The Fundamentals of the NP-Gram Method for the Characterisation of Pyrolysis Oils Based on the Estimated Boiling Points of Pyrolysis Products from Polypropylene
Abstract
1. Introduction
 pairs 3 bonds apart:
pairs 3 bonds apart:C1C4, C1C7, C2C5, C7C5, C6C4, C6C7; p=6
ω = 6+12+10+6+6+6 = 46
2. Materials and Methods
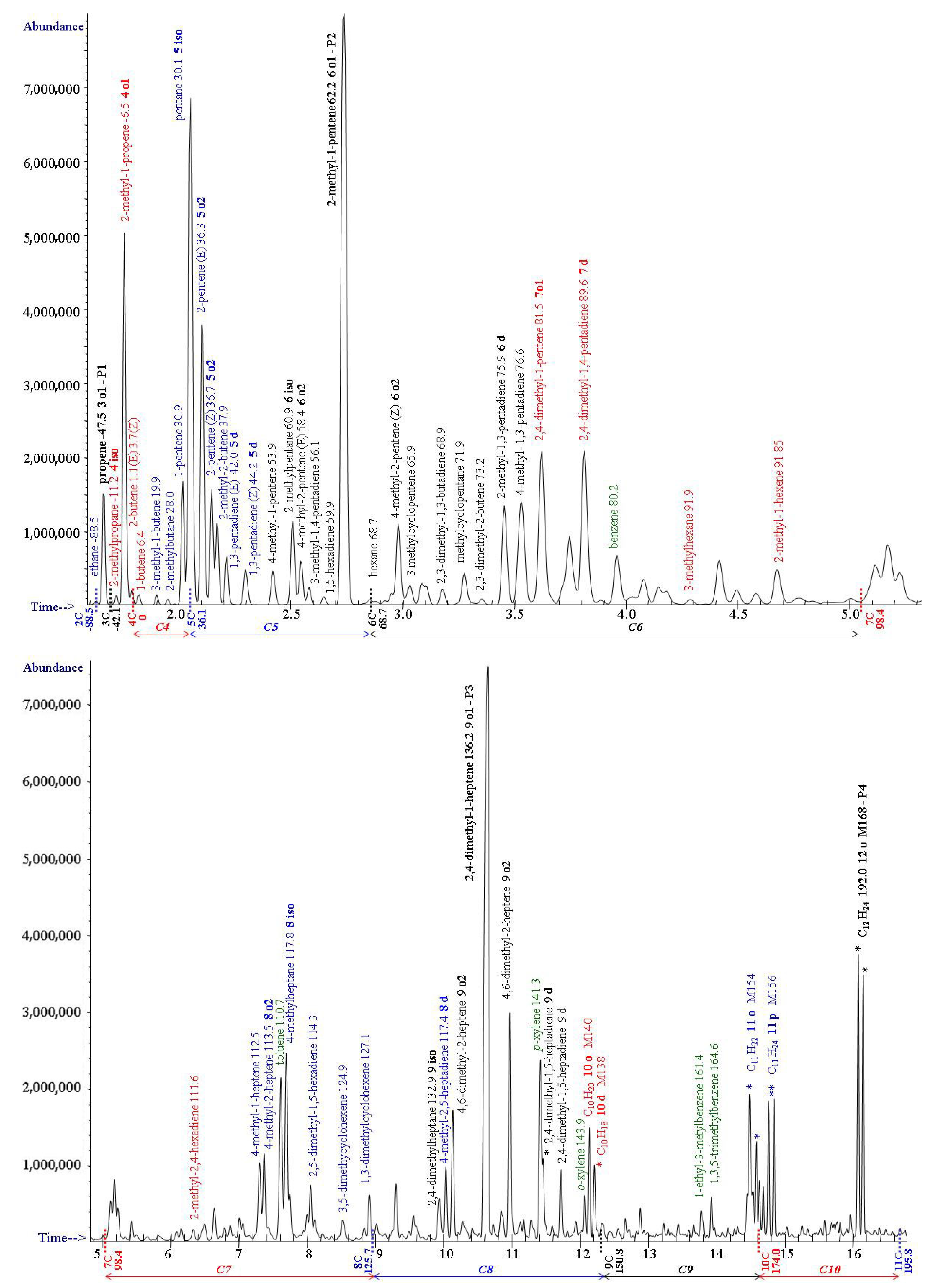
3. Degradation Products of Polypropylene
3m+1 series: p = (4nC − 16)/3; ω = (nC3 + 3nC2 − 9nC + 5)/9
3m+2 series: p = (4nC − 14)/3; ω = (nC3 + 3nC2 − 3nC − 5)/9
3m+1 series: o1: + 1.7 °C; d: + 3.4 °C
3m+2 series: o2: −0.3 °C; d: −0.6 °C
| nC | Tn calc | Tn NIST | Tiso calc | Tiso NIST | To1 calc a | To1 NIST | To2 calc | To2 NIST | Td calc | Td NIST | Cn b | Ri c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | −88.5 | −88.5 | 2 | 200–299 | ||||||||
| 3 | −41.5 | −42.0 | −41.5 (Tn) | −48.0 P1 | −47.5 | 3 | 300–399 | |||||
| 4 | −0.5 | −0.1 | −12.1 | −11.1 | −10.4 | −6.4 | 4 | 400–499 | ||||
| 5 | 35.9 | 36.1 | 35.9 (Tn) | 27.9 | 35.6 | 36.5 | 5 | 500–599 | ||||
| 6 | 68.7 | 68.8 | 60.5 | 60.9 | 62.2 P2 | 61.8 | 60.2 | 58.4 | 61.9 | 75.9 | 6 | 600–699 |
| 7 | 98.4 | 98.4 | 82.4 | 80.6 | 84.1 | 81.5 | 85.8 | 89.6 | 7 | 700–799 | ||
| 8 | 125.6 | 125.6 | 117.3 | 117.8 | 117.0 | 113.5 | 116.7 | 117.4 | 8 | 800–899 | ||
| 9 | 150.7 | 150.8 | 134.4 | 132.9 | 136.1 P3 | 134.0 | 134.1 | 135.8 | 9 | 900–999 | ||
| 10 | 174.0 | 174.1 | 150.1 | 151.8 | 153.5 | 10 | 1000–1099 | |||||
| 11 | 195.7 | 195.5 | 177.6 | 177.3 | 177.0 | |||||||
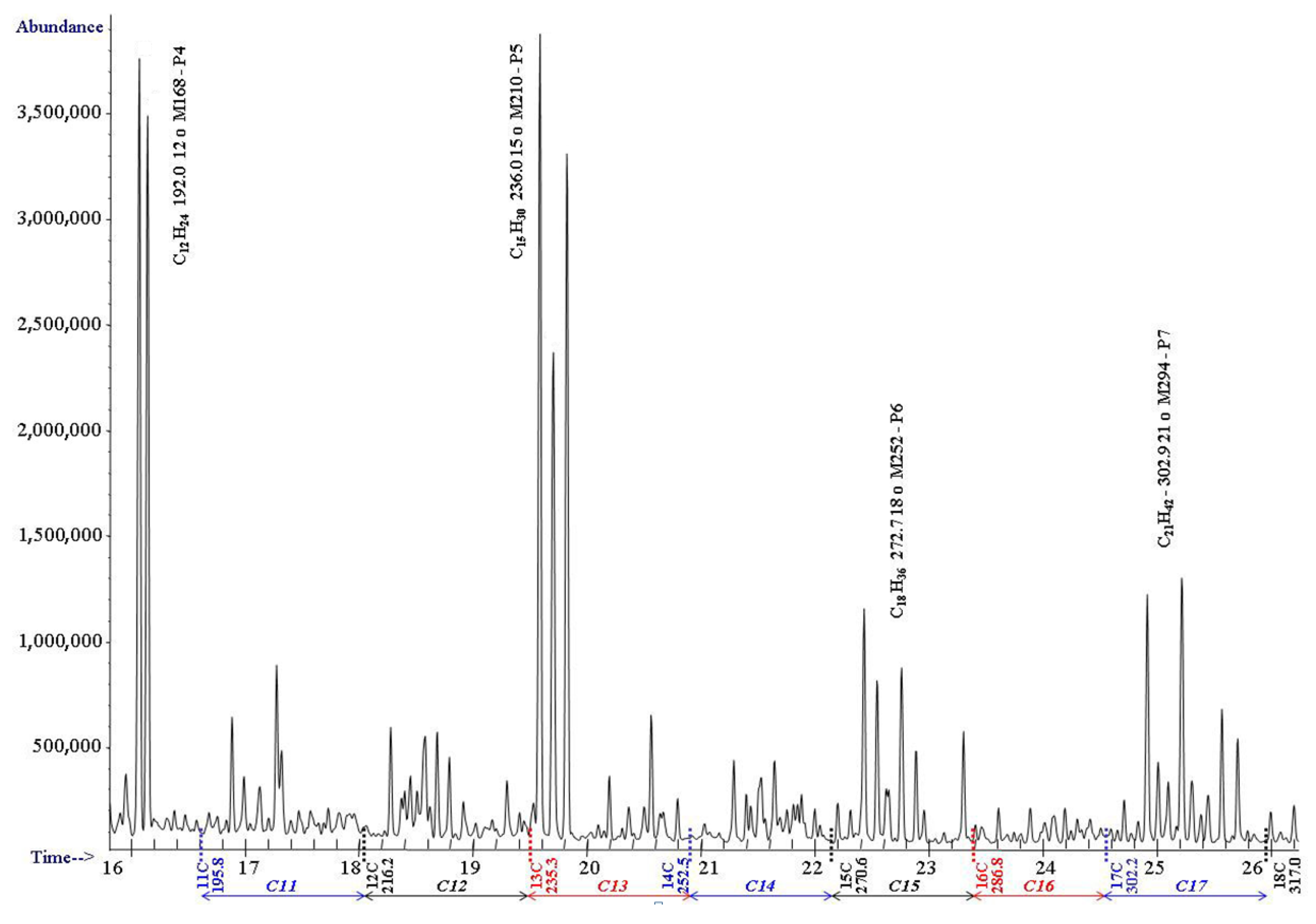
| 12 | 216.1 | 216.4 | 190.4 | 192.1 P4 | 190.1 | 191.8 | 11 | 1100–1199 | ||||
| 13 | 235.3 | 234.5 | 202.2 | 203.9 | 205.6 | 12 | 1200–1299 | |||||
| 14 | 253.4 | 252.9 | 224.9 | 224.6 | 224.3 | 13 | 1300–1399 | |||||
| 15 | 270.5 | 270.6 | 234.7 | 236.4 P5 | 234.4 | 236.1 | ||||||
| 16 | 286.8 | 286.6 | 243.9 | 245.6 | 247.3 | 14 | 1400–1499 | |||||
| 17 | 302.3 | 301.9 | 263.2 | 262.9 | 262.6 | 15 | 1500–1599 | |||||
| 18 | 317.0 | 316.2 | 271.0 | 272.7 P6 | 270.7 | 272.4 | ||||||
| 19 | 331.2 | 329.8 | 278.3 | 280.0 | 281.7 | 16 | 1600–1699 | |||||
| 20 | 344.7 | 343.1 | 295.1 | 294.8 | 294.5 | 17 | 1700–1799 | |||||
| 21 | 357.7 | 356.6 | 301.2 | 302.9 P7 | 300.9 | 302.6 | ||||||
| 22 | 370.2 | 368.7 | 307.0 | 308.7 | 310.4 | 18 | 1800–1899 | |||||
| 23 | 382.3 | 380.1 | 321.9 | 321.6 | 321.3 | |||||||
| 24 | 393.9 | 391.4 | 326.8 | 328.5 P8 | 326.5 | 328.2 | 19 | 1900–1999 | ||||
| 25 | 405.1 | 402.0 | 331.5 | 333.2 | 334.8 | |||||||
| 26 | 415.9 | 344.7 | 344.2 | 20 | 2000–2999 | |||||||
| 27 | 426.4 | 348.7 | 350.4 P9 | 348.8 | 350.1 | 21 | 2100–2199 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egloff, G. The Physical Constants of Hydrocarbons. Volume 1. Parafins, Olefins, and Acetylenes; Reinhold Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Egloff, G.; Sherman, J.; Dull, R.B. Boiling point relationship among aliphatic hydrocarbons. J. Phys. Chem. 1940, 44, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, H. Structural determination of paraffin boiling points. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener, H. Correlation of heats of isomerization, and differences in heats of vaporization of isomers, among the paraffin hydrocarbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2636–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, H. Vapor pressure-temperature relationships among the branched paraffin hydrocarbons. J. Phys. Chem. 1948, 52, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, H. Relation of the physical properties of the isomeric alkanes to molecular structure. Surface tension, specific dispersion, and critical solution temperature in aniline. J. Phys. Chem. 1948, 52, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, H. Topological index. A newly proposed quantity characterizing the topological nature of structural isomers of saturated hydrocarbons. Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan 1971, 44, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randić, M. Characterization of molecular branching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 6609–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, I.; Yeh, Y.N.; Lee, S.L.; Luo, Y.L. Some recent results in the theory of the Wiener number. Indian J. Chem. A 1993, 32, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić, S.; Trinajstić, N.; Mihalić, Z. The Wiener index: Developments and applications. Croat. Chim. Acta 1995, 68, 105–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya, H. Mathematical and chemical analysis of Wiener’s polarity number. In Topology in Chemistry: Discrete Mathematics of Molecules; Rouvray, D.H., King, R.B., Eds.; Chichester: Horwood, NL, Canada, 2002; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Li, Z.G.; Hu, M.L. A novel set of Wiener indices. J. Mol. Graphics Model 2003, 22, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H. The extended Wiener index. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 365, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, L.; Lauderdale, L.-K. On aratio of Wiener indices for embedded graphs. Discrete Math. 2023, 346, 113320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lee, H.-Y. The prediction of thermal pressure coefficients for both normal and branched paraffins from molecular structure. Fluid Ph. Equilib. 1996, 122, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.-B.; Xun, Y.-M.; Cheng, W.-T. Structure/property correlation of substituted compounds based on graph theory. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 234, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.Y.; Tong, C.M.; Durrant, M.C. Estimation of boiling points using density functional theory with polarized continuum model solvent corrections. J. Mol. Graphics Model 2011, 30, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, S.; Soave, G.S.; Pellegrini, L.A. Use of normal boiling point correlations for predicting critical parameters of paraffins for vapour–liquid equilibrium calculations with the SRK equation of state. Fluid Ph. Equilib. 2009, 276, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Sanada, Y. Structural analysis and estimation of boiling point of hydrocarbons in a coal-derived liquid by a group contribution method. Fuel 1992, 71, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santak, P.; Conduit, G. Predicting physical properties of alkanes with neural networks. Fluid Ph. Equilib. 2019, 501, 112259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Kearsley, A.J.; Schneider, B.I.; Keyrouz, W.; Allison, T.C. Graph convolutional neural network applied to the prediction of normal boiling point. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2022, 112, 108149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Ji, X.M.; Li, J.L. Molecular inductive effect index and boiling point of paraffinic hydrocarbons. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 22, 440–445. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.-T.; Cao, C. Using the intermolecular interaction index to understand the change in boiling points of alkanes. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.-T.; Cao, C. General equation to express changes in the physicochemical properties of organic homologues. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 26670–26679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H. The valence hyper-Wiener index for unsaturated hydrocarbons of chemical trees. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 357, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jalbout, A.F. On the valence Wiener index for unsaturated hydrocarbons. J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem) 2003, 625, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST Chemistry WebBook. Available online: http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Kovats, E. Gas-chromatographische Charakterisierung organischer Verbindungen. Teil 1: Retentionsindices aliphatischer halogenide, alkohole, aldehyde und ketone. Helv. Chim. Acta 1958, 41, 1915–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Makino, T. Thermal degradation of polypropylene. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1975, 1, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnaru, E.; Stoleru, E.; Ioniță, D.; Brebu, M. Thermal properties of seed cake biomasses and their valorisation by torrefaction. Polymers 2024, 16, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebu, M.; Spiridon, I. Co-pyrolysis of LignoBoost® lignin with synthetic polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 2104–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| nC | pn nC − 3 | ωn (nC − 1)nC(nC + 1)/6 | piso | ωiso | ΔTn-iso * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3m series | |||||
| 3 | 0 | 4 | - | - | 0.00 |
| 6 | 3 | 35 | 3 | 32 | 8.17 |
| 9 | 6 | 120 | 7 | 102 | 16.28 |
| 12 | 9 | 286 | 11 | 232 | 25.75 |
| 15 | 12 | 560 | 15 | 440 | 35.77 |
| 18 | 15 | 969 | 19 | 744 | 46.06 |
| 21 | 18 | 1540 | 23 | 1162 | 56.50 |
| 24 | 21 | 2300 | 27 | 1712 | 67.04 |
| 27 | 24 | 3276 | 31 | 2412 | 77.65 |
| 3m+1 series | |||||
| 4 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 9 | 11.63 |
| 7 | 4 | 56 | 4 | 48 | 16.00 |
| 10 | 7 | 165 | 8 | 135 | 23.90 |
| 13 | 10 | 364 | 12 | 288 | 33.07 |
| 16 | 13 | 680 | 16 | 525 | 42.84 |
| 19 | 16 | 1140 | 20 | 864 | 52.93 |
| 22 | 19 | 1771 | 24 | 1323 | 63.21 |
| 25 | 22 | 2600 | 28 | 1920 | 73.62 |
| 3m+2 series | |||||
| 5 | 2 | 20 | - | - | - |
| 8 | 5 | 84 | 6 | 75 | 8.28 |
| 11 | 8 | 220 | 10 | 184 | 18.16 |
| 14 | 11 | 455 | 14 | 365 | 28.50 |
| 17 | 14 | 816 | 18 | 636 | 39.04 |
| 20 | 17 | 1330 | 22 | 1015 | 49.68 |
| 23 | 20 | 2024 | 26 | 1520 | 60.37 |
| 26 | 23 | 2925 | 30 | 2169 | 71.10 |
| Compound | bp | RI | nC | Equivalent Normal Paraffin | bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid | 117.9 | 624 | 6 | Heptane | 98.4 |
| Acetol (hydroxyacetone) | 145 | 655 | 6 | Octane | 125.7 |
| 2,3-butanediol | 177 | 791 | 7 | Decane | 174 |
| Furfural | 161.7 | 828 | 8 | Nonane | 150.8 |
| Furfuryl alcohol | 171 | 850 | 8 | Nonane | 150.8 |
| Phenol | 181.7 | 975 | 9 | Decane | 174 |
| Guaiacol | 205 | 1086 | 10 | Undecane | 195.8 |
| Syringol | 261 | 1350 | 13 | Tetradecane | 252 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brebu, M.; Murata, K. The Fundamentals of the NP-Gram Method for the Characterisation of Pyrolysis Oils Based on the Estimated Boiling Points of Pyrolysis Products from Polypropylene. Polymers 2025, 17, 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131855
Brebu M, Murata K. The Fundamentals of the NP-Gram Method for the Characterisation of Pyrolysis Oils Based on the Estimated Boiling Points of Pyrolysis Products from Polypropylene. Polymers. 2025; 17(13):1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131855
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrebu, Mihai, and Katsuhide Murata. 2025. "The Fundamentals of the NP-Gram Method for the Characterisation of Pyrolysis Oils Based on the Estimated Boiling Points of Pyrolysis Products from Polypropylene" Polymers 17, no. 13: 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131855
APA StyleBrebu, M., & Murata, K. (2025). The Fundamentals of the NP-Gram Method for the Characterisation of Pyrolysis Oils Based on the Estimated Boiling Points of Pyrolysis Products from Polypropylene. Polymers, 17(13), 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131855








