Nanostructured Copper Selenide Coatings for Antifouling Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CuSe Nanoparticle Synthesis
2.2. Preparation of CuSe Nanostructured Coatings and Deposition
2.3. Mechanical Performance Tests
2.4. Microbiological Test
3. Results and Discussion
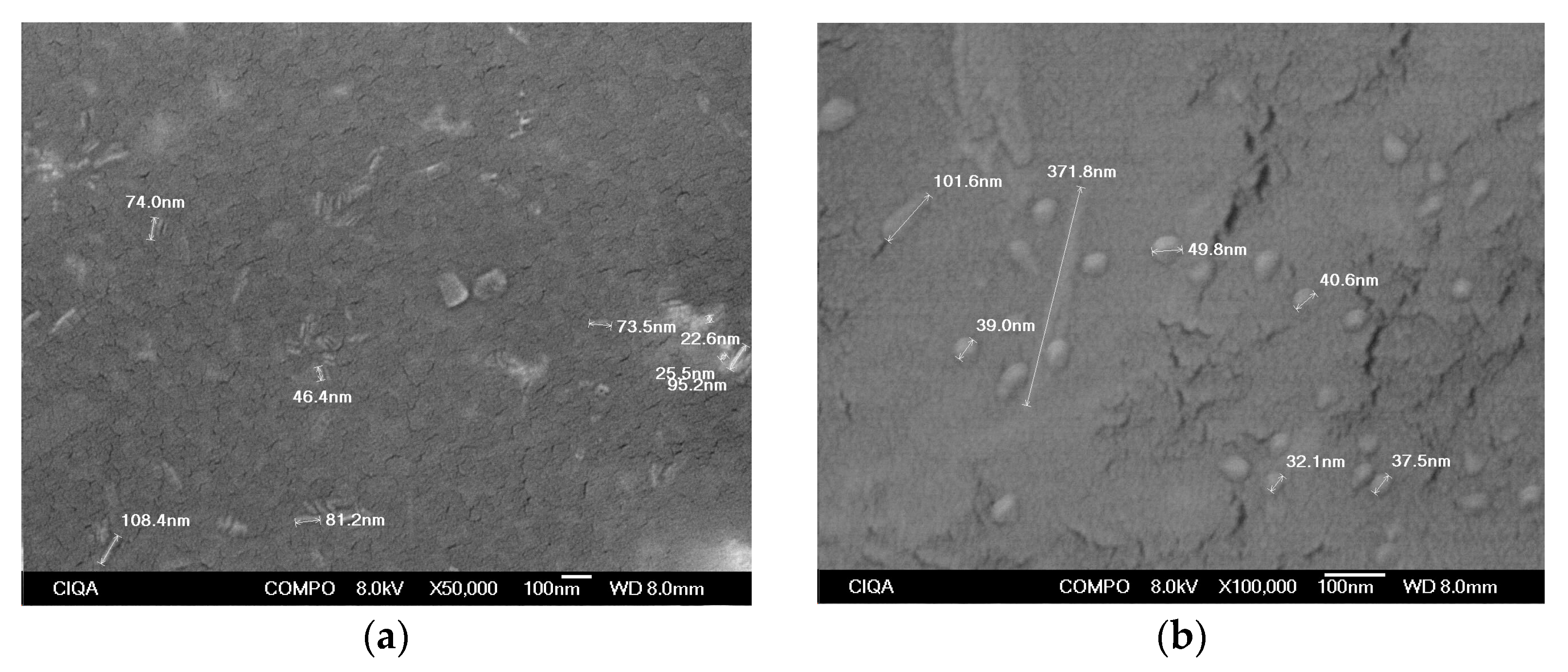
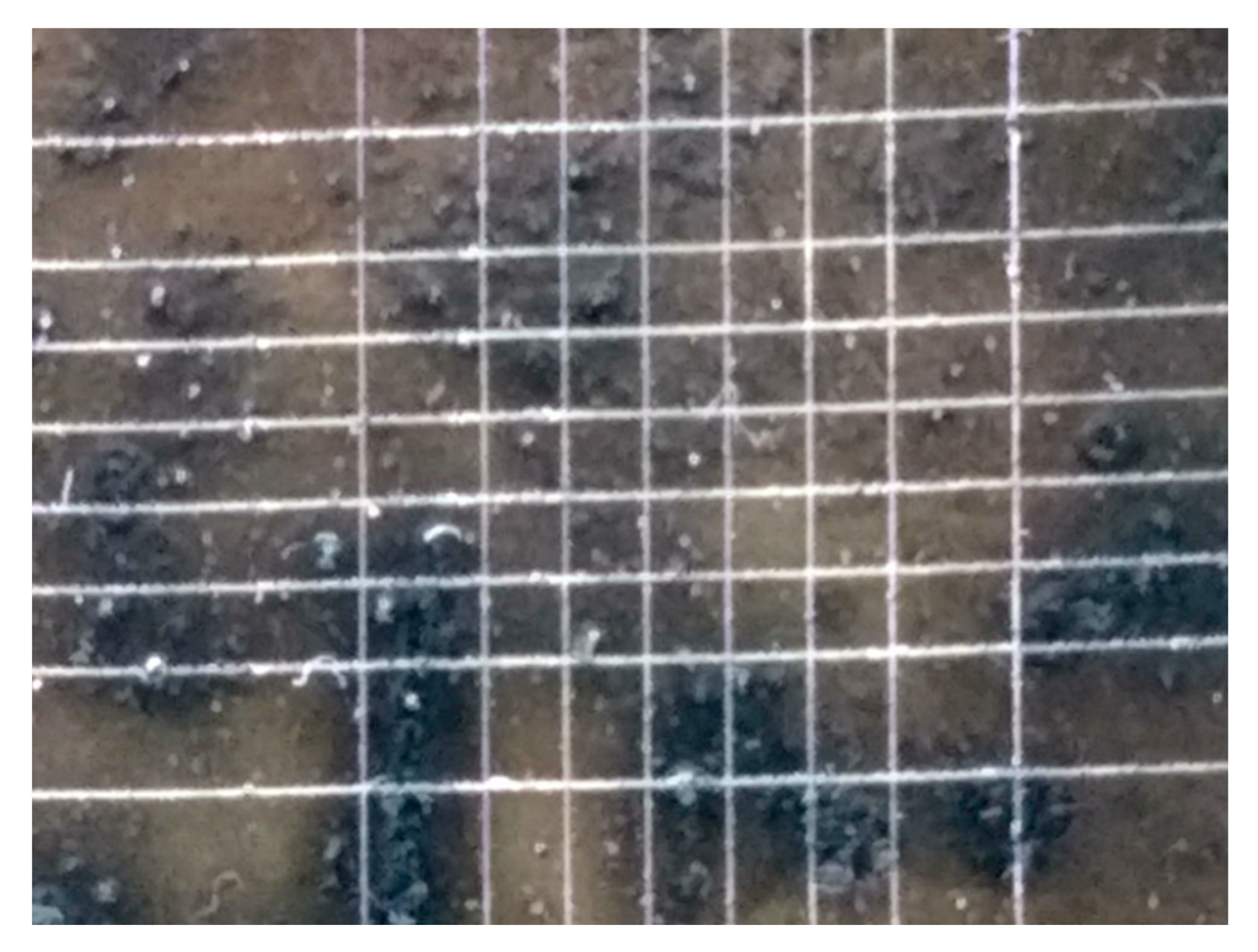
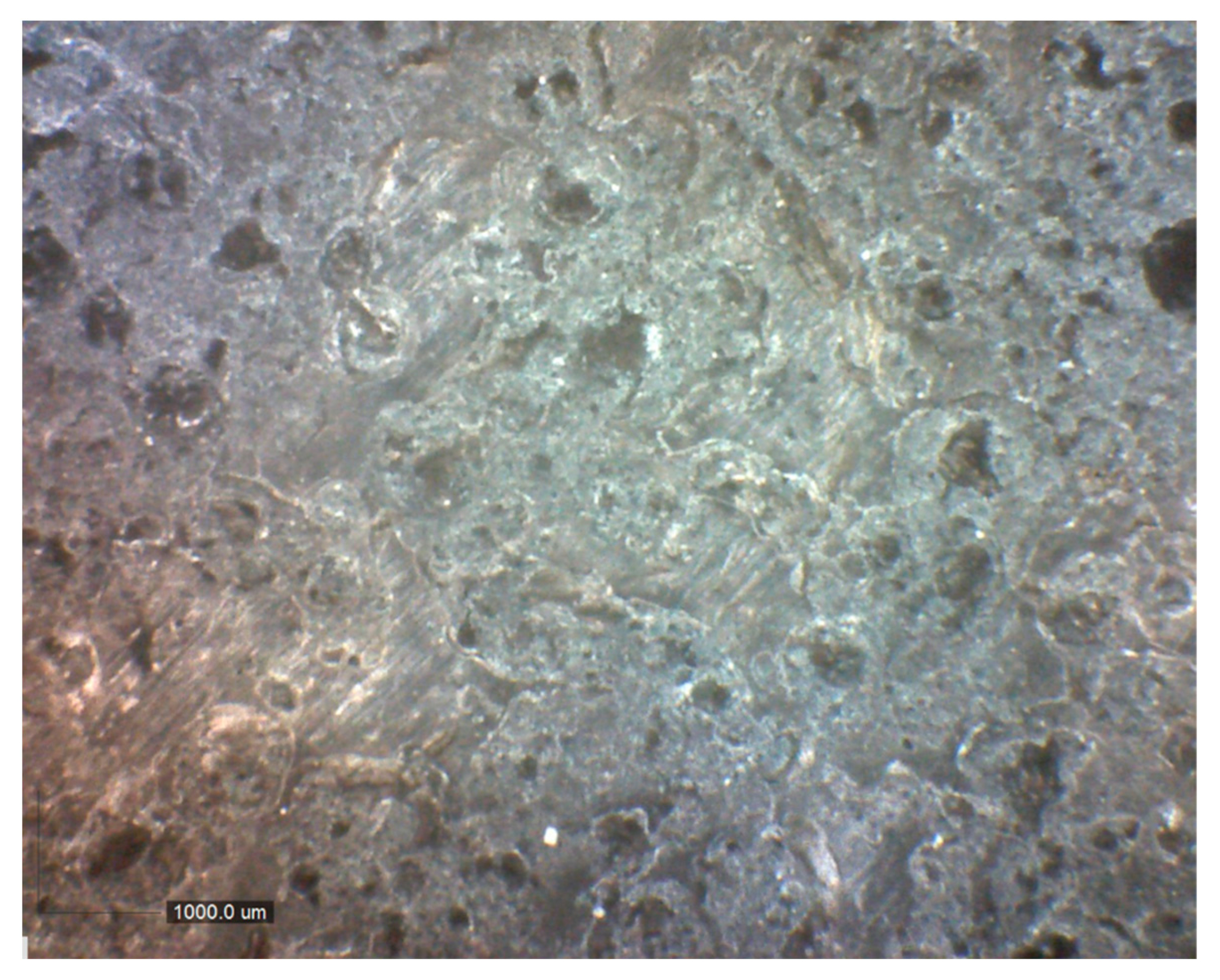
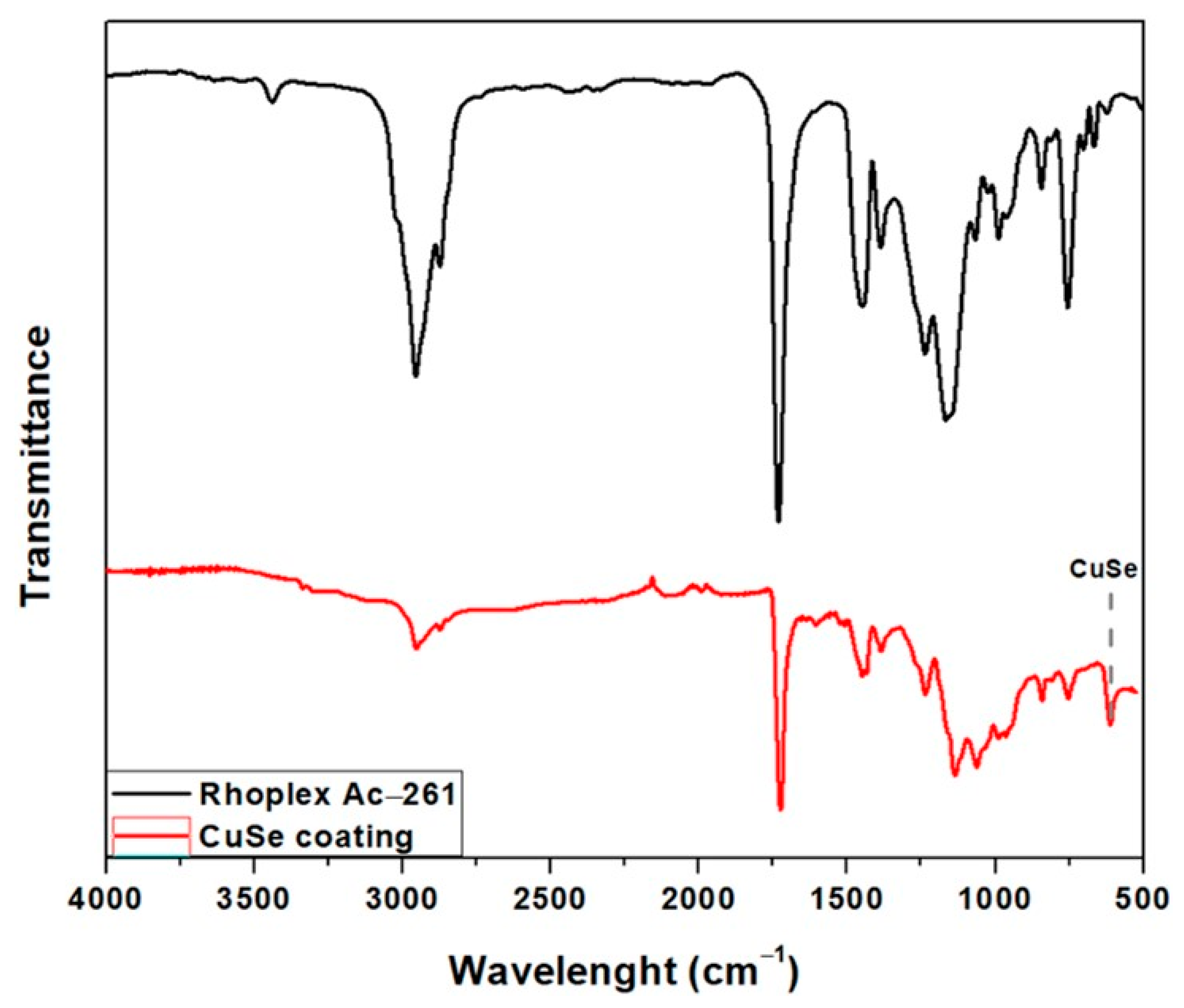
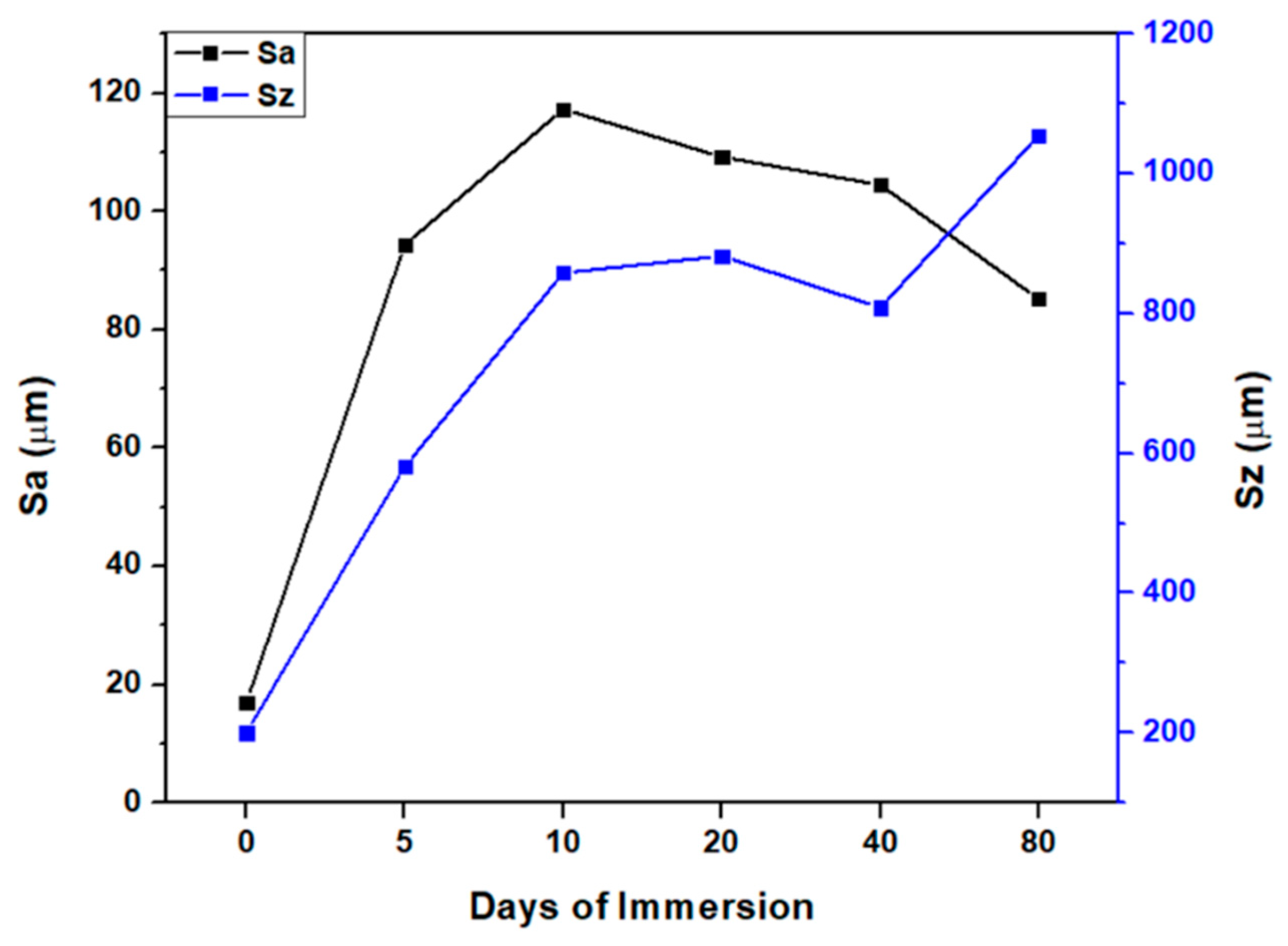
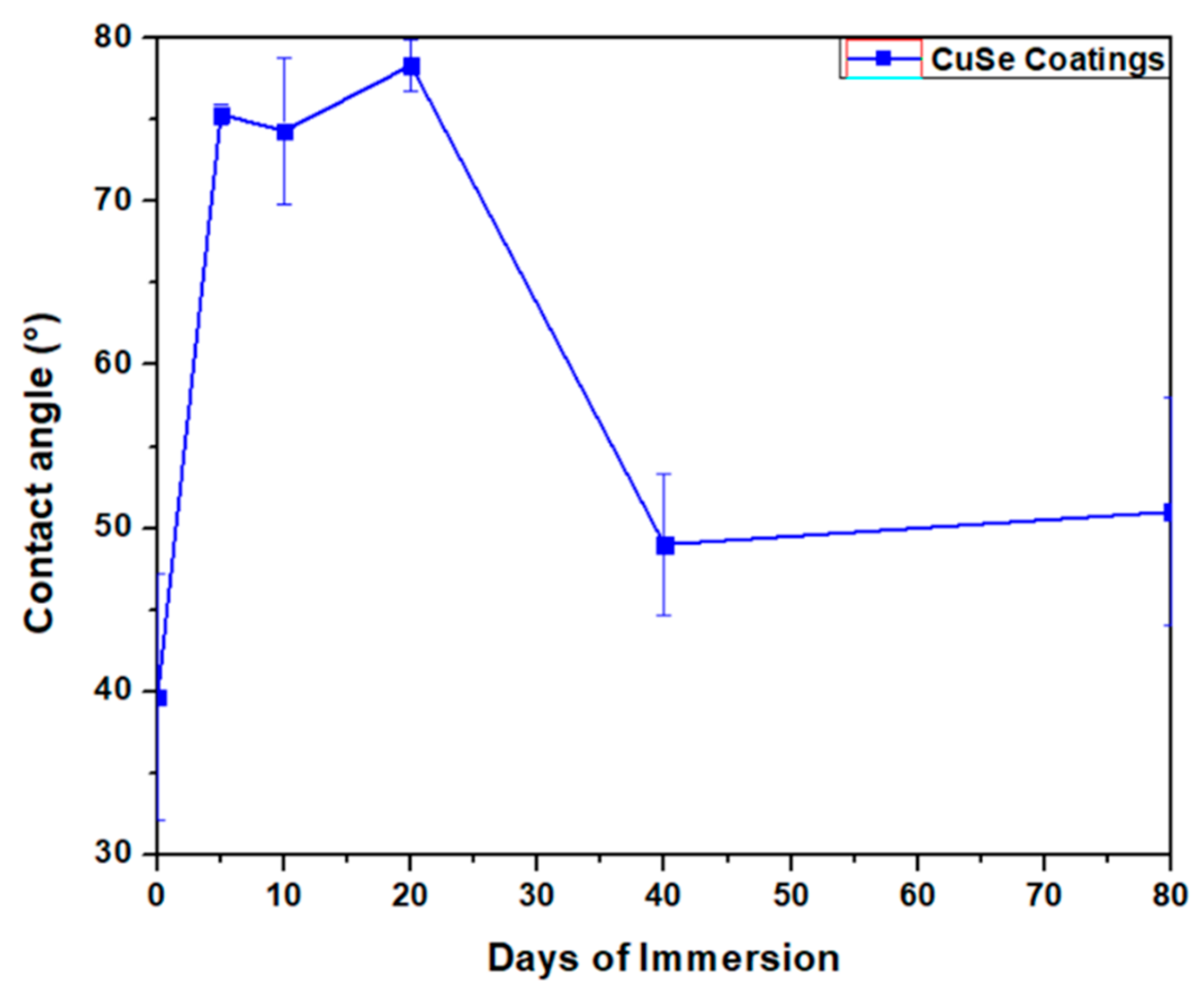
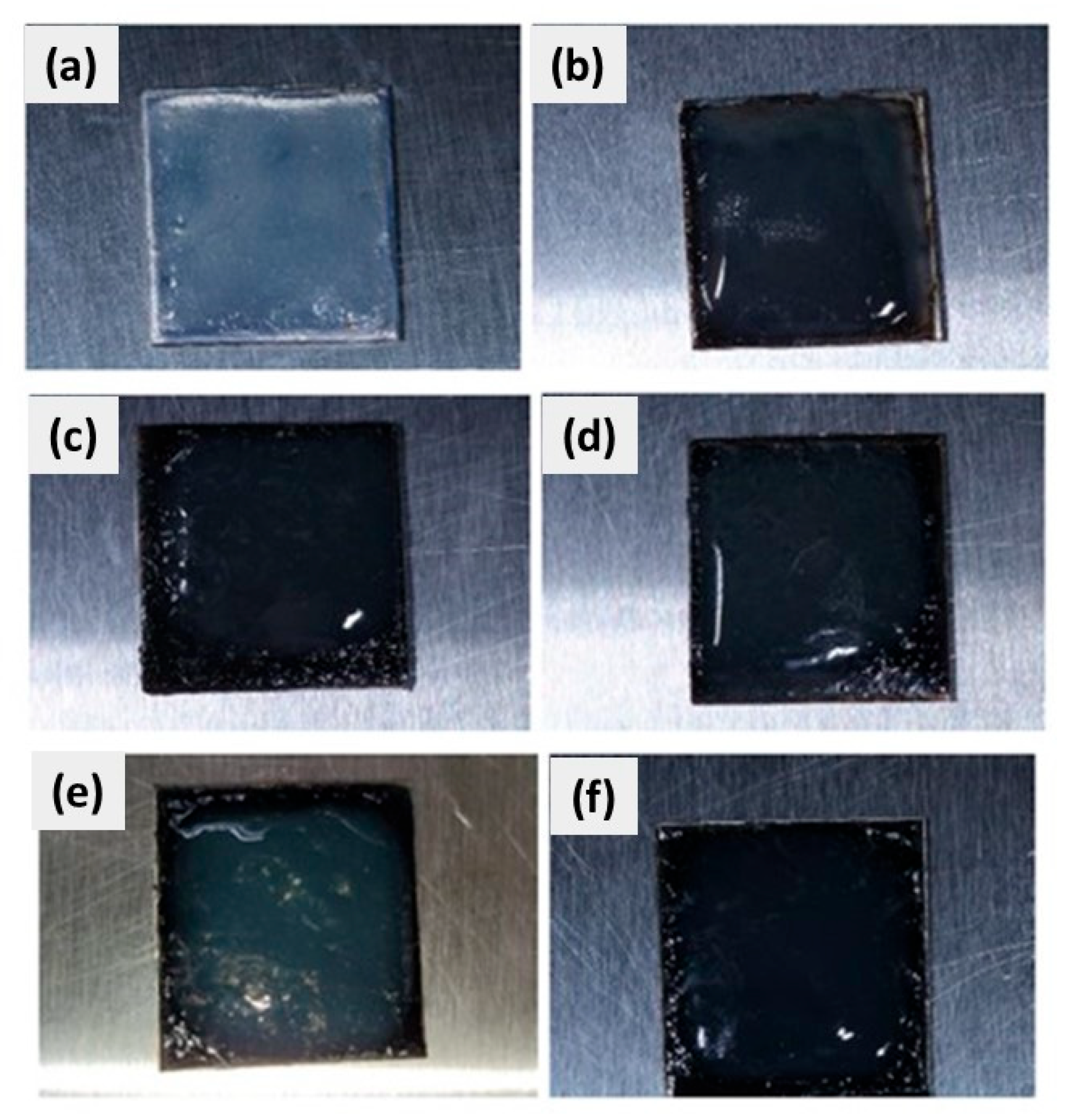
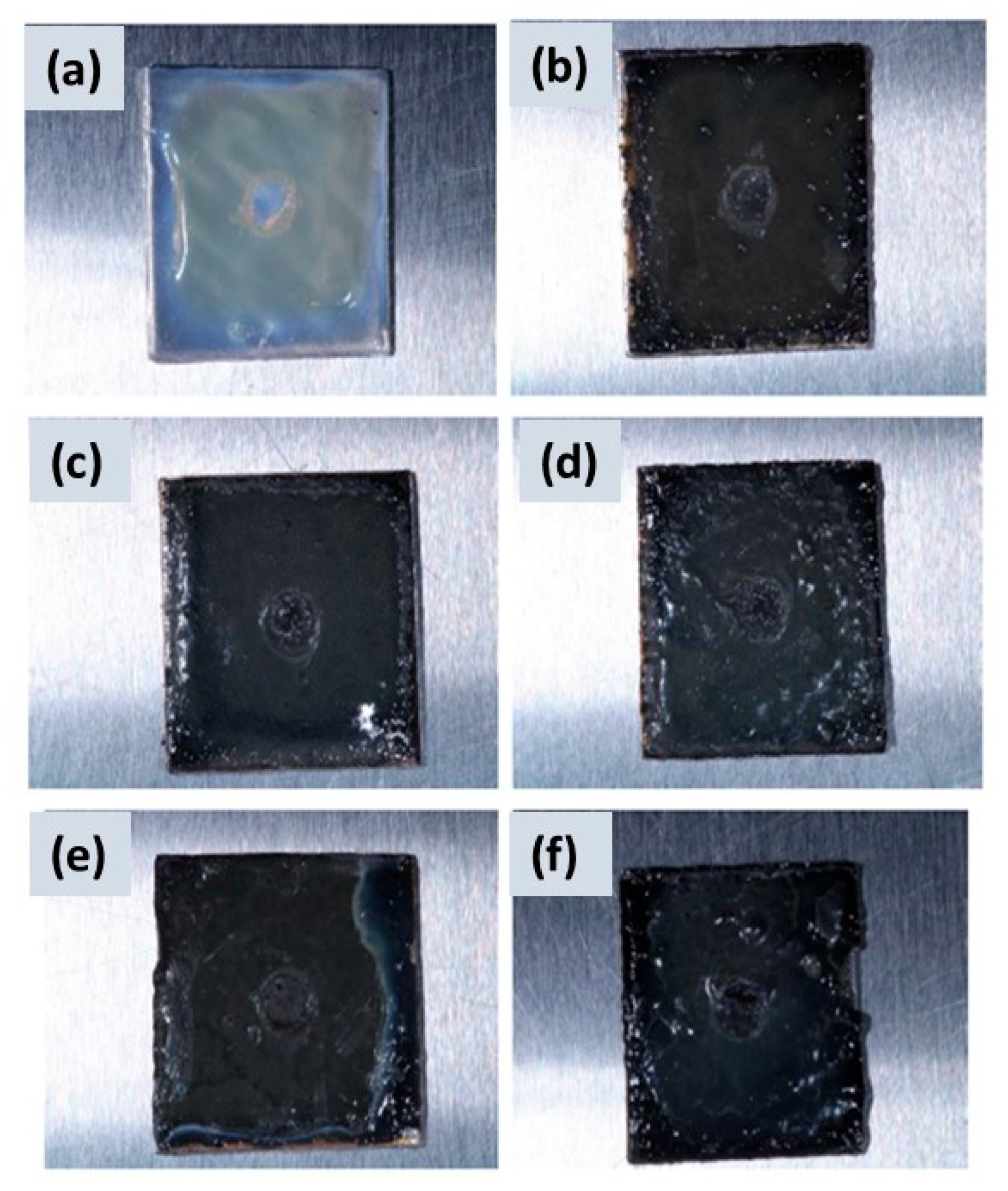
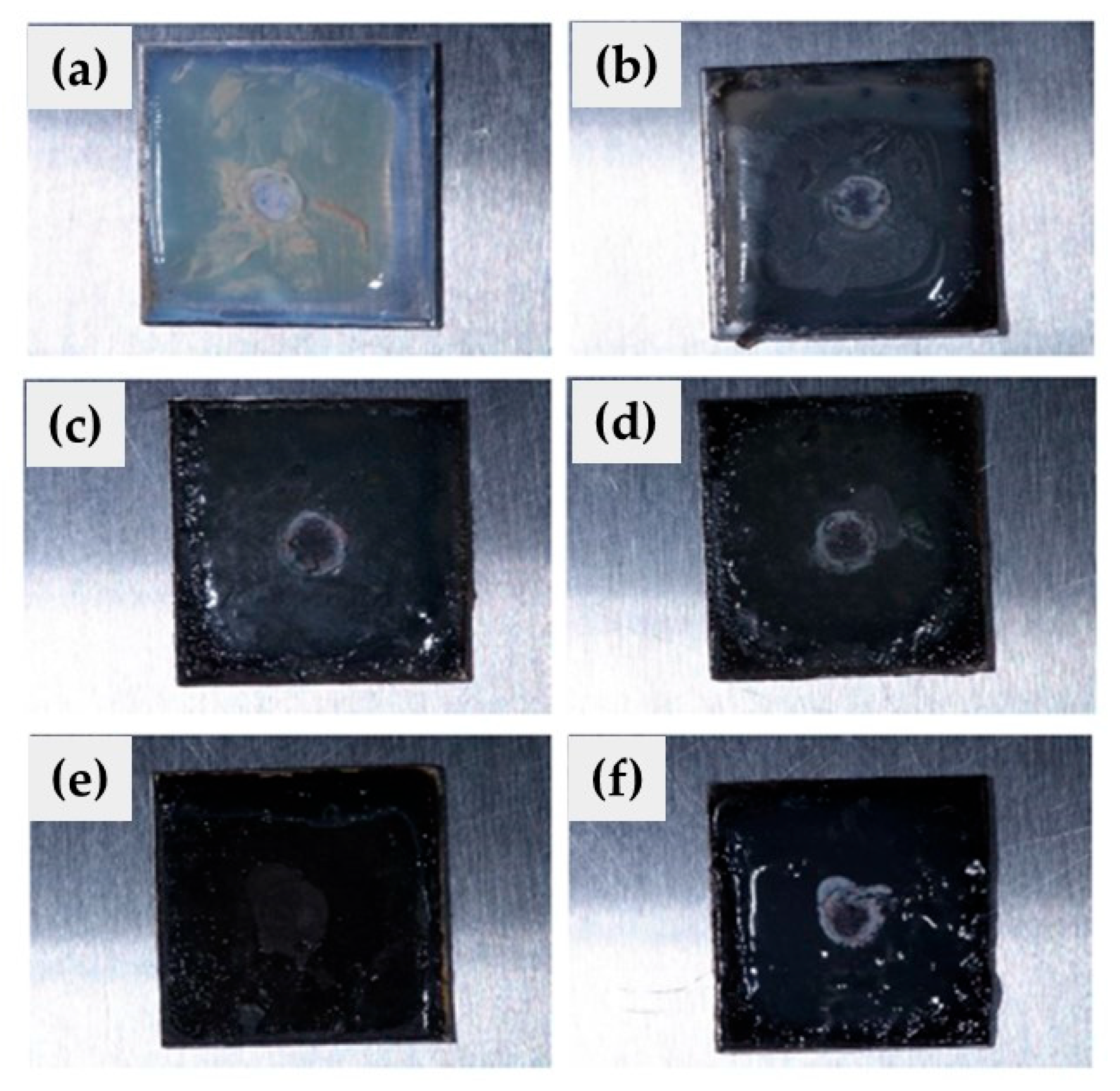
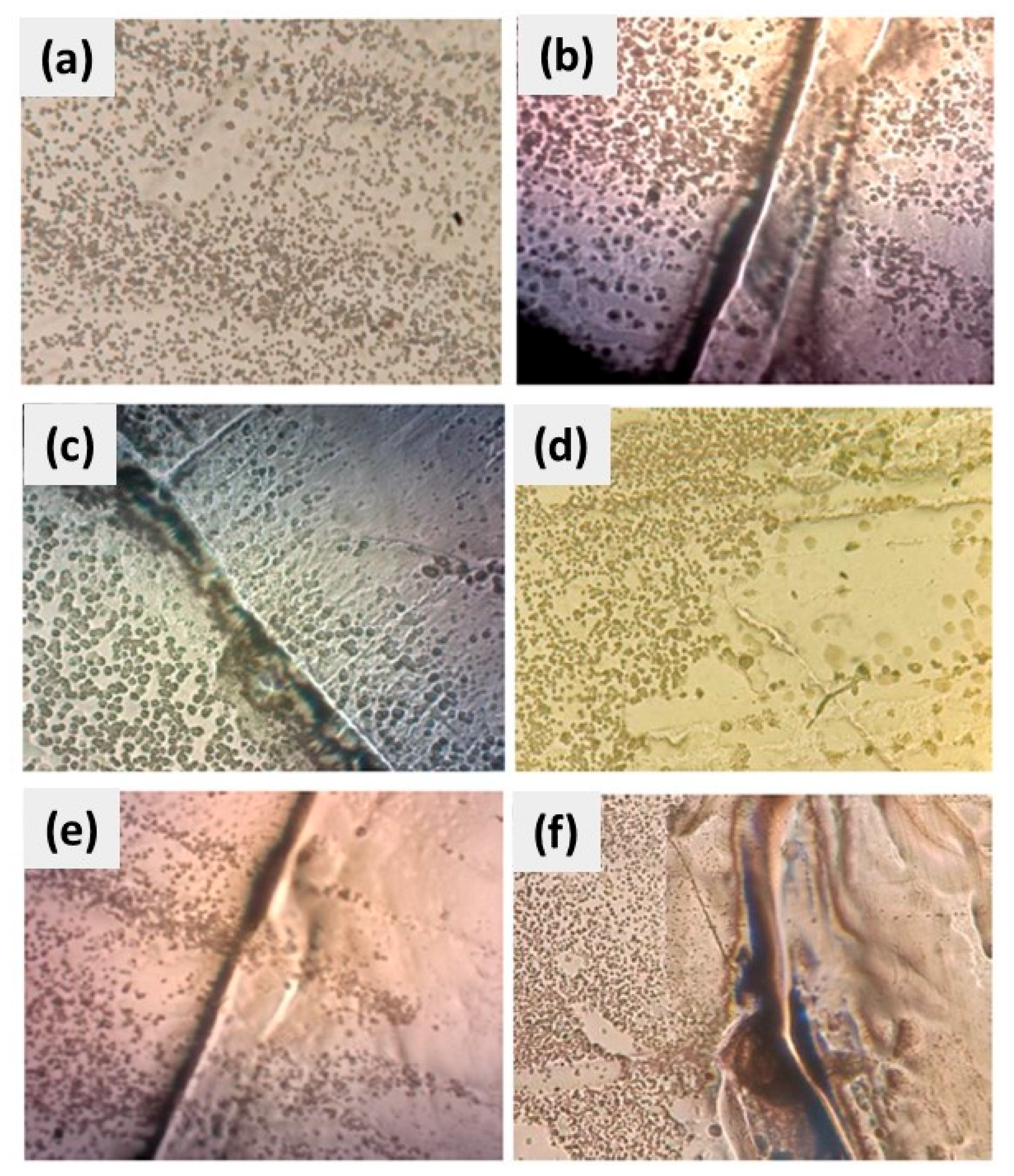
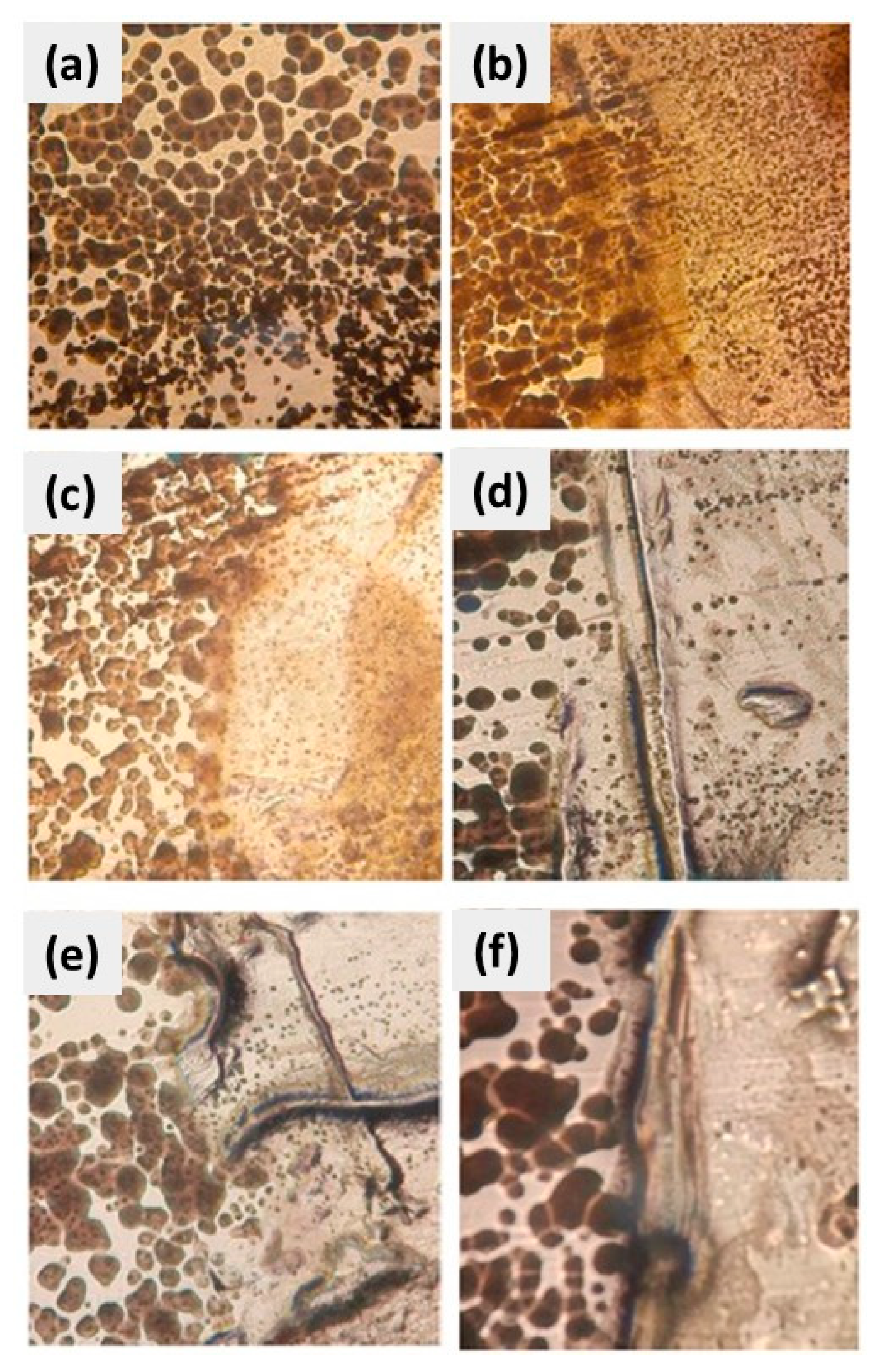
3.1. CuSe Nanostructured Coatings’ Characterization
- The release by “burst”: This occurs when the ions that are closest to the surface are released; this could be due to a release due to the swelling of the material [39], to the bad interaction between the matrix and the active principle, or to the porosity of the matrix when it comes into contact with an environment that dissolves it [40].
3.2. Mechanical Tests Analysis
3.3. Microbiological Tests Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling technology-past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, C. Latest research progress of marine microbiological corrosion and bio-fouling, and new approaches of marine anti-corrosion and anti-fouling. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.J.; Neoh, K.-G.; Kang, E.-T.; Teo, S.L.-M.; Rittschof, D. Polymer brush coatings for combating marine biofouling. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1017–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callow, J.A.; Callow, M.E. Trends in the development of environmentally friendly fouling-resistant marine coatings. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venettacci, S.; Ponticelli, G.S.; Tagliaferri, F.; Guarino, S. Environmental and Economic Impact of an Innovative Biocide-Free Antifouling Coating for Naval Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Yu, L.; Mou, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, M.; Zhou, P.; Ren, Y. Research Strategies to Develop Environmentally Friendly Marine Antifouling Coatings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, D. Progress of marine biofouling and antifouling technologies. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, B.; Du, Q.; Liu, D.; Shi, X.; Tu, J.; Xia, X. A review on synthesis and antibacterial potential of bio-selenium nanoparticles in the food industry. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1229838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; La Parola, V.; Testa, M.L.; Liotta, L.F. Antifouling and antimicrobial activity of Ag, Cu and Fe nanoparticles supported on silica and titania. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 529, 120636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, D.; Behrends, B. A review of surface roughness in antifouling coatings illustrating the importance of cutoff length. Biofouling 2006, 22, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittens, J.E.; Smith, T.J.; Suleiman, R.; Akid, R. Current and emerging environmentally-friendly systems for fouling control in the marine environment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1738–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskens, P.; Wouters, M.; Rentrop, C.; Vroon, Z. A brief review of environmentally benign antifouling and foul-release coatings for marine applications. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2013, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistone, A.; Scolaro, C.; Visco, A. Mechanical Properties of Protective Coatings against Marine Fouling: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poornima Vijayan, P.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.R.; Chithra, P.G.; Thomas, S. Integration of antifouling properties into epoxy coatings: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2022, 19, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, N.; Torsi, L.; Ditaranto, N.; Tantillo, G.; Ghibelli, L.; Sabbatini, L.; Bleve-Zacheo, T.; D’Alessio, M.; Zambonin, P.G.; Traversa, E. Copper Nanoparticle/Polymer Composites with Antifungal and Bacteriostatic Properties. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5255–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; Sun, L.; Kong, F.; Tang, J.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y.; Zuo, Y. Comparative Study on the Degradation of Two Self-Polishing Antifouling Coating Systems with Copper-Based Antifouling Agents. Coatings 2022, 12, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardón-Maximino, N.; Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Lugo-Uribe, L.E.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Mata-Padilla, J.M.; Barriga-Castro, E.D. Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles Stabilized with Organic Ligands and Their Antimicrobial Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Pérez-Camacho, O.; Comparán-Padilla, V.E.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.J.; Saucedo-Salazar, E. Green Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles Using Cotton. Polymers 2021, 13, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Ávila, R.; Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Valdez-Garza, J.; Avila-Orta, C.A.; Jiménez-Regalado, E.J.; Mata-Padilla, J.M.; Soto-Castruita, E.; Cadenas-Pliego, G. Synthesis and Thermomechanical Characterization of Nylon 6/Cu Nanocomposites Produced by an Ultrasound-Assisted Extrusion Method. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4792735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardón-Maximino, N.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Comparán-Padilla, V.E.; Lugo-Uribe, L.E.; Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Tavizón, S.F.; Santillán, G.d.J.S. Antimicrobial Property of Polypropylene Composites and Functionalized Copper Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O. Synthesis and antioxidant properties of gum arabic-stabilized selenium nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, N.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K. Selenium nanoparticles: A review on synthesis and biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Tekula, S.; Saifi, M.A.; Venkatesh, P.; Godugu, C. Therapeutic applications of selenium nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Z.; Lu, M.; Yang, P.; Zhou, G. Controllable synthesis of copper selenide nanocrystals through a green paraffin-acetate method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 124, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.A.; Hussain, I. Copper selenide thin films from growth to applications. Solid. State Sci. 2020, 100, 106101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitu, I.G.; Talib, Z.A.; Chi, J.L.Y.; Kechick, M.M.A.; Baqiah, H. Influence of tartaric acid concentration on structural and optical properties of CuSe nanoparticles synthesized via microwave assisted method. Results Phys. 2020, 17, 103041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jing, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Shi, L. Characterization of the phases and morphology in synthesizing Cu2-xSe and CuSe films. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2018, 189, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Kong, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, F.; Cui, D. Copper Selenide Nanosnakes: Bovine Serum Albumin-Assisted Room Temperature Controllable Synthesis and Characterization. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Birkett, M.; Dover, L.; Cherian Lukose, C.; Wasy Zia, A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Recent Advances in Metal-Based Antimicrobial Coatings for High-Touch Surfaces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, F.S.; Kaminsky, V.V.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Boinovich, L.B. Effect of Biological Contamination of Copper Surfaces with Extreme Wettability on Their Antibacterial Properties. Colloid J. 2023, 85, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Kaminsky, V.V.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Aleshkin, A.V.; Zulkarneev, E.R.; Kiseleva, I.A.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Bactericidal Activity of Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Copper in Bacterial Dispersions. Langmuir 2019, 37, 2832–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A380/A380M-13; Standard Practice for Cleaning, Descaling, and Passivation of Stainless Steel Parts, Equipment, and Systems. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
- ASTM D3359-22; Standard Test Methods for Rating Adhesion by Tape Test. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
- Montero, D.A.; Arellano, C.; Pardo, M.; Vera, R.; Gálvez, R.; Cifuentes, M.; Berasain, M.A.; Gómez, M.; Ramírez, C.; Vidal, R.M. Antimicrobial properties of a novel copper-based composite coating with potential for use in healthcare facilities. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanzadeh, I.; Barikani, M.; Mahdavian, A.R. Ultrasound-assisted emulsion polymerization of poly(methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate): Effect of initiator content and temperature. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, M.Z.; Sarac, A.S. Transparent poly(methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate) nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 4264–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liao, Y.; Xie, H.; Huang, Q.; Li, W. Polyethylene-supported poly(methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate)-based novel gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Ionics 2016, 22, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansari, M.M.; Al-Dahmash, N.D.; Ranjitsingh, A.J.A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using gum Arabic: Evaluation of its inhibitory action on Streptococcus mutans causing dental caries and endocarditis. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, P.A.; Baena, Y.; Aragón, M.; Rosas, J.E. Overall Mechanisms that Rule the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient’s Delivery Process from Hydrophilic Matrices Elaborated with Ether Cellulose. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Químico Farm. 2008, 37, 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Caro-León, F.J.; López-Martínez, L.M.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Argüelles-Monal, W.; Goycoolea-Valencia, F.M.; Carvajal-Millán, E.; López-Franco, Y.L. Métodos de Preparación de Nanopartículas de Quitosano: Una Revisión. Biotecnia 2019, 11, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón Muñoz, L.; Lecumberri Lima, E.; Expósito Harris, R.; López Mengíbar, M.A.; Acosta Contreras, N.; Heras Caballero, A.M. Chemical Properties of Chitosan as a Marine Cosmeceutical. In Marine Cosmeceuticals Trends and Prospects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Aragón, J.; González, R.; Fuentes, G. Cinética de Liberación de Cefalexiana desde un Biomaterial Compuesto por HAP-200/POVIAC/CaCO3. Acad. Nac. Farm. 2009, 75, 345–363. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Intrinsically robust hydrophobicity. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.J.; Adeleye, A.S.; Page, H.M.; Kui, L.; Lenihan, H.S.; Keller, A.A. Nano and traditional copper and zinc antifouling coatings: Metal release and impact on marine sessile invertebrate communities. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
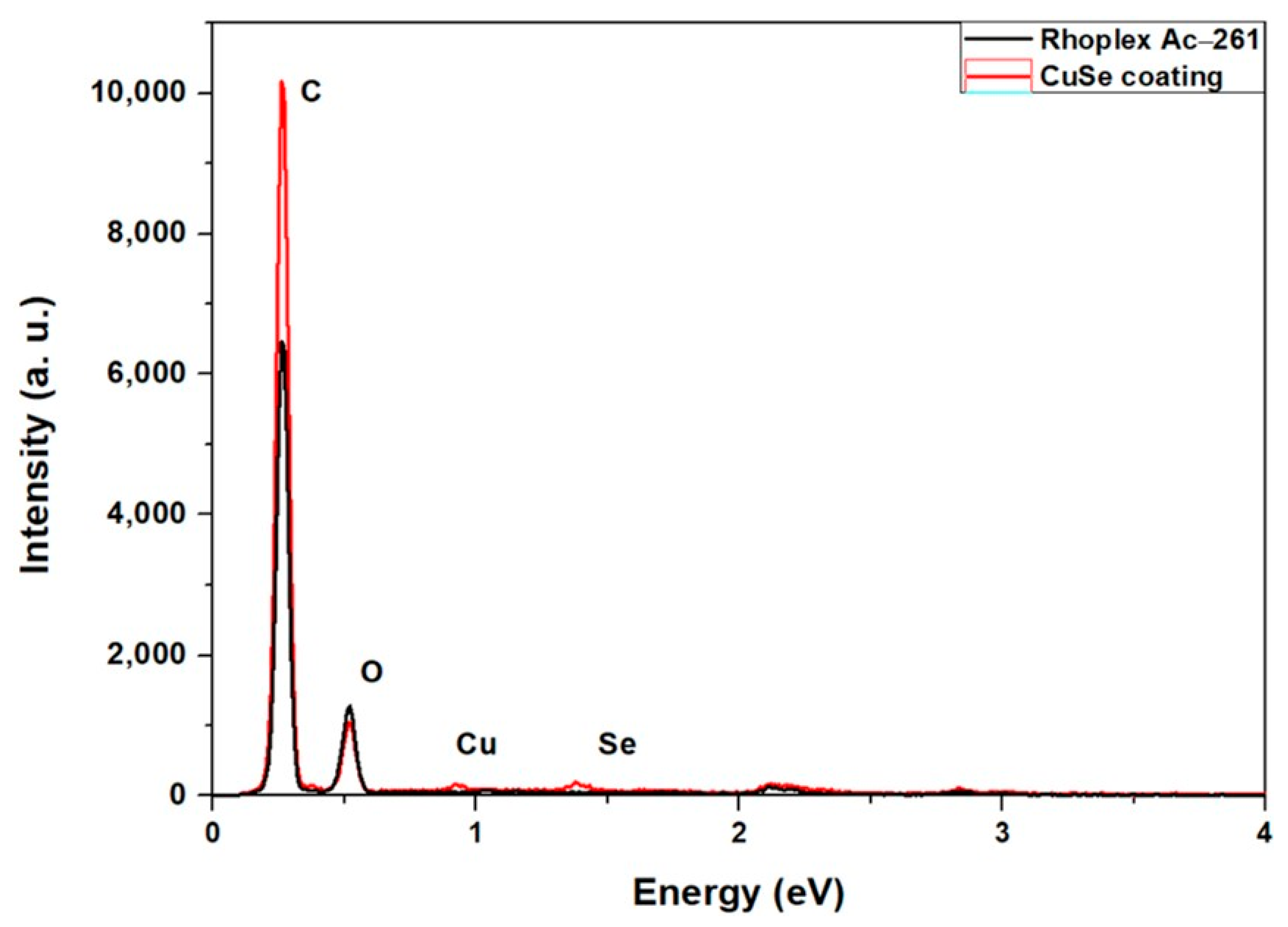
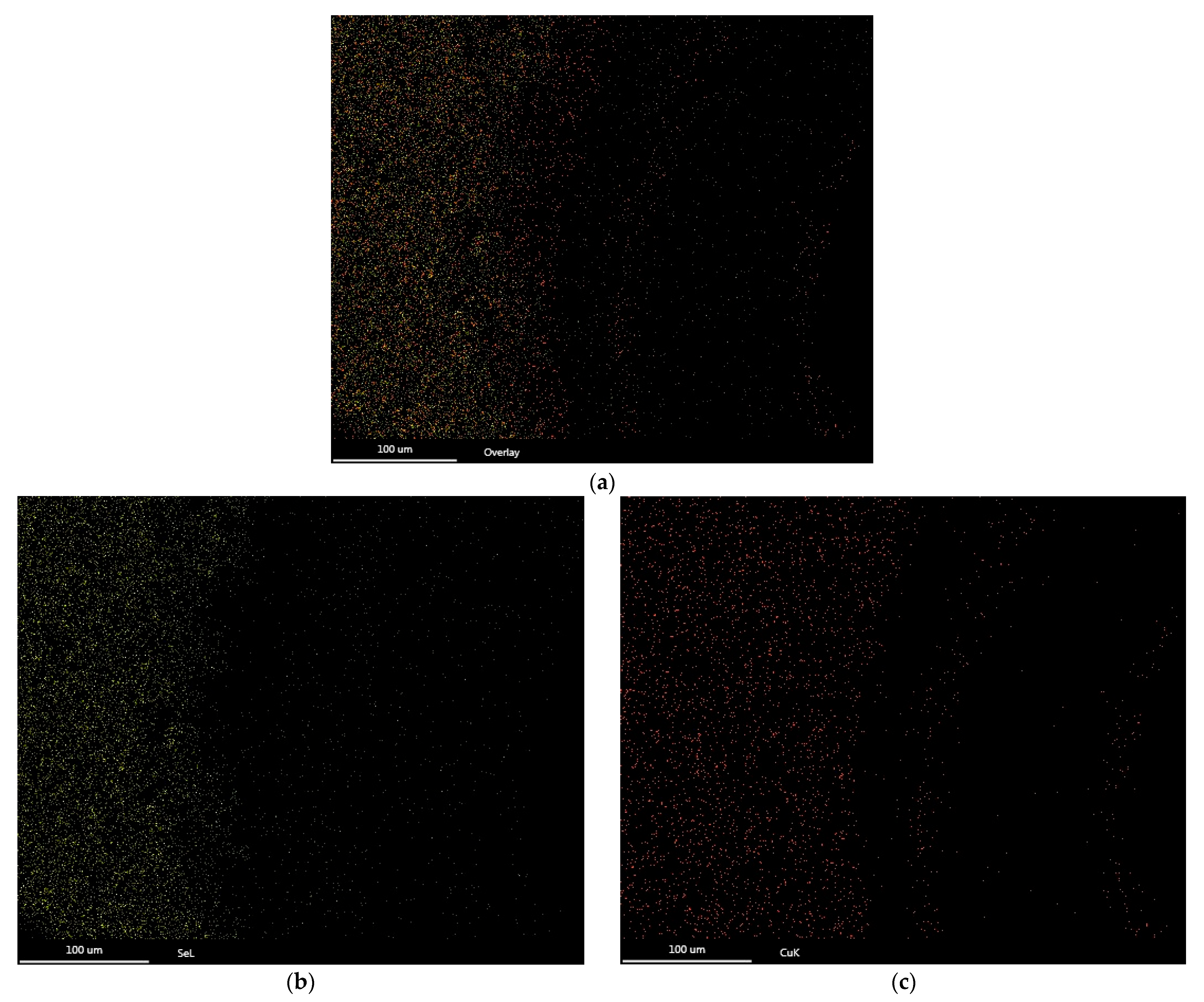


| Element | Wt. % |
|---|---|
| Oxygen | 77.4 |
| Carbon | 20.62 |
| Selenium | 1.14 |
| Copper | 0.84 |
| Sample Supernatant | Se (ppm) | Cu (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| Blank (distilled water) | 0 | 0 |
| Black 5 days | 0.088 | 0.009 |
| Black 10 days | 0.125 | 0.014 |
| Black 20 days | 0.414 | 0.034 |
| Black 40 days | 0.737 | 0.047 |
| Black 80 days | 0.519 | 0.132 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mancillas-Salas, S.; Ledón-Smith, J.Á.; Pérez-Álvarez, M.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Mata-Padilla, J.M.; Andrade-Guel, M.; Esparza-González, S.C.; Vargas-Gutiérrez, G.; Sierra-Gómez, U.A.; Saucedo-Salazar, E.M. Nanostructured Copper Selenide Coatings for Antifouling Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040489
Mancillas-Salas S, Ledón-Smith JÁ, Pérez-Álvarez M, Cadenas-Pliego G, Mata-Padilla JM, Andrade-Guel M, Esparza-González SC, Vargas-Gutiérrez G, Sierra-Gómez UA, Saucedo-Salazar EM. Nanostructured Copper Selenide Coatings for Antifouling Applications. Polymers. 2024; 16(4):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040489
Chicago/Turabian StyleMancillas-Salas, Sergio, José Ángel Ledón-Smith, Marissa Pérez-Álvarez, Gregorio Cadenas-Pliego, José Manuel Mata-Padilla, Marlene Andrade-Guel, Sandra Cecilia Esparza-González, Gregorio Vargas-Gutiérrez, Uriel Alejandro Sierra-Gómez, and Esmeralda Monserrat Saucedo-Salazar. 2024. "Nanostructured Copper Selenide Coatings for Antifouling Applications" Polymers 16, no. 4: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040489
APA StyleMancillas-Salas, S., Ledón-Smith, J. Á., Pérez-Álvarez, M., Cadenas-Pliego, G., Mata-Padilla, J. M., Andrade-Guel, M., Esparza-González, S. C., Vargas-Gutiérrez, G., Sierra-Gómez, U. A., & Saucedo-Salazar, E. M. (2024). Nanostructured Copper Selenide Coatings for Antifouling Applications. Polymers, 16(4), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040489








