High-Strength and Rapidly Degradable Nanocomposite Yarns from Recycled Waste Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
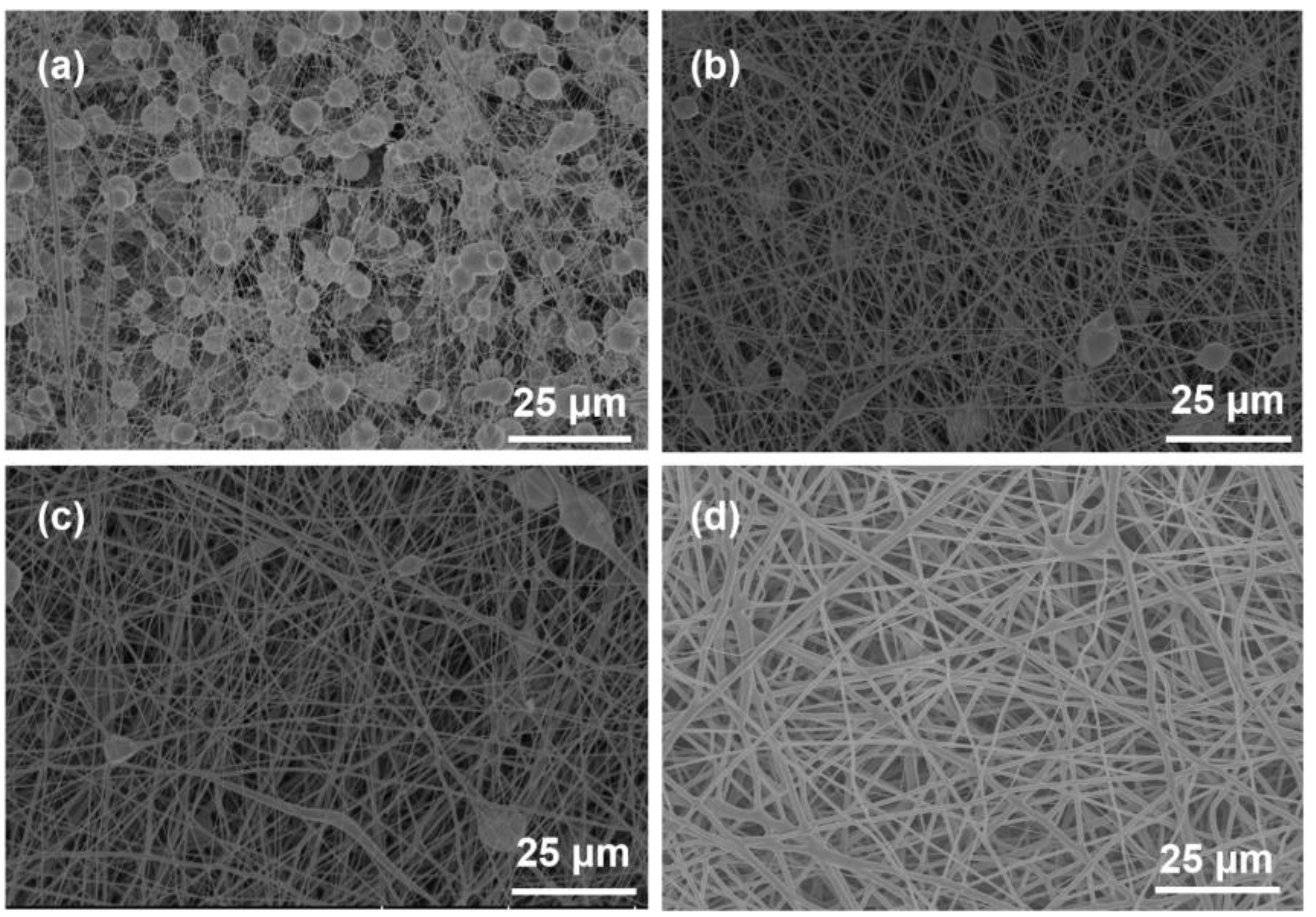
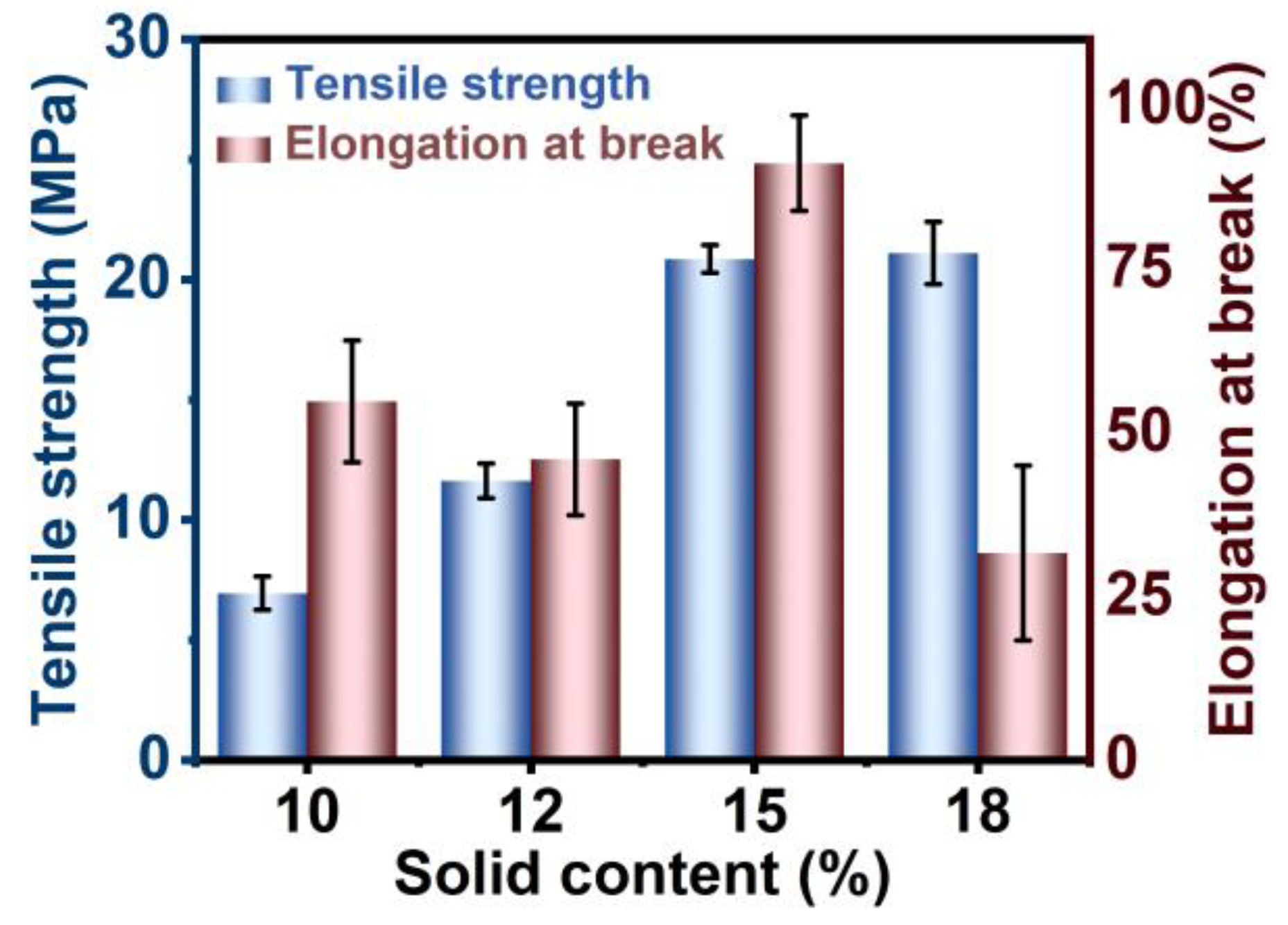
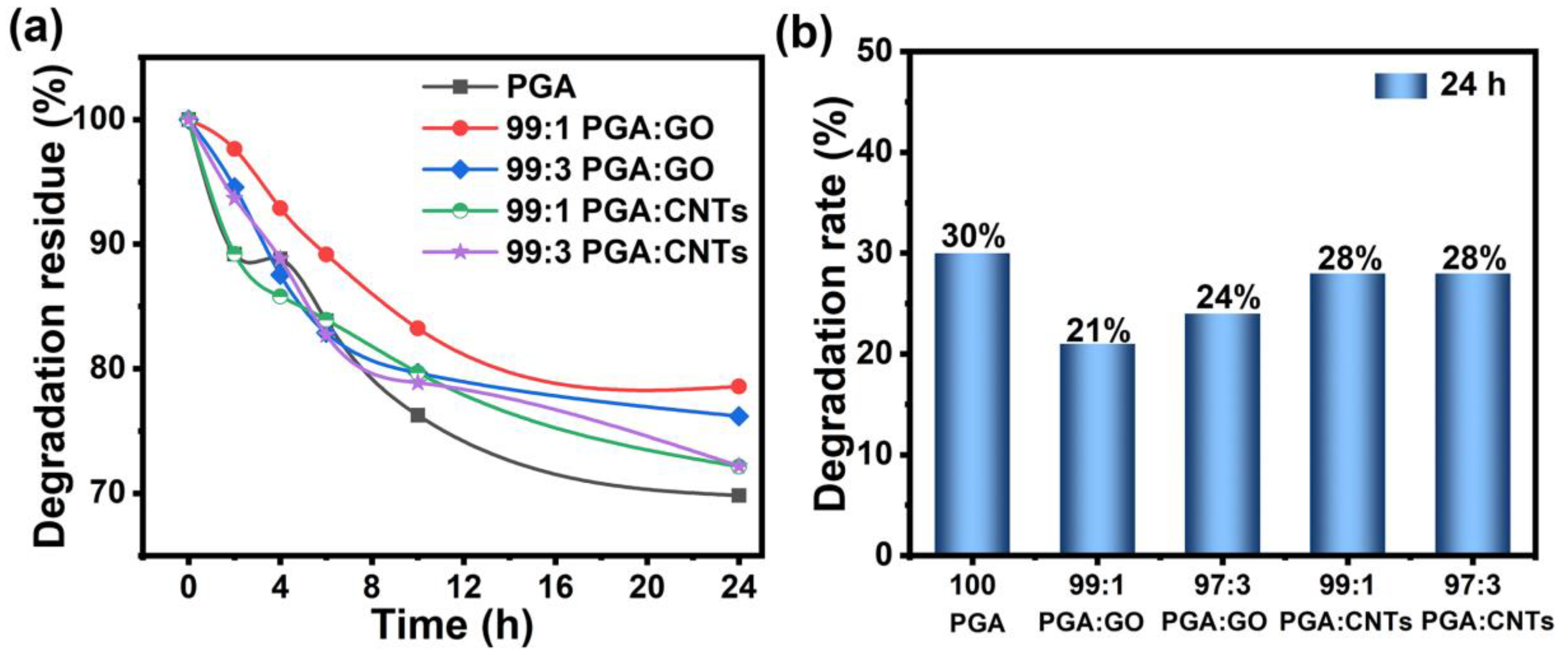
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamane, K.; Sato, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sunagawa, K.; Shigaki, Y. Development of an industrial production technology for high-molecular-weight polyglycolic acid. Polym. J. 2014, 46, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, K.; Sogut, O.; Aydemir Sezer, U. A review on synthesis and biomedical applications of polyglycolic acid. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.Z.; Li, Y.C.; Tjong, S.C. Polyetheretherketone and its composites for bone replacement and regeneration. Polymers 2020, 12, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, X.Y.; Gu, J.L.; Yan, C.; Yin, S.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.H.; Geng, F. Polylactic-co-glycolic acid-based nanoparticles modified with peptides and other linkers cross the blood-brain barrier for targeted drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2023, 18, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundak, H.; Bilisik, K. Development of three-dimensional (3D) biodegradable polyglycolic acid fiber (PGA) preforms for scaffold applications: Experimental patterning and fiber volume fraction-porosity modeling study. Polymers 2023, 15, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, D.; Suresh, A.; Nayak, R.; Shetty, M.; Sarda, R.K.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.W.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, B.N. Biosubstitutes for dural closure: Unveiling research, application, and future prospects of dura mater alternatives. J. Tissue Eng. 2024, 15, 20417314241228118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, D.J.A.; Shaver, M.P. Aliphatic polyester polymer stars: Synthesis, properties and applications in biomedicine and nanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1761–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samantaray, P.K.; Little, A.; Haddleton, D.M.; McNally, T.; Tan, B.; Sun, Z.; Huang, W.; Ji, Y.; Wan, C. Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA): A versatile building block expanding high performance and sustainable bioplastic applications. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4055–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.; Ma, S.; Haddleton, D.M.; Tan, B.; Sun, Z.; Wan, C. Synthesis and Characterization of High Glycolic Acid Content Poly(glycolic acid-co-butylene adipate-co-butylene terephthalate) and Poly(glycolic acid-co-butylene succinate) Copolymers with Improved Elasticity. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 38658–38667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Díez-Vicente, A.L. Multifunctional poly(glycolic acid-co-propylene fumarate) electrospun fibers reinforced with graphene oxide and hydroxyapatite nanorods. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4084–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Z.; Weng, Y. In Situ Formation of Microfibrillar PBAT in PGA Films: An Effective Way to Robust Barrier and Mechanical Properties for Fully Biodegradable Packaging Films. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 21280–21290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Jing, B.; Zou, X. High melt viscosity, low yellowing, strengthened and toughened biodegradable polyglycolic acid via chain extension of aliphatic diisocyanate and epoxy oligomer. React. Funct. Polym. 2024, 200, 105926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.Y.; Xu, P.W.; Liu, B.; Shao, H.H.; He, C.B.; Liu, T.X.; Yang, W.J.; Ma, P.M. Toward high strength, ductility, and barrier performance for poly(glycolic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) green films through reactive compatibilization and biaxial drawing. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 8236–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, E.D.; Telemeco, T.A.; Simpson, D.G.; Wnek, G.E.; Bowlin, G.L. Utilizing acid pretreatment and electrospinning to improve biocompatibility of poly(glycolic acid) for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 71B, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdhanie, L.I.; Aubuchon, S.R.; Boland, E.D.; Knapp, D.C.; Barnes, C.P.; Simpson, D.G.; Wnek, G.E.; Bowlin, G.L. Thermal and Mechanical Characterization of Electrospun Blends of Poly(lactic acid) and Poly(glycolic acid). Polym. J. 2006, 38, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabzdyk, C.S.; Chun, M.; Pathan, S.G.; Nelson, D.W.; You, J.-O.; Phaneuf, M.D.; LoGerfo, F.W.; Pradhan-Nabzdyk, L.; Chipara, M. Development of a Composite Electrospun Polyethylene Terephthalate-Polyglycolic Acid Material: Potential Use as a Drug-Eluting Vascular Graft. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 340981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz, L.I.S.; Rodríguez, F.J.M.; Velasco-Santos, C.; Martínez-Hernández, A.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, M. Hydrolytic Degradation and Morphological Characterization of Electrospun Poly(glycolic acid) [PGA] Thin Films of Different Molecular Weights Containing TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, S. Compressible polyglycolic acid-based nanofibrous matrices as a bone filler: Fabrication, physicochemical characterisations, and biocompatibility evaluation. Mater. Technol. 2021, 37, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghazali, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Khatri, M.; Phan, D.-N.; Khatri, Z.; Mahar, S.K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kim, I.-S. Preparation of a Cage-Type Polyglycolic Acid/Collagen Nanofiber Blend with Improved Surface Wettability and Handling Properties for Potential Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, N.; Zhuge, Y.; Ji, H.; Liu, F. Effective preparation of environmentally friendly polyglycolic acid (PGA) nanofibrous membrane with antibacterial property for high-efficiency and low-resistance air filtration. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 200, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, N.; Derakhshan, M.A.; Faridi-Majidi, R.; Ghanbari, H. Novel electro-conductive nanocomposites based on electrospun PLGA/CNT for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci.-Materails Med. 2018, 29, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, L.L.; Chen, N.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mo, X.M. The cellular response of nerve cells on poly-L-lysine coated PLGA-MWCNTs aligned nanofibers under electrical stimulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 91, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, V.O.; Livi, S.; Sperling, L.E.; Dos Santos, M.G.; Merlini, C. Biodegradable Electrospun Conduit with Aligned Fibers Based on Poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) (PLGA)/Carbon Nanotubes and Choline Bitartrate Ionic Liquid. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.Y.; Chen, N.; Peng, S.; Li, L.; Tian, L.; Thakor, N.; Ramakrishna, S. Polymer-based composites by electrospinning: Preparation & functionalization with nanocarbons. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 86, 40–84. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno, H.; Eto, R.; Fujii, M.; Totani, M.; Tanaka, K. Effect of segmental motion on hydrolytic degradation of polyglycolide in electro-spun fiber mats. Soft Matter 2023, 19, 7459–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Samples | PGA/Nanofiller (wt/wt) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGA | 100/0 | 20.86 ± 0.57 | 91.11 ± 7.28 | 180.19 ± 41.27 |
| PGA/GO | 99/1 | 18.08 ± 1.15 | 38.75 ± 15.1 | 246.23 ± 21.95 |
| PGA/GO | 97/3 | 21.36 ± 0.85 | 60.98 ± 18.47 | 259.51 ± 29.72 |
| PGA/GO | 95/5 | 8.18 ± 2.84 | 17.23 ± 9.71 | 113.09 ± 34.87 |
| PGA/GO | 90/10 | 2.23 ± 1.12 | 2.31 ± 0.81 | 120.94 ± 18.53 |
| PGA/CNT | 99/1 | 16.61 ± 1.3 | 46.06 ± 13.08 | 151.28 ± 25.97 |
| PGA/CNT | 97/3 | 16.75 ± 1.75 | 61.19 ± 16.81 | 103.74 ± 27.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Yin, H.; Song, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, D. High-Strength and Rapidly Degradable Nanocomposite Yarns from Recycled Waste Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA). Polymers 2025, 17, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010100
Liu B, Wang S, Guo H, Yin H, Song Y, Gong M, Zhang L, Lin X, Wang D. High-Strength and Rapidly Degradable Nanocomposite Yarns from Recycled Waste Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA). Polymers. 2025; 17(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ben, Shixiao Wang, Hanling Guo, Huibo Yin, Yuqiu Song, Min Gong, Liang Zhang, Xiang Lin, and Dongrui Wang. 2025. "High-Strength and Rapidly Degradable Nanocomposite Yarns from Recycled Waste Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA)" Polymers 17, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010100
APA StyleLiu, B., Wang, S., Guo, H., Yin, H., Song, Y., Gong, M., Zhang, L., Lin, X., & Wang, D. (2025). High-Strength and Rapidly Degradable Nanocomposite Yarns from Recycled Waste Poly(glycolic acid) (PGA). Polymers, 17(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010100







