Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Praseodymium Doped Zinc Ferrite Composites as Promising Polyelectrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Proton Exchange Membranes Preparation
2.2.1. Sulfonation of PEEK
2.2.2. Synthesis of ZnFe1.96Pr0.04O4
2.2.3. SPEEK and Composite Membranes Casting
2.3. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. PEEK Sulfonation
3.2. Doped Zinc Ferrite
3.3. Composite Membranes
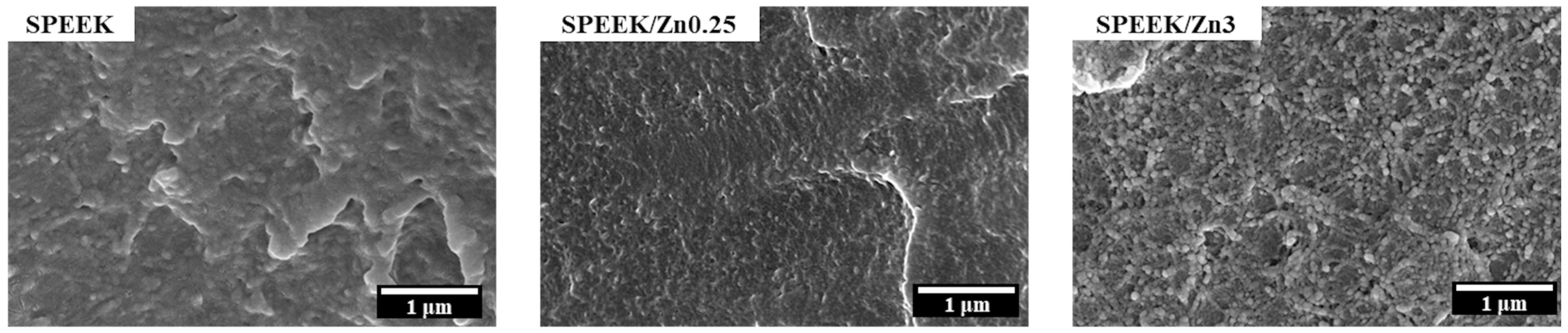
3.3.1. Membrane Morphology
3.3.2. Ionic Exchange and Water Uptake Capacities
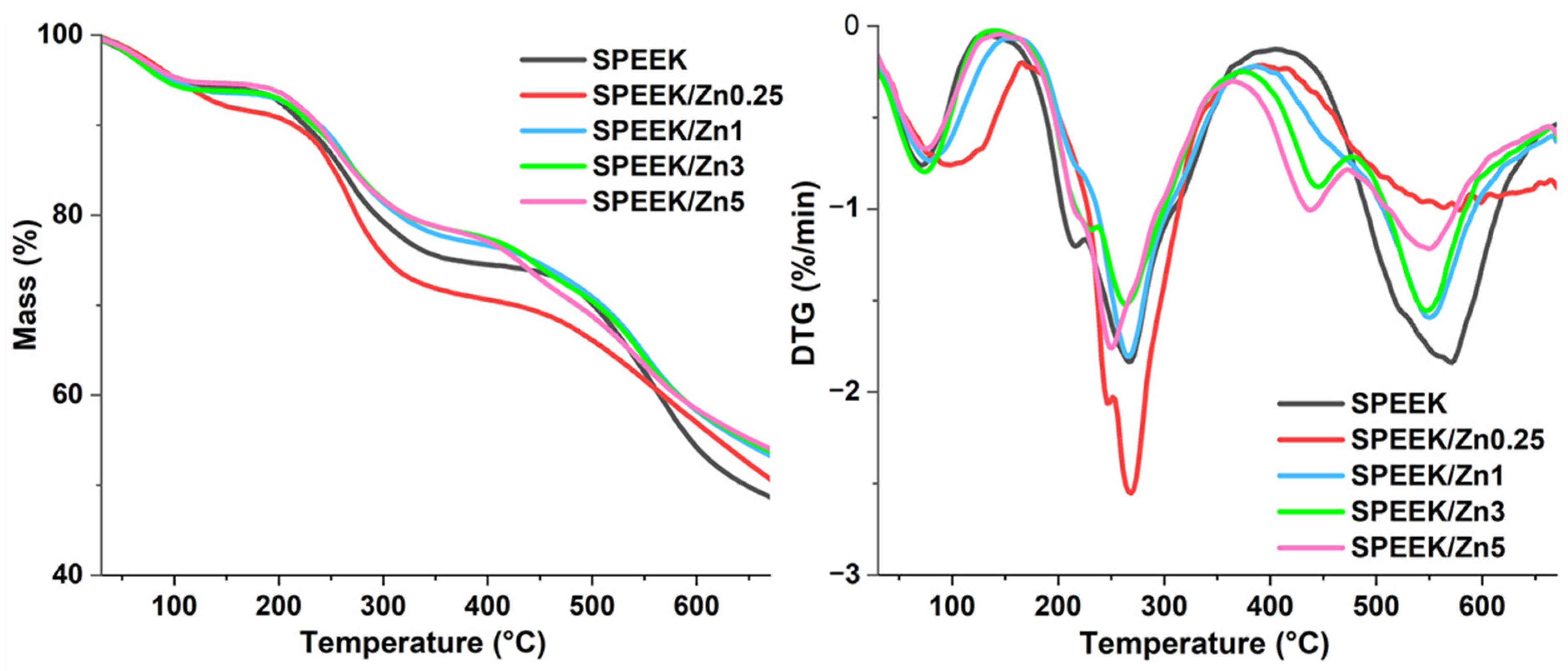
3.3.3. Oxidative Stability of Membranes
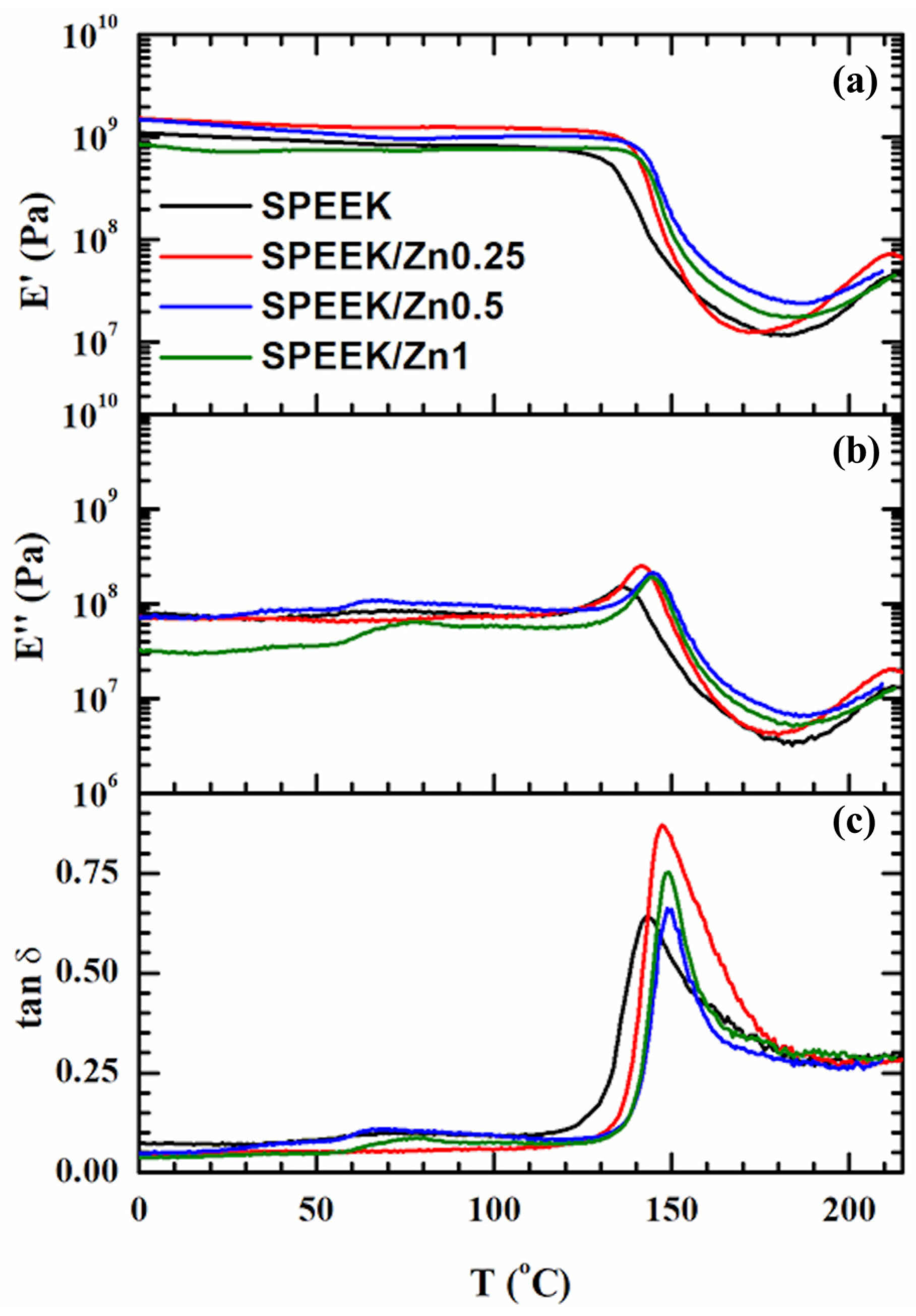
3.3.4. Thermo-Mechanical Properties
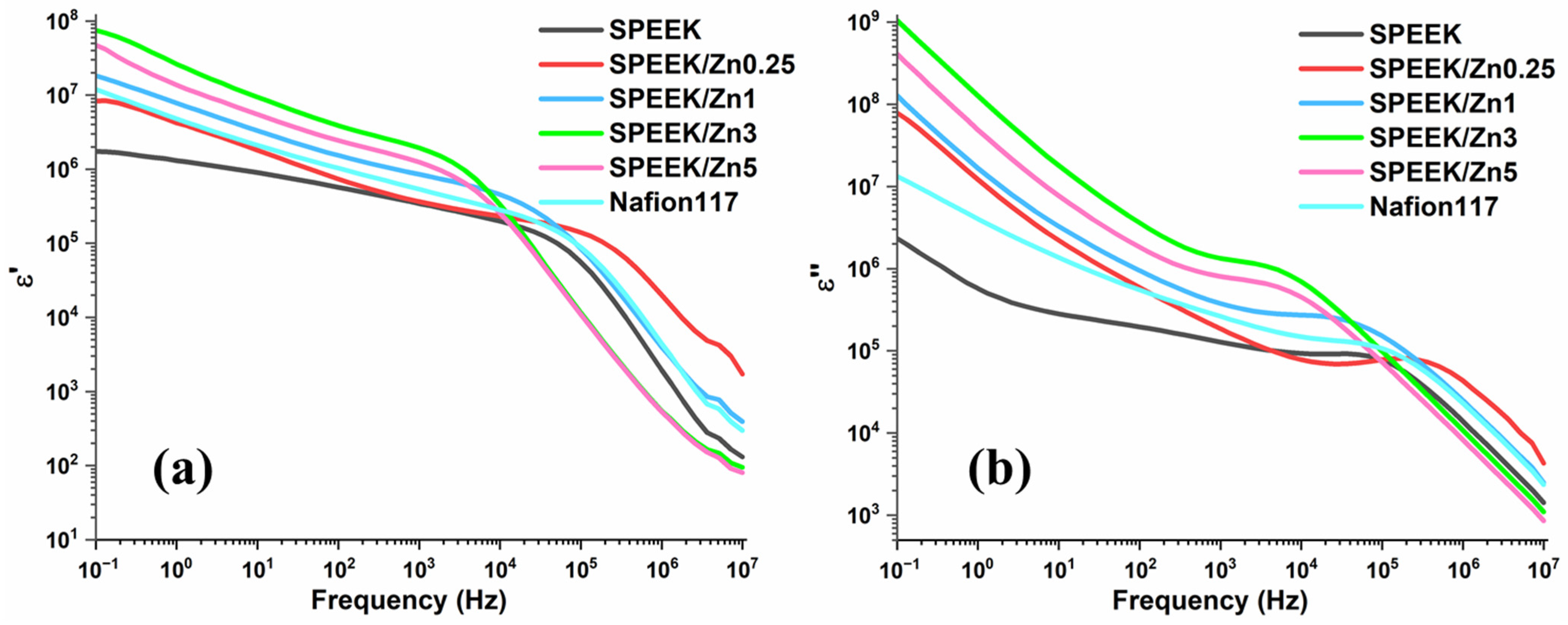
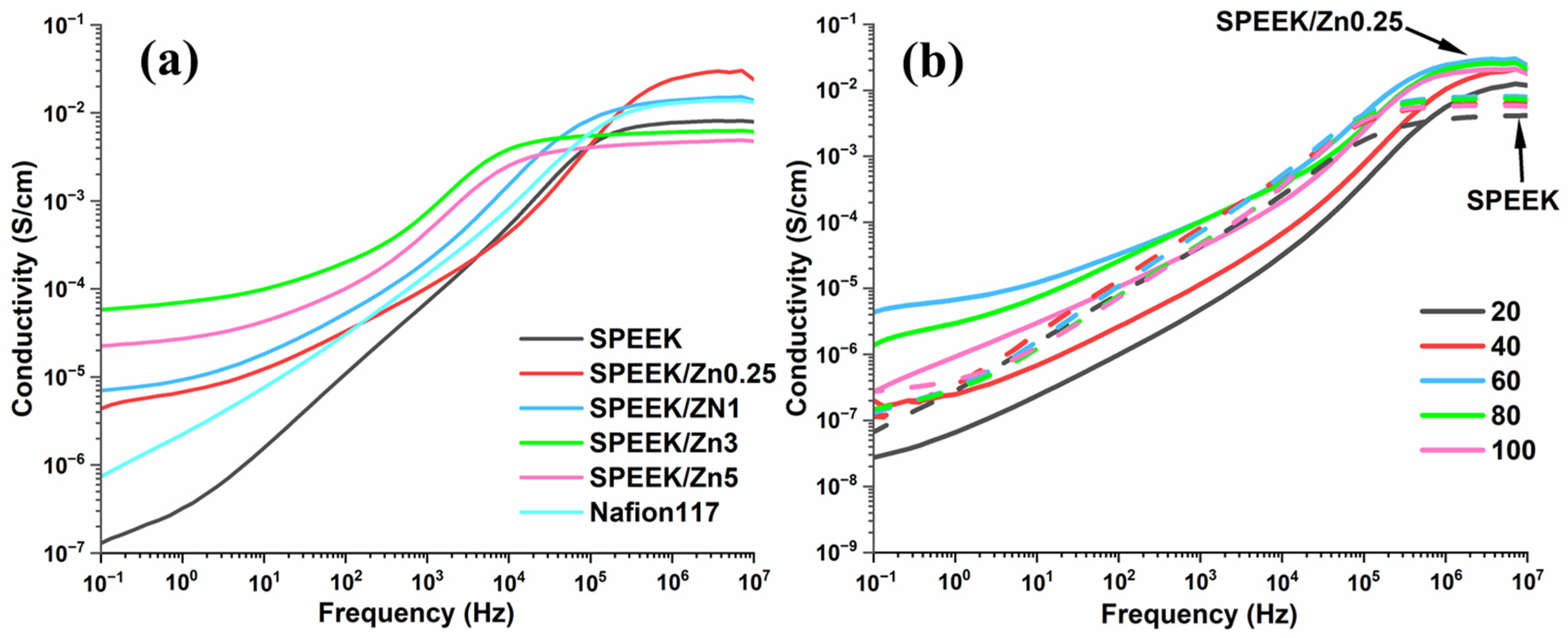
3.3.5. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devanathan, R. Recent Developments in Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D.; Paddison, S.J.; Spohr, E.; Schuster, M. Transport in Proton Conductors for Fuel-Cell Applications: Simulations, Elementary Reactions, and Phenomenology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4637–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, D.E.; Lousenberg, R.D.; Henry, T.J.; Tangeman, P.C.; Tisack, M.E. Advanced Materials for Improved PEMFC Performance and Life. J. Power Sources 2004, 131, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.E.; Jang, S.; Seo, D.J.; Hwang, J.; Seo, M.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Kim, W.B. A Reinforced Composite Membrane of Two-Layered Asymmetric Structure with Nafion Ionomer and Polyethylene Substrate for Improving Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.J.; Lai, J.Y.; Liu, Y.L. Nanohybrids of Graphene Oxide Chemically-Bonded with Nafion: Preparation and Application for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 514, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of Understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickner, M.A.; Ghassemi, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Einsla, B.R.; McGrath, J.E. Alternative Polymer Systems for Proton Exchange Membranes (PEMs). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4587–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Rafidah, R.S.; Rashmi, W.; Khalid, M.; Wong, W.Y.; Priyanka, J. Recent Progress in the Development of Aromatic Polymer-Based Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xue, H.; Wang, Q.; Jia, L. Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether)s Based Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 31727–31753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S.C.; Adroher, X.C. A Review of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: Technology, Applications, and Needs on Fundamental Research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiston, M.M.; Azevedo, I.L.; Litster, S.; Whitefoot, K.S.; Samaras, C.; Whitacre, J.F. Expert Assessments of the Cost and Expected Future Performance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells for Vehicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4899–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.M.; Shao, P.; Burns, C.M.; Feng, X. Sulfonation of Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)(PEEK): Kinetic Study and Characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollá, S.; Compañ, V. Nanocomposite SPEEK-Based Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells at Intermediate Temperatures. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 492, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yin, J.; Liu, M.; Tolj, I.; Grigoriev, S.A.; Ge, M.; Sun, C. Investigations of the Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Membranes with Various Degrees of Sulfonation by Considering Durability for the Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Xing, Z.; Wang, S. Multiple Hydrogen Bond Systems Boosting High Proton Conductivity of the Comb-Shaped Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Proton Exchange Membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 8535–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokprasert, A.; Theato, P.; Chirachanchai, S. Proton Donor/Acceptor Copolymer Brushes on Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Membrane: An Approach to Construct Efficient Proton Transfer Pathway in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. Polymer 2022, 240, 124523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Guo, H.; Sun, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhi, X.; Li, Z. N-Substitute Polyphosphazenes Cross-Linked Hydroxyl-Terminated SPEEK High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane to Achieve High Proton Conductivity over Low Relative Humidity. J. Memb. Sci. 2023, 666, 121159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Cheng, F.; Zheng, G.; Wen, S.; Law, W.C.; Tsui, C.P.; Tang, C.Y. A New Strategy for Designing High-Performance Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Using Inorganic Proton Conductor-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Power Sources 2016, 325, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjola, A.; Escorihuela, J.; Andrio, A.; Giménez, E.; Compañ, V. Enhanced Conductivity of Composite Membranes Based on Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) with Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIFs). Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Duan, J.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Li, X. Improving the Proton Conductivity of Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) Membranes by Incorporating a Crystalline Nanoassembly of Trimesic Acid and Melamine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 29883–29891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjola, A.; Reyes-Rodríguez, J.L.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Giménez, E.; Compañ, V. Novel SPEEK-ZIF-67 Proton Exchange Nanocomposite Membrane for PEMFC Application at Intermediate Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 9107–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, P.; Gayathri, R.; Pugalenthi, M.R.; Cao, G.; Liu, C.; Prabhu, M.R. Nanosulfonated Silica Incorporated SPEEK/SPVdF-HFP Polymer Blend Membrane for PEM Fuel Cell Application. Ionics 2020, 26, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Pugalenthi, M.; Gayathri, R.; Cao, G.; Ramesh Prabhu, M. Study of Amine Customized Exfoliated BN Sheets in SPEEK-PES Based Blend Membrane for Acid-Base Cation Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 10, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Poudel, M.B.; Chu, J.Y.; Vinothkannan, M.; Santhosh Kumar, R.; Logeshwaran, N.; Park, B.-H.; Han, M.-K.; Yoo, D.J. Advanced Performance and Ultra-High, Long-Term Durability of Acid-Base Blended Membranes over 900 Hours Containing Sulfonated PEEK and Quaternized Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) in H2/O2 Fuel Cells. Compos. B Eng. 2023, 254, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalı, A.; Şahin, A.; AR, İ. Experimental Investigation of Boron Phosphate Incorporated SPEEK/PVDF Blend Membrane for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 40476–40490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.S.; Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.Y.; So, S.; Yu, D.M. Sulfonated Poly(p-Phenylene)-Based Ionomer/PTFE Composite Membrane with Enhanced Performance and Durability for Energy Conversion Devices. J. Power Sources 2023, 580, 233422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Sharma, Y. Integrated Proton Transport Architecture in Fiber-Reinforced Sulfonated Membrane for High-Performance Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. J. Power Sources 2025, 653, 237763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haragirimana, A.; Li, N.; Hu, Z.; Chen, S. A Facile, Effective Thermal Crosslinking to Balance Stability and Proton Conduction for Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Blend Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 15866–15877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagizatli, Y.; Sahin, A.; Ar, I. Effect of Thermal Crosslinking Process on Membrane Structure and PEM Fuel Cell Applications Performed with SPEEK-PVA Blend Membranes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 40445–40461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.; Lee, D.; Bae, I. Dual-Crosslinked Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) Membranes with Isophthalic Acids for Enhanced Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2025, 633, 236450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Trindade, L.G.; Zanchet, L.; Martins, P.C.; Borba, K.M.N.; Santos, R.D.M.; Paiva, R.D.S.; Vermeersch, L.A.F.; Ticianelli, E.A.; de Souza, M.O.; Martini, E.M.A. The Influence of Ionic Liquids Cation on the Properties of Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone)/Polybenzimidazole Blends Applied in PEMFC. Polymer 2019, 179, 121723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, A.; Al-Ahmed, A. Nanomaterial-Incorporated Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) Based Proton-Conducting Membranes: Properties and Applications. In Advanced Nanomaterials for Membrane Synthesis and Its Applications; Lau, W.-J., Ismail, A.F., Isloor, A., Al-Ahmed, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 227–252. ISBN 978-0-12-814503-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Sui, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, B.; Cong, C.; Meng, X.; Zhou, Q. Sandwich-Structure PI/SPEEK/PI Proton Exchange Membrane Developed for Achieving the High Durability on Excellent Proton Conductivity and Stability. J. Memb. Sci. 2022, 644, 120116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul Joseph Helen Therese, J.B.; Gayathri, R.; Selvakumar, K.; Li, W.; Fu, Y.; Manthiram, A. Fabrication of Proton Exchange Membranes and Effect of Sulfonated SiO2 (S-SiO2) in Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone (SPEEK) for Fuel Cells Applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 577, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Maranesi, B.; Chailan, J.F.; Khadhraoui, M.; Polini, R.; Di Vona, M.L.; Knauth, P. Crosslinked SPEEK Membranes: Mechanical, Thermal, and Hydrothermal Properties. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Woo, H.S.; Won Shin, D.; Sohn, J.Y.; Moo Lee, Y.; Shin, J. EB-Crosslinked SPEEK Electrolyte Membrane with 1,4-Butanediol Divinyl Ether/Triallyl Isocyanurate for Fuel Cell Application. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 469, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, V.R.; Rath, S.K.; Rao, S.; Patri, M. Cross-Linked Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK)/Reactive Organoclay Nanocomposite Proton Exchange Membranes (PEM). J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 372, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, G.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Lew, C.M.; Na, H. Considerations of the Morphology in the Design of Proton Exchange Membranes: Cross-Linked Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)s Using a New Carboxyl-Terminated Benzimidazole as the Cross-Linker for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Sun, J.; Ge, J.; Wang, C.; Hu, P.; Liu, Y. Cross-Linked Proton Exchange Membrane Covalently Bonded with Silicotungstic Acid for Enhanced Proton Conductivity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 141, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Liu, L.; Min, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Enhanced Proton Conductivity of Nafion Membrane with Electrically Aligned Sulfonated Graphene Nanoplates. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 17784–17792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulakrishnan, S.A.; Kumar, V.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J. Thermally Stable Nanoclay and Functionalized Graphene Oxide Integrated SPEEK Nanocomposite Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Application. Fuel 2022, 329, 125407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourasi, M.; Wills, R.G.A.; Shah, A.A.; Walsh, F.C. Heteropolyacids for Fuel Cell Applications. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 127, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wei, Z.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Grigoriev, S.A. In-Situ Sulfonation of Targeted Silica-Filled Nafion for High-Temperature PEM Fuel Cell Application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29711–29716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourzare, K.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Farhadi, S.; Hasani Sadrabadi, M.M.; Frost, I.; Ulbricht, M. Improving the Efficiency of Nafion-Based Proton Exchange Membranes Embedded with Magnetically Aligned Silica-Coated Co3O4 Nanoparticles. Solid State Ion. 2020, 351, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Lin, B.; Qiu, B.; Si, Z.; Qiu, L.; Gu, Z.; Ding, J.; Yan, F.; Lu, J. Polybenzimidazole/Zwitterion-Coated Silica Nanoparticle Hybrid Proton Conducting Membranes for Anhydrous Proton Exchange Membrane Application. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18411–18417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rong, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q. High Performance Proton Exchange Membranes with Double Proton Conduction Pathways by Introducing MOF Impregnated with Protic Ionic Liquid into SPEEK. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 346, 112314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Jin, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, K.; Li, W.; et al. Triazine-Rich Covalent Organic Framework Composited Proton Exchange Membranes for Flexible Operating Temperature and Enhanced Long-Term Stability Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2025, 632, 236351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, S.; Gao, K.; Cai, J.J.; Han, J.; Nie, Y.; Lun, H.J.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.M. Covalent Integration of NH2-MIL-53(Al) into SPEEK for Enhanced Proton Exchange Membrane Performance. J. Power Sources 2025, 638, 236574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-hua, T.; Peng-fei, G.; Zhi-yuan, Z.; Wen-hui, L.; Zhong-qiang, S. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of a Nafion-TiO2 Composite Membrane for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 5686–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, L.V.; Choi, E.; Jang, S.; Kim, S.M. Patterned Mesoporous TiO2 Microplates Embedded in Nafion® Membrane for High Temperature/Low Relative Humidity Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Operation. Renew. Energy 2021, 180, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizov, V.E.; Zefirov, V.V.; Abramchuk, S.S.; Korlyukov, A.A.; Kondratenko, M.S.; Vasil’ev, V.G.; Gallyamov, M.O. Composite Nafion-Based Membranes with Nanosized Tungsten Oxides Prepared in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 609, 118244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humelnicu, A.C.; Samoila, P.; Asandulesa, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Bele, A.; Marinoiu, A.T.; Sacca, A.; Harabagiu, V. Chitosan-Sulfated Titania Composite Membranes with Potential Applications in Fuel Cell: Influence of Cross-Linker Nature. Polymers 2020, 12, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoila, P.; Grecu, I.; Asandulesa, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Harabagiu, V. Bio-Based Ionically Cross-Linked Alginate Composites for PEMFC Potential Applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 165, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.N.; Devi, N.; Chen, Y.S.; Sharma, M.; Singh, P. High-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membranes: Proton Conductivity and Performance of Polybenzimidazole/Ti0.9Mn0.1P2O7. J. Power Sources 2025, 645, 237172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, T.; Meng, X.; He, D.; Li, L.; Song, K.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. Advances in the Application of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) and Its Organic Composite Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Polymers 2024, 16, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; He, H.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S. Fabrication of an Ultra-Thin and Ordered SPEEK Proton Exchange Membrane by a Langmuir-Blodgett Self-Assembly Process. J. Memb. Sci. 2024, 690, 122196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Huang, D.; Luo, C.; Sui, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, B.; Cong, C.; Zhou, Q.; Meng, X. High-Performance Sandwich-Structure PI/SPEEK+HPW Nanofiber Composite Membrane with Balanced Proton Conductivity and Stability. Polymer 2023, 271, 125800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.H.; Thiam, H.S.; Tee, S.F.; Lim, Y.S.; Saw, L.H.; Lai, S.O. Self-Healing Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)-Based Polymer Electrolyte Membrane for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells: Effect of Solvent Content. Polymers 2023, 15, 4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Basem, A.; Jasim, A.S.; Jasim, D.J.; Azam, A.; Rizvi, S.J.A.; AlBahadli, Y.A.; Abdulameer, M.H. Optimization of SPEEK/S-TiO2 Nanocomposite Membranes Using Response Surface Methodology for Low-Temperature Fuel Cell. RINENG 2024, 24, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, T.; Liu, W.; Meng, G.; Guo, W.; Grigoriev, S.A.; He, D.; Sun, C. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)–Zirconia Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Membranes with Enhanced Ion Selectivity and Hydrophilicity for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. Polymers 2025, 17, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Kujawski, W. Different Approaches for the Preparation of Composite Ionic Liquid-Based Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Applications-Recent Advancements. Membranes 2023, 13, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulwahab, K.O.; Khan, M.M.; Jennings, J.R. Ferrites and Ferrite-Based Composites for Energy Conversion and Storage Applications. Crit. Rev. Solid. State. Mater. Sci. 2024, 49, 807–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Akanksha; Sheetal; Thakur, S.; Kumar, V.; Pani, B.; Singh, M.; Singh, A.K. A Critical Review on Nano Ferrites Pioneering a Paradigm Shift in Corrosion Inhibition towards Different Metal/Alloys in Diverse Corrosive Environments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.; Okba, E.A.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Elshami, F.I.; Shaban, S.Y. A Kinetic and Mechanistic Study of Chitosan-Functionalized Lanthanum Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles: Balancing Biomolecular Affinity with Anticancer, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Functions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 181, 115230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagesan, S.; Hashim, M.; Aziz, S.A.B.; Ismail, I.; Tamilselvan, S.; Alitheen, N.B.; Swamy, M.K.; Chandra Rao, B.P. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Cytotoxicity Activities of Copper Ferrite (CuFe2O4) and Zinc Ferrite (ZnFe2O4) Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol-Gel Self-Combustion Method. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltag, L.; Cojocaru, C.; Enache, A.C.; Samoila, P.; Harabagiu, V. Ultrasonic-Assisted Rapid Preparation of Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) and Its Testing in Adsorption of Cationic Species from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2022, 15, 7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoila, P.; Baltag, L.; Cojocaru, C.; Ignat, M.; Harabagiu, V. Quick Process for Poly(Aryl-Ether)Ketone Sulphonation 2021, RO134943A2. Available online: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/076070108/publication/RO134943A2?q=RO134943A2 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Ignat, M.; Rotaru, R.; Samoila, P.; Sacarescu, L.; Timpu, D.; Harabagiu, V. Relationship between the Component Synthesis Order of Zinc Ferrite–Titania Nanocomposites and Their Performances as Visible Light-Driven Photocatalysts for Relevant Organic Pollutant Degradation. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, A.R.; Gnana Kumar, G.; Yoon, J.M.; Yoo, D.J. Toward Improved Mechanical Strength, Oxidative Stability and Proton Conductivity of an Aligned Quadratic Hybrid (SPEEK/FPAPB/Fe3O4-FGO) Membrane for Application in High Temperature and Low Humidity Fuel Cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39034–39048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AfterMath Electrochemical Studio 1.6.10523|Pine Research Instrumentation. Available online: https://pineresearch.com/downloads/aftermath-1-6-10523/ (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Pourzare, K.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Farhadi, S. Advanced Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Biofuel 2016, 3, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotunjanu, S.; Racoviceanu, R.; Gogulescu, A.; Mioc, A.; Milan, A.; Marangoci, N.L.; Dascălu, A.I.; Mioc, M.; Negrea-Ghiulai, R.; Trandafirescu, C.; et al. Newly Synthesized CoFe2−yPryO4 (y = 0; 0.01; 0.03; 0.05; 0.1; 0.15; 0.2) Nanoparticles Reveal Promising Selective Anticancer Activity Against Melanoma (A375), Breast Cancer (MCF-7), and Colon Cancer (HT-29) Cells. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatineanu, T.; Diana, E.; Nica, V.; Oancea, V.; Caltun, O.F.; Iordan, A.R.; Palamaru, M.N. The Influence of the Chelating/Combustion Agents on the Structure and Magnetic Properties of Zinc Ferrite. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2012, 10, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoila, P.; Cojocaru, C.; Cretescu, I.; Stan, C.D.; Nica, V.; Sacarescu, L.; Harabagiu, V. Nanosized Spinel Ferrites Synthesized by Sol-Gel Autocombustion for Optimized Removal of Azo Dye from Aqueous Solution. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 713802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pund, S.N.; Nagwade, P.A.; Nagawade, A.V.; Thopate, S.R.; Bagade, A.V. Preparation Techniques for Zinc Ferrites and Their Applications: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 2194–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, S.M.; Chandekar, K.V.; Badwaik, D.S.; Warhate, V.V.; Gahane, N.M.; Daf, S.R. Structural, Surface, Magnetic, and Dielectric Properties of Ni0.3Cu0.3Zn0.4Fe1.4Cr0.6O4 Spinel Ferrite Nanocrystals Prepared by Sol-Gel Auto Combustion Route. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 156, 111204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Khalid, M.; Kareem Khan, J.; Younas, M.; Ashiq, M.G.B.; Kebaili, I.; Naz, K.; Ahmed, Z.; Ahmed, A.; Bashir, S. Physical Properties of Pr3+ Substituted Zinc Spinel (ZnPrxFe2−xO4) Nanoferrites Synthesized via Sol–Gel Auto-Combustion Route. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 168, 112856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.C.; Kim, D. Porous PTFE Reinforced SPEEK Proton Exchange Membranes for Enhanced Mechanical, Dimensional, and Electrochemical Stability. Polymer 2021, 218, 123506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Wang, H.; Benziger, J. Transport of Liquid Water through Nafion Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 392–393, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.; Cooney, J.D.; Wiles, D.M. The Thermal Degradation of Poly(Aryl—Ether—Ether—Ketone) (PEEK) as Monitored by Pyrolysis—GC/MS and TG/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1990, 18, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, A.; Legras, R. Thermal Stability and Crystallization of Poly(Aryl Ether Ether Ketone). Polymer 1991, 32, 2691–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sean, N.A.; Chandren, S.; Jaafar, J.; Othman, M.H.D.; Nur, H. Tailoring the Oxidative Stability of Magnetically Oriented Polybenzimidazole-Based Membrane and Proton Conductivity Performances for Fuel Cell Applications. J. Power Sources 2025, 654, 237884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Chávez, M.E.; Hernández, M.; Picken, S.J.; Kelder, E.M. Optimisation of Proton-Conducting SPEEK Membranes through a Thermal Treatment Method Monitored by Dielectric Spectroscopy. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Shin, J.; Sohn, J.Y.; Nho, Y.C. Ionic Aggregation Characterization of Sulfonated PEEK Ionomers Using by X-Ray and DMA Techniques. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.A.; Cable, K.M.; Moore, R.B. Molecular Origins of the Thermal Transitions and Dynamic Mechanical Relaxations in Perfluorosulfonate Ionomers. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 6472–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, M.; Ionita, D.; Hulubei, C.; Timpu, D.; Popovici, D.; Simionescu, B.C. Chain Packing versus Chain Mobility in Semialiphatic BTDA-Based Copolyimides. Polymer 2011, 52, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D. On the Development of Proton Conducting Polymer Membranes for Hydrogen and Methanol Fuel Cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2001, 185, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Shahriar, M.; Islam, M.T.; Teo, S.H.; Khan, M.A.R.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Mohanta, S.C.; Rehan, A.I.; Rasee, A.I.; Kubra, K.T.; et al. Advances in Filler-Crosslinked Membranes for Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Sustainable Energy Generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 140, 745–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Duan, J.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Li, X. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Doped with Ammonium Ionic Liquids and Nano-Silicon Dioxide for Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Polymers 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Negro, E.; Vezzù, K.; Pagot, G.; Cavinato, G.; Nale, A.; Herve Bang, Y.; Di Noto, V. Hybrid Inorganic-Organic Proton-Conducting Membranes Based on SPEEK Doped with WO3 Nanoparticles for Application in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 309, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Schaetzel, P.; Lixon-Buquet, C.; Colasse, L.; Ratieuville, V.; Marais, S. Proton Exchange Membranes from Sulfonated Polyetheretherketone and Sulfonated Polyethersulfone-Cardo Blends: Conductivity, Water Sorption and Permeation Properties. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 111, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramly, N.N.; Aini, N.A.; Sahli, N.; Aminuddin, S.F.; Yahya, M.Z.A.; Ali, A.M.M. Dielectric Behaviour of UV-Crosslinked Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) with Methyl Cellulose (SPEEK-MC) as Proton Exchange Membrane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9284–9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Kang, J.; Yang, S.; Lu, M.; Wei, H. Influence of Structure Construction on Water Uptake, Swelling, and Oxidation Stability of Proton Exchange Membranes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 279–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Pugalenthi, M.; Punyawudho, K.; Anbu Arasi, M.; Shah, A.A.; Ramesh Prabhu, M.; Kouthaman, M.; Velsankar, K.; Gayathri, R. Designing High Performance Electrospuned SPEEK Nanofibers Composite Membrane for PEMFC Application. Mater. Lett. 2023, 339, 134117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, K.; Raja Pugalenthi, M.; Ramesh Prabhu, M. Investigation on SPEEK/PAI/SrTiO3-Based Nanocomposite Membrane for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Ionics 2019, 25, 5177–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarizadeh, P.; Bagheri, A.; Beydaghi, H.; Hooshyari, K. Enhanced Properties of SPEEK with Incorporating of PFSA and Barium Strontium Titanate Nanoparticles for Application in DMFCs. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 4840–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhao, J.; Su, B.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Mu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; et al. Preparation and Study on H–MoS2/SLS Modified SPI@SPEEK Blend Proton Exchange Membrane with Balanced Proton Conductivity and Stability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 72, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harameen, H.M.A.; Akay, R.G. Investigation into the Influence of Boron Nitride Addition on the Properties of SPEEK/PBI Based Electrolyte Membrane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 54, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.C.; Teixeira, A.P.S.; Rangel, C.M. New Modified SPEEK-Based Proton Exchange Membranes. Polymers 2025, 17, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | IEC (meq/g) | WU% a (25 °C) | WU% a (80 °C) | λ b (H2O/SO3H) | Weight Loss (%) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPEEK | 1.71 | 24.0 | 44.2 | 7.79 | 0.8 |
| SPEEK/Zn0.25 | 1.67 | 24.5 | 40.2 | 8.14 | 1.2 |
| SPEEK/Zn1 | 1.69 | 25.3 | 41.6 | 8.31 | 1.0 |
| SPEEK/Zn3 | 1.78 | 25.8 | 32.1 | 8.05 | 0.9 |
| SPEEK/Zn5 | 1.80 | 26.3 | 32.6 | 8.11 | 0.9 |
| Sample | Water | Sulfonic Acid Groups | Polymer Backbone | Residual Mass % (at 670 °C) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tpeak (°C) | Mass Loss (%) | Tonset (°C) | Tpeak (°C) | Mass Loss (%) | Tonset (°C) | Tpeak (°C) | Mass Loss (%) | ||
| SPEEK | 71 | 6 | 190 | 255 | 20 | 464 | 564 | 26 | 49 |
| SPEEK/Zn0.25 | 100 | 8 | 187 | 267 | 20 | 423 | 558 | 21 | 51 |
| SPEEK/Zn1 | 78 | 7 | 197 | 266 | 17 | 433 | 550 | 23 | 53 |
| SPEEK/Zn3 | 73 | 6 | 194 | 262 | 16 | 411 | 548 | 22 | 56 |
| SPEEK/Zn5 | 75 | 5 | 191 | 250 | 16 | 400 | 550 | 25 | 53 |
| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Young’s Modulus * (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPEEK | 49.9 | 1059 | 195 |
| SPEEK/Zn0.25 | 42.9 | 1130 | 128 |
| SPEEK/Zn1 | 39.2 | 1060 | 60 |
| SPEEK/Zn3 | 39.2 | 1002 | 34 |
| SPEEK/Zn5 | 39.4 | 1001 | 16 |
| Samples | Conductivity × 10−2 S/cm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 40 °C | 60 °C | 80 °C | 100 °C | |
| SPEEK | 0.43 | 0.64 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.63 |
| SPEEK/Zn0.1 | 0.62 | 1.14 | 1.79 | 1.68 | 0.71 |
| SPEEK/Zn0.25 | 1.44 | 2.75 | 3.41 | 2.82 | 2.25 |
| SPEEK/Zn0.5 | 0.79 | 1.41 | 2.50 | 2.72 | 1.80 |
| SPEEK/Zn1 | 0.50 | 1.04 | 1.57 | 1.26 | 0.82 |
| SPEEK/Zn3 | 0.21 | 0.49 | 0.62 | 0.47 | 0.24 |
| SPEEK/Zn5 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 0.02 |
| Nafion117 | 1.36 | 1.56 | 1.60 | 1.26 | 0.73 |
| Membrane | Filler | DS * (%) | Conductivity × 10−2 S/cm | RH (%) | Temperature (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPEEK | doped zinc ferrite (0.25 wt.%) | 61 | 3.41 | - | 60 | This work |
| Nafion117 | - | - | 1.60 | - | 60 | This work |
| SPEEK | cobalt-based zeolitic imidazolate framework (1 wt.%) | 61 | 0.94 | - | 80 | [21] |
| SPEEK/SPVdF-HFP (4:1) | sulfated SiO2 (6 wt.%) | 65 | 7.90 | - | 90 | [22] |
| SPEEK/PVDF (9:1) | - | - | 0.97 | - | 80 | [25] |
| SPEEK/PVDF (9:1) | boron phosphate (10 wt.%) | - | 3.90 | - | 80 | [25] |
| SPEEK | sulfated TiO2 (0.1 wt.%) | 60 | 6.07 | 100 | - | [59] |
| SPEEK | SPEEK nanofibers | 65 | 5.58 | 100 | 80 | [94] |
| SPEEK/PAI (9:1) | SrTiO3 (6 wt.%) | 65 | 1.08 | 100 | 150 | [95] |
| SPEEK/PFSA (85:15) | - | 68 | 6.20 | - | 80 | [96] |
| SPEEK/PFSA (85:15) | Ba0.9Sr0.1TiO3 (6 wt.%) | 68 | 6.70 | - | 80 | [96] |
| SPEEK/SPI (1:1) | H-MoS2 (1 wt.%) and SLS (2 wt.%) | 64 | 5.02 | 100 | 80 | [97] |
| SPEEK/PBI (10:1) | - | 70 | 1.70 | 100 | RT | [98] |
| SPEEK/PBI (10:1) | 10% boron nitride | 70 | 2.45 | 100 | RT | [98] |
| SPEEK | bisphosphonic acid (2 wt. %) | 64 | 22.6 | 100 | 60 | [99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baltag, L.; Samoila, P.; Cojocaru, C.; Asandulesa, M.; Cristea, M.; Harabagiu, V. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Praseodymium Doped Zinc Ferrite Composites as Promising Polyelectrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cells. Polymers 2025, 17, 3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223058
Baltag L, Samoila P, Cojocaru C, Asandulesa M, Cristea M, Harabagiu V. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Praseodymium Doped Zinc Ferrite Composites as Promising Polyelectrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cells. Polymers. 2025; 17(22):3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223058
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaltag, Laurentiu, Petrisor Samoila, Corneliu Cojocaru, Mihai Asandulesa, Mariana Cristea, and Valeria Harabagiu. 2025. "Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Praseodymium Doped Zinc Ferrite Composites as Promising Polyelectrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cells" Polymers 17, no. 22: 3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223058
APA StyleBaltag, L., Samoila, P., Cojocaru, C., Asandulesa, M., Cristea, M., & Harabagiu, V. (2025). Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Praseodymium Doped Zinc Ferrite Composites as Promising Polyelectrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cells. Polymers, 17(22), 3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223058








