Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate-Mediated Self-Assembly of Silk Particles from Formic Acid Solutions into Robust Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Silk Solutions
2.2. Characterization of Silk Films
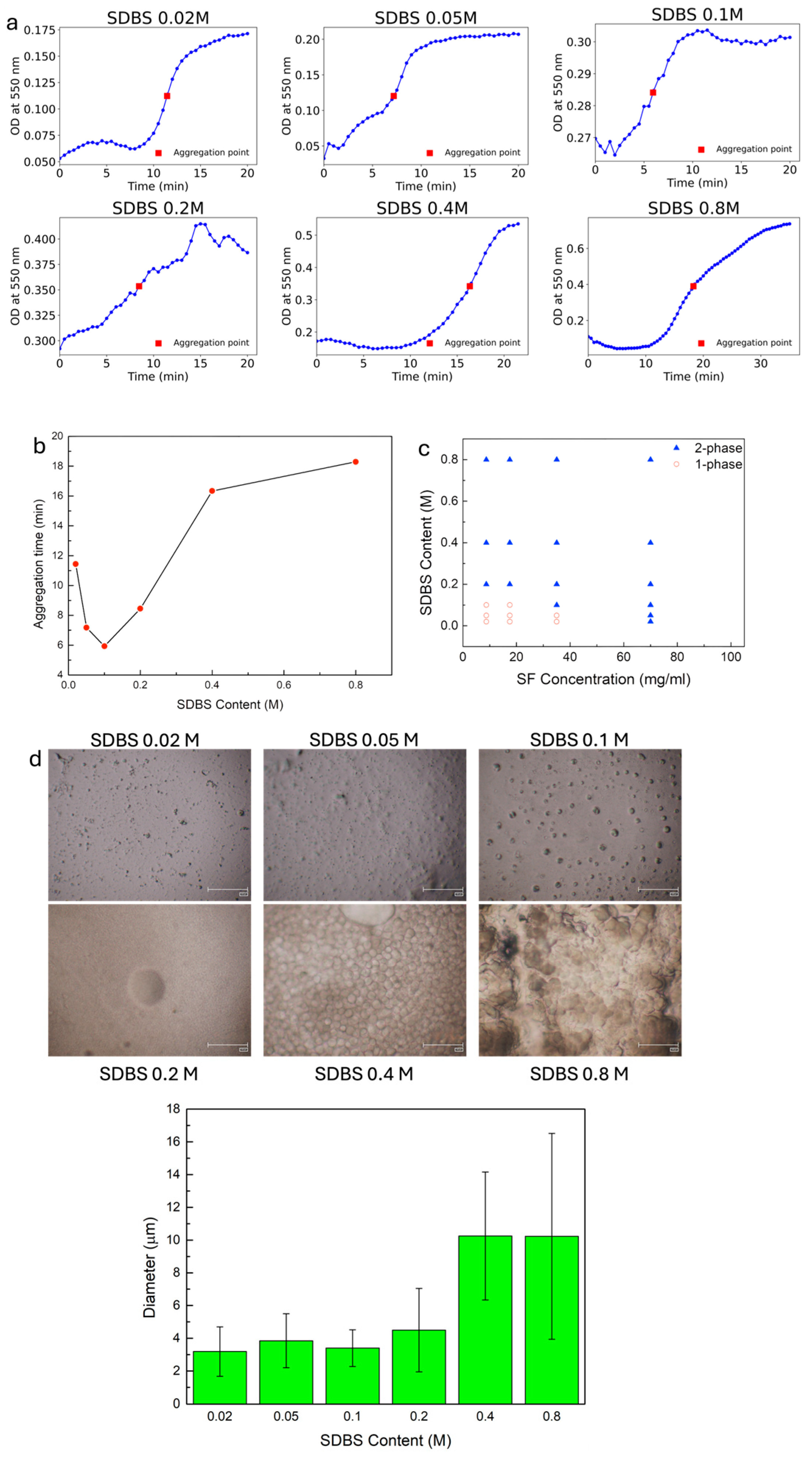
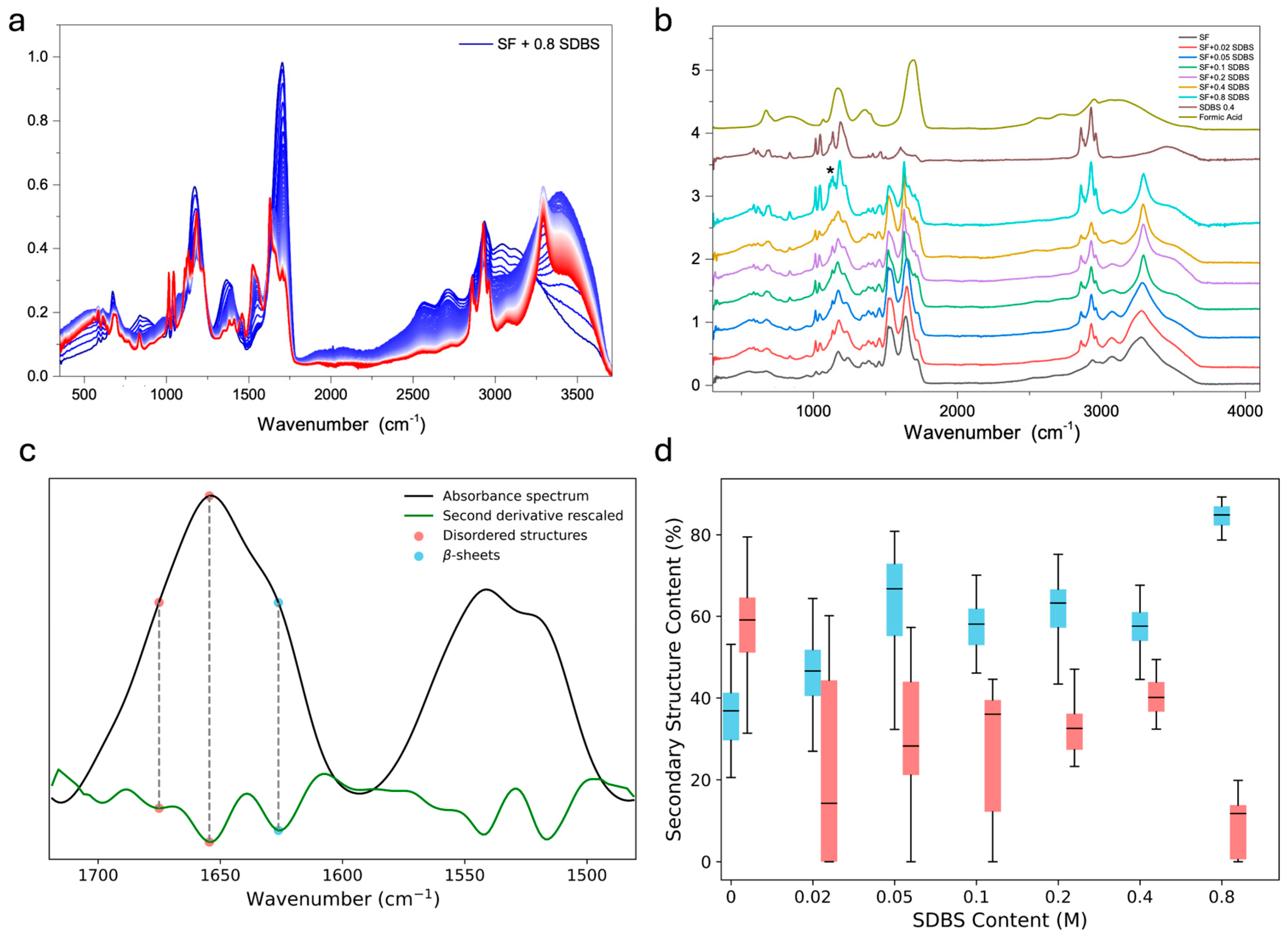
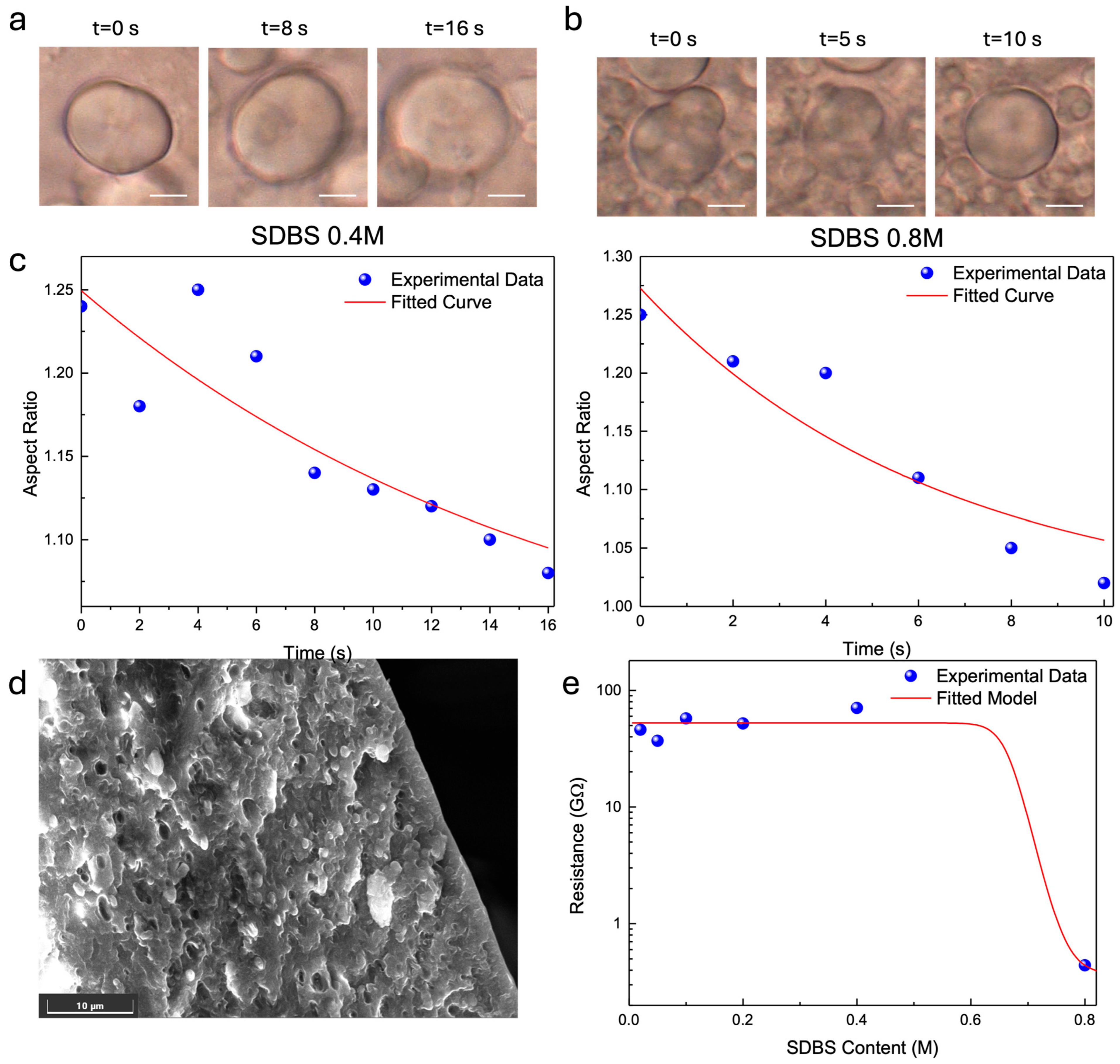
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials Fabrication from Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikman, E.L.; Eccles, L.E.; Stoppel, W.L. Native Silk Fibers: Protein Sequence and Structure Influences on Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Biomacromolecules 2025, 26, 2043–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Kim, B.; Velev, O.D. Sustainable Biopolymer Colloids: Advances in Morphology for Enhanced Functionalities. Langmuir 2025, 41, 7160–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, I.J.; McClements, D.J. Biopolymer-Based Nanoparticles and Microparticles: Fabrication, Characterization, and Application. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayakumar, G.P.; Muthusamy, S.; Selvaganesh, B.; Sivarajasekar, N.; Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Sivamani, S.; Sivakumar, N.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Show, P.L. Biopolymers and Composites: Properties, Characterization and Their Applications in Food, Medical and Pharmaceutical Industries. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate Gel Particles–A Review of Production Techniques and Physical Properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Aisyah, H.A.; Nordin, A.H.; Ngadi, N.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zainudin, E.S.; Sharma, S.; Abral, H.; et al. Natural-Fiber-Reinforced Chitosan, Chitosan Blends and Their Nanocomposites for Various Advanced Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirk, B.D.; Heichel, D.L.; Eccles, L.E.; Rodgers, L.I.; Lateef, A.H.; Burke, K.A.; Stoppel, W.L. Modifying Naturally Occurring, Nonmammalian-Sourced Biopolymers for Biomedical Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 5915–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, C.; Guo, B.; Zhai, X.; Lao, S.; Zhao, P.; Ruan, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, K.; Chen, D. Bioinspired Strong and Tough Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Fibers. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2300080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, B.; Wu, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, P.; Ruan, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, K.; et al. Strong and Tough Biofibers Designed by Dual Crosslinking for Sutures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2313131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepari, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a Biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomun, J.I.; Totten, J.D.; Wongpinyochit, T.; Florence, A.J.; Seib, F.P. Manual Versus Microfluidic-Assisted Nanoparticle Manufacture: Impact of Silk Fibroin Stock on Nanoparticle Characteristics. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 2796–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, M.O.; Lutz, H.M.; Armada, J.; Davies, N.; Gerzenshtein, I.K.; Cakley, A.S.; Spiess, B.D.; Stoppel, W.L. Silk Fibroin Particles as Carriers in the Development of Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers. Adv. Nanobiomed Res. 2023, 3, 2300019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yucel, T.; Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Nanospheres and Microspheres from Silk/Pva Blend Films for Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammel, A.S.; Hu, X.; Park, S.H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Scheibel, T.R. Controlling Silk Fibroin Particle Features for Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libera, V.; Malaspina, R.; Bittolo Bon, S.; Cardinali, M.A.; Chiesa, I.; De Maria, C.; Paciaroni, A.; Petrillo, C.; Comez, L.; Sassi, P.; et al. Conformational Transitions in Redissolved Silk Fibroin Films and Application for Printable Self-Powered Multistate Resistive Memory Biomaterials. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 22393–22402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Ou, X.; Tao, J.; Zheng, M.; Huang, Y.; Bai, S. Injectable Silk Fibroin-Based Hydrogels with Ultrafast In Situ Gelation via an Unfolding-Aggregating Strategy for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Biomacromolecules 2025, 26, 7447–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hou, J.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Kaplan, D.L.; Lu, S. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Induced Rapid Gelation of Silk Fibroin. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shmelev, K.; Sun, L.; Gil, E.S.; Park, S.H.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Regulation of Silk Material Structure by Temperature-Controlled Water Vapor Annealing. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, B.K.; Liu, C.; Haritos, V.S.; He, L. Understanding the Interplay between Self-Assembling Peptides and Solution Ions for Tunable Protein Nanoparticle Formation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6956–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, L.E.; Orozco, A.A.; Liwang, R.K.; Stoppel, W.L. Self-Assembly of Plodia Interpunctella Silk Particles: Mechanisms and Encapsulation Strategies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 14913–14926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roamcharern, N.; Brady, D.J.; Parkinson, J.A.; Rattray, Z.; Seib, F.P. Optimizing Silk Nanoparticle Assembly with Potassium Ions: Effects on Physicochemical Properties and Encapsulation Efficiency. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2025, 8, 6854–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yu, Y.; Jo, S.; Lee, Y.; Son, S.; Lee, K.H. Calcium Ion-Triggered Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of Silk Fibroin and Spinning through Acidification and Shear Stress. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, I.; De Maria, C.; Tonin, R.; Ripanti, F.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Salvatori, C.; Mussolin, L.; Paciaroni, A.; Petrillo, C.; Cesprini, E.; et al. Biocompatible and Printable Ionotronic Sensing Materials Based on Silk Fibroin and Soluble Plant-Derived Polyphenols. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 43729–43737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alunni Cardinali, M.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Chiesa, I.; Bittolo Bon, S.; Rondini, T.; Serrano-Ruiz, M.; Caporali, M.; Tacchi, S.; Verdini, A.; Petrillo, C.; et al. Mechanical Transfer of Black Phosphorus on a Silk Fibroin Substrate: A Viable Method for Photoresponsive and Printable Biomaterials. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 17977–17988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, Q.; Ming, J.; Dou, H.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, B.; Qin, M.; Li, F.; Kaplan, D.L.; Zhang, X. Silk Dissolution and Regeneration at the Nanofibril Scale. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3879–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; You, X.; Dou, H.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, B.; Zhang, X. Facile Fabrication of Robust Silk Nanofibril Films via Direct Dissolution of Silk in CaCl2-Formic Acid Solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belton, D.J.; Plowright, R.; Kaplan, D.L.; Perry, C.C. A Robust Spectroscopic Method for the Determination of Protein Conformational Composition—Application to the Annealing of Silk. Acta Biomater. 2018, 73, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brangwynne, C.P.; Mitchison, T.J.; Hyman, A.A. Active Liquid-like Behavior of Nucleoli Determines Their Size and Shape in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4334–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roamcharern, N.; Matthew, S.A.L.; Brady, D.J.; Parkinson, J.A.; Rattray, Z.; Seib, F.P. Biomimetic Silk Nanoparticle Manufacture: Calcium Ion-Mediated Assembly. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 11, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, X.; Li, P.; Liu, C.; Lou, J.; Wang, Z.; Wen, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Biology: Mechanisms, Physiological Functions and Human Diseases. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 953–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guseva, S.; Schnapka, V.; Adamski, W.; Maurin, D.; Ruigrok, R.W.H.; Salvi, N.; Blackledge, M. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation Modifies the Dynamic Properties of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10548–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.; Qiao, Y. Membrane-Confined Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation toward Artificial Organelles. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wu, F.; Xing, T.; Yadavalli, V.K.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. A Silk Fibroin Hydrogel with Reversible Sol-Gel Transition. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24085–24096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wei, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Peng, H.; Wang, D.; Yuan, J.; Waite, J.H.; Zhao, Q. A Cation-Methylene-Phenyl Sequence Encodes Programmable Poly(Ionic Liquid) Coacervation and Robust Underwater Adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Kistler, S.; Zhou, J.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Victorelli, F.D.; Meneguin, A.B.; Spósito, L.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M.; Mezzenga, R. Amyloid-Polysaccharide Interfacial Coacervates as Therapeutic Materials. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, A. Infrared Spectroscopy of Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, L.M.; Mobley, P.W.; Pilpa, R.; Sherman, M.A.; Waring, A.J. Conformational Mapping of the N-Terminal Peptide of HIV-1 Gp41 in Membrane Environments Using 13 C-Enhanced Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembr 2002, 1559, 96–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goormaghtigh, E.; Raussens, V.; Ruysschaert, J.-M. Attenuated Total Re£ection Infrared Spectroscopy of Proteins and Lipids in Biological Membranes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Rev. Biomembr. 1999, 1422, 105–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surewicz, W.K.; Mantsch, H.H. Review New Insight into Protein Secondary Structure from Resolution-Enhanced Infrared Spectra. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1988, 952, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Ozhukil Kollath, V.; Karan, K. The Key Mechanism of Conductivity in PEDOT:PSS Thin Films Exposed by Anomalous Conduction Behaviour upon Solvent-Doping and Sulfuric Acid Post-Treatment. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2020, 8, 3982–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, T.; Kuwae, A.; Saito, Y.; Machida, K. Normal Vibrations of Benzenesulfonate and Benzene-D5-Sulfonate Ions. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1975, 45, 2231–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, D.G.A.L.; Schmidt, M.; Lekkerkerker, H.N.W. Direct Visual Observation of Thermal Capillary Waves. Science 2004, 304, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malaspina, R.; Alunni Cardinali, M.; Libera, V.; Comez, L.; Petrillo, C.; Paciaroni, A.; Sassi, P.; Valentini, L. Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate-Mediated Self-Assembly of Silk Particles from Formic Acid Solutions into Robust Films. Polymers 2025, 17, 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243277
Malaspina R, Alunni Cardinali M, Libera V, Comez L, Petrillo C, Paciaroni A, Sassi P, Valentini L. Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate-Mediated Self-Assembly of Silk Particles from Formic Acid Solutions into Robust Films. Polymers. 2025; 17(24):3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243277
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalaspina, Rocco, Martina Alunni Cardinali, Valeria Libera, Lucia Comez, Caterina Petrillo, Alessandro Paciaroni, Paola Sassi, and Luca Valentini. 2025. "Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate-Mediated Self-Assembly of Silk Particles from Formic Acid Solutions into Robust Films" Polymers 17, no. 24: 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243277
APA StyleMalaspina, R., Alunni Cardinali, M., Libera, V., Comez, L., Petrillo, C., Paciaroni, A., Sassi, P., & Valentini, L. (2025). Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate-Mediated Self-Assembly of Silk Particles from Formic Acid Solutions into Robust Films. Polymers, 17(24), 3277. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243277







