Property Enhancement of Waste Printed Circuit Boards Powders Reinforced Polypropylene by In Situ Magnesium Hydroxide Impregnation from Waste Lye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
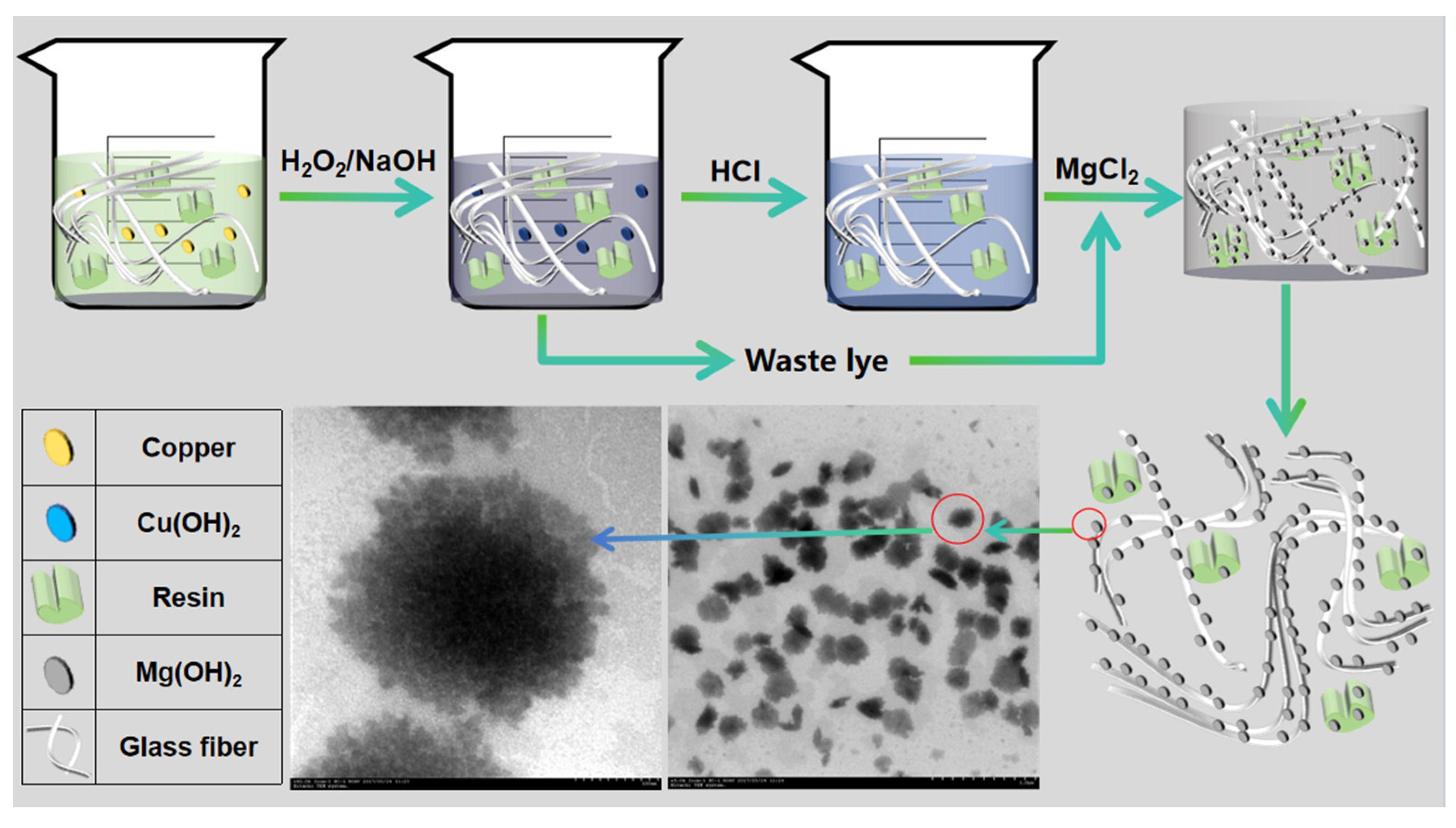
2.2.1. Modification of WPCBP
2.2.2. Preparation of PP Blends
2.3. Testing and Characterization
2.3.1. Particle Size Analysis
2.3.2. Mechanical Property Testing
2.3.3. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
2.3.4. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
2.3.6. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
2.3.7. Limiting Oxygen Index Test (LOI)
2.3.8. Horizontal Combustion Test
2.3.9. Transmission Electron Microscope Analysis (TEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Mg(OH)2
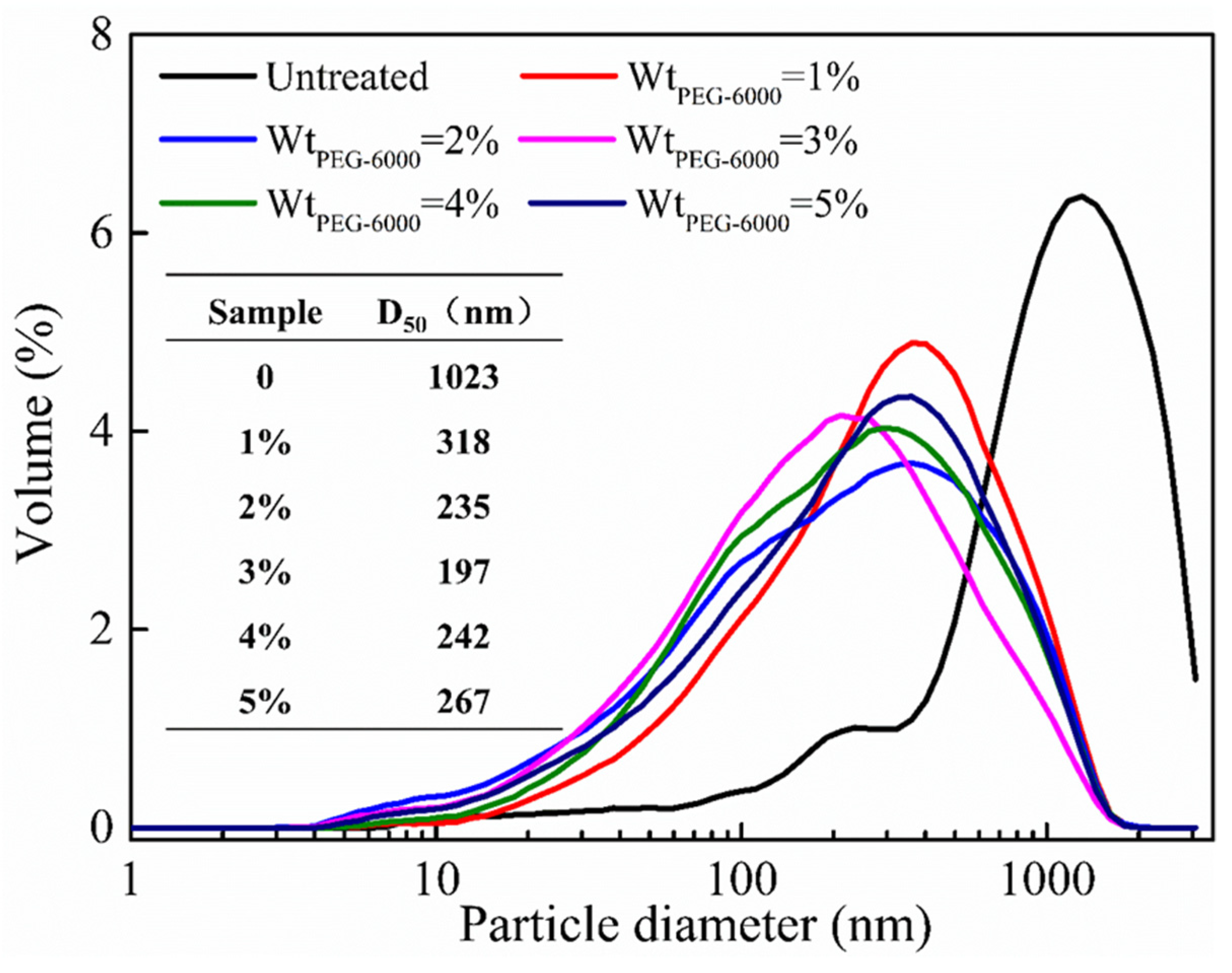
3.1.1. Particle Size Analysis
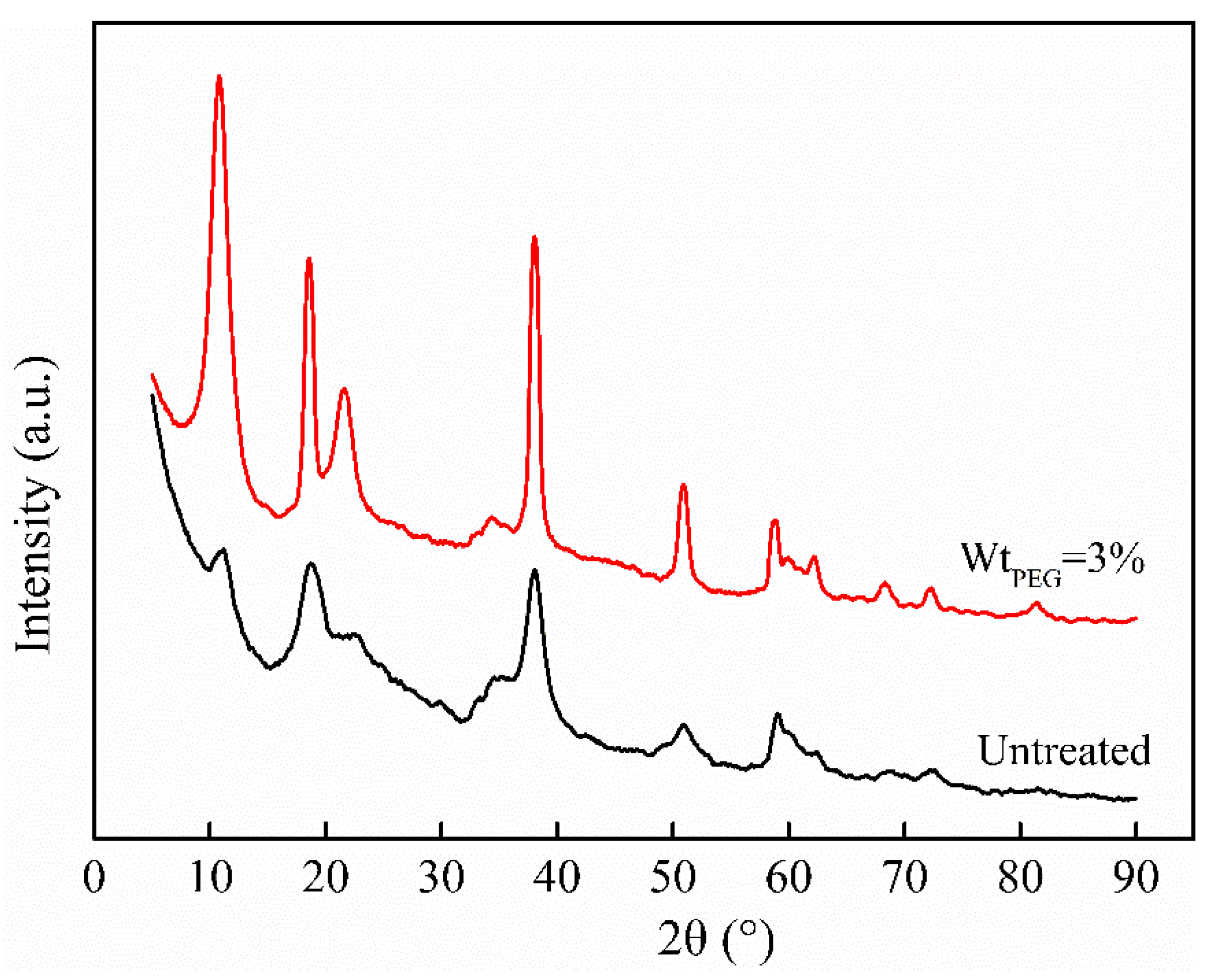
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
3.1.3. TGA Analysis
3.1.4. SEM Analysis
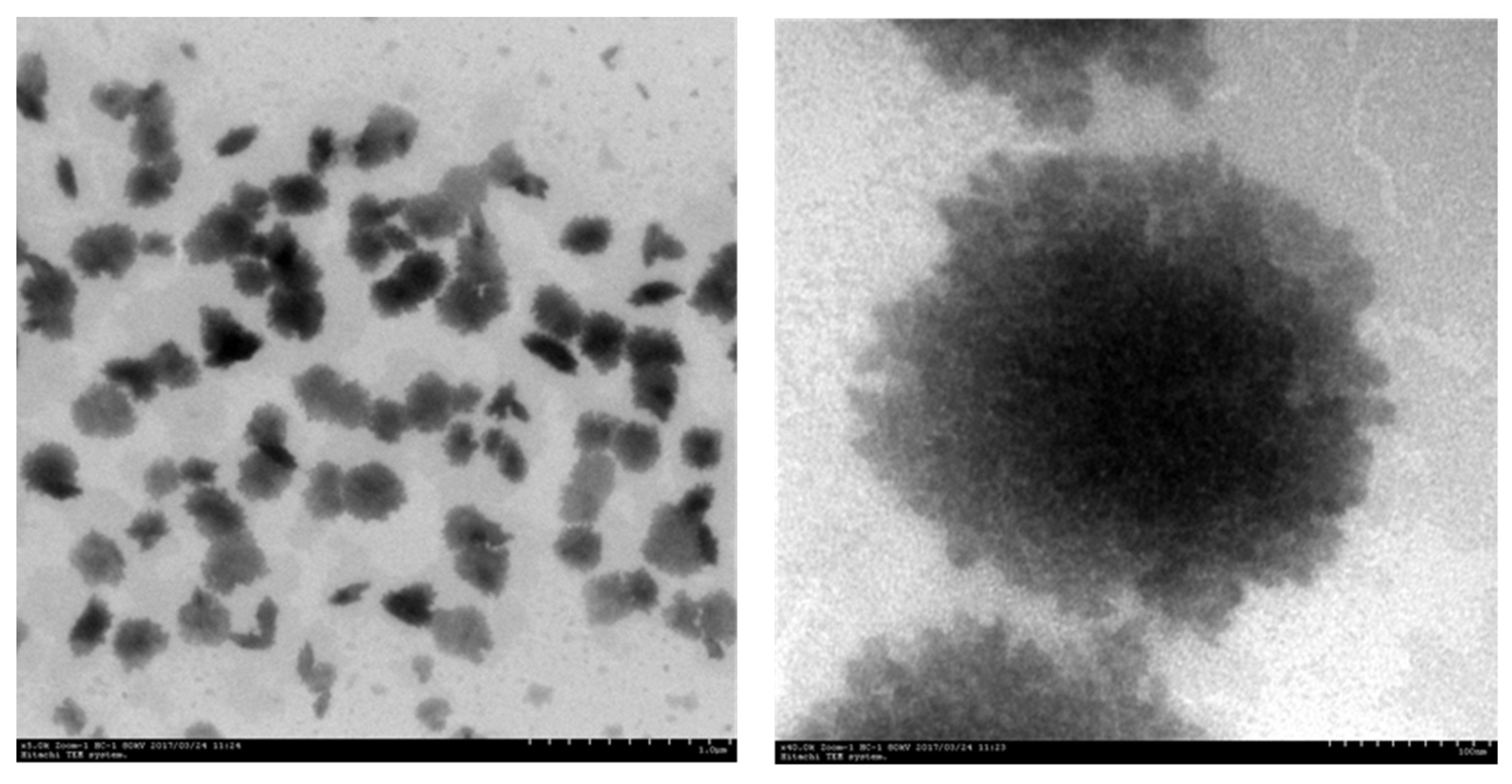
3.1.5. TEM Analysis
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Different MW Hybrids
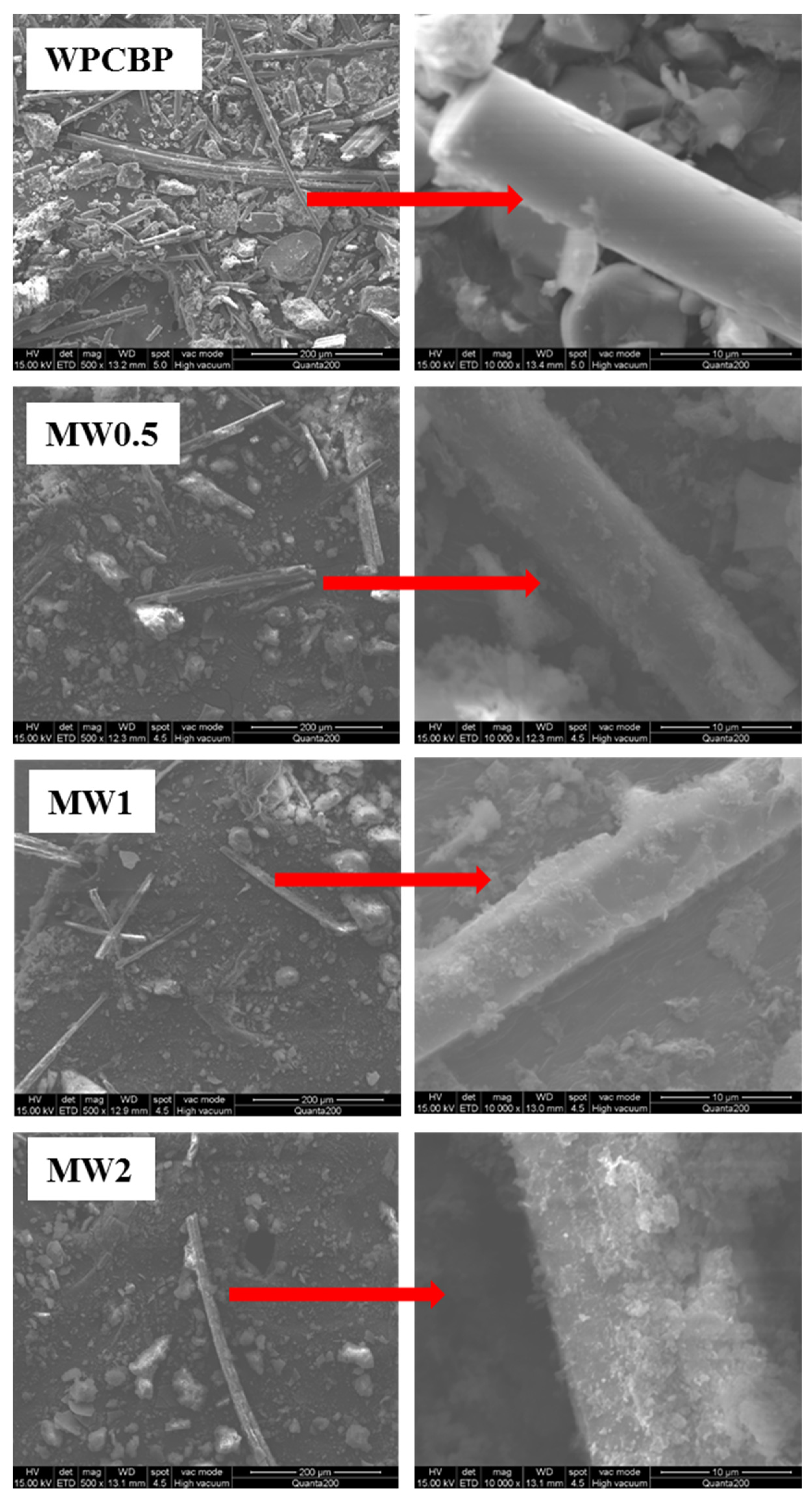
3.2.1. SEM Analysis of Different MW Hybrids
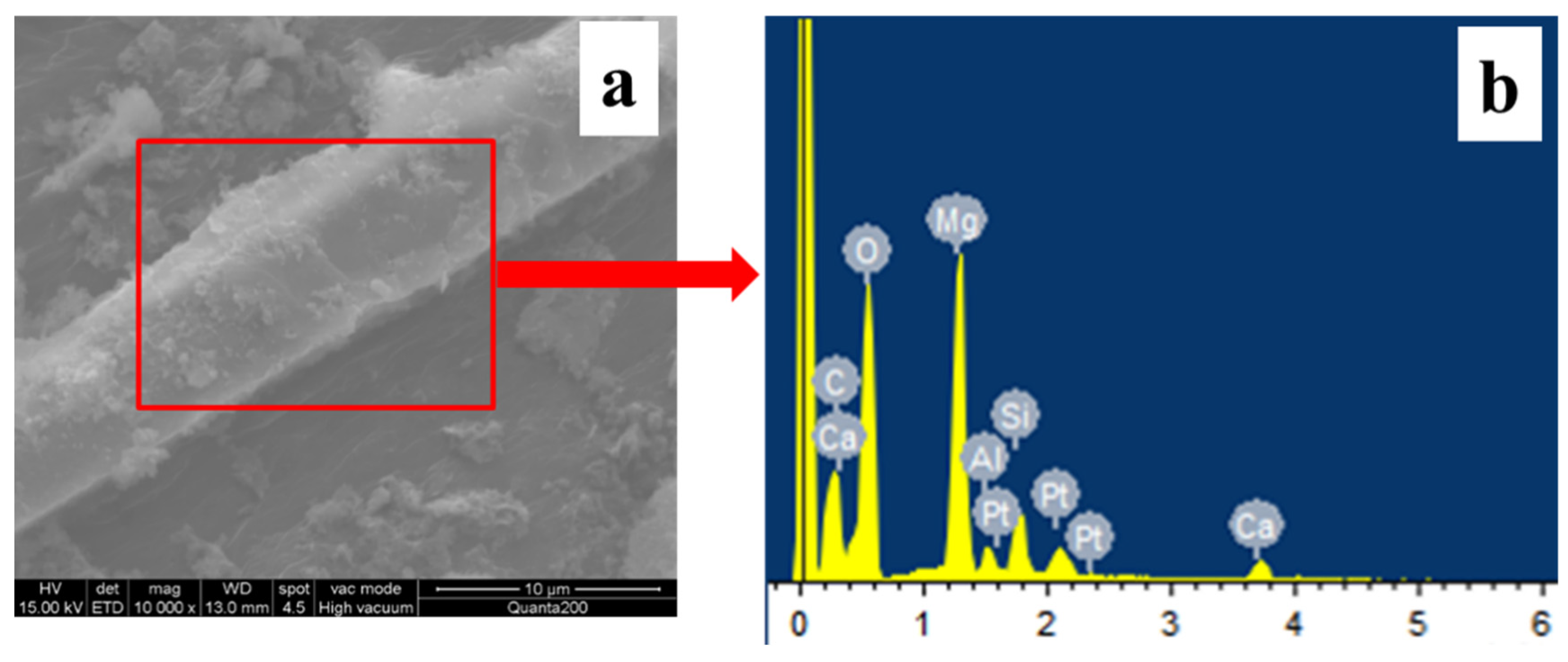
3.2.2. EDS Analysis of Different MW Hybrids
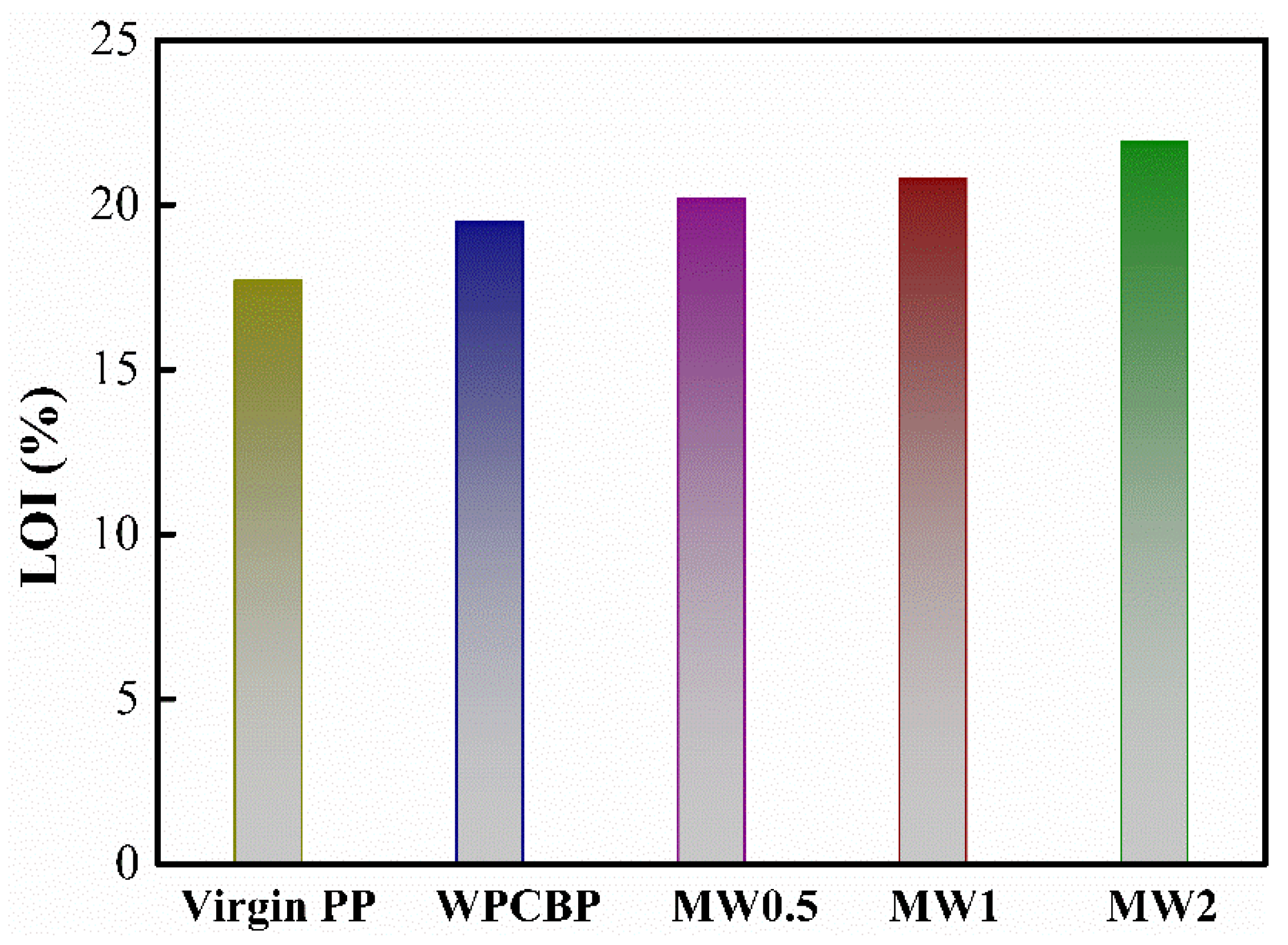
3.3. Flame-Retardant Properties of Different PP Blends
3.4. Thermal Properties of Different PP Blends
3.5. Mechanical Properties of Different PP Blends
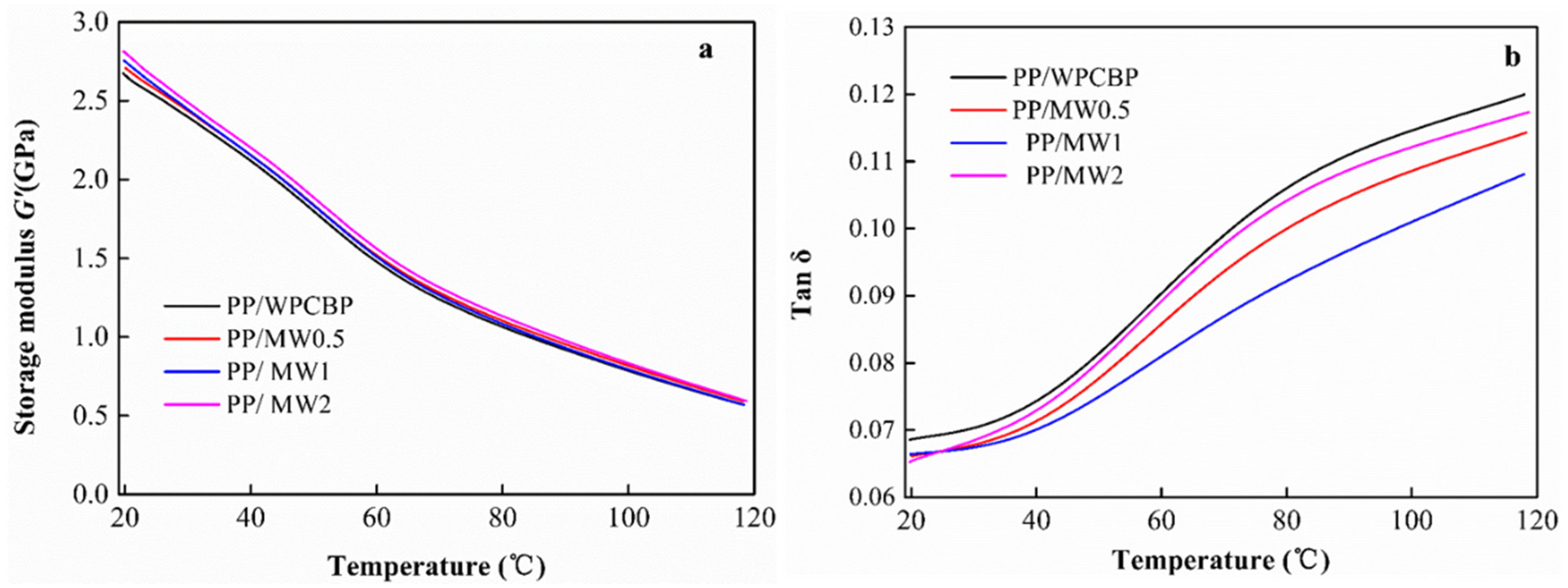
3.6. Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Different PP Blends
3.7. Morphology Analysis of Different PP Blends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, W.; Xu, J.; Fei, W.; Liu, Z.; He, W.; Li, G. The reuse of electronic components from waste printed circuit boards: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 196–214. [Google Scholar]
- Priyan, M.V.; Annadurai, R.; Onyelowe, K.C.; Alaneme, G.U.; Giri, N.C. Recycling and sustainable applications of waste printed circuit board in concrete application and validation using response surface methodology. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martelo, L.M.; Bastos, M.M.S.M.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Separation of the metallic and non-metallic fractions of waste printed circuit boards–A review focused on the organic swelling. Miner. Eng. 2024, 206, 108529. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, S.; Ho, W.; Wang, Y.; Ho, J.Y.T.; Shih, K. Simple and environmentally friendly metal recovery from waste printed circuit boards by using deep eutectic solvents. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 138508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L. Study on particle characteristics and metal distribution of waste printed circuit boards based on a shear crusher. Powder Technol. 2023, 415, 118103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Ruan, J. A novel technology of vacuum low-temperature pyrolysis with NVZI for the high-efficiency debromination of resin particles from waste printed circuit boards. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.-C.; Jiang, S.-Q.; Li, X.-G.; Lyu, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhu, X.-N. Surface characteristic driven in waste printed circuit boards flotation: Floatability mechanism of resin and glass fiber in non-metallic component. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 178, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Jiang, J.; Meng, C.; Hu, X.; Xie, H.; Wu, M.; Guo, Q. Polypropylene Composites Reinforced by Nonmetallic from Waste Printed Circuit Boards Using Spout-Fluid Bed Coating with PP Particles Enhance Fluidization. Polymers 2021, 13, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; He, H.; Yu, P.; Zhou, L.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D. Sustainable utilization of waste printed circuit boards powders in HDPE-wood composites: Synergistic effects of multicomponents on structure and properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, A.K.; Chungprempree, J.; Preechawong, J.; Sapsrithong, P.; Nithitanakul, M. Recycling Waste Nonmetallic Printed Circuit Boards for Polyvinyl Chloride Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Ling, L.; Lei, J.; Fang, G.; Luo, X. Recycling of waste printed circuit boards: Effect of PCB on aging resistance property of SBR modified asphalt. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 72, 106617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zeng, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Jia, Z.; Lin, J. High Value-Added Reutilization of Waste-Printed Circuit Boards Non-Metallic Components in Sustainable Polymer Composites. Molecules 2023, 28, 6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, H. Recycling potential of waste printed circuit boards using pyrolysis: Status quo and perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 173, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Li, B.; He, H.; Liu, X.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Z. Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of High-Durability Polypropylene Composites via Reutilization of SiO2 In-Situ-Synthesized Waste Printed Circuit Board Powder. Polymers 2022, 14, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Luo, Y.; Ma, Y.; He, H.; Jia, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. Effects of decoppering pretreatment on accelerated weathering behaviors of waste printed circuit boards powders reinforced polypropylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48224. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu, R.M.; Ghioca, P.; Iancu, L.; David, M.E.; Andrei, E.R.; Filipescu, M.I.; Ion, R.-M.; Vuluga, Z.; Anghel, I.; Sofran, I.-E.; et al. Development of thermoplastic composites based on recycled polypropylene and waste printed circuit boards. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Zhang, S.; Shi, S.Q.; Cai, L.; Huang, J. Property enhancement of kenaf fiber reinforced composites by in situ aluminum hydroxide impregnation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 79, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638-02; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- ASTM D790-03; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- ASTM D256-02; Standard Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002.
- ASTM D 635-10; Standard Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Lv, J.; Qiu, L.; Qu, B. Controlled growth of three morphological structures of magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles by wet precipitation method. J. Cryst. Growth 2004, 267, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Li, L.; Xu, D.; Zhu, D.; Liu, Z.; Nie, F. Surface modification of magnesium hydroxide using vinyltriethoxysilane by dry process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 382, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Content (wt.%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | CuO | Fe2O3 | Cr2O3 | Others | |
| WPCBP | 52.7 | 20.7 | 14.8 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 6.7 |
| Alkali-treated WPCBP | 60.1 | 19.3 | 12.9 | 0.6 | 0.4 | - | 0.2 | 6.5 |
| Sample | Tonset (°C) | Char Residue (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated Mg(OH)2 | 151.4 | 55.6 |
| PEG treated Mg(OH)2 | 294.7 | 59.1 |
| Element | C | O | Mg | Al | Si | Ca | Pt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per. (wt.%) | 19.39 | 49.05 | 17.93 | 1.63 | 3.95 | 2.23 | 5.82 |
| Sample | Virgin PP | WPCBP | MW0.5 | MW1 | MW2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VHB (mm/min) | 26 | 42 | 35 | 26 | 18 |
| Sample | Tonset 10 wt.% (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Char Residue (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP/WPCBP | 317.8 | 390.6 | 10.6 |
| PP/MW0.5 | 318.2 | 399.2 | 11.5 |
| PP/MW1 | 321.4 | 407.7 | 10.8 |
| PP/MW2 | 328.1 | 418.7 | 11.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, S.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.; Xie, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Property Enhancement of Waste Printed Circuit Boards Powders Reinforced Polypropylene by In Situ Magnesium Hydroxide Impregnation from Waste Lye. Polymers 2024, 16, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060822
Tian S, Liu J, Gu J, Xie C, Zhang X, Liu X. Property Enhancement of Waste Printed Circuit Boards Powders Reinforced Polypropylene by In Situ Magnesium Hydroxide Impregnation from Waste Lye. Polymers. 2024; 16(6):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060822
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Shenghui, Jingwei Liu, Jiabao Gu, Chaoting Xie, Xiong Zhang, and Xinlu Liu. 2024. "Property Enhancement of Waste Printed Circuit Boards Powders Reinforced Polypropylene by In Situ Magnesium Hydroxide Impregnation from Waste Lye" Polymers 16, no. 6: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060822
APA StyleTian, S., Liu, J., Gu, J., Xie, C., Zhang, X., & Liu, X. (2024). Property Enhancement of Waste Printed Circuit Boards Powders Reinforced Polypropylene by In Situ Magnesium Hydroxide Impregnation from Waste Lye. Polymers, 16(6), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060822








