N.; Kemsawasd, V.; Jain, S.; Winuprasith, T. Encapsulation of β-Carotene in oil-in-water emulsions containing nanocellulose: Impact on emulsion properties, in vitro digestion, and bioaccessibility. Polymers 2022, 14, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaris, S.; Plazzotta, S.; Bot, F.; Grasselli, S.; Malchiodi, A.; Anese, M. Nanoemulsion preparation by combining high pressure homogenization and high power ultrasound at low energy densities. Food Res. Int. 2016, 83, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, F.; Calligaris, S.; Cortella, G.; Nocera, F.; Peressini, D.; Anese, M. Effect of high pressure homogenization and high power ultrasound on some physical properties of tomato juices with different concentration levels. J. Food Eng. 2017, 213, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrumaux, A.; Marcand, J. Formation of sunflower oil emulsions stabilized by whey proteins with high-pressure homogenization (up to 350 MPa): Effect of pressure on emulsion characteristics. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, W.D. Ultrasound-biophysics mechanisms. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2007, 93, 212–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.M.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Nano-emulsion production by sonication and microfluidization-a comparison. Int. J. Food Prop. 2006, 9, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitbumrung, W.; Suphantharika, M.; McClements, D.; Winuprasith, T. Encapsulation of vitamin D3 in Pickering emulsion stabilized by nanofibrillated mangosteen cellulose: Effect of environmental stresses. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasseuguette, E.; Roux, D.; Nishiyama, Y. Rheological properties of microfibrillar suspension of TEMPO-oxidized pulp. Cellulose 2008, 15, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz-Palma, G.; Betancourt, F.; Mendonça, R.; Chinga-Carrasco, G.; Pereira, M. Relationship between rheological and morphological characteristics of cellulose nanofibrils in dilute dispersions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ez-zaki, H.; Riva, L.; Bellotto, M.; Valentini, L.; Garbin, E.; Punta, C.; Artioli, G. Influence of cellulose nanofibrils on the rheology, microstructure and strength of alkali activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag: A comparison with ordinary Portland cement. Mater. Struct. 2021, 54, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saechio, S.; Akanitkul, P.; Thiyajai, P.; Jain, S.; Tangsuphoom, N.; Suphantharika, M.; Winuprasith, T. Astaxanthinloaded Pickering emulsions stabilized by nanofibrillated cellulose: Impact on emulsion characteristics, digestion behavior, and bioaccessibility. Polymers 2023, 15, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.-S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B. Chitosan hydrochloride/carboxymethyl starch complex nanogels stabilized Pickering emulsions for oral delivery of β-carotene: Protection effect and in vitro digestion study. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Abdirym, A.; Wu, X.; Liu, B. Comparison Between Ultrasound and High-Pressure Homogenization for Encapsulation of β-Carotene in CNF-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions. Polymers 2026, 18, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010126
Abdirym A, Wu X, Liu B. Comparison Between Ultrasound and High-Pressure Homogenization for Encapsulation of β-Carotene in CNF-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions. Polymers. 2026; 18(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdirym, Adila, Xue Wu, and Bin Liu. 2026. "Comparison Between Ultrasound and High-Pressure Homogenization for Encapsulation of β-Carotene in CNF-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions" Polymers 18, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010126
APA StyleAbdirym, A., Wu, X., & Liu, B. (2026). Comparison Between Ultrasound and High-Pressure Homogenization for Encapsulation of β-Carotene in CNF-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions. Polymers, 18(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010126






