Liquid Hot Water and Steam Explosion Pretreatment Methods for Cellulosic Raw Materials: A Review
Abstract
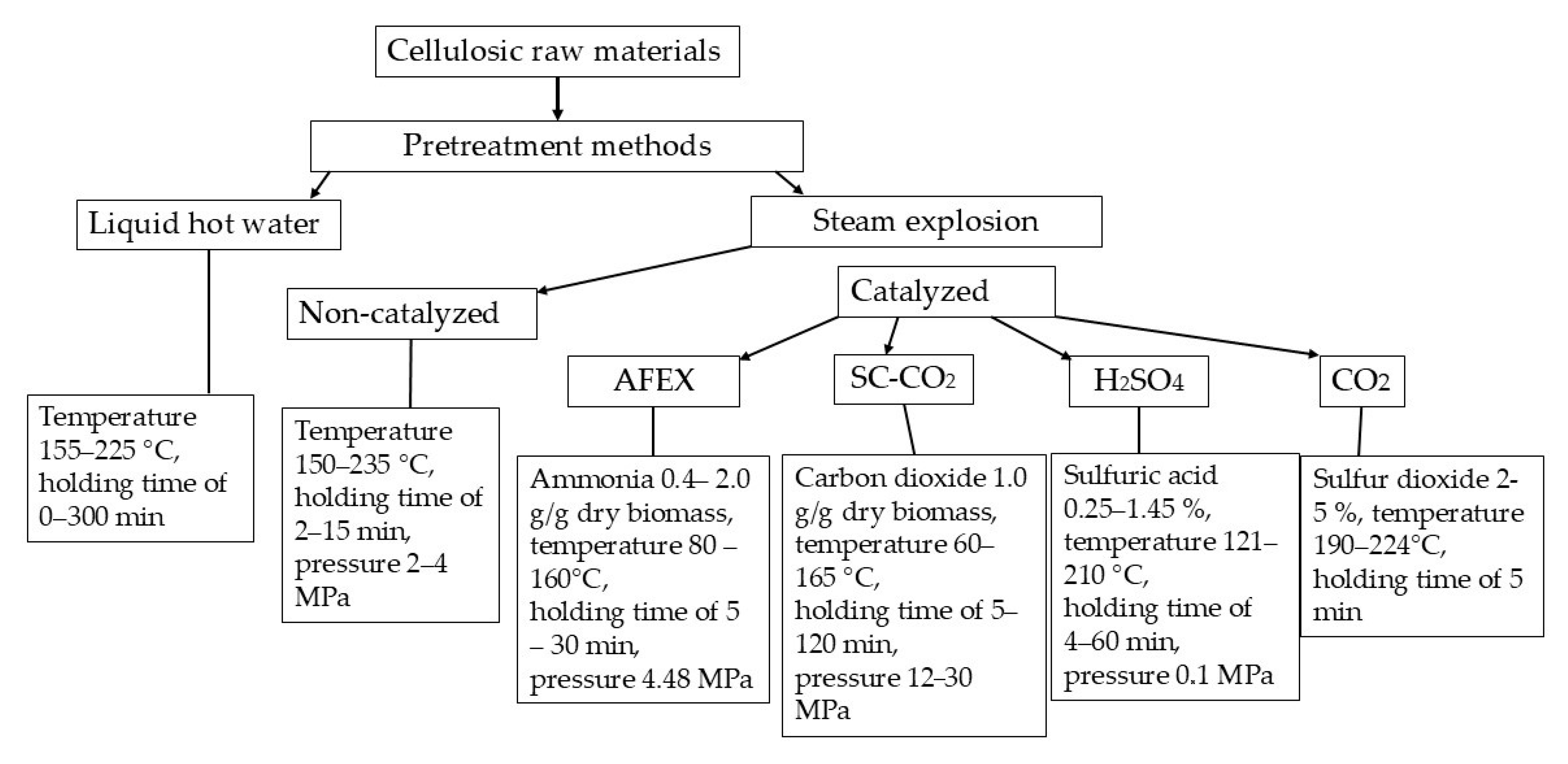
1. Introduction
2. Liquid Hot Water Pretreatment
3. Non-Catalyzed Steam Explosion Pretreatment
4. Catalyzed Steam Explosion Pretreatment
5. Techno-Economic Analysis or Life Cycle Assessment of Liquid Hot Water and Steam Explosion Methods
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.H.; Nižetić, S.; Sirohi, R.; Huang, Z.; Luque, R.; Papadopoulos, A.M.; Sakthivel, R.; Nguyen, X.P.; Hoang, A.T. Liquid hot water as sustainable biomass pretreatment technique for bioenergy production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D. Physico-chemical conversion of lignocellulose: Inhibitor effects and detoxification strategies: A mini review. Molecules 2018, 23, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Jiang, X.; Shen, X.; Hu, J.; Tang, W.; Wu, X.; Ragauskas, A.; Jameel, H.; Meng, X.; Yong, Q. Lignin-enzyme interaction: A roadblock for efficient enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D. Biomass recalcitrance. Part I: The chemical compositions and physical structures affecting the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2012, 6, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Chang, X.; Chen, D.; Xue, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, H.; Han, S. A review on the pretreatment of lignocellulose for high-value chemicals. Fuel Process Technol. 2017, 160, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhao, X. Conversion of lignocellulose to biofuels and chemicals via sugar platform: An updated review on chemistry and mechanisms of acid hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Wang, C.W.; Ong, H.C.; Show, P.L.; Hsieh, T.H. Torrefaction, pyrolysis and two-stage thermodegradation of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin. Fuel 2019, 258, 116168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, H.A.; Thomsen, M.H.; Trajano, H.L. Hydrothermal Processing in Biorefineries; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Z.; Liu, Z.H. Steam explosion and its combinatorial pretreatment refining technology of plant biomass to bio-based products. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 866–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejczyk, M.; Soszka, E.; Czapnik, M.; Ruppert, A.M.; Grams, J. Physical and chemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. In Second and Third Generation of Feedstocks; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 143–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.C.; Hallett, J.P. Recent advances in the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 20, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nizetic, S.; Ong, H.C.; Chong, C.T.; Atabani, A.E. Acid-based lignocellulosic biomass biorefinery for bioenergy production: Advantages, application constraints, and perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.G.; Meng, X.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. The critical role of lignin in lignocellulosic biomass conversion and recent pretreatment strategies: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Ragauskas, A. Pretreatment and lignocellulosic chemistry. Bioenergy Res. 2012, 5, 1043–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtasz-Mucha, J.; Hasani, M.; Theliander, H. Hydrothermal pretreatment of wood by mild steam explosion and hot water extraction. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, S. Impact of pretreatment technologies for biomass to biofuel production. In Substrate Analysis for Effective Biofuels Production; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 173–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.K.; Kim, Y.; Ximenes, E.; Ladisch, M.R. Effect of liquid hot water pretreatment severity on properties of hardwood lignin and enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Du, J.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Y. Influence of lignin addition on the enzymatic digestibility of pretreated lignocellulosic biomasses. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 181, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladeira Ázar, R.I.; Bordignon-Junior, S.E.; Laufer, C.; Specht, J.; Ferrier, D.; Kim, D. Effect of lignin content on cellulolytic saccharification of liquid hot water pretreated sugarcane bagasse. Molecules 2020, 25, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, D.; Purkait, M.K. Lignocellulosic conversion into value-added products: A review. Process Biochem. 2020, 89, 110–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvira, P.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; Ballesteros, M.; Negro, M.J. Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4851–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Kisielewska, M.; Dudek, M.; Rusanowska, P.; Nowicka, A.; Krzemieniewski, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Dębowski, M. Comparison of microwave thermohydrolysis and liquid hot water pretreatment of energy crop Sida hermaphrodita for enhanced methane production. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 128, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, F.; Qiu, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, F. Liquid hot water pretreatment to enhance the anaerobic digestion of wheat straw—Effects of temperature and retention time. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29424–29434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varongchayakul, S.; Songkasiri, W.; Chaiprasert, P. Optimization of cassava pulp pretreatment by liquid hot water for biomethane production. Bioenergy Res. 2021, 14, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, G.; Papadopoulou, K.; Alexandropoulou, M.; Lyberatos, G. Liquid hot water treatment of woody biomass at different temperatures: The effect on composition and energy production in the form of gaseous biofuels. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 38, 101485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Pérez, A.S.; Guerrero-Fajardo, C.A. Liquid Hot Water (LHW) and Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC) of Coffee Berry Waste: Kinetics, Catalysis, and Optimization for the Synthesis of Platform Chemicals. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imman, S.; Laosiripojana, N.; Champreda, V. Effects of liquid hot water pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis and physicochemical changes of corncobs. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 184, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Tao, Y.; Du, J.; Lv, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, H. Bioconversion of spray corn husks into L-lactic acid with liquid hot water pretreatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 129154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.; Singhania, R.R.; Patel, A.K.; Chen, C.W.; Piechota, G.; Dong, C.D. Sustainable production of cellulose and hemicellulose-derived oligosaccharides from pineapple leaves: Impact of hydrothermal pretreatment and controlled enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 398, 130526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, N.; Hendrickson, R.; Ho, N.; Sedlak, M.; Ladisch, M.R. Optimization of pH controlled liquid hot water pretreatment of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Hendrickson, R.; Mosier, N.S.; Ladisch, M.R. Liquid Hot Water Pretreatment of Cellulosic Biomass. In Biofuels; Mielenz, J., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols); Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Mosier, N.S.; Ladisch, M.R. Enzymatic digestion of liquid hot water pretreated hybrid poplar. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 25, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Zhang, B.; Niu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q. Enhancement of Liquid Hot Water Pretreatment on Corn Stover with Ball Milling to Improve Total Sugar Yields. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, E.; Llano, B.; Peñuela, M.; Peña, J.; Rios, L.A. Liquid-hot-water pretreatment of palm-oil residues for ethanol production: An economic approach to the selection of the processing conditions. Energy 2018, 160, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Loaiza, S.; Dias, M.; Daza-Serna, L.; de Carvalho, C.C.; Friedl, A. Integral analysis of liquid-hot-water pretreatment of wheat straw: Evaluation of the production of sugars, degradation products, and lignin. Sustainability 2021, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kreke, T.; Mosier, N.S.; Ladisch, M.R. Severity factor coefficients for subcritical liquid hot water pretreatment of hardwood chips. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shi, Z.; Xu, G.; Qin, Y.; Deng, J.; Yang, J. Bioethanol production from bamboo with alkali-catalyzed liquid hot water pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Fu, S. Improvement of xylo-oligosaccharides dissolution from Caragana korshinskii through liquid hot water pretreatment with tiny choline chloride. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelin, M.; Liebentritt, S.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A. Lignin from an integrated process consisting of liquid hot water and ethanol organosolv: Physicochemical and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyachai, N.; Weerasai, K.; Upajak, S.; Khongchamnan, P.; Wanmolee, W.; Laosiripojana, N.; Champreda, V.; Kowit, S.; Imman, S. Efficiency of Catalytic Liquid Hot Water Pretreatment for Conversion of Corn Stover to Bioethanol. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 29872–29881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risanto, L.; Fajriutami, T.; Hermiati, E. Enzymatic saccharification of liquid hot water and dilute sulfuric acid pretreated oil palm empty fruit bunch and sugarcane bagasse. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 141, No. 1, p. 012025. [Google Scholar]
- Sabanci, K.; Buyukkileci, A.O. Comparison of liquid hot water, very dilute acid and alkali treatments for enhancing enzymatic digestibility of hazelnut tree pruning residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, M.; Garcia Martin, J.F.; Bravo, V.; Sánchez, S. Ethanol production from olive stones through liquid hot water pre-treatment, enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation. Influence of enzyme loading, and pre-treatment temperature and time. Fermentation 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.C.; Jang, S.K.; Kwak, H.W.; Koo, B.; Choi, I.G. Production of succinic acid from liquid hot water hydrolysate derived from Quercus mongolica. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 150, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larnaudie, V.; Ferrari, M.D.; Lareo, C. Enzymatic hydrolysis of liquid hot water-pretreated switchgrass at high solid content. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 4361–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Wang, M.; Yu, Q.; Ma, Z.Y.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Wang, R.; Wen, J.N.; Lukuyu, B.A.; Tan, Z.L. Liquid hot water treatment of rice straw enhances anaerobic degradation and inhibits methane production during in vitro ruminal fermentation. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 4252–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Lai, C.; Li, X.; Yong, Q. Prewashing enhances the liquid hot water pretreatment efficiency of waste wheat straw with high free ash content. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qi, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, H. Two-step liquid hot water pretreatment of Eucalyptus grandis to enhance sugar recovery and enzymatic digestibility of cellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4895–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Lv, S.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Qi, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Tan, X. Liquid hot water pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse and its comparison with chemical pretreatment methods for the sugar recovery and structural changes. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Qi, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Tan, X. Pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse with liquid hot water and aqueous ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, L.V.A.; Pimenta, M.T.B.; da Silva Curvelo, A.A. Enhancing liquid hot water (LHW) pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse by high pressure carbon dioxide (HP-CO2). Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 57, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Song, F.; Liu, H.; Chang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H. Production of high concentration bioethanol from reed by combined liquid hot water and sodium carbonate-oxygen pretreatment. Energy 2021, 217, 119332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Gong, J.; Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhai, S.; An, Q.; Wang, H. Combined liquid hot water with sodium carbonate-oxygen pretreatment to improve enzymatic saccharification of reed. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, T.; Wang, K.; Cui, B.; Dai, Y. Combination of biological pretreatment with liquid hot water pretreatment to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of Populus tomentosa. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Du, J.; Tao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Combinatorial pretreatments of reed straw using liquid hot water and lactic acid for fermentable sugar production. Fuel 2023, 331, 125916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinwurm, F.; Turk, T.; Denner, J.; Whitmore, K.; Friedl, A. Combined liquid hot water and ethanol organosolv treatment of wheat straw for extraction and reaction modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, A.O.; Cortez, A.A.; Pellegrini, V.O.A.; Ngom, B.D.; Filgueiras, J.G.; de Azevedo, E.R.; Polikarpov, I. Combined liquid hot water and sulfonation pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse to maximize fermentable sugars production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 201, 116849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chang, S.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J. Changes on structural properties of biomass pretreated by combined deacetylation with liquid hot water and its effect on enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machineni, L. Lignocellulosic biofuel production: Review of alternatives. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 10, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, F.L.; Lu, M.; Fang, X.C. Emerging technologies for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic materials for bio-based products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z. Lignocellulose Biorefinery Engineering: Principles and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sulzenbacher, D.; Atzmüller, D.; Hawe, F.; Richter, M.; Cristobal-Sarramian, A.; Zwirzitz, A. Optimization of steam explosion parameters for improved biotechnological use of wheat straw. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volynets, B.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Dahman, Y. Biomass processing into ethanol: Pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, fermentation, rheology, and mixing. Green Process. Synth. 2017, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbor, V.B.; Cicek, N.; Sparling, R.; Berlin, A.; Levin, D.B. Biomass pretreatment: Fundamentals toward application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, T.R.; Pattnaik, F.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K.; Meda, V.; Naik, S. Hydrothermal pretreatment technologies for lignocellulosic biomass: A review of steam explosion and subcritical water hydrolysis. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chundawat, S.P.; Donohoe, B.S.; da Costa, S.L.; Elder, T.; Agarwal, U.P.; Lu, F.; Ralph, J.; Himmel, M.E.; Balan, V.; Dale, B.E. Multi-scale visualization and characterization of lignocellulosic plant cell wall deconstruction during thermochemical pretreatment. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, P.; Petridis, L.; O’Neill, H.M.; Pingali, S.V.; Foston, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Schulz, R.; Lindner, B.; Hanson, B.L.; Harton, S. Common processes drive the thermochemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2013, 16, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, A.; Zeeman, G. Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Chen, H.Z. Xylose production from corn stover biomass by steam explosion combined with enzymatic digestibility. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.C.; Geng, Z.C.; Fowler, P.; Baird, M.S. Characteristics of degraded hemicellulosic polymers obtained from steam exploded wheat straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulie, N.W.; Woldeyes, B.; Demsash, H.D.; Jabasingh, A.S. An insight into the valorization of hemicellulose fraction of biomass into furfural: Catalytic conversion and product separation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiagi, F.; Madeira, T.B.; Nixdorf, S.L.; Mali, S. Pretreatment efficiency using autoclave high-pressure steam and ultrasonication in sugar production from liquid hydrolysates and access to the residual solid fractions of wheat bran and oat hulls. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 190, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, F.P.; Silva, L.M.A.; Lomonaco, D.; de Freitas Rosa, M.; Leitão, R.C. Steam explosion pretreatment to obtain eco-friendly building blocks from oil palm mesocarp fiber. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 143, 111907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarella, M.; Cantarella, L.; Gallifuoco, A.; Spera, A.; Alfani, F. Effect of inhibitors released during steam-explosion treatment of poplar wood on subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis and SSF. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Gentina, J.C.; Aroca, G.; Mussatto, S.I. Development of an acetic acid tolerant Spathaspora passalidarum strain through evolutionary engineering with resistance to inhibitors compounds of autohydrolysate of Eucalyptus globulus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 106, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, O.; Ndimba, B.K. Molecular adaptation mechanisms employed by ethanologenic bacteria in response to lignocellulose-derived inhibitory compounds. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.D.M.; Gonçalves, A.R.; Oliveira, B.R.; Olivares, E.G.; Rossell, C.E.V. Steam explosion pretreatment reproduction and alkaline delignification reactions performed on a pilot scale with sugarcane bagasse for bioethanol production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 35, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvira, P.; Negro, M.J.; Ballesteros, I.; González, A.; Ballesteros, M. Steam explosion for wheat straw pretreatment for sugars production. Bioethanol 2016, 2, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, S.J.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Westereng, B.; Nilsen, P.J.; Eijsink, V.G. Screening of steam explosion conditions for glucose production from non-impregnated wheat straw. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4879–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, N.R.; Shah, A. Comparative techno-economic analysis of steam explosion, dilute sulfuric acid, ammonia fiber explosion and biological pretreatments of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Suhag, M.; Dhaka, A. Augmented digestion of lignocellulose by steam explosion, acid and alkaline pretreatment methods: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbanera, M.; Buratti, C.; Cotana, F.; Foschini, D.; Lascaro, E. Effect of steam explosion pretreatment on sugar production by enzymatic hydrolysis of olive tree pruning. Energy Procedia 2015, 81, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, J.; Bhaskar, T. Utilization of lignin: A sustainable and eco-friendly approach. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, B.C.; Dien, B.S.; Ting, K.C.; Singh, V. Influence of feedstock particle size on lignocellulose conversion—A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nguyen, X.P.; Duong, X.Q.; Ağbulut, Ü.; Len, C.; Nguyen, P.Q.P.; Kchaou, M.; Chen, W.H. Steam explosion as sustainable biomass pretreatment technique for biofuel production: Characteristics and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, D. Effects of particle size on biomass pretreatment and hydrolysis performances in bioethanol conversion. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 13023–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Qin, L.; Pang, F.; Jin, M.J.; Li, B.Z.; Kang, Y.; Dale, B.E.; Yuan, Y.J. Effects of biomass particle size on steam explosion pretreatment performance for improving the enzyme digestibility of corn stover. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMartini, J.D.; Foston, M.; Meng, X.; Jung, S.; Kumar, R.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Wyman, C.E. How chip size impacts steam pretreatment effectiveness for biological conversion of poplar wood into fermentable sugars. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitarelo, A.P.; Silva, T.A.D.; Peralta-Zamora, P.G.; Ramos, L.P. Efeito do teor de umidade sobre o pré-tratamento a vapor e a hidrólise enzimática do bagaço de cana-de-açúcar. Química Nova 2012, 35, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sui, W.; Chen, H. Effects of water states on steam explosion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Yu, F.; Xu, G.; Song, A. A real explosion: The requirement of steam explosion pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, N.H.; Huynh, K.T.T.; Nguyen, T.A.D.; Do, V.V.T.; Van Tran, M. Hydrothermal and steam explosion pretreatment of bambusa stenostachya bamboo. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 4103–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizasoain, J.; Rincón, M.; Theuretzbacher, F.; Enguídanos, R.; Nielsen, P.J.; Potthast, A.; Zweckmair, T.; Gronauer, A.; Bauer, A. Biogas production from reed biomass: Effect of pretreatment using different steam explosion conditions. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 95, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Sampedro, R.; Revilla, E.; Villar, J.C.; Eugenio, M.E. Enhancement of enzymatic saccharification of Eucalyptus globulus: Steam explosion versus steam treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Lizasoain, J.; Theuretzbacher, F.; Agger, J.W.; Rincón, M.; Menardo, S.; Saylor, M.K.; Enguídanos, R.; Nielsen, P.J.; Potthast, A.; et al. Steam explosion pretreatment for enhancing biogas production of late harvested hay. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitrone, F.; Ramos, D.; Vitagliano, V.; Ferrando, F.; Salvadó, J. All-lignocellulosic fiberboards from giant reed (Arundo donax L.): Effect of steam explosion pre-treatment on physical and mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, E.; Farriol, X.; Salvadó, J. Steam explosion as a fractionation step in biofuel production from microalgae. Fuel Process Technol. 2015, 131, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auxenfans, T.; Crônier, D.; Chabbert, B.; Paës, G. Understanding the structural and chemical changes of plant biomass following steam explosion pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, J.D.C.; Woiciechowski, A.; Zandona Filho, A.; Nigam, P.S.; Ramos, L.P.; Soccol, C.R. Steam explosion pretreatment of oil palm empty fruit bunches (EFB) using autocatalytic hydrolysis: A biorefinery approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Q. Effect of steam explosion of oil palm frond and empty fruit bunch on nutrient composition and ruminal fermentation characteristics. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Linares, J.C.; Ballesteros, I.; Tourán, J.; Cara, C.; Castro, E.; Ballesteros, M.; Romero, I. Optimization of uncatalyzed steam explosion pretreatment of rapeseed straw for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yan, B.H.; Wang, Y.; Yong, X.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Jia, H.H.; Jianga, M.; Wei, P. Effect of steam explosion pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion of rice straw. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88417–88425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, C.; George, K.E. Sisal nanofibril reinforced polypropylene/polystyrene blends: Morphology, mechanical, dynamic mechanical and water transmission studies. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 71, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielhop, T.; Amgarten, J.; von Rohr, P.R.; Studer, M.H. Steam explosion pret reatment of softwood: The effect of the explosive decompression on enzymatic digestibility. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankó, B.; Jovanovic, H.; Galbe, M.; Wallberg, O. The effect of blending spruce and poplar on acid-catalyzed steam pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.; Baudel, H.M.; Sendelius, J.; Modig, T.; Roslander, C.; Galbe, M.; Hahn-Hägerdal, B.; Zacchi, G.; Lidén, G. SO2-catalyzed steam pretreatment and fermentation of enzymatically hydrolyzed sugarcane bagasse. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 46, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Bansal, P.; Realff, M.J.; Bommarius, A.S. SO2-catalyzed steam explosion: The effects of different severity on digestibility, accessibility, and crystallinity of lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol. Prog. 2013, 29, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, C.C.; Quispe, L.F.; Lidén, G. Study of sulphuric acid catalysed steam pretreatment of the hardwood anadenanthera colubrina. enerLAC Rev. Energía Latinoamérica Caribe 2018, 2, 56–70. [Google Scholar]
- John, I.; Yaragarla, P.; Muthaiah, P.; Ponnusamy, K.; Appusamy, A. Statistical optimization of acid catalyzed steam pretreatment of citrus peel waste for bioethanol production. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalaglio, G.; Gelosia, M.; Giannoni, T.; Temporim, R.B.L.; Nicolini, A.; Cotana, F.; Bertini, A. Acid-catalyzed steam explosion for high enzymatic saccharification and low inhibitor release from lignocellulosic cardoon stalks. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 174, 108121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, R.S.; Silveira, M.H.L.; Pitarelo, A.P.; Corazza, M.L.; Ramos, L.P. Kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of steam-exploded sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, V.; Bals, B.; Chundawat, S.P.; Marshall, D.; Dale, B.E. Lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment using AFEX. Biofuels 2009, 581, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, C.; Sousa, L.D.C.; Jin, M.; Chang, L.; Dale, B.E.; Balan, V. Alkali-based AFEX pretreatment for the conversion of sugarcane bagasse and cane leaf residues to ethanol. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 107, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, M.W.; Gunawan, C.; Dale, B.E. The impacts of pretreatment on the fermentability of pretreated lignocellulosic biomass: A comparative evaluation between ammonia fiber expansion and dilute acid pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2009, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bals, B.; Rogers, C.; Jin, M.; Balan, V.; Dale, B. Evaluation of ammonia fibre expansion (AFEX) pretreatment for enzymatic hydrolysis of switchgrass harvested in different seasons and locations. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnen, H.K.; Balan, V.; Chundawat, S.P.; Bals, B.; Sousa, L.D.C.; Dale, B.E. Optimization of ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of Miscanthus x giganteus to fermentable sugars. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chundawat, S.P.; Venkatesh, B.; Dale, B.E. Effect of particle size based separation of milled corn stover on AFEX pretreatment and enzymatic digestibility. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 96, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun, S.; Balan, V.; Takriff, M.S.; Hassan, O.; Jahim, J.; Dale, B.E. Performance of AFEX™ pretreated rice straw as source of fermentable sugars: The influence of particle size. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Z.; Balan, V.; Yuan, Y.J.; Dale, B.E. Process optimization to convert forage and sweet sorghum bagasse to ethanol based on ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, E.L.N.; Da Silva, T.A.; Pirich, C.L.; Corazza, M.L.; Pereira Ramos, L. Supercritical fluids: A promising technique for biomass pretreatment and fractionation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.K.; Sharma, S. Recent updates on different methods of pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, S.; Ratnaparkhe, S.; Kumar, A. Biomass pre-treatment methods and their economic viability for efficient production of biofuel. Br. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Xu, F.; Li, S.; Ji, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, D. Effect of SC-CO2 pretreatment in increasing rice straw biomass conversion. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 106, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Li, Y.; Tan, X.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Advances in pretreatment of straw biomass for sugar production. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 696030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzi, T.; Calgaroto, S.; Astolfi, V.; Dalla Rosa, C.; Oliveira, J.V.; Mazutti, M.A. Pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse using supercritical carbon dioxide combined with ultrasound to improve the enzymatic hydrolysis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2013, 52, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, S.; Sharafi, A.; Motamedi, H.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Doherty, W.O. Environmentally friendly acetic acid/steam explosion/supercritical carbon dioxide system for the pre-treatment of wheat straw. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 37867–37881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Held, M.A.; Faik, A. Supercritical CO2 and ionic liquids for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass in bioethanol production. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che Hamzah, N.H.; Markom, M.; Hassan, O.; Harun, S. Investigation of the effect of supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment on sugar yield prior to enzymatic hydrolysis of empty fruit bunches. Ind. Biotechnol. 2015, 11, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Q.; Ren, H.; Yin, J. Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of sorghum stalk by supercritical carbon dioxide and ultrasonic pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.L.F.; Kawase, K.Y.F.; Coelho, G.L.V. Enzymatic saccharification of lignocellulosic materials after treatment with supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 56, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Hong, J. Supercritical CO2 pretreatment of lignocellulose enhances enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Jagtap, S.S.; Bedekar, A.A.; Bhatia, R.K.; Patel, A.K.; Pant, D.; Banu, J.R.; Rao, C.V.; Kim, Y.-G.; Yang, Y.H. Recent developments in pretreatment technologies on lignocellulosic biomass: Effect of key parameters, technological improvements, and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larnaudie, V.; Ferrari, M.D.; Lareo, C. Life cycle assessment of ethanol produced in a biorefinery from liquid hot water pretreated switchgrass. Renew. Energy 2021, 176, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larnaudie, V.; Ferrari, M.D.; Lareo, C. Techno-economic analysis of a liquid hot water pretreated switchgrass biorefinery: Effect of solids loading and enzyme dosage on enzymatic hydrolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 130, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Sotenko, M.; Blenkinsopp, T.; Coles, S.R. Life cycle assessment of lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment methods in biofuel production. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espada, J.J.; Villalobos, H.; Rodríguez, R. Environmental assessment of different technologies for bioethanol production from Cynara cardunculus: A Life Cycle Assessment study. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 144, 105910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Initial Feedstock | Pretreatment Conditions | Product | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bamboo (Neosino calamus affinis) | solid-to-water ratio of 1:10 (wt./vol.), temperature of 170 °C | Bioethanol | [37] |
| Caragana korshinskii | solid-to-water ratio of 1:20 (wt./vol.), temperature of 160 °C, holding time of 120 min, stirring speed of 150 rpm | - | [38] |
| Coffee cherry | solid-to-water ratio of 1:9 (wt./vol.), temperature of 180 °C, holding time of 5 h | - | [26] |
| Corncobs | solid content of 10% (by weight), temperature of 160 °C, holding time of 10 min, initial pressure of 25 bar under nitrogen | - | [27] |
| solid content of 10% (by weight), temperature of 200 °C, holding time of 30 min, stirring speed of 150 rpm | - | [39] | |
| Corn husks | solid-to-water ratio of 1:20 (wt./vol.), temperature of 155 °C, holding time of 15 min | lactic acid | [28] |
| Corn Stover | solid-to-water ratio of 1:15 (wt./vol.), temperature of 162.4 °C, holding time of 29.5 min | bioethanol | [40] |
| Empty palm fruit bunch | solid content of 15% (by weight), temperature of 185 °C, holding time of 0 min | ethanol | [34] |
| temperature of 121 °C, holding time of 60 min | ethanol | [41] | |
| Hazelnut tree pruning residue | solid-to-water ratio of 1:10 (wt./vol.), temperature of 210 °C, holding time of 45 min, stirring speed of 300 rpm | - | [42] |
| Olive stones | temperature of 225 °C, holding time of 0 min | ethanol | [43] |
| Pineapple leaves | solid-to-water ratio of 1:10 (wt./vol.), temperature of 160 °C, holding time of 60 min | - | [29] |
| Quercus mongolica | solid-to-water ratio of 1:8 (wt./vol.), temperature of 200 °C, holding time of 10 min | succinic acid | [44] |
| Sida hermaphrodita (L.) | temperature of 180 °C, holding time of 30 min, stirring speed of 13,000 rpm | methane | [22] |
| Switchgrass | solid content of 15% (by weight), temperature of 200 °C, holding time of 5 min | - | [45] |
| Rice straw | solid content of 20.0% (by weight), temperature of 180 °C, holding time of 10 min, stirring speed of 500 rpm | methane | [46] |
| Waste wheat straw | solid-to-water ratio of 1:10–1:500 (wt./vol.), temperature of 180 °C, holding time of 10 min | - | [47] |
| Initial Feedstock | Pretreatment Conditions | Product | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bamboo | solid-to-water ratio of 1:10 (wt./vol.), temperature of 230 °C, holding time of 3 min | - | [92] |
| Common reed (Phragmites australis) | pressure of 3.4 MPa, temperature of 200 °C; holding time of 15 min | biogas | [93] |
| Corn stalk | temperature of 190 °C, pressure of 1.37 MPa, holding time of 5–10 min | - | [91] |
| Eucalyptus globulus | temperature of 198 °C, temperature of 5 min | - | [94] |
| Hay | temperature of 220 °C, holding time of 15 min | biogas | [95] |
| Giant reed (Arundo donax L.) | pressure of 4 MPa, temperature of 204 °C, holding time of 9.5 min | - | [96] |
| Microalgae | temperature of 150 °C, holding time of 5 min | bioethanol | [97] |
| Miscanthus × giganteus | - | bioethanol | [98] |
| Olive tree pruning | pressure of 2 MPa, temperature of 210 °C, holding time of 15 min, severity factor of 4.41 | - | [82] |
| Palm empty fruit bunches | temperature of 195 °C, holding time of 6 min | - | [99] |
| pressure of 1.5 MPa, holding time of 1 min | [100] | ||
| Poplar | - | bioethanol | [98] |
| Rapeseed straw | temperature of 215 °C, holding time of 7.5 min | bioethanol | [101] |
| Rice straw | temperature of 220 °C, holding time of 2 min | - | [102] |
| Sisal | pressure of 137 Pa, holding time of 60 min | cellulose nano fibers | [103] |
| Spruce wood chips | temperature of 235 °C, pressure of 3.1 MPa, holding time of 10 min | - | [104] |
| Wheat straw | - | bioethanol | [98] |
| solid-to-water ratio of 1:10 (wt./vol.), 60% moisture of starting material, temperature of 200 °C, holding time of 10 min | sugars | [78] |
| Pretreatment Methods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Hot Water | Steam Explosion | |||||
| Non-Catalyzed | Catalyzed | |||||
| SO2 | H2SO4 | AFEX | SC-CO2 | |||
| Grinding | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Addition of chemicals and catalysts | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| Utilization of low-cost reactor design | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| Hemicelluloses passing into the liquid fraction | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Removal of lignin from the solid fraction | insignificant | insignificant | complete | complete | complete | complete |
| Formation of inhibitors | insignificant | + | + | + | + | insignificant |
| High energy inputs and costs for equipment | + | + | − | − | + | + |
| Harmful environmental impact | − | − | + | + | + | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gladysheva, E.K. Liquid Hot Water and Steam Explosion Pretreatment Methods for Cellulosic Raw Materials: A Review. Polymers 2025, 17, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131783
Gladysheva EK. Liquid Hot Water and Steam Explosion Pretreatment Methods for Cellulosic Raw Materials: A Review. Polymers. 2025; 17(13):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131783
Chicago/Turabian StyleGladysheva, Evgenia K. 2025. "Liquid Hot Water and Steam Explosion Pretreatment Methods for Cellulosic Raw Materials: A Review" Polymers 17, no. 13: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131783
APA StyleGladysheva, E. K. (2025). Liquid Hot Water and Steam Explosion Pretreatment Methods for Cellulosic Raw Materials: A Review. Polymers, 17(13), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17131783







