Development and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Graft-Modified Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
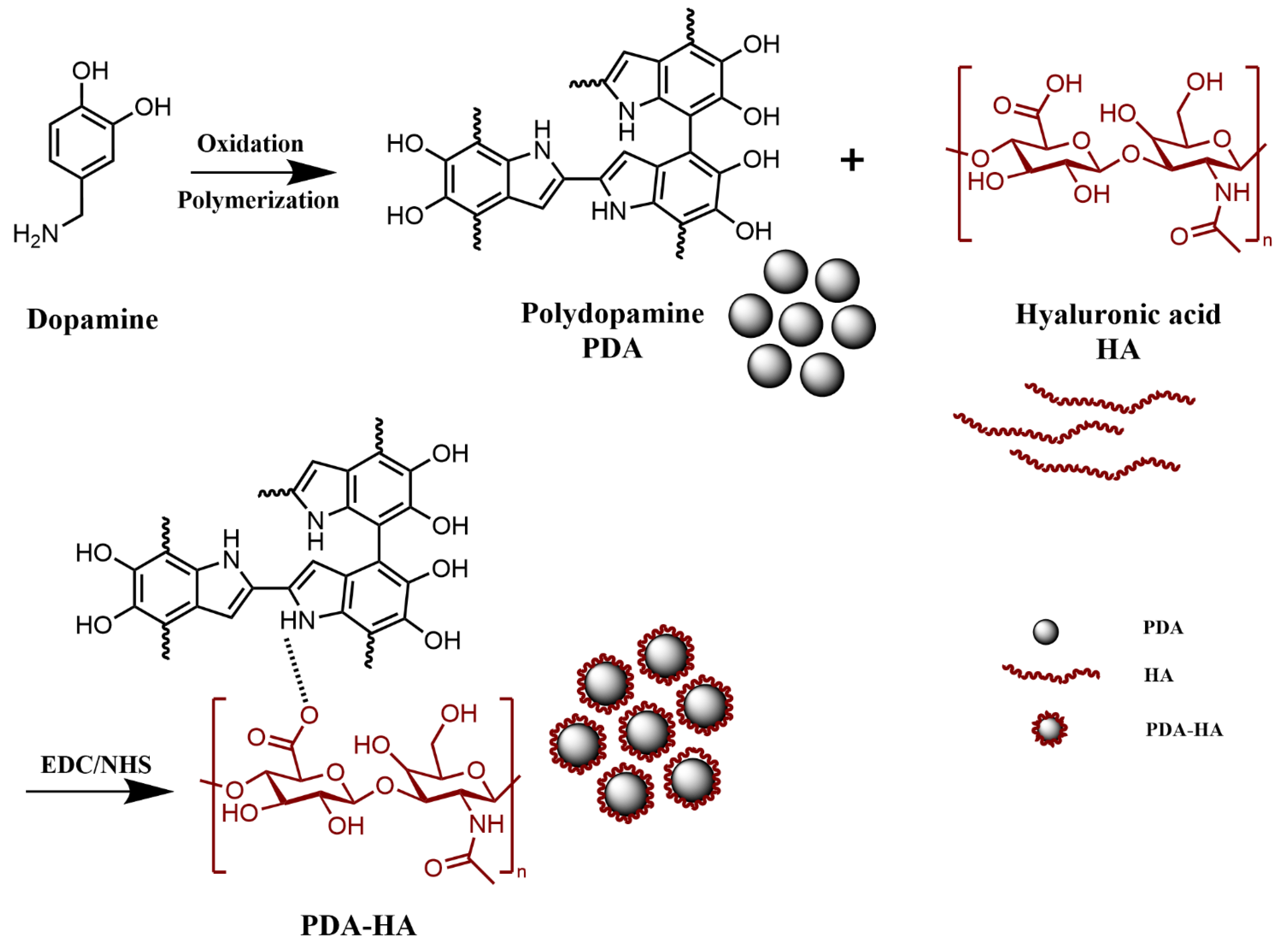
2.2. Preparation of Hyaluronic Acid Graft-Modified Polydopamine (PDA-HA) Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization of Materials
2.4. NIR Performance Evaluation
2.5. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Structure Analysis
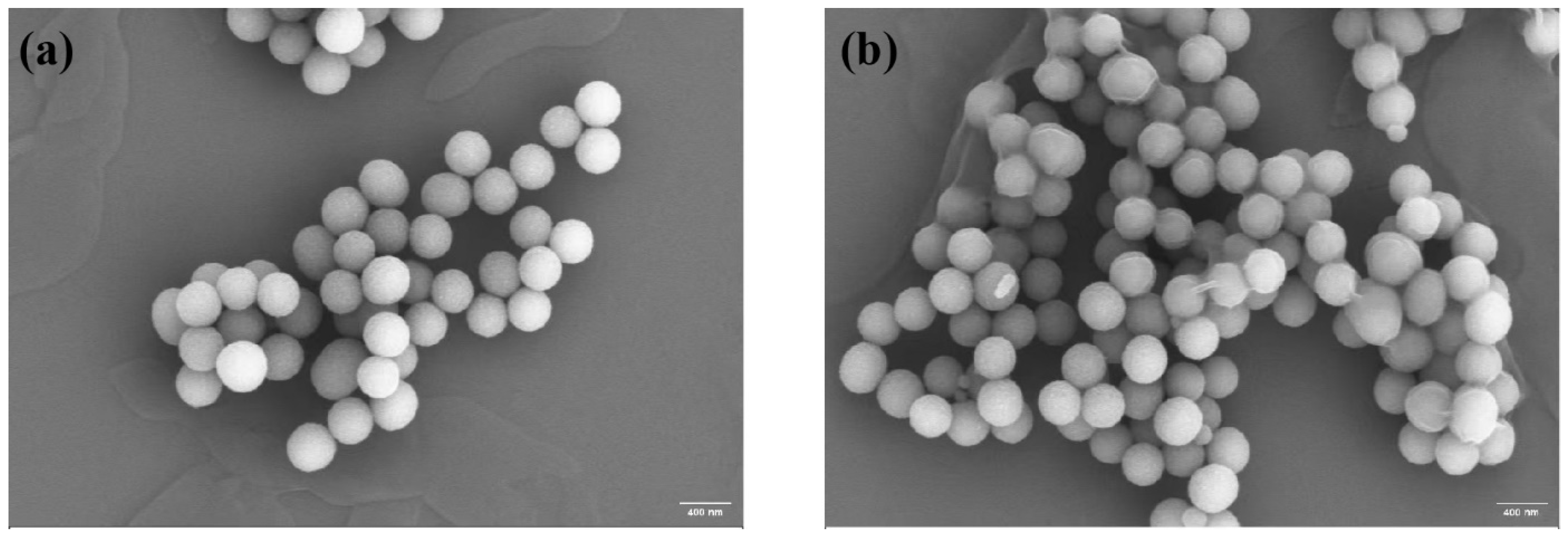
3.2. Microscopic Morphology Analysis
3.3. Surface and Stability Analysis
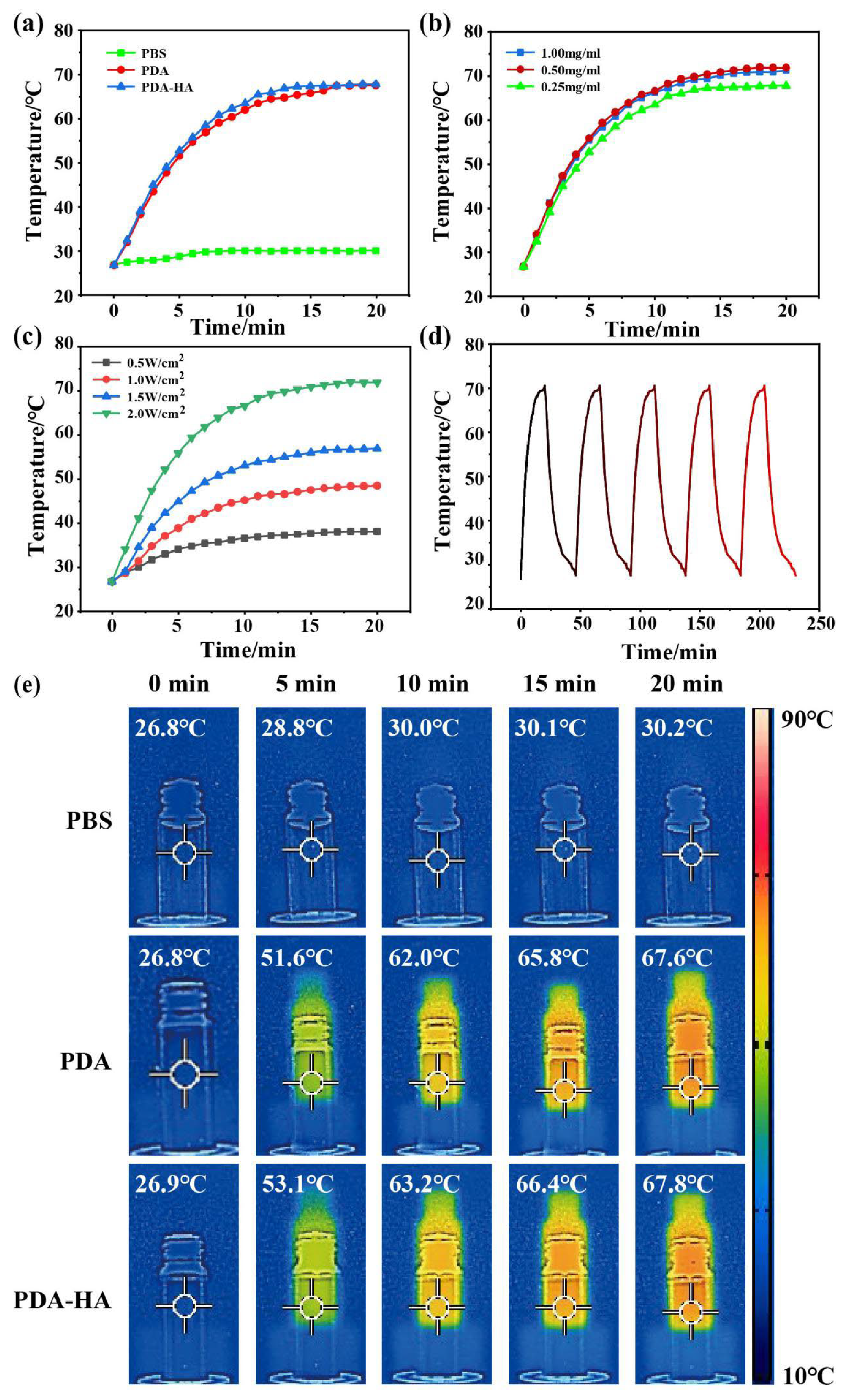
3.4. Evaluation of the Near-Infrared Performance of PDA-HA
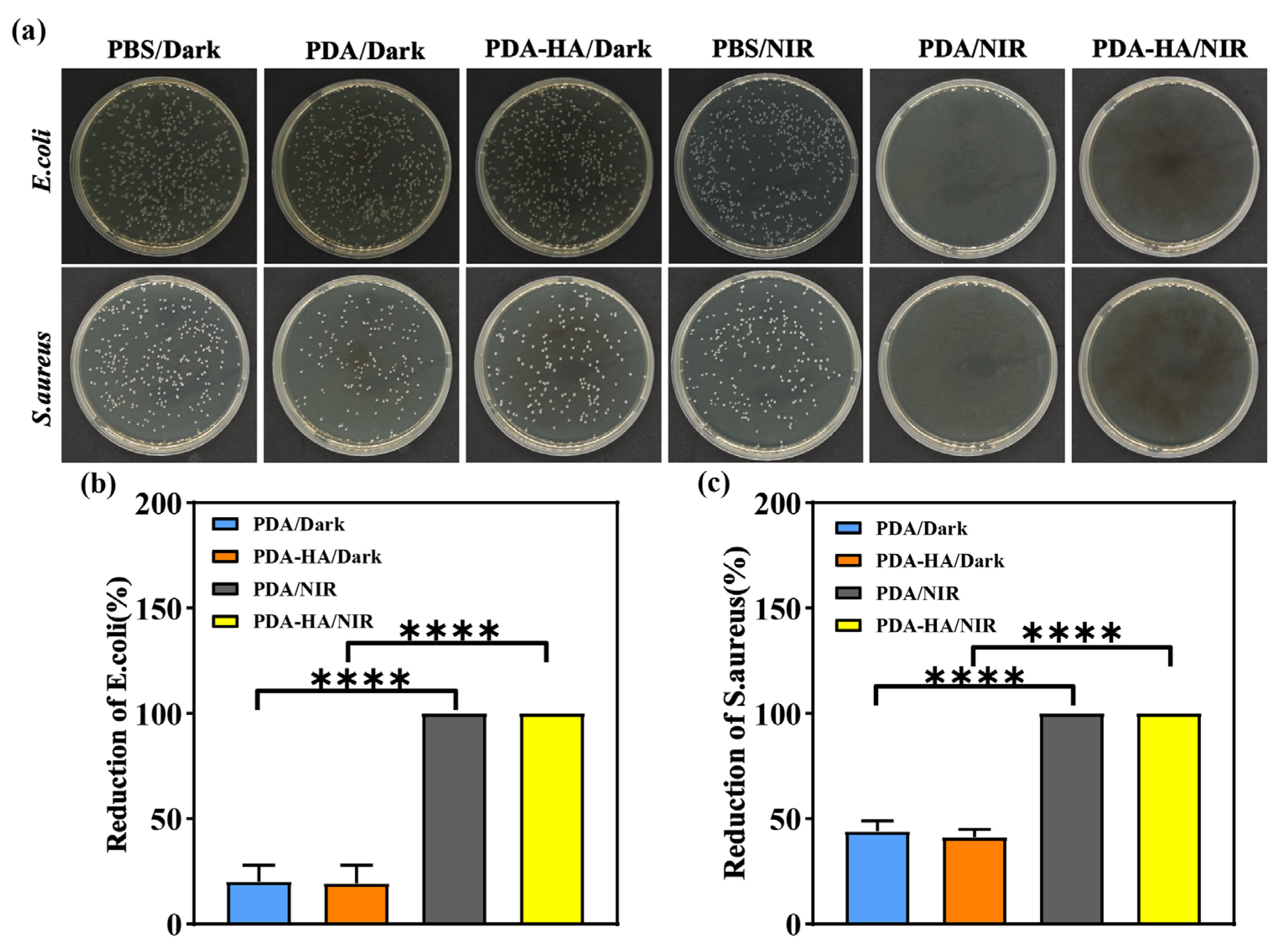
3.5. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Properties of PDA-HA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sethulekshmi, A.S.; Saritha, A.; Joseph, K.; Aprem, A.S.; Sisupal, S.B. MoS(2) based nanomaterials: Advanced antibacterial agents for future. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 158–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.; Dong, L.; Hou, Y.; Mu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhong, X.; Shan, G. NIR-driven multifunctional PEC biosensor based on aptamer-modified PDA/MnO(2) photoelectrode for bacterial detection and inactivation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 257, 116320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Da, J.; Wu, W.; Zheng, C.; Hu, N. Niobium carbide-mediated photothermal therapy for infected wound treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 934981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmal, G.R.; Lin, Z.C.; Chiu, T.S.; Alalaiwe, A.; Liao, C.C.; Fang, J.Y. Chemo-photothermal therapy of chitosan/gold nanorod clusters for antibacterial treatment against the infection of planktonic and biofilm MRSA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268 Pt 1, 131673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Lau, J.W.; Do, T.C.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, B. Near-Infrared Light Brightens Bacterial Disinfection: Recent Progress and Perspectives. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3937–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Wang, R.; Fan, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Natural polyphenol assisted delivery of single-strand oligonucleotides by cationic polymers. Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, J. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles: Structural Effects. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbins, N.D.; Ouimet, M.A.; Uhrich, K.E. Antibiotic-containing polymers for localized, sustained drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 78, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Yao, K.; Xu, Z.K. Nanomaterials with a photothermal effect for antibacterial activities: An overview. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8680–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overchuk, M.; Weersink, R.A.; Wilson, B.C.; Zheng, G. Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapies: Synergy Opportunities for Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 7979–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Huang, Y.; You, S.; Xiang, Y.; Cai, E.; Mao, R.; Pan, W.; Tong, X.; Dong, W.; Ye, F.; et al. Engineering Robust Ag-Decorated Polydopamine Nano-Photothermal Platforms to Combat Bacterial Infection and Prompt Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2106015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y. A multi-responsive targeting drug delivery system for combination photothermal/chemotherapy of tumor. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2023, 34, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, P.; Liang, G.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Regulating the absorption spectrum of polydopamine. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhurakkat, P.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.B.; Shin, Y.M.; Lee, E.J.; Mikos, A.G.; Shin, H. Materials from Mussel-Inspired Chemistry for Cell and Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.L.; Li, H.Y.; Ye, W.Y.; Zhao, M.Q.; Huang, D.N.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, B.Q.; Ren, K.F.; Ji, J.; Fu, G.S. Magainin-modified polydopamine nanoparticles for photothermal killing of bacteria at low temperature. Colloid Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zeng, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, W.; Mei, L.; Zhao, Y. Versatile Polydopamine Platforms: Synthesis and Promising Applications for Surface Modification and Advanced Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8537–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, C.; Guo, T.; Tian, Y.; Song, W.; Lei, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Bai, S.; et al. Hydrogel Nanoarchitectonics of a Flexible and Self-Adhesive Electrode for Long-Term Wireless Electroencephalogram Recording and High-Accuracy Sustained Attention Evaluation. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2209606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El, Y.S.; Ball, V. Polydopamine as a stable and functional nanomaterial. Colloid Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight on Structural, Physical, Physico-Chemical, and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Gholami, M.H.; Hashemi, F.; Zabolian, A.; Raei, M.; Hushmandi, K.; Zarrabi, A.; Voelcker, N.H.; Aref, A.R.; et al. Hyaluronic acid-based nanoplatforms for Doxorubicin: A review of stimuli-responsive carriers, co-delivery and resistance suppression. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 272, 118491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Mi, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Cheng, J.P. Functionalized chiral ionic liquids as highly efficient asymmetric organocatalysts for Michael addition to nitroolefins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Gao, Q.; Hu, F.; Zheng, C.; Chen, W.; Sun, N.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Lu, T. Chitosan and hyaluronic-based hydrogels could promote the infected wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wen, F.; Su, W. Polydopamine/tannic acid/chitosan/poloxamer 407/188 thermosensitive hydrogel for antibacterial and wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.P.; Jin, M.Y.; Huang, S.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Zhang, T.; Cao, L.L.; Lin, X.Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Versatile dopamine-functionalized hyaluronic acid-recombinant human collagen hydrogel promoting diabetic wound healing via inflammation control and vascularization tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaw, O.; Noon, S.A.N.; Daduang, J.; Proungvitaya, S.; Wongwattanakul, M.; Ngernyuang, N.; Daduang, S.; Shinsuphan, N.; Phatthanakun, R.; Jearanaikoon, N.; et al. DNA aptamer-functionalized PDA nanoparticles: From colloidal chemistry to biosensor applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1427229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranu, R.; Chauhan, Y.; Ratan, A.; Singh, P.K.; Bhattacharya, B.; Tomar, S.K. Biogenic synthesis and thermo-magnetic study of highly porous carbon nanotubes. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F.; Zamanian, A.; Sahranavard, M. Mussel-inspired polydopamine-mediated surface modification of freeze-cast poly (epsilon-caprolactone) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. Biomed. Tech. 2020, 65, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zeng, X.; Wu, B.; Zeng, Q.; Pang, W.; Tang, J. Electrochemical co-deposition of reduced graphene oxide-gold nanocomposite on an ITO substrate and its application in the detection of dopamine. Sci. China (Chem.) 2017, 60, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Babadinia, P.; Shariati, F.S.; Ahangari, C.R. Synthesis and characterization of Gd(3+)-loaded hyaluronic acid-polydopamine nanoparticles as a dual contrast agent for CT and MRI scans. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, J.; Guan, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, K.; Li, J. Injectable multifunctional CMC/HA-DA hydrogel for repairing skin injury. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 14, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Niu, K.; Ni, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Hyaluronic Acid-Modified Gold-Polydopamine Complex Nanomedicine for Tumor-Targeting Drug Delivery and Chemo-Photothermal-Therapy Synergistic Therapy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Su, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, K.; Xie, M.; Cai, B.; Li, J. A hyaluronic acid/chitosan composite functionalized hydrogel based on enzyme-catalyzed and Schiff base reaction for promoting wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 255, 128284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Ye, H.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, X. Mechanically tough, adhesive, self-healing hydrogel promotes annulus fibrosus repair via autologous cell recruitment and microenvironment regulation. Acta Biomater. 2024, 178, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, S.; Pei, M.; Yang, H.; Gu, S.; Tao, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P. Dopamine-Modified Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Adhesives with Fast-Forming and High Tissue Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18225–18234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.M.; Hong, G.L.; Gwak, M.A.; Kim, K.H.; Jeong, J.E.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, S.A.; Park, W.H. Self-crosslinkable hyaluronate-based hydrogels as a soft tissue filler. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z. Polydopamine antibacterial materials. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1618–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Li, J.; Xing, J.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C. Development and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Graft-Modified Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Studies. Polymers 2025, 17, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020162
Li S, Li J, Xing J, Li L, Wang L, Wang C. Development and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Graft-Modified Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Studies. Polymers. 2025; 17(2):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020162
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shu, Jia Li, Jun Xing, Ling Li, Long Wang, and Cai Wang. 2025. "Development and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Graft-Modified Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Studies" Polymers 17, no. 2: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020162
APA StyleLi, S., Li, J., Xing, J., Li, L., Wang, L., & Wang, C. (2025). Development and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Graft-Modified Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Studies. Polymers, 17(2), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020162




