Bio-Based and Solvent-Free Epoxy Vitrimers Based on Dynamic Imine Bonds with High Mechanical Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
3. Results
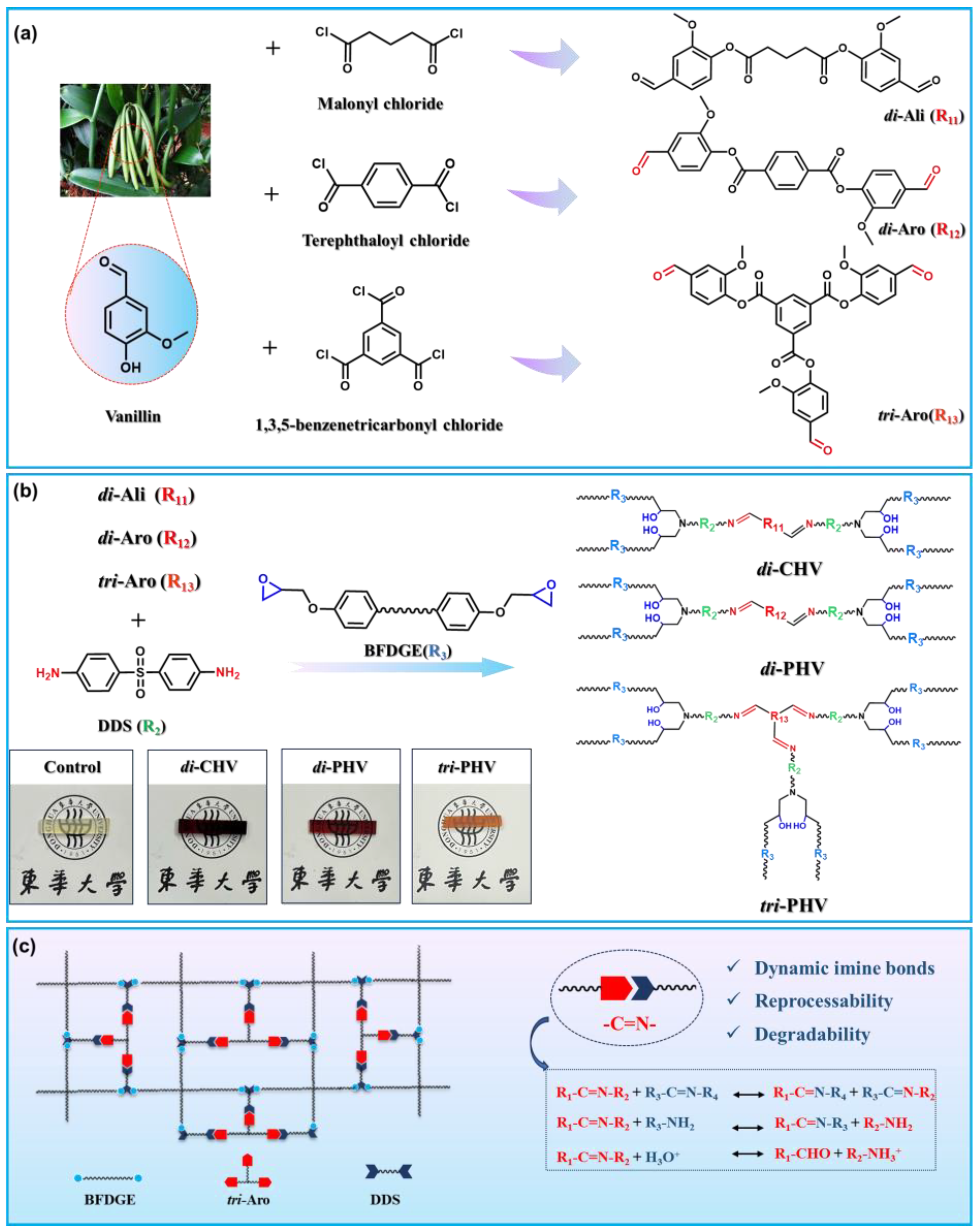
3.1. Synthesis of Biobased Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
3.1.1. Synthesis of Vanillin-Based Aldehyde Monomers
3.1.2. Synthesis of Vanillin-Based Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
3.2. Thermal Properties of Bio-Based Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
3.3. Stress Relaxation of Bio-Based Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
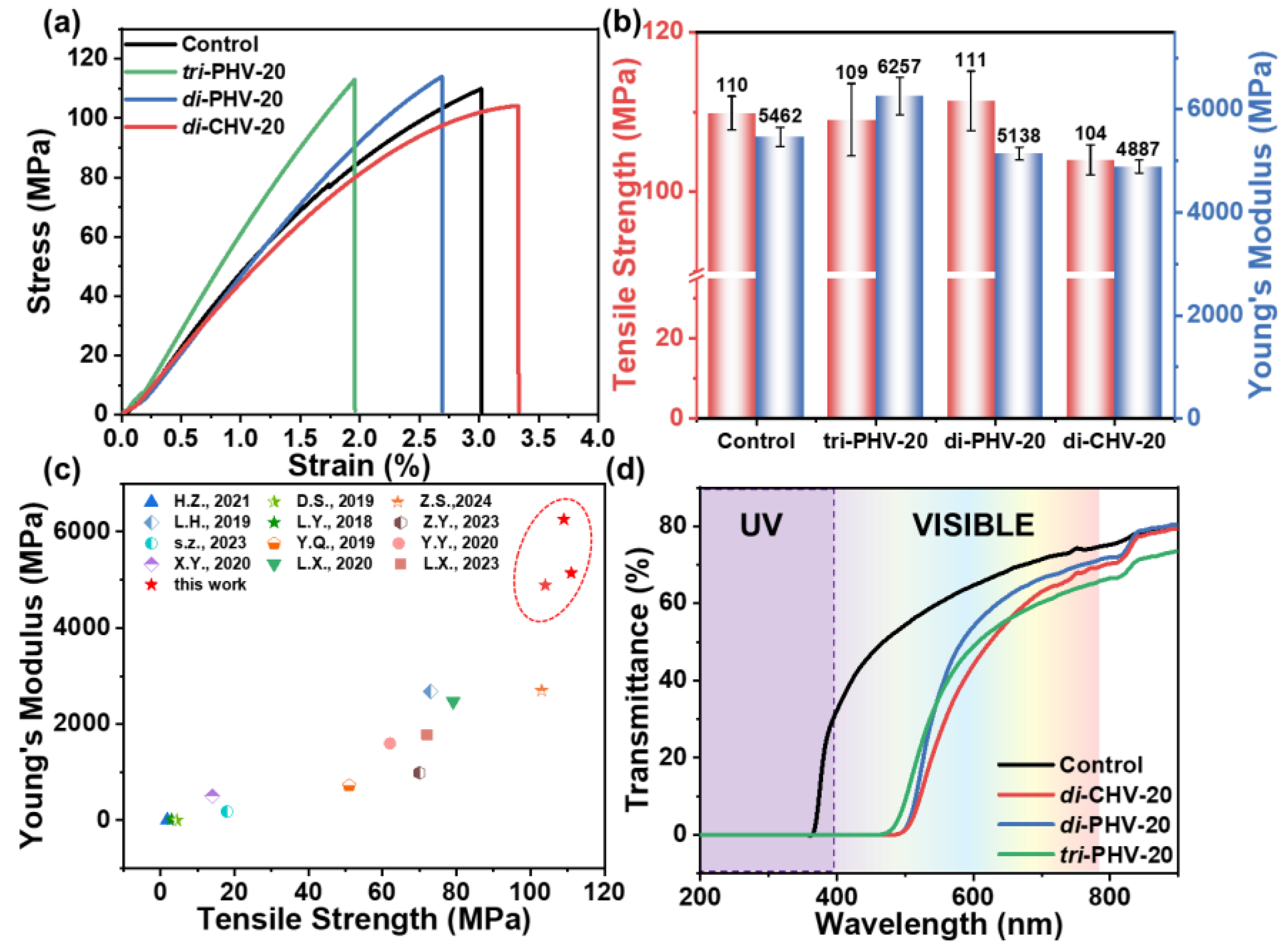
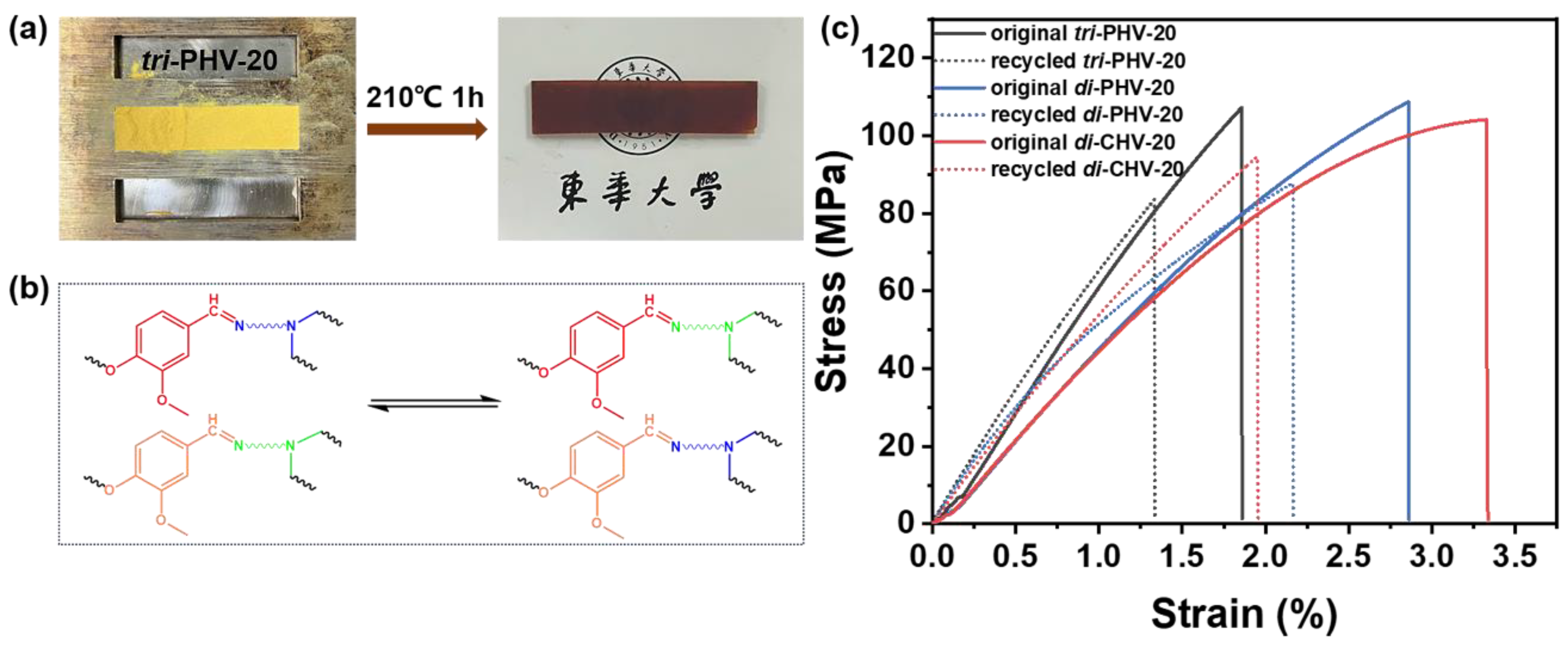
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Bio-Based Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
3.5. UV-Shielding Properties of Bio-Based Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
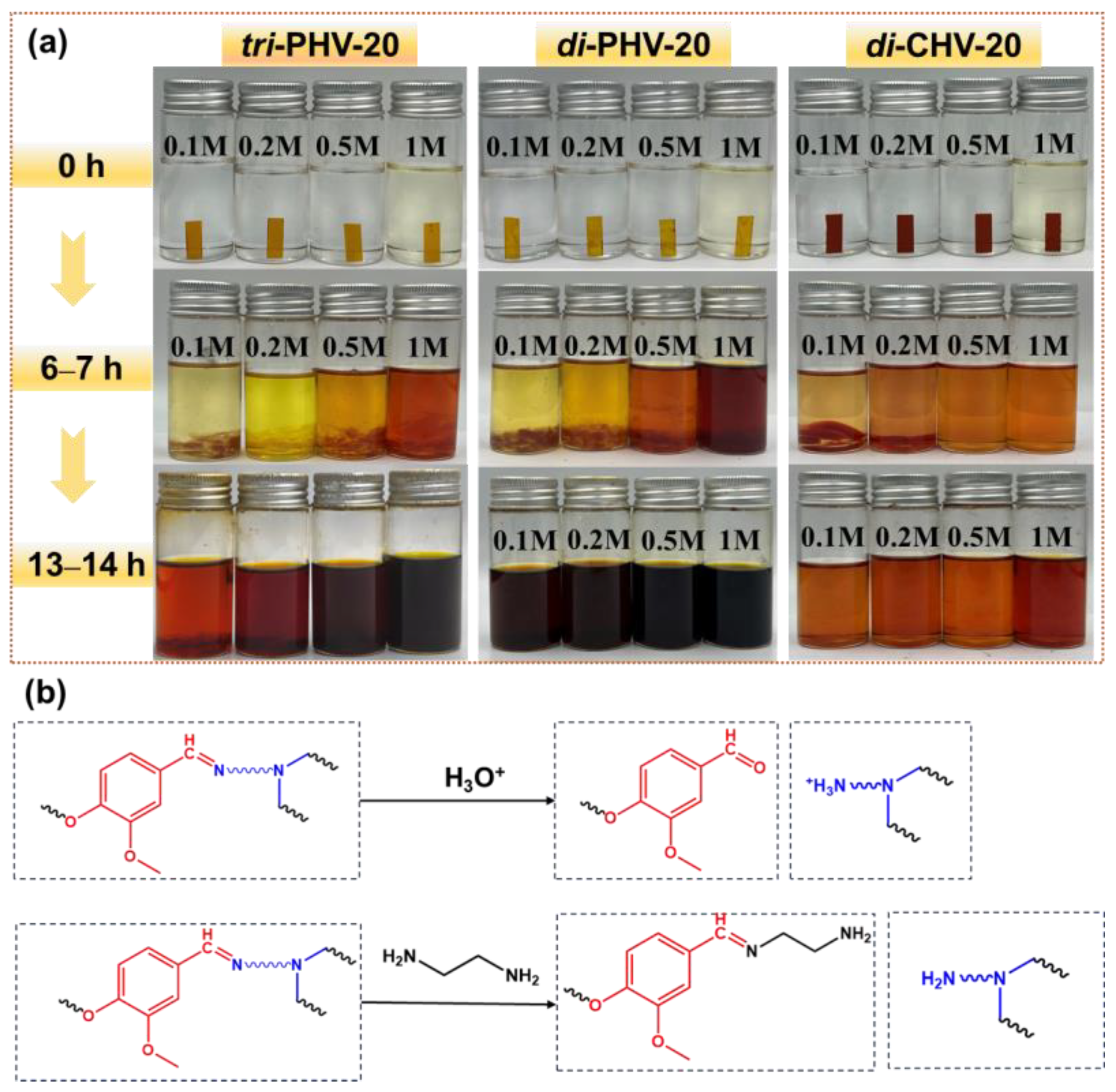
3.6. Degradability and Reprocessability of Bio-Based Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
3.7. Solvent Resistance and Gel Fraction of Bio-Based Imine Epoxy Vitrimers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mashouf Roudsari, G.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Green Approaches to Engineer Tough Biobased Epoxies: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9528–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.-L.; Li, X.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capricho, J.C.; Fox, B.; Hameed, N. Multifunctionality in Epoxy Resins. Polym. Rev. 2019, 60, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.-S.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Hou, X.-L. Review of chemical recycling and reuse of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites. New Carbon Mater. 2022, 37, 1021–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D. Bio-based hyperbranched epoxy resins: Synthesis and recycling. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 624–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Jeong, J.; Oh, D.; Kim, M.; Lee, M.W.; Goh, M. On-demand and fast recyclable bio-epoxy. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 117, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakma, P.; Konkolewicz, D. Dynamic Covalent Bonds in Polymeric Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 9682–9969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reuther, J.F.; Dahlhauser, S.D.; Anslyn, E.V. Tunable Orthogonal Reversible Covalent (TORC) Bonds: Dynamic Chemical Control over Molecular Assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Cui, M.; Xu, X.; Kong, F.; Chen, P.; Yan, N.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J. Degradable and Biobased Covalent Adaptable Networks for Light Controllable Switch. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 6289–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-L.; Tian, P.-X.; Li, Y.-D.; Zeng, J.-B. Biobased covalent adaptable networks: Towards better sustainability of thermosets. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4363–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wei, Y. Functional epoxy vitrimers and composites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 120, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, F.; Shi, L.; Lyu, B.; Ma, J. Recyclable, repairable and malleable bio-based epoxy vitrimers: Overview and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 39, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorero, I.; Mujica, A.; Campo, M.; Prolongo, S.G. Mechanical recycling and electro-thermal welding of epoxy vitrimer nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 6041–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ding, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, T.; Xu, P.; Puglia, D.; Kenny, J.M.; Ma, P. Design of inherent fire retarding and degradable bio-based epoxy vitrimer with excellent self-healing and mechanical reprocessability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 230, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhai, M.; Wei, B.; Lyu, B.; Liu, L. Self-Healing and Recyclable Castor Oil-Based Epoxy Vitrimer Based on Dual Dynamic Bonds of Disulfide and Ester Bonds. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 8399–8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wang, T.; Luo, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Ma, Y.; Ren, S.; Jia, L.; Li, S. Lignin-based vitrimer containing dynamic borate ester bonds with intrinsic photoconversion and excellent photothermal remoldability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, W.; Guo, J.; Yang, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, N. Direct and Catalyst-Free Ester Metathesis Reaction for Covalent Adaptable Networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 20927–20935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ge, Q.; Liu, C.; Li, X. Double-dynamic crosslinked epoxy vitrimer resin prepared using transesterification and dynamic disulfide bonds: High-performance, degradable, self-healing, environment-friendly. Polym. Test. 2023, 126, 108145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tratnik, N.; Tanguy, N.R.; Yan, N. Recyclable, self-strengthening starch-based epoxy vitrimer facilitated by exchangeable disulfide bonds. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Xu, T.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, Y. Covalent Adaptable Networks with Dual Dynamic Covalent Bonds for Self-Repairing Infrared Transmitting Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2315469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Weng, Y.; Li, Y.-D.; Zeng, J.-B. Sustainable Epoxy Vitrimers from Epoxidized Soybean Oil and Vanillin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 15020–15029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, B.; Huang, Y. Facile preparation of reprocessable and degradable phenolic resin based on dynamic acetal motifs. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 196, 109818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova-Pérez, A.; De la Flor, S.; Fernández-Francos, X.; Serra, À.; Roig, A. Biobased Imine Vitrimers Obtained by Photo and Thermal Curing Procedures-Promising Materials for 3D Printing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 3364–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, T.E.; Ku, K.; Yeo, H. Reprocessable and Chemically Recyclable Hard Vitrimers Based on Liquid-Crystalline Epoxides. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2209912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Xie, T.; Rzayev, J. Synthesis of thermally degradable epoxy adhesives. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 4992–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.K.; Chen, Y.-C.; Jeng, R.-J.; Abu-Omar, M.M.; Lin, C.-H. Upcycling Waste Polycarbonate to Poly(carbonate imine) Vitrimers with High Thermal Properties and Unprecedented Hydrolytic Stability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 8580–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hou, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X. High-performance vitrimer films containing acylhydrazone dynamic covalent bonds. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 3266–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, A.; Petrauskaité, A.; Ramis, X.; De la Flor, S.; Serra, À. Synthesis and characterization of new bio-based poly(acylhydrazone) vanillin vitrimers. Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Niu, H.; Liu, L.; Xie, S.; Hua, Z.; Li, Y. Elastomeric polyolefin vitrimer: Dynamic imine bond cross-linked ethylene/propylene copolymer. Polymer 2021, 229, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhers, S.; Vantomme, G.; Avérous, L. A fully bio-based polyimine vitrimer derived from fructose. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yi, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Lu, Z. Weldable, Reprocessable, and Water-resistant Polybenzoxazine Vitrimer Crosslinked by Dynamic Imine Bonds. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202301708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Lu, X.; Xin, Z. Biobased Polybenzoxazine Vitrimer with Imine Bonds: Shape Memory, Reprocessing, and Degradation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 7739–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C. Functional bio-based vitrimer with excellent healing and recyclability based on conjugated deflection self-toughening. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Weldable, malleable and programmable epoxy vitrimers with high mechanical properties and water insensitivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, M.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hao, C.; Shao, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Highly engineerable Schiff base polymer matrix with facile fiber composite manufacturability and hydrothermal recyclability. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 248, 110366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Liu, G.-L.; Li, Y.-D.; Weng, Y.; Zeng, J.-B. Biobased High-Performance Epoxy Vitrimer with UV Shielding for Recyclable Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4638–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Guo, B. Programming dynamic imine bond into elastomer/graphene composite toward mechanically strong, malleable, and multi-stimuli responsive vitrimer. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, T.; He, H.; Lv, Z.; Xu, J.; Ding, D.; Dai, L.; Huang, Z.; Si, C. Lignin-based epoxy composite vitrimers with light-controlled remoldability. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Cui, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, L.; Chi, B.; Xu, H.; Ning, L.; Jia, S.; Wang, X. Robust, waterproof, and degradable cellulose-based polyimine vitrimer for plastic replacement. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, T. Synthesis of facilely healable and recyclable imine vitrimers using biobased branched diamine and vanillin. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 196, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Peng, X.; Wang, Y.; Geng, H.; Xu, A.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Ye, D. Vanillin-based degradable epoxy vitrimers: Reprocessability and mechanical properties study. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; He, J.; Li, Y.-D.; Zhao, X.-L.; Zeng, J.-B. Biobased epoxy vitrimer from epoxidized soybean oil for reprocessable and recyclable carbon fiber reinforced composite. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.A.; Mian, M.M.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. A vanillin-derived hardener for recyclable, degradable and self-healable high-performance epoxy vitrimers based on transimination. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, E.; Feng, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Liang, L. Degradable bio-based epoxy vitrimers based on imine chemistry and their application in recyclable carbon fiber composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 15733–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Hou, W.; Huang, Y. Catalyst-Free and Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Vitrimer Prepared Based on Ester Exchange and Imine Bonding. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 4912–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Odelius, K.; Hakkarainen, M. Photocurable, Thermally Reprocessable, and Chemically Recyclable Vanillin-Based Imine Thermosets. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 17272–17279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genua, A.; Montes, S.; Azcune, I.; Rekondo, A.; Malburet, S.; Dayde-Cazals, B.; Graillot, A. Build-To-Specification Vanillin and Phloroglucinol Derived Biobased Epoxy-Amine Vitrimers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ke, Y.; Chen, Q.; Shen, L.; Xue, J.; Quirino, R.L.; Yan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, C. Efficient transformation of renewable vanillin into reprocessable, acid-degradable and flame retardant polyimide vitrimers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, L.; Lu, M.; Song, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, G. Water-resistant bio-based vitrimers based on dynamic imine bonds: Self-healability, remodelability and ecofriendly recyclability. Polymer 2020, 210, 123030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, E.; Liu, J.; Qin, J.; Wu, M.; Yang, C.; Liang, L. Self-healing, reprocessable, degradable, thermadapt shape memory multifunctional polymers based on dynamic imine bonds and their application in nondestructively recyclable carbon fiber composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 139992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tian, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. A biomass-based Schiff base vitrimer with both excellent performance and multiple degradability. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 6527–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Gu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, X.; Ye, D. Vanillin-Based Polyschiff Vitrimers: Reprocessability and Chemical Recyclability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15463–15470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Jiang, H.; Pang, W.; He, T.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, S.; Hu, S. Preparation and self-healing properties of epoxy vitrimer materials based on imine bonds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhou, X.; Fang, Y.; Xue, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, X.; Cui, J. Water-Assisted Reprocessing and Shape Programming of Epoxy Vitrimer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2403681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Multifunctional Recyclable Glassy Polymeric Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amber, M.H.; Ren, Y.; Dominik, K.; Alireza, S.; Catalin, R.P.; Gary, S.K.; Ajit, R.; Vikas, V.; Dhriti, N. Vitrimer Transition Temperature Identification: Coupling Various Thermomechanical Methodologies. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo, L.M.; Xiao, Z.; Zoriana, D.; Luo, J.; Gregory, P.C.; Gaukhar, T. Viscoelasticity of Polymers with Dynamic Covalent Bonds: Concepts and Misconceptions. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 8688–8696. [Google Scholar]
- Shalini, J.R.; Kim, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Xiao, Z.; Alexei, P.S.; Saito, T.; Petridis, L.; Carrillo, J.; Savara, A. Source of Processable Vitrimer Viscosities: Swap Frequencies and Steric Factors. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 11020–11029. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.A.; Hasan, M.N.; Kafi, M.A. Synthesis of novel vanillin-amine hardeners fully derived from renewable bio feedstocks and their curing with epoxy resins to produce recyclable reprocessable vitrimers. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
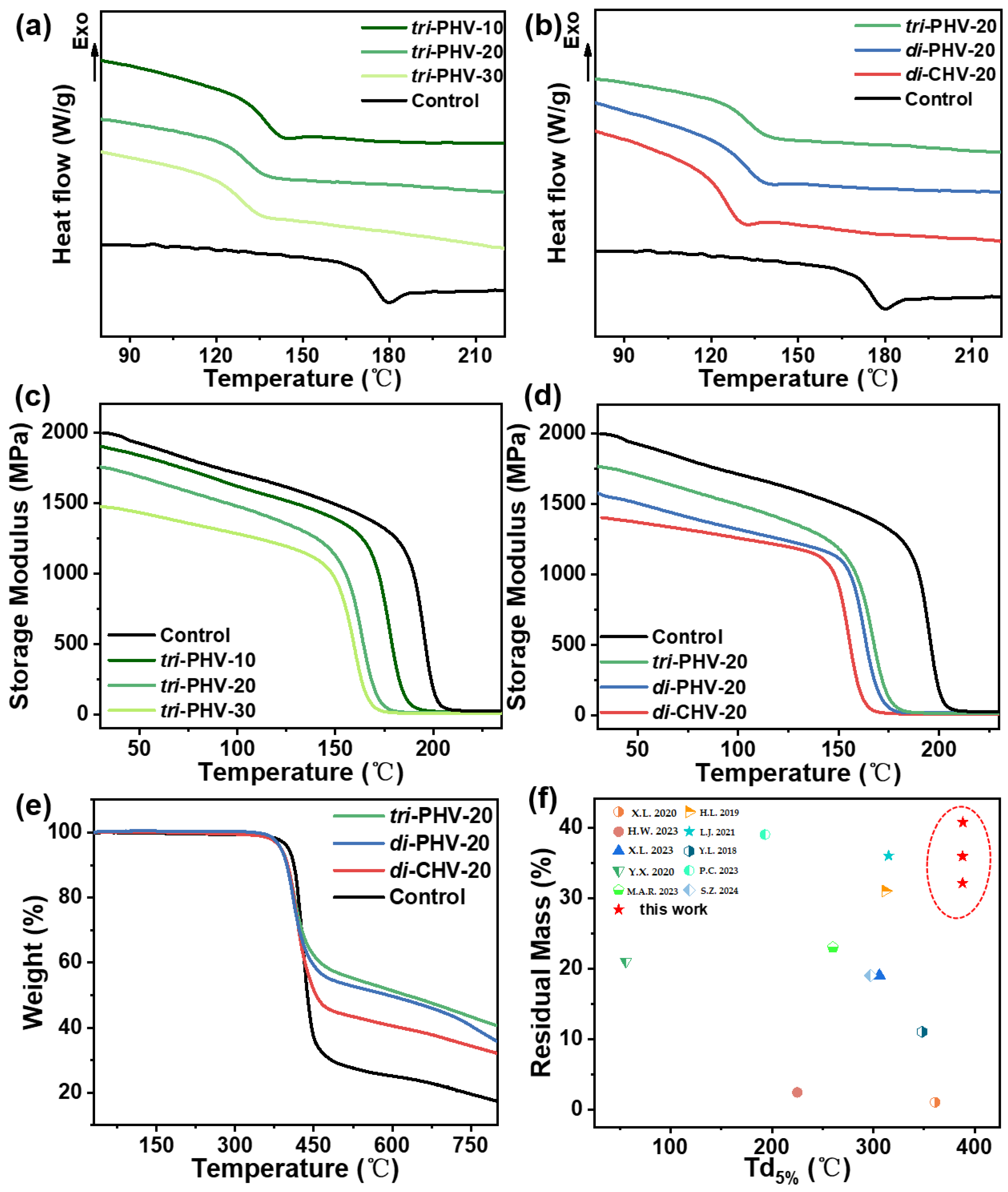



| Sample | Imine Bond Content | Tg(DMA) (°C) | Tg(DSC) (°C) | Td5% (°C) 1 | R800 (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | / | 187.0 | 173.2 | 402.0 | 17.5 |
| tri-PHV | 10% | 168.3 | 145.1 | / | / |
| 20% | 154.1 | 132.8 | 387.9 | 40.7 | |
| 30% | 150.7 | 128.8 | / | / | |
| di-PHV | 10% | 167.3 | 145.8 | / | / |
| 20% | 155.6 | 132.4 | 387.3 | 35.9 | |
| 30% | 150.2 | 127.5 | / | / | |
| di-CHV | 10% | 161.5 | 137.0 | / | / |
| 20% | 148.4 | 125.6 | 388.2 | 32.1 | |
| 30% | 141.4 | 118.9 | / | / |
| Sample | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Recovery 1 (%) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Recovery (%) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 110 | / | 5462 | / | 3.0 |
| Original tri-PHV-20 | 109 | 76 | 6257 | 113 | 1.9 |
| Recycled tri-PHV-20 | 83 | 7068 | 1.3 | ||
| Original di-PHV-20 | 111 | 78 | 5138 | 115 | 2.6 |
| Recycled di-PHV-20 | 87 | 5886 | 2.2 | ||
| Original di-CHV-20 | 104 | 89 | 4887 | 113 | 3.4 |
| Recycled di-CHV-20 | 93 | 5498 | 1.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Ning, N.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Feng, S.; Guo, Z.; Wei, Y. Bio-Based and Solvent-Free Epoxy Vitrimers Based on Dynamic Imine Bonds with High Mechanical Performance. Polymers 2025, 17, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050571
Chen L, Ning N, Zhou G, Li Y, Feng S, Guo Z, Wei Y. Bio-Based and Solvent-Free Epoxy Vitrimers Based on Dynamic Imine Bonds with High Mechanical Performance. Polymers. 2025; 17(5):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050571
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lei, Na Ning, Gang Zhou, Yan Li, Shicheng Feng, Zhengyan Guo, and Yi Wei. 2025. "Bio-Based and Solvent-Free Epoxy Vitrimers Based on Dynamic Imine Bonds with High Mechanical Performance" Polymers 17, no. 5: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050571
APA StyleChen, L., Ning, N., Zhou, G., Li, Y., Feng, S., Guo, Z., & Wei, Y. (2025). Bio-Based and Solvent-Free Epoxy Vitrimers Based on Dynamic Imine Bonds with High Mechanical Performance. Polymers, 17(5), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050571







