Polylactic Acid and Polybutylene Succinate Biopolymer Blends for Extrusion Processing: Dry Blending vs. Masterbatch Dilution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Twin-Screw Extrusion Processing
2.3. Single-Screw Extrusion Processing
2.4. Characterizations
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.6. Differential-Scanning Calorimetry
2.7. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.9. Rheological Tests
2.10. Mechanical Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Process-Induced Degradation
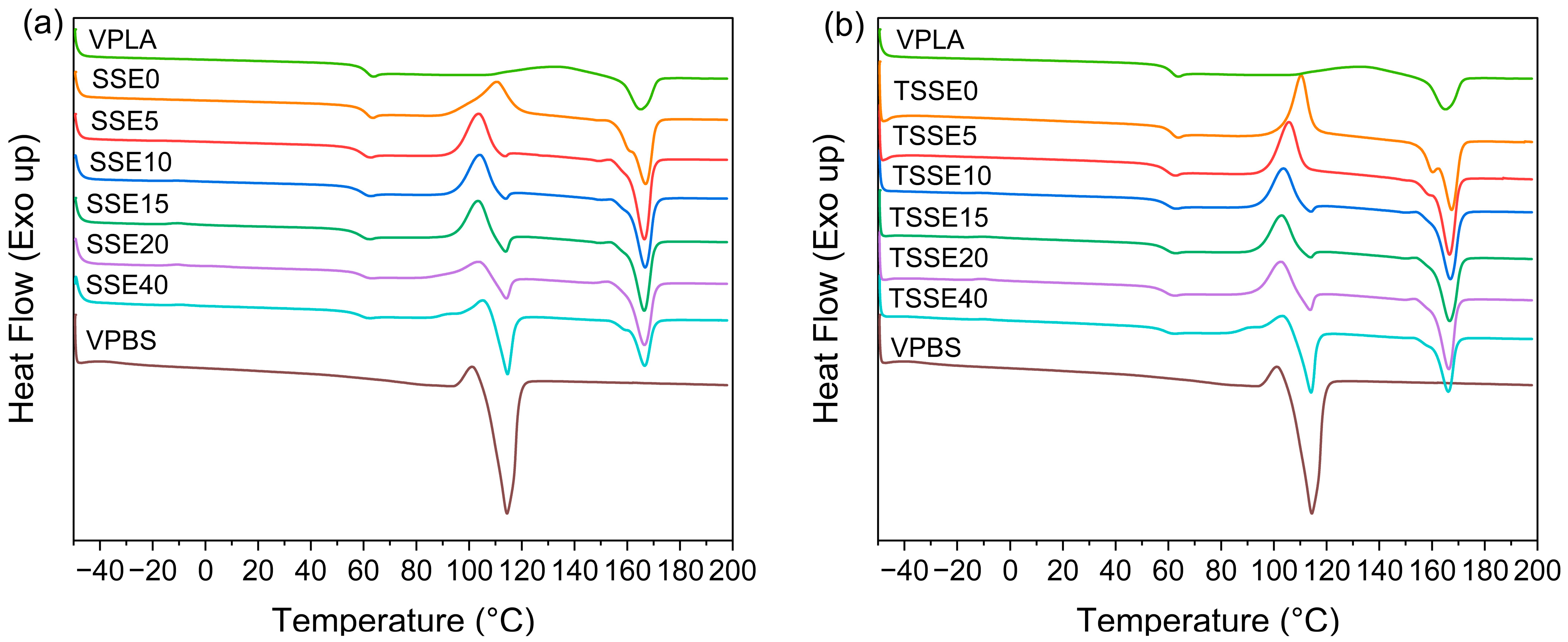
3.2. Thermal Behavior
3.3. XRD Studies
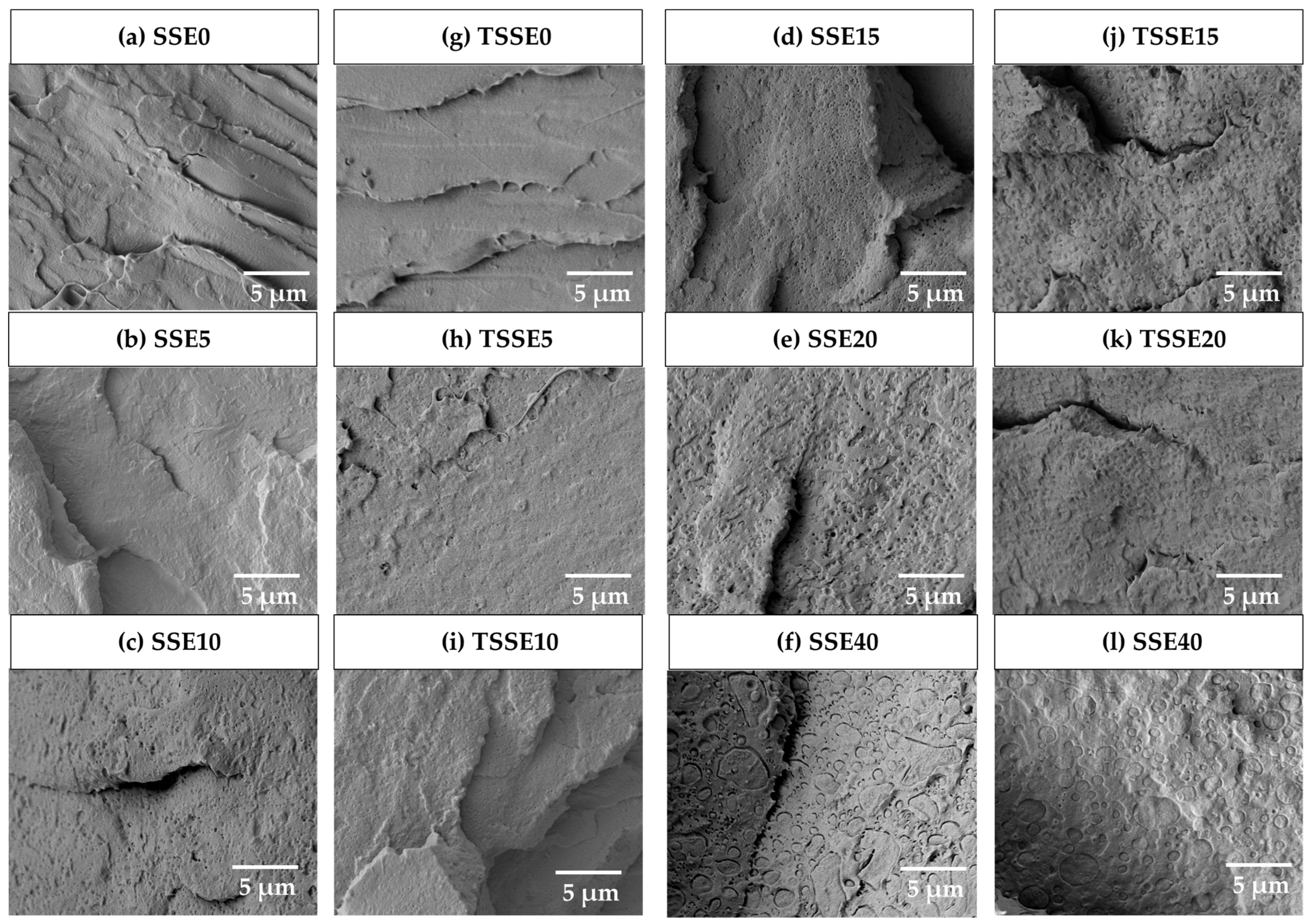
3.4. Chemical Structure and Blend Morphology
3.5. Rheological Analysis of Blend Miscibility
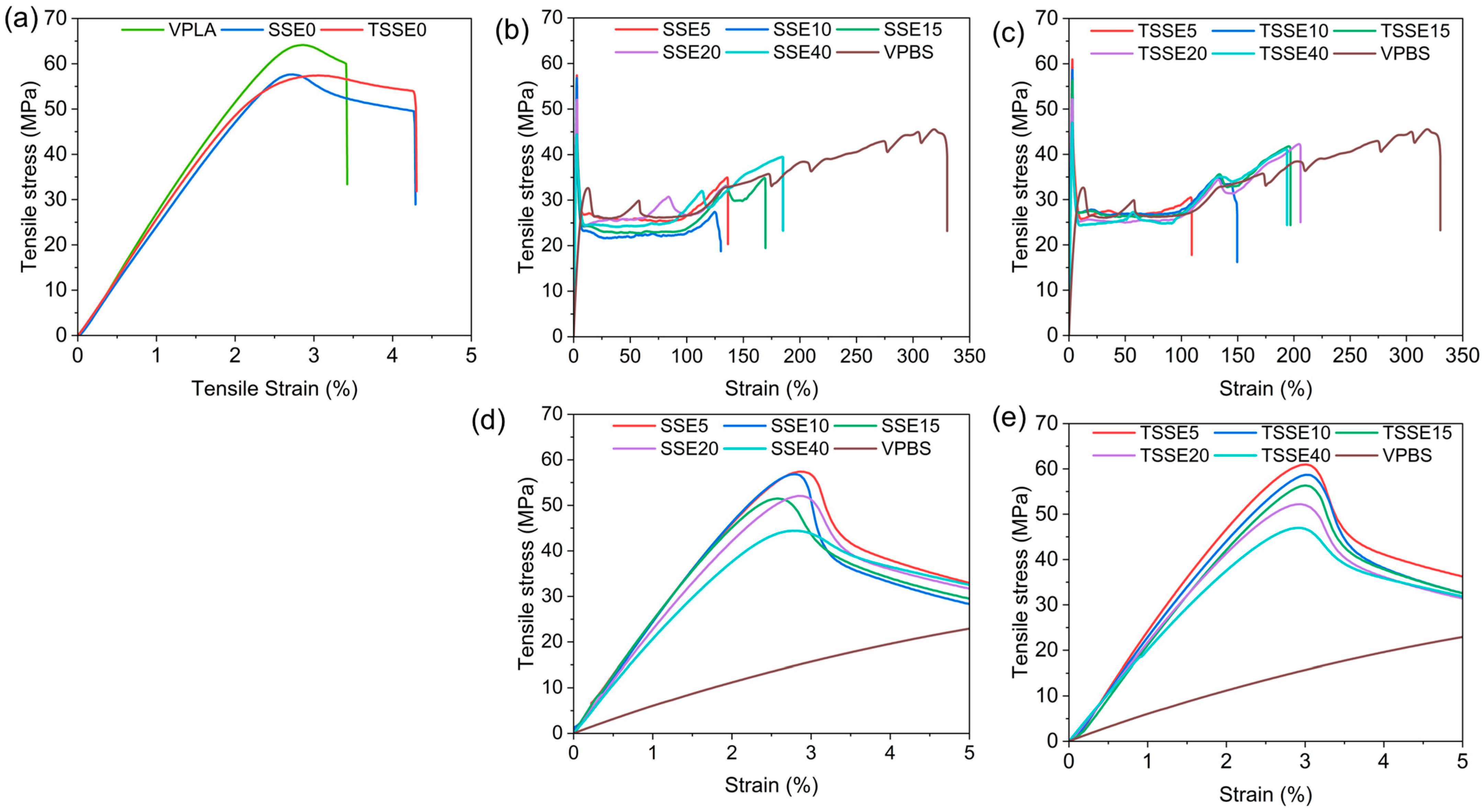
3.6. Mechanical Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taib, N.-A.A.B.; Rahman, M.R.; Huda, D.; Kuok, K.K.; Hamdan, S.; Bakri, M.K.B.; Julaihi, M.R.M.B.; Khan, A. A Review on Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) as a Biodegradable Polymer. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 1179–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Mohanty, A.K. Modification of Brittle Polylactide by Novel Hyperbranched Polymer-Based Nanostructures. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2476–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Zhu, W.; Park, C.B.; Randall, J. Crystallization Kinetics of Linear and Long-Chain-Branched Polylactide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 13789–13798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, T.; Nunes, J.; Lopes, M.A.; Marinho, E.; Proença, M.F.; Lopes, P.E.; Paiva, M.C. Poly(Lactic Acid) Composites with Few Layer Graphene Produced by Noncovalent Chemistry. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 8409–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, V.; De Meo, A.; Pantani, R. Thermal and Hydrolytic Degradation Kinetics of PLA in the Molten State. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 100, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawale, S.; Kalia, K.; Alshammari, S.; Cronin, D.; Zhang, X.; Ameli, A. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Extracted Lignin as an Efficient Additive for Entirely Biobased Polylactic Acid Composites. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 5861–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, S.; Ameli, A. Polylactic Acid Biocomposites with High Loadings of Melt-Flowable Organosolv Lignin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofar, M.; Ameli, A.; Park, C.B. A Novel Technology to Manufacture Biodegradable Polylactide Bead Foam Products. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokohara, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Structure and Properties for Biomass-Based Polyester Blends of PLA and PBS. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S. Polylactide (PLA) and Its Blends with Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS): A Brief Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homklin, R.; Hongsriphan, N. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of PLA/PBS Co-Continuous Blends Adding Nucleating Agent. Energy Procedia 2013, 34, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.; Ma, P. Toughening Modification of PLLA/PBS Blends via in Situ Compatibilization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Thomas, N.L. Blending Poly(Butylene Succinate) with Poly(Lactic Acid): Ductility and Phase Inversion Effects. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 71, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska, J.; Sadurski, W.; Paluch, M.; Tyński, P.; Bogusz, J. The Effect of Poly(Butylene Succinate) Content on the Structure and Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Its Blends with Polylactide. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Duan, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Accelerated Hydrolytic Degradation of Poly (Lactic Acid) Achieved by Adding Poly (Butylene Succinate). Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 1067–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauwendaal, C. Polymer Extrusion; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH Co KG: Munich, Germany, 2014; ISBN 1-56990-516-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, V.; Maia, J.M. Extension-dominated Improved Dispersive Mixing in Single-screw Extrusion. Part 1: Computational and Experimental Validation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, M. Compounding with Single-Screw Extruders. Adv. Polym. Technol. 1997, 16, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwei, S.-P. Distributive Mixing in a Single-Screw Extruder?Evaluation in the Flow Direction. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, T. Enhancement of Mixing Performance of Single-screw Extrusion Processes via Chaotic Flows: Part I. Basic concepts and experimental study. Adv. Polym. Technol. J. Polym. Process. Inst. 1996, 15, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, L.; Mokhtarian, F. Analysis of Mixing in Modified Single Screw Extruders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1983, 23, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.L.; Brown, E.C.; Coates, P.D. The Effect of Screw Geometry on Melt Temperature Profile in Single Screw Extrusion. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Manas-Zloczower, I.; Kaufman, M. Entropic Characterization of Distributive Mixing in Polymer Processing Equipment. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eteläaho, P.; Nevalainen, K.; Suihkonen, R.; Vuorinen, J.; Hanhi, K.; Järvelä, P. Effects of Direct Melt Compounding and Masterbatch Dilution on the Structure and Properties of Nanoclay-filled Polyolefins. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghvami-Panah, M.; Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Seraji, A.A.; Jamalpour, S.; Ghaffarian, S.R.; Park, C.B. LDPE/MWCNT and LDPE/MWCNT/UHMWPE Self-Reinforced Fiber-Composite Foams Prepared via Supercritical CO2: A Microstructure-Engineering Property Perspective. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2021, 174, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, E.; Puglia, D.; Iannoni, A.; Terenzi, A.; Kenny, J.M.; Torre, L. Processing Conditions, Thermal and Mechanical Responses of Stretchable Poly (Lactic Acid)/Poly (Butylene Succinate) Films. Materials 2017, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Yu, L.; Khalid, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Duan, Q.; Chen, L. Preparation, Microstructure and Performance of Poly (Lactic Acid)-Poly (Butylene Succinate-Co-Butyleneadipate)-Starch Hybrid Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 177, 107384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysiukiewicz, O.; Barczewski, M.; Skórczewska, K.; Matykiewicz, D. Correlation between Processing Parameters and Degradation of Different Polylactide Grades during Twin-Screw Extrusion. Polymers 2020, 12, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhafeeri, T.; Alotaibi, M.; Barry, C.F. Impact of Melt Processing Conditions on the Degradation of Polylactic Acid. Polymers 2022, 14, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.G.; Tanifuji, S.; Takahashi, K.; Koyama, K. Mixing Efficiency in a Pin Mixing Section for Single-screw Extruders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Takahashi, K.; Koyama, K.; Yamashita, Y. The Effect of a New Type of Pin Mixing Section on the Performance of a Single-screw Extruder. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, J.; Sugumaar, P.; Wenzel, M.N.; Hill, G.; Wallis, C. Determination of the Carbonyl Index of Polyethylene and Polypropylene Using Specified Area under Band Methodology with ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. e-Polymers 2020, 20, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the Structure of Solution Grown Crystals of Lactide Copolymers by Means of Chemical Reactions. Kolloid-Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, N.; Heuzey, M.C.; Carreau, P.J.; Wood-Adams, P.M. Control of Thermal Degradation of Polylactide (PLA)-Clay Nanocomposites Using Chain Extenders. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velghe, I.; Buffel, B.; Cardinaels, R.; Vandeginste, V.; Thielemans, W.; Desplentere, F. Quantification of PLA Degradation in the Melt Phase Using a Parallel Plate Rheometer. Polym. Test. 2024, 137, 108506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.S.; Fernandes, A.N.; Waldman, W.R. How to Measure Polymer Degradation? An Analysis of Authors’ Choices When Calculating the Carbonyl Index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 7609–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Strömberg, E.; Karlsson, S.; Ribes-Greus, A. Material Valorisation of Amorphous Polylactide. Influence of Thermo-Mechanical Degradation on the Morphology, Segmental Dynamics, Thermal and Mechanical Performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Hernández, T.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R.; González-López, M.E.; Del Campo, A.S.M.; González-Núñez, R.; Rodrigue, D.; Pérez Fonseca, A.A. Mechanical Recycling of PLA: Effect of Weathering, Extrusion Cycles, and Chain Extender. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasselet, D.; Ruellan, A.; Guinault, A.; Miquelard-Garnier, G.; Sollogoub, C.; Fayolle, B. Oxidative Degradation of Polylactide (PLA) and Its Effects on Physical and Mechanical Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 50, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.S.; Yildirim, R.; Kodal, M.; Ozkoc, G. Reactive Compatibilization of PLA / PBS Bio-blends via a New Generation of Hybrid Nanoparticles. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2023, 29, 737–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahtani, M.; Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Gregori, S.; Mielewski, D.F.; Mohanty, A.K. Experimental Design of Sustainable 3D-Printed Poly(Lactic Acid)/Biobased Poly(Butylene Succinate) Blends via Fused Deposition Modeling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14460–14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Shi, J.; Ye, H.; Zhou, Q. Distinctive Tensile Properties of the Blends of Poly(l-Lactic Acid) (PLLA) and Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS). J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Lan, X.; Wu, F.; Xie, B.; Yang, M. Morphology, Rheology, Crystallization Behavior, and Mechanical Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate)/Dicumyl Peroxide Reactive Blends. J Appl. Polym. Sci 2014, 131, app.39580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, D.G.; Chrissafis, K.; Pavlidou, E.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Effect of Nanofiller’s Size and Shape on the Solid State Microstructure and Thermal Properties of Poly(Butylene Succinate) Nanocomposites. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 590, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-T.; Wu, C.-J.; Tsou, C.-H.; Chai, W.-L.; Chow, J.-D.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-N.; Wu, C.-S. Study on the Crystallization, Miscibility, Morphology, Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Blends. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2009, 48, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikish, T.A.; Kumar, A.; Kim, J.Y. Study on the Miscibility of Polypyrrole and Polyaniline Polymer Blends. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3890637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Su, T.; Li, P.; Wang, Z. Blending Modification of PBS/PLA and Its Enzymatic Degradation. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yuan, L.; Laredo, E.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, W. Interfacial Properties, Viscoelasticity, and Thermal Behaviors of Poly(Butylene Succinate)/Polylactide Blend. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassagnau, P.; Michel, A. New Morphologies in Immiscible Polymer Blends Generated by a Dynamic Quenching Process. Polymer 2001, 42, 3139–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, M.; Luca, P. Fourier Transform Rheology: A New Tool to Characterize Material Properties. In Fourier Transforms—New Analytical Approaches and FTIR Strategies; Nikolic, G., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-232-6. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Xue, B.; He, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, G.; Xiong, C. Morphology Evolution of Poly(Lactic Acid) during in Situ Reaction with Poly(Butylenesuccinate) and Ethylene-methyl Acrylate-glycidyl Methacrylate: The Formation of a Novel 3D Star-like Structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed Ullah, M.; Yildirim, R.; Caraseva, L.; Zuza, E.; Ozkoc, G.; Kodal, M. Miscibility and Phase Behavior of Reactively Compatibilized Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Bio-blends Using Various Rheological Analyses. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosate De Andrade, M.F.; Fonseca, G.; Morales, A.R.; Mei, L.H.I. Mechanical Recycling Simulation of Polylactide Using a Chain Extender. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillin, I.; Montrelay, N.; Bourmaud, A.; Grohens, Y. Effect of Thermo-Mechanical Cycles on the Physico-Chemical Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.Y.; Song, M.; Zhao, L.G. Testing, Characterization and Modelling of Mechanical Behaviour of Poly (Lactic-Acid) and Poly (Butylene Succinate) Blends. Mech. Adv. Mater. Mod. Process 2016, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jompang, L.; Thumsorn, S.; On, J.W.; Surin, P.; Apawet, C.; Chaichalermwong, T.; Kaabbuathong, N.; O-Charoen, N.; Srisawat, N. Poly(Lactic Acid) and Poly(Butylene Succinate) Blend Fibers Prepared by Melt Spinning Technique. Energy Procedia 2013, 34, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Bhattacharya, S.N.; Choi, H. Compatibility of Biodegradable Poly (Lactic Acid)(PLA) and Poly (Butylene Succinate)(PBS) Blends for Packaging Application. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2007, 19, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.-L.; Hu, B.; Huang, W.-T.; Chen, L.; Yin, X.-C.; Cao, X.-W.; He, G.-J. Improvement of Rheology and Mechanical Properties of PLA/PBS Blends by in-Situ UV-Induced Reactive Extrusion. Polymer 2022, 259, 125336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
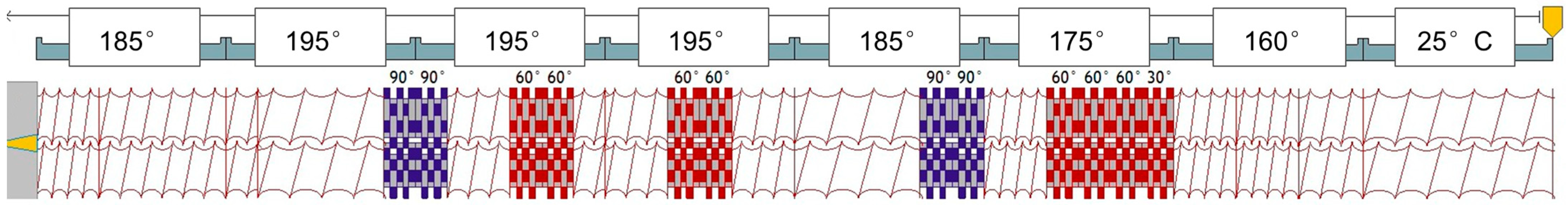





| Zone 1 (°C) | Zone 2 (°C) | Zone 3 (°C) | Zone 4 (°C) | Die (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180 | 195 | 195 | 195 | 190 |
| SSE Route | TSSE Route | PBS Composition (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| SSE0 | TSSE0 | 0 |
| SSE5 | TSSE5 | 5 |
| SSE10 | TSSE10 | 10 |
| SSE15 | TSSE15 | 15 |
| SSE20 | TSSE20 | 20 |
| SSE40 | TSSE40 | 40 |
| Sample | (kDa) | (kDa) | Polydispersity, PDI | (Pa.s) | Carbonyl Index, CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPLA | 179.6 ± 4.9 | 82.5 ± 4.9 | 2.19 ± 0.17 | 591 ± 67 | 4.6 ± 0.3 |
| SSE0 | 176.9 ± 4.6 | 81.9 ± 4.1 | 2.17 ± 0.13 | 549 ± 84 | 4.9 ± 0.2 |
| TSSE0 | 146.1 ± 14 | 82.2 ± 1.6 | 1.93 ± 0.21 | 343 ± 19 | 5.8 ± 0.3 |
| Processing-PBS (wt.%) | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Hcc (J/g) | Tm (°C) | Normalized Hm (J/g) | Xc (%) First Scan | Xc (%) Second Scan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPLA | 60 | 120 | 17.4 | 165 | 17.5 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| SSE/TSSE0 | 59.8/60.3 | 110/110 | 28.6/27.9 | 167/167 | 30.7/30.9 | 5.3/7.3 | 2.3/3.3 |
| SSE/TSSE5 | 58.0/58.7 | 104/106 | 22.3/27.6 | 167/167 | 30.3/30.9 | 10.9/11.2 | 9.1/3.7 |
| SSE/TSSE10 | 58.4/58.7 | 104/103 | 22/21.3 | 167/167 | 27.0/28 | 10.3/13.3 | 6.0/8.1 |
| SSE/TSSE15 | 58.2/58.7 | 104/102 | 18.5/20.1 | 166/166 | 26.3/27.1 | 10.8/18.2 | 9.8/9 |
| SSE/TSSE20 | 58.7/58.7 | 104/102 | 10.3/17.7 | 166/166 | 25.2/25.5 | 16.4/14.6 | 20.0/10.5 |
| SSE/TSSE40 | 58.2/58.2 | 105/104 | 9.1/11.5 | 166/166 | 17.9/19 | 9.0/17 | 15.7/13.4 |
| VPBS | −33.8 | 100 | 5.57 | 114 | 59.4 | 49.7 | 48.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azami, M.; Maurya, A.K.; Nagarajan, R.; Ameli, A. Polylactic Acid and Polybutylene Succinate Biopolymer Blends for Extrusion Processing: Dry Blending vs. Masterbatch Dilution. Polymers 2025, 17, 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233117
Azami M, Maurya AK, Nagarajan R, Ameli A. Polylactic Acid and Polybutylene Succinate Biopolymer Blends for Extrusion Processing: Dry Blending vs. Masterbatch Dilution. Polymers. 2025; 17(23):3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233117
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzami, Milad, Atul Kumar Maurya, Ramaswamy Nagarajan, and Amir Ameli. 2025. "Polylactic Acid and Polybutylene Succinate Biopolymer Blends for Extrusion Processing: Dry Blending vs. Masterbatch Dilution" Polymers 17, no. 23: 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233117
APA StyleAzami, M., Maurya, A. K., Nagarajan, R., & Ameli, A. (2025). Polylactic Acid and Polybutylene Succinate Biopolymer Blends for Extrusion Processing: Dry Blending vs. Masterbatch Dilution. Polymers, 17(23), 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233117








