Combating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Dual-Mechanism Hydrogel Delivering Salvianolic Acid A and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A to Block TLR4/NF-κB and Boost Angiogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Cells, and Animals
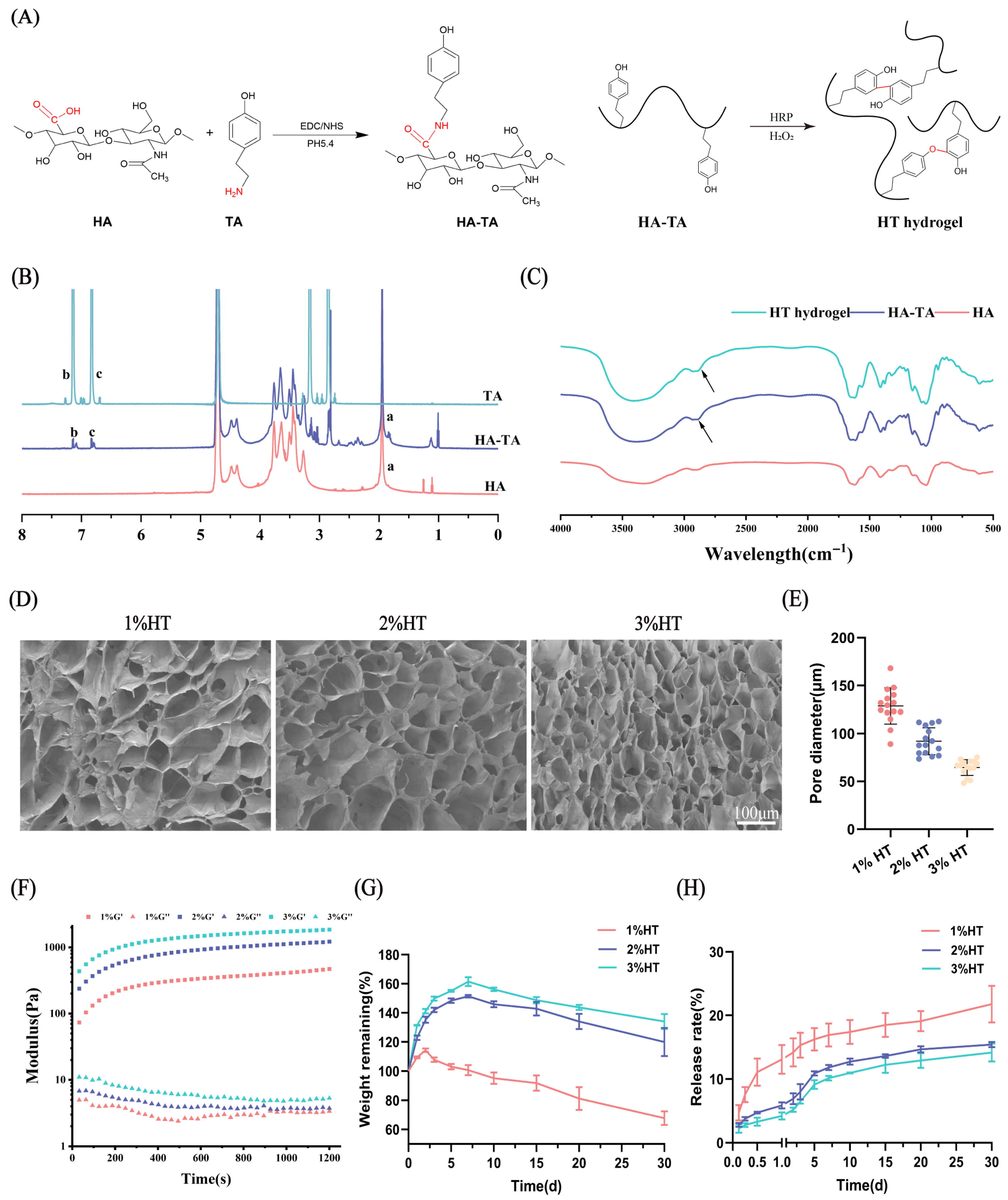
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of HA-TA
2.3. Preparation and Physical Characterization of HT Hydrogels
2.4. Evaluation of Cytocompatibility of Hydrogels
2.5. Matrigel-Based Angiogenesis Assay
2.6. Inflammatory Effects of SAA and HSYA In Vitro
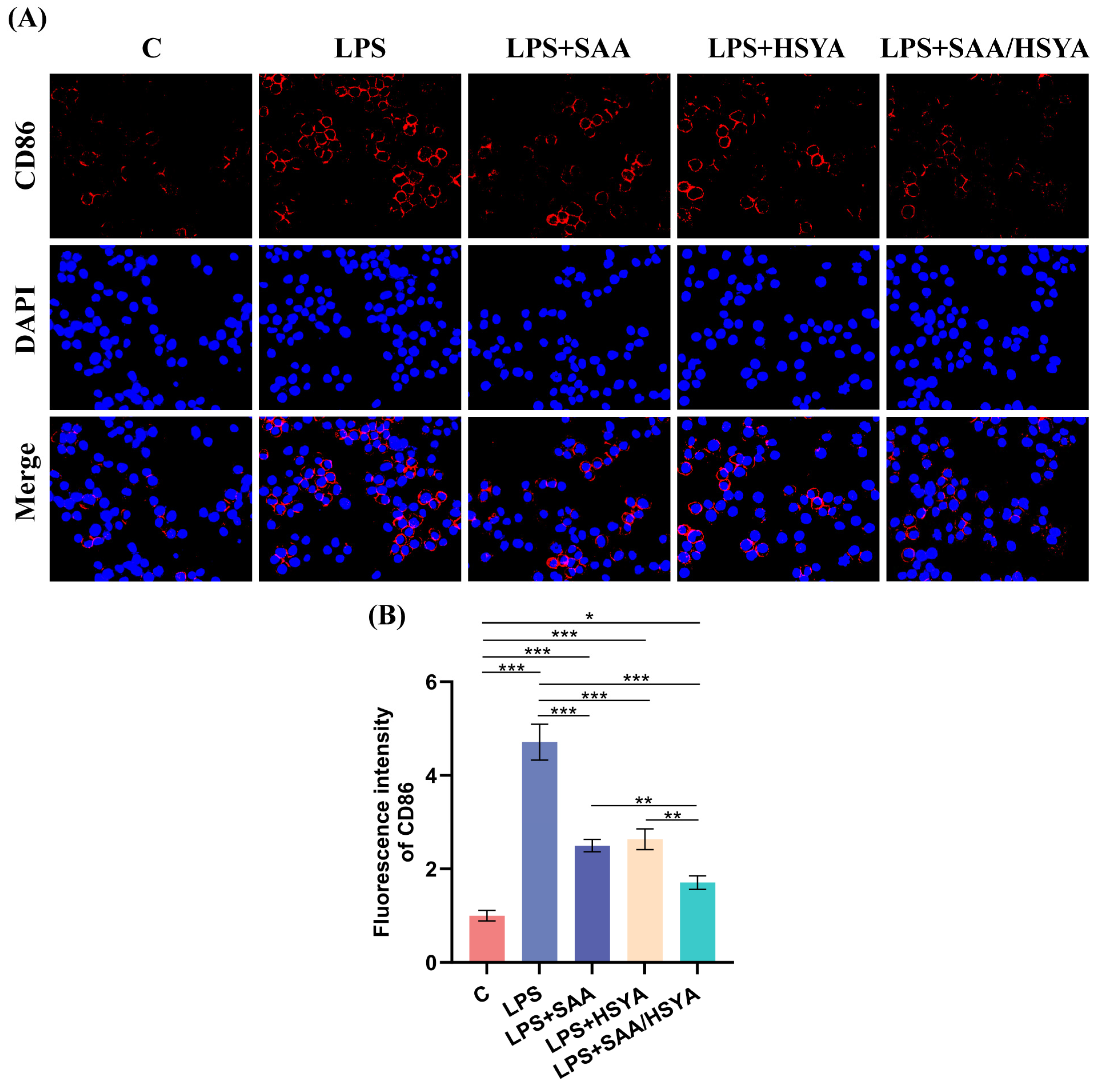
2.7. Cell Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. In Vivo Biocompatibility of HT Hydrogels
2.9. Establishment of Mouse TBI Model and Hydrogel Implantation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Hydrogels
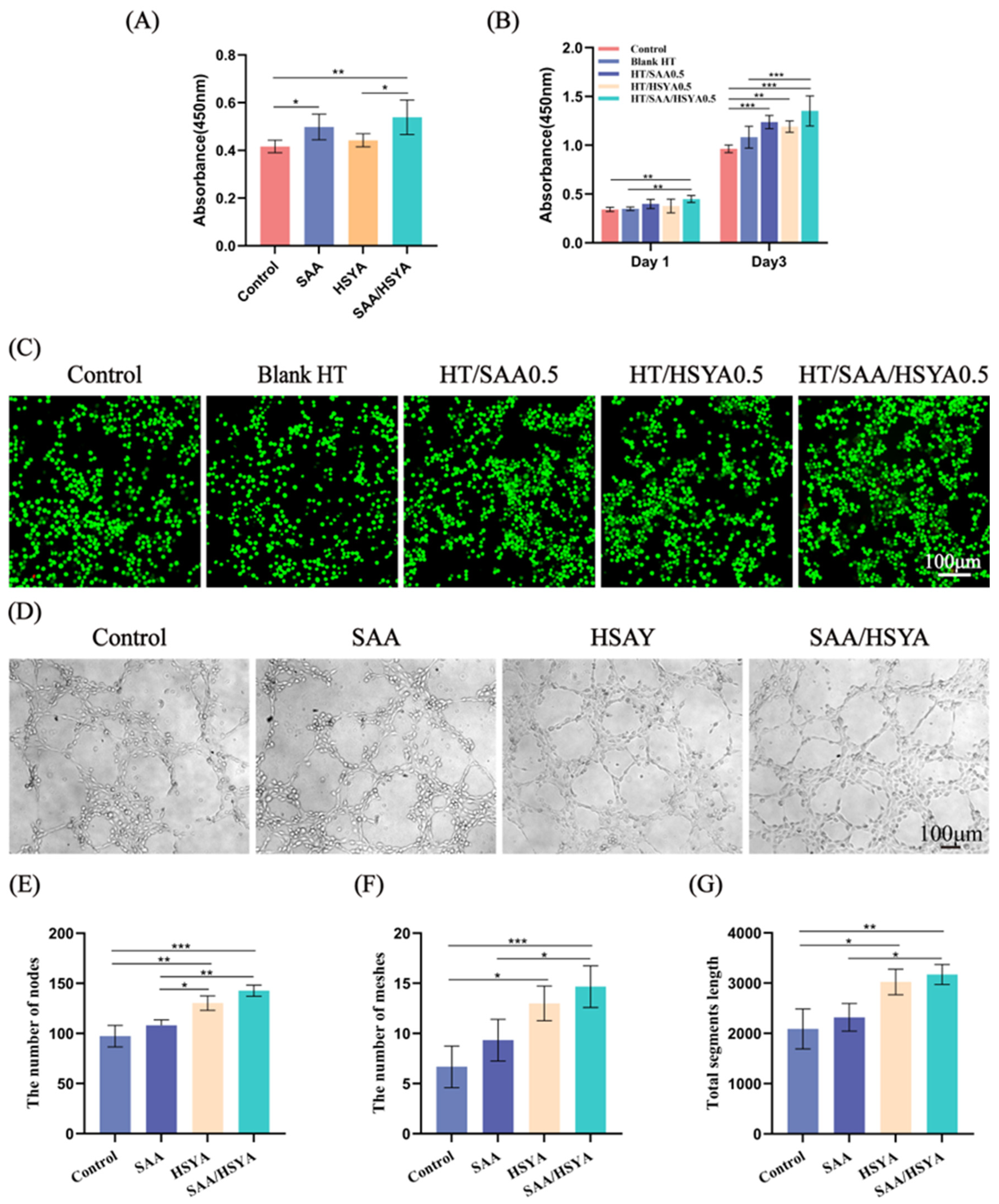
3.2. Cytocompatibility Evaluation of the Hydrogels
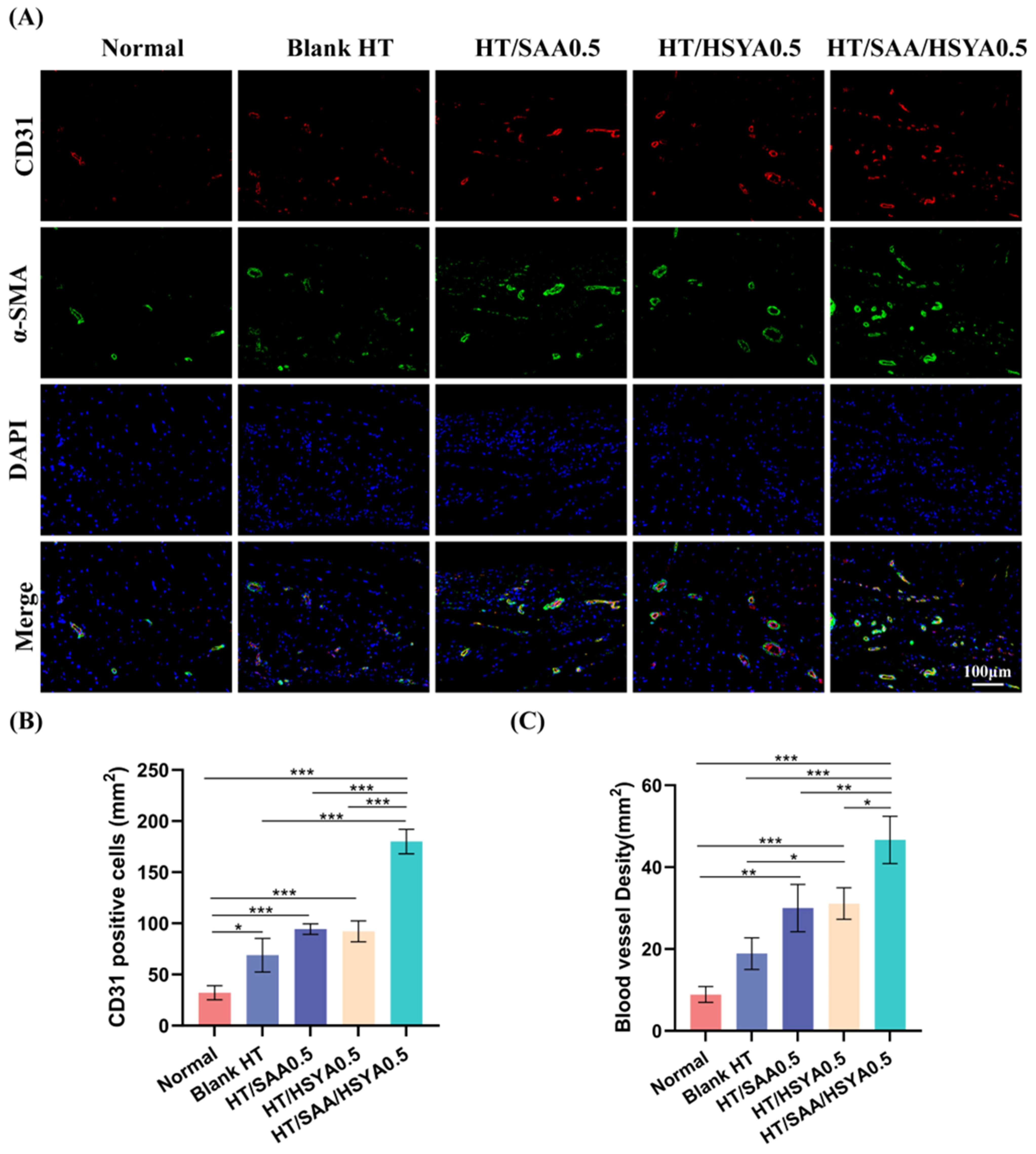
3.3. In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay
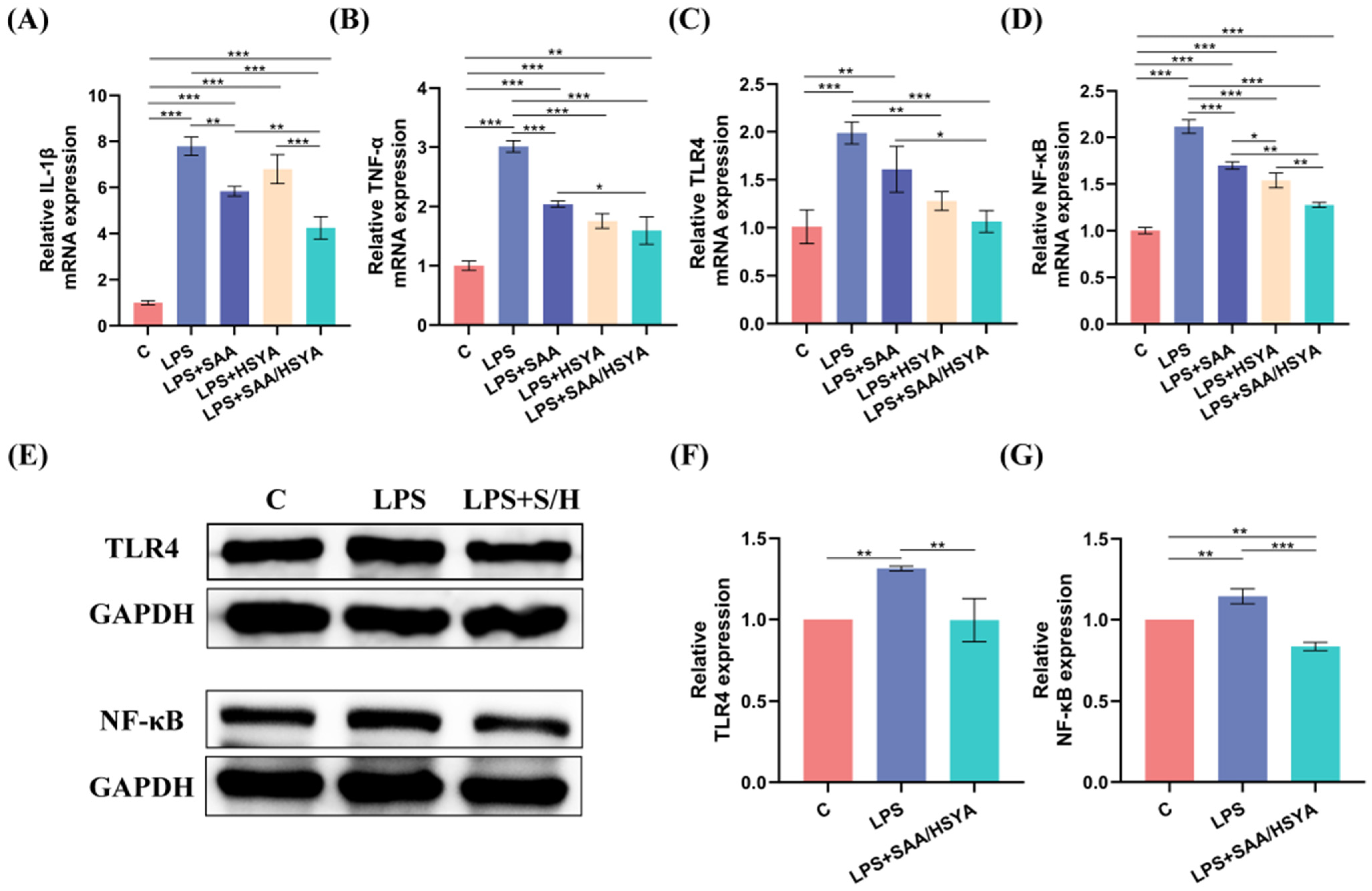
3.4. In Vitro Inflammatory Regulation
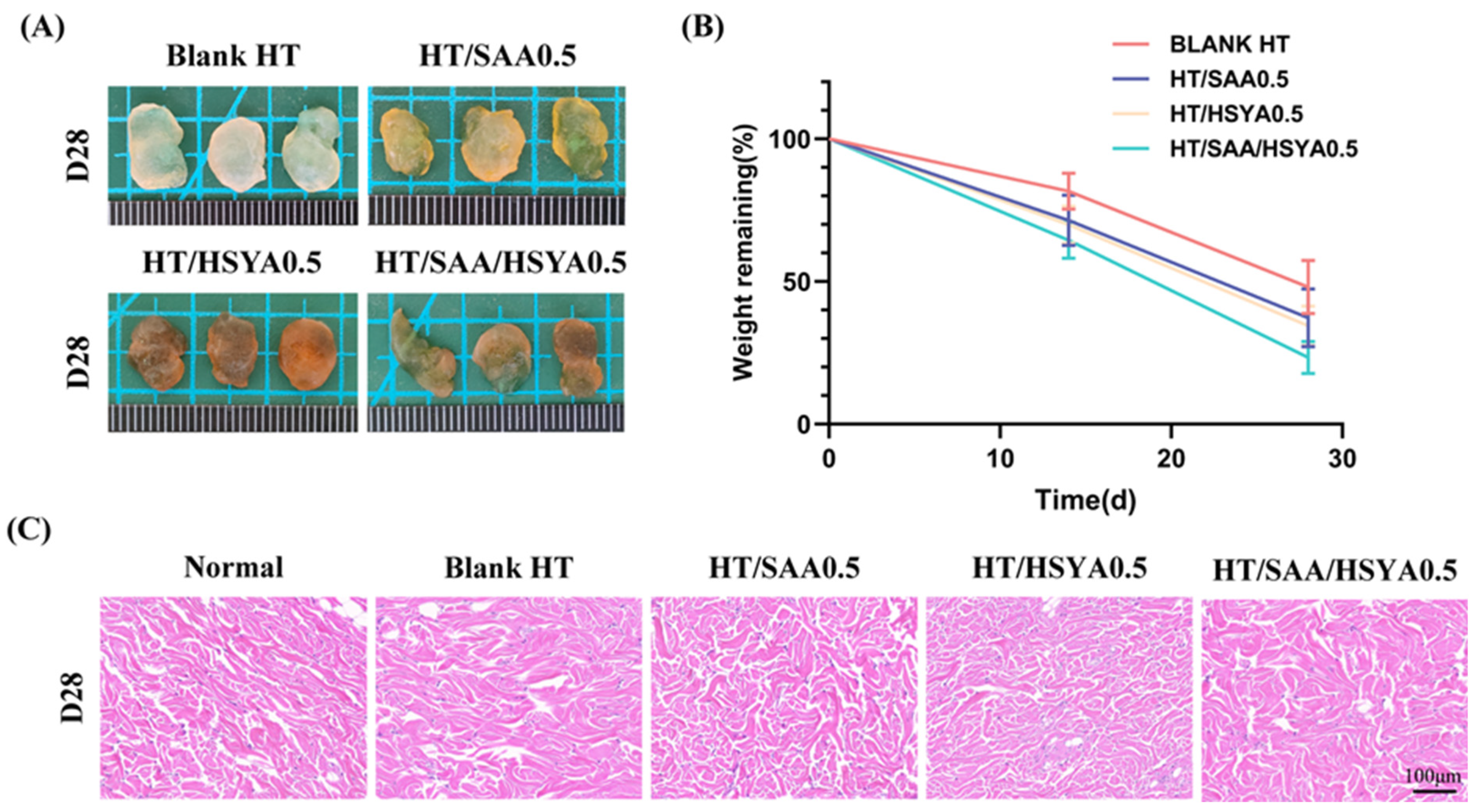
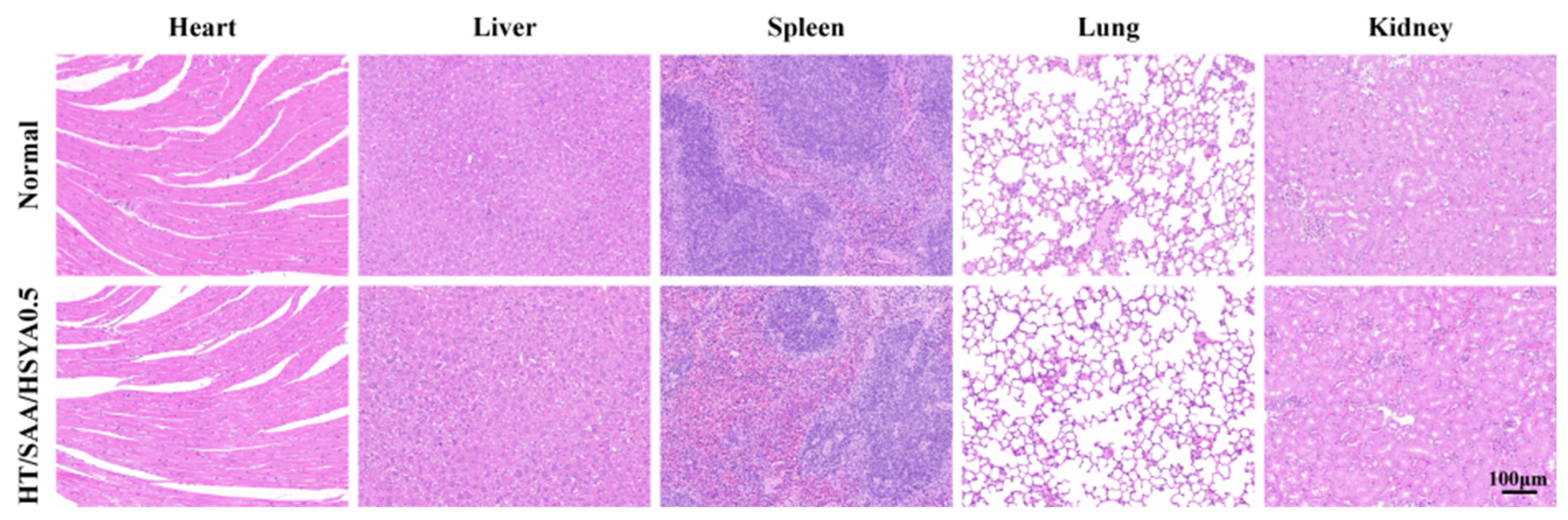
3.5. Evaluation of In Vivo Compatibility of Hydrogels
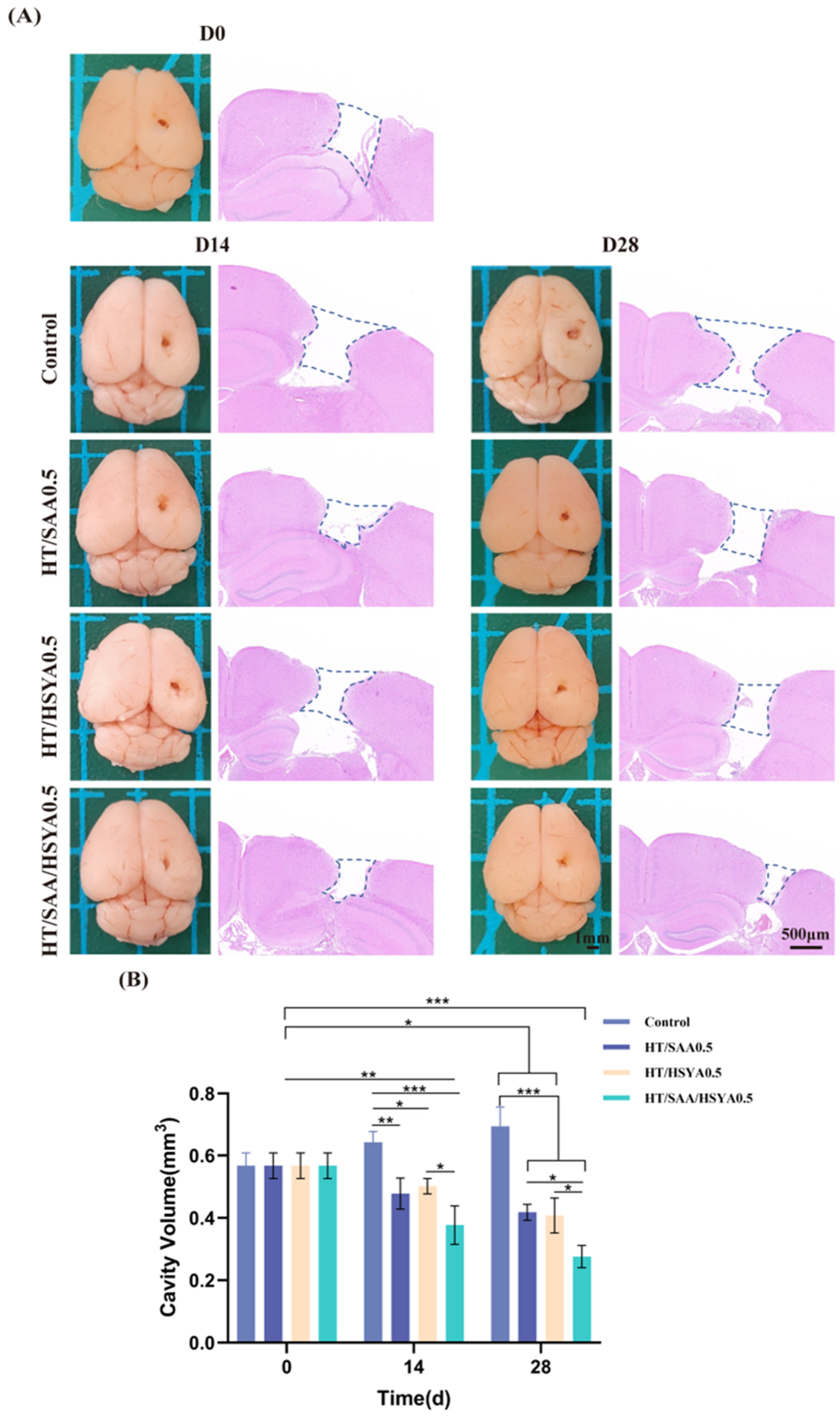
3.6. HT/SAA/HSYA0.5 Hydrogel Promotes Repair of Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| SAA | Salvianolic acid A |
| HSYA | Hydroxysafflor yellow A |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| EPCs | Endothelial progenitor cells |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| DFO | Deferoxamine |
| BV2 | Mouse microglia |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
References
- Luo, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, D.; Guo, X.; Wang, S.; He, F.; Wang, Y. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Dynamic Pathophysiology Across Different Stages in a Rat Model of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 785938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainé, A.; Brot, S.; Gaillard, A. Beneficial Effects of Hyaluronan-Based Hydrogel Implantation after Cortical Traumatic Injury. Cells 2022, 11, 3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corps, K.N.; Roth, T.L.; McGavern, D.B. Inflammation and Neuroprotection in Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macks, C.; Jeong, D.; Bae, S.; Webb, K.; Lee, J.S. Dexamethasone-Loaded Hydrogels Improve Motor and Cognitive Functions in a Rat Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Ren, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Ma, S.; Yao, M.; Guan, F. Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Loaded with BMSC and NGF for Traumatic Brain Injury Treatment. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 13, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ding, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, K.; Wu, X.; Zhou, T.; Zeng, M.; et al. Hyaluronan-Based Hydrogel Integrating Exosomes for Traumatic Brain Injury Repair by Promoting Angiogenesis and Neurogenesis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Xie, F.; Zhang, J. Research Progress of Neuroinflammation-Related Cells in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review. Medicine 2023, 102, e34009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, T.; Xu, L.; Tao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X. Fatty Acid Metabolism Disorders and Potential Therapeutic Traditional Chinese Medicines in Cardiovascular Diseases. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4976–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Yi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. A Green and Highly Efficient Method to Deliver Hydrophilic Polyphenols of Salvia Miltiorrhiza and Carthamus Tinctorius for Enhanced Anti-Atherosclerotic Effect via Metal-Phenolic Network. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 215, 112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Su, N.; Guo, C.; Feng, X.; Dou, F.; Ding, Y.; Shi, L.; Wen, A. Synergistic Neuroprotective Effects of Danshensu and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115434–115443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-M.; Xu, S.-W.; Liu, P.-Q. Salvia miltiorrhizaBurge (Danshen): A Golden Herbal Medicine in Cardiovascular Therapeutics. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 802–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-F.; Wang, Y.-L.; Gao, C.; Gu, Y.-T.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.-H.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhang, Z. Salvianolic Acid A Attenuates Kidney Injury and Inflammation by Inhibiting NF-κB and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathways in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Qin, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, G.Y.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, J.H. In Silico Analysis and Experimental Validation of Molecular Mechanisms of Salvianolic Acid A-Inhibited LPS-Stimulated Inflammation, in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Song, J.-K.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.-M.; He, G.-R.; Xu, X.-N.; Rong, Y.; Zhou, W.-X.; Du, G.-H. Salvianolic Acid A Attenuates Ischemia Reperfusion Induced Rat Brain Damage by Protecting the Blood Brain Barrier Through MMP-9 Inhibition and Anti-Inflammation. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Jin, L.; Ma, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, M.; Shou, Q. Salvianolic Acid A Alleviated Inflammatory Response Mediated by Microglia through Inhibiting the Activation of TLR2/4 in Acute Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion. Phytomedicine 2021, 87, 153569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Yin, Y.; Duan, J.; Guo, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xi, M.; Wen, A. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Promotes Neovascularization and Cardiac Function Recovery Through HO-1/VEGF-A/SDF-1α Cascade. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Huo, X.; Ma, S.; Hu, J.; Pavalko, F.M.; Liu, Q. Hydroxy-Safflower Yellow A Inhibits the TNFR1-Mediated Classical NF-κB Pathway by Inducing Shedding of TNFR1. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.-P.; Fan, L.-H.; Nan, K.; Li, J.; Dang, X.-Q.; Wang, K.-Z. HSYA Alleviates Secondary Neuronal Death Through Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Response, and Neural Apoptosis in SD Rat Spinal Cord Compression Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Meng, H.; Wan, H.; He, Y. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A and Anhydrosafflor Yellow B Alleviate Ferroptosis and Parthanatos in PC12 Cells Injured by OGD/R. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 179, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Du, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Regulates Lymphangiogenesis and Inflammation via the Inhibition of PI3K on Regulating AKT/mTOR and NF-κB Pathway in Macrophages to Reduce Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- Mice. Phytomedicine 2023, 112, 154684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taisescu, O.; Dinescu, V.C.; Rotaru-Zavaleanu, A.D.; Gresita, A.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Hydrogels for Peripheral Nerve Repair: Emerging Materials and Therapeutic Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z. Dynamic Hydrogel-Based Strategy for Traumatic Brain Injury Modeling and Therapy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2025, 31, e70148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, R. Hydrogel in the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury. Biomater. Res. 2024, 28, 0085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Han, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Jin, G.; Feng, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, H. An Injectable Refrigerated Hydrogel for Inducing Local Hypothermia and Neuroprotection Against Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yan, T.; Wan, H. Injectable Hydrogels Based on Hyaluronic Acid and Gelatin Combined with Salvianolic Acid B and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor for Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. Molecules 2024, 29, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudanan, P.; Raju, G.; Shankarappa, S. Hydrogel Systems and Their Role in Neural Tissue Engineering. J. R. Soc. Interface 2020, 17, 20190505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Yu, X.; He, X.; Cheng, H.; Jin, L.; Wang, C.; Guo, R. Bioactive Hydrogel Synergizes Neuroprotection, Macrophage Polarization, and Angiogenesis to Improve Repair of Traumatic Brain Injury. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 29, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y. Remodeling Brain Pathological Microenvironment to Lessen Cerebral Ischemia Injury by Multifunctional Injectable Hydrogels. J. Control. Release 2024, 369, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça, M.F.P.; Miguel, S.P.; Cabral, C.S.D.; Correia, I.J. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Wound Dressings: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broguiere, N.; Isenmann, L.; Zenobi-Wong, M. Novel Enzymatically Cross-Linked Hyaluronan Hydrogels Support the Formation of 3D Neuronal Networks. Biomaterials 2016, 99, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, P.; Du, Y.; Hecker, P.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Cartilage Endplate-Targeted Engineered Exosome Releasing and Acid Neutralizing Hydrogel Reverses Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2403315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.-Q.; Chang, C.; Li, J.-J.; Li, Y.; Niu, X.-Q.; Zhang, D.-P.; Li, L.-J.; Gao, J.-Q. Co-Delivery of Deferoxamine and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A to Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing via Enhanced Angiogenesis. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamahkar, E.; Özkahraman, B.; Süloğlu, A.K.; İdil, N.; Perçin, I. A Novel Multilayer Hydrogel Wound Dressing for Antibiotic Release. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, S.; Ebisu, Y.; Sedlačík, T.; Semba, S.; Nonoyama, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Hirota, A.; Takahashi, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Imajo, M.; et al. Engineering of an Electrically Charged Hydrogel Implanted into a Traumatic Brain Injury Model for Stepwise Neuronal Tissue Reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, R.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yu, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Hua, Z.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Hybridized with Au-Triptolide Nanoparticles for Intraarticular Targeted Multi-Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 849101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbu, R.; Brocchini, S.; Khaw, P.T.; Awwad, S. Antibody Loaded Collapsible Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Intraocular Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 124, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Dickerson, E.B.; Auerbach, R. The Sponge/Matrigel Angiogenesis Assay. Angiogenesis 2002, 5, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccilli, B.; Alan, A.; Baha’, A.; Shahzad, A.; Almealawy, Y.F.; Chisvo, N.S.; Ennabe, M.; Weinand, M. Neuroprotection Strategies in Traumatic Brain Injury: Studying the Effectiveness of Different Clinical Approaches. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2024, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revete, A.; Aparicio, A.; Cisterna, B.A.; Revete, J.; Luis, L.; Ibarra, E.; Segura González, E.A.; Molino, J.; Reginensi, D. Advancements in the Use of Hydrogels for Regenerative Medicine: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biomater. 2022, 2022, 3606765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Miao, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Xue, B.; Chen, J.; Xian, C.; Bi, L. 3D Printed Structured Porous Hydrogel Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of BMSCs. Mater. Des. 2023, 227, 111729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.A.; Bilston, L.E.; Sinkus, R. In Vivo Brain Viscoelastic Properties Measured by Magnetic Resonance Elastography. NMR Biomed. 2008, 21, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budday, S.; Nay, R.; de Rooij, R.; Steinmann, P.; Wyrobek, T.; Ovaert, T.C.; Kuhl, E. Mechanical Properties of Gray and White Matter Brain Tissue by Indentation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 46, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaster, T.; Sack, I.; Samani, A. Measurement of the Hyperelastic Properties of Ex Vivo Brain Tissue Slices. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Guo, K.; Mi, J.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.; Jin, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Hydrogels with Programmed Spatiotemporal Mechanical Cues for Stem Cell-Assisted Bone Regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chu, C.; Kuddannaya, S.; Yuan, Y.; Walczak, P.; Singh, A.; Song, X.; Bulte, J.W.M. In Vivo Imaging of Composite Hydrogel Scaffold Degradation Using CEST MRI and Two-Color NIR Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassam, Y.N.; Izzy, S.; Whalen, M.; McGavern, D.B.; El Khoury, J. Neuroimmunology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Time for a Paradigm Shift. Neuron 2017, 95, 1246–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loane, D.J.; Kumar, A. Microglia in the TBI Brain: The Good, the Bad, and the Dysregulated. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 275 Pt 3, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-A.; Yan, L.; Wen, J.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Yu, F.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.U.; Su, H. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in Vascular Repair After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Narrative Review. Burns Trauma 2023, 11, tkad033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullienne, A.; Obenaus, A.; Ichkova, A.; Savona-Baron, C.; Pearce, W.J.; Badaut, J. Chronic Cerebrovascular Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Huang, G.; Ding, T.; Feng, D.; Genin, G.M.; Wei, Z.; Xu, F. An ECM-Mimicking, Injectable, Viscoelastic Hydrogel for Treatment of Brain Lesions. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2201594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| Mouse IL-1β | F: TGGTGTGTGACGTTCCCATT R: TGTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCT |
| Mouse TNF-α | F: TGTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCT R: GGCCAGTGAGTGAAAGGGACA |
| Mouse TLR4 | F: TGGGTCAAGGAACAGAAGCA R: ATCCAACACTAAGGAGGTATTCATC |
| Mouse NF-κB | F: TGGACGACTCTTGGGAGAAGG R: AACACAGGCTCATACGGTTTCC |
| Mouse GAPDH | F: TGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCTGA R: TTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCAGGAG |
| Hydrogel | Zero Order Model | First Order Model | Higuchi Model | Korsmeyer-Peppas Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | R2 | R2 | |
| 1%HT | 0.600 | 0.919 | 0.947 | 0.926 |
| 2%HT | 0.787 | 0.919 | 0.816 | 0.983 |
| 3%HT | 0.892 | 0.945 | 0.984 | 0.987 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, G.; Yan, Y.; Nguyen, L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, X.; Gan, L.; Yan, T.; Wan, H. Combating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Dual-Mechanism Hydrogel Delivering Salvianolic Acid A and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A to Block TLR4/NF-κB and Boost Angiogenesis. Polymers 2025, 17, 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141900
Zhou G, Yan Y, Nguyen L, Fan J, Zhang X, Gan L, Yan T, Wan H. Combating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Dual-Mechanism Hydrogel Delivering Salvianolic Acid A and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A to Block TLR4/NF-κB and Boost Angiogenesis. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141900
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Guoying, Yujia Yan, Linh Nguyen, Jiangkai Fan, Xiao Zhang, Li Gan, Tingzi Yan, and Haitong Wan. 2025. "Combating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Dual-Mechanism Hydrogel Delivering Salvianolic Acid A and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A to Block TLR4/NF-κB and Boost Angiogenesis" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141900
APA StyleZhou, G., Yan, Y., Nguyen, L., Fan, J., Zhang, X., Gan, L., Yan, T., & Wan, H. (2025). Combating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Dual-Mechanism Hydrogel Delivering Salvianolic Acid A and Hydroxysafflor Yellow A to Block TLR4/NF-κB and Boost Angiogenesis. Polymers, 17(14), 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141900







