Advances in the Application of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) and Its Organic Composite Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)
Abstract
1. Introduction

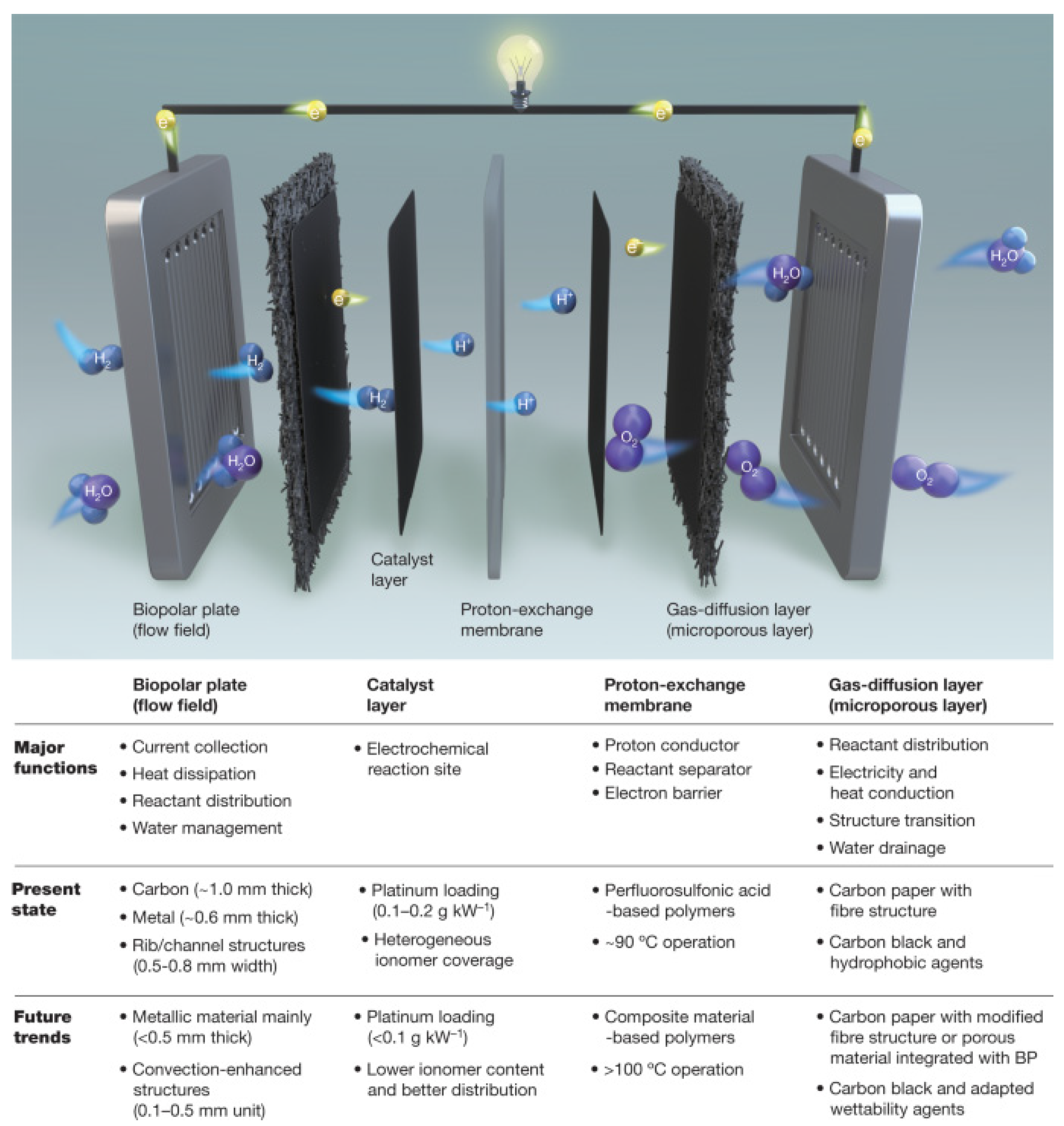
2. Preparation of SPEEK Membranes
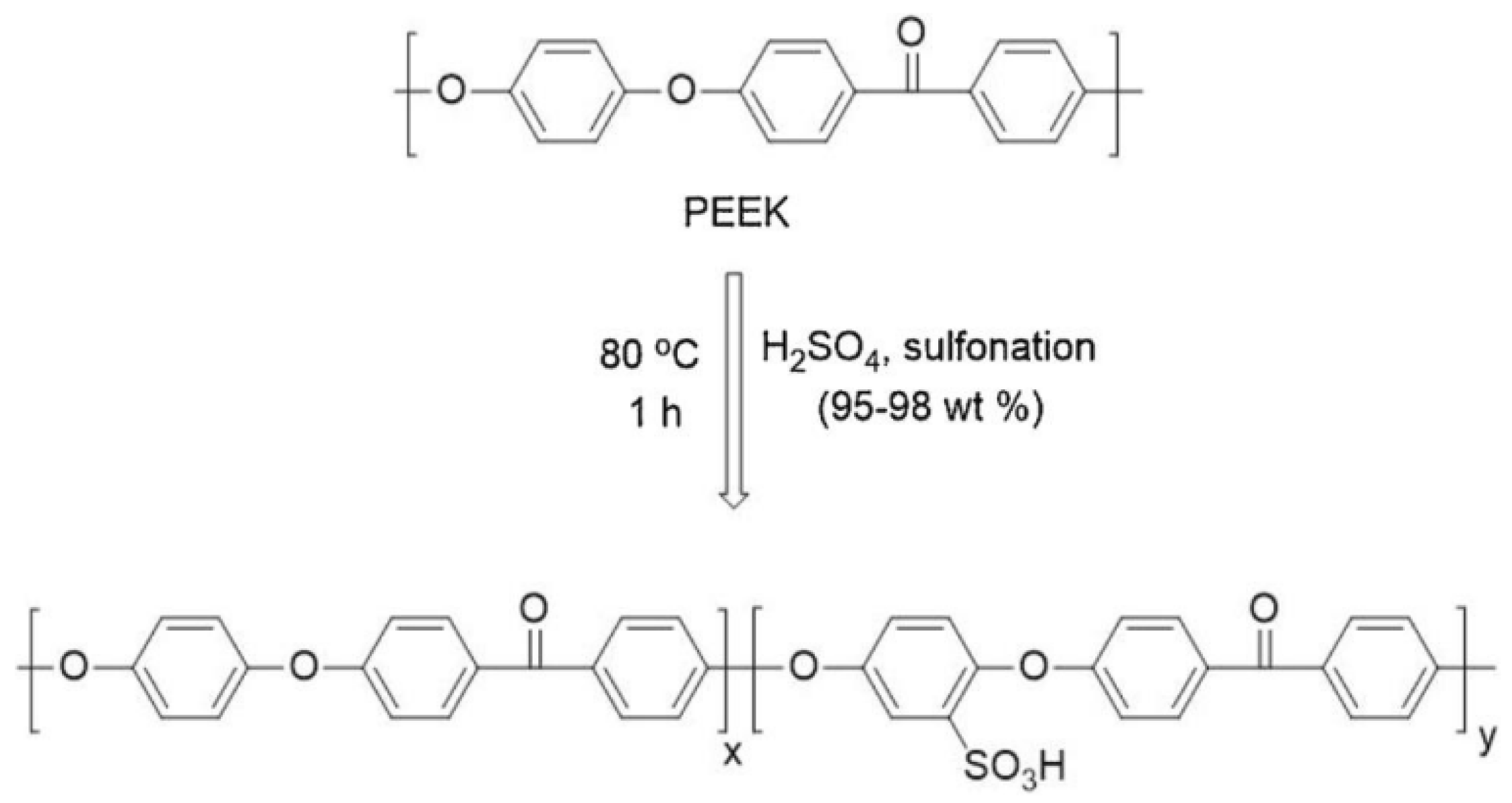
3. SPEEK/Organic Composite Membrane
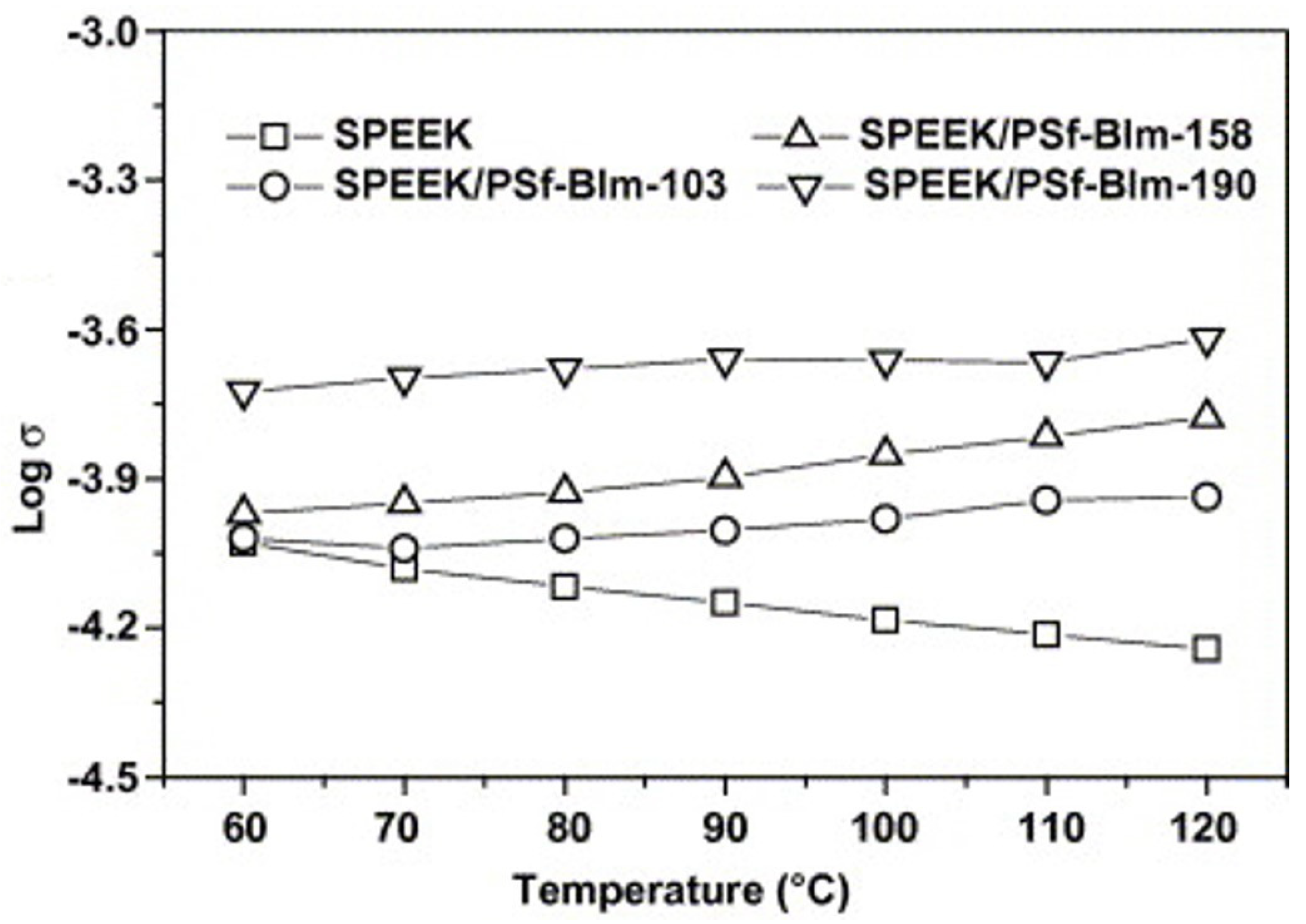
3.1. SPEEK/Polysulfone (PSF) Composite Membrane
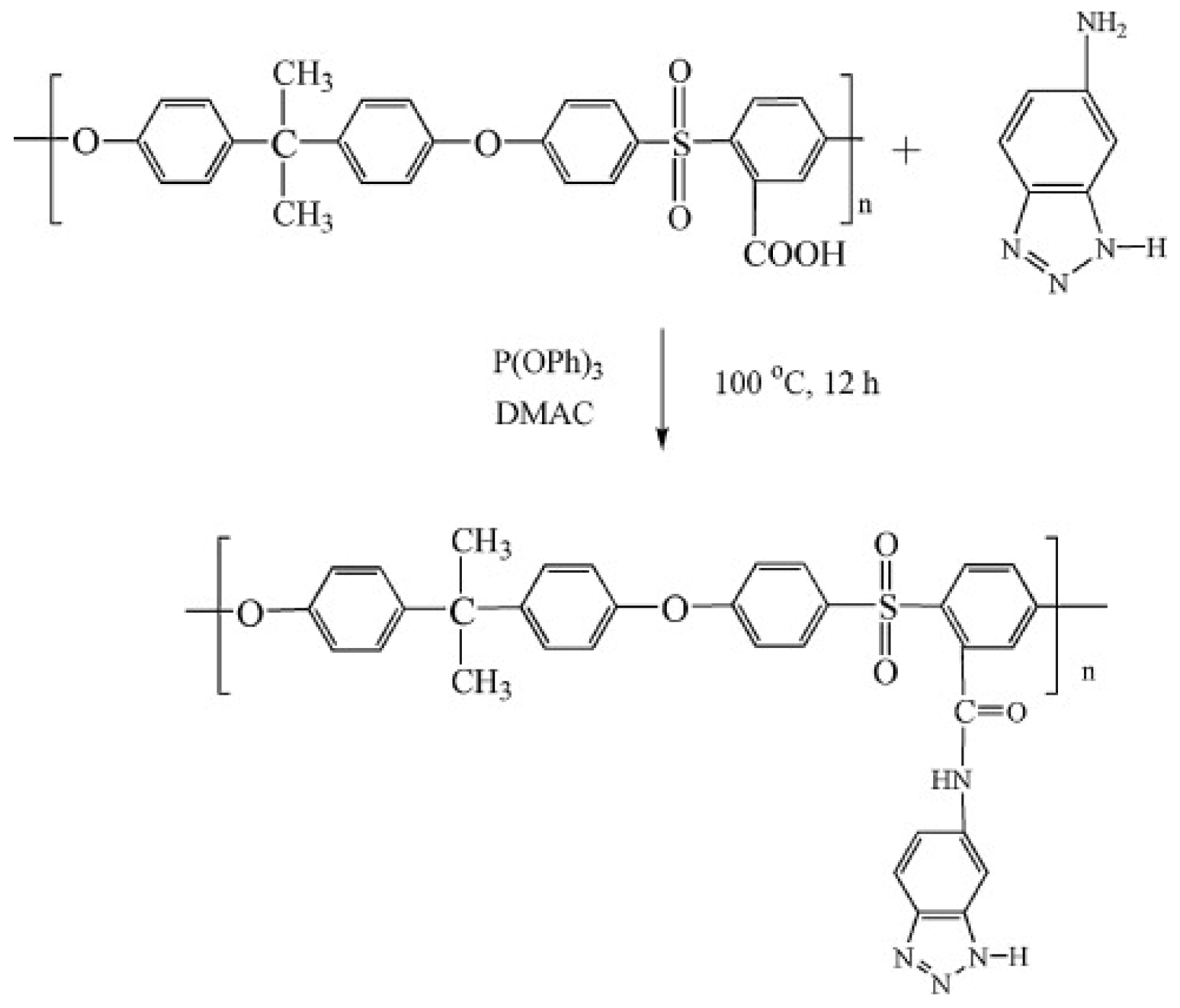
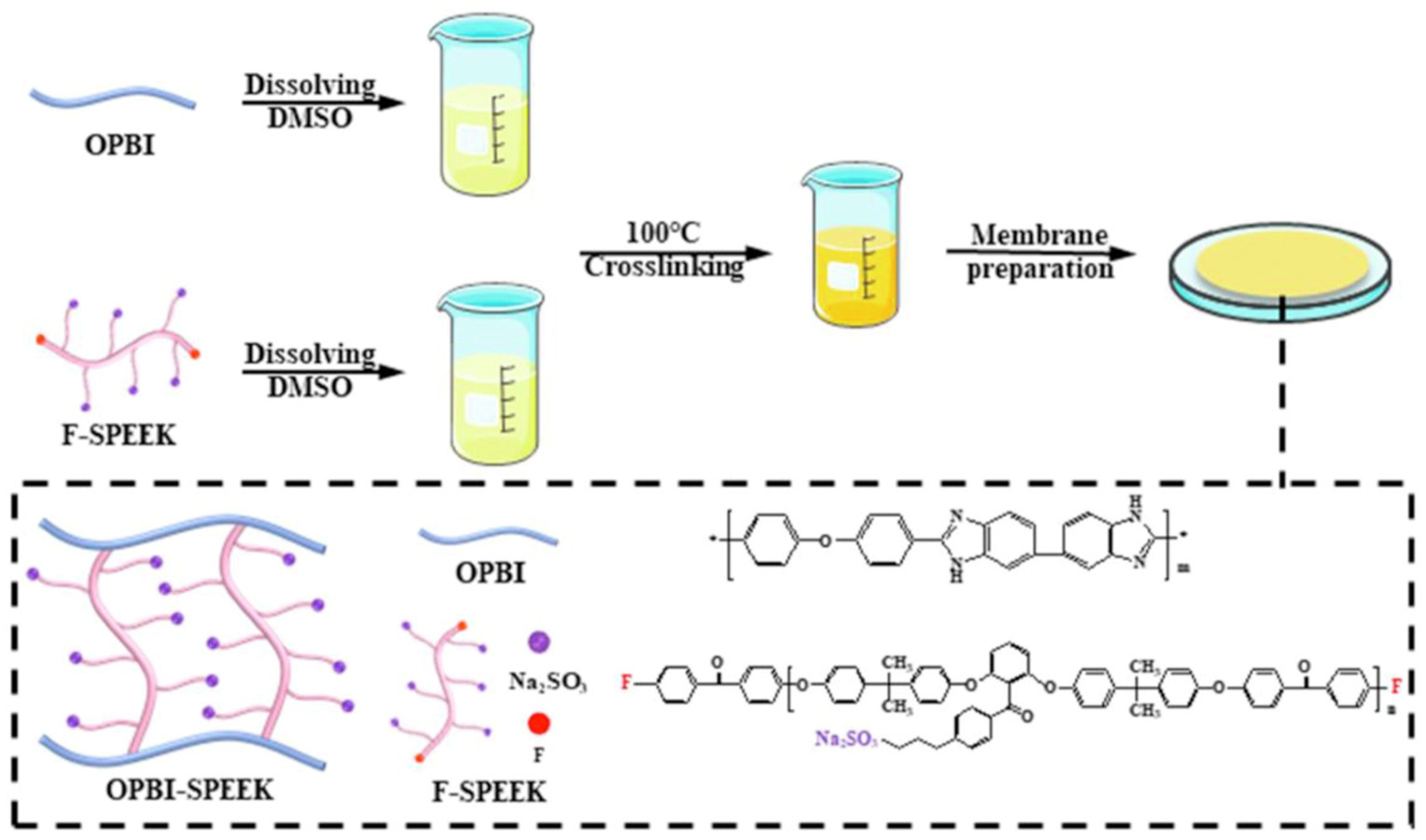
3.2. SPEEK/Imidazole Composite Membrane
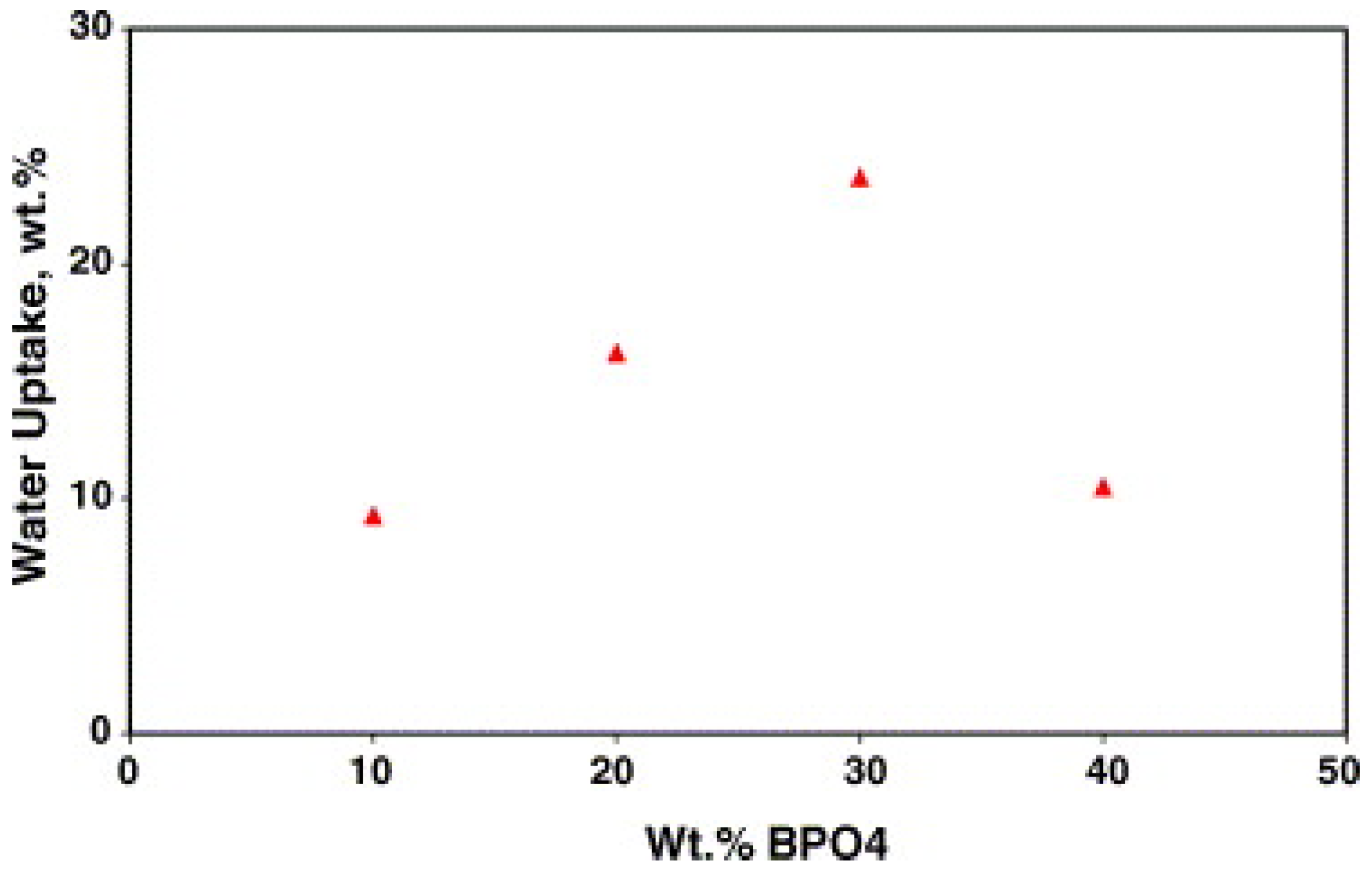
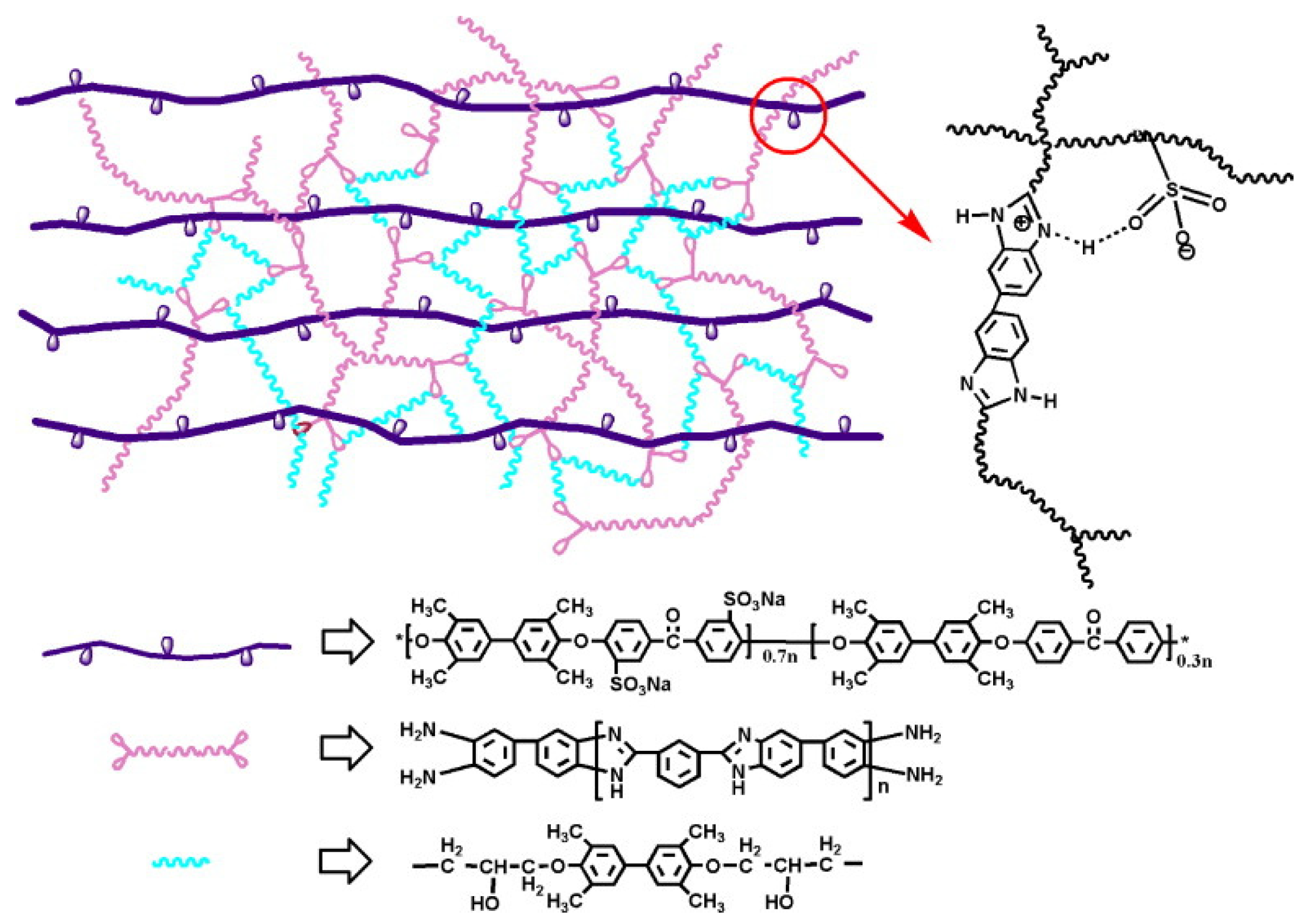
3.3. SPEEK/Fluorinated Polymer Composite Membrane
4. Conclusions and Outlook
- The proton conductivity of the composite membrane material needs to be balanced: Reducing its water uptake and swelling to maintain the dimensional stability of the membrane often comes at the expense of reducing proton conductivity. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce materials such as graphene, functionalized graphene, or conductive inorganic materials to maintain a high level of proton conduction performance for the SPEEK membranes;
- Chemical stability still needs to be improved: The development of new composite membranes or modification methods have effectively enhanced the antioxidant properties and chemical degradation resistance of SPEEK membranes, which is usually tested and verified using the Fenton test. However, there is still a lack of long-term in situ PEMFC operation tests, especially the dry–wet cycles during the start–stop process of the fuel cell, which may intensify the free radical reactions of the composite membrane, thereby accelerating the chemical degradation of the membrane. Current comprehensive performance tests of fuel cells lack in situ tests of the membrane to evaluate the stability of the membrane material in actual fuel cell work;
- Cost-effectiveness still needs to be comprehensively considered based on cost–performance: Research and development of cost-effective preparation and sulfonation methods for SPEEK, as well as manufacturing processes for composite membranes, are needed to promote its commercial application. Among the currently developed composite membranes, Nafion has the highest comprehensive energy efficiency, but its high price and complex preparation process limit its widespread commercial application. In addition, Nafion membrane may degrade during long-term use. The degradation products of Nafion may include short-chain fluorides, sulfur-containing compounds, and volatile organic compounds containing fluorine. These substances may have an impact on the environment, especially when they are released into it. Fluorides and certain fluorinated compounds have been proven to be bioaccumulative and toxic, potentially posing a threat to ecosystems and human health. However, new materials that do not contain F such as SPEEK, SPBI, PVDF, SPI, etc., have been developed as a new generation of PEMs due to their price advantage and excellent mechanical properties. However, these new materials still have a significant gap compared to Nafion in terms of proton conductivity and hydrophilicity, and it is hoped that by combining them with other organic or inorganic materials with good proton conductivity and price advantage, the performance of the membrane can reach and even surpass that of Nafion, while improving the cost-effectiveness of the membrane;
- Environmental impact assessment: It is still necessary to assess the life cycle environmental impact of SPEEK and its composite membranes in PEMFCs, especially the main components after the degradation of SPEEK, as well as whether the components after degradation are toxic, environmentally friendly, and whether they pollute the environment, which still needs to be studied, in order to truly promote the green and healthy development of sustainable energy technology;
- Exploration of new composite strategies: Explore and develop new organic–inorganic composite strategies, using nanotechnology and other advanced materials science methods to further improve the performance of SPEEK-based membranes. For example, zipper membranes, amphoteric membranes, self-healing membranes, etc., have been reported in some applications. It is well known that PEMs are prone to stress concentration during operation, which may lead to local physical defects in the membrane material, such as pinholes, cracks, etc. Membranes with self-healing functions can recover their integrity after physical defects by the movement of molecular chain segments and the recombination of intermolecular chemical bonds. Whether such membranes can be further used in PEMFCs still needs to be explored.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S.C.; Adroher, X.C. A Review of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: Technology, Applications, and Needs on Fundamental Research Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovač, A.; Paranos, M.; Marciuš, D. Hydrogen in Energy Transition: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 10016–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, H.; Louis, C.; Jose, S.; Prakash, J.; Muthuswamy, N.; Buan, M.E.M.; Flox, C.; Chavan, S.; Shi, X.; Kauranen, P.; et al. Is the H2 Economy Realizable in the Foreseeable Future? Part I: H2 Production methods. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 13777–13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su-ungkavatin, P.; Tiruta-Barna, L.; Hamelin, L. Biofuels, Electrofuels, Electric or Hydrogen?: A Review of Current and Emerging Sustainable Aviation Systems. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2023, 96, 101073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veziroğlu, T.N.; Şahin, S. 21st Century’s Energy: Hydrogen Energy System. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Dooner, M.; Clarke, J. Overview of Current Development in Electrical Energy Storage Technologies and the Application Potential in Power System Operation. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 511–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.O.; Popoola, A.P.I.; Ajenifuja, E.; Popoola, O.M. Hydrogen Energy, Economy and Storage: Review and Recommendation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15072–15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, M.K.; Nijhawan, P.; Oberoi, A.S. Hydrogen fuel and fuel cell technology for cleaner future: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 15607–15626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, F.; Yusuf, M.; Arham Khan, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Ekeoma, B.C.; Kamyab, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Nadda, A.K.; Chelliapan, S. A State-of-The-Art Review on the Latest Trends in Hydrogen Production, Storage, and Transportation Techniques. Fuel 2023, 340, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, E.B.; Nutakor, C.; Agwa, A.M.; Kamel, S. A Critical Review of Renewable Hydrogen Production Methods: Factors Affecting Their Scale-Up and Its Role in Future Energy Generation. Membranes 2022, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.A.; Ramadan, H.S.; Saleh, M.A.; Hissel, D. Hydrogen Storage Technologies for Stationary and Mobile Applications: Review, Analysis and Perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 149, 111311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, O.Z.; Orhan, M.F. An Overview of Fuel Cell Technology: Fundamentals and Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 810–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahimai, B.M.; Sivasubramanian, G.; Sekar, K.; Kannaiyan, D.; Deivanayagam, P. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone): Efficient Ion-Exchange Polymer Electrolytes for Fuel Cell Applications–a Versatile Review. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 6085–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, Y.; Hosseini, S.E.; Butler, B.; Alzhahrani, H.; Fou, B.T.; Ashuri, T.; Krohn, J. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles; Current Status and Future Prospect. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Meng, X.; Tang, X.; Li, H.; Hasanien, H.; Alharbi, M.; Dong, Z.; Shen, J.; Sun, C.; Fan, F.; et al. An Accurate Parameter Estimation Method of the Voltage Model for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Energies 2024, 17, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Xuan, J.; Du, Q.; Bao, Z.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; et al. Designing the next Generation of Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Nature 2021, 595, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikukawa, M.; Sanui, K. Proton-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Based on Hydrocarbon Polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1463–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Review of Advanced Materials for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7303–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.B.; Mohammadi, F.; Hooshyari, K. Recent Approaches to Improve Nafion Performance for Fuel Cell Applications: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28919–28938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, D.N.; Timurkutluk, B.; Altinisik, K. Effects of Operation Temperature and Reactant Gas Humidity Levels on Performance of PEM Fuel Cells. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Shukla, A.K. Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: Principles and Advances. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lei, J.-D. Recent Developments in High-Performance Nafion Membranes for Hydrogen Fuel Cells applications. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, G.H.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, N.Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Park, C.R. Molecular Engineering of Hydrocarbon Membrane to Substitute Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Membrane for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Operation. Mater. Today Energy 2020, 17, 100483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorgna, M.; Mensitieri, G.; Scherillo, G.; Shaw, M.T.; Swier, S.; Weiss, R.A. Polymer Blend for Fuel Cells Based on SPEKK: Effect of Cocontinuous Morphology on Water Sorption and Proton Conductivity. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2007, 45, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, Y.; Devrim, Y. Micro-Cogeneration Application of a High-Temperature PEM Fuel Cell Stack Operated with Polybenzimidazole Based membranes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 35198–35207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailenko, S.D.; Zaidi, S.M.J.; Kaliaguine, S. Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone Based Composite Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Catal. Today 2001, 67, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanwar, P.; Bhattad, S.S. Preparation and Physical Characterization of Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) and Polypyrrole Composite Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2019, 5, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocakulak, T.; Taşkın, G.; Tabanlıgil Calam, T.; Solmaz, H.; Calam, A.; Arslan, T.A.; Şahin, F. A New Nanocomposite Membrane Based on Sulfonated Polysulfone Boron Nitride for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Its Fabrication and Characterization. Fuel 2024, 374, 132476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.F.M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kuroda, C.S.; Takimoto, N.; Ohira, A. Free Volume, Oxygen Permeability, and Uniaxial Compression Storage Modulus of Hydrated Biphenol-Based Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone). J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, J.A.; Benicewicz, B.C. Sulfonated Polybenzimidazoles for High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6706–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Jana, T.; Modestra, J.A.; Naresh Kumar, A.; Mohan, S.V. Highly Efficient Sulfonated Polybenzimidazole as a Proton Exchange Membrane for Microbial Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 317, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Olvera-Mancilla, J.; Alexandrova, L.; del Castillo, L.F.; Compañ, V. Recent Progress in the Development of Composite Membranes Based on Polybenzimidazole for High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kins, C.F.; Sengupta, E.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Wagner, M.; Lieberwirth, I.; Spiess, H.W.; Hansen, M.R. Morphological Anisotropy and Proton Conduction in Multiblock Copolyimide Electrolyte Membranes. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 2645–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Wang, G.; Tanaka, M.; Kawakami, H. Sulfonated Block-Graft Copolyimide for High Proton Conductive and Low Gas Permeable Polymer Electrolyte Membrane. J. Power Sources 2012, 216, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, P.; Kamarudin, S.; Masdar, M. Improved Performance of Sulfonated Polyimide Composite Membranes with Rice Husk Ash as a Bio-Filler for Application in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.M.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Dickmann, M.; Abdel-Hady, E.E.; Mohamed, H.F.M.; Abdel-Hamed, M.O. Crosslinked PVA/SSA Proton Exchange Membranes: Correlation between Physiochemical Properties and Free Volume Determined by Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 28287–28299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hady, E.E.; Mohamed, H.F.; Abdel-Hamed, M.O.; Gomaa, M.M. Physical and electrochemical properties of PVA/TiO2 nanocomposite membrane. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3842–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, S.; Abdel-Hady, E.E.; Mohamed, H.F.M.; Elsharkawy, Y.S.; Gomaa, M.M. Non-Fluorinated PVA/SSA Proton Exchange Membrane Studied by Positron Annihilation Technique for Fuel Cell Application. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 3322–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.M.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Dickmann, M.; Abdel-Hamed, M.O.; Abdel-Hady, E.E.; Mohamed, H.F.M. Free Volume of PVA/SSA Proton Exchange Membrane Studied by Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectroscopy. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 132, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Mei, J.; Tang, X.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C.; Song, K. The Degradation Prediction of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance Based on a Transformer Model. Energies 2024, 17, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, D.; Arai, H.; Morita, S.; Kitagawa, K. Chemical Degradation of Nafion Ionomer at a Catalyst Interface of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell by Hydrogen and Oxygen Feeding in the anode. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.O.; Kunz, H.R.; Fenton, J.M. Membrane Degradation Mechanisms in PEMFCs. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, B652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, P.C.; Ben Belgacem, I.; Emori, W.; Uzoma, P.C. Nafion Degradation Mechanisms in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) System: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 27956–27973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, X.Z.; Martin, J.J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Wu, S.; Merida, W. A Review of PEM Fuel Cell Durability: Degradation Mechanisms and Mitigation Strategies. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Negro, E.; Nale, A.; Pagot, G.; Vezzù, K.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Meda, L.; Gambaro, C.; Di Noto, V. An Efficient Barrier toward Vanadium Crossover in Redox Flow Batteries: The Bilayer [Nafion/(WO3)x] Hybrid Inorganic-Organic Membrane. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 378, 138133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickner, M.A.; Ghassemi, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Einsla, B.R.; McGrath, J.E. Alternative Polymer Systems for Proton Exchange Membranes (PEMs). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4587–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhao, C.; Na, H.; Zhao, C. Electrochemical Properties of Sulfonated PEEK Used for Ion Exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 254, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, S.; Ruffmann, B.; Buder, I.; Nunes, S.P. Proton Conductive Membranes of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ketone Ketone). J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 260, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliaguine, S.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Wang, K.P.; Xing, P.; Robertson, G.; Guiver, M. Properties of SPEEK Based PEMs for Fuel Cell application. Catal. Today 2003, 82, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Liu, B.; Han, X.; Song, Y. Novel Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Keton)/Polyetherimide Acid-Base Blend Membranes for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Applications. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 130, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Ho, W.S.W. New Sulfonated Polybenzimidazole (SPBI) Copolymer-Based Proton-Exchange Membranes for Fuel cells. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2009, 40, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Yin, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L. Effect of Degree of Sulfonation and Casting Solvent on Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Membrane for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. J. Power Sources 2015, 285, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Kar, K.K. Impact of Degree of Sulfonation on Microstructure, Thermal, Thermomechanical and Physicochemical Properties of Sulfonated Poly Ether Ether Ketone. Polymer 2017, 109, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Manthiram, A. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2003, 6, A229–A231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Hu, J. Electrochemical Properties of Proton Exchange Membrane I: The Influence of Sulfonation Degree and Solvent. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, G.; Oh, T.H. TiO2 Containing Hybrid Composite Polymer Membranes for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. Polymers 2022, 14, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Duan, J.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Li, X. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Doped with Ammonium Ionic Liquids and Nano-Silicon Dioxide for Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Polymers 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. A Comparative Study on Physiochemical, Thermomechanical, and Electrochemical Properties of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Block Copolymer Membranes with and without Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Polymers 2019, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Mistri, E.A.; Banerjee, S.; Komber, H.; Voit, B. Highly Fluorinated Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) Copolymers: Synthesis and Evaluation of Proton Exchange Membrane Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2772–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Pak, C.; Kim, E.A.; Lee, Y.H.; Chang, H.; Seung, D.; Choi, Y.S.; Park, J.-B.; Kim, T.K. Functionalized Carbon Nanotube-Poly(Arylene Sulfone) Composite Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells with Enhanced Performance. J. Power Sources 2008, 180, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Basem, A.; Azam, A.; Rizvi, S.J.A.; Rashid, F.L. Synthesis, Characterization and Optimization of Sulfonated Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone (sPEEK)/Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes (c-CNTs) Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell application. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2024, 52, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasubramanian, G.; Hariharasubramanian, K.; Deivanayagam, P.; Ramaswamy, J. High-Performance SPEEK/SWCNT/Fly Ash Polymer Electrolyte Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Polym. J. 2017, 49, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Zhong, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Fu, T.; Na, H. Synthesis and Characterization of a Series of SPEEK/TiO2 Hybrid Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarizadeh, P.; Javanbakht, M.; Pourmahdian, S.; Hazer, M.S.A.; Hooshyari, K.; Askari, M.B. Novel Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Proton Conductive Sulfonated PAMPS/PSSA-TiO2 Hybrid Nanoparticles and Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 3099–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Trindade, L.G.; Borba, K.M.N.; Zanchet, L.; Lima, D.W.; Trench, A.B.; Rey, F.; Diaz, U.; Longo, E.; Bernardo-Gusmão, K.; Martini, E.M.A. SPEEK-Based Proton Exchange Membranes Modified with MOF-Encapsulated Ionic liquid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 236, 121792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard Bowen, W.; Doneva, T.A.; Yin, H.B. Polysulfone—Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether) Ketone Blend Membranes: Systematic Synthesis and Characterisation. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 181, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.H.; Thiam, H.S.; Tee, S.F.; Lim, Y.S.; Saw, L.H.; Lai, S.O. Self-Healing Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)-Based Polymer Electrolyte Membrane for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells: Effect of Solvent Content. Polymers 2023, 15, 4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J. A Highly Stretchable, Self-Healing, Recyclable and Interfacial Adhesion Gel: Preparation, Characterization and Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Hu, P.; Liu, Y. Construction of Proton Transport Channels in Cross-Linked Composite Membrane with Highly Sulfonated SPEEK nanofibers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, X.; Miao, J.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Q. Novel Nanofiber-Enhanced SPEEK Proton-Exchange Membranes with High Conductivity and stability. Polymer 2020, 210, 123016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.-H.; Lee, K.-S.; Lee, J.-S. Cross-Linking Density Effect of Fluorinated Aromatic Polyethers on Transport Properties. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, R.; Ledjeff, K.; Bauer, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Partially Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone)—A Versatile Proton Conducting Membrane Material for Modern Energy Conversion Technologies. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 83, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Wang, K.; Kaliaguine, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) for Proton Exchange Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 229, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, E.R.; Xie, X.Y.; Zhu, H.T.; Liu, G.C.; Xu, C.Y.; Wu, S. Research progress on Nafion and SPEEK modification of all vanadium redox flow battery separator. Ind. Miner. Process. 2024, 53, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.; Advani, S.G.; Prasad, A.K. A Functional Monomer to Synthesize Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) with Sulfonic Acid Group in the Pendant Side Chain. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 3331–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, P.; Huang, J.; Chen, W. Preparation of Highly H+ Permeable Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Cation Exchange Membranes and Their Applications in Electro-Generation of Thioglycolic Acid. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. A Significantly Improved Membrane for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4380–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Marvel, C.S. Polyaromatic Ether-Ketone Sulfonamides Prepared from Polydiphenyl Ether-Ketones by Chlorosulfonation and Treatment with Secondary Amines. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1984, 22, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.T.; Karasz, F.E.; Russo, P.S.; Langley, K.H. Solubility and Properties of a Poly(Aryl Ether Ketone) in Strong Acids. Macromolecules 1985, 18, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmazoğlu, M.; Bayıroğlu, F.; Erdemi, H.; Abaci, U.; Guney, H.Y. Dielectric Properties of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) Electrolytes with 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate Salt: Ionic Liquid-Based Conduction Pathways. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 611, 125825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 226, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Clarizia, G.; Gugliuzza, A.; Ebrasu, D.; Bevilacqua, A.; Trotta, F.; Basile, A. Sulfonation of PEEK-WC Polymer via Chloro-Sulfonic Acid for Potential PEM Fuel Cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12688–12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, D.; Frey, H.; Kreuer, K.D.; Heinzel, A.; Mülhaupt, R. Carboxylated and Sulfonated Poly(Arylene-Co-Arylene Sulfone)s: Thermostable Polyelectrolytes for Fuel Cell Applications. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 7936–7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haragirimana, A.; Li, N.; Hu, Z.; Chen, S. A Facile, Effective Thermal Crosslinking to Balance Stability and Proton Conduction for Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Blend Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 15866–15877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; He, G. Facile Fabrication of Amphoteric Semi-Interpenetrating Network Membranes for Vanadium Flow Battery Applications. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; De Feyter, S.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Poly(Sulfone)/Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Blend Membranes: Morphology Study and Application in the Filtration of Alcohol Based Feeds. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 324, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arigonda, M.; Deshpande, A.P.; Varughese, S. Effect of PES on the Morphology and Properties of Proton Conducting Blends with Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 5100–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, E.; Erdener, H.; Akay, R.G.; Yücel, H.; Baç, N.; Eroğlu, İ. Effects of Sulfonated Polyether-Etherketone (SPEEK) and Composite Membranes on the Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhan, S.; Muruganantham, R.; Sangeetha, D.; Guhan, S.; Muruganantham, R.; Sangeetha, D. Development of a Solid Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Based on Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether)Ketone and Polysulfone for Fuel Cell Applications. Can. J. Chem. 2012, 90, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Manthiram, A.; Guiver, M.D. Blend Membranes Based on Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) and Polysulfone Bearing Benzimidazole Side Groups for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, Y.-Z.; Manthiram, A.; Guiver, M.D. Blend Membranes Consisting of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) and Polysulfone Bearing 4-Nitrobenzimidazole for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, B258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Manthiram, A.; Guiver, M.D. Acid–Base Blend Membranes Consisting of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) and 5-Amino-Benzotriazole Tethered Polysulfone for DMFC. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-L.; Ma, C.-C.M.; Liu, F.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Chiang, C.-L. Preparation and Characterization of Poly(Ether Sulfone)/Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Blend Membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, S.N.S.S.; Norddin, M.N.A.M.; Jaafar, J.; Sudirman, R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F. Highly Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Blend with Hydrophobic Polyether Sulfone as an Alternative Electrolyte for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 6189–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Ning, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, N.; Hu, Z.; Chen, S. Preparation and Characterizations of Cross-linked Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Partially Fluorinated Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Blend Membranes. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Poudel, M.B.; Chu, J.Y.; Vinothkannan, M.; Santhosh Kumar, R.; Logeshwaran, N.; Park, B.-H.; Han, M.-K.; Yoo, D.J. Advanced Performance and Ultra-High, Long-Term Durability of Acid-Base Blended Membranes over 900 Hours Containing Sulfonated PEEK and Quaternized Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) in H2/O2 Fuel cells. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 254, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Im, K.S.; Kabir, M.M.; Shon, H.K.; Nam, S.Y. Polybenzimidazole (PBI)-Based Membranes for Fuel Cell, Water Electrolysis and desalination. Desalination 2024, 579, 117500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yang, M.; Sun, C.; Xu, S. Liquid Water Characteristics in the Compressed Gradient Porosity Gas Diffusion Layer of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Using the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Energies 2023, 16, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authayanun, S.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K.; Arpornwichanop, A. Comparison of High-Temperature and Low-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Systems with Glycerol Reforming Process for Stationary Applications. Appl. Energy 2013, 109, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.; Wen, Y.; Ma, Z.-F.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Song, S.; Zhang, J. High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Progress in Advanced Materials and Key Technologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1138–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Qu, E.; Xiao, M.; Han, D.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. 3D Network Structural Poly (Aryl Ether Ketone)-Polybenzimidazole Polymer for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 4563860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartarone, E.; Angioni, S.; Mustarelli, P. Polymer and Composite Membranes for Proton-Conducting, High-Temperature Fuel Cells: A Critical Review. Materials 2017, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, E.; Hao, X.; Xiao, M.; Han, D.; Huang, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. Proton Exchange Membranes for High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Challenges and Perspectives. J. Power Sources 2022, 533, 231386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Fu, T.; Shi, Y.; Na, H. Composite Membranes Based on Highly Sulfonated PEEK and PBI: Morphology Characteristics and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.; Ullrich, A.; Meier, F.; Häring, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Acid–Base Polymer Blends for Application in Membrane Fuel Cells. Solid State Ion. 1999, 125, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviani, M.; Fluitman, S.P.; Loos, K.; Portale, G. Highly Stable Membranes of Poly(Phenylene Sulfide Benzimidazole) Cross-Linked with Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes for High-Temperature Proton Transport. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 7873–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Choi, S.-W.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.-H.; Sung, Y.-E.; Lee, J.-C. Cross-Linked Highly Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) Membranes Prepared by in-Situ Casting and Thiol-Ene Click Reaction for Fuel Cell Application. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, R.G.; Ata, K.C.; Kadıoğlu, T.; Çelik, C. Evaluation of SPEEK/PBI Blend Membranes for Possible Direct Borohydride Fuel Cell (DBFC) application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18702–18711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, T.K.; Singh, J.; Majhi, J.; Ahuja, A.; Maiti, S.; Dixit, P.; Bhushan, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Advances in Polybenzimidazole Based Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications That Overcome Nafion Membranes constraints. Polymer 2022, 255, 125151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupathi, S.; Ji, S.; Jan Bladergroen, B.; Linkov, V. High DMFC Performance Output Using Modified Acid–Base Polymer blend. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 3132–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.-W.; Hsu, S.L.-C. Synthesis and Properties of a New Fluorine-Containing Polybenzimidazole for High-Temperature Fuel-Cell Applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 4508–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y. Compatible Ionic Crosslinking Composite Membranes Based on SPEEK and PBI for High Temperature Proton Exchange membranes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 12069–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman Javed, R.M.; Al-Othman, A.; Tawalbeh, M.; Olabi, A.G. Recent Developments in Graphene and Graphene Oxide Materials for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, H.A.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. A Review of Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Protic Ionic Liquid/Polymer Blends for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 484, 229197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, R.R.R.; Walvekar, R.; Wong, W.Y.; Khalid, M.; Pang, M.M. Proton Conductivity Enhancement at High Temperature on Polybenzimidazole Membrane Electrolyte with Acid-Functionalized Graphene Oxide Fillers. Membranes 2022, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.M.J. Preparation and Characterization of Composite Membranes Using Blends of SPEEK/PBI with Boron phosphate. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 4771–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Ji, J. Highly Compatible Acid–Base Blend Membranes Based on Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) and Poly(Ether Ether Ketone-Alt-Benzimidazole) for Fuel Cells Application. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Novel Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/ Polybenzimidazole Blends for Proton Exchange Membranes. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Robertson, G.P.; Kim, D.-S.; Guiver, M.D.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z. Aromatic Poly(Ether Ketone)s with Pendant Sulfonic Acid Phenyl Groups Prepared by a Mild Sulfonation Method for Proton Exchange Membranes. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, H.; Luo, T.; Ouadah, A.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Jing, C.; Zhu, C. Sulfonated Graphene Oxide-doped Proton Conductive Membranes Based on Polymer Blends of Highly Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) and Sulfonated Polybenzimidazole. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, T.K.; Dixit, P.; Singh, J.; Talapatra, N.; Ray, M.; Chattopadhyay, S. A Novel Strategy toward the Advancement of Proton Exchange Membranes through the Incorporation of Propylsulfonic Acid-Functionalized Graphene Oxide in Crosslinked Acid-Base Polymer Blends. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 1482–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, G.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Ni, J.; et al. Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Polybenzimidazole Oligomer/Epoxy Resin Composite Membranes in Situ Polymerization for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Usages. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9916–9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, J.; Tang, N.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Du, W. Macromolecule Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Crosslinked Poly(4,4′-Diphenylether-5,5′-Bibenzimidazole) Proton Exchange Membranes: Broaden the Temperature Application Range and Enhanced Mechanical Properties. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 28246–28257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Park, J.-K. Blend Membranes Based on Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) and Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) for High Performance Direct Methanol Fuel Cell. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7464–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, T.Y.; Doğan, H.; Unveren, E.E.; Eker, E. Sulfonated PEEK and Fluorinated Polymer Based Blends for Fuel Cell Applications: Investigation of the Effect of Type and Molecular Weight of the Fluorinated Polymers on the Membrane’s Properties. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12038–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed Daud, S.N.S.; Mohd Norddin, M.N.A.; Jaafar, J.; Sudirman, R. High degree sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) blend with polyvinylidene fluoride as a potential proton-conducting membrane fuel cell. High Perform. Polym. 2020, 32, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
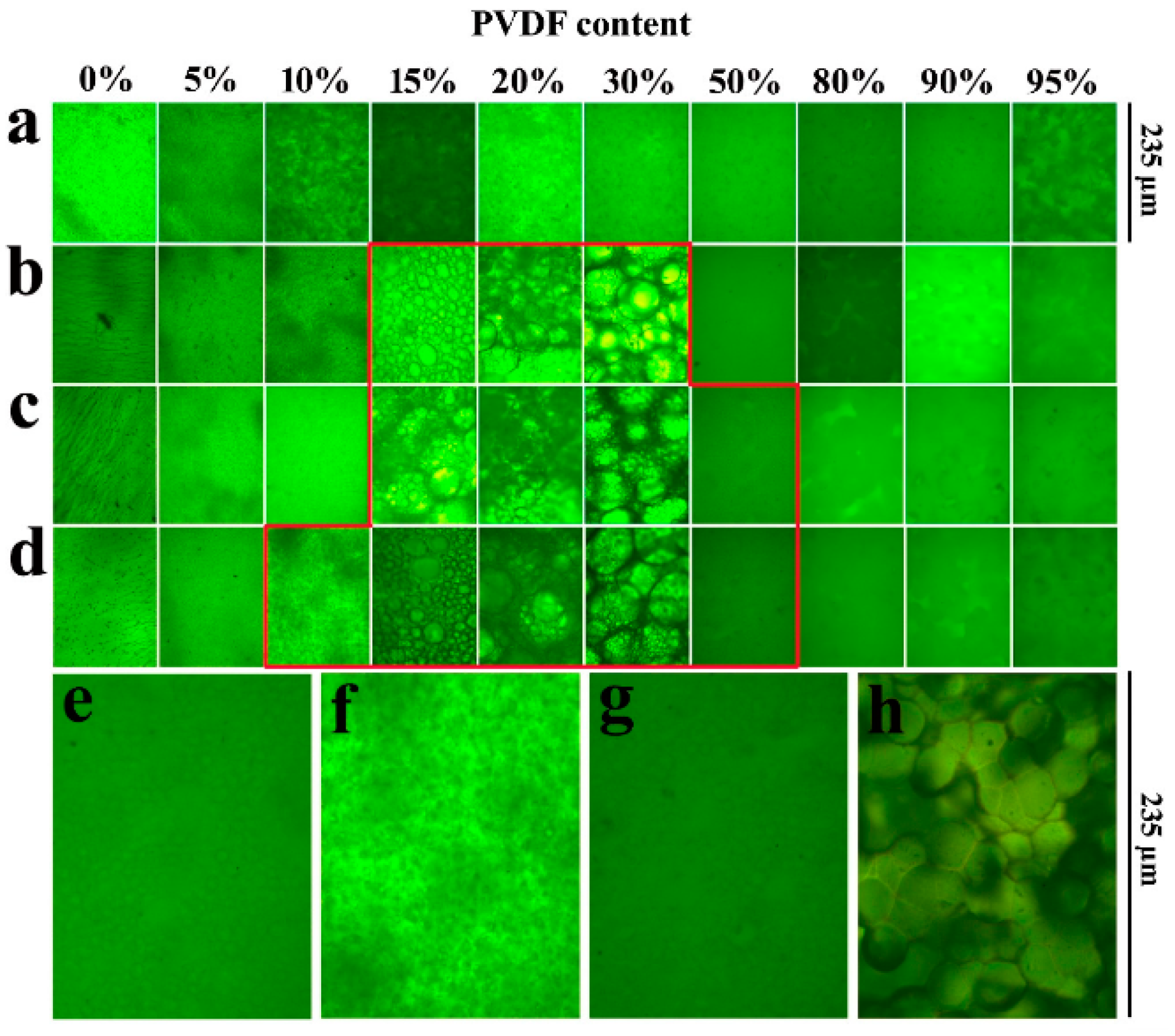
- He, S.; Zhai, S.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Y.; Yang, W.; Lin, J. Effect of Sulfonation Degree and PVDF Content on the Structure and Transport Properties of SPEEK/PVDF Blend Membranes. Polymers 2019, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Park, J.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Choi, Y.-W.; Yang, T.-H.; Yoon, Y.-G.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, W.-Y.; Park, S.-B. A Study on the Preferable Preparation Method of SPEEK/BPO4 Composite Membranes via an In Situ Sol–Gel Process. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalı, A.; Şahin, A.; Ar, İ. Experimental Investigation of Boron Phosphate Incorporated Speek/Pvdf Blend Membrane for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 40476–40490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.U.; Neelakandan, S.; Nagendran, A. Highly Selective Sulfonated Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride-Co-Hexafluoropropylene)/Poly(Ether Sulfone) Blend Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakandan, S.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Muthumeenal, A.; Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A. Fabrication and Electrochemical Properties of Surface Modified Sulfonated Poly(Vinylidenefluoride-Co-Hexafluoropropylene) Membranes for DMFC application. Solid State Ion. 2014, 268, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Beydaghi, H.; Salarizadeh, P.; Shabanikia, A.; Amoli, H.S. Sulfonated Poly(Etheretherketone) and Sulfonated Polyvinylidene Fluoride-Co-Hexafluoropropylene Based Blend Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39500–39510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, P.; Gayathri, R.; Pugalenthi, M.R.; Cao, G.; Liu, C.; Prabhu, M.R. Nanosulfonated Silica Incorporated SPEEK/SPVdF-HFP Polymer Blend Membrane for PEM Fuel Cell Application. Ionics 2020, 26, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tsen, W.-C.; Jang, S.-C.; Hu, F.; Zhong, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Wen, S.; Zheng, G.; Gong, C. Mechanically Robust and Highly Methanol-Resistant Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone)/Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Nanofiber Composite Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
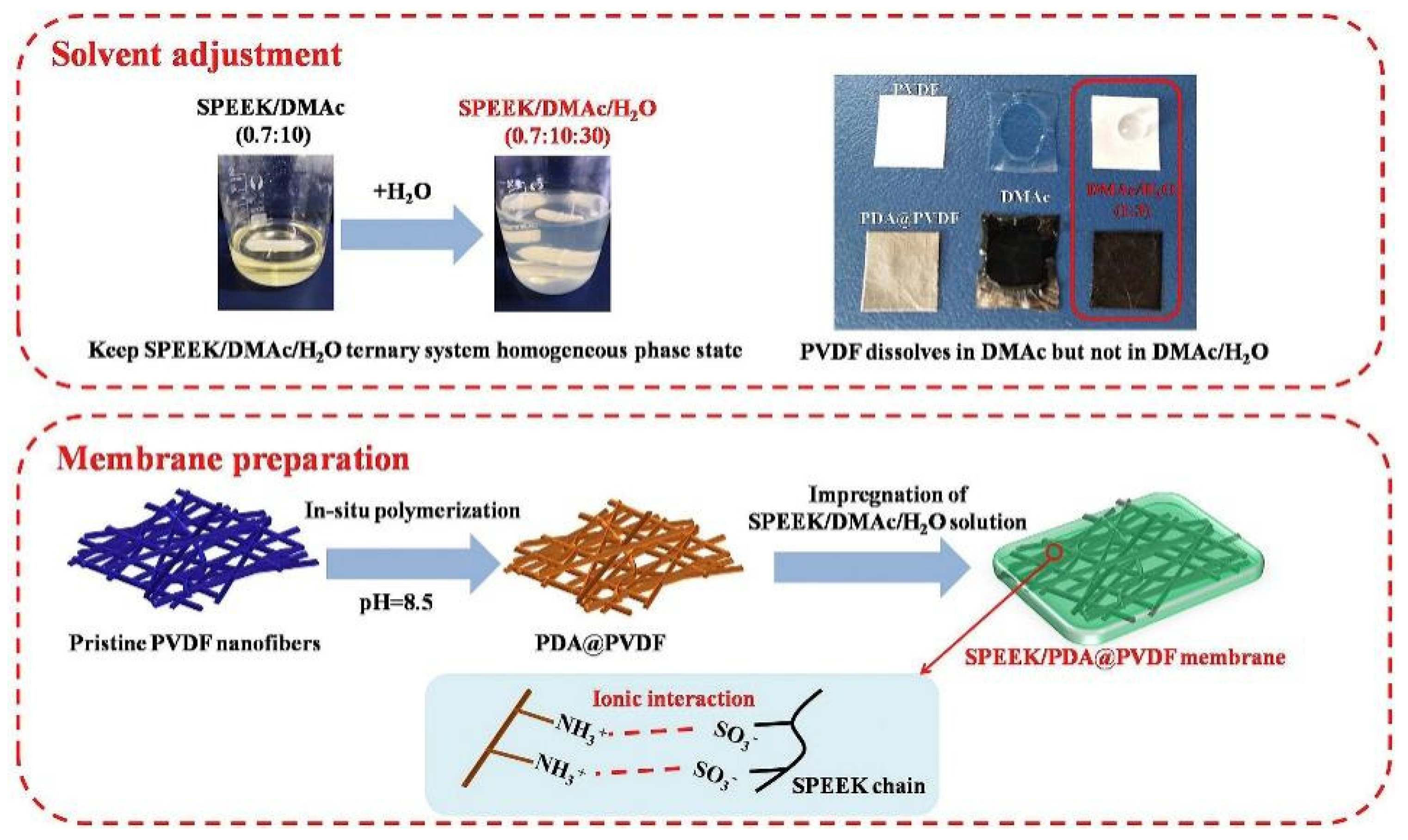
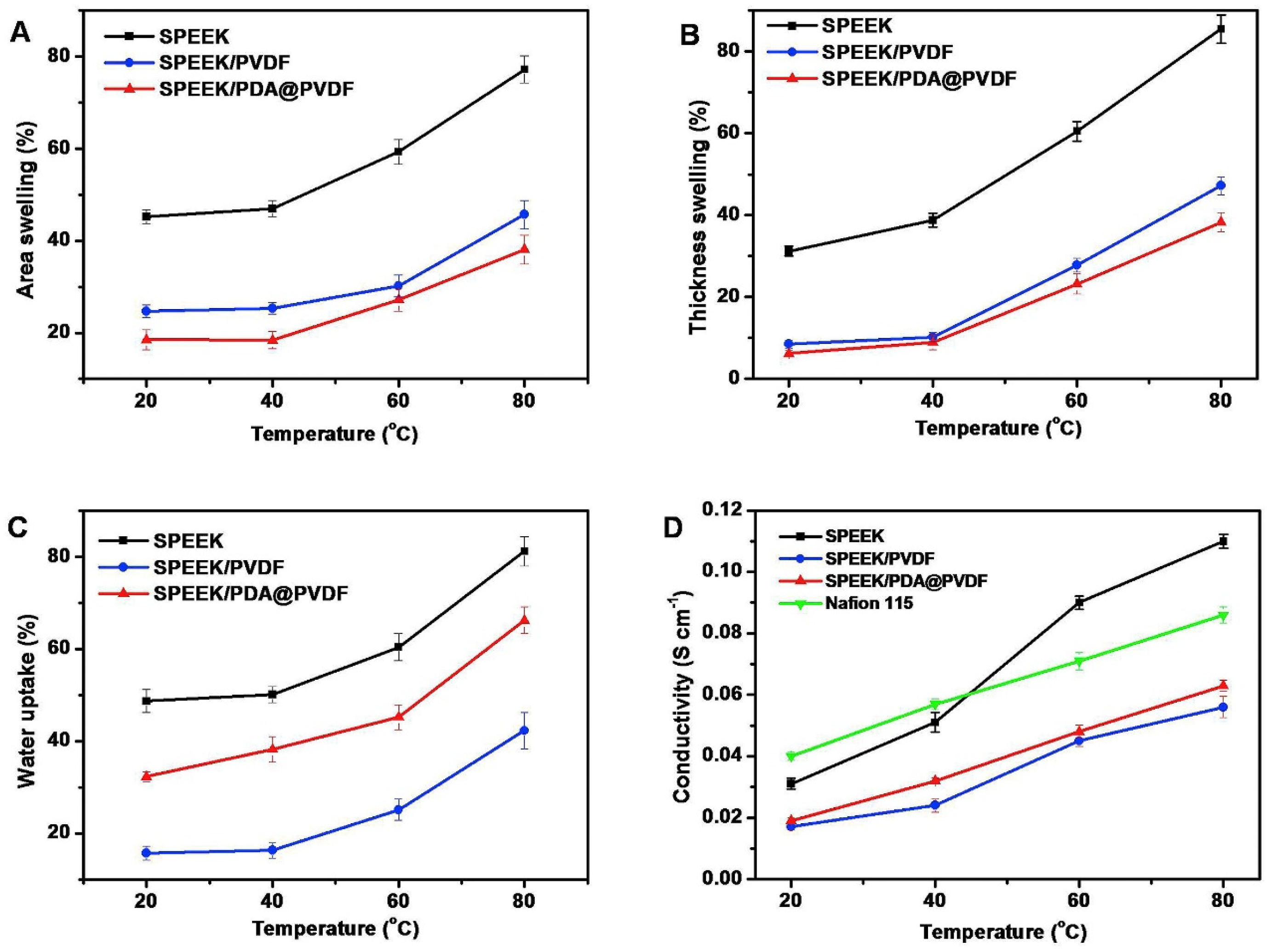
- Chu, J.; Ou, Y.; Cheng, F.; Liu, H.; Luo, N.; Hu, F.; Wen, S.; Gong, C. Achieving Better Balance on the Mechanical Stability and Conduction Performance of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Proton Exchange Membranes through Polydopamine/Polyethyleneimine Co-Modified Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Nanofiber as Support. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
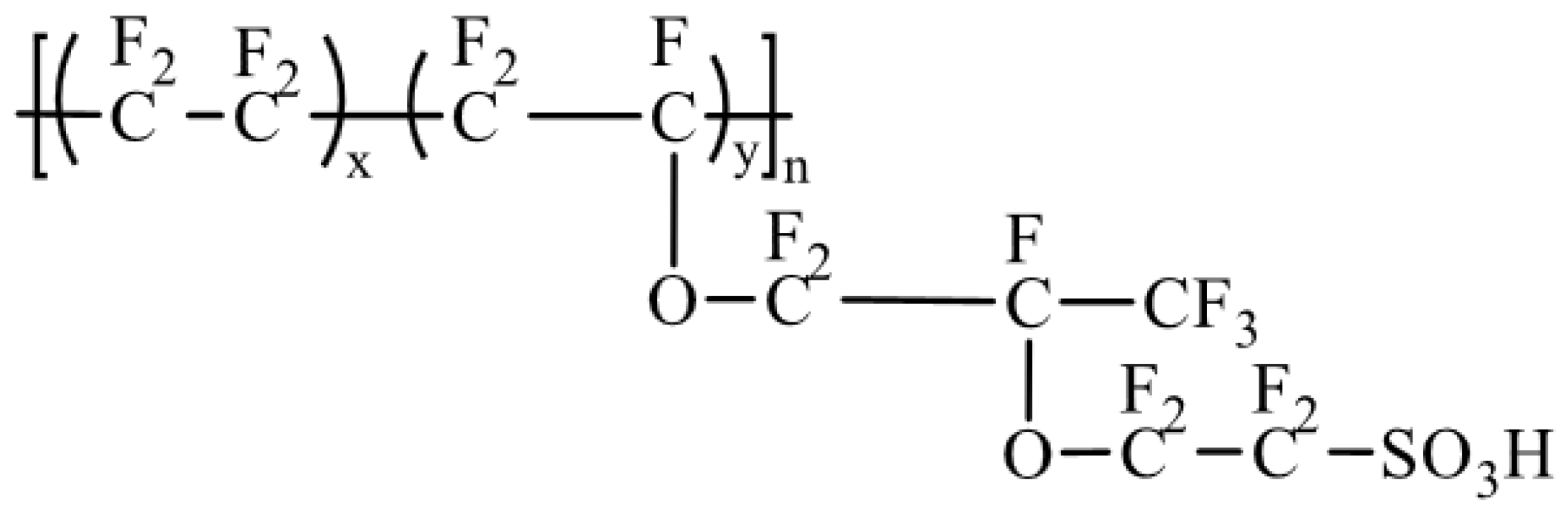
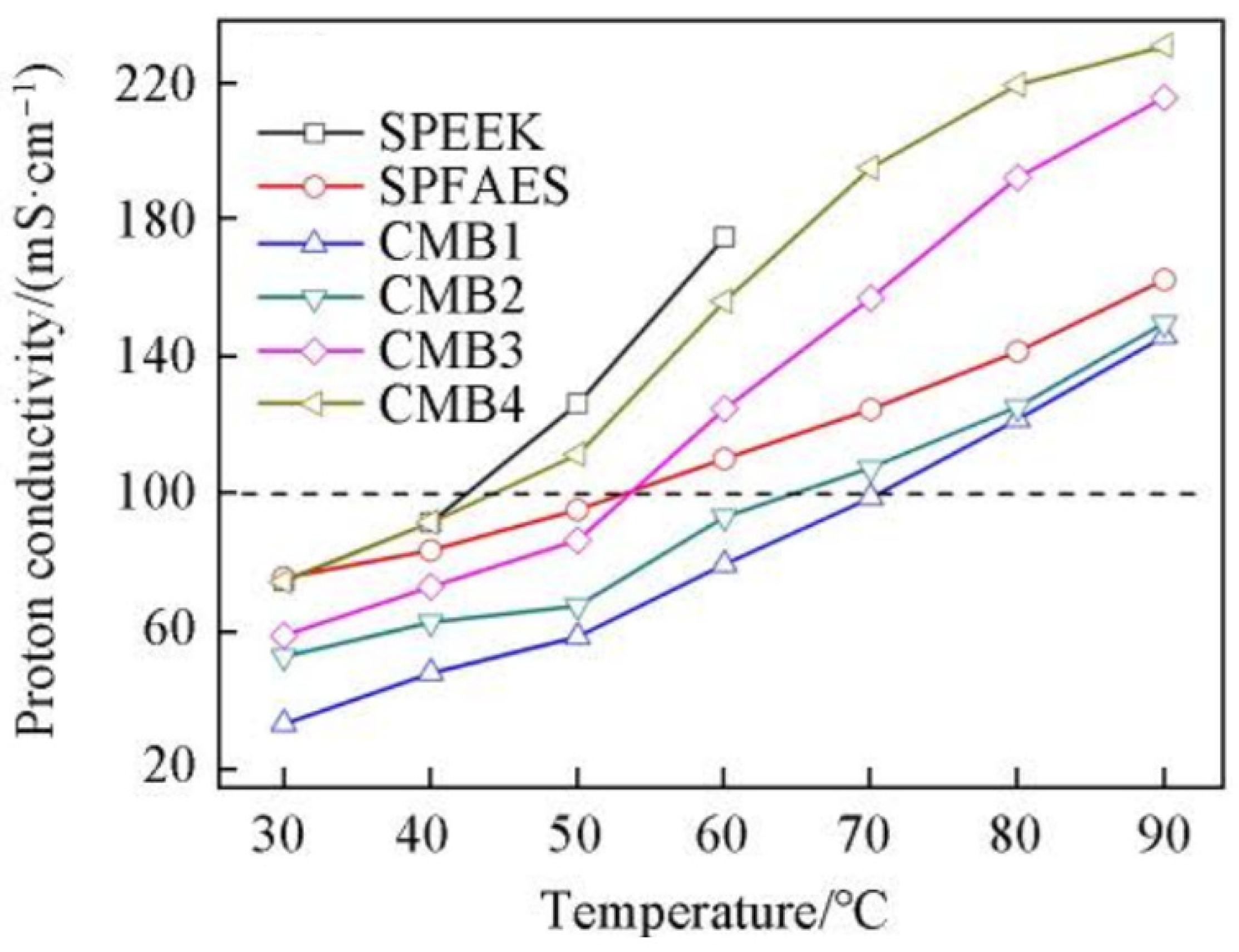



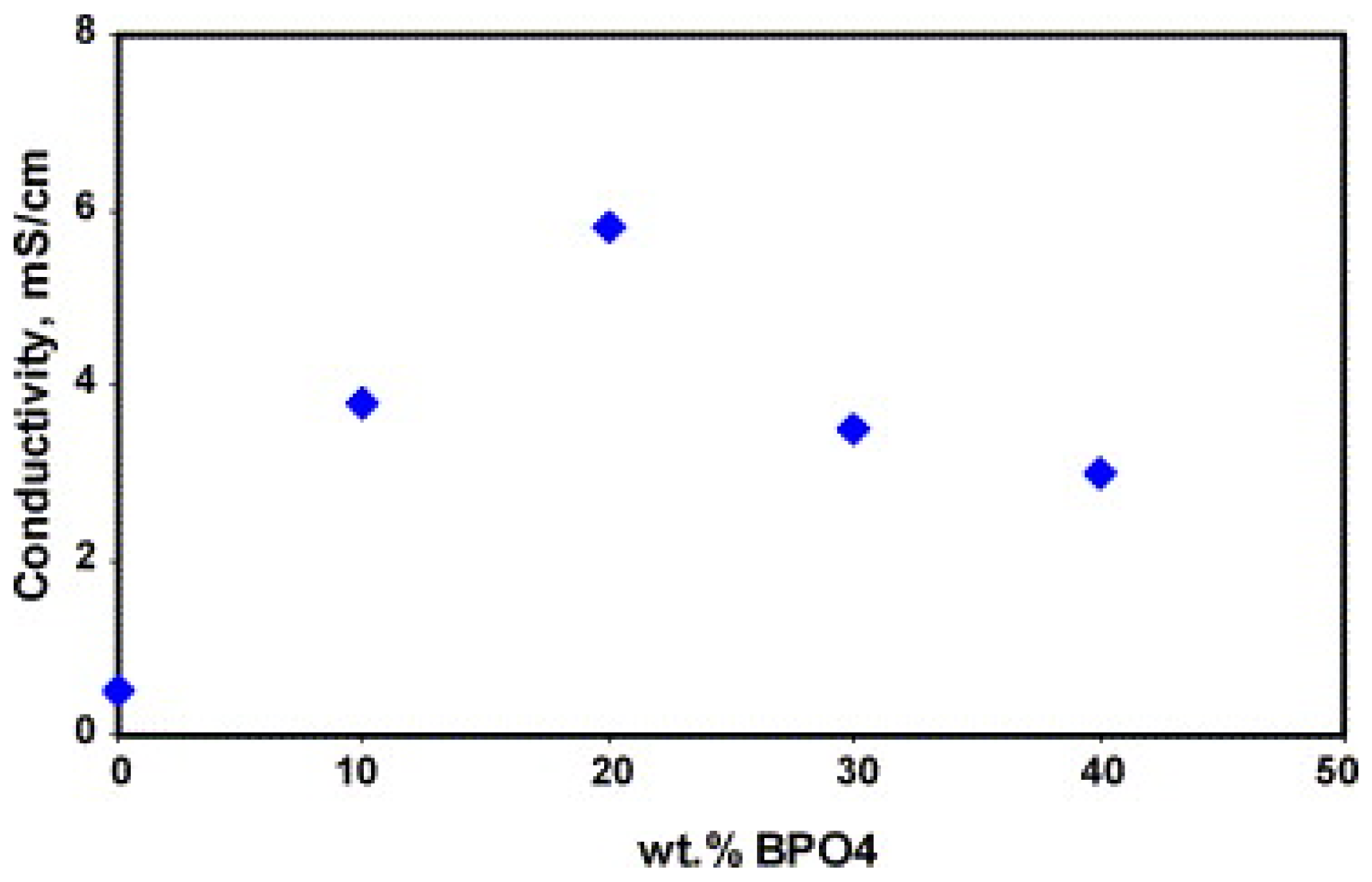
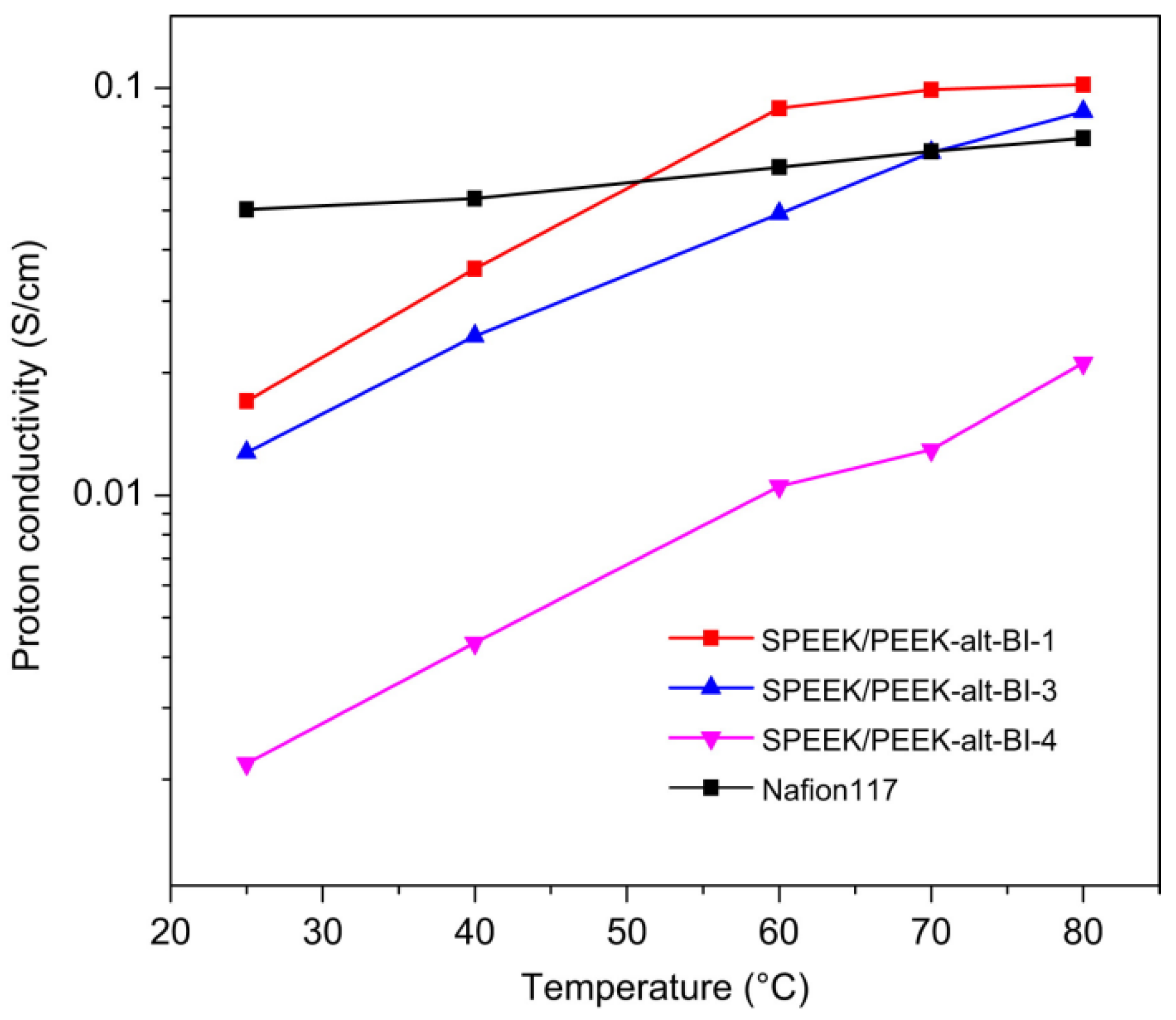
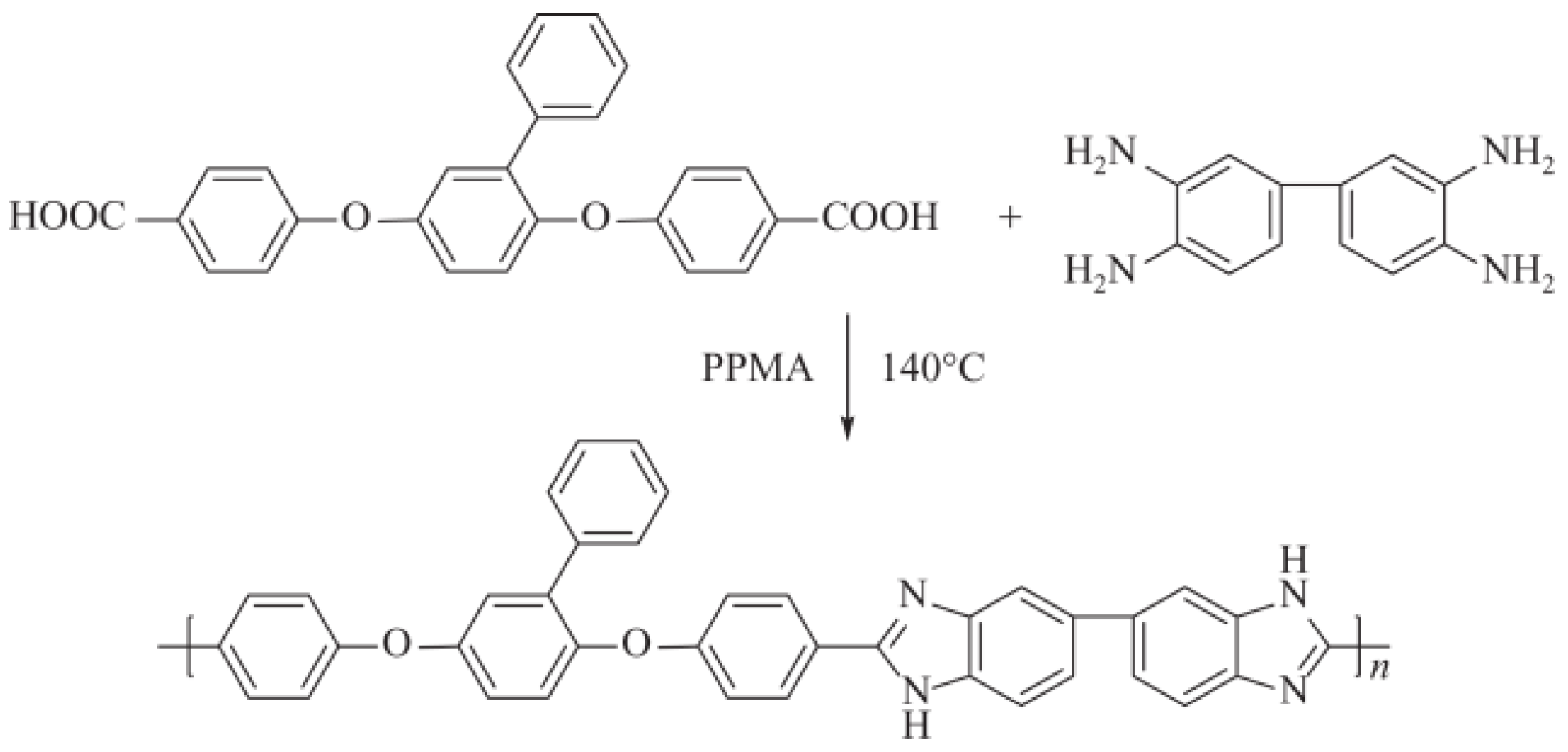



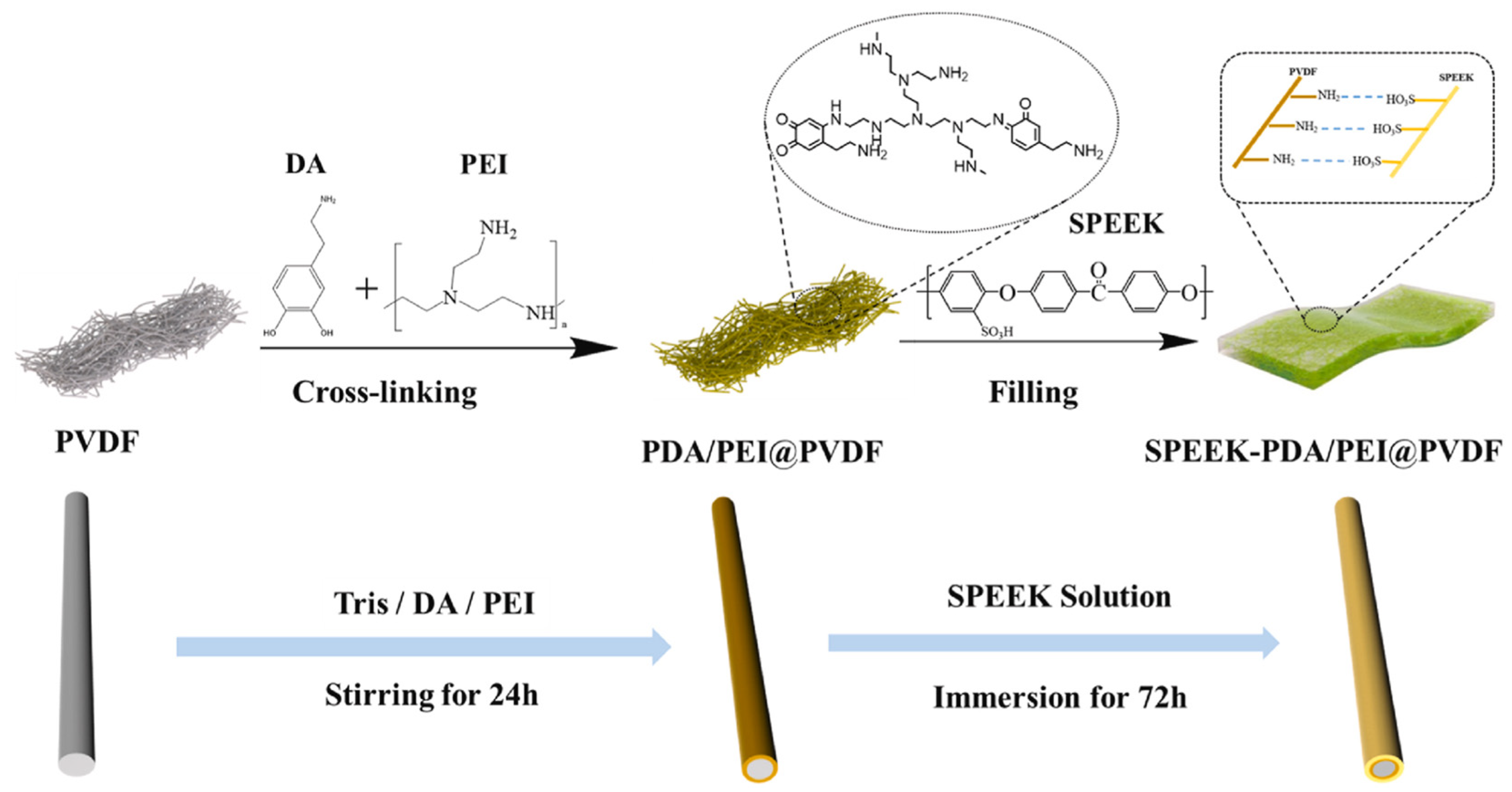
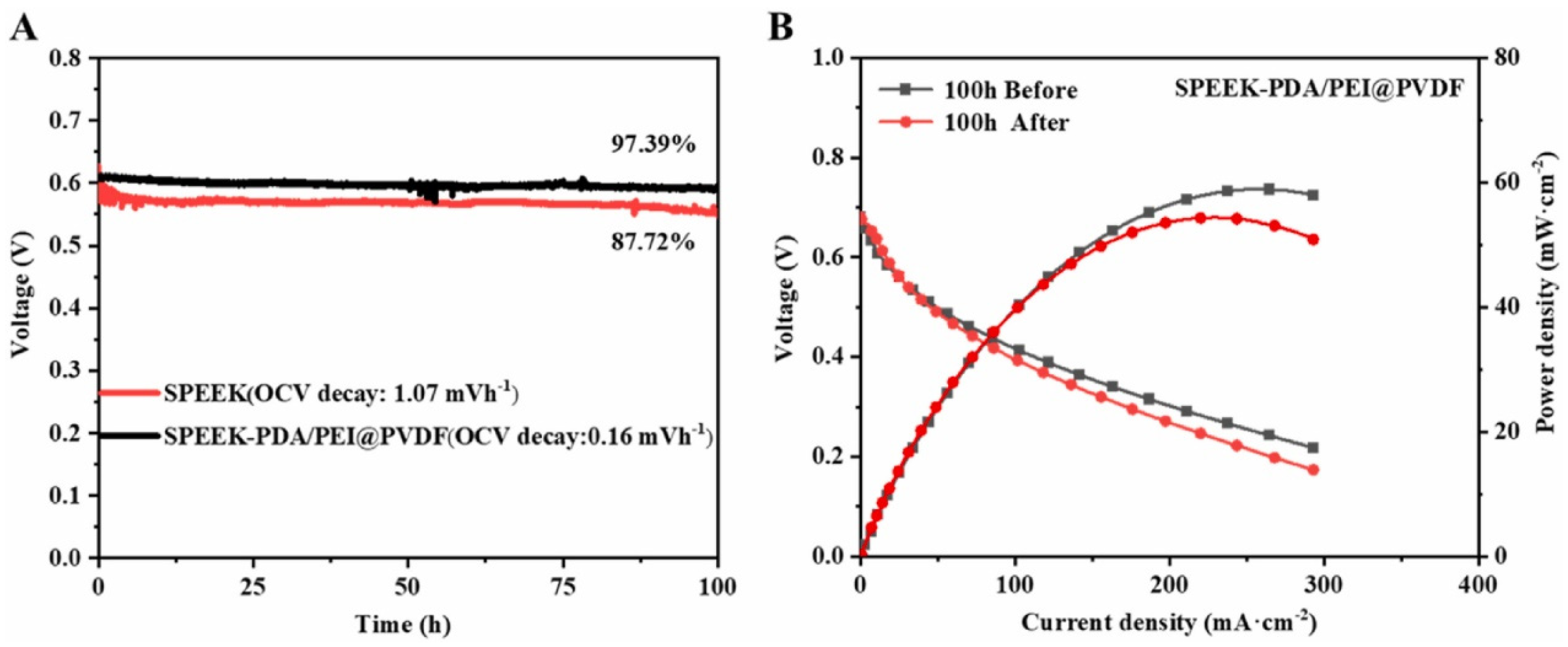
| Membrane | Proton Conductivity (S cm−1) | IEC (meq/g) | WU (%) | Swelling Ratio (%) | Max Fuel Cell Power Density (mW.cm−2) | Max Current Density (mA cm−2) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (Gpa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Methanol Penetration (cm2 s−1) | Oxidative Stability (wt%/h) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPEEK/PSf-NBIm (2.5 wt%) | 0.092 (65 °C, 100%RH) | 1.26 | 41.6 (65 °C) | - | 56 | - | - | - | - | - | - | [91] |
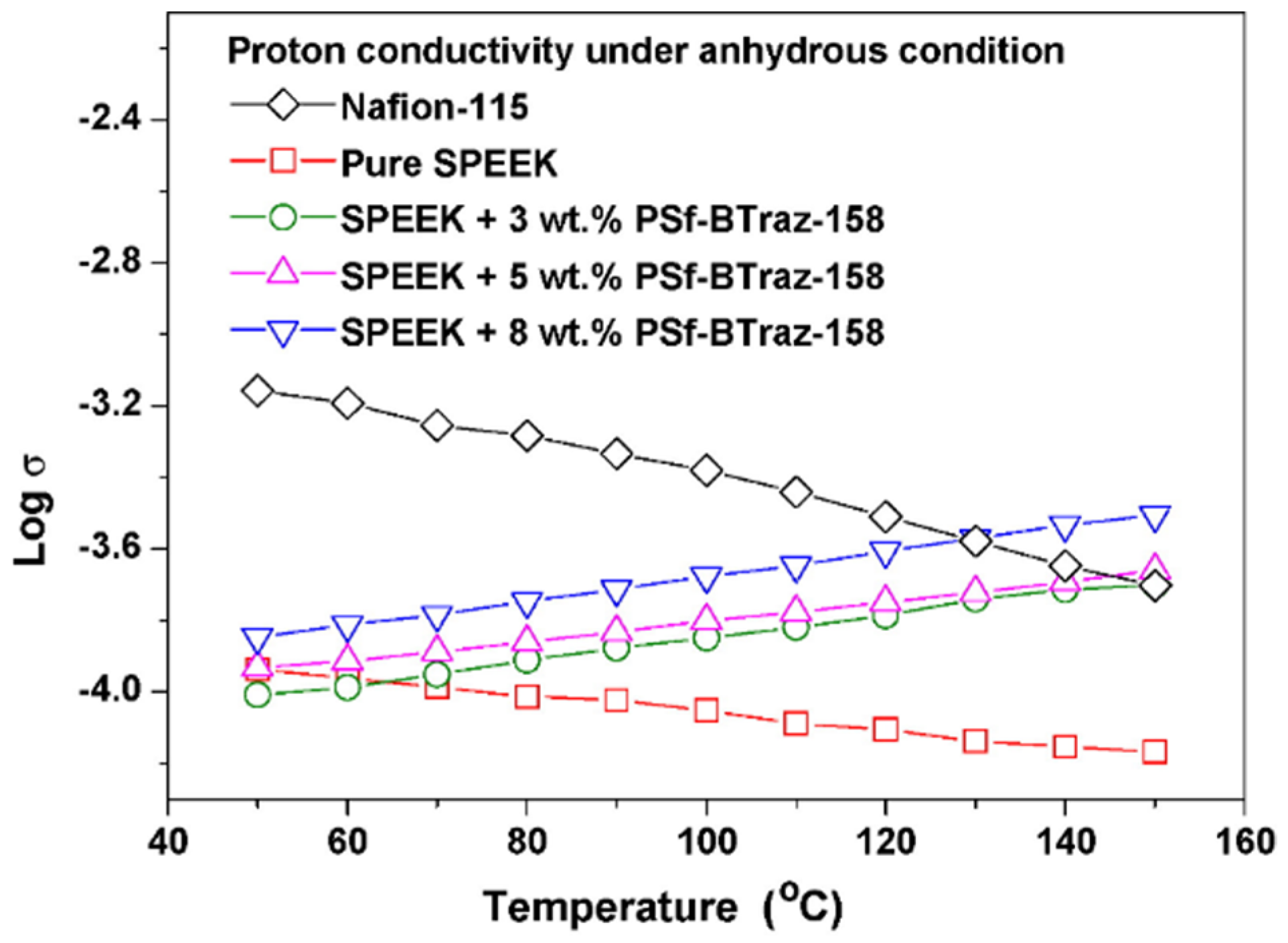
| SPEEK/ PSf-Btraz (5 wt%) | 0.054 (25 °C, 100%RH) | 1.27 (25 °C, 100%RH) | 27.2 (65 °C) | - | 174 | - | - | - | - | -- | - | [92] |
| SPEEK/ PES-5 | 0.007 | - | 48 | - | 99.29 (60 °C, 100%RH) | 367.46 (60 °C, 100% RH) | 24.53 | - | 6.42 | - | - | [94] |
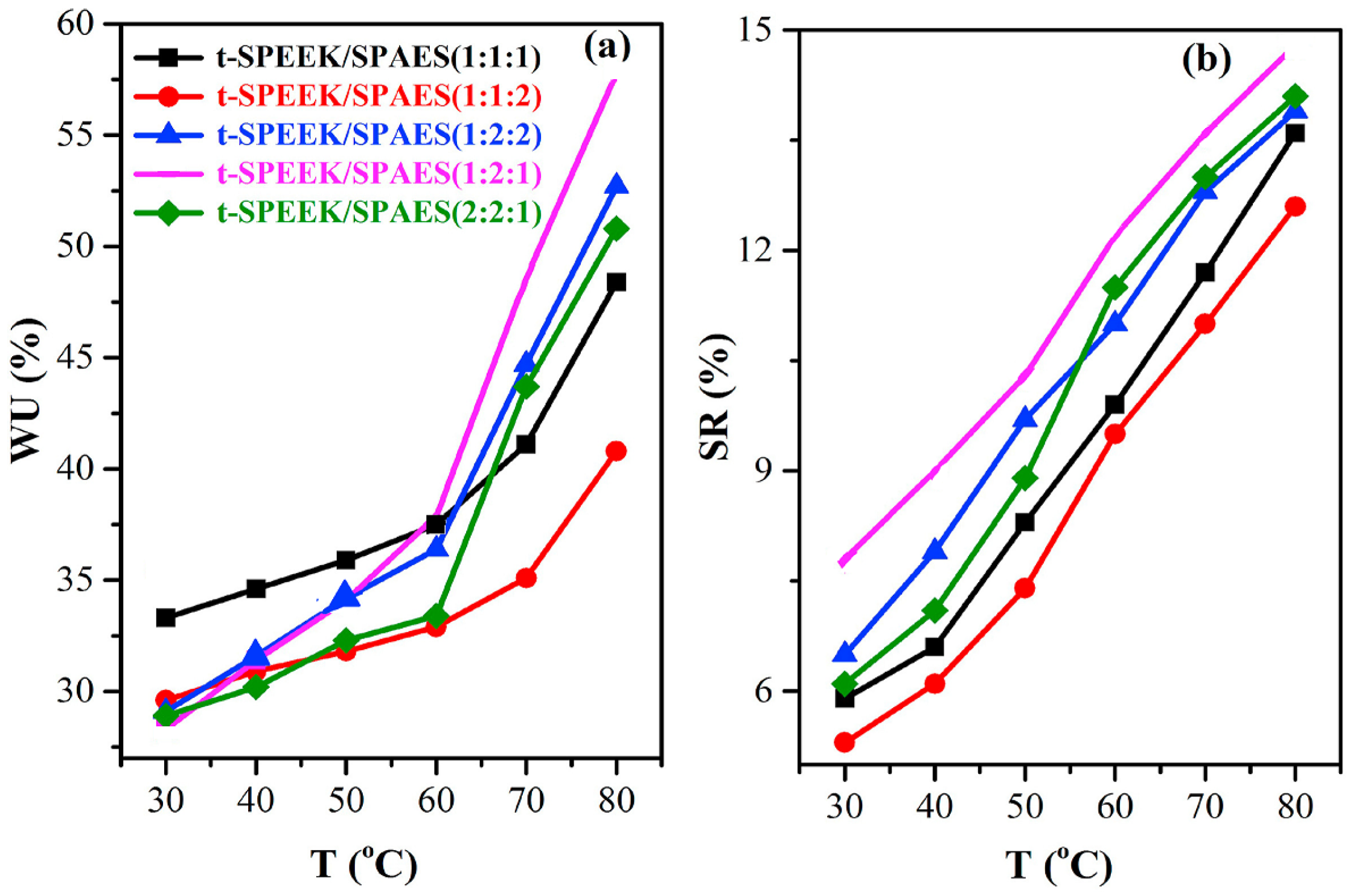
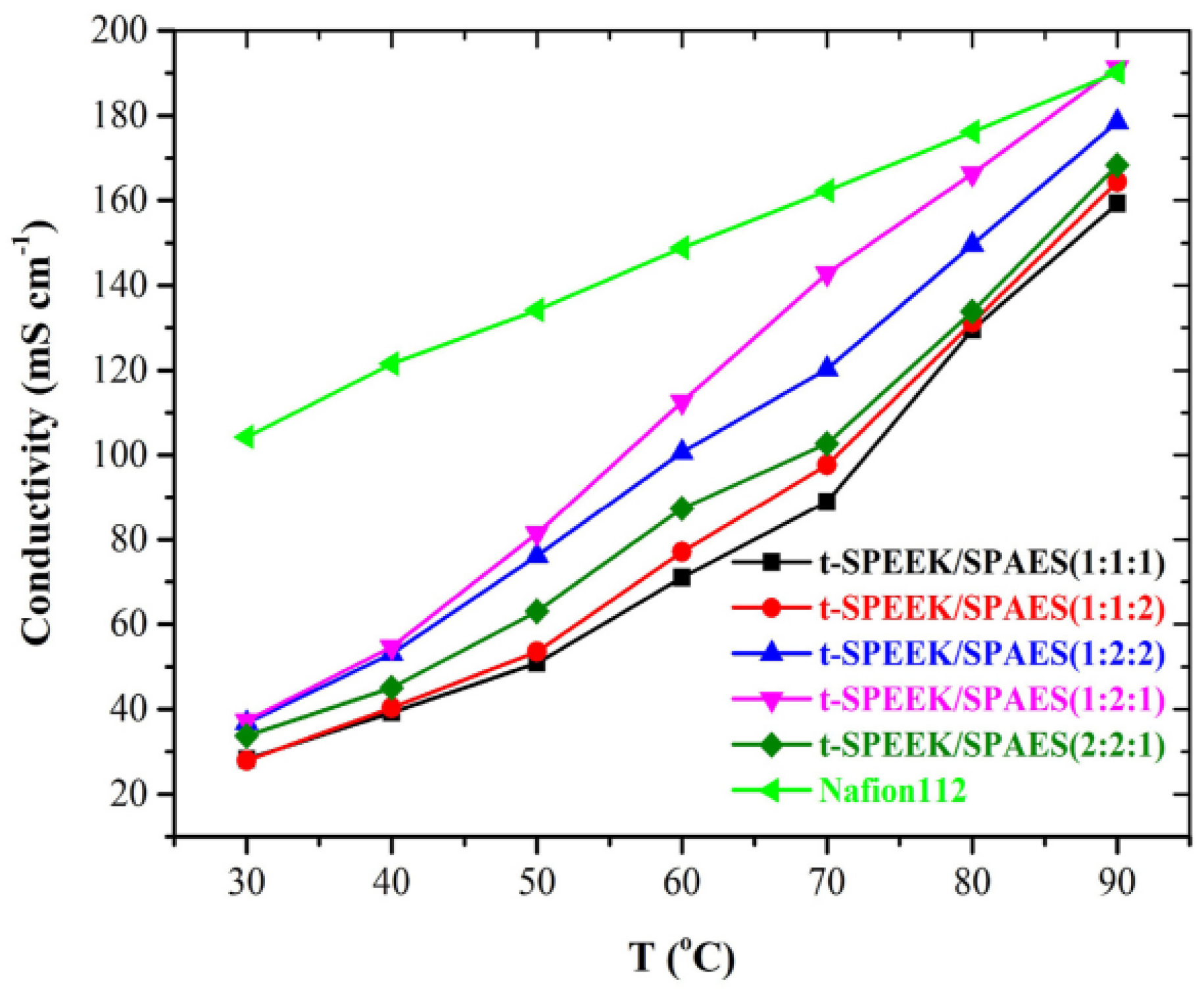
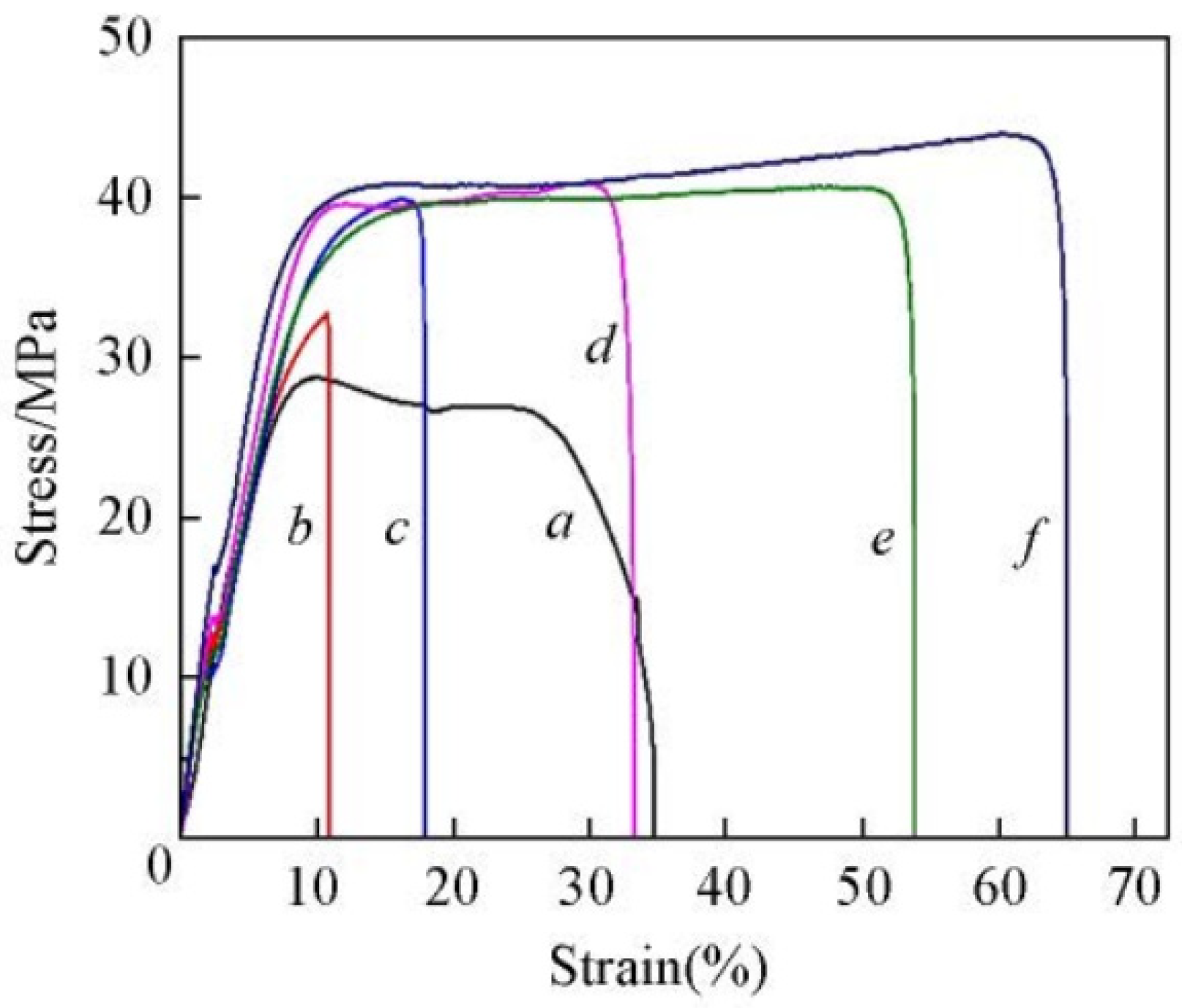
| t-SPEEK/ SPAES (1:2:2) | 0.133 (80 °C, 100%RH) | 1.7 | 57.8 | 13.9 | 665 (80 °C, 100% RH) | - | 46.5 | 1.5 | 99.1 | - | 0.77 | [84] |
| CMB4 | 0.219 | 1.51 | 121 | 21.3 | 530.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | [95] |
| SPEEK/ QNPAES (6 wt%) | 0.03 (60 °C, 20%RH) | 2.1 | 43.7 | 42.4 | 150 (60 °C, 20%RH) | 150 (60 °C, 20% RH) | 44.2 | 2.4 | 2.4 | - | [96] |
| Membrane | Proton Conductivity (S cm−1) | IEC (meq/g) | WU (%) | Swelling Ratio (%) | Max Fuel Cell Power Density (mW·cm−2) | Max Current Density (mA cm−2) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (Gpa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Methanol Penetration (cm2 s−1) | Oxidative Stability (wt%/h) | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | ||||||||||
| SPEEK/PBI | 0.0046 | 1.58 | 28% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [110] | |||
| SPEEK/PBI (5 wt%) | 0.080 (80 °C, 100%RH) | 1.54 | 52.26% (80 °C) | - | - | - | 47.42 | 1.2 | 15.44 | 5.0 × 10−7 | - | [95] | |||
| SPEEK/ PBI (20 wt%) | 0.1985 (170 °C, 100% RH) 0.099 (170 °C, 50% RH) | 14.9% (30 °C) | 3.1 (30 °C) | - | - | 45.06 | - | - | 3.96 × 10−8 | 0.417 | [112] | ||||
| SPEEK/PBI/ BPO4 (20 wt%) | 0.0059 | 16 wt% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [116] | ||||
| SPEEK/ PEEK-alt-BI (15 wt%) | 0.087 (80 °C, 100%RH) | 1.62 | 130% | 45 | - | - | 32.8 | 0.726 | 17.9 | 4.6 × 10−7 | 5 (began to break) | [117] | |||
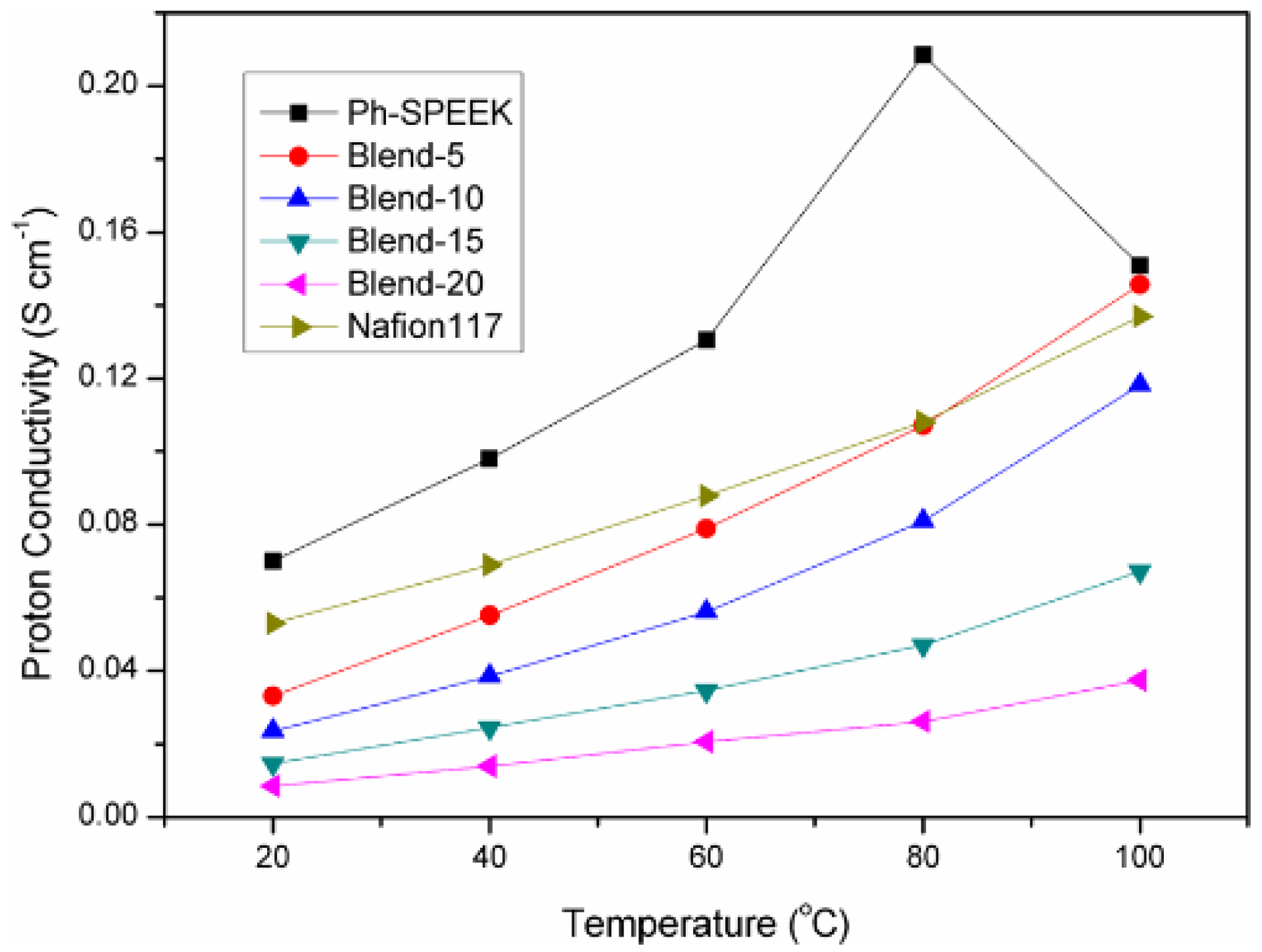
| Ph-SPEEK/ Ph-PBI (5 wt%) | 0.107 (80 °C, 100%RH) | 21.37 wt% | 55 | - | - | 22.3 | 0.51 | 4.05 | 5.27 × 10−7 | 16 | [118] | ||||
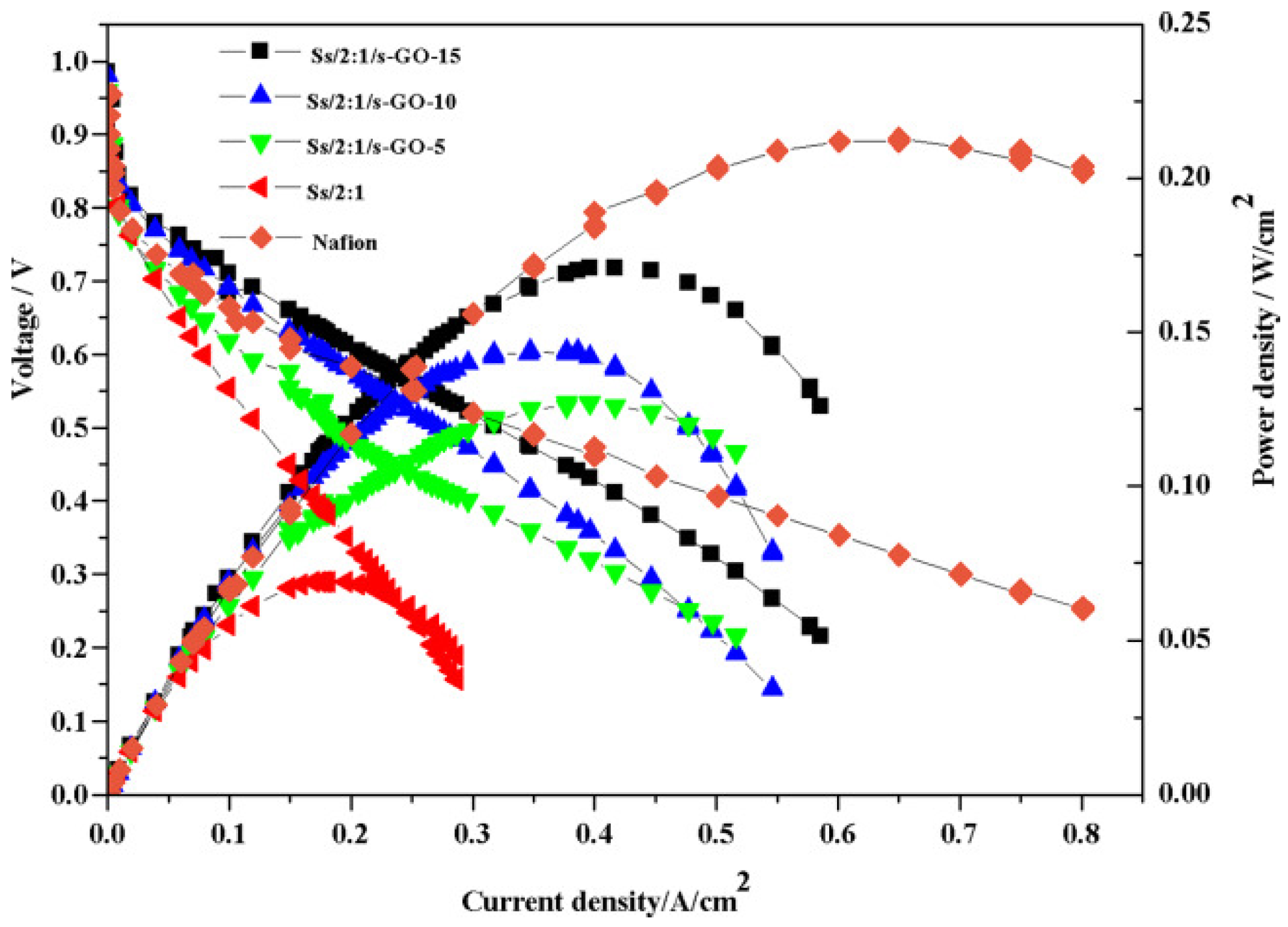
| Ss/2:1/s-GO-15 | 0.217 | 1.43 | 143.6% | 63.5 | 171(25 °C) | 417 (25 °C) | 10.7 | 0.397 | 8.4 | - | 2.5 | [120] | |||
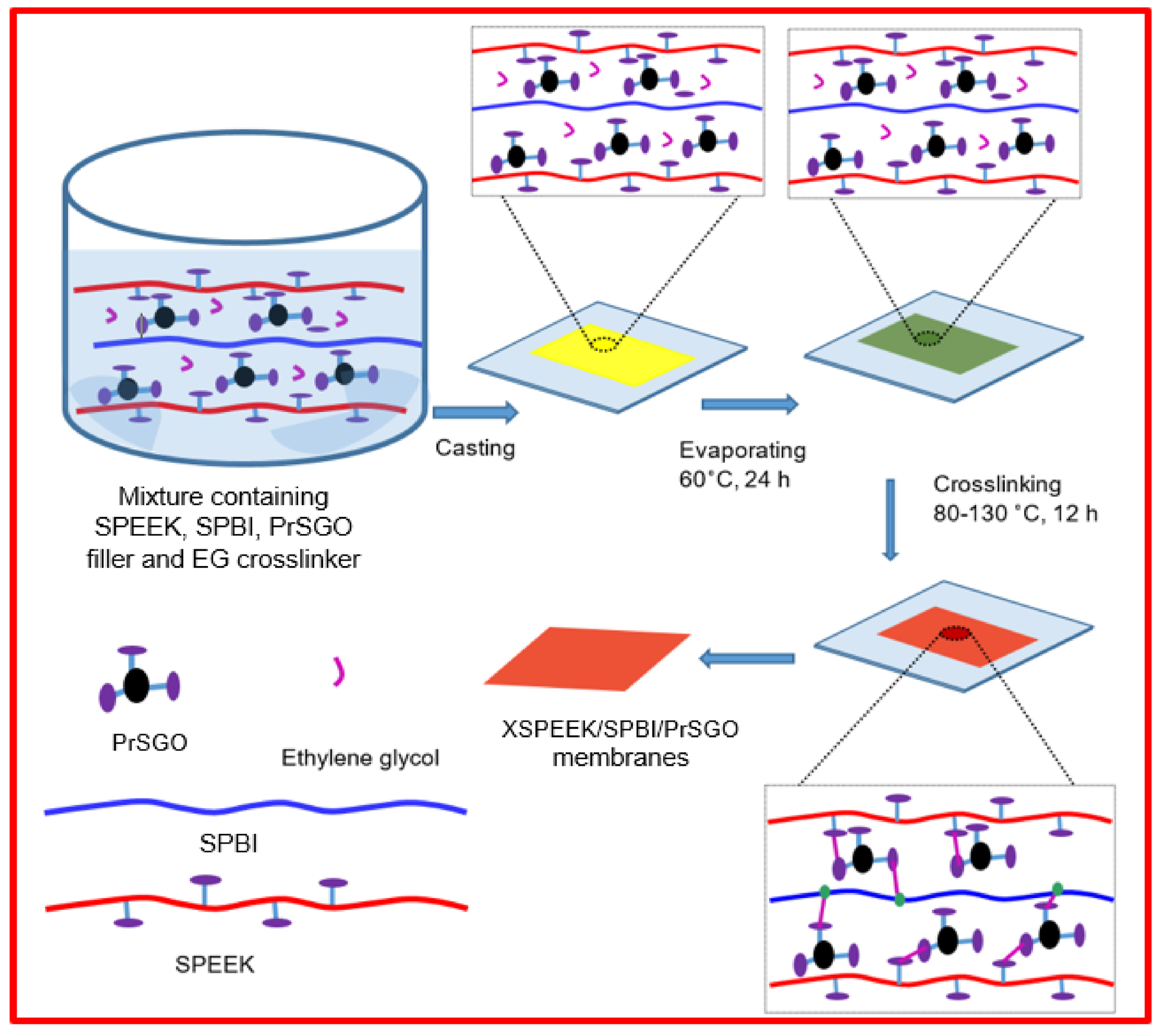
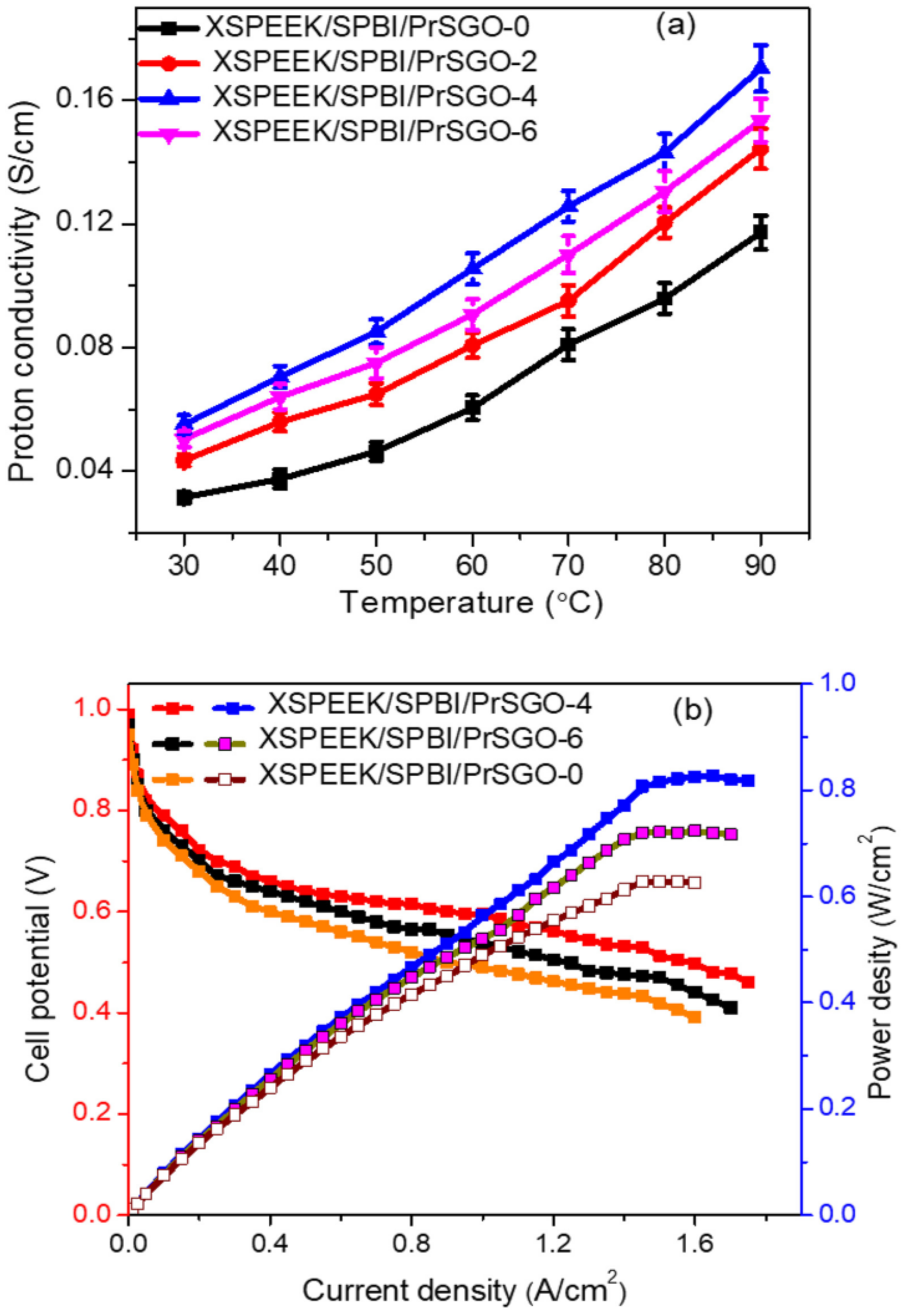
| XSPEEK/ SPBI/PrSGO (4 wt%) | 0.17 (90 °C, 100%RH) | 1.94 | - | - | 820 (80 °C, 100%RH) | - | - | - | - | - | [121] | ||||
| 15 wt% oPBI/TMBP/SPEEK | 0.142(80 °C) | 1.32 | 27.62 (80 °C) | 7.67 (80 °C) | - | - | 52.8 | 22.57 | 1.40 | 0.58 | 21.24 | 14.34 | 2.38 × 10−8 | 0.88 | [122] |
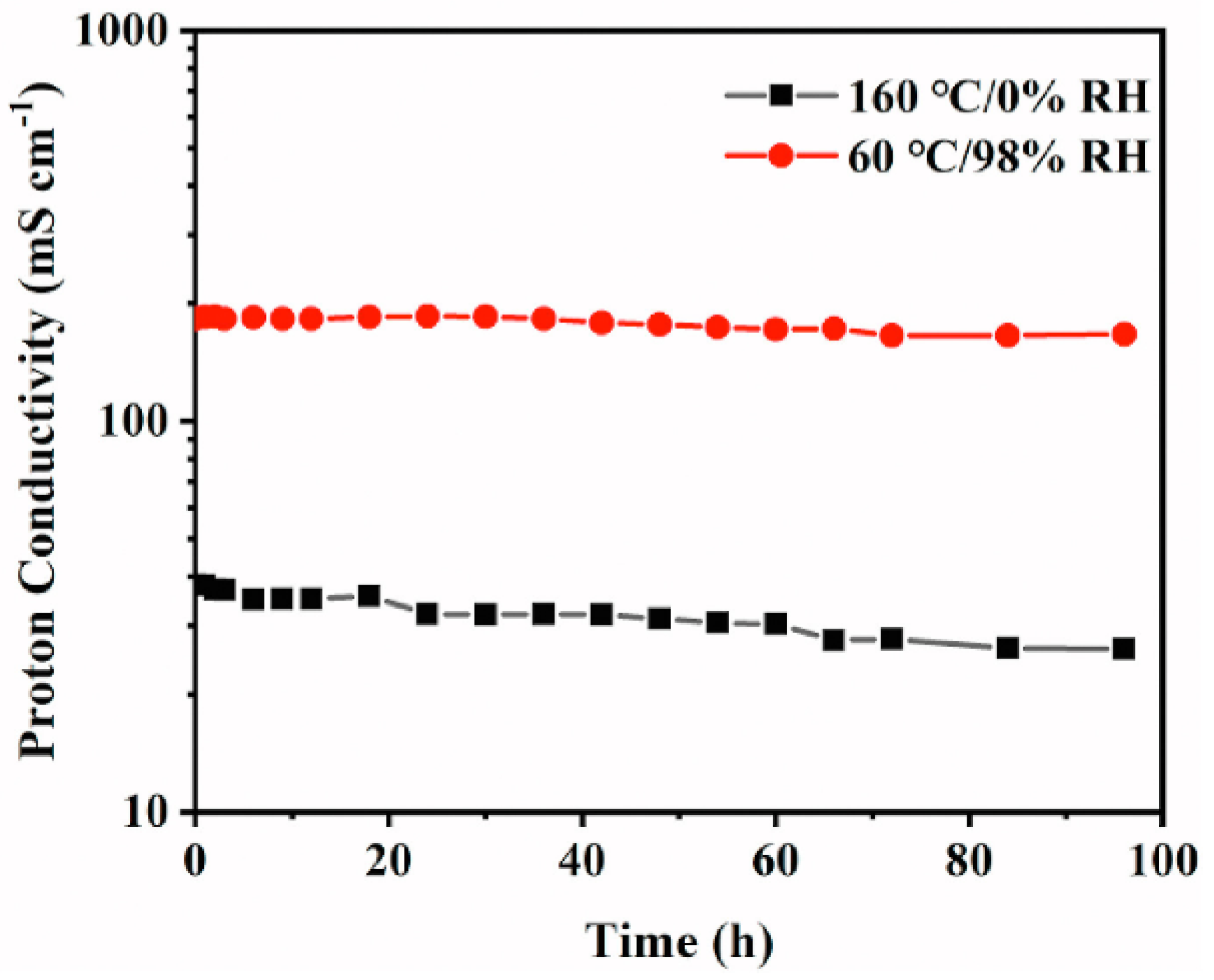
| OPBI- 30 wt% SPEEK | 0.191 (80 °C, 98% RH) | - | - | - | 115.7 (80 °C, 98%) | - | 41.1 | - | - | - | - | [123] | |||
| 0.038 (160 °C, 0 RH) | -- | - | 193.2 (160 °C, 0 RH) | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| Membrane | Proton Conductivity (S cm−1) | IEC (meq/g) | WU | Swelling Ratio (%) | Max Fuel Cell Power Density (mW·cm−2) | Max Current Density (mA cm−2) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Stress (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Methanol Penetration (cm2 s−1) | Oxidative Stability | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | |||||||||||
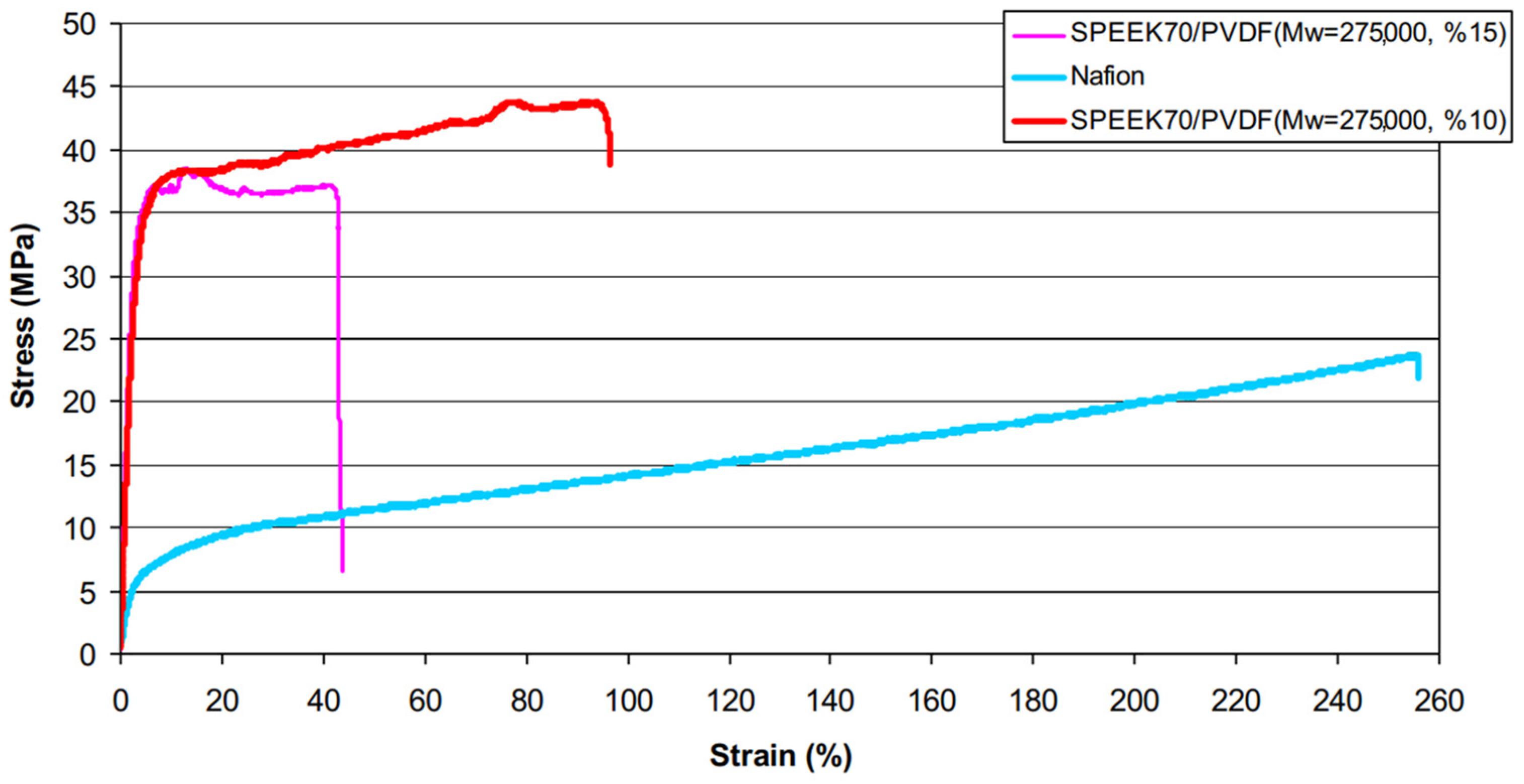
| SPEEK70/PVDF (Mw = 275,000) | 0.123 | - | 43.8 wt% | - | - | - | 34.5 | - | - | 70.2 | 3.13 × 10−7 | 3 h | [125] | |||
| SPEEK/PVDF15 | 0.046 | 130.84% (60 °C) | 25(60 °C) | - | - | 32.73 | - | - | - | - | [126] | |||||
| SPEEK/PVDF/ BP-10 | 0.039 (80 °C) | 1.38 | 52% | 4.8 | 242 | 400 | - | 36.15 | - | 74 | - | 90 h | [129] | |||
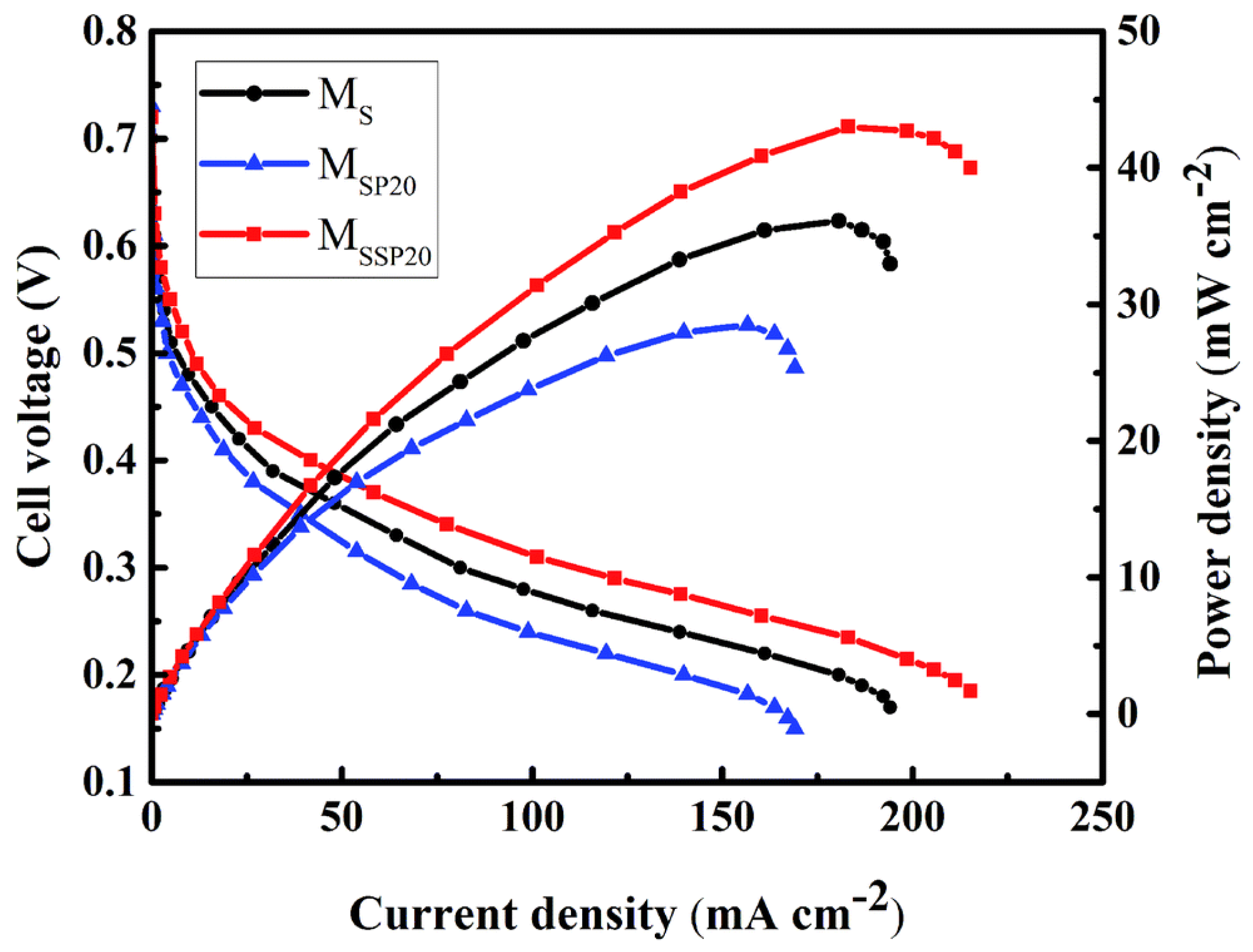
| MSSP20 | 0.032 | 1.35 | 56% | 35 | 43.02 | 215.3 | 25.63 | - | 825 | 10.95 | 2.11 × 10−7 | 3 h | [132] | |||
| SPEEK/ SPVdF-HFP/ S-SiO2 (6 wt%) | 0.079 (90 °C) | 1.70 | 36.5% | 15.9% | 110 | 354 | 38.5 | - | 875 | 35.8 | - | - | [133] | |||
| SPEEK/ PDA@PVDF | 0.06 | - | 32.3% | - | 104 | 156.5 | - | - | 1002 | 539 | 188 | 268 | 23.5 × 10−7 | - | [134] | |
| SPEEK-PDA/PEI@PVDF | 0.048 (80 °C) | - | 32.53% (60 °C) | 19.96 (60 °C) | 58.9 (80 °C) | 34 | - | - | 174 | 11.94 × 10−7 | - | [135] | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Ye, T.; Meng, X.; He, D.; Li, L.; Song, K.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. Advances in the Application of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) and Its Organic Composite Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Polymers 2024, 16, 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192840
Li X, Ye T, Meng X, He D, Li L, Song K, Jiang J, Sun C. Advances in the Application of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) and Its Organic Composite Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Polymers. 2024; 16(19):2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192840
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiang, Tengling Ye, Xuan Meng, Dongqing He, Lu Li, Kai Song, Jinhai Jiang, and Chuanyu Sun. 2024. "Advances in the Application of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) and Its Organic Composite Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)" Polymers 16, no. 19: 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192840
APA StyleLi, X., Ye, T., Meng, X., He, D., Li, L., Song, K., Jiang, J., & Sun, C. (2024). Advances in the Application of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) (SPEEK) and Its Organic Composite Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Polymers, 16(19), 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192840










