Efficient Bioprocess for Mixed PET Waste Depolymerization Using Crude Cutinase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Plasmids, and Enzymes
2.2. Expression and Purification of Enzymes
2.3. Estimation of Esterase Activity and Protein Concentration
2.4. Evaluating Enzyme Performance on a Small Scale on Different Powder and Films
2.5. Evaluation of Different Reaction Variables for PET Hydrolysis
2.6. Evaluating Enzyme Performance in 10 mL (Without pH Control) and 1 L Bioreactor (pH Control)
2.7. Production of LCCICCG in the Bioreactor and PET Hydrolysis
2.8. Depolymerization of Mixed PET Waste Using LCCICCG in 1 L
2.9. Advanced Analysis
2.9.1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.9.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.9.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis of PET Materials
3. Results and Discussion
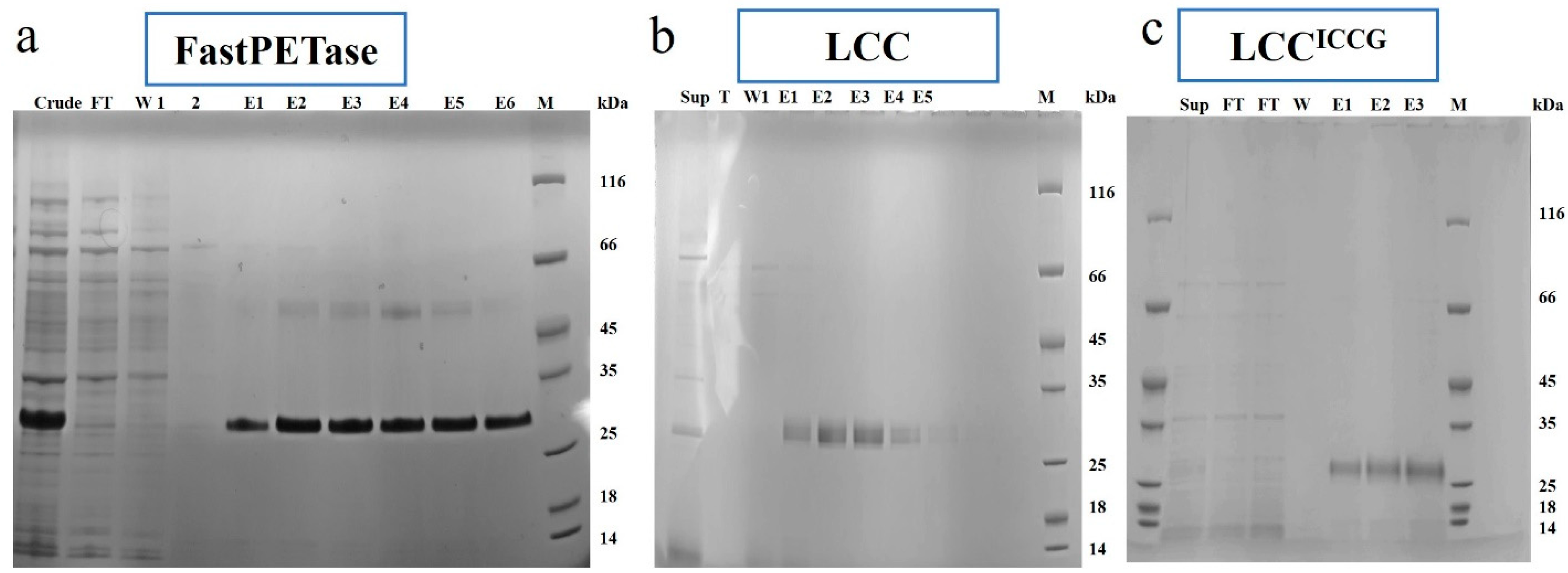
3.1. Expression, Production, and Purification of FastPETase, LCC, and LCCICCG
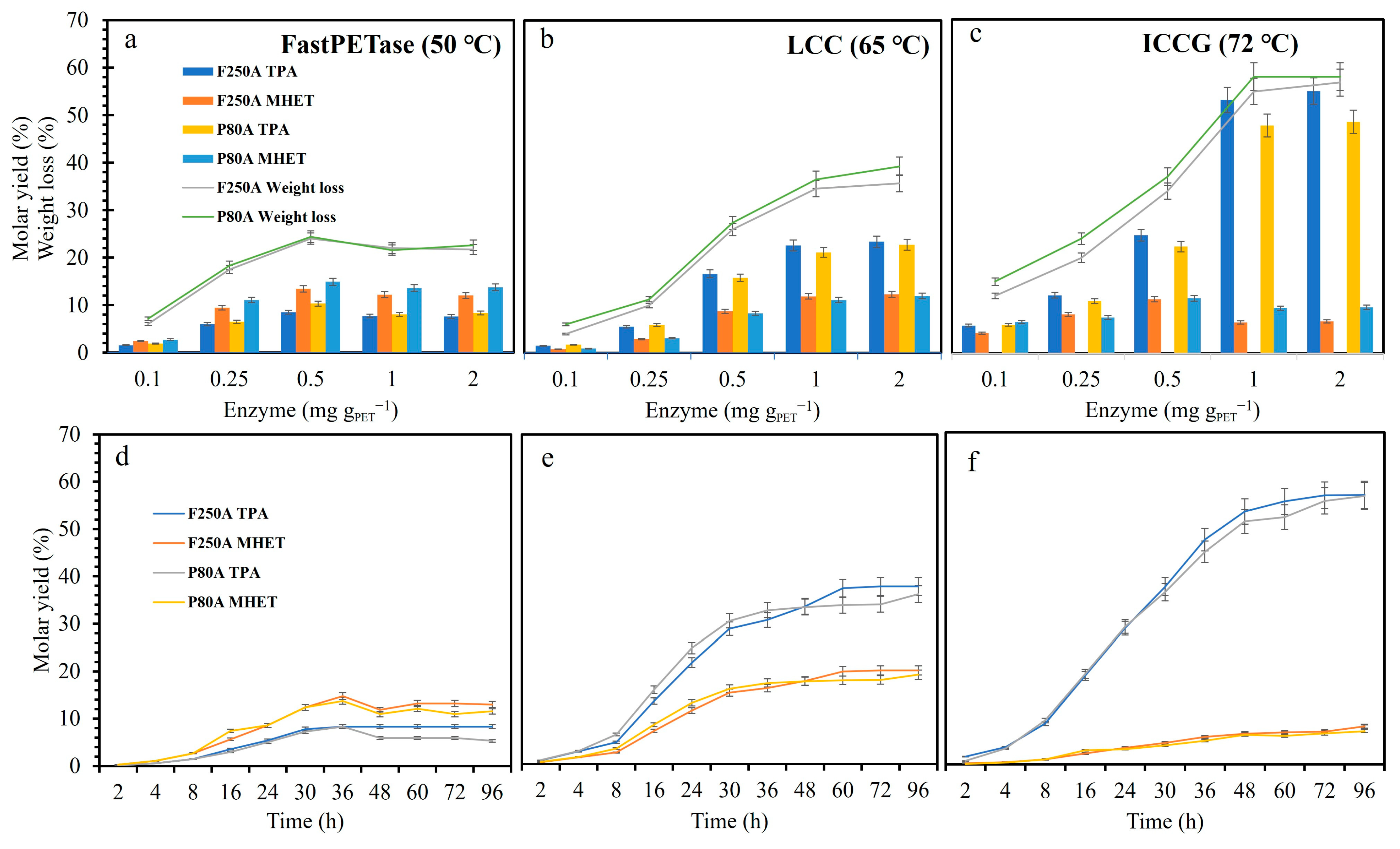
3.2. Enzymatic Depolymerization of Different Powders and Films in Small-Scale
3.3. Different Variables Influencing Enzymatic PET Hydrolysis
3.4. PET Depolymerization in 10 mL
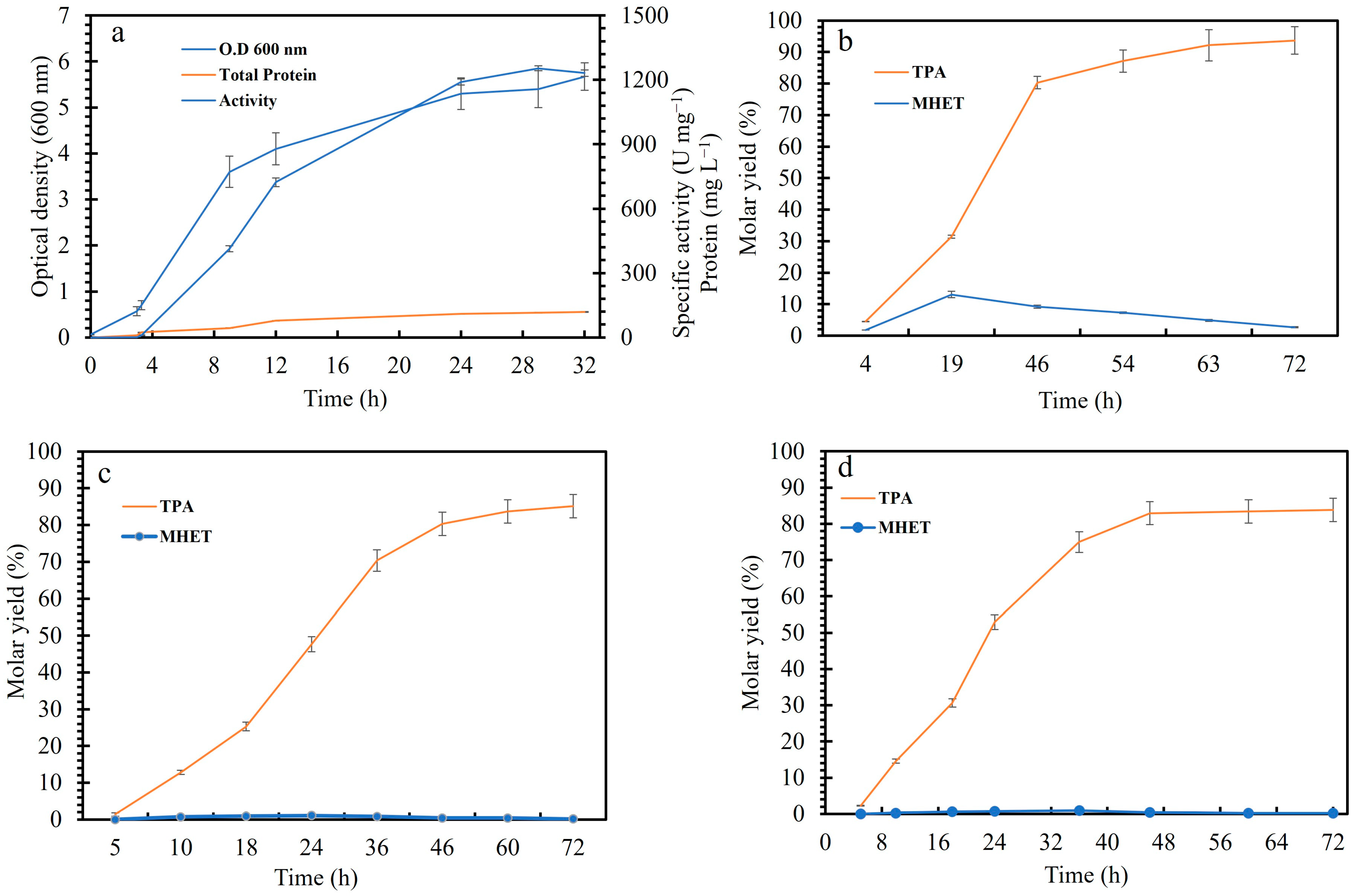
3.5. Depolymerization of Different PET Substrates Using Crude LCCICCG in a Bioreactor (1 L)
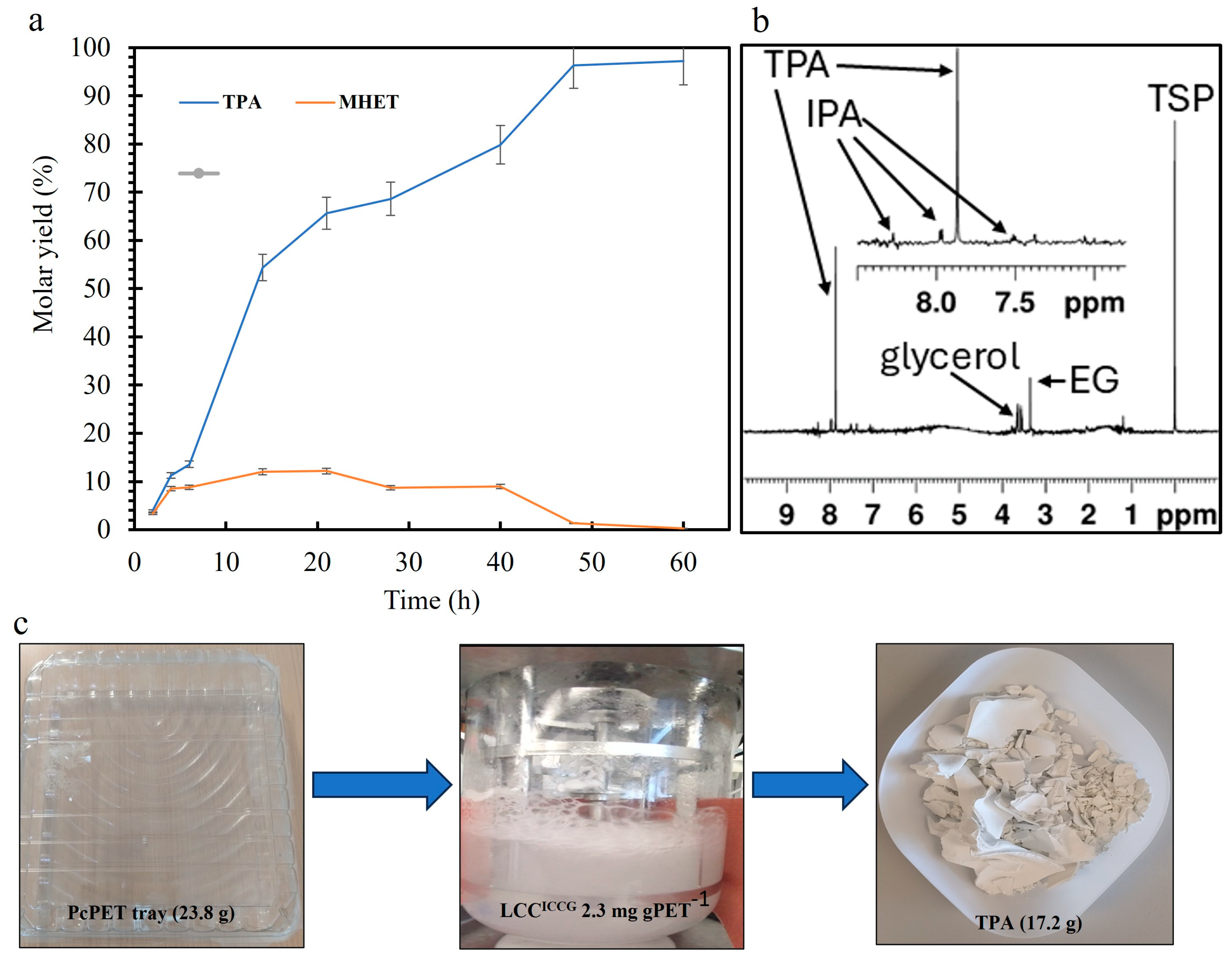
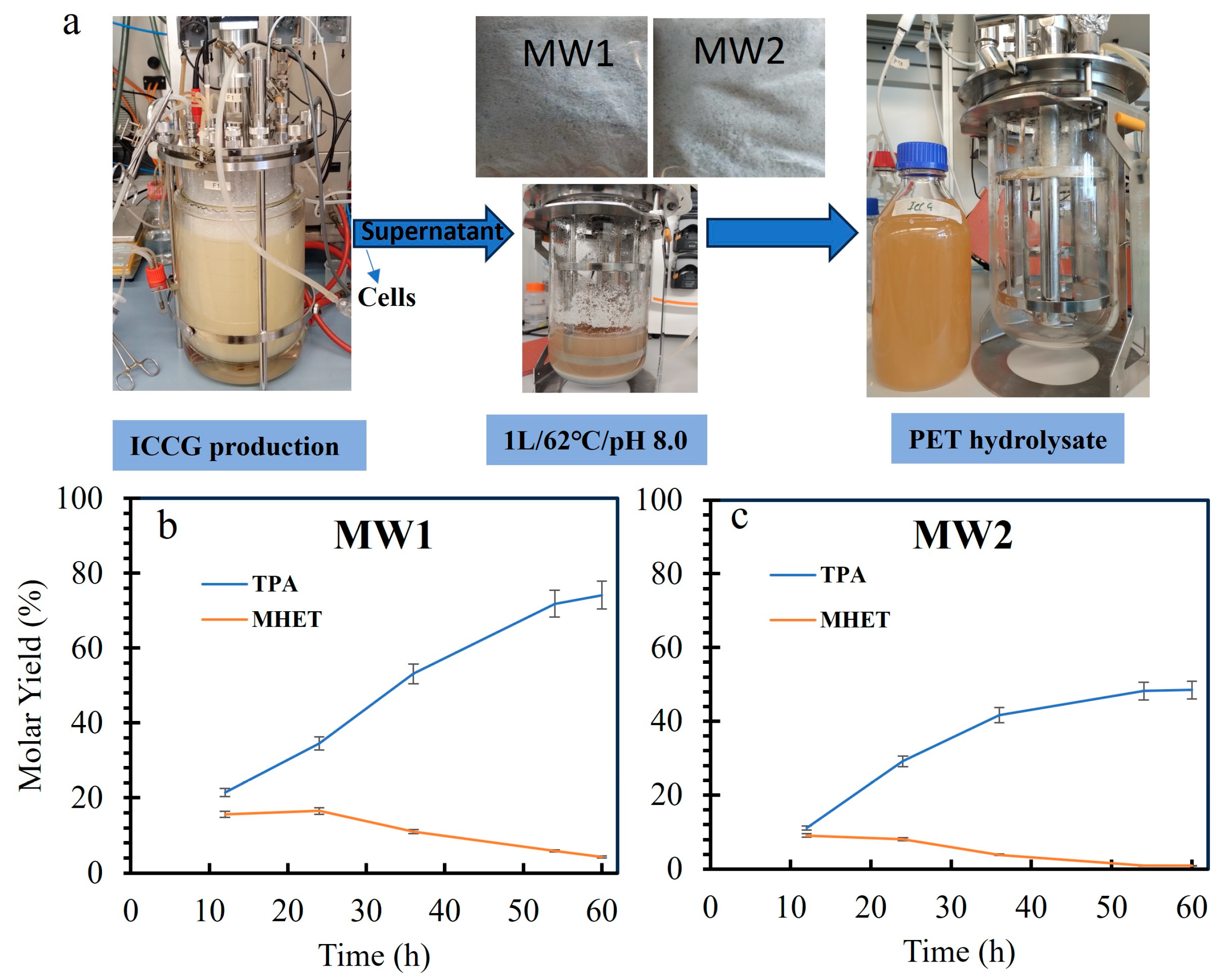
3.6. Mixed PET Waste Depolymerization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tournier, V.; Duquesne, S.; Guillamot, F.; Cramail, H.; Taton, D.; Marty, A.; André, I. Enzymes’ Power for Plastics Degradation. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 5612–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, G.; Anglade, J.; Gavalda, S.; Tournier, V.; Chabot, N.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Weber, G.; Marty, A. Assessment of Four Engineered PET Degrading Enzymes Considering Large-Scale Industrial Applications. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 13156–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zuo, Z.; Niu, Z. Recent Advances in Plastic Recycling and Upgrading under Mild Conditions. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 6949–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, B.C. Plastics Are Forever. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Jiao, L.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, C. Easily Recoverable and Reusable P-Toluenesulfonic Acid for Faster Hydrolysis of Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.B.; Noor, Z.Z.; Hassan, A.; Abd Hamid, M.K.; Samsudin, S.A.; Sabeen, A.H. Current Developments in Chemical Recycling of Post-Consumer Polyethylene Terephthalate Wastes for New Materials Production: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van Geem, K. Mechanical and Chemical Recycling of Solid Plastic Waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, S.; Liu, P.; et al. Depolymerization of Polyesters by a Binuclear Catalyst for Plastic Recycling. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, S. Tandem Chemical Depolymerization and Photoreforming of Waste PET Plastic to High-Value-Added Chemicals. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Tan, T. PET Recycling under Mild Conditions Via Substituent-Modulated Intramolecular Hydrolysis. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 6558–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuara, A.J.; Pedersen, T.H.; Wimmer, R. Process Optimization by NMR-Assisted Investigation of Chemical Pathways during Depolymerization of PET in Subcritical Water. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 2711–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, S.; Tian, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Mitra, R.; Han, J.; Li, C.; Han, X.; et al. Computational Redesign of a PETase for Plastic Biodegradation under Ambient Condition by the GRAPE Strategy. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.L.; Smithson, R.; Kilbride, S.; Foster, J.; Hardy, F.J.; Ramachandran, S.; Tedstone, A.A.; Haigh, S.J.; Garforth, A.A.; Day, P.J.R.; et al. Directed Evolution of an Efficient and Thermostable PET Depolymerase. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, L.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Jäckering, A.; Weber, G.; Mičan, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, W.; Han, X.; Feiler, C.; et al. Multiple Substrate Binding Mode-Guided Engineering of a Thermophilic PET Hydrolase. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 9790–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.-W.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ko, T.-P.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Guo, R.-T. Structural Insight into Catalytic Mechanism of PET Hydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A Bacterium That Degrades and Assimilates Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Diaz, D.J.; Czarnecki, N.J.; Zhu, C.; Kim, W.; Shroff, R.; Acosta, D.J.; Alexander, B.R.; Cole, H.O.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Machine Learning-Aided Engineering of Hydrolases for PET Depolymerization. Nature 2022, 604, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, S.; Yamato, S.; Kanaya, E.; Kim, J.-J.; Koga, Y.; Takano, K.; Kanaya, S. Isolation of a Novel Cutinase Homolog with Polyethylene Terephthalate-Degrading Activity from Leaf-Branch Compost by Using a Metagenomic Approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 78, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, V.; Topham, C.M.; Gilles, A.; David, B.; Folgoas, C.; Moya-Leclair, E.; Kamionka, E.; Desrousseaux, M.-L.; Texier, H.; Gavalda, S.; et al. An Engineered PET Depolymerase to Break down and Recycle Plastic Bottles. Nature 2020, 580, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F.; Kawabata, T.; Oda, M. Current State and Perspectives Related to the Polyethylene Terephthalate Hydrolases Available for Biorecycling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8894–8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, E.; Gado, J.E.; Avilán, L.; Bratti, F.; Brizendine, R.K.; Cox, P.A.; Gill, R.; Graham, R.; Kim, D.-J.; König, G.; et al. Sourcing Thermotolerant Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Hydrolase Scaffolds from Natural Diversity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Rorrer, N.A.; Nicholson, S.R.; Erickson, E.; DesVeaux, J.S.; Avelino, A.F.T.; Lamers, P.; Bhatt, A.; Zhang, Y.; Avery, G.; et al. Techno-Economic, Life-Cycle, and Socioeconomic Impact Analysis of Enzymatic Recycling of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). Joule 2021, 5, 2479–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Pellis, A.; Wimmer, R.; Popok, V.; Christiansen, J.D.C.; Varrone, C. Efficient Depolymerization of Poly(Ethylene 2,5-Furanoate) Using Polyester Hydrolases. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 9658–9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribitsch, D.; Acero, E.H.; Greimel, K.; Eiteljoerg, I.; Trotscha, E.; Freddi, G.; Schwab, H.; Guebitz, G.M. Characterization of a New Cutinase From Thermobifida Alba for PET-Surface Hydrolysis. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2011, 30, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.; Abouhmad, A.; Warlin, N.; Pyo, S.-H.; Örn, O.; Al-Rudainy, B.; Tullberg, C.; Zhang, B.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Closing The Loop For Poly(Butylene-Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) Recycling: Depolymerization, Monomers Separation, and Upcycling. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Woodard, R.W.; Chen, J.; Wu, J. Extracellular Location of Thermobifida fusca Cutinase Expressed in Escherichia Coli BL21(DE3) without Mediation of a Signal Peptide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4192–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aer, L.; Qin, H.; Wo, P.; Feng, J.; Tang, L. Signal Peptide Independent Secretion of Bifunctional Dual-Hydrolase to Enhance the Bio-Depolymerization of Polyethylene Terephthalate. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 391, 129884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, I.; Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. Biodegradation of PET: Current Status and Application Aspects. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4089–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, N.A.; Wei, R.; Brott, S.; Pfaff, L.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Lendlein, A.; Machatschek, R. Rapid Depolymerization of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Thin Films by a Dual-Enzyme System and Its Impact on Material Properties. Chem Catal. 2022, 2, 3573–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, T.B.; Hunt, C.J.; Meyer, A.S. Influence of Substrate Crystallinity and Glass Transition Temperature on Enzymatic Degradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). New Biotechnol. 2022, 69, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasula, R.R.; Lim, S.; Ghadessy, F.J.; Sana, B. The Influences of Substrates’ Physical Properties on Enzymatic PET Hydrolysis: Implications for PET Hydrolase Engineering. Eng. Biol. 2022, 6, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizendine, R.K.; Erickson, E.; Haugen, S.J.; Ramirez, K.J.; Miscall, J.; Salvachúa, D.; Pickford, A.R.; Sobkowicz, M.J.; McGeehan, J.E.; Beckham, G.T. Particle Size Reduction of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Increases the Rate of Enzymatic Depolymerization but Does Not Increase the Overall Conversion Extent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9131–9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, T.; Pang, H.; Li, C.; Geng, W.-C.; Wu, B. Computational Redesign of a Hydrolase for Nearly Complete PET Depolymerization at Industrially Relevant High-Solids Loading. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bååth, J.A.; Jensen, K.; Borch, K.; Westh, P.; Kari, J. Sabatier Principle For Rationalizing Enzymatic Hydrolysis of a Synthetic Polyester. JACS Au 2022, 2, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäckering, A.; Göttsch, F.; Schäffler, M.; Doerr, M.; Bornscheuer, U.; Wei, R.; Strodel, B. From Bulk To Binding: Decoding The Entry Of PET Into Hydrolase Binding Pockets. JACS Au 2024, 4, 4000–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, M.; Honak, A.; Oeser, T.; Wei, R.; Belisário-Ferrari, M.R.; Then, J.; Schmidt, J.; Zimmermann, W. A Dual Enzyme System Composed of a Polyester Hydrolase and a Carboxylesterase Enhances the Biocatalytic Degradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Films. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, B.C.; Erickson, E.; Allen, M.D.; Gado, J.E.; Graham, R.; Kearns, F.L.; Pardo, I.; Topuzlu, E.; Anderson, J.J.; Austin, H.P.; et al. Characterization and Engineering of a Two-Enzyme System for Plastics Depolymerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25476–25485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, Y.-H.V.; Abid, U.; Chang, A.C.; Ayafor, C.; Patel, A.; Qin, J.; Xu, J.; Lawton, C.; Wong, H.; Sobkowicz, M.J.; et al. Enzyme Selection, Optimization, and Production toward Biodegradation of Post-Consumer Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) at Scale. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 18, 2300119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, A.M.; Carniel, A.; Nicomedes Junior, J.; da Conceição Gomes, A.; Valoni, É. Screening of Commercial Enzymes for Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) (PET) Hydrolysis and Synergy Studies on Different Substrate Sources. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, A.M.; Carniel, A.; Stahelin, D.; Chinelatto Junior, L.S.; Honorato, H.d.A.; de Menezes, S.M.C. High-Fold Improvement of Assorted Post-Consumer Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) (PET) Packages Hydrolysis Using Humicola insolens Cutinase as a Single Biocatalyst. Process Biochem. 2019, 81, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-R.; Jang, Y.-A.; Song, J.K.; Eom, G.T. Secretory Production of an Engineered Cutinase in Bacillus subtilis for Efficient Biocatalytic Depolymerization of Polyethylene Terephthalate. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezazadeh, A.; Thomsen, K.; Gavala, H.N.; Skiadas, I.V.; Fosbøl, P.L. Solubility and Freezing Points of Disodium Terephthalate in Water–Ethylene Glycol Mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Li, X.; Min, J.; Zeng, Z.; Ning, Z.; He, H.; Long, X.; Niu, D.; Peng, R.; Liu, X.; et al. Complete Decomposition of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) by Crude PET Hydrolytic Enzyme Produced in Pichia pastoris. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S.; Hübner, H.; Oldiges, M.; Castiglione, K. Comparative Evaluation of the Extracellular Production of a Polyethylene Terephthalate Degrading Cutinase by Corynebacterium glutamicum and Leaky Escherichia coli in Batch and Fed-Batch Processes. Microb. Cell Factories 2024, 23, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Code | Sample Name | Source | Size or Thickness (mm) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P80A | PET powder cryo-milled | Goodfellow | 0.08 | 9.3 |
| P750A | PET powder cryo-milled | Goodfellow | 0.75 | 16.6 |
| P750C | PET powder cryo-milled | Goodfellow | 0.75 | 37.7 |
| P250C | PET powder cryo-milled | Goodfellow | 0.25 | 42.6 |
| P100C | PET powder cryo-milled | Goodfellow | 0.1 | 39.1 |
| P750C | PET powder cryo-milled | Goodfellow | 0.05 | 37.7 |
| F250A | PET film | Goodfellow | 0.25 | 0.6 |
| F250C | PET film | Goodfellow | 0.25 | 35.1 |
| MW1 | PET trays (real waste, origin Spain) cryo-milled at <500 microns | Waste stream | <0.5 | 15.9 |
| MW2 | PET Bottle (real waste, origin: Spain) cryo-milled at >500 microns | Waste stream | <0.5 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, V.; Wimmer, R.; Varrone, C. Efficient Bioprocess for Mixed PET Waste Depolymerization Using Crude Cutinase. Polymers 2025, 17, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060763
Kumar V, Wimmer R, Varrone C. Efficient Bioprocess for Mixed PET Waste Depolymerization Using Crude Cutinase. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060763
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Virender, Reinhard Wimmer, and Cristiano Varrone. 2025. "Efficient Bioprocess for Mixed PET Waste Depolymerization Using Crude Cutinase" Polymers 17, no. 6: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060763
APA StyleKumar, V., Wimmer, R., & Varrone, C. (2025). Efficient Bioprocess for Mixed PET Waste Depolymerization Using Crude Cutinase. Polymers, 17(6), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060763









