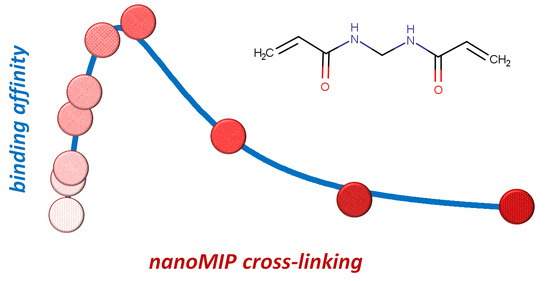
The Amount of Cross-Linker Influences Affinity and Selectivity of NanoMIPs Prepared by Solid-Phase Polymerization Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of NanoMIPs
2.3. Measurement of Size and Charge of NanoMIPs
2.4. Measurement of NanoMIPs Binding Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Size and Charge of NanoMIPs
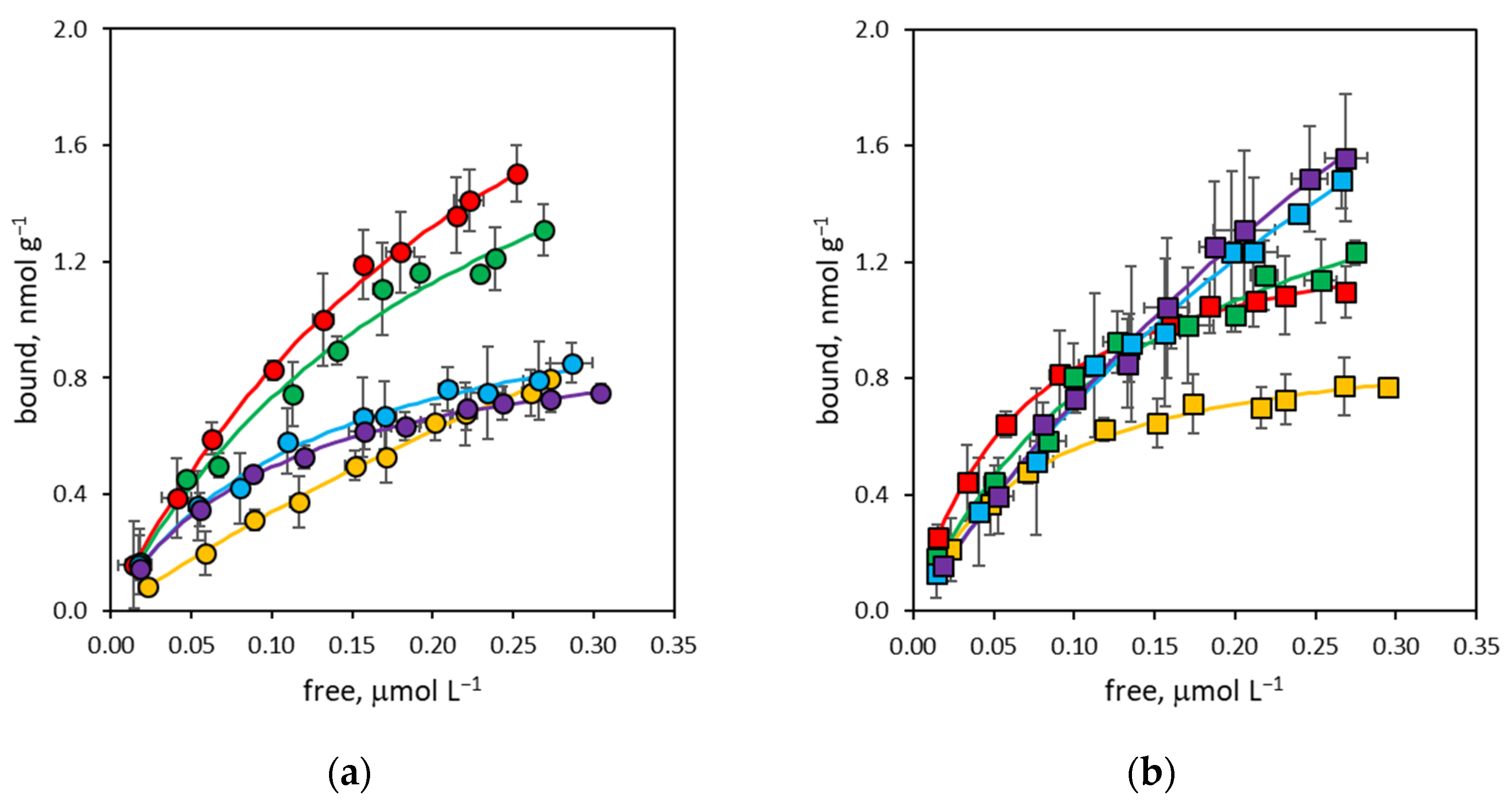
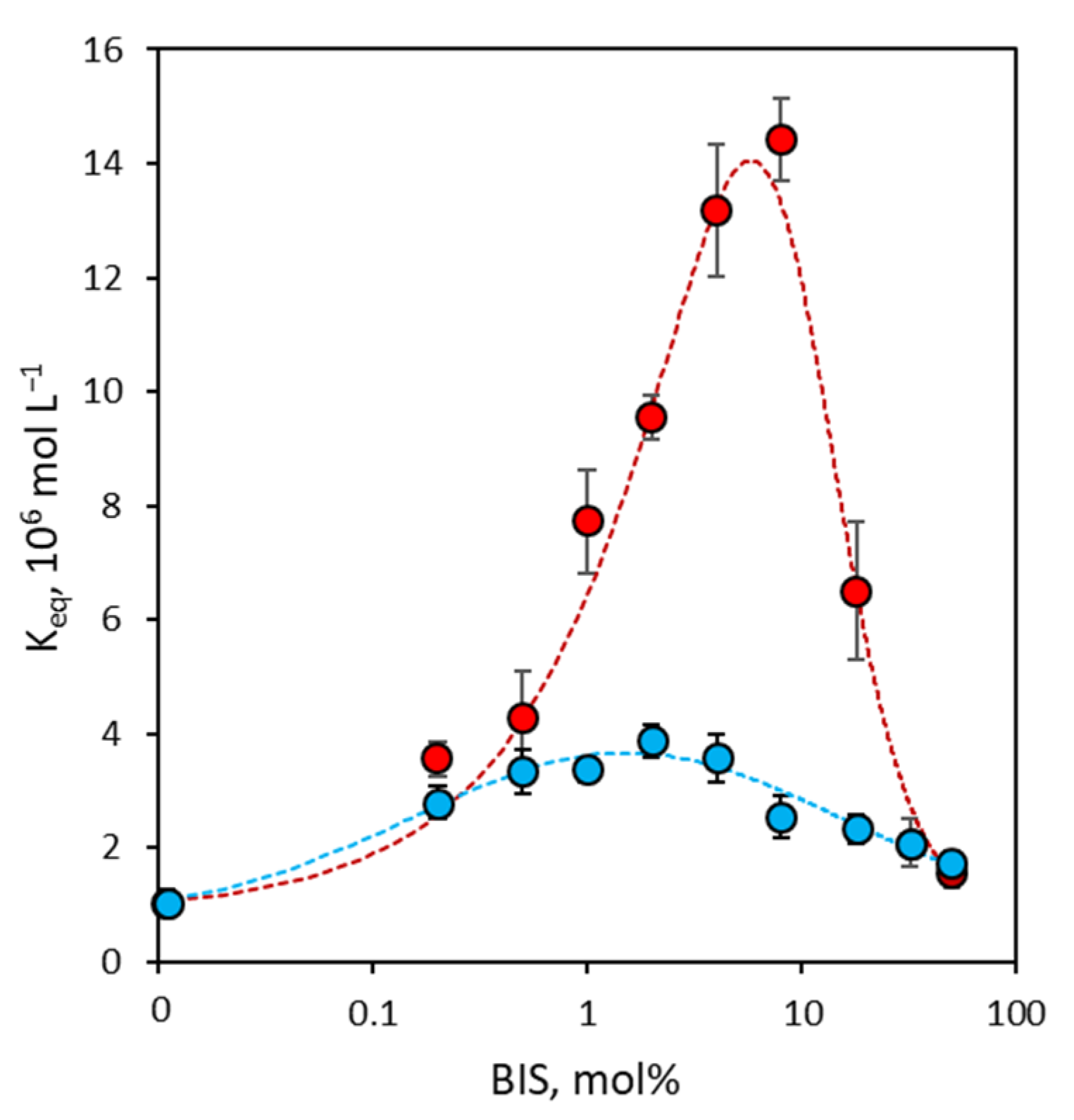
3.2. Binding Affinity of NanoMIPs
3.3. Binding Site Density of NanoMIPs
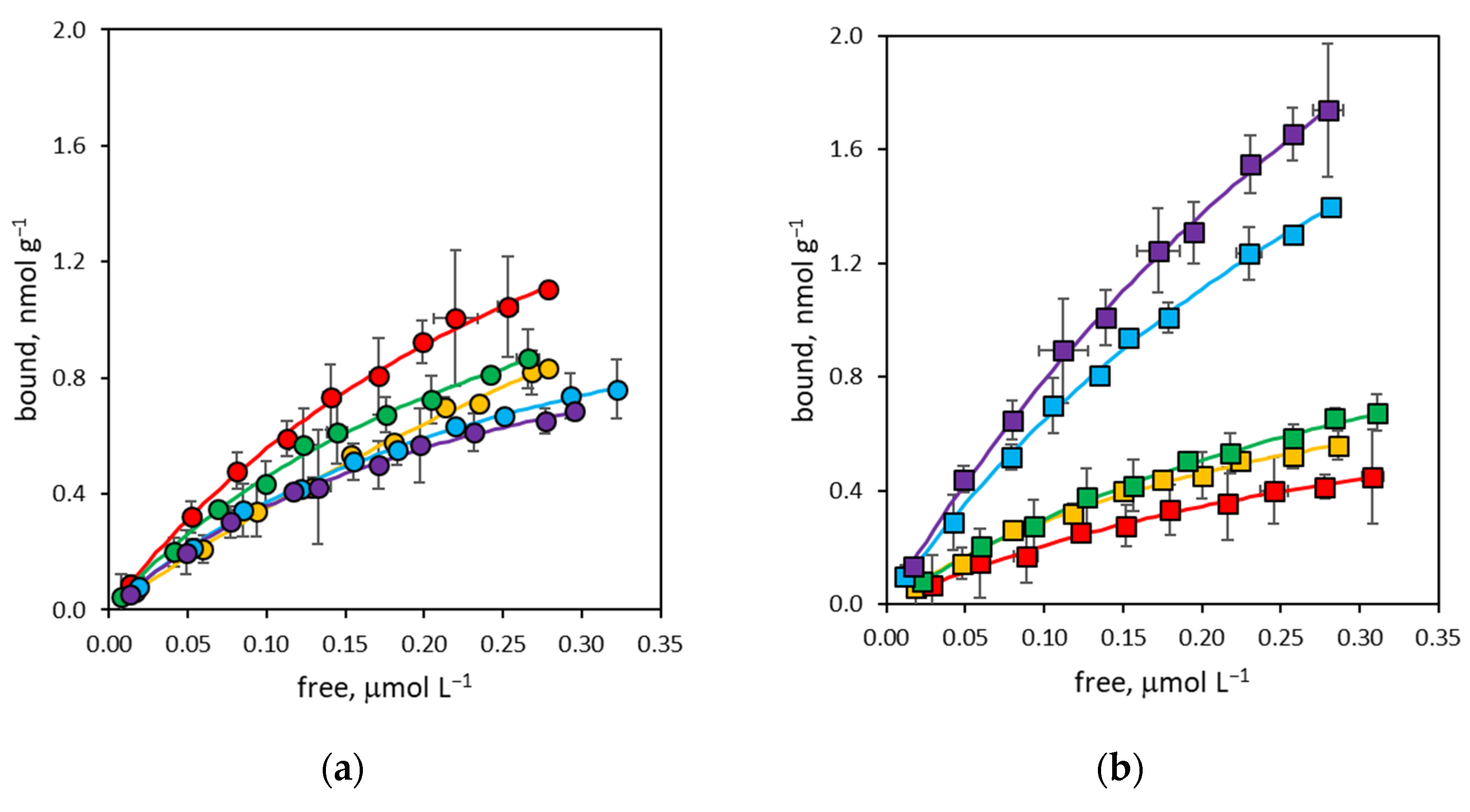
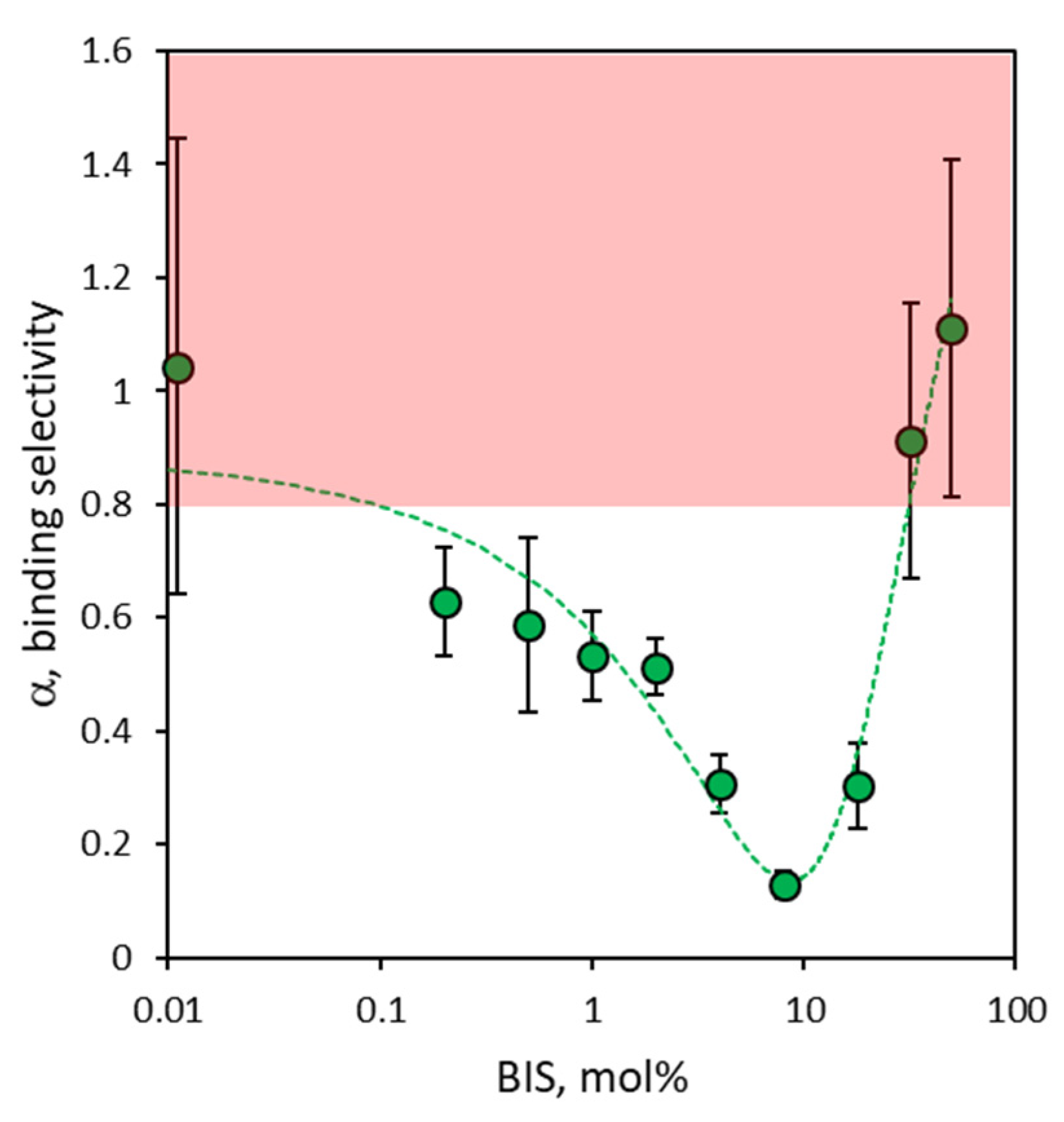
3.4. Binding Selectivity of NanoMIPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, X.; Heiden, P.A. Recent developments in molecularly imprinted nanoparticles by surface imprinting techniques. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Schirhagl, R. Applications of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and their advances toward industrial use: A review. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Pan, G.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.-Z.; Zhang, H.-Q. Narrowly dispersed hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for efficient molecular recognition in real aqueous samples including river water, milk, and bovine serum. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 2013, 52, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-G.; Berg, M.M.; Zhao, C.-S.; Ye, L. One-pot synthesis of hydrophilic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8739–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaihinger, D.; Landfester, K.; Krauter, I.; Brunner, H.; Tovar, G.E.M. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres as synthetic affinity receptors obtained by miniemulsion polymerisation. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, G.; Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Use of molecular imprinted nanoparticles as biorecognition element on surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sens. Actuat. B 2011, 160, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Kodama, Y.; Okahata, Y.; Shea, K.J. Peptide imprinted polymer nanoparticles: A plastic antibody. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15242–15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowen, T.; Stefanucci, E.; Piletska, E.; Marrazza, G.; Canfarotta, F.; Piletsky, S.A. Synthetic mechanism of molecular imprinting at the solid phase. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Guerreiro, A.; Canfarotta, F.; Cáceres, C.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S.A. A comparison of the performance of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for small molecule targets and antibodies in the ELISA format. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Puertollano, D.; Cowen, T.; García-Cruz, A.; Piletska, E.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A.; Piletsky, S. Study of epitope imprinting for small templates: Preparation of nanoMIPs for Ochratoxin A. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalera, S.; Chiarello, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C. Effect of experimental conditions on the binding abilities of ciprofloxacin-imprinted nanoparticles prepared by solid-phase synthesis. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 163, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truta, F.; Garcia Cruz, A.; Tertis, M.; Zaleski, C.; Adamu, G.; Allcock, N.S.; Suciu, M.; Ștefan, M.G.; Kiss, B.; Piletska, E.; et al. NanoMIPs-based electrochemical sensors for selective detection of amphetamine. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, C.; Sullivan, M.V.; Wild, M.I.; O’Connor, A.J.; Turner, N.W. Utilisation of molecularly imprinting technology for the detection of glucocorticoids for a point of care surface plasmon resonance (SPR) device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1285, 342004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ambrosini, S.; Tamahkar, E.; Rossi, C.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Toward a universal method for preparing molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles with antibody-like affinity for proteins. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletska, E.V.; Mirkes, E.; Piletsky, S.S.; Abosoglu, H.; Cassim, A.; Chu, E.; Doughty, S.; Eganda, S.-J.; Fuchigami, H.; Hussein, A.; et al. Combinatorial screening of polymer nanoparticles for their ability to recognize epitopes of AAV-neutralizing antibodies. J. Mol. Recognit. 2019, 32, e2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletska, E.V.; Guerreiro, A.; Mersiyanova, M.; Cowen, T.; Canfarotta, F.; Piletsky, S.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, S. Probing peptide sequences on their ability to generate affinity sites in molecularly imprinted polymers. Langmuir 2020, 36, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Caballero, A.; Elejaga-Jimeno, A.; García del Caño, G.; Unceta, N.; Guerreiro, A.; Saumell-Esnaola, M.; Sallés, J.; Aránzazu Goicolea, M.; Barrio, R.J. Solid-phase synthesis of imprinted nanoparticles as artificial antibodies against the C-terminus of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor: Exploring a viable alternative for bioanalysis. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.S.; Baidyuk, E.; Piletska, E.V.; Lezina, L.; Shevchenko, K.; Jones, D.J.L.; Cao, T.H.; Singh, R.; Spivey, A.C.; Aboagye, E.O.; et al. Modulation of EGFR activity by molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles targeting intracellular epitopes. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 9677–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, Y.; Oino, D.; Ohira, H.; Muguruma, H.; Moczko, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Size of heparin-imprinted nanoparticles reflects the matched interactions with the target molecule. Sensors 2019, 19, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina Rangel, P.X.; Laclef, S.; Xu, J.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Kovensky, J.; Tse Sum Bui, B.; Haupt, K. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer nanolabels: Affinity tools for cellular bioimaging of glycans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdekova, J.; Canfarotta, F.; Grillo, F.; Yesilkaya, H.; Vaculovicova, M.; Piletsky, S. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for pathogen visualisation. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 2602–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmbhatt, H.; Poma, A.; Pendergraff, H.M.; Watts, J.K.; Turner, N.W. Improvement of DNA recognition through molecular imprinting: Hybrid oligomer imprinted polymeric nanoparticles (oligoMIP NPs). Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z.; Gittens, M.; Guerreiro, A.; Thompson, K.A.; Walker, J.; Piletsky, S.; Tothill, I.E. Detection of waterborne viruses using high affinity molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6801–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Cai, C.; Gong, H. A point-to-point “cap” strategy to construct a highly selective dual-function molecularly-imprinted sensor for the simultaneous detection of HAV and HBV. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 219, 114794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpenyong-Akiba, A.E.; Canfarotta, F.; Abd, B.H.; Poblocka, M.; Casulleras, M.; Castilla-Vallmanya, L.; Kocsis-Fodor, G.; Kelly, M.E.; Janus, J.; Althubiti, M.; et al. Detecting and targeting senescent cells using molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Ahmad, O.S.; Guerreiro, A.; Karim, K.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S. New potentiometric sensor based on molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for cocaine detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motib, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Al-Bayati, F.; Piletska, E.; Manzoor, I.; Shafeeq, S.; Kadam, A.; Kuipers, O.; Hiller, L.; Cowen, T.; et al. Modulation of quorum sensing in a gram-positive pathogen by linear molecularly imprinted polymers with anti-infective properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16555–16558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Guerreiro, A.; Czulak, J.; Piletsky, S. Negative selection of MIPs to create high specificity ligands for glycated haemoglobin. Sens. Actuat. B 2019, 301, 126967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Pereira, E.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S. Development of competitive ‘pseudo’-ELISA assay for measurement of cocaine and its metabolites using molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4592–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Canfarotta, F.; Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Piletsky, S.A.; Pereira, E. Competitive pseudo-ELISA based on molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for microcystin-LR detection in water. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, H.; Safaryan, A.H.M.; De Girolamo, A.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Marote, P.; Karim, K.; Lippolis, V.; Pascale, M.; Piletsky, S.A. Determination of Fumonisin B1 in maize using molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based assay. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cruz, A.; Cowen, T.; Voorhaar, A.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles-based assay (MINA)—Detection of leukotrienes and insulin. Analyst 2020, 145, 4224–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, S.; Beyazit, S.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for protein recognition. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6746–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarello, M.; Anfossi, L.; Cavalera, S.; Di Nardo, F.; Serra, T.; Sordello, F.; Baggiani, C. Rabbit IgG-imprinted nanoMIPs by solid phase synthesis: The effect of cross-linkers on their affinity and selectivity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6724–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goicolea, M.A.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Saumell-Esnaola, M.; García del Cano, G.; Unceta, N.; Salles, J.; Barrio, R.J. A line-ar-polymer-based lactoferrin-selective recognition element for an ELISA mimic: A proof of concept. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1191, 339309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, G.D.; Karlsson, B.C.G.; Schillinger, E.; Sellergren, B.; Nicholls, I.A. Theoretical studies of 17-β-estradiol-imprinted prepolymerization mixtures: Insights concerning the roles of cross-linking and functional monomers in template complexation and polymerization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13965–13970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golker, K.; Karlsson, B.C.G.; Olsson, G.D.; Rosengren, A.M.; Nicholls, I.A. Influence of composition and morphology on template recognition in molecularly imprinted polymers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, I.A.; Adbo, K.; Andersson, H.S.; Andersson, P.O.; Ankarloo, J.; Hedin-Dahlström, J.; Jokela, P.; Karlsson, J.G.; Olofsson, L.; Rosengren, J.; et al. Can we rationally design molecularly imprinted polymers? Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpleby, R.J.; Bode, M.; Shimizu, K.D. Measurement of the continuous distribution of binding sites in molecularly imprinted polymers. Analyst 2000, 125, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpleby, R.J.; Baxter, S.C.; Chen, Y.; Shah, R.N.; Shimizu, K.D. Characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers with the Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4584–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frutiger, A.; Tanno, A.; Hwu, S.; Tiefenauer, R.F.; Vörös, J.; Nakatsuka, N. Nonspecific binding—Fundamental concepts and consequences for biosensing applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 8095–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| NanoMIP | BIS, mol% | BIS, µmoles | AA, µmoles | NIPAM, µmoles | TBAm, µmoles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 0 | - | 66.3 | 99.5 | 159.1 |
| P02 | 0.2 | 0.65 | 66.2 | 99.3 | 158.9 |
| P05 | 0.5 | 1.63 | 66 | 99 | 158.4 |
| P1 | 1 | 3.25 | 65.7 | 98.59 | 157.6 |
| P2 | 2 | 6.5 | 65 | 97.5 | 156 |
| P4 | 4 | 13 | 63.7 | 95.5 | 152.8 |
| P8 | 8 | 26 | 61 | 91.5 | 146.5 |
| P18 | 18 | 58.5 | 54.4 | 81.6 | 130.5 |
| P32 | 32 | 104 | 45.1 | 67.7 | 108.2 |
| P50 | 50 | 162.5 | 33.2 | 49.7 | 79.6 |
| NanoMIP | BIS, mol% | dp (nm) | PDI | ζ (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 0 | 165 ± 68 | 0.38 | −24.9 |
| P02 | 0.2 | 163 ± 66 | 0.32 | −23.7 |
| P05 | 0.5 | 168 ± 67 | 0.30 | −24.4 |
| P1 | 1 | 160 ±77 | 0.31 | −23.5 |
| P2 | 2 | 141 ± 65 | 0.28 | −24.5 |
| P4 | 4 | 129 ± 53 | 0.29 | −21.6 |
| P8 | 8 | 109 ± 40 | 0.28 | −17.4 |
| P18 | 18 | 96 ± 22 | 0.27 | −14.5 |
| P32 | 32 | 90 ± 20 | 0.29 | −13.4 |
| P50 | 50 | 90 ± 17 | 0.26 | −10.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Testa, V.; Anfossi, L.; Cavalera, S.; Di Nardo, F.; Serra, T.; Baggiani, C. The Amount of Cross-Linker Influences Affinity and Selectivity of NanoMIPs Prepared by Solid-Phase Polymerization Synthesis. Polymers 2024, 16, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040532
Testa V, Anfossi L, Cavalera S, Di Nardo F, Serra T, Baggiani C. The Amount of Cross-Linker Influences Affinity and Selectivity of NanoMIPs Prepared by Solid-Phase Polymerization Synthesis. Polymers. 2024; 16(4):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040532
Chicago/Turabian StyleTesta, Valentina, Laura Anfossi, Simone Cavalera, Fabio Di Nardo, Thea Serra, and Claudio Baggiani. 2024. "The Amount of Cross-Linker Influences Affinity and Selectivity of NanoMIPs Prepared by Solid-Phase Polymerization Synthesis" Polymers 16, no. 4: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040532
APA StyleTesta, V., Anfossi, L., Cavalera, S., Di Nardo, F., Serra, T., & Baggiani, C. (2024). The Amount of Cross-Linker Influences Affinity and Selectivity of NanoMIPs Prepared by Solid-Phase Polymerization Synthesis. Polymers, 16(4), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040532