Preparation of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Bending Plate and Its Long-Term Performance Exposed in Alkaline Solution Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Raw Materials
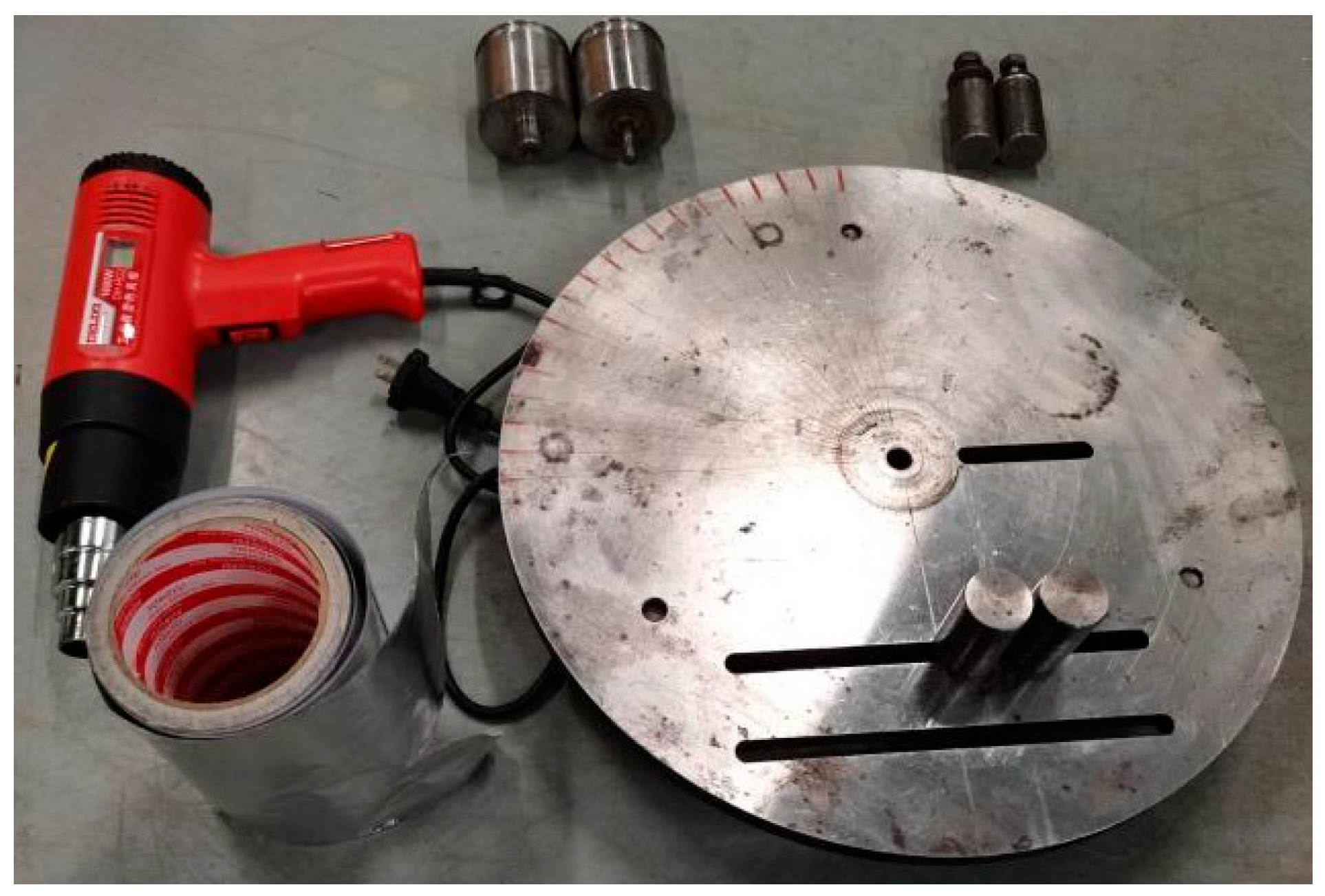
2.2. Preparation Technology of Bending Plate
2.2.1. Design Idea and Equipment Design
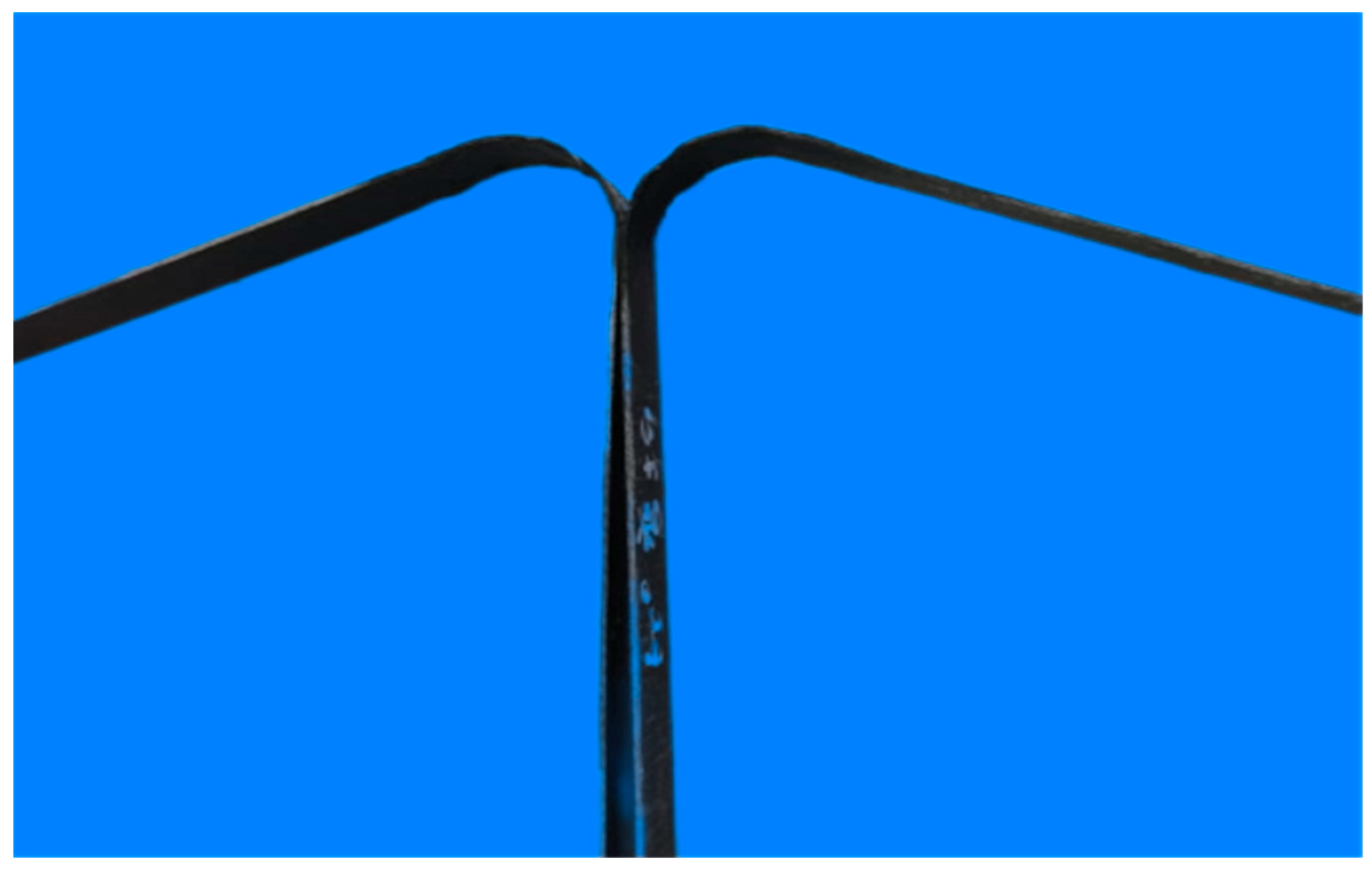
2.2.2. Preparation Process of Bending Plate
2.3. Exposure Condition
2.4. Mechanical Tests
2.4.1. Tensile Tests
2.4.2. Short Beam Shear Tests
2.5. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis Tests (TGA)
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
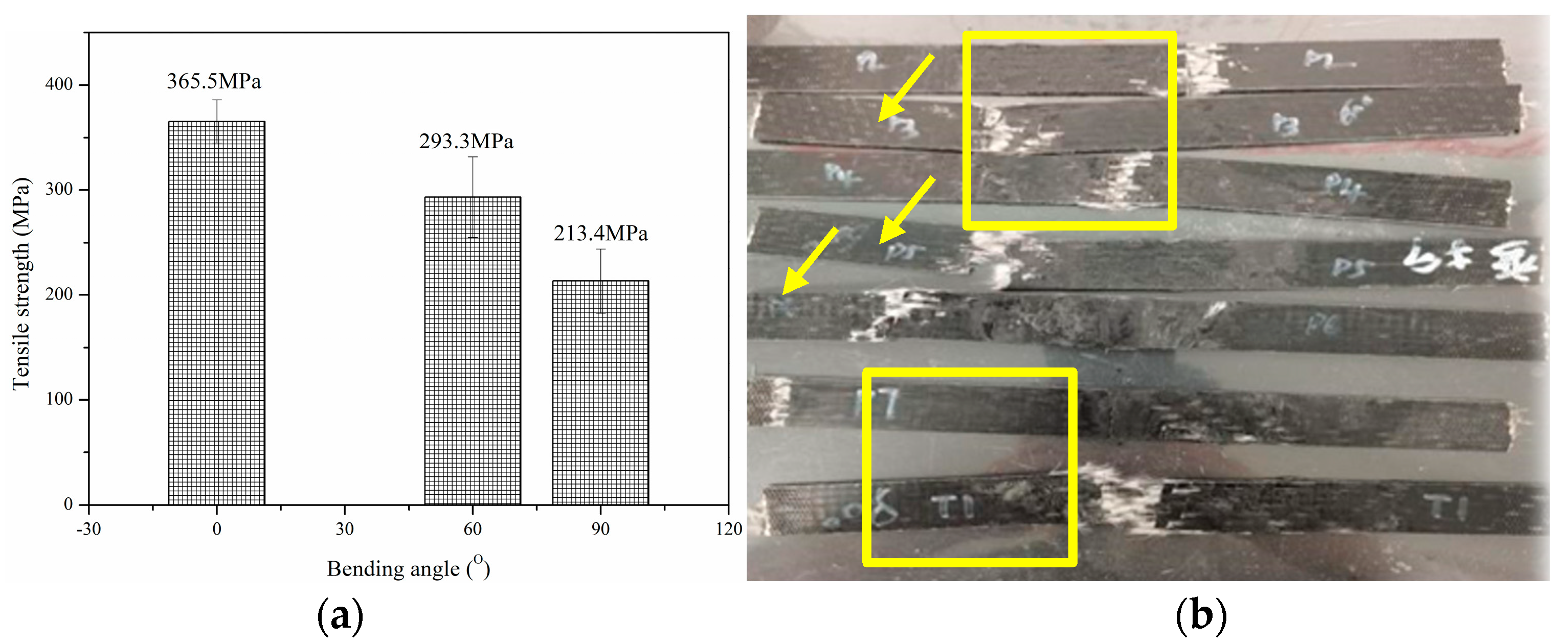
3.1. Tensile Properties of Thermoplastic Bending Plate
3.2. Effect of Alkali Solution Immersion on Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Bending Plate
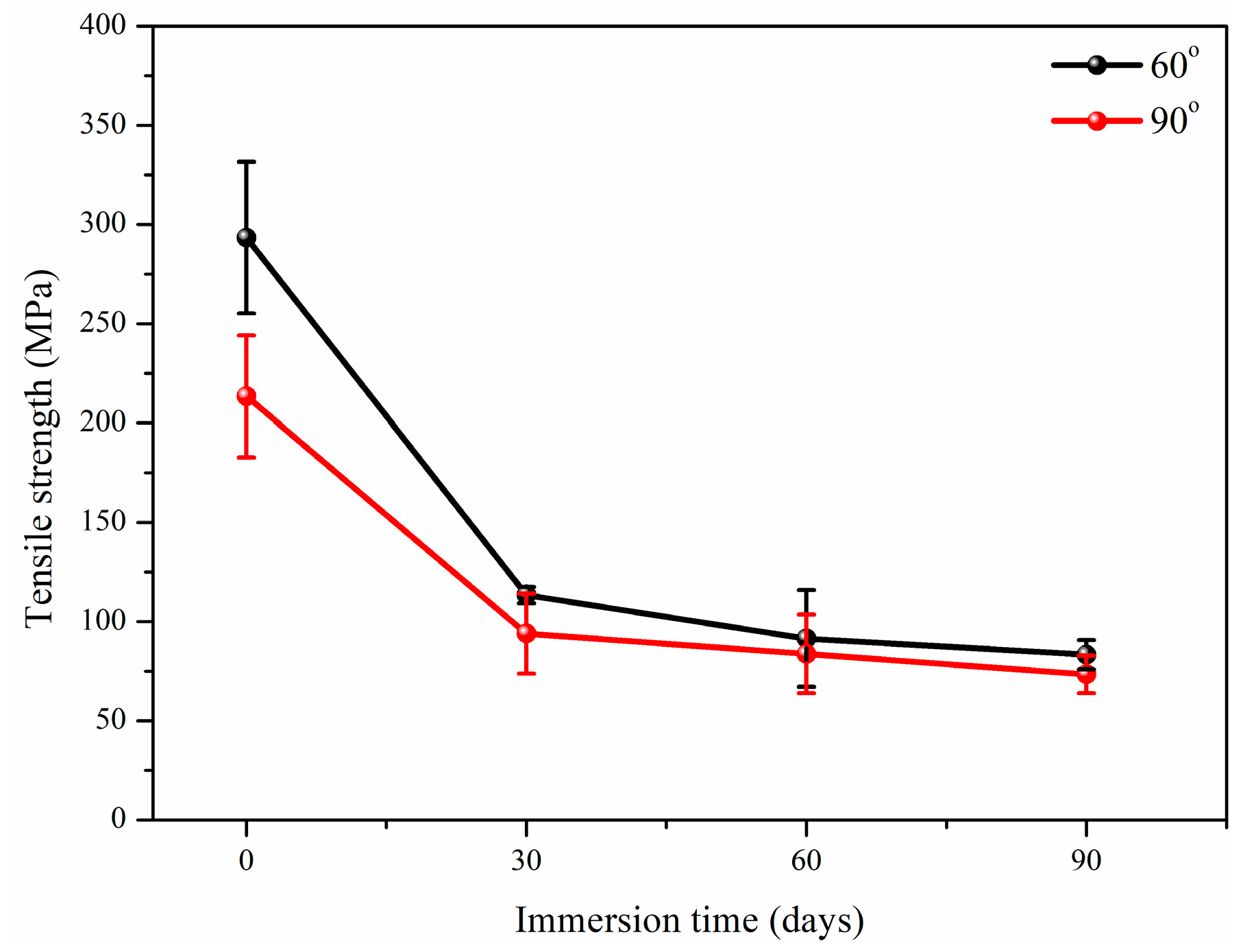
3.2.1. Tensile Properties
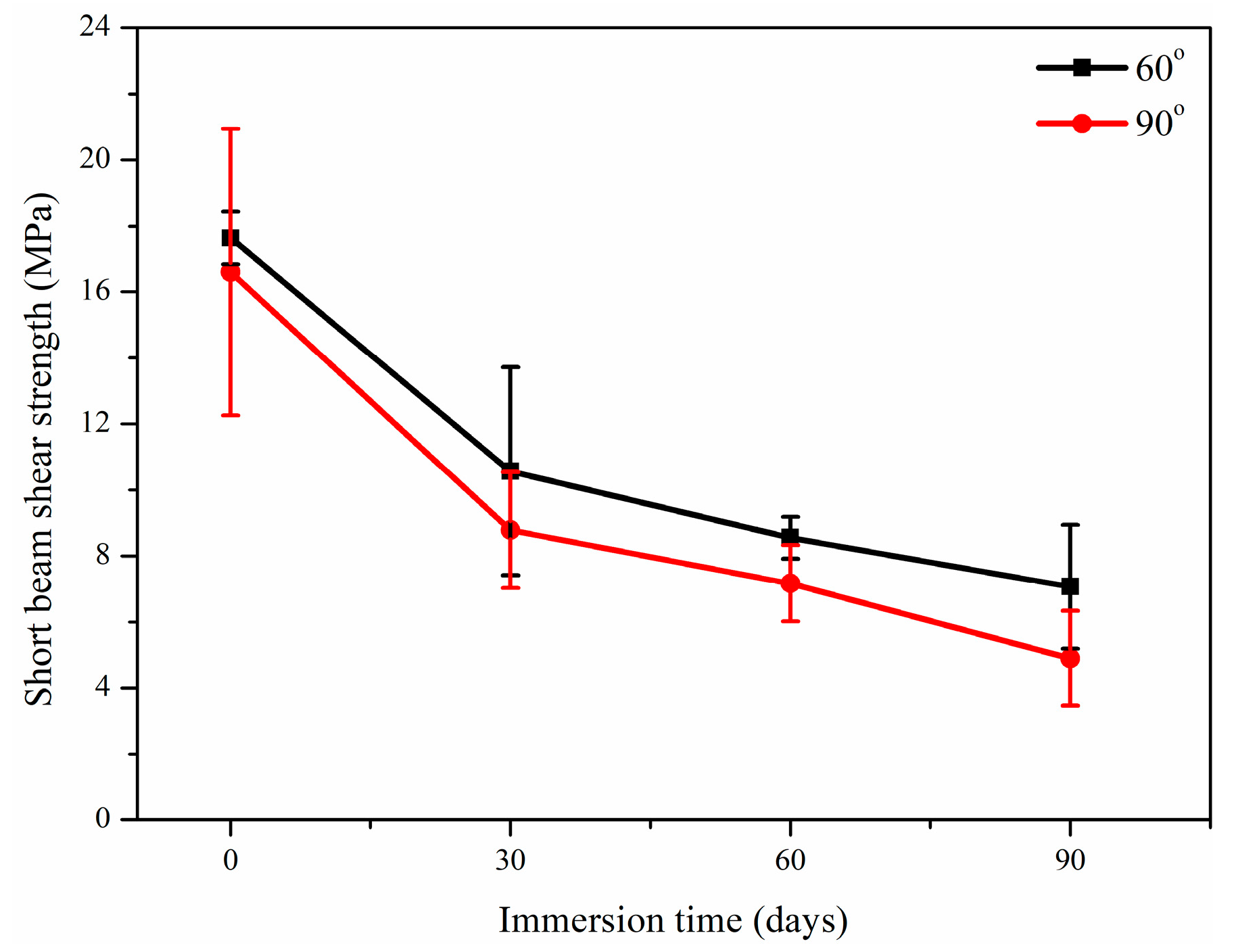
3.2.2. Short Beam Shear Strength
3.2.3. Summary of Mechanical Properties
3.3. Long-Term Evolution of Thermal Properties
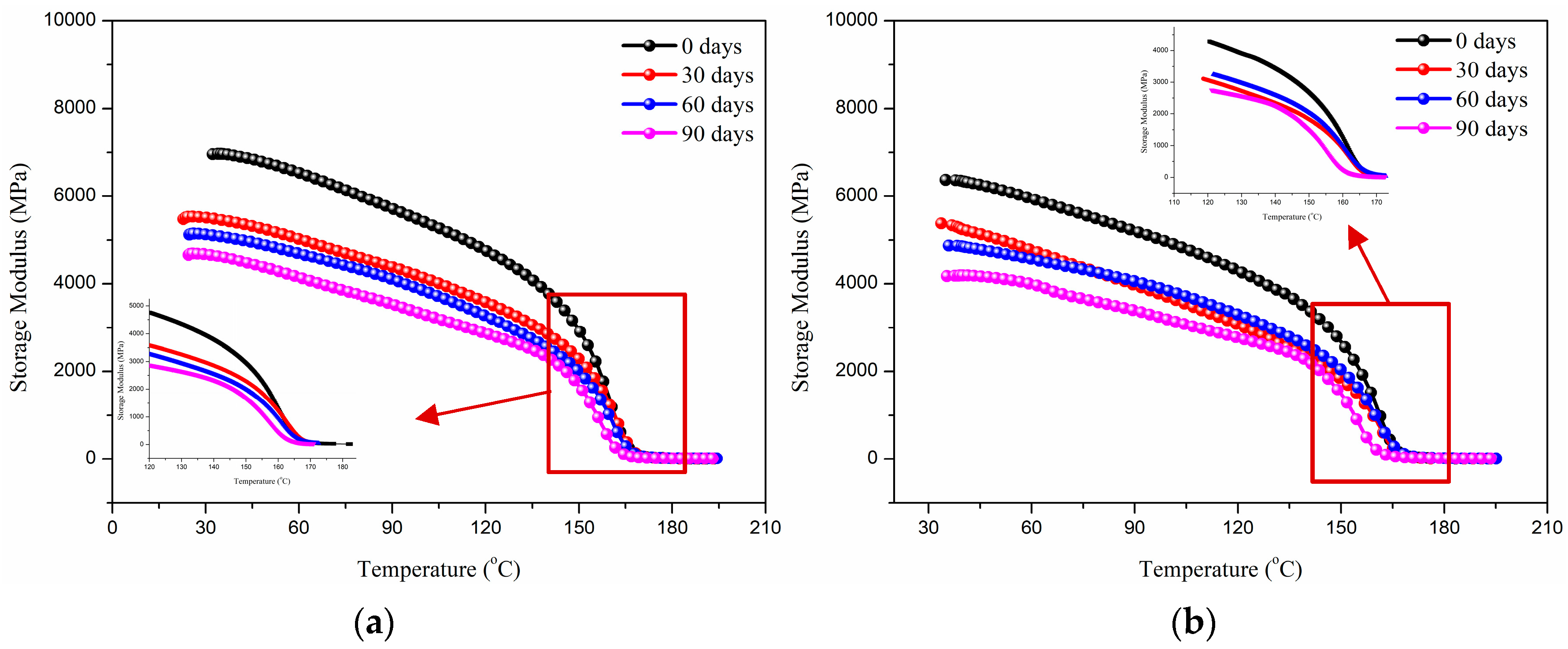
3.3.1. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
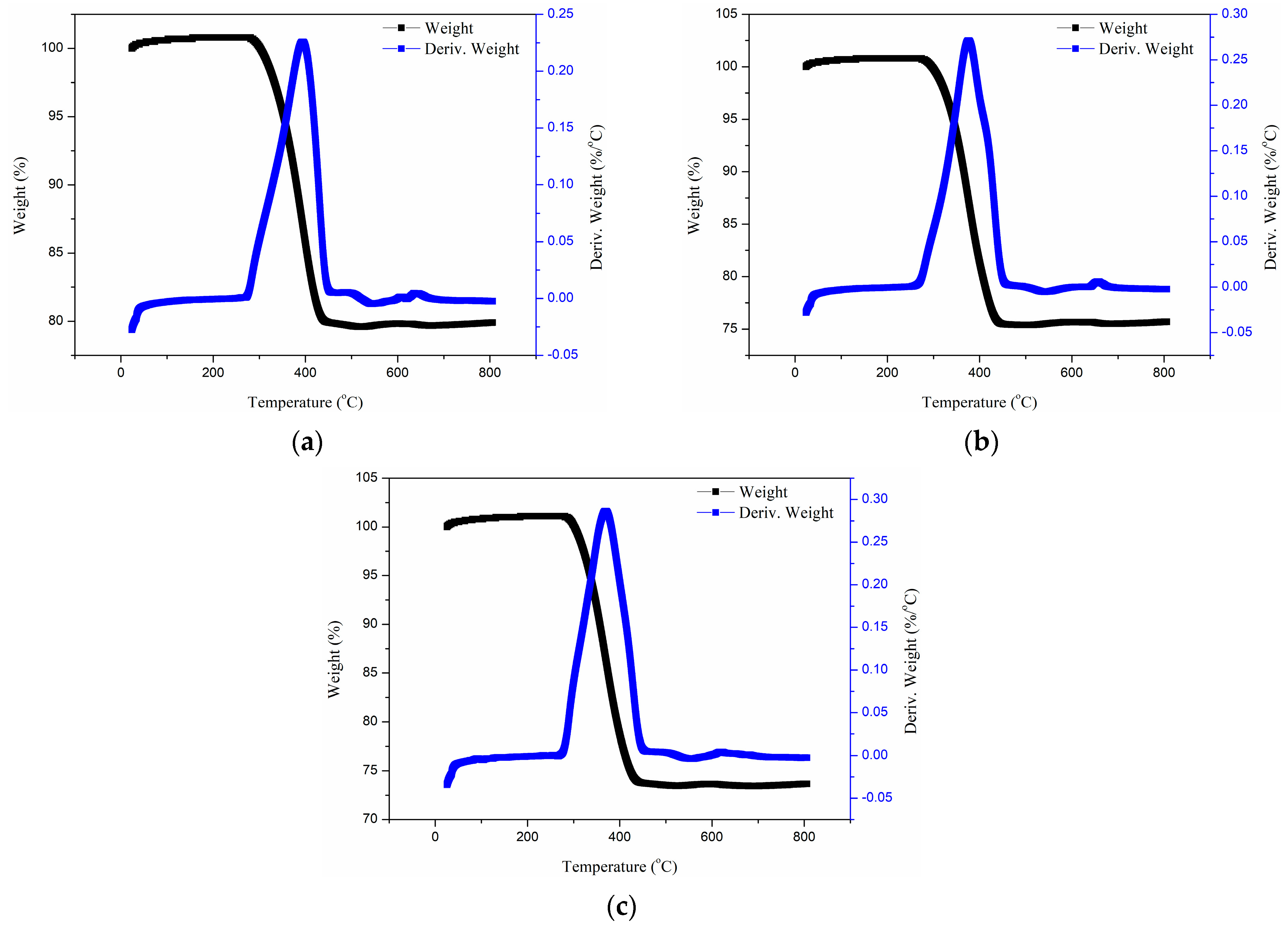
3.3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Bending Plate
3.4. Degradation Mechanism Analysis
3.5. Comparison with Others’ Work
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The effect of bending angle on the tensile strength of thermoplastic composite plates is essentially multi-scale damage accumulation and failure mode transition induced by geometric defects. Bending effect leads to the continuous failure of fibers, and the outer fibers break under tension, and the inner fibers buckle under compression, resulting in the debonding of the fiber–matrix interface.
- (2)
- Alkali solution (OH− ions) corrode the surface of glass fiber to form soluble silicate, which is obviously proved by the mass fraction of glass fiber decreased from 79.9% to 73.65%. In addition, alkali solution penetrates into the fiber/matrix interface to cause debonding and weakens the stress transfer efficiency. This contributes to the highest degradation ratio of tensile strength being 71.6% (60° bending) and 65.6% (90° bending), respectively.
- (3)
- High curvature bending (such as 90°) leads to local buckling of fibers and plastic deformation of the matrix, forming microcracks and fiber–resin interface bonding at the bending area. This not only directly weakens the local stiffness of the material, but also provides a fast channel for alkali penetration, accelerating the chemical erosion and debonding process in the interface area, bringing about an additional maximum 10.56% degradation of the shear strength.
- (4)
- The alkali immersion process leads to the obvious degradation of storage modulus and thermal decomposition temperature of the composite plate. SEM images revealed the dual degradation characteristics of dissolution of the glass fiber surface and interface debonding dominant failure. Compared with other works, it can be found that the long-term performance of glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composites is controlled by the corrosive media type, bending angle, and immersion time.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomez, E.; Leporace-Guimil, B.; Conforti, A.; Plizzari, G.; Duffó, G.; Zerbino, R. A practical approach for monitoring reinforcement corrosion in steel fiber reinforced concrete elements exposed to chloride rich environments. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, R.; Bautista, A.; Velasco, F.; Soleimani, M.; Pourfath, M. Green corrosion inhibition for carbon steel reinforcement in chloride-polluted simulated concrete pore solution using extract. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imjai, T.; Garcia, R.; Guadagnini, M.; Pilakoutas, K. Strength Degradation in Curved Fiber-reinforced Polymer (FRP) Bars Used as Concrete Reinforcement. Polymers 2020, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, L.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, K.; Zeng, J. Bond behavior of CFRP-strengthened steel structures and its environmental influence factors: A critical review. Sustain. Struct. 2024, 4, 000038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazedj, S.; Morais, A.J.; Jalai, S. Comparison of embodied energy and carbon dioxide emissions of masonry building and conventional building with reinforced concrete structure. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Life Cycle Assessment and Construction: Civil Engineering and Buildings, Nantes, France, 10–12 July 2012; Volume 86, p. 387. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.; Wang, X.; Ding, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, Z. Evaluation of the long-term performance and durability of basalt fiber reinforced polymer bars in concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 448, 138226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yan, D. Study on the durability of GFRP bars and carbon/glass hybrid fiber reinforced polymer (HFRP) bars aged in alkaline solution. Compos. Struct. 2021, 261, 113285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, C.; Hong, B. Effect of fiber hybrid mode on the tension-tension fatigue performance for the pultruded carbon/glass fiber reinforced polymer composite rod. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 260, 108208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.; Ploeckl, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Lissner, M.; Pohl, C.; Quino, G.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Toenjes, M.; Cui, H.; Petrinic, N. A review of the effect of loading rate on the mechanical properties of unidirectional carbon fibre reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2025, 193, 108773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Zheng, L.; Wang, H.Z.; Liu, W.K.; Harkin-Jones, E.; Ma, J.X.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, L.B.; Wu, Y.P.; Zhao, C.X.; et al. Enhanced mechanical and tribological properties of basalt fiber reinforced polymer composites with a soft-rigid interfacial structure. Polym. Compos. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of simulated seawater on static and fatigue performance of GFRP bar-concrete bond. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 68, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.M.; Yu, Y.X.; Xu, G.J.; Li, Q.C.; Pan, Y.F. Experimental study on bond performance between carbon/glass-hybrid-fiber-reinforced polymer bars and concrete. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2024, 27, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, A.; Rana, R.S. Characterization of eco-engineered hybrid polymer composites: Reinforcing epoxy with basalt fibers and recycled biochar from rice husk for enhanced mechanical and environmental performance. Compos. Interfaces 2025, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pan, Y.; Xian, G.; Yang, M. Durability of basalt fibers, glass fibers, and their reinforced polymer composites in artificial seawater. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Hong, B. Hygrothermal resistance of pultruded carbon, glass and carbon/glass hybrid fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.G.; Yin, X.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Guo, R.; Xian, G.J. Long-term service evaluation of a pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod exposed to elevated temperature, hydraulic pressure and fatigue load coupling. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhou, P.; Ning, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Xian, G. Durability of carbon- and glass-fiber reinforced thermoplastic polymer composites: A literature review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertuz, A.D.; Díaz-Cardona, S.; González-Estrada, O.A. Static and fatigue behaviour of continuous fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites manufactured by fused deposition modelling technique. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 130, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.; Kim, M. Impact resistance and interlaminar shear strength enhancement of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites by introducing MWCNT-anchored carbon fiber. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 217, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Zhou, P.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Dong, S.; Guo, R.; Li, J.; Du, H.; Zhong, J. Design, preparation and mechanical properties of novel glass fiber reinforced polypropylene bending bars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 429, 136455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Tian, J.W.; Li, C.G.; Guo, R.; Bai, Y.B.; Ji, Q.K.; Peng, Z.; He, T.P.; et al. Design of novel glass fiber reinforced polypropylene cable-anchor component and its long-term properties exposed in alkaline solution. Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2024, 20, e03383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Dong, S.; Li, C.; Kong, D.; Bai, Y.; Xian, G.; Yue, Q. Study on the durability of compression behavior for glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene thermoplastic composite bars in various aging environments. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 8555–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSuhaibani, F.A.; Falath, W.; Theravalappil, R. Improved fracture toughness of glass fibers reinforced polypropylene composites through hybridization with polyolefin elastomers and polymeric fibers for automotive applications. Polym. Compos. 2025, 46, 6553–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höftberger, T.; Zitzenbacher, G.; Burgstaller, C. Influence of Processing Parameters in Injection Molding on the Properties of Short Carbon and Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Xian, G.; Tian, J.; Ma, Z.; Li, C.; Xin, M.; Zhang, Y. Effect of fiber surface treatment with silane coupling agents and carbon nanotubes on mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced polyamide 6 composites. Polym. Compos. 2025, 46, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.W.; Dong, J.F.; Wang, Q.Y. Effect of CFRP reinforcement on loading capacity of recycled concrete column under cycled free-thaw environment. J. Build. Mater. 2019, 22, 451–458+466. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.F.; Xue, W.C. Strength Retention Rate Distribution Model and Reliability Analysis of FRP Stirrups. J. Build. Mater. 2024, 27, 496–502. [Google Scholar]
- Bachtiar, D.; Mohammed, A.A.; Palanisamy, S.; Imran, A.; Siregar, J.P.; Rejab, M.R.B.; Syaubari, S.; Cionita, T.; Fitriyana, D.F.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; et al. Effect of alkaline treatment on the thermal and mechanical properties of sugar palm fibre reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzi, A.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Jawaid, M.; Mansor, M.R. Effect of Alkaline Treatment on Mechanical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Roselle/Sugar Palm Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Polyurethane Hybrid Composites. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Zhou, G.; Wen, F.S.; Jiao, Y.Z. Degradation Law and Mechanism of GFRP Bars in Concrete Environment. J. Build. Mater. 2023, 26, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. New Type of Polypropylene Based FRP Reinforcement, OFBG Sensor and Their Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J. Research on the Basic Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic FRP Reinforcement for Concrete Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Southeast University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Apitz, A.; Schmitz, J.; Hückler, A.; Schlaich, M. New thermoplastic carbon fiber reinforced polymer rebars and stirrups. Struct. Concr. 2022, 23, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imjai, T.; Guadagnini, M.; Pilakoutas, K.; Garcia, R.; Sukontasukkul, P.; Limkatanyu, S. A practical macro-mechanical model for the bend capacity of fibre-reinforced polymer bars. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Struct. Build. 2021, 174, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, C.; Bai, Y.; Dong, S.; Xian, G.; Vedernikov, A.; Akhatov, I.; Safonov, A.; Yue, Q. Durability study on the interlaminar shear behavior of glass-fibre reinforced polypropylene (GFRPP) bars for marine applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 349, 128694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.J.; Bai, Y.B.; Zhou, P.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, C.G.; Dong, S.C.; Guo, R.; Tian, J.W.; Li, J.H.; Zhong, J.; et al. Long-term properties evolution and life prediction of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic bending bars exposed in concrete alkaline environment. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmokrane, B.; Mousa, S.; Mohamed, K.; Sayed-Ahmed, M. Physical, mechanical, and durability characteristics of newly developed thermoplastic GFRP bars for reinforcing concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 122200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Ji, Q.K.; Guo, Z.Y.; Li, C.G.; Guo, R.; Tian, J.W.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.P.; Xian, G.J. Design, preparation, and mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic self-anchor plate cable exposed in alkaline solution environment. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 11687–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Zhou, P.; Li, C.; Dong, S.; Du, H.; Tian, J.; Guo, R.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; He, T. Mechanical properties evaluation of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite plate under combined bending loading and water immersion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 440, 137470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee ACI. Guide Test Methods for Fiber-reinforced Polymers (FRP) Composites for Reinforcing or Strengthening Concrete and Masonry Structures; American Concrete Institute: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, D.; Xian, G.; Li, C. Effect of Immersion in Water or Alkali Solution on the Structures and Properties of Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2021, 13, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffler, C.; Förster, T.; Mäder, E.; Heinrich, G.; Hempel, S.; Mechtcherine, V. Aging of alkali-resistant glass and basalt fibers in alkaline solutions: Evaluation of the failure stress by Weibull distribution function. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, I.; Leman, Z.; Zainudin, E.S.; Ishak, M.R. Hybrid and Nonhybrid Laminate Composites of Sugar Palm and Glass Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene: Effect of Alkali and Sodium Bicarbonate Treatments. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 2019, 1230592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larena, A.; de Ochoa, S.J.; Domínguez, F. Dynamic-mechanical analysis of the photo-degradation of long glass fibre reinforced polypropylene:: Mechanical properties’ changes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J. Experimental Study on Mechanical and Durability Properties of Glass and Polypropylene Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1900–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Immersion Time (Days) | Tensile Strength | Short Beam Shear Strength | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60° Bending Angle | 90° Bending Angle | 60° Bending Angle | 90° Bending Angle | |
| 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 30 | 38.66 | 44.02 | 59.92 | 52.91 |
| 60 | 31.78 | 39.20 | 48.49 | 43.17 |
| 90 | 28.40 | 34.40 | 40.08 | 29.52 |
| Material Type | Exposure Medium | Exposure Time (Days) | Tensile Strength Retention (%) | Shear Strength Retention (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight bars | Distilled water | 0/30/75/120 | / | 100/88.7/72.6/67.0 | [35] |
| Straight bars | Alkaline | 0/30/75/120 | / | 100/91.3/77.0/67.5 | [35] |
| Bending bars (90° bending) | Alkaline | 0/30/105/180 | 100/29.8/23.7/20.6 | / | [36] |
| Bending plate (without bending strain) | Distilled water | 0/90/180 | 100/68.68/58.32 | 100/70.22/61.65 | [39] |
| Bending plate (low bending strain) | Distilled water | 0/90/180 | 100/59.76/55.57 | / | [39] |
| Bending plate (high bending strain) | Distilled water | 0/90/180 | 100/51.72/46.11 | / | [39] |
| Bending plate cable | Alkaline | 0/7/14/21 | 100/60.0/39.6/29.7 | 100/75.5/71.5/69.2 | [38] |
| Bending plate (60° bending) | Alkaline | 0/30/60/90 | 100/38.66/31.18/28.40 | 100/59.92/48.49/40.08 | This paper |
| Bending plate (90° bending) | Alkaline | 0/30/60/90 | 100/44.02/39.20/34.40 | 100/52.91/43.17/29.52 | This paper |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Z.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; Li, C. Preparation of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Bending Plate and Its Long-Term Performance Exposed in Alkaline Solution Environment. Polymers 2025, 17, 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131844
Peng Z, Wang A, Wang C, Li C. Preparation of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Bending Plate and Its Long-Term Performance Exposed in Alkaline Solution Environment. Polymers. 2025; 17(13):1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131844
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Zhan, Anji Wang, Chen Wang, and Chenggao Li. 2025. "Preparation of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Bending Plate and Its Long-Term Performance Exposed in Alkaline Solution Environment" Polymers 17, no. 13: 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131844
APA StylePeng, Z., Wang, A., Wang, C., & Li, C. (2025). Preparation of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Bending Plate and Its Long-Term Performance Exposed in Alkaline Solution Environment. Polymers, 17(13), 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131844






