The Design of a Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Treatment System and The Generation of Biohydrogen from E. crassipes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Results of Characterization Chemistry
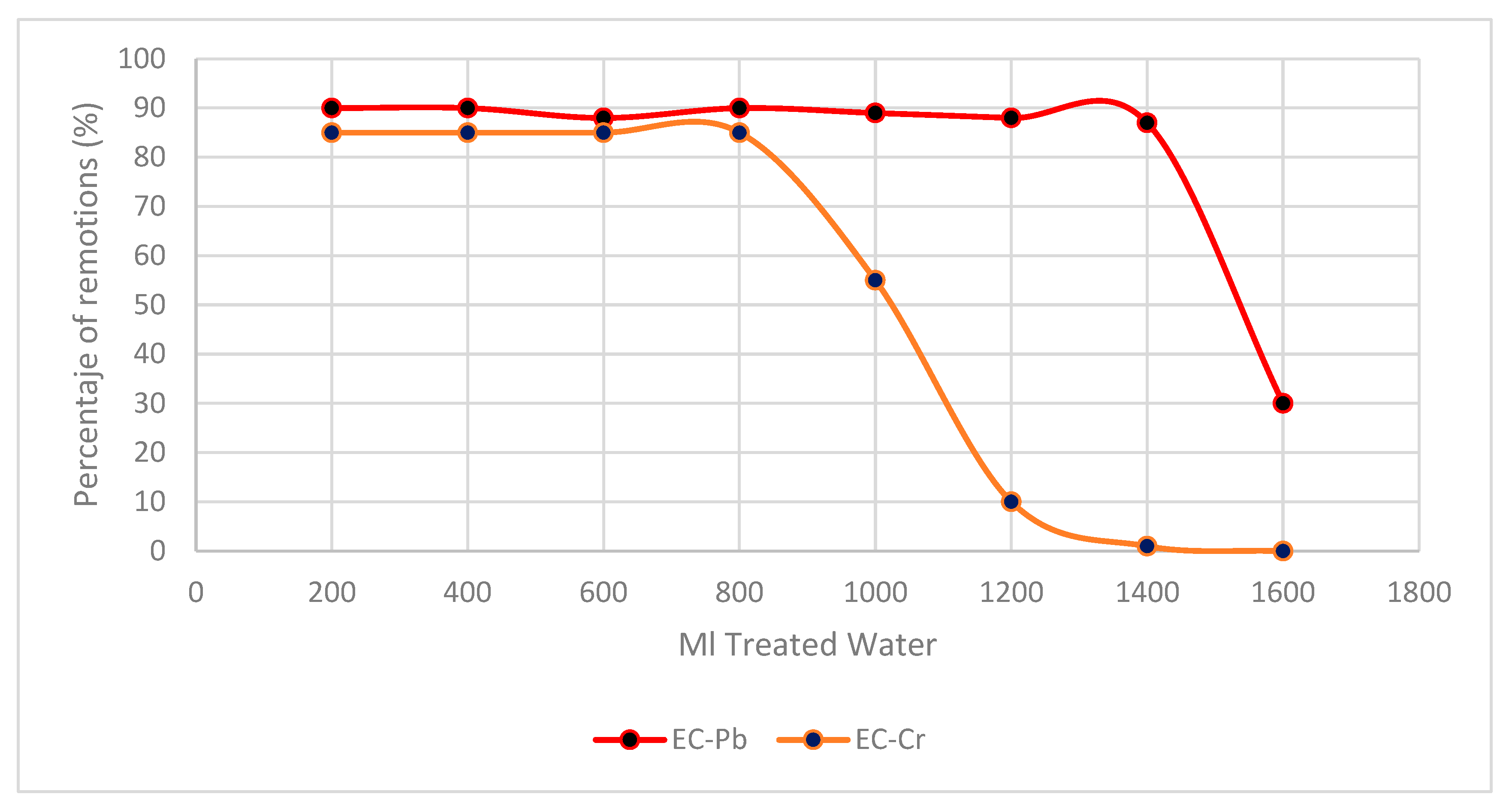
3.2. Results of Adsorptions of Cr (VI) and Pb (II)
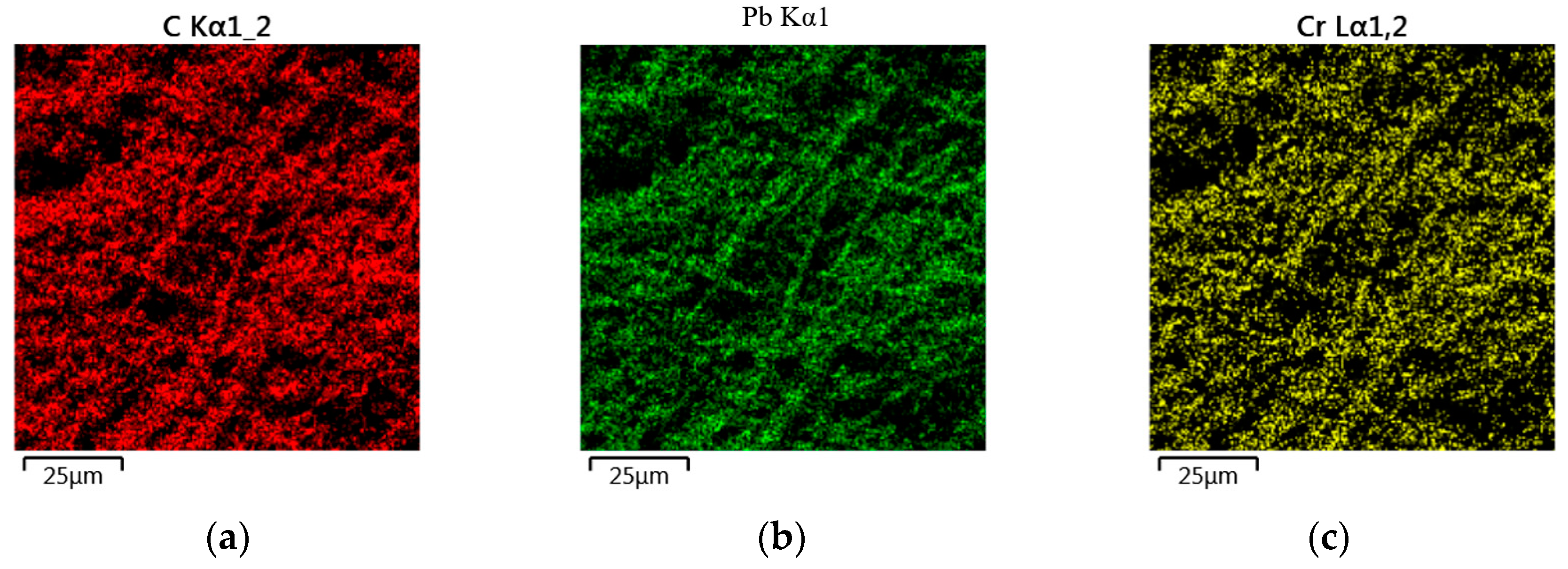
3.3. Analysis EM y EDS
3.4. Hydrolysis Results
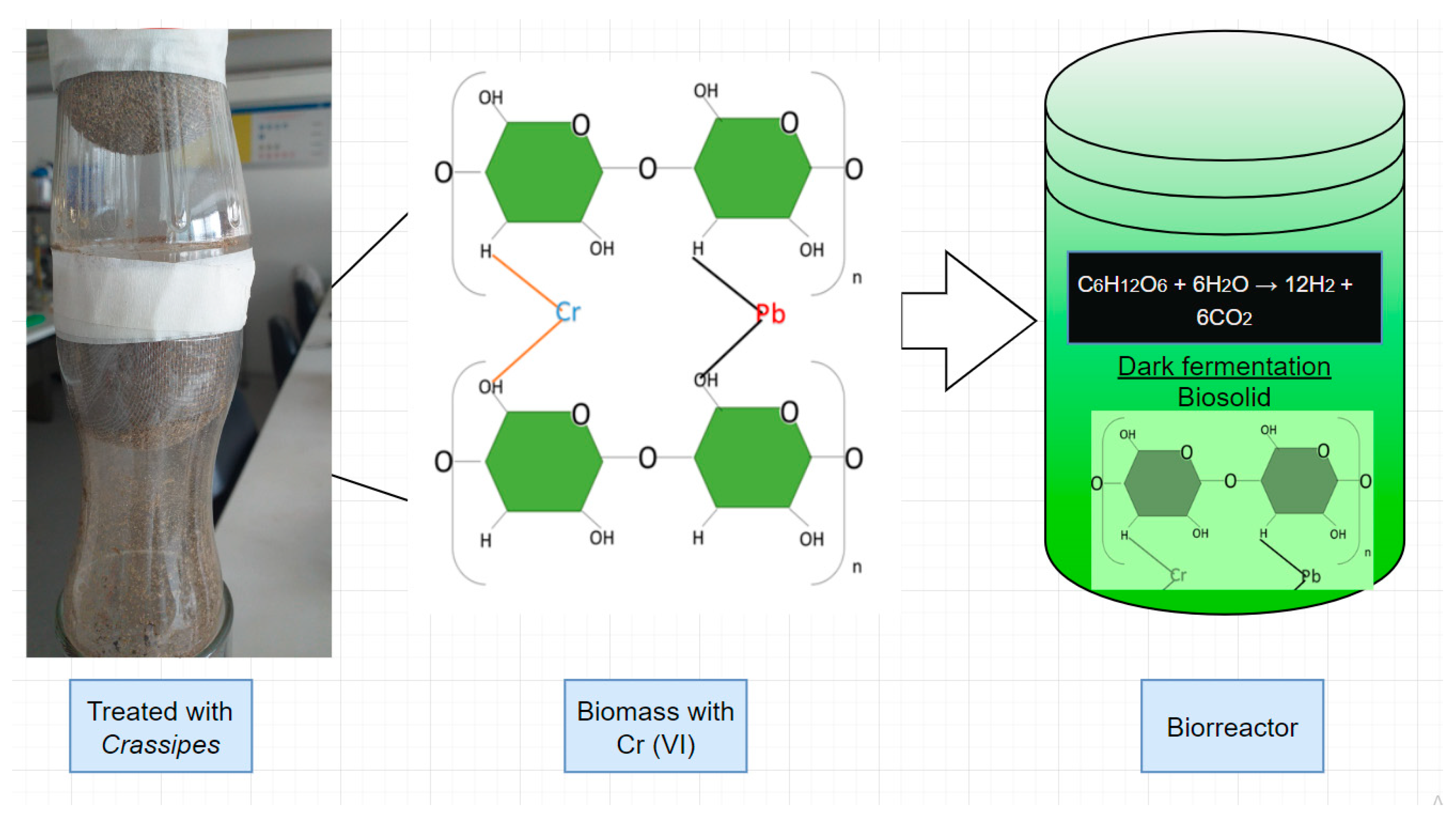
3.5. Production of Biohidrogen
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zia, Z.; Hartland, A.; Mucalo, M.R. Use of low-cost biopolymers and biopolymeric composite systems for heavy metal removal from water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 4389–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Development of a treatment for water contaminated with Cr (VI) using cellulose xanthogenate from E. crassipes on a pilot scale. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Carreño Sayago, U.F.; Piñeros Castro, Y.; Conde Rivera, L.R. Design of a Fixed-Bed Column with Vegetal Biomass and Its Recycling for Cr (VI) Treatment. Recycling 2022, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño Sayago, U.F. Design, scaling, and development of biofilters with e crassipes for treatment of water contaminated with Cr (VI). Water 2021, 13, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fubara, A.G.; Uche, C.C.; Nwoko, C.O.; Tony-Njoku, R.F.; Ojiaku, A.A.; Edo, F.A. Assessment of the effectiveness of water hyacinth (E. crassipes) in the biosorption of heavy metals from Aluminium extruding company effluents. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2022, 26, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardliyah, R.; Kusumadewi, R.A.; Wijayanti, A. Effectiveness test of using natural adsorbent of water hyacinth leaves (eichhornia crassipes) in heavy metal lead (Pb) treatment in batik industry wastewater. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 2706. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, L.; Shah, K.K.; Baruah, G.; Bharali, R.K. Kinetic and equilibrium studies on bioadsorption of copper and lead by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) plant powder. Vietnam J. Chem. 2023, 61, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Zuo, X.; Wang, C. Mechanism, application, influencing factors and environmental benefit assessment of steel slag in removing pollutants from water: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Feng, X.; Wang, R.; Wei, W.; Luo, S.; Zheng, R.; Yang, D.; Mi, H.; Chen, H. High-efficiency core-shell magnetic heavy-metal absorbents derived from spent-LiFePO4 Battery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, Y.; Huang, G.; Yang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J. Adsorption behavior of the antibiotic levofloxacin on microplastics in the presence of different heavy metals in an aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, J.; Ahmad, R.; Mariyam, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Mittal, A. Expedi-tious and enhanced sequestration of heavy metal ions from aqueous envi-ronment by papaya peel carbon: A green and low-cost adsorbent. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 210, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Ma, J.; Wu, F.; Ju, T.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; Shi, H. Mass bal-ance-based inventory of heavy metals inputs to and outputs from agricultur-al soils in Zhejiang Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Bussi, G.; Peters, R.; Hossain, M.A.; Softley, L.; Shawal, S.; Jin, L.; Rampley, C.P.N.; Holdship, P.; Alabaster, G.; et al. Modelling heavy metals in the Buriganga River System, Dhaka, Bangladesh: Impacts of tannery pollution control. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design and development of a biotreatment of E. crassipes for the decontamination of water with Chromium (VI). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design of a sustainable development process between phytoremediation and production of bioethanol with Eichhornia crassipes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño-Sayago, U.F. Desarrollo de un sistema sostenible de fitorremediación y bioetanol con E. crassipes. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2021, 12, 269–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño-Sayago, U.F.; Rodríguez-Parra, C. Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms: An integrated phytoremediation and bioenergy system. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Cienc. For. Ambiente 2019, 25, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.S.; Lay, C.H.; Sen, B.; Chen, C.C.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Wu, J.H.; Lin, C.S.; Lin, C.Y. Biohydrogen and biomethane from water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) fermentation: Effects of substrate concentration and incubation temperature. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 14195–14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Ye, J.; Qian, C. Green synthesis of nickel ferrite nanoparticles for efficient enhancement of lignocellulosic hydrolysate-based biohydrogen production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 194, 108885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, M.K.; Ramkumar, N.; Subudhi, S. Biohydrogen Production from Aquatic Plant and Algae Biomass by Enterobacter cloacae Strain DT-1. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztep, G.; Güngören-Madenoğlu, T.; Özdemir, G.; Işık, E.; Serez, H.; Kabay, N.; Yüksel, M. Optimization and microbial community analysis for anaerobic digestion of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) with waste sludge at different solid contents and temperatures. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Jain, A.; Bora, B.J.; Balakrishnan, D.; Show, P.L.; Ramaraj, R.; Ağbulut, Ü.; Khoo, K.S. Application of modern approaches to the synthesis of biohydrogen from organic waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2023, 48, 21189–21213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, F.R.; Hussy, I.; Kyazze, G.; Dinsdale, R.; Hawkes, D.L. Continuous dark fermentative hydrogen production by mesophilic microflora: Principles and progress. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.B.; Tiwari, A.K.; Srivastava, N.; Ahmad, I.; Abohashrh, M.; Gupta, V.K. Biomass valorization of Eichhornia crassipes root using thermogravimetric analysis. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Girindran, R.; Zacharia, P.U.; Jaya, H.; Kooren, R.; Sayooj, P.; Benny, S.; Joseph, D.; Hussain, S.V. Climate resilient products development through valorization of Eichhornia crassipes to biofuel and biochar. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemida, M.H.; Moustafa, H.; Mehanny, S.; Morsy, M.; Dufresne, A.; Rahman, E.N.A.E.; Ibrahim, M.M. Cellulose nanocrystals from agricultural residues (Eichhornia crassipes): Extraction and characterization. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.K.; Kim, N.; Leu, H.J.; Pham, M.P.; Luong, N.A.; Vo, H.K. The production of hydrogen gas from modified water hyacinth (Eichhornia Crassipes) biomass through pyrolysis process. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 13976–13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu Sherrer, J.S. Aprovechamiento de Bagazo de Agave Tequilana Weber Para la Produccion de Bio-Hidrógeno. Master’s Thesis, Instituto Potosino de Investigación, San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dessì, P.; Lakaniemi, A.M.; Lens, P.N. Biohydrogen production from xylose by fresh and digested activated sludge at 37, 55 and 70 °C. Water Res. 2017, 115, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ri, P.C.; Ren, N.Q.; Ding, J.; Kim, J.S.; Guo, W.Q. CFD optimization of horizontal continuous stirred-tank (HCSTR) reactor for bio-hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 9630–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imizcoz, M.; Puga, A.V. Assessment of photocatalytic hydrogen production from biomass or wastewaters depending on the metal co-catalyst and its deposition method on TiO2. Catalysts 2019, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Conradie, A.V.; Lester, E. Review of supercritical water gasification with lignocellulosic real biomass as the feedstocks: Process parameters, biomass composition, catalyst development, reactor design and its challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boodhun, B.S.F.; Mudhoo, A.; Kumar, G.; Kim, S.H.; Lin, C.Y. Research perspectives on constraints, prospects and opportunities in biohydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 27471–27481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Wang, J. Biohydrogen production from anaerobic digestion and its potential as renewable energy. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, L.U.; Roopnarain, A.; Tekere, M.; Adeleke, R.A. Bioaugmentation potential of inoculum derived from anaerobic digestion feedstock for enhanced methane production using water hyacinth. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarusiripot, C.; Sungthong, D. Biohydrogen and Biomethane Production from Acid Pretreated Water Hyacinth and Kinetics. Trends Sci. 2023, 20, 6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.H.; Khan, M.N.A.; Mukarram, M.; Naqvi, S.R.; Abdullah, A.; Haq, Z.U.; Ullah, H.; Al Mohamadi, H. Cellulosic biomass fermentation for biofuel production: Review of artificial intelligence approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesh, V.; Devi, S.K.; Unni, P.M.; Hemalatha, S.; Venugopalan, V. Chemical Properties of Water Hyancinth Plant Ash. J. Adv. Zool. 2023, 44, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, P.K.; Poddar, M.K.; Chakma, S. Biohydrogen production from waste substrates and its techno-economic analysis. In Hydrogen Economy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 399–429. [Google Scholar]
- Magdum, S.M.; More, S.; Nadaf, A.A. Biochemical conversion of acid pretreatment water hyacinth (eichonnia crassipes) to alcohol using pichia stipitis NCIM 3497. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. 2012, 3, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Mishima, D.; Kuniki, M.; Sei, B.; Soda, S.; Ike, M.; Fujita, M. Ethanol production from candidate energy crops: Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) and water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes L.). Bioreosur. Tecnhol. 2008, 99, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.; Beltrán, M.; Moreno, G.; León, N. Behaviour of Fecal Contamination Indicators (Fecal Coliforms, Somatic Phages and Helminth Eggs) in Biosolid-Soil Mixtures for Ryegrass Sward Farming. In Proceedings of the Residuals and Biosolids Conference 2010, Savannah, Georgia, 23–26 May 2010; Water Environment Federation: St. Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Castro, Y.P.; Rivera, L.R.C.; Mariaca, A.G. Estimation of equilibrium times and maximum capacity of adsorption of heavy metals by E. crassipes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverry-Gallego, R.A.; Espinosa-Barrera, P.A.; Delgado-Vargas, C.A.; Vanegas, J.; Clavijo-Buriticá, D.C.; Martínez-Pachón, D.; Moncayo-Lasso, A. The application of the photo-electro-Fenton process in the treatment of wastewater reduces the abundance of genes associated with pathogenicity factors, antibiotic resistance, and metabolism: A metagenomic analysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, B.; Sen, C.C.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, S.C.; Lee, C.Y.L. Co-fermentation of water hycianth and beverage wastewater in powder and pellet form for hydrogen production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, W.; Mi, W.; Ma, L.; He, W. Preferring cellulose of Eichhornia crassipes to prepare xanthogenate to other plant materials and its adsorption properties on copper. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4460–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Q.; Lei, T.; Negulescu, I.I. Adsorption kinetic and equilibrium studies for methylene blue dye by partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite hydrogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniana, K.; Arunachalama, A.; Dasb, K.; Arunachalama, A. Decomposition and nutrient release of Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms. under different trophic conditions in wetlands of eastern Himalayan foothills. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lee, D.J.; Tahir, N.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Biohydrogen production through active saccharification and photo-fermentation from alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 123007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argun, H.; Dao, S. Bio-hydrogen production from waste peach pulp by dark fermentation: Effect of inoculum addition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 42, 2569–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Ding, L.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.Y. Improving biohydrogen production through dark fermentation of steam-heated acid pretreated Alternanthera philoxeroides by mutant Enterobacter aerogenes ZJU1. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 134695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakojwala, R.; Mohan, S.V. Multi-product biorefinery with sugarcane bagasse: Process development for nanocellulose, lignin and biohydrogen production and lifecycle analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Velayutham, P.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Hafez, H.; Khafipour, E.; Derakhshani, H.; El Naggar, M.H.; Levin, D.B.; Nakhla, G. Co-fermentation of glucose, starch, and cellulose for mesophilic biohydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 20958–20967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Yadav, D.K.; Yadav, A.; Bishnoi, N.R.; Kumar, V.; Ram, C.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, S.S. Frontier in dark fermentative biohydrogen production from lignocellulosic biomass: Challenges and future prospects. Fuel 2024, 366, 131187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.C.; Rodrigues, C.V.; Marin, D.F.C.; Lazaro, C.Z.; Jacobus, A.P.; Pires, L.O.; Maintinguer, S.I. Performance of clostridium species and autochthonous bacteria from citrus wastewater under different carbon sources to produce biofuels. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 49, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.M.; Tripathi, S. Microbial Advancements in Dark Fermentative Biohydrogen Production: Applications and Innovations. In Emerging Trends and Techniques in Biofuel Production from Agricultural Waste; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; pp. 57–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.T.; Ding, J.; Wang, B.Y.; Bao, M.Y.; Liu, B.F.; Pang, J.W.; Ren, N.-Q.; Yang, S.S. Advances in the biomass valorization in dark fermentation systems: A sustainable approach for biohydrogen production. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 2024, 148444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanakrishna, G.; Pengadeth, D. Mixed culture biotechnology and its versatility in dark fermentative hydrogen production. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Lo, Y.C.; Chang, J.S. Multicomponent cellulase production by Cellulomonas biazotea NCIM-2550 and its applications for cellulosic biohydrogen production. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ai, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wu, Q.; Duan, Z.; Liu, H.; Qian, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Co-production process optimization and carbon footprint analysis of biohydrogen and biofertilizer from corncob by photo-fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 375, 128814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.J.; Brar, S.K.; Le Bihan, Y.; Buelna, G. Liquid waste from bio-hydrogen production—A commercially attractive alternative for phosphate solubilizing bio-fertilizer. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 8704–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashyrev, O.B.; Matvieieva, N.A.; Hovorukha, V.M.; Tashyreva, H.O.; Bielikova, O.I.; Havryliuk, O.A.; Duplij, V.P. Application of lignocellulosic substrate obtained after hydrogen dark fermentation of food waste as biofertilizer. Ind. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yong, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Clean style recovery and utilization of residual nutrients in effluents from biohydrogen production: In Situ immobilization based on sodium alginate. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 906968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goria, K.; Kothari, R.; Singh, H.M.; Singh, A.; Tyagi, V.V. Biohydrogen: Potential applications, approaches, and hurdles to overcome. In Handbook of Biofuels; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 399–418. [Google Scholar]




| Model Thomas | (1) |
| Model Carreño | = (2) |
| Lignin (%) | Cellulose (%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Other (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 23 | 43 | 23 | Present |
| 1.1 | 17.3 | 24.7 | [39] | |
| 4.1 | 19.7 | 27.1 | [40] | |
| 1.1 | 17.3 | 24.7 | [44] | |
| 11 | 31 | 27 | 10 | [45] |
| 11 | 27 | 27 | 10 | [46] |
| 12 | 36 | 42 | [47] |
| Element | Weight (g) | Percentage % |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 43.64 | 44.67 |
| Oxygen | 45.15 | 39.94 |
| Cr (VI) | 12.13 | 14.37 |
| Element | Weight (g) | Percentage % |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 43.64 | 43.67 |
| Oxygen | 45.15 | 38.94 |
| Pb (II) | 15.6 | 16.6 |
| Biomass | Yield mL H2/g | |
|---|---|---|
| Present research | Crassipes | 81.7 |
| Present research | Crassipes-Cr (VI) | 71 |
| Present research | Crassipes-Pb (II) | 60 |
| [44] | Crassipes | 73 |
| [48] | Alfalfa | 55.6 |
| [49] | waste peach pulp | 59 |
| [50] | Alternanthera hiloxeroides. | 89 |
| [51] | cellulose | 102.6 |
| [52] | Cellulomonas biazotea | 105.5 |
| [53] | lignocellulosic biomass | 108 |
| [54] | Performance of clostridium species | 120 |
| [55] | Enterobacter, Bacillus, and Clostridium | 109 |
| [56] | Performance of clostridium species Bacillus | 110 |
| [57] | Performance of clostridium species | 112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayago, U.F.C. The Design of a Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Treatment System and The Generation of Biohydrogen from E. crassipes. Polymers 2024, 16, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070893
Sayago UFC. The Design of a Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Treatment System and The Generation of Biohydrogen from E. crassipes. Polymers. 2024; 16(7):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070893
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayago, Uriel Fernando Carreño. 2024. "The Design of a Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Treatment System and The Generation of Biohydrogen from E. crassipes" Polymers 16, no. 7: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070893
APA StyleSayago, U. F. C. (2024). The Design of a Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Treatment System and The Generation of Biohydrogen from E. crassipes. Polymers, 16(7), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070893







