A State-of-the-Art Review on Recent Biomedical Application of Polysaccharide-Based Niosomes as Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
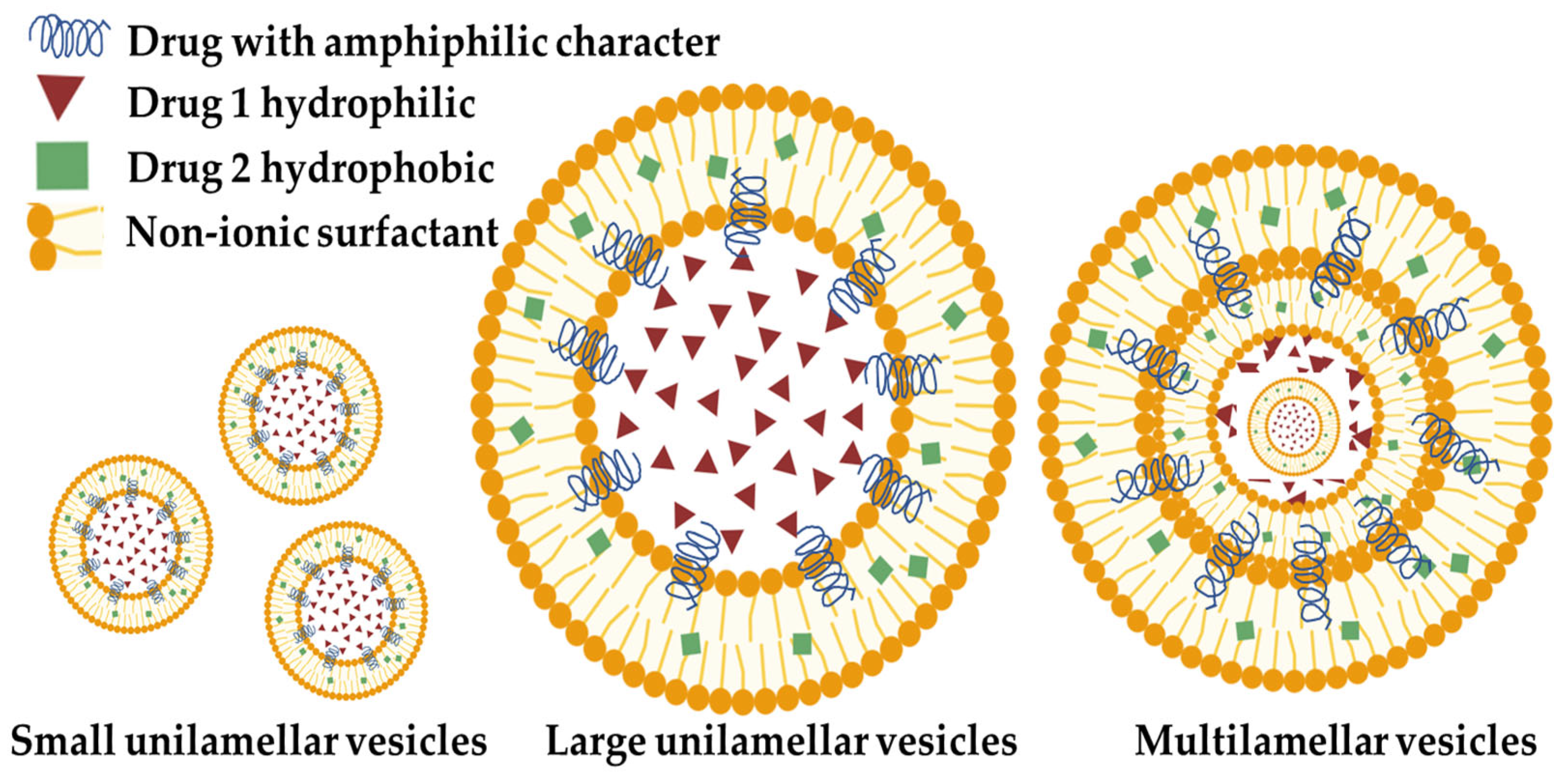
2. Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes)—Definition and Main Characteristics
3. Classification of the Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (NIOs)
- (a)
- Polyhedral niosomes (polyhedral NIOs)
- (b)
- Proniosomes (proNIOs)
- (c)
- Elastic niosomes (elastic NIOs)
- (d)
- Transfersomes
- (e)
- Bilosomes
- (f)
- Discomes
- (g)
- Aspasomes
- (h)
- Bola niosomes (bola NIOs)
- (i)
- Phytoniosomes (phytoNIOs)
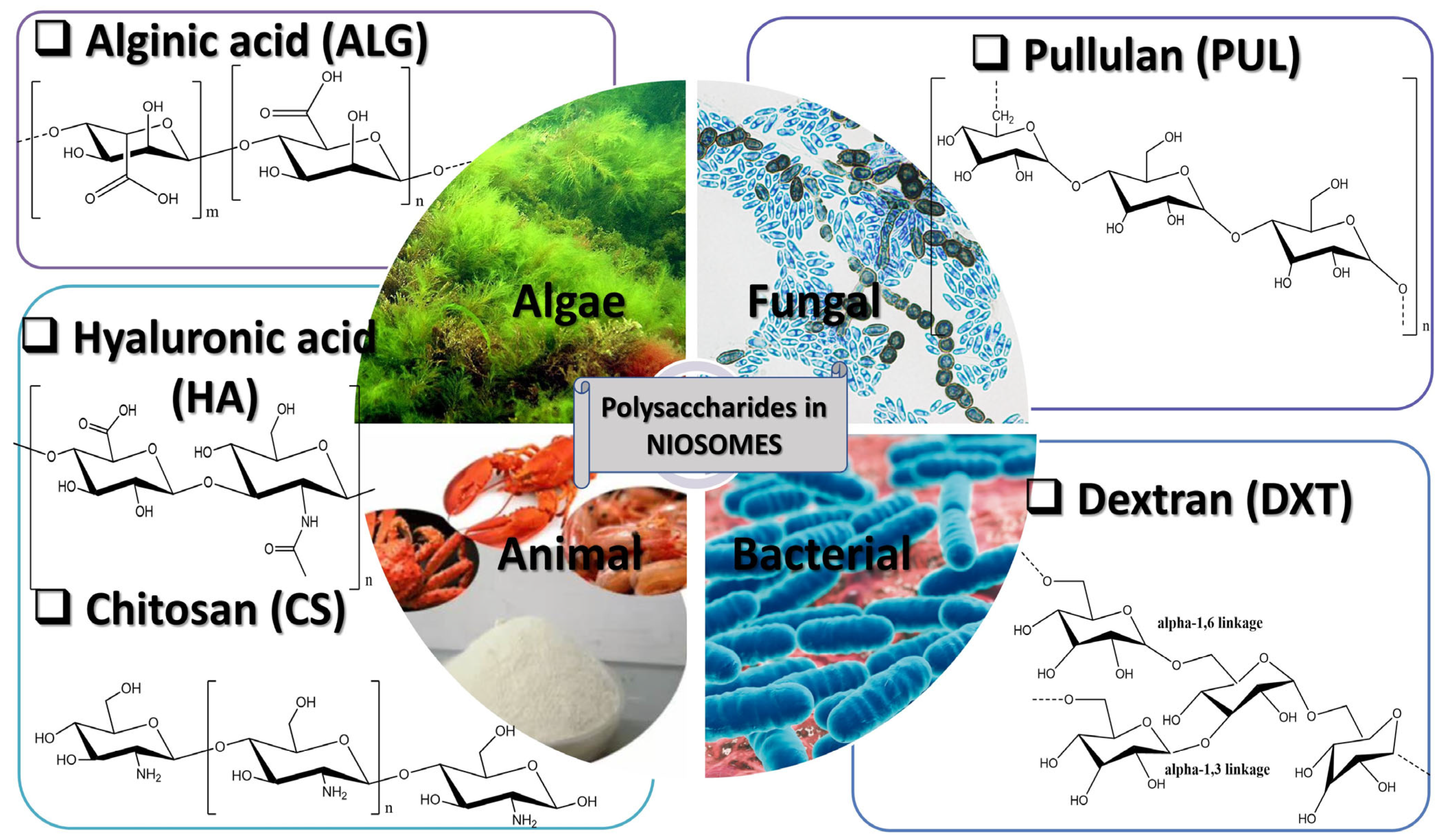
4. Polysaccharide Niosomal Drug Delivery Systems
- ✓
- derived from algae: alginic acid, alginate (ALG);
- ✓
- of animal origin: chitosan (CS), hyaluronic acid (HA);
- ✓
- of bacterial origin: dextran (DXT); and
- ✓
- of fungal origin: pullulan (PUL) (Figure 3).
4.1. Chitosan-Based Niosomal Drug Delivery Systems (CS-DDSs)
4.1.1. DDSs for Cancer Therapy
4.1.2. DDSs with Antibacterial or Anti-Inflammatory Properties
4.1.3. Gene DDSs
4.1.4. Nose-to-Brain DDSs
4.1.5. Oral DDSs
4.1.6. Transdermal DDSs
4.1.7. Ocular DDSs
4.2. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Niosomal Drug Delivery Systems (HA-DDSs)
4.2.1. DDSs for Cancer Therapy
4.2.2. Ocular DDS
4.2.3. Transdermal DDSs
4.2.4. Pulmonary DDSs
4.2.5. Cardiac DDSs
4.3. Alginate-Based Niosomal Drug Delivery Systems (ALG-DDSs)
4.3.1. DDSs for Cancer Therapy
4.3.2. Oral DDSs
4.4. Pullulan-Based Niosomal Drug Delivery Systems (PUL-DDSs)
4.4.1. Oral DDSs
4.4.2. Delivery of Preserving Food Agents
4.5. Dextran-Based Niosomal Drug Delivery Systems (DXT-DDSs)
4.5.1. DDSs for Cancer Therapy
4.5.2. Oral DDSs of Anti-Diabetic Agents
5. The Role of Polysaccharides in the Development of Polysaccharide–NIO-Based DDSs
6. Current Limitations and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chauhan, A.; Chauhan, C. Emerging Trends of Nanotechnology in Beauty Solutions: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 81, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawazi, S.M.; Ann, T.J.; Widodo, R.T. Exploring the Evolution of Niosomes: From Past Techniques to Future Advances in Preparation Methods—a Comprehensive Review. BioNanoScience 2024, 14, 1854–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zubaidi, Z.M.; Nsairat, H.; Shalan, N.M.; Al-Asfoor, L.; Alqudah, D.A.; Mrahleh, M.; Alshaer, W. Hyaluronic Acid – Coated Niosomes for Curcumin Targeted Delivery into Breast Cancer Cells. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202304649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hanning, S.; Falconer, J.; Locke, M.; Wen, J. Recent Advances in Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes): Fabrication, Characterization, Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrati, C.; Marianecci, C.; Sennato, S.; Carafa, M.; Bordoni, V.; Cimini, E.; Tempestilli, M.; Pucillo, L.P.; Turchi, F.; Martini, F.; et al. Multicompartment Vectors as Novel Drug Delivery Systems: Selective Activation of Tγδ Lymphocytes after Zoledronic Acid Delivery. Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moammeri, A.; Chegeni, M.M.; Sahrayi, H.; Ghafelehbashi, R.; Memarzadeh, F.; Mansouri, A.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Abtahi, M.S.; Hejabi, F.; Ren, Q. Current Advances in Niosomes Applications for Drug Delivery and Cancer Treatment. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 23, 100837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatage, S.T.; Manjappa, A.S.; Sankula, K.R.; Nadaf, S.J.; Rao, N.S.; N, S.; Gunnam, S.; Shyamsundar, P.; Kadam, R.J.; Gourisankar, K.; et al. Development and Characterization of Ethosomes of Acacia Senegal for Improved Topical Treatment of Breast Cancer. Next Mater. 2025, 8, 100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.; Chandra, J.; Gupta, G.; Ramaiah, R.; Hani, U.; Kesharwani, P. Harnessing Phytoconstituents in Ethosomes: A New Frontier in Skin Disorder Management. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 671, 125273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, N.; Soltanian, S.; Raeiszadeh, M.; Moeinzadeh, M.; Ohadi, M.; Sharifi, F.; Pardakhty, A.; Sharififar, F. Characteristics and in Vitro Anti Skin Aging Activity and UV Radiation Protection of Morin Loaded in Niosomes. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6326–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.; Gulati, N.; Verma, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Nagaich, U. Role of Nanotechnology in Cosmeceuticals: A Review of Recent Advances. J. Pharm. 2018, 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Alshetaili, A.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Chen, E.-L.; Fang, J.-Y. Lipid-Based Nanoformulation Optimization for Achieving Cutaneous Targeting: Niosomes as the Potential Candidates to Fulfill This Aim. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 186, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sita, V.G.; Jadhav, D.; Vavia, P. Niosomes for Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Bromocriptine: Formulation Development, Efficacy Evaluation and Toxicity Profiling. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, Q.; Wan, T.; Liu, C.; Pan, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Pan, J.; Qin, M.; Lin, Y.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Niosomes Facilitate Tacrolimus Ocular Delivery: Mucoadhesion, Precorneal Retention, Aqueous Humor Pharmacokinetics, and Transcorneal Permeability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrololoumi, S.; Nikazar, S. Chapter 9-Niosomes as a Promising Nanovesicular Drug Delivery. In Advanced and Modern Approaches for Drug Delivery; Nayak, A.K., Hasnain, M.S., Laha, B., Maiti, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 223–258. ISBN 978-0-323-91668-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, S.; Anjum, M.M.; Arya, D.K.; Thakur, S.; Pandey, P.; Deepak, P.; Kanaujiya, S.; Anand, S.; Kaushik, A.S.; Mishra, V.; et al. Surface Entrenched β-Sitosterol Niosomes for Enhanced Cardioprotective Activity against Isoproterenol Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 653, 123872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Seijas, J.; Iglesias-Fente, A.; Miranda-Balbuena, D.; Rey-Rico, A. Exploiting Niosomes as Efficient Non-Viral Vectors for Enhanced Gene Transfer to Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 107, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathi, K.; Kesavan, M.P.; Bhaskar, R.; Renukadevi, C.R.; Ayyanaar, S. Targeted Drug Release and in Vitro Anticancer Activities of Iron Oxide@folic Acid/Chitosan-Based Nano-Niosomes. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 686, 133366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, C.I.O. Design and Optimization Method for Obtaining New Chitosan-Based Nanofibers for Wound Healing Applications. Rev. Medico-Chir. 2022, 126, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, A.-T.; Drăgan, M.; Ionescu, O.-M.; Profire, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Confederat, L.G.; Lupașcu, D. An Overview of Biopolymeric Electrospun Nanofibers Based on Polysaccharides for Wound Healing Management. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Chen, M.; Guo, C.; Wang, W.; Chen, D. Marine Polysaccharides: Biological Activities and Applications in Drug Delivery Systems. Carbohydr. Res. 2024, 538, 109071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Malviya, R.; Sridhar, S.B.; Wadhwa, T.; Shareef, J.; Meenakshi, D.U. Polysaccharide-Based Implant Drug Delivery Systems for Precise Therapy: Recent Developments, and Future Trends. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2025, 83, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelds, R.; Nematollahi, M.H.; Pols, T.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Pardakhty, A.; Asadikaram, G.; Poolman, B. Niosomes, an Alternative for Liposomal Delivery. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugleva, V.; Mihaylova, R.; Momekov, G.; Kamenova, K.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Petrova, M.; Ugrinova, I.; Momekova, D.; Petrov, P.D. pH-Responsive Niosome-Based Nanocarriers of Antineoplastic Agents. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11124–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili Rad, M.; Egil, A.C.; Ozaydin Ince, G.; Yuce, M.; Zarrabi, A. Optimization of Curcumin Loaded Niosomes for Drug Delivery Applications. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 654, 129921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hajleh, M.N.; Abu-Huwaij, R.; AL-Samydai, A.; Al-Halaseh, L.K.; Al-Dujaili, E.A. The Revolution of Cosmeceuticals Delivery by Using Nanotechnology: A Narrative Review of Advantages and Side Effects. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3818–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, M.; Bozorgchami, N.; Almasi Ghale, R.; Esmaeeli, H.; Moosavizadeh, A.; Aghajani, A.; Far, B.F.; Aminzadeh, S. The Emerging Applications of Niosome as a Nanotechnology-Based Approach in Vaccine Delivery. Vacunas Engl. Ed. 2024, 25, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, N.A.; Noronha, M.A.; Câmara, M.C.C.; Kurnik, I.S.; Feng, C.; Araujo, V.H.S.; Santos, J.H.P.M.; Feitosa, V.; Molino, J.V.D.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O.; et al. Doxorubicin Nanoformulations on Therapy against Cancer: An Overview from the Last 10 Years. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Mohamed, M.S.; Raveendran, S.; Rochani, A.K.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Formulation, Characterization and Evaluation of Morusin Loaded Niosomes for Potentiation of Anticancer Therapy. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 32621–32636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkeran, T.; Kamaruddin, A.H.; Ngo, T.X.; Suda, K.; Umakoshi, H.; Watanabe, N.; Nadzir, M.M. Niosomes in Cancer Treatment: A Focus on Curcumin Encapsulation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiepour, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Khanniri, E.; Jahan, F.M.; Nouri, M.; Afraei, M. Nanocarriers for Foods: A Review of Niosomes and Proniosomes in Bioactive Compounds. Food Humanit. 2025, 4, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparajay, P.; Dev, A. Functionalized Niosomes as a Smart Delivery Device in Cancer and Fungal Infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, H.; Alani, A.W.G.; Alany, R.G. Recent Advances in Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes): Self-Assembly, Fabrication, Characterization, Drug Delivery Applications and Limitations. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manosroi, A.; Chankhampan, C.; Manosroi, W.; Manosroi, J. Transdermal Absorption Enhancement of Papain Loaded in Elastic Niosomes Incorporated in Gel for Scar Treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Lu, Y.-H.; Ma, C.-H.; Tao, W.-W.; Zhu, J.-J.; Zhang, X. A Novel Elastic Liposome for Skin Delivery of Papain and Its Application on Hypertrophic Scar. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, N.; Sodhi, R.K.; Bajaj, L.; Pandey, R.S.; Jain, U.K.; Katare, O.P.; Madan, J. Intravaginal Administration of Metformin Hydrochloride Loaded Cationic Niosomes Amalgamated with Thermosensitive Gel for the Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 144, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddapalli, H.; Radha, G.V.; Chinnaiyan, S.K. Formulation Optimization and PK/PD Evaluation of Novel Valsartan Bilosomes Enhancing Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 92, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, H.; Wu, Z.; Al-Kassas, R.; Alany, R.G. Niosomes and Discomes for Ocular Delivery of Naltrexone Hydrochloride: Morphological, Rheological, Spreading Properties and Photo-Protective Effects. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 433, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, D.; Ravi, D.; Rao, B.R.; Apte, S.S.; Renuka, D.; Rambhau, D. Ascorbyl Palmitate Vesicles (Aspasomes): Formation, Characterization and Applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 271, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, D.; Cosco, D.; Muzzalupo, R.; Trapasso, E.; Picci, N.; Fresta, M. Innovative Bola-Surfactant Niosomes as Topical Delivery Systems of 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Skin Cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 353, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masilamani, S.D.; Chokkalingam, P.; Hari, R. Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Anti-Oxidant Studies of Phytoniosome Loaded with Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Tinospora Cordifolia. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, S.J.; Tharmavaram, M.; Rawtani, D.; Prajapati, P.; Pandya, H.; Dey, A. Niosomes as Cutting Edge Nanocarrier for Controlled and Targeted Delivery of Essential Oils and Biomolecules. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 73, 103438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunothayanun, P.; Uchegbu, I.F.; Craig, D.Q.M.; Turton, J.A.; Florence, A.T. In Vitro/in Vivo Characterisation of Polyhedral Niosomes. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 183, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunothayanun, P.; Turton, J.A.; Uchegbu, I.F.; Florence, A.T. Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation of Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone (LHRH)-Loaded Polyhedral and Spherical/Tubular Niosomes. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakdiset, P.; Arce, F.J.; See, G.L.; Sawatdee, S.; Sae Yoon, A. Preparation and Characterization of Lidocaine HCl-Loaded Proniosome Gels with Skin Penetration Enhancers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Apurvi, P.; Aslam, R. A Review on Proniosomes: A Propitious Outlook to the Provesicular DrugDelivery System. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, P.A.; Pushpadass, H.A.; Franklin, M.E.E.; Battula, S.N.; Laxmana Naik, N. Resveratrol-Loaded Proniosomes: Formulation, Characterization and Fortification. LWT 2020, 134, 110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayoush, A.R.A.; Hassan, H.A.F.M.; Asiri, H.; Jafar, M.; Saeed, R.; Harati, R.; Haider, M. Niosomes for Nose-to-Brain Delivery: A Non-Invasive Versatile Carrier System for Drug Delivery in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 89, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambhakar, S.; Paliwal, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, B. Formulation of Risperidone Loaded Proniosomes for Effective Transdermal Delivery: An in-Vitro and in-Vivo Study. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2017, 55, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demartis, S.; Rassu, G.; Murgia, S.; Casula, L.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Improving Dermal Delivery of Rose Bengal by Deformable Lipid Nanovesicles for Topical Treatment of Melanoma. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 4046–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opatha, S.A.T.; Titapiwatanakun, V.; Chutoprapat, R. Transfersomes: A Promising Nanoencapsulation Technique for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanphothong, P.; Kanpipit, N.; Thapphasaraphong, S. The Characteristics and Biological Activity Enhancements of Melatonin Encapsulations for Skin Care Product Applications. Int. J. Pharm. X 2023, 6, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, F.; Ma, J.; Ning, X.; Sun, S.; Hu, Y. Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of the Rudder Vibrations in Propeller Wake. Ocean Eng. 2022, 265, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.; Rathnanand, M.; Tippavajhala, V.K. Unlocking the Potential of Bilosomes and Modified Bilosomes: A Comprehensive Journey into Advanced Drug Delivery Trends. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, A.A.; Saad, G.A.; Maghraby, G.M.E. Permeation Enhancers Loaded Bilosomes for Improved Intestinal Absorption and Cytotoxic Activity of Doxorubicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuBakr, A.-H.; Hassan, H.A.F.M.; Abdalla, A.; Khowessah, O.M.; Abdelbary, G.A. Therapeutic Potential of Cationic Bilosomes in the Treatment of Carrageenan-Induced Rat Arthritis via Fluticasone Propionate Gel. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbari, M.A.; El-Gazar, A.A.; Abdelbary, A.A.; Elshafeey, A.H.; Mosallam, S. Brij® Integrated Bilosomes for Improving the Transdermal Delivery of Niflumic Acid for Effective Treatment of Osteoarthritis: In Vitro Characterization, Ex Vivo Permeability Assessment, and in Vivo Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 640, 123024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.D.; Kamal, I.; Sabry, S.A.; Elghany, M.A.; hakim Ramadan, A.E. Effective Tailoring of Cefepime into Bilosomes: A Promising Nanoplatform for Enhancing Oral Absorption, Extending Half-Life, and Evaluating Biocompatibility, Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, Anti-Breast Cancer Activity, Ex-Vivo, and in-Vivo Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 668, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qushawy, M.; Soliman, G.M.; Mortagi, Y.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Elsherbiny, N. Development, Optimization, and Assessment of Losartan Nano-Bilosomes to Mitigate Diabetes-Induced Microvascular Complications in Sprague Dawley Rats. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 92, 105295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhakeem, E.; Nemr, A.A.; Rashed, H.M.; Selim, A.A.; Essa, B.M.; Hegazy, D. Revitalizing Itraconazole: Unleashing Its Anticancer Potential through Oral Nanosystems for Liver Targeting and Biodistribution Profiling in an Animal Model Using Radiolabeling Technique. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 104, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, N.K.; Alsaidan, O.A.; Zafar, A.; Alhassan, H.H.; Alburaykan, E.A.; Alsaidan, A.A.; Yasir, M.; Singh, L.; Khalid, M. Rizatriptan Loaded Bilosomes for Nose to Brain Delivery: Fabrication, Statistical Optimization, and Biological Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 106489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.; Zeng, B.; Li, M.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; et al. Novel Sodium Tauroursodeoxycholate-Based Multifunctional Liposomal Delivery System for Encapsulation of Oleanolic Acid and Combination Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, H.; Amin, M.M.; Fayad, W.; Zakaria, M.Y. “TPGS Surface Modified Bilosomes as Boosting Cytotoxic Oral Delivery Systems of Curcumin against Doxorubicin Resistant MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells”. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 619, 121717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaidan, O.A.; Elkomy, M.H.; Zaki, R.M.; Tulbah, A.S.; Yusif, R.M.; Eid, H.M. Brain Targeting of Venlafaxine via Intranasal Transbilosomes Thermogel for Improved Management of Depressive Disorder. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 113, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, S.P.; Mysore, N.; Jaitely, V.; Venkatesan, N. Discoidal Niosome Based Controlled Ocular Delivery of Timolol Maleate. Pharmazie 1998, 53, 466–469. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, A.M.; Lakshmi, V.U.; S., G.; Nair, S.C. DISCOSOMES: A FUTURISTIC UPHEAVAL IN VESICULAR DRUG DELIVERY. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2021, 13, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, Ç.; Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Ilbasmis-Tamer, S.; Değim, İ.T. Ferulic Acid-Loaded Aspasomes: A New Approach to Enhance the Skin Permeation, Anti-Aging and Antioxidant Effects. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, M.; Saquib, M.; Jain, D.K. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Aspasomes Containing Skin Whitening Agent. Manipal J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Aboul-Einien, M.H.; Kandil, S.M.; Abdou, E.M.; Diab, H.M.; Zaki, M.S.E. Ascorbic Acid Derivative-Loaded Modified Aspasomes: Formulation, in Vitro, Ex Vivo and Clinical Evaluation for Melasma Treatment. J. Liposome Res. 2020, 30, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuguna, R.; Awasthi, R. Unlocking New Dimensions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy: Harnessing the Power of Lipid Based Vesicles beyond Traditional Therapies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 89, 105106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatem, S.; Nasr, M.; Moftah, N.H.; Ragai, M.H.; Geneidi, A.S.; Elkheshen, S.A. Melatonin Vitamin C-Based Nanovesicles for Treatment of Androgenic Alopecia: Design, Characterization and Clinical Appraisal. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 122, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamie, C.; Elmowafy, E.; Attia, D.A.; Elmazar, M.M.; Mortada, N.D. Diversifying the Skin Cancer-Fighting Worthwhile Frontiers: How Relevant Are the Itraconazole/Ascorbyl Palmitate Nanovectors? Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 43, 102561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeiszadeh, M.; Pardakhty, A.; Sharififar, F.; Mehrabani, M.; Nejat-Mehrab-Kermani, H.; Mehrabani, M. Phytoniosome: A Novel Drug Delivery for Myrtle Extract. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2018, 17, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imtiaz, F.; Islam, M.; Saeed, H.; Ahmed, A.; Asghar, M.; Saleem, B.; Farooq, M.A.; Khan, D.H.; Peltonen, L. Novel Phytoniosomes Formulation of Tradescantia Pallida Leaves Attenuates Diabetes More Effectively than Pure Extract. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 83, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, R.N.; Barlas, F.B.; Yavuz, M.; Ag Seleci, D.; Seleci, M.; Gumus, Z.P.; Guler, E.; Demir, B.; Can, M.; Coskunol, H.; et al. Phyto-Niosomes: In Vitro Assessment of the Novel Nanovesicles Containing Marigold Extract. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2015, 64, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katare, R.; Gupta, P.N.; Mahor, S.; Rawat, A.; Khatri, K.; Katare, Y.; Panda, A.K.; Vyas, S.P. Development of Polysaccharide-Capped Niosomes for Oral Immunization of Tetanus Toxoid. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2006, 16, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Cheng, R.; Xu, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Yang, L. Preparation and Physicochemical Properties of Coenzyme Q10 Loaded Niosomal Hydrogels Based on Carbomer and Scleroglucan. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 2999–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, O.; Amasya, G.; Sezgin Bayindir, Z.; Yuksel, N. Development and Quality Assessment of Glutathione Tripeptide Loaded Niosome Containing Carbopol Emulgels as Nanocosmeceutical Formulations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeev, D.; Rajesh, A.; Kumaar, R.N.; Aswin, D.; Jayakumar, R.; Nair, S.C. Chemically Modified Chitosan as a Functional Biomaterial for Drug Delivery System. Carbohydr. Res. 2025, 548, 109351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh, M.K.; Sayyar, Z.; Mohammadi, M.A.; Baharlounezhad, F. Controlling the Drug Delivery Efficiency of Chitosan-Based Systems through Silver Nanoparticles and Oxygen Plasma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 294, 139407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; He, X.; Tan, C.; Jakhar, A.M.; He, F.; Ma, J. Chitosan-Melanin Complex Microsphere: A Potential Colonic Delivery System for Protein Drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.C.; Toomey, R.; Alcantar, N. Controlled Release Niosome Embedded Chitosan System: Effect of Crosslink Mesh Dimensions on Drug Release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100A, 3296–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sludden, J.; Uchegbu, I.F.; Schätzlein, A.G. The Encapsulation of Bleomycin Within Chitosan Based Polymeric Vesicles Does Not Alter Its Biodistribution. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 52, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Ameen, M.S.M.; Abazari, M.; Badeleh, S.M.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Mohammed, S.S. Chitosan-Decorated and Tripolyphosphate-Crosslinked pH-Sensitive Niosomal Nanogels for Controlled Release of Fluoropyrimidine 5-Fluorouracil. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiranowska, M.; Singh, R.; Falahat, R.; Williams, E.; Johnson, J.O.; Alcantar, N. Preferential Drug Delivery to Tumor Cells than Normal Cells Using a Tunable Niosome–Chitosan Double Package Nanodelivery System: A Novel in Vitro Model. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseli, S.; Pourmadadi, M.; Samadi, A.; Yazdian, F.; Abdouss, M.; Rashedi, H.; Navaei-Nigjeh, M. A Novel pH -responsive Nanoniosomal Emulsion for Sustained Release of Curcumin from a Chitosan-based Nanocarrier: Emphasis on the Concurrent Improvement of Loading, Sustained Release, and Apoptosis Induction. Biotechnol. Prog. 2022, 38, e3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimifard, S.; Rezaei, N.; Jamshidifar, E.; Moradi Falah Langeroodi, S.; Abdihaji, M.; Mansouri, A.; Hosseini, M.; Ahmadkhani, N.; Rahmati, Z.; Heydari, M.; et al. pH-Responsive Chitosan-Adorned Niosome Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Drugs for Breast Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 8811–8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishnamazi, M.; Dhiaa, S.M.; Emadi, R.; Shahrtash, S.A.; Jamali, M.R.; Kaur, J.; Soltani, A. Experimental and Theoretical Studies on the Interaction of Finasteride with Chitosan-Based Nanoniosomes. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1303, 137524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkezari, S.; Abtahi, M.S.; Sattari, Z.; Yaraki, M.T.; Hosseini, F.; Salehi, R.I.; Afzali, E.; Hajihosseini, S.; Mousavi-Niri, N. Antibiotic and Inorganic Nanoparticles Co-Loaded into Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Functionalized Niosome: Synergistic Enhanced Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 83, 104386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, F.; Mehryab, F.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Rabbani, S.; Haeri, A. Thiolated Chitosan Hydrogel-Embedded Niosomes: A Promising Crocin Delivery System toward the Management of Aphthous Stomatitis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 318, 121068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, B.B.M.; Mertins, O.; da Silva, E.R.; Han, S.W. Influence of the Degree of Arginine Substitution on Chitosan-N-Arginine-Based Chitosomes: Insights for Improved Gene Delivery Systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 92, 105368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerli, G.; Robla, S.; Bartalesi, M.; Luceri, C.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Csaba, N.; Maestrelli, F. Chitosan Coated Niosomes for Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Clonazepam: Formulation, Stability and Permeability Studies. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 6, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbah, A.S.; Elkomy, M.H.; Zaki, R.M.; Eid, H.M.; Eissa, E.M.; Ali, A.A.; Yassin, H.A.; Aldosari, B.N.; Naguib, I.A.; Hassan, A.H. Novel Nasal Niosomes Loaded with Lacosamide and Coated with Chitosan: A Possible Pathway to Target the Brain to Control Partial-Onset Seizures. Int. J. Pharm. X 2023, 6, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayed, N.D.; Goda, A.E.; Essa, E.A.; Maghraby, G.M.E. Chitosan-Encapsulated Niosomes for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Atorvastatin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, S.; Haeri, A.; Mahboubi, A.; Mortazavi, A.; Dadashzadeh, S. Chitosan Gel-Embedded Moxifloxacin Niosomes: An Efficient Antimicrobial Hybrid System for Burn Infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri Boroujeni, M.; Barzi, S.M.; Zafari, M.; Chiani, M.; Chehrazi, M.; Nosrati, H.; Shams Nosrati, M.S.; Nayyeri, S.; Khodaei, M.; Bonakdar, S.; et al. Electrosprayed Cefazolin-Loaded Niosomes onto Electrospun Chitosan Nanofibrous Membrane for Wound Healing Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, M.M.; Alsubaie, A.; Bekhit, M.M.S.; Alomrani, A.H.; Almomen, A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Alshora, D.H. Bioadhesive Hybrid System of Niosomes and pH Sensitive in Situ Gel for Itraconazole Ocular Delivery: Dual Approach for Efficient Treatment of Fungal Infections. Saudi Pharm. J. 2024, 32, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Liu, X.-R.; Chen, Q.-B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.-L.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Zou, T. Hyaluronic Acid and Albumin Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Controlled Release 2021, 331, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Chitosan and Hyaluronic Acid in Breast Cancer Treatment: Anticancer Efficacy and Nanoparticle and Hydrogel Development. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Niu, H. Self-Crosslinkable Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid Dialdehyde Nanoparticles for CD44-Targeted siRNA Delivery to Treat Bladder Cancer. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathalizadeh, M.; Homayouni Tabrizi, M.; Tehranipour, M. A Novel Alpha-Terpineol-Loaded Niosome Formulation Coated with Hyaluronic Acid and Evaluation of Its Anticancer Properties in Vitro. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 424, 127139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Park, H.; Feng, C.; Hou, L.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X. Construction of Hyaluronic Acid Noisome as Functional Transdermal Nanocarrier for Tumor Therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori-Kermani, A.; Khalighi, S.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Niavol, F.R.; Motasadizadeh, H.; Mahdieh, A.; Jahed, V.; Abdinezhad, M.; Rahbariasr, N.; Hosseini, M.; et al. Engineered Hyaluronic Acid-Decorated Niosomal Nanoparticles for Controlled and Targeted Delivery of Epirubicin to Treat Breast Cancer. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faddah, H.; Nsairat, H.; Shalan, N.M.; El-Tanani, M.; Alqudah, D.A.; Alshaer, W. Preparation, Optimization and In Vitro Evaluation of Doxorubicin-Loaded into Hyaluronic Acid Coated Niosomes Against Breast Cancer. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202301470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Qi, J.; Wang, H.; Gan, L. Hyaluronic Acid-Modified Cationic Niosomes for Ocular Gene Delivery: Improving Transfection Efficiency in Retinal Pigment Epithelium. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, C.; Fang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cai, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, S.; et al. Deformable Hyaluronic Acid Niosomes Overcome Multi-Barriers for Improved Ergothioneine Transdermal Delivery against UV-Induced Skin Damage. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 110839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Rawtani, D.; Rajpurohit, S.; Vasvani, S.; Barot, T. Self-Assembly Based Aerosolized Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Loaded Niosomes for Lung Delivery: An in-Vitro and in-Vivo Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duciel, L.; Proust, R.; Ponsen, A.-C.; Ziarelli, F.; Coudreuse, A.; Jeanmichel, L.; Samardzic, M.; Uzan, G.; des Courtils, C. Are All Alginate Dressings Equivalent? J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2025, 113, e35557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, J. Smart Stimuli-Responsive Chitosan Hydrogel for Drug Delivery: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Geng, X.; Li, W.; Che, T.; Yan, L.; Yuan, B.; Qin, S. Advance of the Application of Seaweed Polysaccharides on Antitumor Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 675, 125502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, F.; Mirzaei Chegeni, M.; Bidaki, A.; Zaer, M.; Abolhassani, H.; Seyedi, S.A.; Nabipoorashrafi, S.A.; Ashrafnia Menarbazari, A.; Moeinzadeh, A.; Farmani, A.R.; et al. 3D-Printing-Assisted Synthesis of Paclitaxel-Loaded Niosomes Functionalized by Cross-Linked Gelatin/Alginate Composite: Large-Scale Synthesis and in-Vitro Anti-Cancer Evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaer, M.; Moeinzadeh, A.; Abolhassani, H.; Rostami, N.; Tavakkoli Yaraki, M.; Seyedi, S.A.; Nabipoorashrafi, S.A.; Bashiri, Z.; Moeinabadi-Bidgoli, K.; Moradbeygi, F.; et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded Niosomes Functionalized with Gelatine and Alginate as pH-Responsive Drug Delivery System: A 3D Printing Approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari Sharafshadeh, M.; Tafvizi, F.; Khodarahmi, P.; Ehtesham, S. Preparation and Physicochemical Properties of Cisplatin and Doxorubicin Encapsulated by Niosome Alginate Nanocarrier for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, I.; Shayan, M.; Bourbour, M.; Moghtaderi, M.; Noorbazargan, H.; Eshrati Yeganeh, F.; Saffar, S.; Tahriri, M. Preparation, Optimization and In-Vitro Evaluation of Curcumin-Loaded Niosome@calcium Alginate Nanocarrier as a New Approach for Breast Cancer Treatment. Biology 2021, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestrelli, F.; Mura, P.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Cózar-Bernal, M.J.; Rabasco, A.M.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Ghelardini, C. Calcium Alginate Microspheres Containing Metformin Hydrochloride Niosomes and Chitosomes Aimed for Oral Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 530, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Sharma, S.; Naman, S.; Baldi, A. Pullulan Based Polymeric Novel Drug Delivery Systems: A Review on Current State of Art and Prospects. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 90, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoras, A.G. Drug Delivery Systems Using Pullulan, a Biocompatible Polysaccharide Produced by Fungal Fermentation of Starch. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesneau, C.; Pelletier, A.; Dubot, P.; Leroy, E.; Goffin, A.; Jørgensen, L.; Hamadi, S.; Modjinou, T.; Houppe, C.; Wickramanayaka, M.D.; et al. Synthesis and Physico-Chemical Investigation of Thiolated Dextran Derivative: Design and Application of a Redox-Responsive Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 297, 139861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.; Subramanian, S.; Pandey, U.; Samuel, G.; Venkatesh, M.; Martins, M.; Pereira, S.; Correia, J.D.G.; Santos, I. Mannosylated Dextran Derivatives Labeled with Fac-[M(CO)3]+ (M = 99mTc, Re) for Specific Targeting of Sentinel Lymph Node. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Anandhakumar, S.; Sasidharan, M. Self-Degrading Niosomes for Encapsulation of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Drugs: An Efficient Carrier for Cancer Multi-Drug Delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samed, N.; Sharma, V.; Sundaramurthy, A. Hydrogen Bonded Niosomes for Encapsulation and Release of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Anti-Diabetic Drugs: An Efficient System for Oral Anti-Diabetic Formulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 449, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lens, M. Niosomes as Vesicular Nanocarriers in Cosmetics: Characterisation, Development and Efficacy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witika, B.A.; Bassey, K.E.; Demana, P.H.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Poka, M.S. Current Advances in Specialised Niosomal Drug Delivery: Manufacture, Characterization and Drug Delivery Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masjedi, M.; Montahaei, T. An Illustrated Review on Nonionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) as an Approach in Modern Drug Delivery: Fabrication, Characterization, Pharmaceutical, and Cosmetic Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidaki, A.; Rezaei, N.; Kazemi, S.; Ali, S.N.; Ziaei, S.; Moeinzadeh, A.; Hosseini, F.; Noorbazargan, H.; Farmani, A.R.; Ren, Q. 3D Printed Bioengineered Scaffold Containing Chitosan, Alginate, and Barijeh-Loaded Niosomes Enabled Efficient Antibiofilm Activity and Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311, 143743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Types of NIO | Main Characteristics | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Polyhedral niosomes |
| [32] |
| Proniosomes |
| [13] |
| Elastic niosomes |
| [33,34] |
| Transfersomes |
| [35] |
| Bilosomes |
| [36] |
| Discosomes/Discomes |
| [37] |
| Aspasomes |
| [38] |
| Bola niosomes |
| [26,39] |
| Phytoniosomes |
| [40] |
| Active Substance | Main Characteristics | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Cefepime (CFP) |
| [57] |
| Losartan (LST) |
| [58] |
| Itraconazole (ITZ) |
| [59] |
| Rizatriptan (RTP) |
| [60] |
| Sodium tauroursodeoxycholate (TUDCNa)/ oleanoic acid (OA) |
| [61] |
| Curcumin (CUR) |
| [62] |
| Venlafaxine (VLF) |
| [63] |
| Bioactive Agent/Active Substances | Formulation | Type of Cancer/Cell Line Tested | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| biogenic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) Ciprofloxacin (CIF) Folic acid (FA) | Fe3O4 @FA-CS-CIF-NP nano-NIOs. | Cervical cancer/HeLa S3 | [17] |
| 5-Fluorouracil(5-FU) | CS-coated and TPP-crosslinked 5-FU NIOs. | Skin cancer/B16F10 | [83] |
| Paclitaxel (PTX) | PTX NIOs incorporated within a CS hydrogel. | Ovarian cancer/OV2008 | [84] |
| Curcumin (CUR) Montmorillonite (MMT) | CUR-loaded MMT nanoparticles. CS –agarose nano-niosomal emulsion. | Breast cancer/MCF-7 | [85] |
| Finasteride (FIN) | CS-based nano-NIOs encapsulated with FIN. | Prostate cancer | [87] |
| Type of Niosomal CS-DDS | Formulation Considerations | Preclinical Tests and Findings | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial/ anti-inflammatory DDS | Nanocomposite with inorganic nanoparticles and sultamicillin tosylate co-loaded in NIOs coated with carboxymethyl CS. |
|
| [88] |
| DDS for cancer treatment | Paclitaxel-encapsulated NIOs incorporated within a CS hydrogel |
|
| [6] |
| pH-responsive nano-niosomal CS emulsion incorporating montmorillonite/ curcumin nanoparticles |
|
| [85] | |
| Nose-to-brain DDS | Chitosan-coated NIOs (thin layer evaporation–paddle stirring) encapsulating clonazepam |
|
| [91] |
| Oral DDS | NIOs formed from cholesterol, dicetyl-phosphate, and Span 60, coated with CS, crosslinked with tripolyphosphate (TPP), and loaded with atorvastatin |
|
| [93] |
| Transdermal DDS | Electrospraying of cefazolin-loaded NIOs (thin-film hydration) over a CS membrane |
|
| [95] |
| Ocular DDS | Bioadhesive NIOs (hydrating proNIOs containing Span 60, cholesterol, and phospholipid) encapsulating itraconazol coated with CS and integrated into pH-sensitive gels formed in situ |
|
| [96] |
| Type of Niosomal HA-DDS | Formulation Considerations | Preclinical Tests and Findings | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDS for cancer therapy | NIOs formed from cholesterol and Span 60 (thin-film hydration) alpha-terpineol-loaded and coated with HA. |
|
| [100] |
| HA esterified with glycerol-monostearate self-assembled onto small-sized multilamellar NIOs. |
|
| [101] | |
| HA-coated NIOs encapsulating curcumin (thin-film hydration). |
|
| [3] | |
| Doxorubicin-loaded coationic NIOs (thin-film hydration) subsequently modified by electrostatic interaction with HA. |
|
| [103] | |
| Ocular DDS | HA-coated cationic NIOs (Tween 80, squalene, and 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium propane) produced by ethanol injection technique. |
|
| [104] |
| HA-coated NIOs (poloxamer 188, soybean phosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol) produced by reconstituting the proNIOs and loaded with tacrolimus. |
|
| [13] | |
| Transdermal DDS | Ergothioneine-loaded NIOs (steareth-2 as non-ionic surfactant, cholesterol, and cationic lipid) coated with HA. |
|
| [105] |
| Pulmonary DDS | Hyaluronic acid-loaded NIOs (cholesterol, Span 80) were prepared using the ethanol injection method. |
|
| [106] |
| Cardiac DDS | β-sitosterol-loaded NIOs (Tween 80, cholesterol, using the ether injection method, followed by ultrasonication) and coated with HA. |
|
| [15] |
| Type of Niosomal ALG-DDS | Formulation Considerations | Preclinical Tests and Findings | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDS for cancer therapy | 3D-printed gelatin-alginate scaffolds embedded with NIOs loaded with paclitaxel (cholesterol and Span 60) using thin-layer hydration method. |
|
| [110] |
| pH-sensitive 3D-printed gelatin–alginate nanocomposites including NIOs (cholesterol and Span 60) loaded with doxorubicin using thin-layer hydration method. |
|
| [111] | |
| NIO-based nanocarrier coated with alginate, designed for the co-delivery of doxorubicin (DOX) and cisplatin (CIS). |
|
| [112] | |
| NIOs coated with calcium ALG encapsulating curcumin (Span 80, dicetyl phosphate, and cholesterol via thin-layer hydration method). |
|
| [113] | |
| Oral DDS | Calcium alginate microspheres containing metformin-loaded NIOs (Span 60, dicetyl phosphate, and cholesterol via thin-layer evaporation method). |
|
| [114] |
| Type of Niosomal DDS | Polysaccharide Used/Active Substance | Role of the Polysaccharide | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
Oral DDSs |
|
| [75,93,114] |
|
| [75] | |
|
| [120] | |
Cardiac DDSs |
|
| [15] |
DDSs for cancer therapy |
|
| [83,87] |
|
| [3,100] | |
|
| [119] | |
|
| [113] | |
Pulmonary DDSs |
|
| [106] |
Ocular DDSs |
|
| [96] |
|
| [13] | |
Gene DDSs |
|
| [90] |
Nose-to-brain DDSs |
|
| [91,92] |
Transdermal DDSs |
|
| [94,95] |
|
| [105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iacob, A.-T.; Ababei-Bobu, A.; Chirliu, O.-M.; Lupascu, F.G.; Vasincu, I.-M.; Apotrosoaei, M.; Profire, B.-S.; Tauser, G.-R.; Lupascu, D.; Profire, L. A State-of-the-Art Review on Recent Biomedical Application of Polysaccharide-Based Niosomes as Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2025, 17, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111566
Iacob A-T, Ababei-Bobu A, Chirliu O-M, Lupascu FG, Vasincu I-M, Apotrosoaei M, Profire B-S, Tauser G-R, Lupascu D, Profire L. A State-of-the-Art Review on Recent Biomedical Application of Polysaccharide-Based Niosomes as Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111566
Chicago/Turabian StyleIacob, Andreea-Teodora, Andra Ababei-Bobu, Oana-Maria Chirliu, Florentina Geanina Lupascu, Ioana-Mirela Vasincu, Maria Apotrosoaei, Bianca-Stefania Profire, Georgiana-Roxana Tauser, Dan Lupascu, and Lenuta Profire. 2025. "A State-of-the-Art Review on Recent Biomedical Application of Polysaccharide-Based Niosomes as Drug Delivery Systems" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111566
APA StyleIacob, A.-T., Ababei-Bobu, A., Chirliu, O.-M., Lupascu, F. G., Vasincu, I.-M., Apotrosoaei, M., Profire, B.-S., Tauser, G.-R., Lupascu, D., & Profire, L. (2025). A State-of-the-Art Review on Recent Biomedical Application of Polysaccharide-Based Niosomes as Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers, 17(11), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111566










