Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid/Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-Terephthalate) Modified with Maleic Anhydride
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PLA or PBAT Composites and Blend Samples
2.3. Instrumentation and Equipment
3. Results and Discussion
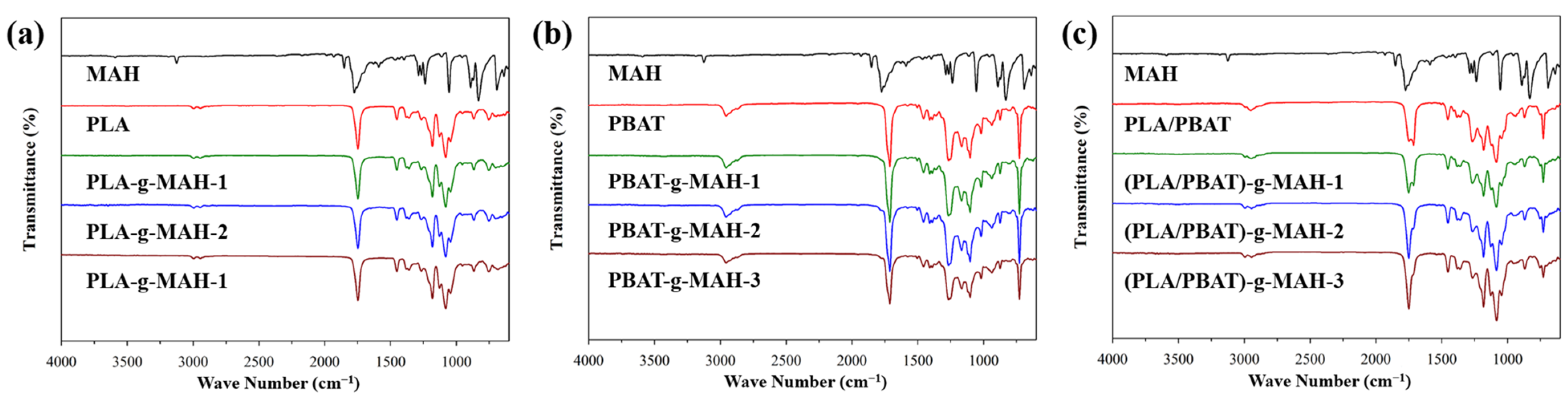
3.1. Spectrophotometric Analysis and Grafting Yield
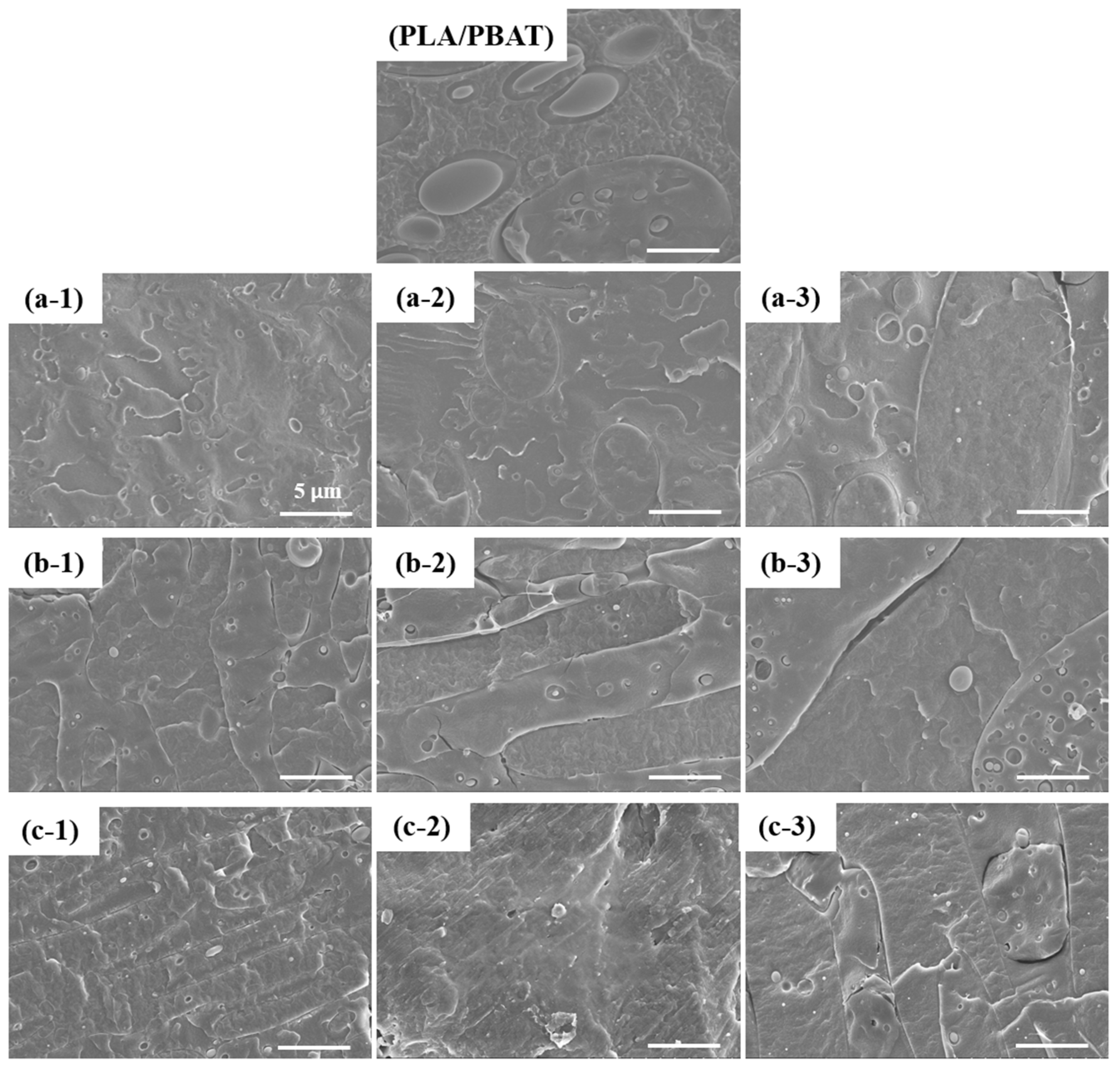
3.2. Morphology Characterization
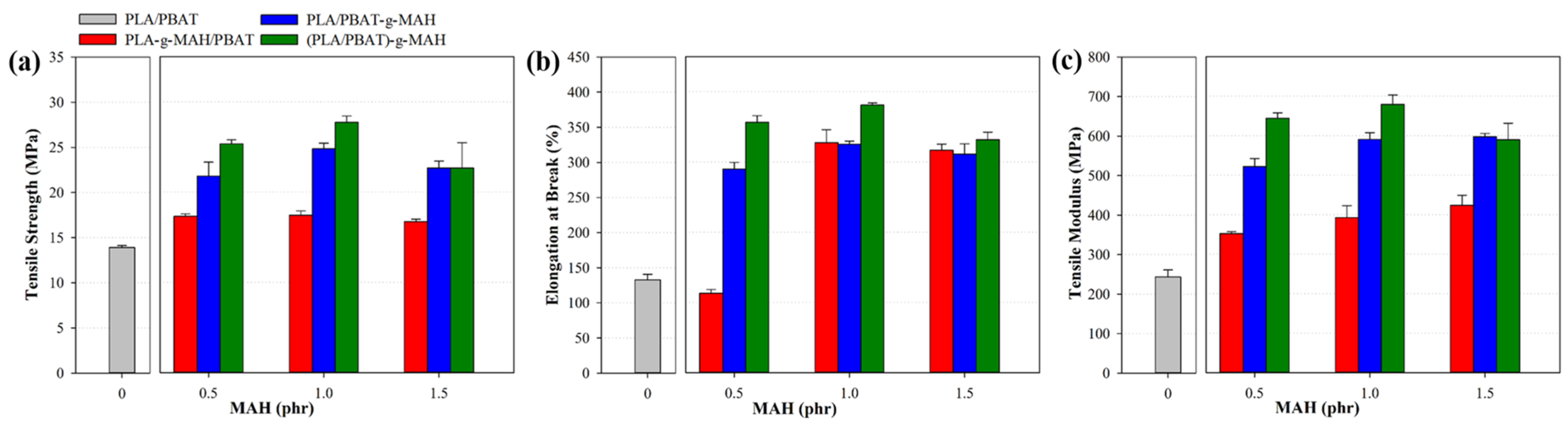
3.3. Rheological and Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haider, T.P.; Völker, C.; Kramm, J.; Landfester, K.; Wurm, F.R. Plastics of the Future? The Impact of Biodegradable Polymers on the Environment and on Society. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, C.Y.; Morgan, D.C. Polymer film packaging for food: An environmental assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2013, 78, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Song, K.Y.; Kang, J.R.; Seo, W.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, W.K. Study on Properties of Eco-friendly Pot with Biodegradable PLA/PBAT Blend Film. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2015, 24, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, M.S. A Study on Environment-friendly Plastic materials due to the Global Environmental Regulation. Bull. Korean Soc. Basic Design Art 2010, 11, 287. [Google Scholar]
- Iles, A.; Martin, A.N. Expanding bioplastics production: Sustainable business innovation in the chemical industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 45, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-González, I.; López-Rubio, A.; Martínez-Sanz, M. High-performance starch biocomposites with celullose from waste biomass: Film properties and retrogradation behaviour. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnaswamy, R.; Hanna, M. Optimum extrusion-cooking conditions for maximum expansion of corn starch. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekielski, A.; Żelaziński, T.; Mishra, P.K.; Skudlarski, J. Properties of Biocomposites Produced with Thermoplastic Starch and Digestate: Physicochemical and Mechanical Characteristics. Materials 2021, 14, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dash, A.A.; Gonzales, R.; Ciol, M. Response surface methodology in the control of thermoplastic extrusion of starch. J. Food Eng. 1983, 2, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hirschberg, V.; Rodrigue, D. Mechanical fatigue of biodegradable polymers: A study on polylactic acid (PLA), polybutylene succinate (PBS) and polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT). Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 159, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajgond, V.; Mohite, A.; More, N.; More, A. Biodegradable polyester-polybutylene succinate (PBS): A review. Polym. Bull. 2023, 9, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Cheng, L.; Yang, X. Biodegradability of poly (butylene succinate)(PBS) composite reinforced with jute fibre. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zeng, X.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Li, X. Preparation and characterization of polyacrylate/polymerized rosin composite emulsions by seeded semicontinuous emulsion polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Qin, Z.; Hu, L.; Rudd, C.; Yi, X. Study on Toughness Improvement of a Rosin-Sourced Epoxy Matrix Composite for Green Aerospace Application. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Sacligil, D.; Carreau, P.J.; Kamal, M.R.; Heuzey, M.C. Poly (lactic acid) blends: Processing, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, V.; Rocculi, P.; Romani, S.; Rosa, M.D. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: A review. Trends. Food. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.J.; Zhang, X.; He, C. Fully biodegradable Poly(lactic acid)/Starch blends: A review of toughening strategies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Kim, D.Y.; Nam, K.B.; Seo, K.H.; Lee, D.Y. Compatibility and Impact Properties of Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Blend Using Poly(butyl acrylate). Polym. Korea 2020, 44, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiao, J.; Brosse, N.; Hoppe, S.; Du, G.; Zhou, X.; Pizzi, A. One-step compatibilization of poly(lactic acid) and tannin via reactive extrusion. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108603. [Google Scholar]
- Pivsa-Art, S.; Kord-Sa-Ard, J.; Pivsa-Art, W.; Wongpajan, R.; O-Charoen, N.; Pavasupree, S.; Hamada, H. Effect of Compatibilizer on PLA/PP Blend for Injection Molding. Energy Procedia 2016, 89, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokohara, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Structure and properties for biomass-based polyester blends of PLA and PBS. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, L.C.; Magaton, M.; Bretas, R.E.S.; Ueki, M.M. Influence of chain extender on mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of blown films of PLA/PBAT blends. Polym. Test. 2015, 43, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.X.; Jin, Y.J.; Meng, Q.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.Z. Biodegradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), poly(lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend under soil conditions. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signori, F.; Coltelli, M.B.; Bronco, S. Thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) and their blends upon melt processing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Min, C.H.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Seo, K.H. Modification of PLA/PBAT Blends and Thermal/Mechanical Properties. Appl. Chem. Eng. 2013, 24, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Rhim, J.W. and Hong, S.I. Preparation of poly (lactide)/poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend films using a solvent casting method and their food packaging application. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F.; Micale, G.D. PLA-based functionally graded laminates for tunable controlled release of carvacrol obtained by combining electrospinning with solvent casting. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 148, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.W.; Mohanty, A.K.; Singh, S.P.; Ng, P.K. Effect of the processing methods on the performance of polylactide films: Thermocompression versus solvent casting. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkoc, G.; Kemaloglu, S. Morphology, biodegradability, mechanical, and thermal properties of nanocomposite films based on PLA and plasticized PLA. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Lee, J.B.; Lee, D.Y.; Seo, K.H. Plasticization Effect of Poly(Lactic Acid) in the Poly(Butylene Adipate–co–Terephthalate) Blown Film for Tear Resistance Improvement. Polymers 2020, 12, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J. Properties of Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/Nanoparticle Ternary Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, D.B.; Carvalho, J.S.D.; de Oliveira, S.A.; Rosa, D.D.S. A new approach for flexible PBAT/PLA/CaCO3 films into agriculture. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.S.; Yun, Y.H.; Hyung, T.G.; Yoon, S.D. Preparation and Physical Properties of Eco-Friendly Biodegradable PLA/PBAT/HCO Blended Films. Appl. Chem. Eng. 2020, 31, 416. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.Y.; Cha, J.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Jeon, H.Y. Study of Properties for Compatibility and Composition of PLA/PMMA/PBAT Blends. Int. J. Text. Eng. 2015, 52, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K.; Parvaiz, M.R. Effect of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) on the thermal, mechanical and morphological property of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blend and its nanocomposites. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lv, S.; Sun, C.; Wan, L.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Y. Effect of MAH-g-PLA on the Properties of Wood Fiber/Polylactic Acid Composites. Polymers 2017, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D882-03; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- ASTM D1922-09; Standard Test Method for Propagation Tear Resistance of Plastic Film and Thin Sheeting by Pendulum Method. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Nabar, A.Y.; Raquez, J.M.; Dubois, P.; Narayan, R. Production of starch foams by twin-screw extrusion: Effect of maleated poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) as a compatibilizer. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Tang, J. Functionalization of polyesters with maleic anhydride by reactive extrusion. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1999, 37, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratawidjaja, A.S.; Gitopadmoyo, I.; Watanabe, Y.; Hatakeyama, T. Adhesive property of polypropylene modified with maleicanhydride by extrusion molding. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1989, 37, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.; Nie, L.; Narayan, R.; Dubois, P. Maleation ofpolylactide (PLA) by reactive extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 72, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani Rahimi, S.; Aeinehvand, R.; Kim, K.; Otaigbe, J.U. Structure and biocompatibility of bioabsorbable nanocomposites of aliphatic-aromatic copolyester and cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2179–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teamsinsungvon, A.; Jarapanyacheep, R.; Ruksakulpiwat, Y.; Jarukumjorn, K. Melt Processing of Maleic Anhydride Grafted Poly(lactic acid) and Its Compatibilizing Effect on Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Blend and Their Composite. Polym. Sci. A. 2017, 59, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.W.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Shim, J.K.; Selke, S.E.M.; Soto-Valdez, H.; Matuana, L.; Rubino, M.; Auras, R. Grafting of maleic anhydride on poly(L-lactic acid). Effects on physical and mechanical properties. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraj, R.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Biodegradable biocomposites from poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and miscanthus: Preparation, compatibilization, and performance evaluation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y. Study on short ramie fiber/poly(lactic acid) composites compatibilized by maleic anhydride. Compos. A Appl. 2014, 64, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, D.C.; Almeida, T.G.; Abels, G.; Canedo, E.L.; Carvalho, L.H.; Wellen, R.M.R.; Haag, K.; Koschek, K. Tailoring PBAT/PLA/Babassu films for suitability of agriculture mulch application. J. Nat. Fibers 2019, 16, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Lemstra, P.J. In-situ compatibilization of poly(lactic acid) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends by using dicumyl peroxide as a free-radical initiator. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 102, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, J. Fabricating sea-island structure and co-continuous structure in PMMA/ASA and PMMA/CPE blends: Correlation between impact property and phase morphology. Polym. Test. 2019, 73, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Kwon, S.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S. Maleic Anhydride-Grafted PLA Preparation and Characteristics of Compatibilized PLA/PBSeT Blend Films. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R. Combinatorial rheology of branched polymer melts. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 4556–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattamaprom, C.; Larson, R.G.; Van Dyke, T.J. Quantitative predictions of linear viscoelastic rheological properties of entangled polymers. Rheol. Acta 2000, 39, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.S.; Helfand, E. Viscoelastic properties of star-shaped polymers. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, M.; Colby, R.H. Polymer Physics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, Å.; Neldin, C. Physical extruder foaming of poly (lactic acid)—Processing and foam properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.S.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J. Universality of linear viscoelasticity of monodisperse linear polymers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, S.; McLeish, T. Parameter-free theory for stress relaxation in star polymer melts. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, G.; Zhao, D. Study on rheological behavior of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 3609–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Cho, E.; Jeon, S.H.; Youn, J.R. Rheological and electrical properties of polypropylene composites containing functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and compatibilizers. Carbon 2007, 45, 2810–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J.; Wang, L. Preparation and properties of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend with glycidyl methacrylate as reactive processing agent. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.L.; Qu, J.P. Super-Toughened Poly(lactic Acid) with Poly(ε-caprolactone) and Ethylene-Methyl Acrylate-Glycidyl Methacrylate by Reactive Melt Blending. Polymers 2019, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ai, X.; Pan, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, G.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Dong, L. The morphological, mechanical, rheological, and thermal properties of PLA/PBAT blown films with chain extender. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Pan, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, G.; Dong, L. Influence of methyl methacrylate-butadiene-styrene copolymer on plasticized polylactide blown films. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58 (Suppl. S1), E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.E.; Nam, B.U. Preparation of MA-PLA Using Radical Initiator and Miscibility Improvement of PLA/PA11 Blends. J. Korea Acad. Industr. Coop. Soc. 2019, 20, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Marsilla, K.I.K.; Verbeek, C.J.R. Modification of poly (lactic acid) using itaconic anhydride by reactive extrusion. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.; Morshed, M.; Bagheri, R.; Karimi, K. Effect of various parameters on the chemical grafting of amide monomers to poly (lactic acid). Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, X.; Peng, S. Effect of maleic anhydride grafted poly (lactic acid) on rheological behaviors and mechanical performance of poly (lactic acid)/poly (ethylene glycol)(PLA/PEG) blends. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 31629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Zhao, X. Mechanical properties, rheological behaviors, and phase morphologies of high-toughness PLA/PBAT blends by in-situ reactive compatibilization. Compos. B. Eng. 2019, 173, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Tan, S.; Niu, D.; Yang, W.; Sun, Y.; Ma, P. Super-toughed polylactide/poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends in-situ compatibilized by poly (glycidyl methacrylate) with different molecular weight. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 205, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
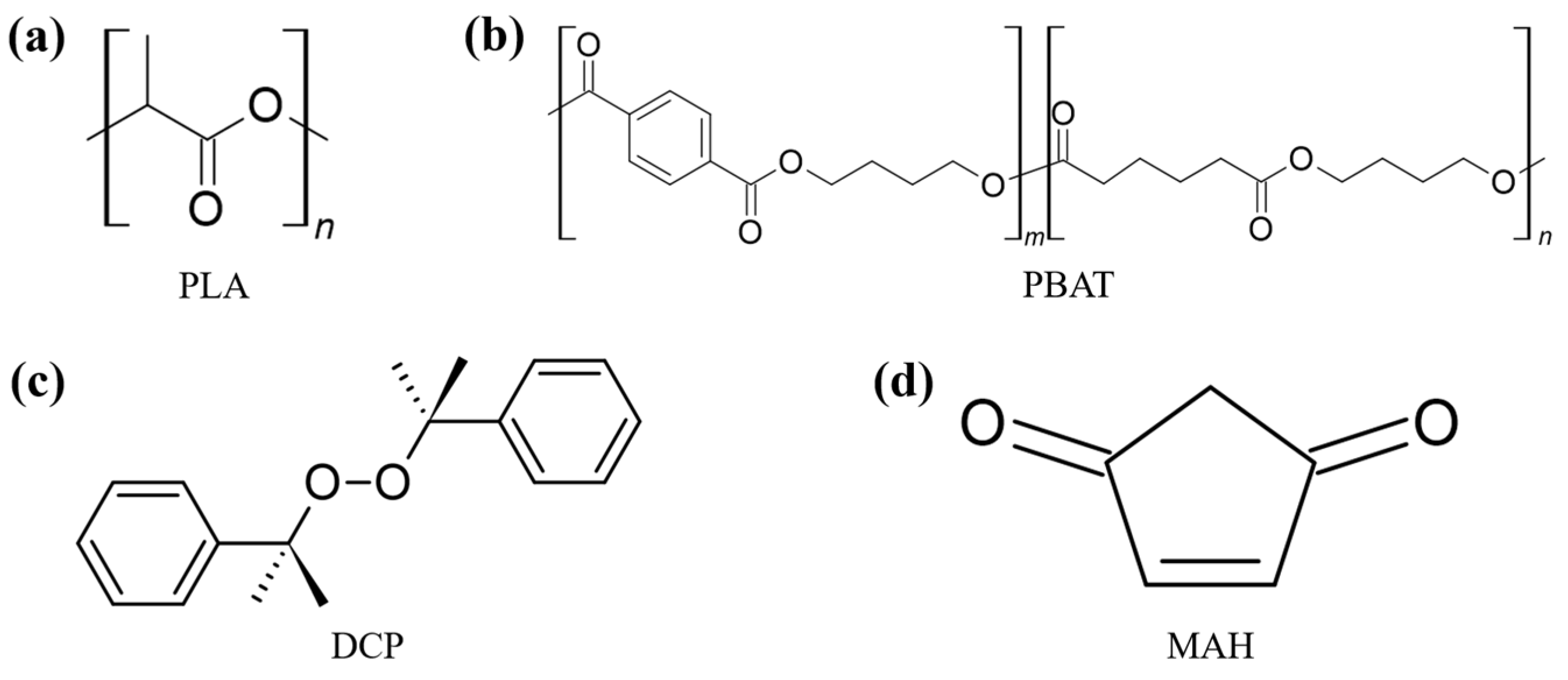



| (a) | ||||
| Description | PLA (wt%) | PBAT (wt%) | DCP (phr) | MAH (phr) |
| PLA | 100 | |||
| PBAT | - | 100 | ||
| PLA/PBAT | 50 | 50 | ||
| DCP_0.5 | 50 | 50 | 0.5 | |
| MAH_0.5 | - | 0.5 | ||
| MAH_1.0 | - | 1.0 | ||
| MAH_1.5 | - | 1.5 | ||
| PLA-g-MAH-1 | 100 | - | 1 | 1 |
| PLA-g-MAH-2 | 2 | |||
| PLA-g-MAH-3 | 3 | |||
| PBAT-g-MAH-1 | - | 100 | 1 | |
| PBAT-g-MAH-2 | 2 | |||
| PBAT-g-MAH-3 | 3 | |||
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH-1 | 50 | 50 | 1 | |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH-2 | 2 | |||
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH-3 | 3 | |||
| (b) | ||||
| Description | Component 1 (50 wt%) | Component 2 (50 wt%) | ||
| PLA-g-MAH/PBAT_0.5 | PLA-g-MAH-1 | Neat PBAT | ||
| PLA-g-MAH/PBAT_1.0 | PLA-g-MAH-2 | |||
| PLA-g-MAH/PBAT_1.5 | PLA-g-MAH-3 | |||
| PLA/PBAT-g-MAH_0.5 | Neat PLA | PBAT-g-MAH-1 | ||
| PLA/PBAT-g-MAH_1.0 | PBAT-g-MAH-2 | |||
| PLA/PBAT-g-MAH_1.5 | PBAT-g-MAH-3 | |||
| (c) | ||||
| Description | PLA (wt%) | PBAT (wt%) | DCP (phr) | MAH (phr) |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_0.5 | 50 | 50 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_1.5 | 1.5 | |||
| Description | DCP (phr) | MAH (phr) | Grafting Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA-g-MAH-1 | 1 | 1 | 0.51 |
| PLA-g-MAH-2 | 2 | 0.62 | |
| PLA-g-MAH-3 | 3 | 0.66 | |
| PBAT-g-MAH-1 | 1 | 0.59 | |
| PBAT-g-MAH-2 | 2 | 1.1 | |
| PBAT-g-MAH-3 | 3 | 1.20 | |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH-1 | 1 | 1.00 | |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH-2 | 2 | 1.05 | |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH-3 | 3 | 1.08 |
| Description | PBAT Tg (°C) | PLA Tg (°C) | PLA Tg–PBAT Tg (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT | −26.7 | 61.3 | 88.0 |
| PLA-g-MAH_0.5 | −30.5 | 59.6 | 90.1 |
| PLA-g-MAH_1.0 | −31.0 | 59.0 | 90.0 |
| PLA-g-MAH_1.5 | −31.5 | 58.7 | 89.7 |
| PBAT-g-MAH_0.5 | −27.8 | 59.4 | 87.2 |
| PBAT-g-MAH_1.0 | −25.8 | 58.5 | 84.3 |
| PBAT-g-MAH_1.5 | −27.5 | 59.5 | 87.1 |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_0.5 | −29.1 | 58.3 | 87.4 |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_1.0 | −27.1 | 58.6 | 85.7 |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_1.5 | −29.5 | 58.3 | 87.8 |
| Description | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA/PBAT | 243.1 ± 18.1 | 13.9 ± 0.2 | 132.7 ± 8.0 |
| PLA-g-MAH_0.5 | 352.0 ± 4.3 | 17.3 ± 0.3 | 113.1 ± 5.4 |
| PLA-g-MAH_1.0 | 392.7 ± 30.4 | 17.4 ± 0.5 | 327.8 ± 18.3 |
| PLA-g-MAH_1.5 | 423.7 ± 25.8 | 16.8 ± 0.2 | 316.7 ± 8.8 |
| PBAT-g-MAH_0.5 | 521.6 ± 20.9 | 21.8 ± 1.6 | 289.8 ± 9.7 |
| PBAT-g-MAH_1.0 | 590.4 ±17.1 | 24.8 ± 0.6 | 325.3 ± 4.7 |
| PBAT-g-MAH_1.5 | 597.5 ± 8.2 | 22.7 ± 0.8 | 311.3 ± 14.6 |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_0.5 | 644.3 ± 13.3 | 25.3 ± 0.4 | 256.7 ± 9.4 |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_1.0 | 679.3 ± 23.4 | 27.7 ± 0.7 | 380.9 ± 3.1 |
| (PLA/PBAT)-g-MAH_1.5 | 589.7 ± 41.9 | 22.7 ± 2.8 | 311.8 ± 10.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, K.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, D.Y. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid/Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-Terephthalate) Modified with Maleic Anhydride. Polymers 2024, 16, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040518
Nam K, Kim SG, Kim DY, Lee DY. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid/Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-Terephthalate) Modified with Maleic Anhydride. Polymers. 2024; 16(4):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040518
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Kibeom, Sang Gu Kim, Do Young Kim, and Dong Yun Lee. 2024. "Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid/Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-Terephthalate) Modified with Maleic Anhydride" Polymers 16, no. 4: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040518
APA StyleNam, K., Kim, S. G., Kim, D. Y., & Lee, D. Y. (2024). Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Polylactic Acid/Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-Terephthalate) Modified with Maleic Anhydride. Polymers, 16(4), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040518







