Application of Electrospun Drug-Loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Drug-loaded Nanofibers via Electrospinning
2.1. Single-Fluid Electrospinning
2.2. Double-Fluid Electrospinning
2.3. Multi-Fluid Electrospinning
3. Drug Release Modes of Drug-Loaded Nanofibers
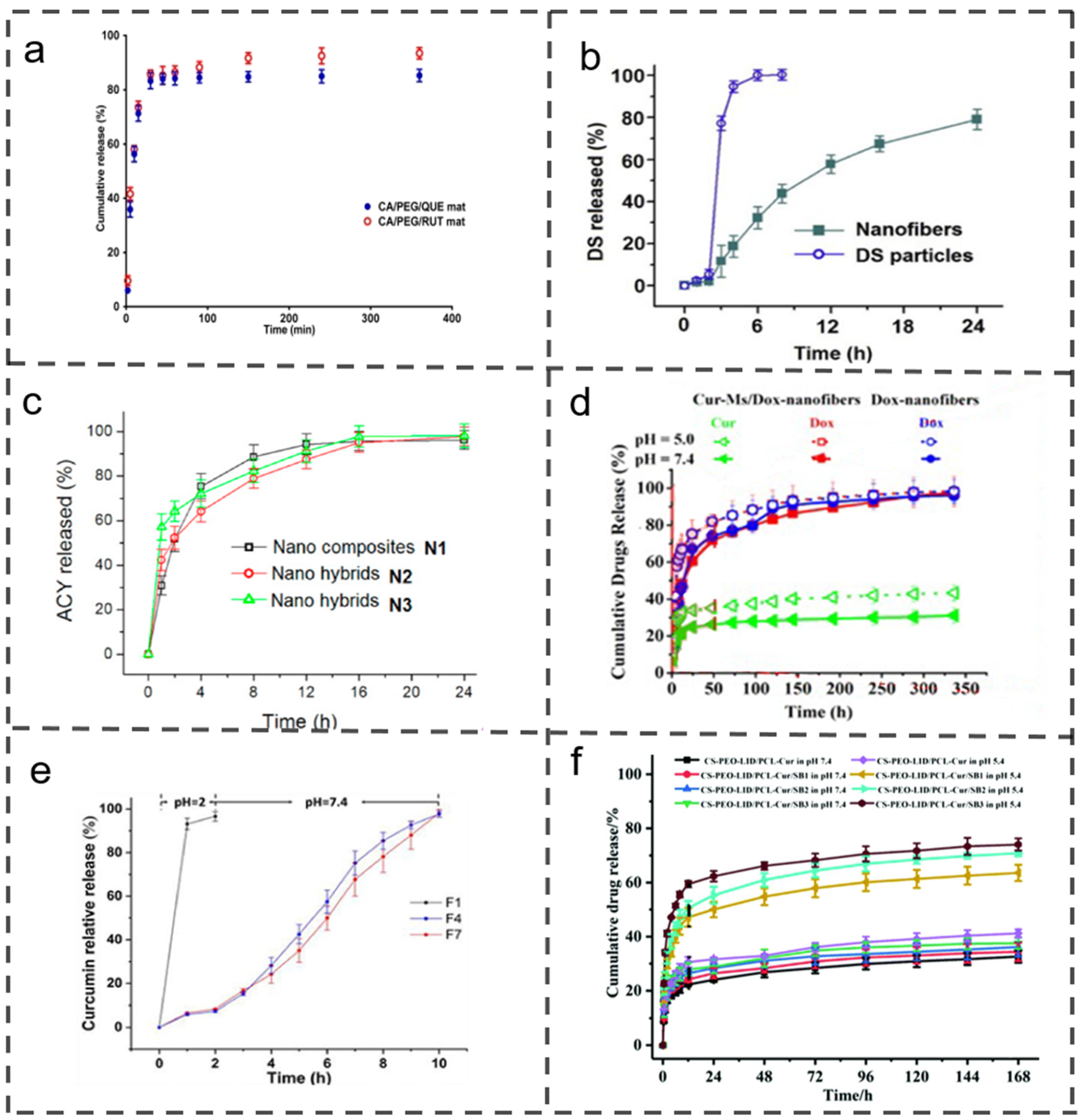
3.1. Quick Release
3.2. Sustained Release
3.3. Biphasic Release
3.4. Targeted Release
3.5. Drug Combination
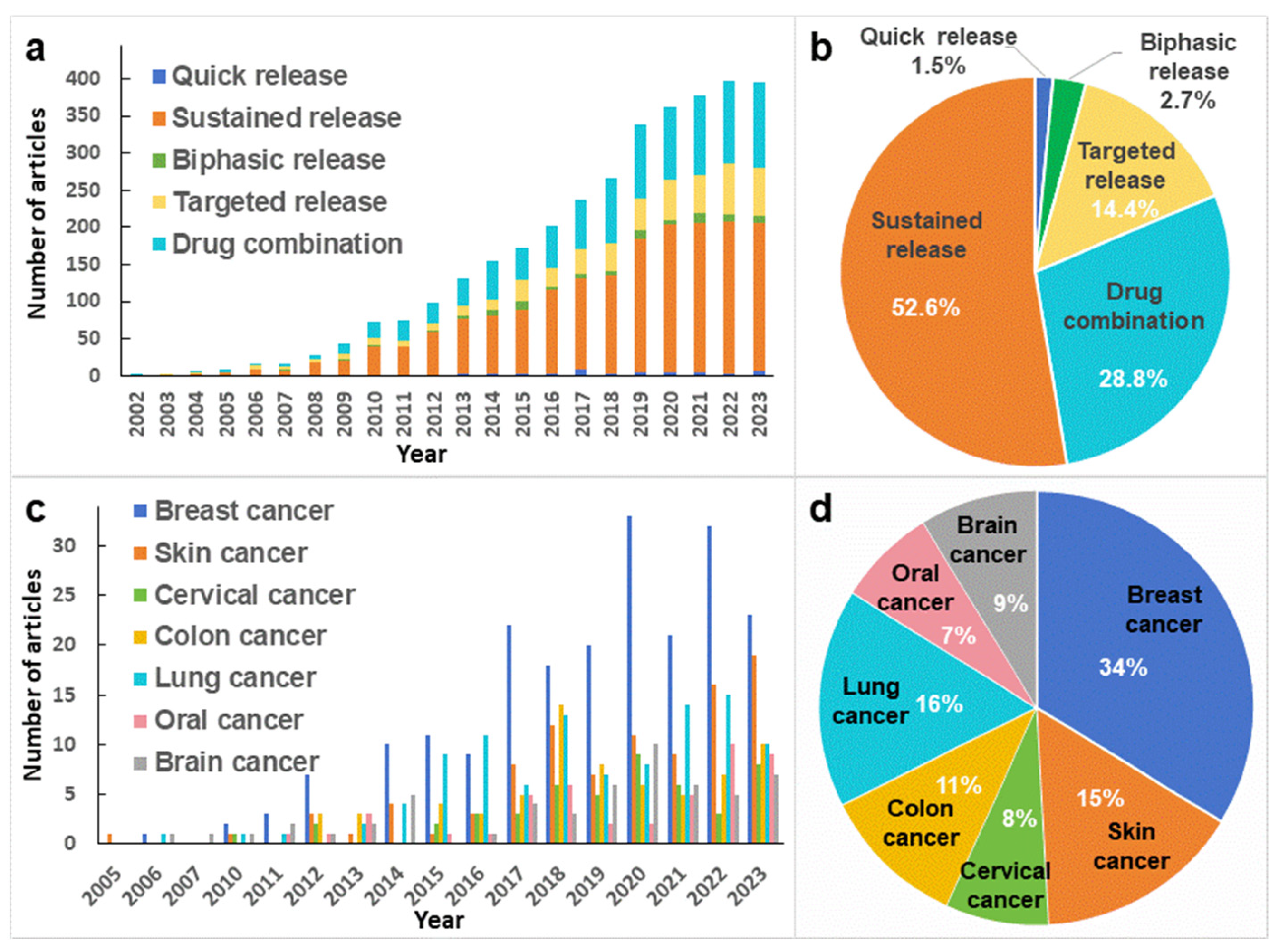
4. Application of Drug-loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy
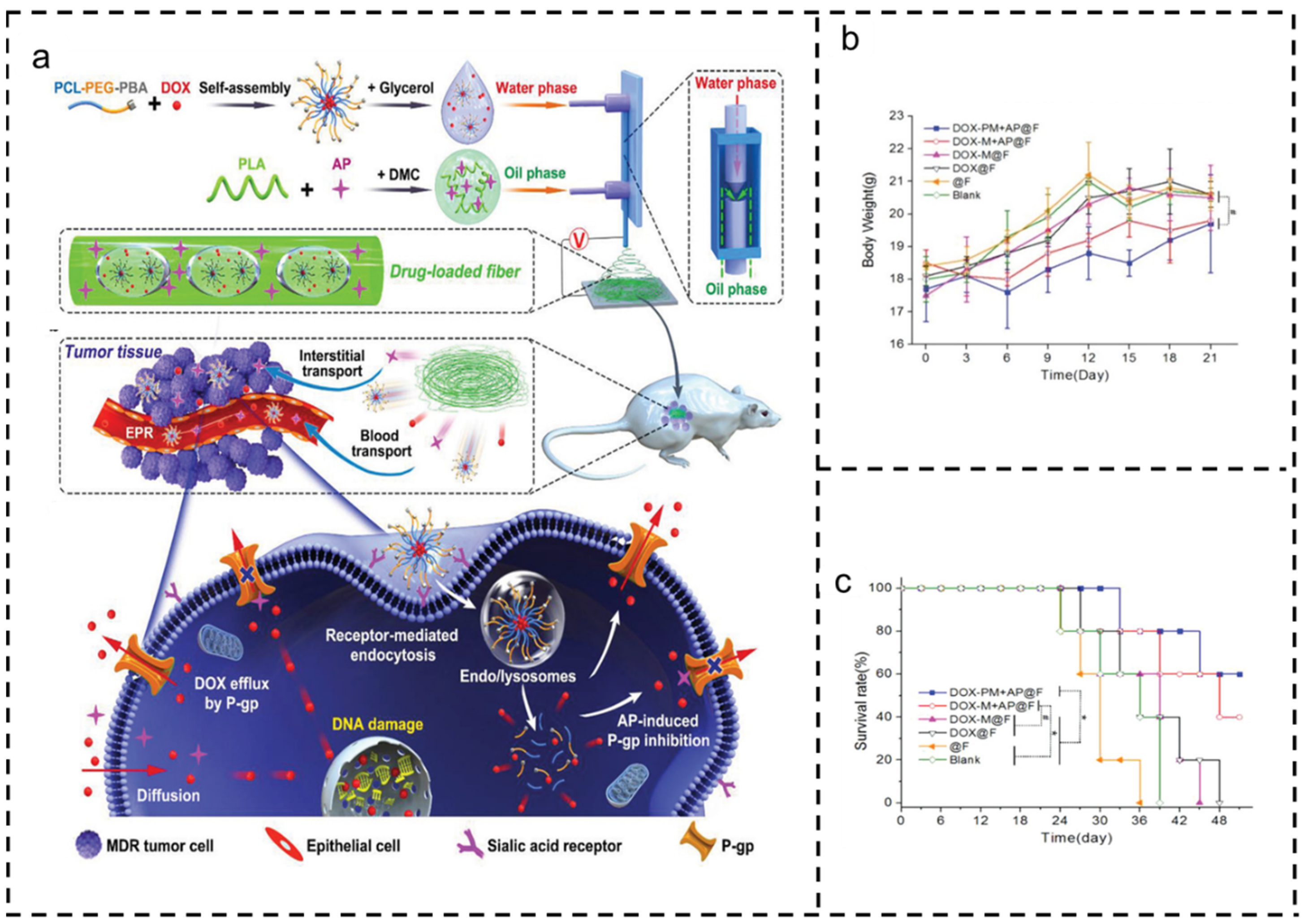
4.1. Breast Cancer
4.2. Skin Cancer
4.3. Cervical Cancer
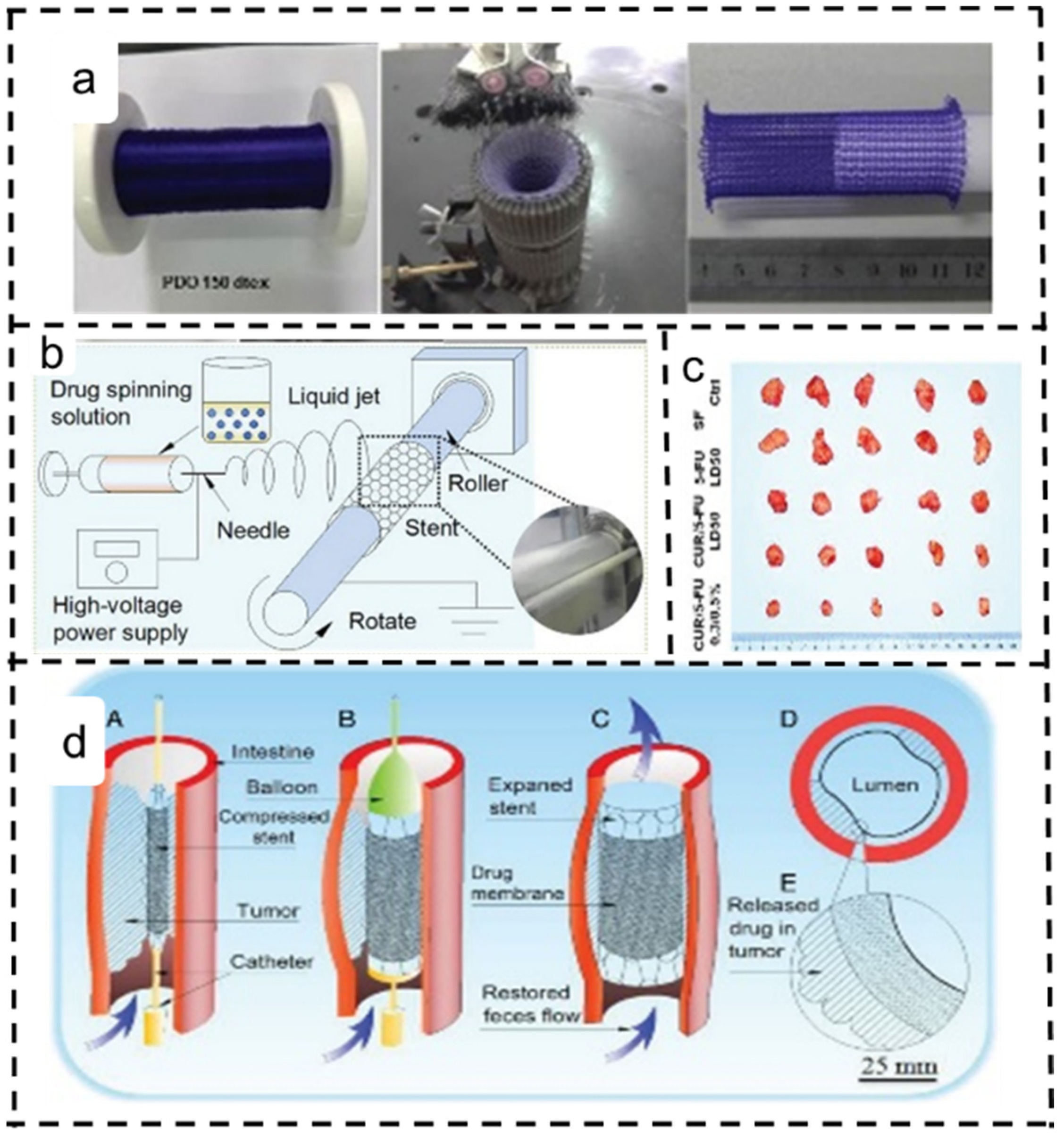
4.4. Colon Cancer
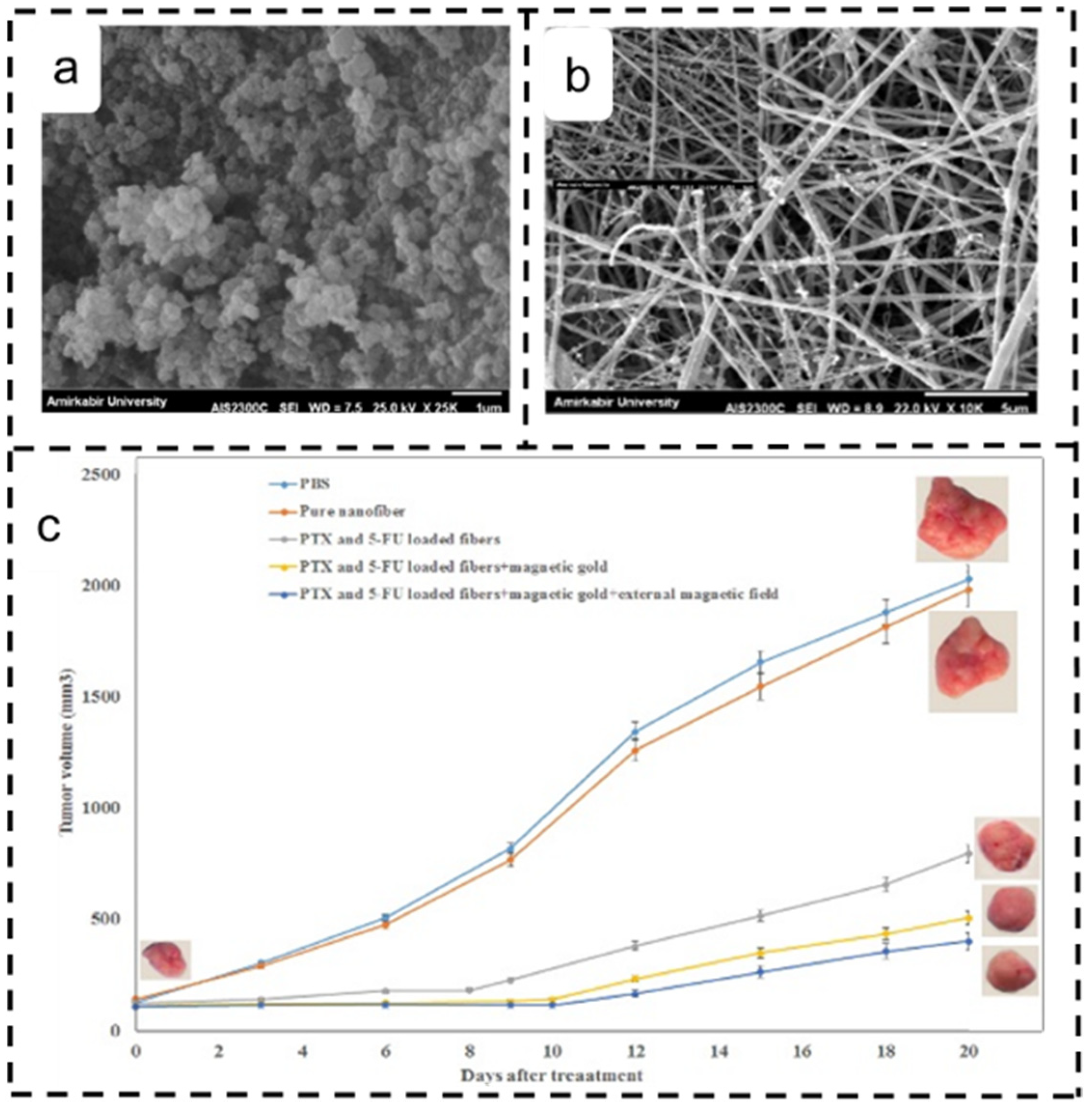
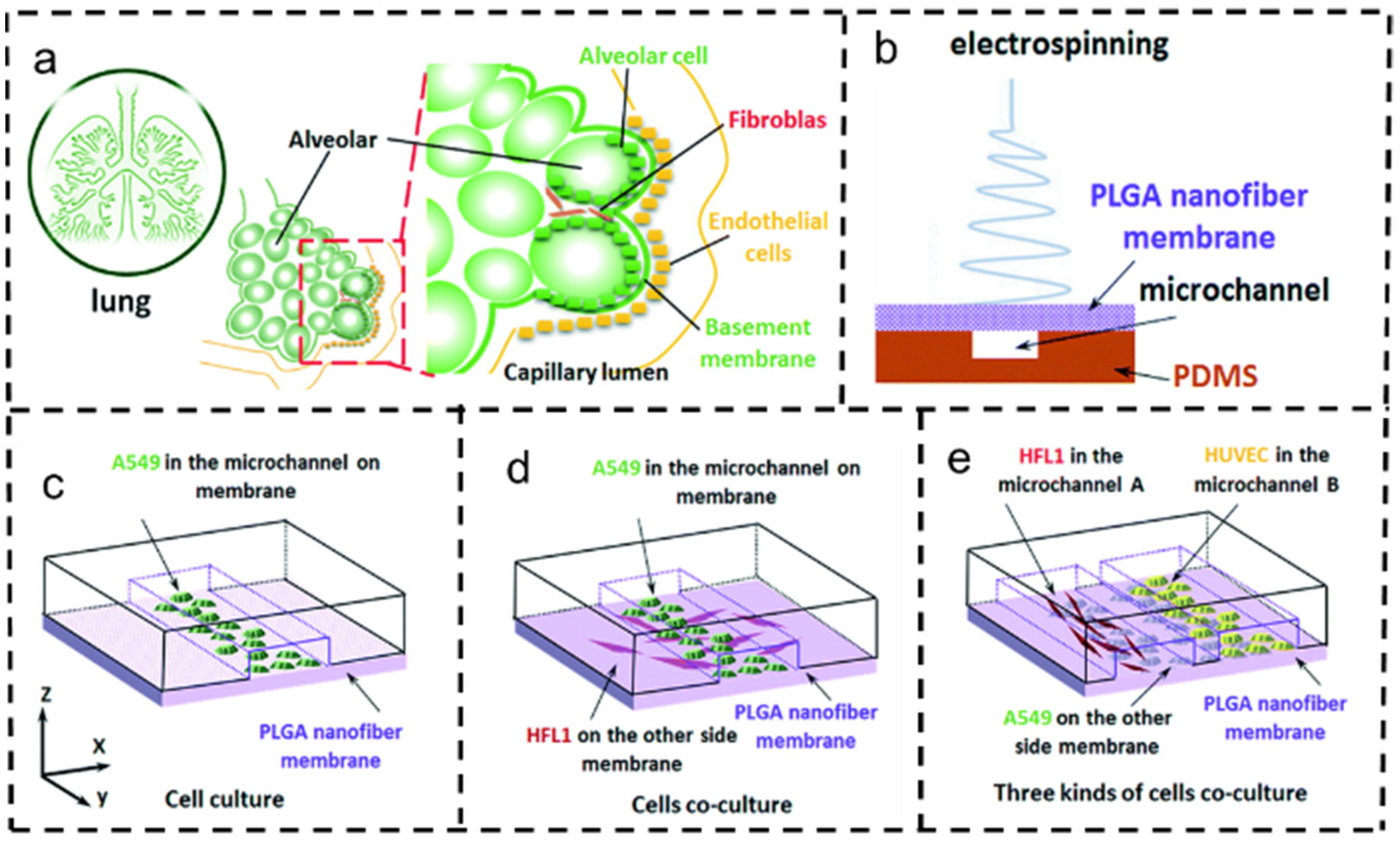
4.5. Lung Cancer
4.6. Brain Cancer
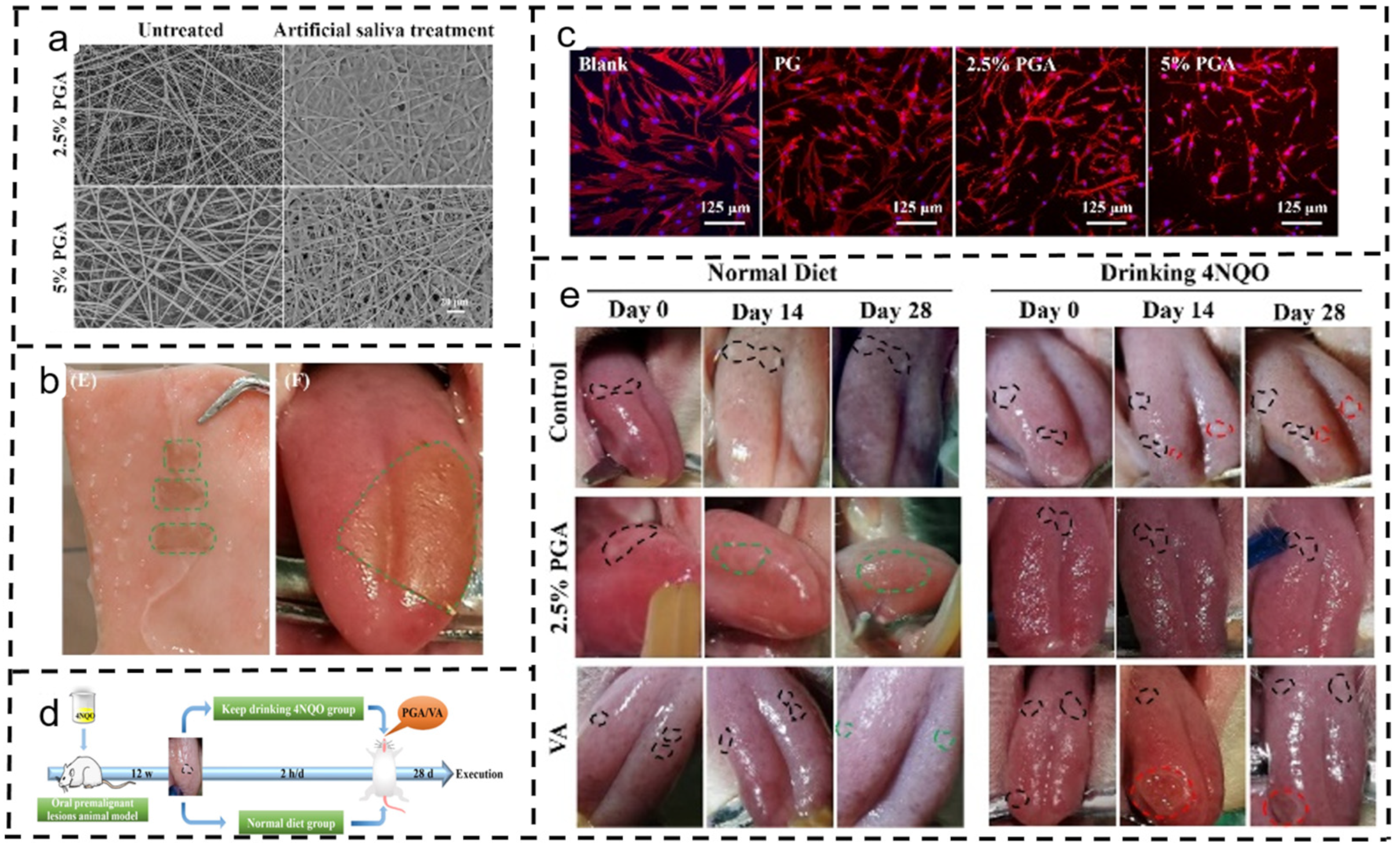
4.7. Oral Cancer
4.8. Other Cancers
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fawal, G.E.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; El-Gendi, H.; El-Fakharany, E.M. Fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation of disulfiram-loaded cellulose acetate/poly(ethylene oxide) nanofiber scaffold for breast and colon cancer cell lines treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 204, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Ran, P.; Chen, W.; Li, X. Janus rod-like micromotors to promote the tumor accumulation and cell internalization of therapeutic agents. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 127073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Huang, C. Electrospun Biomolecule-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-G.; Xu, L. Impact Evaluations of Articles in Current Drug Delivery Based on Web of Science. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Zhou, J. How Can Electrospinning Further Service Well for Pharmaceutical Researches? J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 2719–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachwal, V.; Tan, J. Stimuli-responsive electrospun fluorescent fibers augmented with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) for smart applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 10, 2204848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, F.; Nikiforov, A.; Morent, R.; Geyter, N.D. Plasma modification of poly lactic acid solutions to generate high quality electrospun PLA nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Chen, H.; Qi, C.; Lv, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. A novel electrospun nanofiber system with PEGylated paclitaxel nanocrystals enhancing the transmucus permeability and in situ retention for an efficient cervicovaginal cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 650, 123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Guo, S.; Zhang, G.; He, W.; Wu, Y.; Yu, D. Electrospun structural hybrids of acyclovir-polyacrylonitrile at acyclovir for modifying drug release. Polymers 2021, 13, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, F.; Baharian, A.; Akbari-Birgani, S.; Nikfarjam, N. Tubular scaffold made by gelatin/polylactic acid nanofibers for breast ductal carcinoma in situ tumor modeling. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 85, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, A.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Electrospinning of bilayer emulsions: The role of gum Arabic as a coating layer in the gelatin-stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; An, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D. pH-sensitive core-shell electrospun nanofibers based on polyvinyl alcohol/polycaprolactone as a potential drug delivery system for the chemotherapy against cervical cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.H.; Liu, Y.B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, X.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, P. Electrospun core-sheath PCL nanofibers loaded with nHA and simvastatin and their potential bone regeneration applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1205252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yu, D.; Pan, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Bligh, W.A.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun pH-sensitive core–shell polymer nanocomposites fabricated using a tri-axial process. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brako, F.; Luo, C.; Matharu, R.K.; Ciric, L.; Harker, A.; Edirisinghe, M.; Craig, D.Q.M. A Portable device for the generation of drug-loaded three-compartmental fibers containing metronidazole and iodine for topical application. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chi, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Gong, M.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, L.; Xue, J. Electrospun quad-axial nanofibers for controlled and sustained drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2021, 206, 109732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.; Wan, F.; Williams, G.R.; Bligh, S.A. Combination of structure-performance and shape-performance relationships for better biphasic release in electrospun Janus fibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 596, 120203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Shen, H. Sheath-separate-core nanocomposites fabricated using a tri-fluid electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Gu, W.; Cui, X.; Dai, S.; Zhang, B.; Ji, G. Nanofiber network with adjustable nanostructure controlled by PVP content for an excellent microwave absorption. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Anastasova, I.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Markova, N.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R. Bio-based electrospun fibers from chitosan Schiff base and polylactide and their Cu2+ and Fe3+ complexes: Preparation and antibacterial and anticancer activities. Polymers 2022, 14, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardi, M.; Kossyvaki, D.; Picone, P.; Summa, M.; Guo, X.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Giacomazza, D.; Carzino, R.; Goldoni, L.; Scoponi, G.; et al. Electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) hydrogels containing hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives as potential wound dressings. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Meng, Z. Melt electrospinning vs. solution electrospinning: A comparative study of drug-loaded poly (ε-caprolactone) fibres. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhou, X. Synergistic enhancement of cytotoxicity against cancer cells by incorporation of rectorite into the paclitaxel immobilized cellulose acetate nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, J.; Mai, J.; Chang, M. Three-dimensional electrohydrodynamic printing and spinning of flexible composite structures for oral multidrug forms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24876–24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.-N. Progress of Electrospun Nanofibrous Carriers for Modifications to Drug Release Profiles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-G.; Zhao, P. The Key Elements for Biomolecules to Biomaterials and to Bioapplications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Meng, Z. Melt electrospinning of daunorubicin hydrochloride-loaded poly (ε-caprolactone) fibrous membrane for tumor therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, M.; Xie, Y.; Yu, D. Comparisons of antibacterial performances between electrospun polymer@drug nanohybrids with drug-polymer nanocomposites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, G.T.V.; Dhurai, B. A novel profiled multi-pin electrospinning system for nanofiber production and encapsulation of nanoparticles into nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Wang, B.; Yu, D.-G.; Zhu, Y. Integrating Chinese Herbs and Western Medicine for New Wound Dressings through Handheld Electrospinning. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, H.; Zhao, H. Silk fibroin coaxial bead-on-string fiber materials and their drug release behaviors in different pH. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 4246–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ding, X.; Tian, L.; Ramakrishna, S. Engineering BSA-dextran particles encapsulated bead-on-string nanofiber scaffold for tissue. engineering applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 10661–10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Ding, X. Solid drug particles encapsulated bead-on-string nanofibers: The control of bead number and its corresponding release profile. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 1454–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Electrospinning of polycaprolacton/chitosan core-shell nanofibers by a stable emulsion system. Colloid Surf. A 2019, 583, 123956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, D.; Xu, C.; Gan, X.; Ge, P.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Lv, Y. Preparation of flexible hollow TiO2 fibrous membranes for thermal-insulation applications by coaxial electrospinning. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 22875–22881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.J.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Etrati, S.M. Fabrication and characterization of elastic hollow nanofibrous PU yarn. Mater. Des. 2016, 99, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, J.; Qin, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, G.; Gu, X.; Pan, K. Janus-structural AIE nanofiber with white light emission and stimuli-response. Small 2022, 18, 2201117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Dai, Y.; Fu, J.; Yan, C.; Yu, D.-G.; Yi, T. Dual-Step Controlled Release of Berberine Hydrochloride from the Trans-Scale Hybrids of Nanofibers and Microparticles. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, J.; Fang, B.; Ying, Y.; Yu, D.G.; He, H. Three EHDA Processes from A Detachable Spinneret for Fabricating Drug Fast Dissolution Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 2300361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Qin, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yew, P.Y.M.; Jiang, X.; Kai, D.; Song, F.; Zhao, J. Ros-responsive nanocomposite scaffolds for sustained releasing puerarin toachieve chondroprotection in OA rats. Mater. Des. 2023, 233, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Ali, A.; Zaman, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Chen, X.; Chang, M. Novel core-shell fiber delivery system for synergistic treatment of cervical cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Orlu, M.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun fixed dose combination fibers for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, W.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun Porous Nanofibers: Pore-Forming Mechanisms and Applications for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Wastewater. Polymers 2022, 14, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghe, A.K.; Gupta, B.S. C-axial electrospinning for nanofiber structures: Preparation and applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, J.; Williams, G.R.; Zhao, M. Electrospun amorphous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs: A review. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, D.-G.; Lu, X. The Influence of the Ultrasonic Treatment of Working Fluids on Electrospun Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1184767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Xi, Y.; Weng, Y. Functional electrospun nanofibers: Fabrication, properties, and applications in wound-healing Process. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.G.; Zhou, J. Electrospun multi-chamber nanostructures for sustainable biobased chemical nanofibers. Next Mater. 2024, 2, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, Q.; Wan, J.; Yu, D.G.; Tan, F.; Yang, X. Improved synergistic anticancer action of quercetin and tamoxifen citrate supported by an electrospun complex nanostructure. Mater. Des. 2024, 238, 112657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba-Perez, A.; Jayawarna, V.; Childs, P.G.; Dalby, M.J.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M. Plasma polymerised nanoscale coatings of controlled thickness for efficient solid-phase presentation of growth factors. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagiah, N.; Murdock, C.J.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Nair, L.; Laurencin, C.T. Development of tripolymeric triaxial electrospun fibrous matrices for dual-drug delivery applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouybari, M.H.; Hosseini, S.; Mahboobnia, K.; Boloursazd, L.A.; Moradie, M.; Irani, M. Simultaneous controlled release of 5-FU, DOX and PTX from chitosan/PLA/5-FU/g-C3N--DOX/g-C3N4-PTX triaxial nanofibers for breast cancer treatment in vitro. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P. Electrospun Core–Sheath Nanofibers with a Cellulose Acetate Coating for the Synergistic Release of Zinc Ion and Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, L.-y. Tri-Layer Core–Shell Fibers from Coaxial Electrospinning for a Modified Release of Metronidazole. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Kim, E.J.; Tang, Y.; Xu, H.; Yu, D.; Song, W.; Kim, B.J. Rational Design of Hyper-Crosslinked Polymers for Biomedical Applications. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Triaxial electrospun nanofiber membranes for controlled dual release of functional molecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8241–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, P. A Combined Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Method for Preparing Nanofiber/Microparticle Hybrid Medicines. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1308004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanova, N.; Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R. Quercetin- and rutin-containing electrospun cellulose acetate and polyethylene glycol fibers with antioxidant and anticancer properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, H.; Du, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, P. Electrosprayed Core (Cellulose Acetate)–Shell (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) Nanoparticles for Smart Acetaminophen Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, P.; Yu, D.-G. Electrosprayed Stearic-Acid-Coated Ethylcellulose Microparticles for an Improved Sustained Release of Anticancer Drug. Gels 2023, 9, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xu, B.; Xia, C.; Xu, M.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C. Dual drug-loaded core-shell nanofibers membranes via emulsion electrospinning and their controllable sustained release property. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hao, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H. A biodegradable core-sheath nanofibrous 3D hierarchy prepared by emulsion electrospinning for sustained drug release. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 16730–16743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Ding, S.; Zhou, S. Electrospun micelles/drug-loaded nanofibers for time-programmed multi-agent release. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Shen, J.; Tang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Yu, D. Engineered shellac beads-on-the-string fibers using triaxial electrospinning for improved colon-targeted drug delivery. Polymers 2023, 15, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Tan, S.; Gao, L.J.; Wang, J. Sequential release of drugs form a dual-delivery system based on pH-responsive nanofibrous mats towards wound care. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhary, H.; Williams, G.R.; Orlu, M. Electrospun fixed dose formulations of amlodipine besylate and valsartan. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kang, W.; Cho, H. Angelica gigas Nakai extract-loaded fast-dissolving nanofiber based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and Soluplus for oral cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Song, W.; Yu, D.; Bligh, S.W.A. The effect of drug heterogeneous distributions within core-sheath nanostructures on its sustained release profiles. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um-i-Zahra, S.; Shen, X.X.; Li, H.; Zhu, L. Study of sustained release drug-loaded nanofibers of cellulose acetate and ethyl cellulose polymer blends prepared by electrospinning and their in-vitro drug release profiles. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.; Wan, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z. Electrospun lipid-coated medicated nanocomposites for an improved drug sustained-release profile. Mater. Des. 2019, 162, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun tri-layer nanodepots for sustained release acyclovir. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, M.; Williams, G.R. Tunable zero-order drug delivery systems created by modified triaxial electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Williams, G.R. Nanofibers fabricated using triaxial electrospinning as zero order drug delivery systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18891–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemraski, E.G.; Alibeigi, S.; Abbasi, Z. Ibuprofen@silver loaded on poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan co-polymer scaffold as a novel drug delivery system. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, E.A.; Craig, D.Q.M.; Barker, S.A. Dual drug-loaded coaxial nanofibers for the treatment of corneal abrasion. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Sun, Q.; Xia, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Song, X. Controlled release of resveratrol and xanthohumol via coaxial electrospinning fibers. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niiyama, E.; Uto, K.; Lee, C.M.; Sakura, K.; Ebara, M. Hyperthermia nanofiber platform synergized by sustained release of paclitaxel to improve antitumor efficiency. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, A.; Cao, B.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Tang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, A.; Xiong, R.; Lei, J.; et al. A tunable temperature-responsive and tough platform for controlled drug delivery. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 13056–13063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Pandit, J.; Ahmed, S.; Zameer, S.; Nikita; Ahmad, S.; Bano, S.; Ansari, M.D.; Solanki, P.; Jahan, R.N.; et al. Development and evaluation of biodegradable polymeric lomustine nanofibres for the efficient tumor targeting: In vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and degradation study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Hou, J.; Yang, G.; Zhou, S. A time-programmed release of dual drugs from an implantable trilayer structured fiber device for synergistic treatment of breast cancer. Small 2020, 16, 1902262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-García, P.; Reyes, R.; Segredo-Morales, E.; Pérez-Herrero, E.; Delgado, A.; Évora, C. PLGA-BMP-2 and PLA-17β-estradiol microspheres reinforcing a composite hydrogel for bone regeneration in osteoporosis. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, L.; Attik, N.; Belkessam, L.; Chevalier, C.; Bousige, C.; Brioude, A.; Salles, V. Direct-writing electrospun functionalized scaffolds for periodontal regeneration: In vitro studies. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, K.; Jia, W.; Jiang, K.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, G.; Luo, Y. A periodontal tissue regeneration strategy via biphasic release of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 and FK506 using a uniaxial electrospun Janus nanofiber. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Song, F.; Ju, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tang, C.; Yang, H.; Huang, C. NAC-loaded electrospun scaffolding system with dual compartments for the osteogenesis of rBMSCs in vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Saito, Y.; Ullah, S.; Haider, M.K.; Nawaz, H.; Duy-Nam, P.; Kharaghani, D.; Kim, I.S. Bioactive Sambong oil-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers: Preparation, characterization, and in-vitro biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Wei, S.; Luo, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, A.; Wei, F. Long-term effect against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus of emodin released from coaxial electrospinning nanofiber membranes with a biphasic profile. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, M.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Zandi, M. Biphasic, tough composite core/shell PCL/PVA-GEL nanofibers for biomedical application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. A 2020, 137, 48713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; McCarthy, A.; Wong, S.L.; Hollins, R.R.; Wang, G.; Xie, J. Simultaneous delivery of multiple antimicrobial agents by biphasic scaffolds for effective treatment of wound biofilms. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaissy, R.; Richard, M.; Morris, H.; Snelling, S.; Pinchbeck, H.; Carr, A.; Mouthuy, P. Manufacture of soft-hard implants from electrospun filaments embedded in 3d printed structures. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2200156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, D.K.; Pradhan, D.; Halder, J.; Biswasroy, P.; Kar, B.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Design and optimization of gatifloxacin loaded polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber for the treatment of dry eye infection: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Nadeem, M.; Bhutto, M.A.; Yu, F.; Xie, X.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Faham, A.; Ibrahim, U.A.; Mo, X. Physico-chemical and biological evaluation of PLCL/SF nanofibers loaded with oregano essential oil. Pharmaceuticsal 2019, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, N.D.; Koumentakou, I.; Michailidou, G.; Kostoglou, M.; Vlachou, M.; Barmpalexis, P.; Karavas, E.; Papageorgiou, G.Z. Investigation of molecular weight, polymer concentration and process parameters factors on the sustained release of the anti-multiple-sclerosis agent teriflunomide from poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun nanofibrous matrices. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 14, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boncu, T.E.; Ozdemir, N. Electrospinning of ampicillin trihydrate loaded electrospun PLA nanofibers I: Effect of polymer concentration and PCL addition on its morphology, drug delivery and mechanical properties. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, G.; Demirci, C.; Can, G.K.; Meydan, A.E.; Daşan, B.G.; Mutlu, M. A comparative study of single-needle and coaxial electrospun amyloid-like protein nanofibers to investigate hydrophilic drug release behavior. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifino, G.; Gasparini, C.; Drudi, S.; Giannelli, M.; Sotgiu, G.; Posati, T.; Zamboni, R.; Treossi, E.; Maccaferri, E.; Giorgini, L.; et al. Keratin/Polylactic acid/graphene oxide composite nanofibers for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yi, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, P.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y. Electrospun Janus Core (Ethyl Cellulose//Polyethylene Oxide) @ Shell (Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose Acetate Succinate) Hybrids for An Enhanced Colon-Targeted Prolonged Drug Absorbance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinbasak, I.; Kocak, S.; Colby, A.H.; Alp, Y.; Sanyal, R.; Grinstaff, M.W.; Sanyal, A. pH-Responsive nanofiber buttresses as local drug delivery devices. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, W. Poly(Glutamic Acid)-Engineered Nanoplatforms for Enhanced Cancer Phototherapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.S.; Lee, E.S. Honeycomb-like pH-responsive γ-cyclodextrin electrospun particles for highly efficient tumor therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham-Gurysh, E.G.; Murthy, A.B.; Moore, K.M.; Hingtgena, S.D.; Bacheldera, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Synergistic drug combinations for a precision medicine approach to interstitial glioblastoma therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, C.K.; Carey, L.A. Biology, metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2009, 9, S73–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attar, T.; Madihally, S.V. Influence of controlled release of resveratrol from electrospun fibers in combination with siRNA on leukemia cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, X.; Che, X.; Yang, M.; Zhai, G. Biomedical application and controlled drug release of electrospun fibrous materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yu, N.; Li, J.; Bai, J.; Ding, D.; Tang, Q.; Xu, H. Novel “carrier-free” nanofiber codelivery systems with the synergistic antitumor effect of paclitaxel and tetrandrine through the enhancement of mitochondrial apoptosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10096–10106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lübtow, M.M.; Hahn, L.; Haider, M.S.; Luxenhofer, R. Title of the article. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10980–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Yin, T. Co-delivery of silybin and paclitaxel by dextran-based nanoparticles for effective anti-tumor treatment through chemotherapy sensitization and microenvironment modulation. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Jiang, K.; Xie, C.; Zhan, C.; Wang, H.; Lu, W. Co-delivery of paclitaxel and melittin by glycopeptide-modified lipodisks for synergistic anti-glioma therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Zou, Y.; Qu, X.; He, C.; Deng, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Concurrently suppressing multidrug resistance and metastasis of breast cancer by co-delivery of paclitaxel and honokiol with pH-sensitive polymeric micelles. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slivicki, R.A.; Xu, Z.; Mali, S.S.; Hohmann, A.G. Brain permeant and impermeant inhibitors of fatty-acid amide hydrolase suppress the development and maintenance of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain without producing tolerance or physical dependence in vivo and synergize with paclitaxel to reduce tumor cell line viability in vitro. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Chen, P.; Wei, K.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Yang, H. Rapid in situ MRI traceable gel-forming dual-drug delivery for synergistic therapy of brain tumor. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2524–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, S.; Seyedabadi, S.; Alemzadeh, E. Anticancer efficiency of doxorubicin and berberine-loaded PCL nanofibers in preventing local breast cancer recurrence. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Uppal, S.; Mansi, K.; Das, J.; Pandey, S.K.; Kaur, K.; Mehta, S.K. Ultrasonication induced synthesis of TPGS stabilized clove oil nanoemulsions and their synergistic effect against breast cancer cells and harmful bacteria. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnath, S.; Chitra, K.; Karthikeyan, K.; Jeyaraj, M. Localized delivery of active targeting micelles from nanofibers patch for effective breast cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawal, G.E.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Mo, X.; Wang, H. Diethyldithiocarbamate/silk fibroin/polyethylene oxide nanofibrous for cancer therapy: Fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Markova, N.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Oshkova, R.T. 8-Hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid-containing poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan electrospun materials and their Cu2+ and Fe3+ complexes: Preparation, Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antitumor Activities. Polymers 2021, 13, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabionet, M.; Yeste, M.; Puig, T.; Ciurana, J. Electrospinning PCL scaffolds manufacture for three-dimensional breast cancer cell culture. Polymers 2017, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, J.; Smolarczyk, R.; Musiał-Kulik, M.; Cicho’n, T.; Karpeta-Jarząbek, P.; Włodarczyk, J.; Stojko, M.; Janeczek, H.; Kordyka, A.; Kaczmarczyk, B.; et al. Electrospun paclitaxel delivery system based on PGCL/PLGA in local therapy combined with brachytherapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasalta, M.; Asefnejad, A.; Khorasani, M.T.; Saadatabadi, A.R. Adsorption and sustained release of doxorubicin from N-carboxymethyl chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/poly(ε-caprolactone) composite and core-shell nanofibers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, J.; Yang, G.; Zhou, S. A Hierarchical Structured Ultrafine Fiber Device for Preventing Postoperative Recurrence and Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, U.M.; Pellegrini, M.; Obayemi, J.D.; Ezenwafor, T.; Browl, D.; Ani, C.J.; Yipo, D.; Salifu, A.; Dozie-Nwachukwu, S.; Odusanya, S.; et al. Prodigiosin-loaded electrospun nanofibers scaffold for localized treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmady, A.R.; Solouk, A.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Akbari, S.; Ghanbari, H.; Brycki, B.E. Capsaicin-loaded alginate nanoparticles embedded polycaprolactone-chitosan nanofibers as a controlled drug delivery nanoplatform for anticancer activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 638, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D.; Lei, H.; Cheng, S.; Ge, J.; Ma, X.; Ni, C.; Liu, Z.; et al. Eddy current thermal effect based on magnesium microrods for combined tumor therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S.; Moradkhani, B.M.; Beheshti, H.; Irani, M.; Aliabadi, M. Fabrication of chitosan/poly(lactic acid)/graphene oxide/TiO2 composite nanofibrous scaffolds for sustained delivery of doxorubicin and treatment of lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Falahi, F.; Akbari-Birgani, S.; Nikfarjam, N. Trilayer tubular scaffold to mimic ductal carcinoma breast cancer for the study of chemo-photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 2394–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Doostan, M.; Shojaei, S.; Doostan, M.; Stamatis, H.; Gkantzou, E.; Bonkdar, A.; Khoshnevisan, K. Nanofiber-based systems against skin cancers: Therapeutic and protective approaches. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 82, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasalta, M.; Asefnejad, A.; Khorasani, M.T.; Saadatabadi, A.R. Fabrication of carboxymethyl chitosan/poly(ε-caprolactone)/doxorubicin/nickel ferrite core-shell fibers for controlled release of doxorubicin against breast cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebian, Z.; Babazadeh, M.; Zarghami, N.; Mousazadeh, H. Anticancer efficiency of curcumin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles/nanofiber composites for potential postsurgical breast cancer treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farboudi, A.; Nouri, A.; Shirinzad, S.; Sojoudi, P.; Davaran, S.; Akrami, M.; Irani, M. Synthesis of magnetic gold coated poly (ε-caprolactonediol) based polyurethane/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted-chitosan core-shell nanofibers for controlled release of paclitaxel and 5-FU. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaweera, I.; Levesque-Bishop, D.; Shi, Y.; Di Pasqua, A.J.; Balkus, K.J.J. Radiotherapeutic bandage based on electrospun polyacrylonitrile containing holmium-166 iron garnet nanoparticles for the treatment of skin cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22250–22256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, N.; Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R. Antioxidant and antitumor activities of novel quercetin-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate/polyethylene glycol fibrous materials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C. Direct site-specific treatment of skin cancer using doxorubicin-loaded nanofibrous membranes. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadzadeh, S.; Babazadeh, M.; Zarghami, N.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Mousazadeh, H. An implantable smart hyperthermia nanofiber with switchable, controlled and sustained drug release: Possible application in prevention of cancer local recurrence. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthulakshmi, L.; Prabakaran, S.; Ramalingam, V.; Rajulu, A.V.; Rajan, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Luo, H. Sodium alginate nanofibers loaded Terminalia catappa scaffold regulates intrinsic apoptosis signaling in skin melanoma cancer. Process Biochem. 2022, 118, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Li, M.; Sutrisno, L.; Yan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cai, K.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Luo, Z. Bioresorbable scaffolds with biocatalytic chemotherapy and in situ microenvironment modulation for postoperative tissue repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen, C.G.; Dündar, M.A.; Kars, M.D.; Avcı, A. Enhancement of PCL/PLA electrospun nanocomposite fibers comprising silver nanoparticles encapsulated with thymus vulgaris l. molecules for antibacterial and anticancer activities. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3717–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, U.; Goyal, A.K.; Rath, G. Development and characterization of the cisplatin loaded nanofibers for the treatment of cervical cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; LeeL, D.; Qiu, J.T.; Lee, T.; Liu, S. Biodegradable andrographolide-eluting nanofibrous membranes for the treatment of cervical cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakub, G.; Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Toshkova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Markova, N. Chitosan/ferulic acid-coated poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun materials with antioxidant, antibacterial and antitumor properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šišková, A.O.; Cková, M.B.; Kroneková, Z.; Kleinová, A.; Nagy, Š.; Rydz, J.; Opálek, A.; Sláviková, M.; Andicsová, A.E. The drug-loaded electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) mats for therapeutic application. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zong, S.; Qiu, R.; Liu, S. Use of multifunctional composite nanofibers for photothermal chemotherapy to treat cervical cancer in mice. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zheng, X.; Han, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Kaplan, D.L.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; et al. A biodegradable stent with surface functionalization of combined-therapy drugs for colorectal cancer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1801213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, M.; Ghorbani, M.; MohammadiM, M.A.; Delavar, M.; Tabibiazar, M.; Ramezani, S. Development of resveratrol loaded chitosan-gellan nanofiber as a novel gastrointestinal delivery system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellatyar, H.; Talaei, S.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Dadashpour, M.; Barzegar, A.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Zarghami, N. 17-DMAG-loaded nanofibrous scaffold for effective growth inhibition of lung cancer cells through targeting HSP90 gene expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadzadeh, S.; Mousazadeh, H.; Ghareghomi, S.; Dadashpour, M.; Babazadeh, M.; Zarghami, N. In vitro anticancer efficacy of Metformin-loaded PLGA nanofibers towards the post-surgical therapy of lung cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, S.; Dai, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Gong, J.; Yao, Y. Human lung epithelial cells A549 epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by PVA/Collagen nanofiber. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, B.; Wen, W.; Gao, X. Nanofiber membrane supported lung-on-a-chip microdevice for anti-cancer drug testing. Lab. Chip 2018, 18, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, M.; Sadeghi, G.M.M.; Haririan, I. The sustained delivery of temozolomide from electrospun PCL-Diol-b-PU/gold nanocomposite nanofibers to treat glioblastoma tumors. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Peña, R.; Mansor, M.H.; Najberg, M.; Thomassin, J.; Gueza, B.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Garcion, E.; Jérôme, C.; Boury, F. Nanoparticle-containing electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for sustained release of SDF-1α. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Ding, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Hui, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Zhang, J.; Long, Y. NIR-II-Triggered Composite Nanofibers to Simultaneously Achieve Intracranial Hemostasis, Killing Superbug and Residual Cancer Cells in Brain Tumor Resection Surgery. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2023, 5, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, O.M.; Purcz, N.; Chalaris, A.; Heneweer, C.; Boretius, S.; Purcz, L.; Nikkola, L.; Ashammakhi, N.; Kalthoff, H.; Glüer, C.; et al. Increased survival rate by local release of diclofenac in a murine model of recurrent oral carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5311–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Y.; Yuan, C.; Sun, P.; Xu, Q.; Lin, D.; Han, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Deng, J. Fabrication of astaxanthin-loaded electrospun nanofiber-based mucoadhesive patches with water-insoluble backing for the treatment of oral premalignant lesions. Mater. Design 2022, 223, 111131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Shan, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhuang, X.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Gradiently degraded electrospun polyester scaffolds with cytostatic for urothelial carcinoma therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musciacchio, L.; Mardirossian, M.; Guagnini, B.; Raffini, A.; Rizzo, M.; Trombetta, C.; Liguori, G.; Turco, G.; Porrelli, D. Rifampicin-loaded electrospun polycaprolactone membranes: Characterization of stability, antibacterial effects and urotheliocytes proliferation. Mater. Design 2022, 224, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anothra, P.; Pradhan, D.; Naik, P.K.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Development and characterization of 5-fluorouracil nanofibrous film for the treatment of stomach cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Dai, F.; Cheng, G.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, H. Incorporation of Layered Rectorite into Biocompatible Core–Sheath Nanofibrous Mats for Sustained Drug Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4509–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, E.R.; Chim, L.K.; Salazar, M.C.; Mehta, S.M.; Menegaz, B.A.; Lamhamedi-Cherradi, S.; Satish, T.; Mohiuddin, S.; McCall, D.; Zaske, A.M.; et al. Mechanically tunable coaxial electrospun models of YAP/TAZ mechanoresponse and IGF-1R activation in osteosarcoma. Acta Biomater. 2019, 100, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Kokulnathan, T.; Chen, S.; Allen, J.A.; Viswanathan, C.; Therese, H.A. Nitrogen doped carbon nanofibers loaded with hierarchical vanadium tetrasulfide for the voltammetric detection of the non-steroidal anti-prostate cancer drug nilutamide. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, J.; Orchel, A.; Kaps, A.; Jaworska-Kik, M.; Hercog, A.; Stojko, M.; Włodarczyk, J.; Musiał-Kulik, M.; Pastusiak, M.; Bochenek, M.; et al. Bioresorbable nonwoven patches as taxane delivery systems for prostate cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q.; Shen, B.; Fang, Y.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Peng, C.; Li, H. Drug-eluting scaffold inhibited in vivo pancreatic tumorigenesis by engaging murine CCR4+CD8+ T cells. Colloid Surf. B 2017, 158, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, F.; Hermosilla, J.; Sanhueza, C.; Mora-Lagos, B.; Fuentes, I.; Rubilar, M.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Gallic acid loaded PEO-core/zein-shell nanofibers for chemopreventive action on gallbladder cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 119, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Release Mode | Fluid Composition | Spinning Condition | Loaded Drug | Released Time (h) | Application | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core | Middle | Sheath | Voltage (kV) | Core-to-Sheath Velocity Ratio (ml/h) | |||||
| Quick release | CA, PEG, RUT | / | CA, PEG, QUE | 25 | 3.0; 3.0 | Quercetin (QUE); Rutin (RUT) | 6 | Cervical cancer treatment and wound dressing | [58] |
| PVP, AB, VAL | / | / | 15 | 1.3 | Amlodipine besylate; Valsartan | 0.1 | Hypertension treatment | [66] | |
| PVA, SP, AGN | / | / | 25 | 1.0 | Angelica gigas Nakai (AGN) | 0.25 | Oral patch, instant pad preparation for oral cancer | [67] | |
| Sustained release | CA, MET | CA, MET | Acetone; DMAc; Ethanol | 15 | 0–2.0; 2.0–0; 0.5 | Metformin hydrochloride (MET) | 23.4 | Type II diabetes | [68] |
| PLA | / | / | 15 | 1.5 | Theophylline | 288 | Treatment of bronchial asthma, asthmatic bronchitis, and obstructive emphysema | [62] | |
| CA, EC | / | / | 15 | 0.5–1.0 | Ketoprofen (KET) | 500 | Anti-inflammatory action | [69] | |
| EC; Berberine hydrochloride | / | Glycerol Monostearate | 16 | 1.5; 0.5 | Berberine hydrochloride | 32 | Dysentery, cancer, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia | [70] | |
| ACY | ACY, CA | CA | 14 | 0; 0.3; 1.0/0.3; 1.0; 0.3 | Acyclovir (ACY) | 42 | Antiviral treatment | [71] | |
| FA; Gliadin | CA | Acetone; Acetate Acid | 15 | 2; 0–0.5; 0.3 | Ferulic acid (FA) | 40 | Cancer, diabetes, and antioxidants | [72] | |
| Biphasic release | PAN, ACY | / | ACY | 18 | 1.5–2.0; 0.5–0 | Acyclovir (ACY) | 16 | Various infections caused by herpes simplex virus | [9] |
| CIP | / | CA | 16 | 0.5; 0–0.1 | Ciprofloxacin (CIP) | 24 | Biphasic drug-controlled release | [28] | |
| PVP | PCL, CF:TFE (3:1) | PCL, TFE | 15 | 0–0.08; 0.4–1.2; 0.2–0.4 | Dyes: key acid blue (KAB); key acid uranine (KAU) | 24 | Wound dressing and cancer treatment | [56] | |
| Targeted release | DS; Ethanol | ES100; DMAc | Ethanol | 5 | 0–0.4; 3.0–1.6; 0–1.0 | Diclofenac sodium (DS) | 24 | Oral administration, colonic biofilm penetration | [14] |
| PEO, CUR, 80% Ethanol | Ethanol | Shellac; Ethanol | 6 | 0.6; 0.2; 0.2–0.6 | Curcumin (CUR) | 72 | Oral colonic administration; microbead fibers serve as drug repositories | [65] | |
| EC, KET | EC, KET | EC, KET | 12 | 0.2; 0.5; 2 | Ketoprofen (KET) | 20 | Incorporated into the intestinal sol capsule, released linearly, and administered orally | [73] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liang, Z.; Guo, J.; Chen, B.; Zhou, S.; Yu, D. Application of Electrospun Drug-Loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy. Polymers 2024, 16, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040504
Yang Y, Zhang R, Liang Z, Guo J, Chen B, Zhou S, Yu D. Application of Electrospun Drug-Loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy. Polymers. 2024; 16(4):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040504
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yaoyao, Rui Zhang, Zhiyuan Liang, Junli Guo, Bingying Chen, Shengwei Zhou, and Dengguang Yu. 2024. "Application of Electrospun Drug-Loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy" Polymers 16, no. 4: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040504
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhang, R., Liang, Z., Guo, J., Chen, B., Zhou, S., & Yu, D. (2024). Application of Electrospun Drug-Loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy. Polymers, 16(4), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040504








