Multifaceted Impact of Lipid Extraction on the Characteristics of Polymer-Based Sewage Sludge towards Sustainable Sludge Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Reagent
2.2. Preparation of Sludge Sample
2.3. Extraction and Separation of Lipids
2.4. Separation of Lipids
2.5. Lipids Yield Analysis
2.6. Characterization of DS, WAS, and Polymer Flocculant
2.7. Bibliometric Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DS as a Raw Material in Lipid Feedstock for Biodiesel
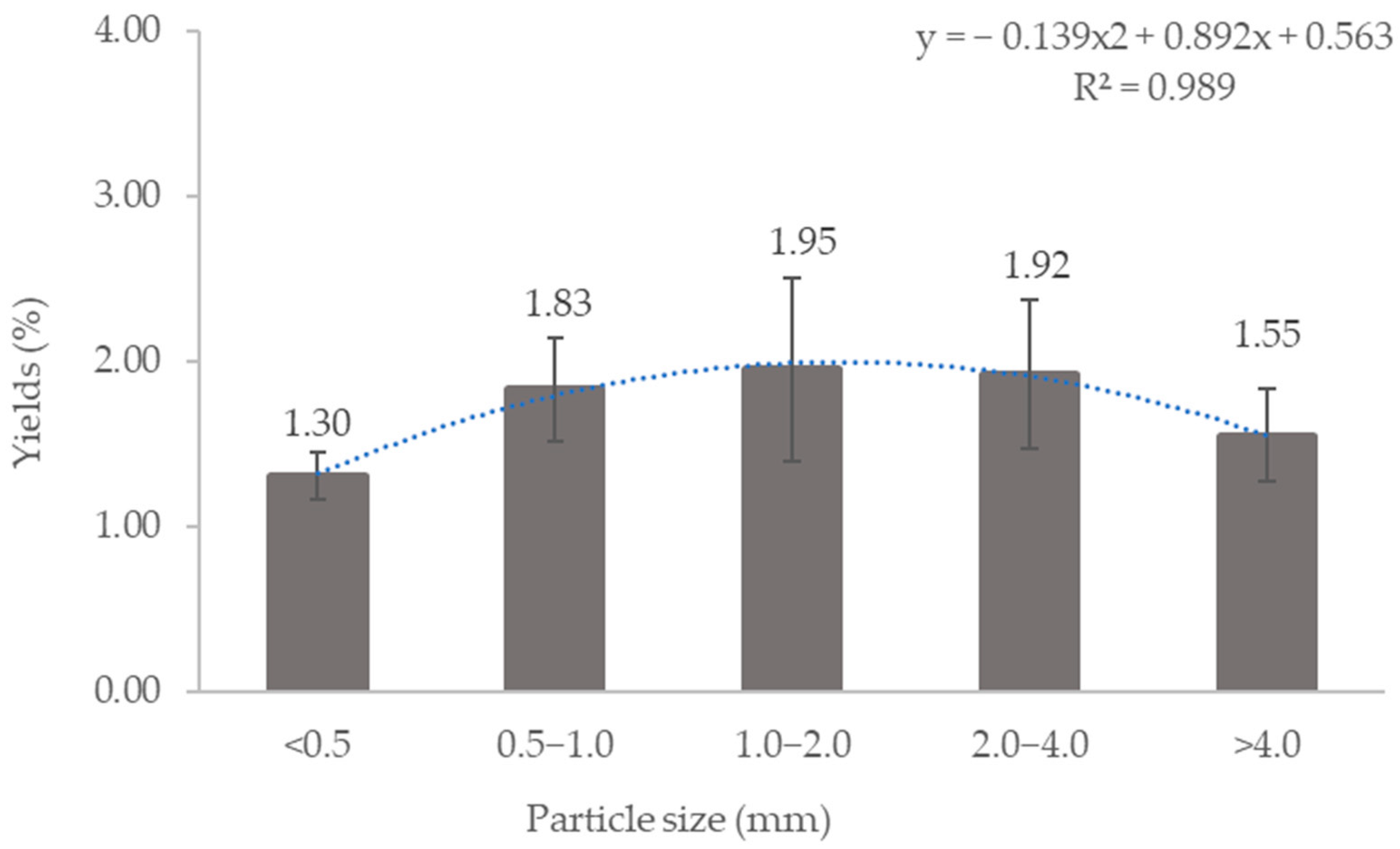
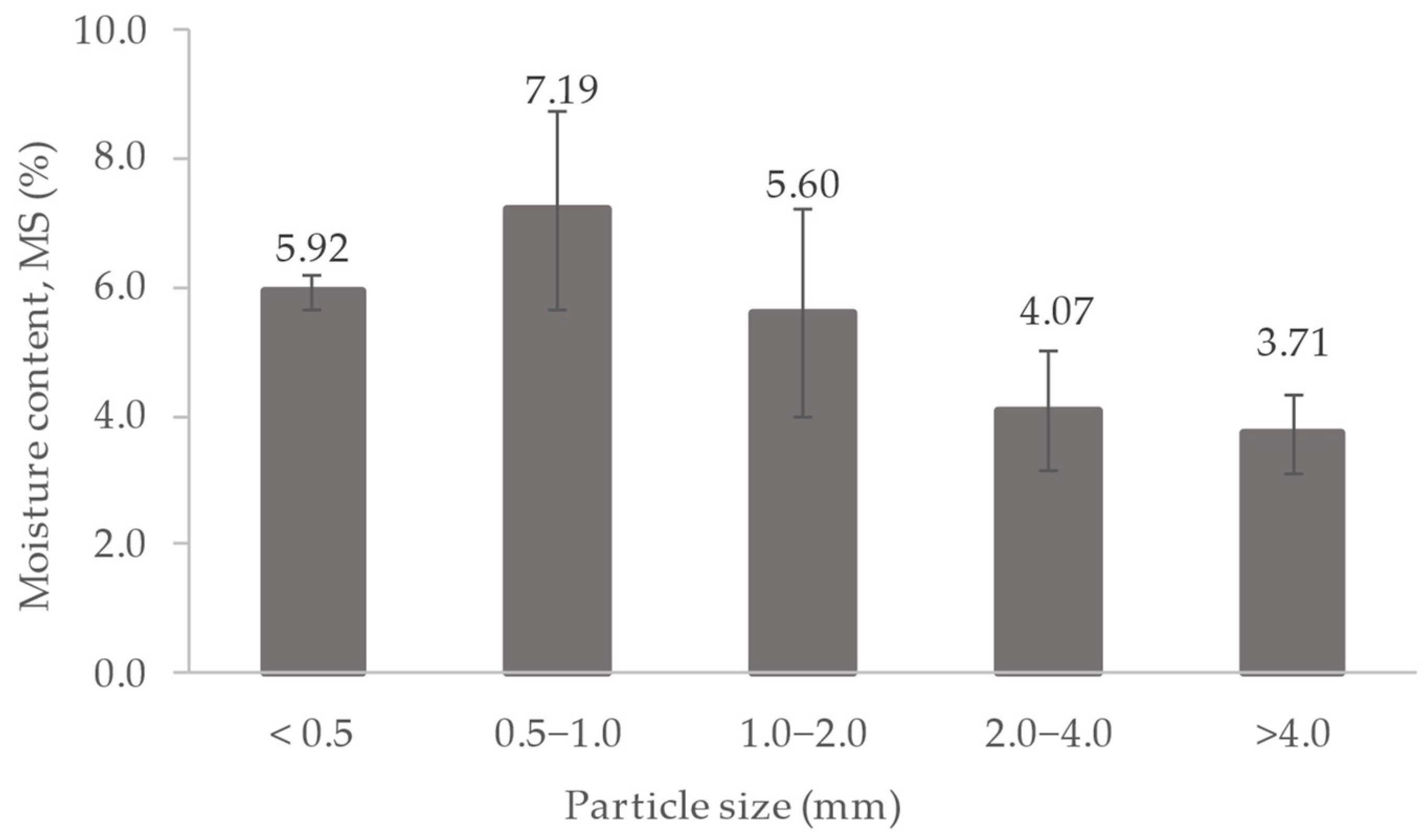
3.2. Lipid Extraction from DS
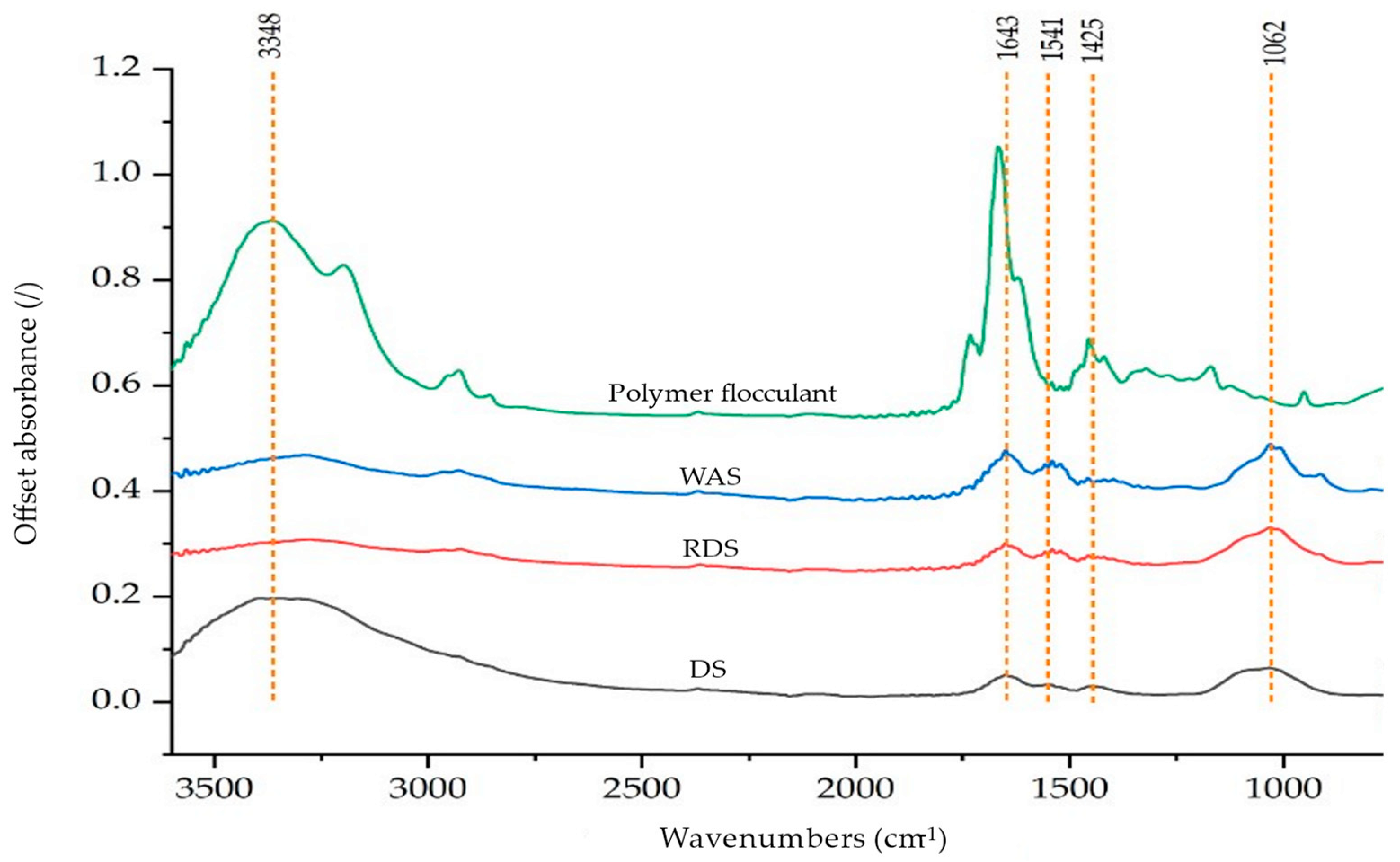
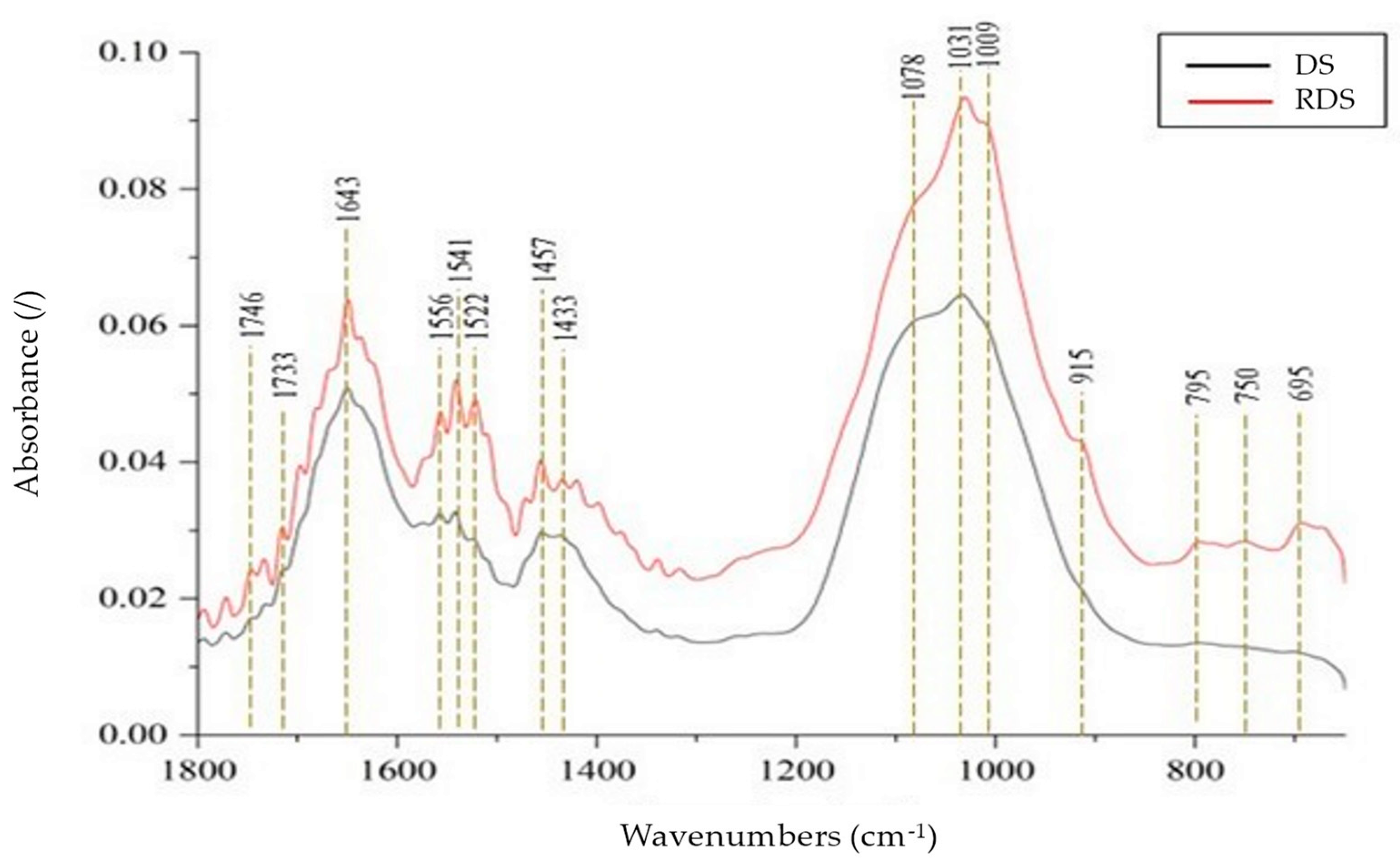
3.3. FTIR Analysis of DS and RDS
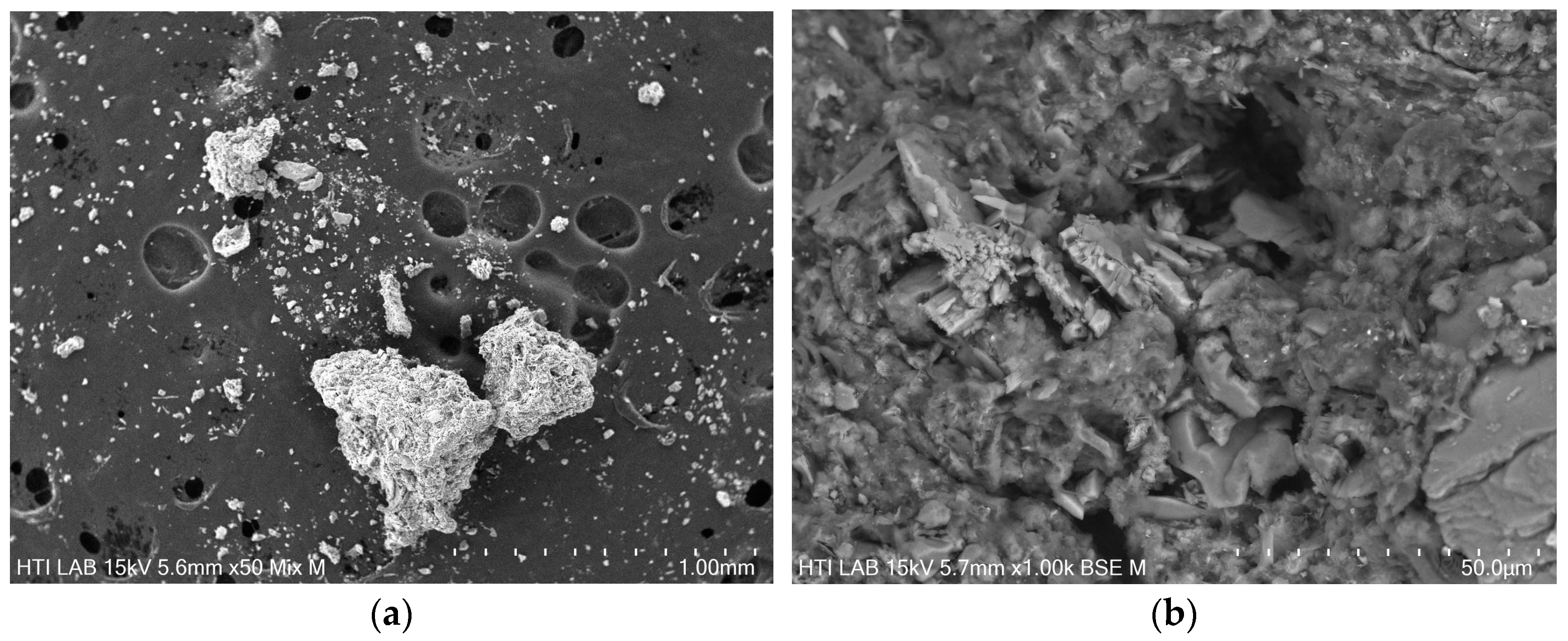
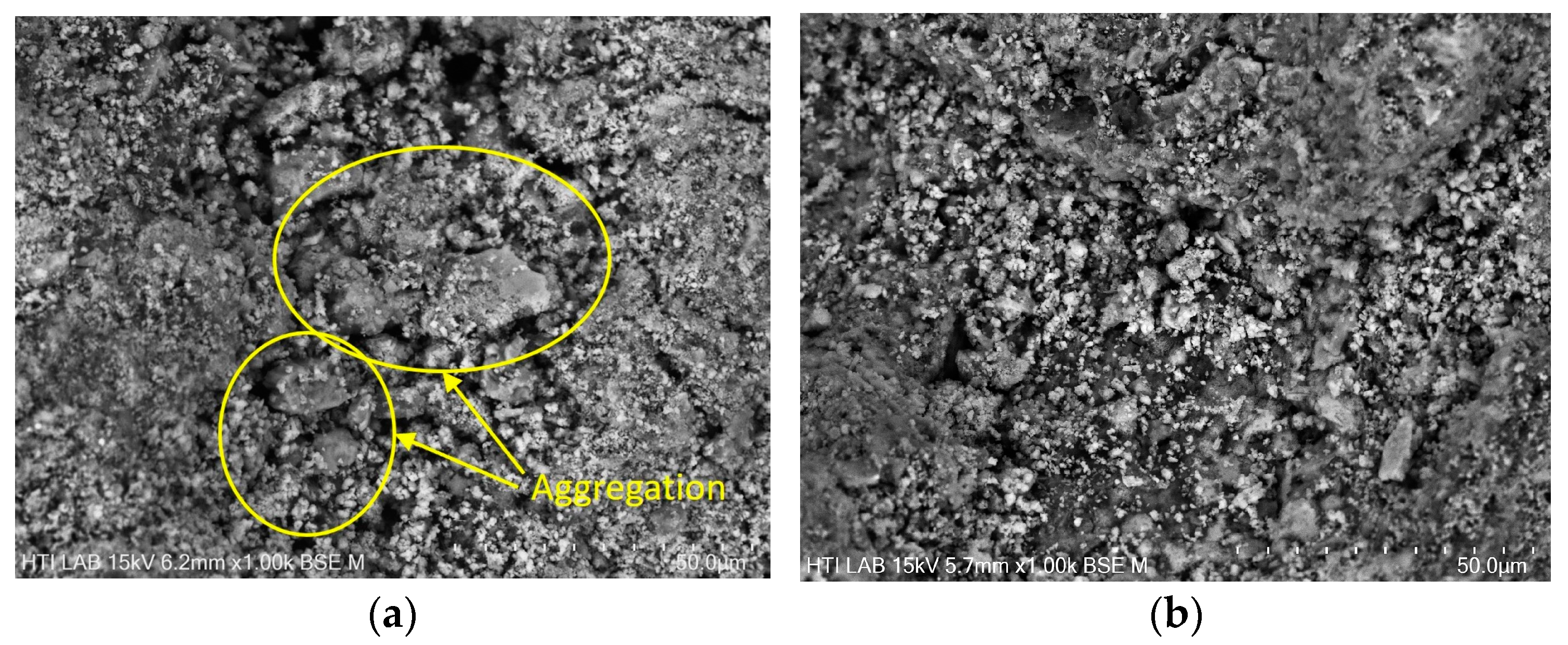
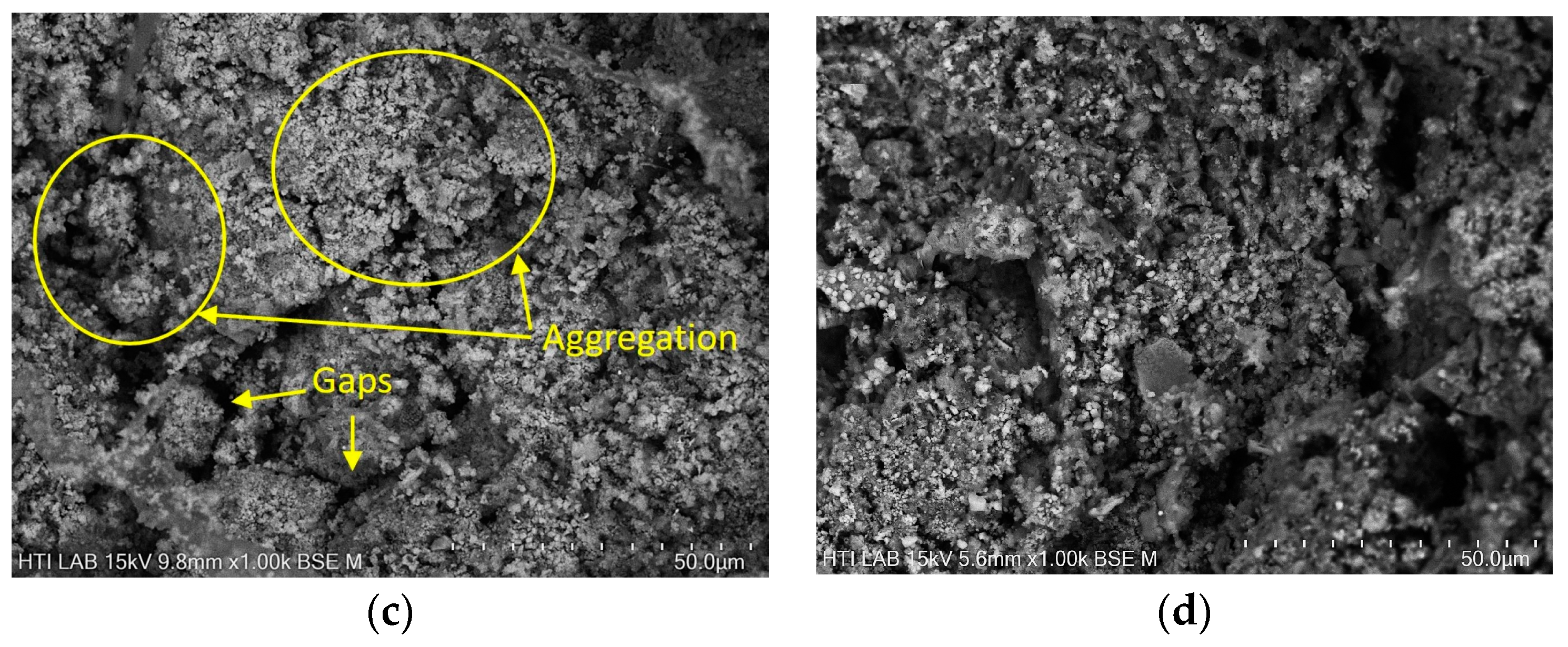
3.4. Morphology of DS and RDS
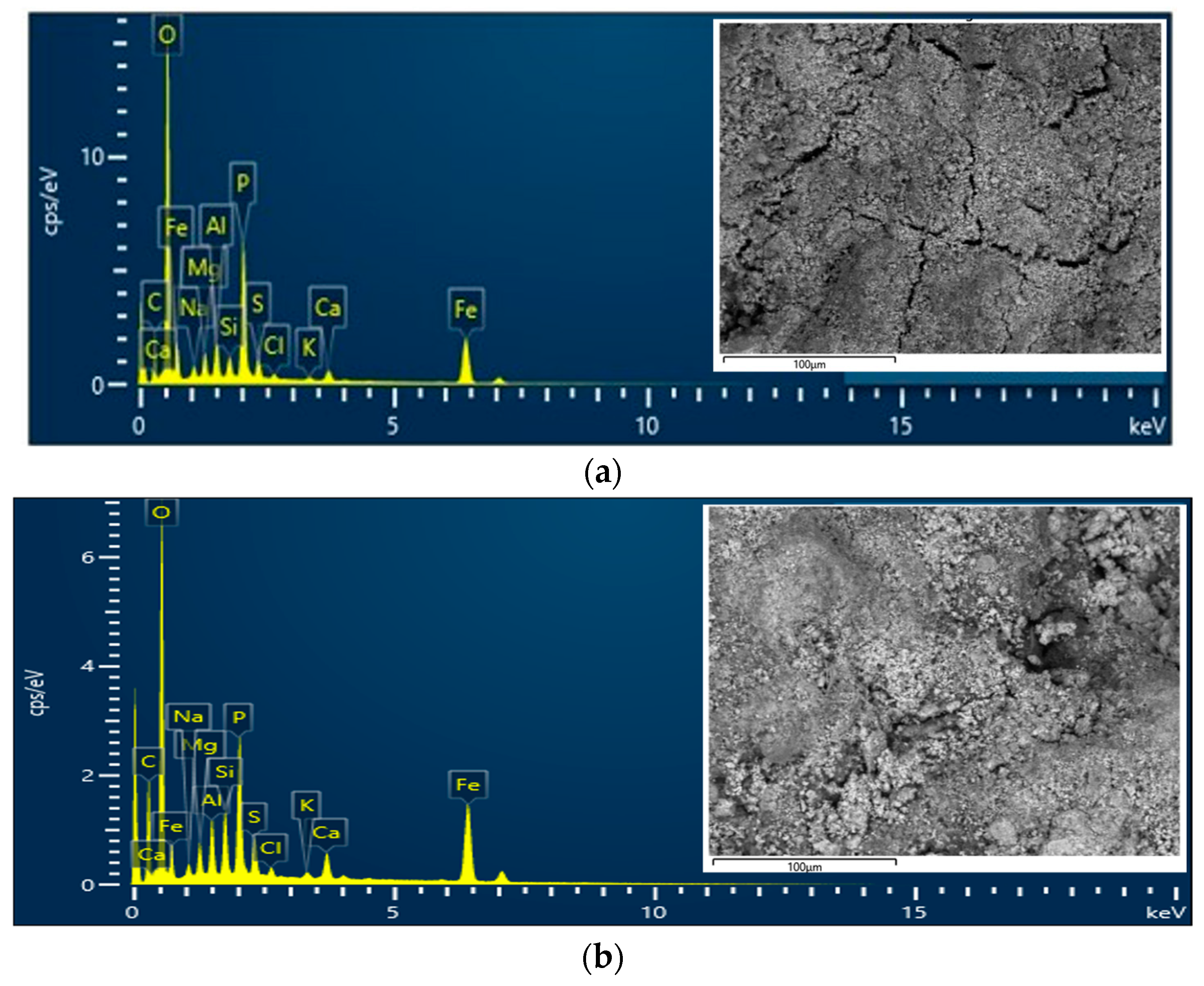
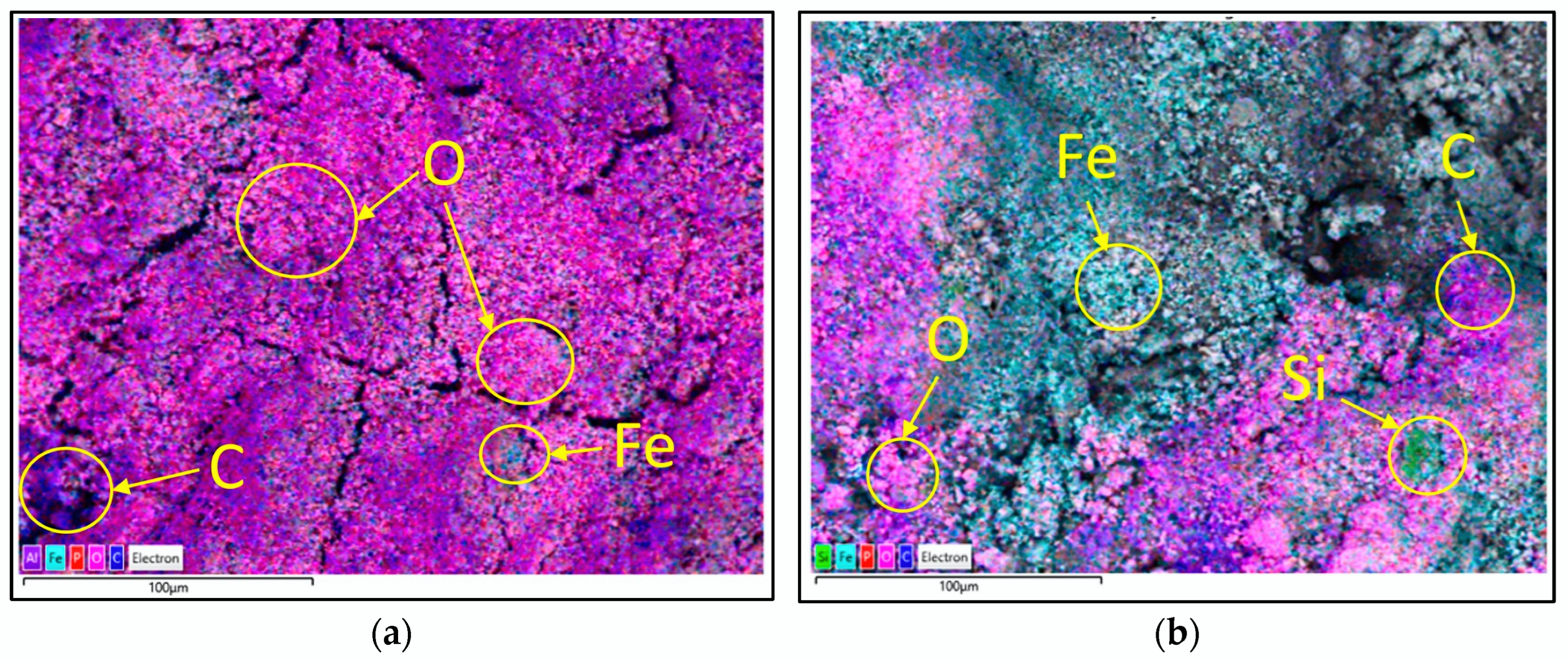
3.5. Elemental Composition of DS and RDS
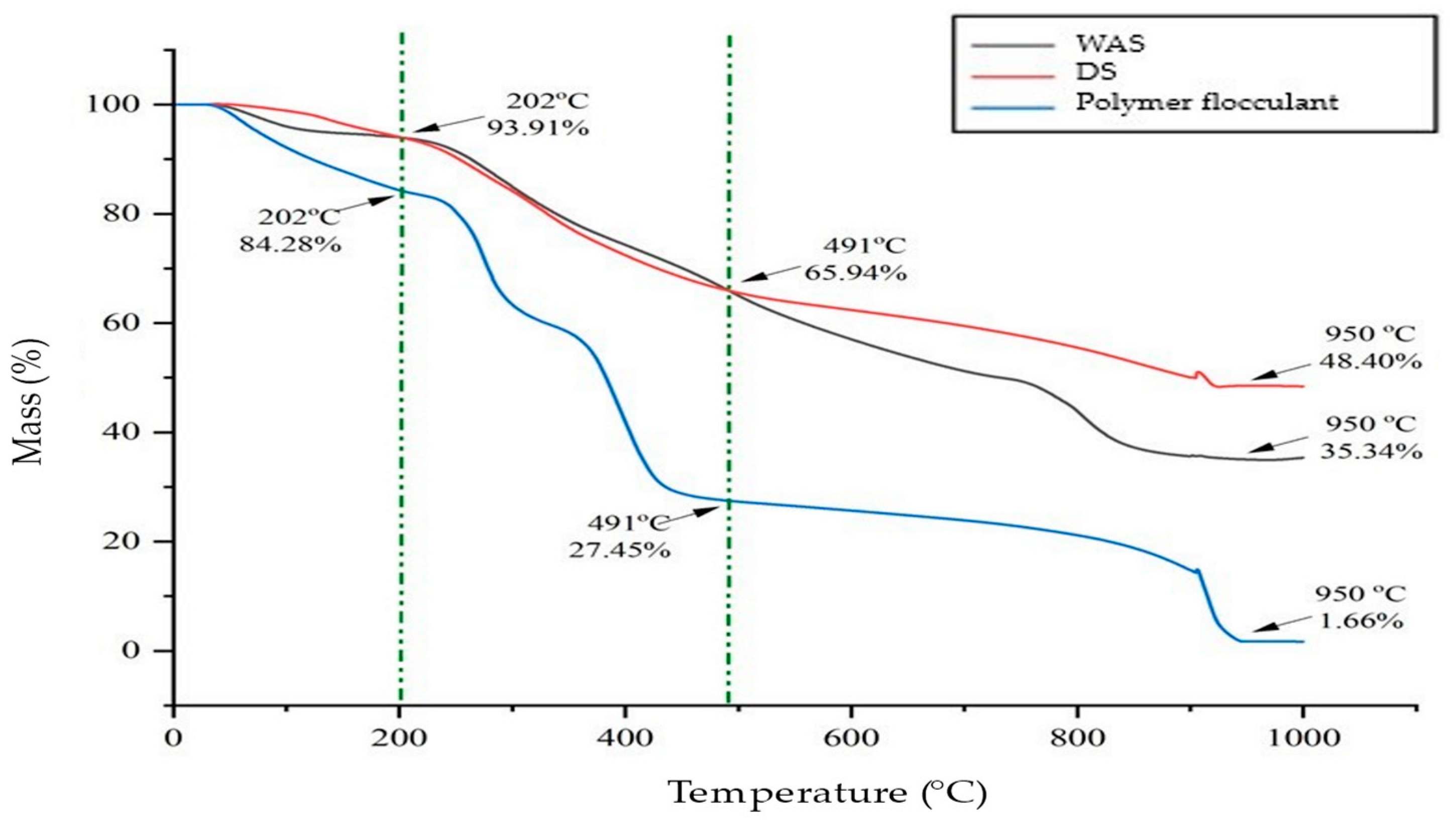
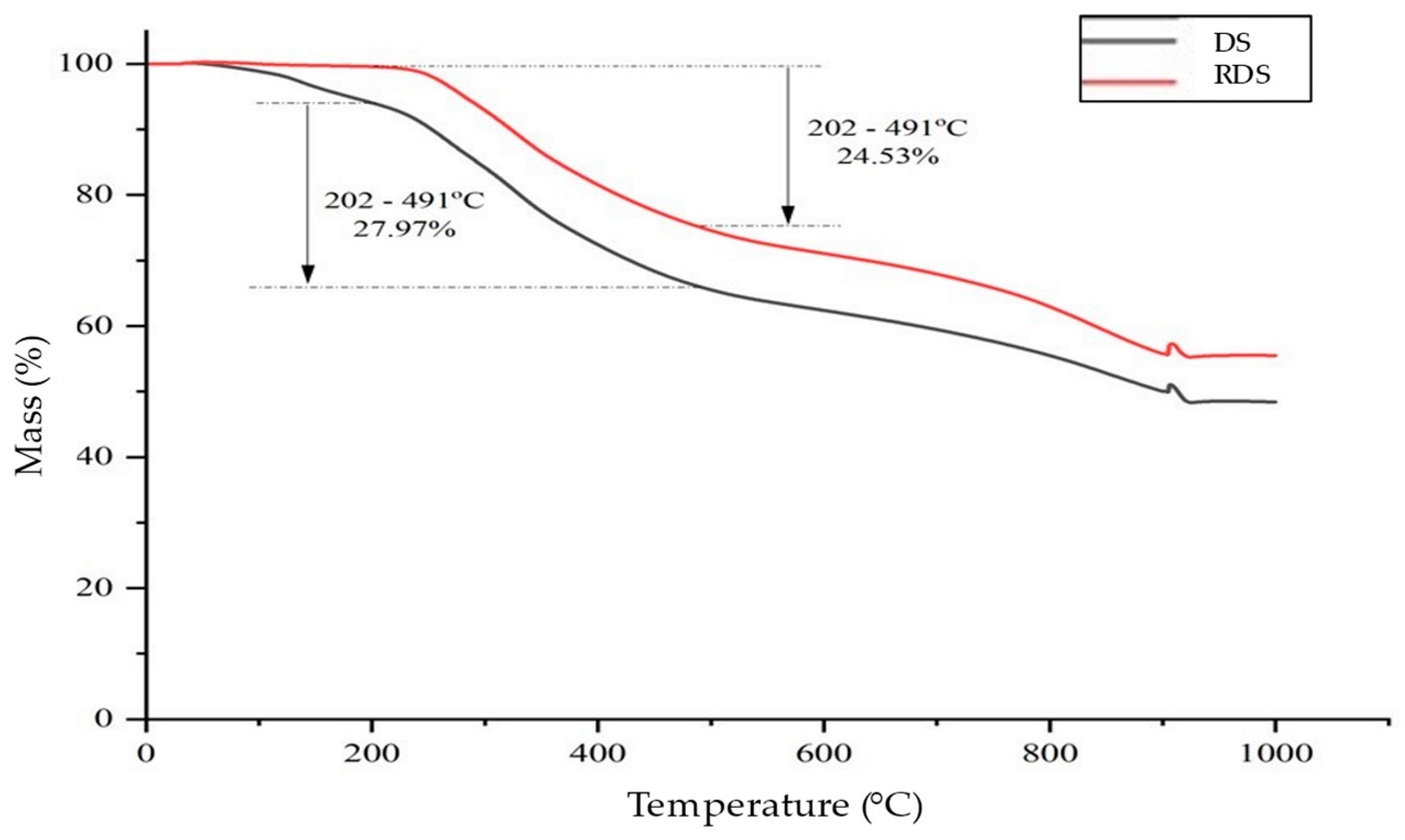
3.6. Thermal Characteristics of DS and RDS
3.7. DS and RDS Management and Disposal
3.8. Mini Bibliometric Analysis
3.8.1. Trend of Publication Related to “Extraction*” and “Sewage Sludge”
3.8.2. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peccia, J.; Westerhoff, P. We Should Expect More out of Our Sewage Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8271–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Su, S.; Xiang, J. Thermochemical Processing of Sewage Sludge to Energy and Fuel: Fundamentals, Challenges and Considerations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 888–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, A. Degradation Properties of Protein and Carbohydrate during Sludge Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Qi, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Lipid Profiling in Sewage Sludge. Water Res. 2017, 116, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista Search Department Sewage Sludge Produced and Disposed in Europe in 2020, by Country. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1393771/sewage (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Siddiquee, M.N.; Rohani, S. Experimental Analysis of Lipid Extraction and Biodiesel Production from Wastewater Sludge. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Qi, J.; Wang, J. Comparison of the Lipid Content and Biodiesel Production from Municipal Sludge Using Three Extraction Methods. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 5277–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, J.A.; Sánchez-Vázquez, R.; Vasiliadou, I.A.; Martínez Castillejo, F.; Bautista, L.F.; Iglesias, J.; Morales, G.; Molina, R. Municipal Sewage Sludge to Biodiesel by Simultaneous Extraction and Conversion of Lipids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canziani, R.; Spinosa, L. Sludge from Wastewater Treatment Plants. In Industrial and Municipal Sludge: Emerging Concerns and Scope for Resource Recovery; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3–30. ISBN 9780128159071. [Google Scholar]
- Miron, Y. The Role of Sludge Retention Time in the Hydrolysis and Acidification of Lipids, Carbohydrates and Proteins during Digestion of Primary Sludge in CSTR Systems. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.; Quintelas, C.; Ferreira, E.C.; Mesquita, D.P. The Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Micropollutant Removal. Front. Chem. Eng. 2022, 4, 778469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, H.H.P. Influences of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) on Flocculation, Settling, and Dewatering of Activated Sludge. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 33, 237–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Guo, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, L. Treatment of Municipal Sewage Sludge in Supercritical Water: A Review. Water Res. 2016, 89, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Rao, T.; Ji, J.; He, B.; Liu, A.; Sun, Y. Enhanced Dewatering of Activated Sludge by Skeleton-Assisted Flocculation Process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, Q.; Yang, J. The Fate and Impact of Coagulants/Flocculants in Sludge Treatment Systems. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zizeng, W.; Feng, L.; Xie, J.; Lin, Z.; Xu, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Zheng, H. Research on a New Cationic Polyacrylamide (CPAM) with a Cationic Microblock Structure and Its Enhanced Effect on Sludge Condition and Dewatering. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 51865–51878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, X.; Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, T. The Porous Structure Effects of Skeleton Builders in Sustainable Sludge Dewatering Process. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Dong, B.; Dai, L.; He, Q.; Dai, X. Change of Thermal Drying Characteristics for Dewatered Sewage Sludge Based on Anaerobic Digestion. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, M.D.; Tyagi, R.D.; Valero, J.R. Wastewater Treatment Sludge as a Raw Material for the Production of Bacillus Thuringiensis Based Biopesticides. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijałkowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Almås, Å.; Singh, B.R. Sewage Sludge Disposal Strategies for Sustainable Development. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Sun, J.; Lü, X.; Peng, Z.; Dong, B.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.-J. Impacts of Norfloxacin on Sewage Sludge Anaerobic Digestion: Bioenergy Generation and Potential Environmental Risks. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajao, V.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.; Temmink, H. Natural Flocculants from Fresh and Saline Wastewater: Comparative Properties and Flocculation Performances. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Critical Review on Dewatering of Sewage Sludge: Influential Mechanism, Conditioning Technologies and Implications to Sludge Re-Utilizations. Water Res. 2020, 180, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiquee, M.N.; Rohani, S. Lipid Extraction and Biodiesel Production from Municipal Sewage Sludges: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussein Alsaedi, A.; Sohrab Hossain, M.; Balakrishnan, V.; Abdul Hakim Shaah, M.; Mohd Zaini Makhtar, M.; Ismail, N.; Naushad, M.; Bathula, C. Extraction and Separation of Lipids from Municipal Sewage Sludge for Biodiesel Production: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Modeling. Fuel 2022, 325, 124946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.A.; Lima, S.; Jahangiri, H.; Majewski, A.J.; Hofmann, M.; Hornung, A.; Ouadi, M. A Step Change towards Sustainable Aviation Fuel from Sewage Sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 163, 105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holladay, J.; Abdullah, Z.; Heyne, J. Sustainable Aviation Fuel: Review of Technical Pathways; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.B.; Cayetano, R.D.A.; Park, J.; Jo, Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, S.H. Effect of Low-Thermal Pretreatment on the Methanogenic Performance and Microbiome Population of Continuous High-Solid Anaerobic Digester Treating Dewatered Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, N.A.; Hamid, H.A.; Fizal, A.N.S.; Zulkifli, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Utilization of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide (SC-CO 2) in Lipids Extraction from Sewage Sludge Cake: A Preliminary Study. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1195, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Luo, F.; Dai, L.; Dong, B. Degradation of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) in Anaerobic Digestion of Dewatered Sludge. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, D.; Oulego, P.; Collado, S.; Riera, F.A.; Díaz, M. Separation and Purification Techniques for the Recovery of Added-Value Biocompounds from Waste Activated Sludge. A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 182, 106327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiman, N.; Mustapha, H.; Sing, W.; Rahman, R.A. Optimisation of Lipid Extraction from Primary Sludge by Soxhlet Extraction. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 56, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forfang, K.; Zimmermann, B.; Kosa, G.; Kohler, A.; Shapaval, V. FTIR Spectroscopy for Evaluation and Monitoring of Lipid Extraction Efficiency for Oleaginous Fungi. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safder, M.; Temelli, F.; Ullah, A. Extraction, Optimization, and Characterization of Lipids from Spent Hens: An Unexploited Sustainable Bioresource. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safder, M.; Temelli, F.; Ullah, A. Lipid-Derived Hybrid Bionanocomposites from Spent Hens. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Oshita, K.; Nitta, T.; Takaoka, M. Evaluation of a Sludge-Treatment Process Comprising Lipid Extraction and Drying Using Liquefied Dimethyl Ether. Environ. Technol. 2020, 42, 3369–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, E.; Sparr-Eskilsson, C. EXTRACTION | Supercritical Fluid Extraction. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque de Castro, M.D.; Priego-Capote, F. Soxhlet Extraction: Past and Present Panacea. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque de Castro, M.D.; García Ayuso, L.E. ENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS | Soxhlet Extraction. In Encyclopedia of Separation Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 2701–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bascón-Bascon, M.A.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Soxhlet Extraction. In Liquid-Phase Extraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 327–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque de Castro, M.; García-Ayuso, L. Soxhlet Extraction of Solid Materials: An Outdated Technique with a Promising Innovative Future. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 369, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, T.; Liu, G.H.; Xu, X.; Shao, Y.; Qi, L.; Wang, H. Characterization and Reutilization Potential of Lipids in Sludges from Wastewater Treatment Processes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkiewicz, M.; Fortuny, A.; Stüber, F.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J.; Bengoa, C. Effects of Pre-Treatments on the Lipid Extraction and Biodiesel Production from Municipal WWTP Sludge. Fuel 2015, 141, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Prasad, P.; Shang, X.; Keum, Y.S. Advances in Lipid Extraction Methods—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiopoulos, I.; Hellier, P.; Ladommatos, N.; Russo-Profili, A.; Eveleigh, A.; Aliev, A.; Kay, A.; Mills-Lamptey, B. Influence of Solvent Selection and Extraction Temperature on Yield and Composition of Lipids Extracted from Spent Coffee Grounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 119, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, M.; Sangaletti-Gerhard, N.; Acuña, P.; Fuentes, I.; Jorquera, M.; Godoy, K.; Osses, F.; Navia, R. Screening Transesterifiable Lipid Accumulating Bacteria from Sewage Sludge for Biodiesel Production. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 8, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Bai, X.; Zhao, J.; Xia, S. Scum Sludge as a Potential Feedstock for Biodiesel Production from Wastewater Treatment Plants. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufreche, S.; Hernandez, R.; French, T.; Sparks, D.; Zappi, M.; Alley, E. Extraction of Lipids from Municipal Wastewater Plant Microorganisms for Production of Biodiesel. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, A.A.; Hossain, S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Naim, A.; Yahaya, A.; Ismail, N.; Naushad, M.; Bathula, C.; Ahmad, M.I. Extraction of Municipal Sewage Sludge Lipids Using Supercritical CO 2 for Biodiesel Production: Mathematical and Kinetics Modeling. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkiewicz, M.; Fortuny, A.; Stüber, F.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J.; Bengoa, C. Evaluation of Different Sludges from WWTP as a Potential Source for Biodiesel Production. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.A.; Azri, A.D.; Rahman, A.S.A.; Banjar, M.F.; Fizal, A.N.S.; Ahmad, N.; Zulkifli, M.; Taweepreda, W.; Hossain, M.S.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Effect of Particle Size, Solvent to Sludge Ratio and Solvent Temperature on the Extraction of Lipids from Sewage Sludge Cake Using Methanol. In Proceedings of the Green Chemical Engineering and Technology 2021: 5th GCET 2021 Proceedings, Simpang Ampat, Malaysia, 15 December 2021; Sapawe, N., Harun, N.F.C., Hassan, N., Rahim, M.Z.A., Hamzah, A.A., Eds.; AIP Publishing: Simpang Ampat, Malaysia, 2024; p. 040014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanioti, S.; Liadakis, G.; Tzia, C. Solid–Liquid Extraction. In Food Engineering Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 253–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boocock, D.G.B.; Konar, S.K.; Leung, A.; Ly, L.D. Fuels and Chemicals from Sewage Sludge. 1. The Solvent Extraction and Composition of a Lipid from a Raw Sewage Sludge. Fuel 1992, 71, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Rice, E.W., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781625762405. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, M.; Bauer, T.; Burgman, L.E.; Wetterlund, E. Fifty Years of Sewage Sludge Management Research: Mapping Researchers’ Motivations and Concerns. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.N.H. Statistical Optimization of Lipid Extraction from Wastewater Scum Sludge and Saponifiable Lipids Composition Analysis. Sci. J. Energy Eng. 2017, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sugiyama, M. Application of In Situ Heating SEM Observation for Characterization of Metal Microstructure. Available online: https://www.hitachi-hightech.com/global/en/sinews/si_report/130210/ (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Pratomo, S.B.; Oktadinata, H.; Widodo, T.W. Effect of Nickel Additions on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Low-Alloy Cr-Mo Cast Steel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 541, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/ (accessed on 13 June 2024).
- Demirbas, A. Biodiesel from Municipal Sewage Sludge (MSS): Challenges and Cost Analysis. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2017, 12, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Pinelo, M.; Sineiro, J.; Núñez, M.J. Processing of Rosa Rubiginosa: Extraction of Oil and Antioxidant Substances. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3506–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coats, H.B.; Wingard, M.R. Solvent Extraction. III. The Effect of Particle Size on Extraction Rate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1950, 27, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, S.L.; Xu, M.; Wei, Y.; Fan, T.T.; Huang, L.X.; Ma, B.; Guo, J. The Measurements of the Intrinsic Diffusivity in Pores and Surface Diffusivity inside the Porous Materials in Liquid Phase. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 196, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.T.; Wei, Y.Q.; Chen, S.L.; Sun, W.; Fan, T.T.; Xu, M.R.; Zhang, C.C. Measurement of Pore Diffusion Factor of Porous Solid Materials. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gião, M.S.; Pereira, C.I.; Fonseca, S.C.; Pintado, M.E.; Malcata, F.X. Effect of Particle Size upon the Extent of Extraction of Antioxidant Power from the Plants Agrimonia Eupatoria, Salvia Sp. and Satureja Montana. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Lai, Y.M.; Jin, J.F.; Zhou, J.R.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, K. Effect of Particle Size and Solution Leaching on Water Retention Behavior of Ion-Absorbed Rare Earth. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 4921807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkiewicz, M.; Caporgno, M.P.; Fortuny, A.; Stüber, F.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J.; Bengoa, C. Direct Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Lipid from Municipal Sewage Sludge for Biodiesel Production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 128, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondala, A.; Liang, K.; Toghiani, H.; Hernandez, R.; French, T. Biodiesel Production by in Situ Transesterification of Municipal Primary and Secondary Sludges. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Silva, J.; Filho, G.R.; Da Silva Meireles, C.; Ribeiro, S.D.; Vieira, J.G.; Da Silva, C.V.; Cerqueira, D.A. Thermal Analysis and FTIR Studies of Sewage Sludge Produced in Treatment Plants. the Case of Sludge in the City of Uberlândia-MG, Brazil. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 528, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to Read and Interpret Ftir Spectroscope of Organic Material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006; pp. 10815–10837. ISBN 0471976709. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski, M.; Kowalska, K.; Wiszniowski, J.; Turek-Szytow, J. Qualitative Analysis of Activated Sludge Using FT-IR Technique. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.C. The C=O Bond, Part VI: Esters and the Rule of Three. Spectroscopy 2018, 33, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.C. The C=O Bond, Part VIII: Review. Spectroscopy 2018, 33, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Yang, H.; Dong, X.; Lei, H.; Chen, D. PH-Sensitive Polymeric Particles as Smart Carriers for Rebar Inhibitors Delivery in Alkaline Condition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Loss, R.D.; Shields, D.; Pawlik, T.; Hochreiter, R.; Zydney, A.L.; Kumar, M. Polyacrylamide Degradation and Its Implications in Environmental Systems. Npj Clean Water 2018, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 21, ISBN 0471393622. [Google Scholar]
- Borrajo, J.P.; Liste, S.; Serra, J.; González, P.; Chiussi, S.; León, B.; Pérez Amor, M.; Ylänen, H.O.; Hupa, M. Influence of the Network Modifier Content on the Bioactivity of Silicate Glasses. Key Eng. Mater. 2003, 254, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Y.; Yu, P.; Liu, M. Improvement of Activated Sludge Dewatering Properties Using Green Conditioners: Chitosan Hydrochloride and Lysozyme. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6936–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, K.; Chen, T. Preparation of Modified Waterworks Sludge Particles as Adsorbent to Enhance Coagulation of Slightly Polluted Source Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19393–19401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Albahnasawi, A.; Ali, G.A.M.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Nassani, D.E.; Al Maskari, T.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Abujazar, M.S.S. Application of Natural Coagulants for Pharmaceutical Removal from Water and Wastewater: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Sola, A. Metal Particle Shape: A Practical Perspective. Met. Powder Rep. 2018, 73, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Chai, L.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H. Chemical Precipitation Granular Sludge (CPGS) Formation for Copper Removal from Wastewater. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 114405–114411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczyński, L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Kosobucka, M.; Smoczyński, M. Image Analysis of Sludge Aggregates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camassa, R.; Harris, D.M.; Hunt, R.; Kilic, Z.; McLaughlin, R.M. A First-Principle Mechanism for Particulate Aggregation and Self-Assembly in Stratified Fluids. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Cao, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Bai, H. Experiments and Mechanisms for Leaching Remediation of Lead-Contaminated Soil by Enhancing Permeability. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.P.; Wang, J.Y. Comprehensive Characterisation of Sewage Sludge for Thermochemical Conversion Processes—Based on Singapore Survey. Waste Manag. 2016, 54, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detho, A.; Kadir, A.A.; Ahmad, S. Utilization of Wastewater Treatment Sludge in the Production of Fired Clay Bricks: An Approach towards Sustainable Development. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N.F.A.; Saiter, J.M.; Halim, S.I.A.; Lucas, R.; Chan, C.H. Thermal Analysis: Basic Concept of Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Thermogravimetry for Beginners. Chem. Teach. Int. 2021, 3, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Fu, K.; Fu, X.; Guan, Q.; Ding, L.; Shi, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, L. Flocculation Properties and Kinetic Investigation of Polyacrylamide with Different Cationic Monomer Content for High Turbid Water Purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 182, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettler Toledo Thermal Analysis Application No. UC 131: Interpreting TGA Curves. In Mettler Toledo Thermal Analysis UserCom 13; Mettler Toledo: Schwerzenbach, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 1–4.
- Dahhou, M.; El Moussaouiti, M.; Benlalla, A.; El Hamidi, A.; Taibi, M.; Arshad, M.A. Structural Aspects and Thermal Degradation Kinetics of Water Treatment Plant Sludge of Moroccan Capital. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 7, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphahlele, K.; Matjie, R.H.; Osifo, P.O. Thermodynamics, Kinetics and Thermal Decomposition Characteristics of Sewage Sludge during Slow Pyrolysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, Q.V.; Chen, W.H. A Comprehensive Study on Pyrolysis Kinetics of Microalgal Biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 131, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodke, P.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Pandey, J.K.; Chen, W.-H.; Patel, A.; Ashokkumar, V. Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge for Sustainable Biofuels and Value-Added Biochar Production. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 298, 113450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Wang, T.; Lin, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yi, J.; Li, S. Promoting Effects of Polyacrylamide on Ignition and Combustion of Al/H2O Based Fuels: Experimental Studies of Polyacrylamide Aqueous Solution Flash Pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2010, 87, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doble, M.; Kumar, A. Degradation of Polymers. In Biotreatment of Industrial Effluents; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Languer, M.P.; Batistella, L.; Alves, J.L.F.; Da Silva, J.C.G.; da Silva Filho, V.F.; Di Domenico, M.; Moreira, R.d.F.P.M.; José, H.J. Insights into Pyrolysis Characteristics of Brazilian High-Ash Sewage Sludges Using Thermogravimetric Analysis and Bench-Scale Experiments with GC-MS to Evaluate Their Bioenergy Potential. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 138, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuanhchamnong, C.; Kositkanawuth, K.; Wantaneeyakul, N. Granular Waterworks Sludge-Biochar Composites: Characterization and Dye Removal Application. Results Eng. 2022, 14, 100451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gutiérrez, L.R.; Romero-Guzmán, E.T.; Cabral-Prieto, A.; Rodríguez-Castillo, R. Characterization of Chromium in Contaminated Soil Studied by SEM, EDS, XRD and Mössbauer Spectroscopy. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2007, 7, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanudet, V.; Filella, M. Size and Composition of Inorganic Colloids in a Peri-Alpine, Glacial Flour-Rich Lake. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.; Wheeler, R.; Oliver, I.W. Evaluating Land Application of Pulp and Paper Mill Sludge: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, A.; Westerhoff, P. Recovery Opportunities for Metals and Energy from Sewage Sludges. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; ten Hoeve, M.; Christensen, T.H.; Bruun, S.; Jensen, L.S.; Scheutz, C. Life Cycle Assessment of Sewage Sludge Management Options Including Long-Term Impacts after Land Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsybina, A.; Wuensch, C. Analysis of Sewage Sludge Thermal Methods in the Context of Circular Economy. Detritus 2018, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtshali, J.S.; Tiruneh, A.T.; Fadiran, A.O. Sewage Sludge, Nutrient Value, Organic Fertilizer, Soil Amendment, Sludge Reuse, Nitrogen, Phosphorus; Sewage Sludge, Nutrient Value, Organic Fertilizer, Soil Amendment, Sludge Reuse, Nitrogen, Phosphorus. Resour. Environ. 2014, 4, 190–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, Y.; Lee, Y.-J. Sludge Treatment: Current Research Trends. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, S.; Tan, X.; Wan, Y. Strength and Microstructure Properties of Solidified Sewage Sludge with Two Types of Cement-Based Binders. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Gao, M.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q. Past, Current, and Future Research on Microalga-Derived Biodiesel: A Critical Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10596–10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, H.S.; Jaya, D.E.C. Analysis of Esterification Research in Indonesia for 25 Years Using Bibliometric Method. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hong, R.; Xiang, C.; Lv, C.; Li, H. Visualization and Analysis of Mapping Knowledge Domains for Spontaneous Combustion Studies. Fuel 2020, 262, 116598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer Manual Manual for VOSviewer Version 1.6.20 Software Documentation; Univeristeit Leiden: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, I.; Martínez, F.; Cala, V. Heavy Metal Speciation and Phytotoxic Effects of Three Representative Sewage Sludges for Agricultural Uses. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New Trends in Removing Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences Engineering and Medicine. Bioavailability of Contaminants in Soils and Sediments; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-309-08625-7. [Google Scholar]
- Semple, K.T.; Morriss, A.W.J.; Paton, G.I. Bioavailability of Hydrophobic Organic Contaminants in Soils: Fundamental Concepts and Techniques for Analysis. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L. Bioleaching Conditioning Increased the Bioavailability of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons to Promote Their Removal during Co-Composting of Industrial and Municipal Sewage Sludges. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košnář, Z.; Mercl, F.; Pierdonà, L.; Chane, A.D.; Míchal, P.; Tlustoš, P. Concentration of the Main Persistent Organic Pollutants in Sewage Sludge in Relation to Wastewater Treatment Plant Parameters and Sludge Stabilisation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchuk, S.; Tait, S.; Sinha, P.; Harris, P.; Antille, D.L.; McCabe, B.K. Biosolids-Derived Fertilisers: A Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, A.P.; Gupta, D.P.; Durbha, K.S. Sewage Sludge to Bio-Fuel: A Review on the Sustainable Approach of Transforming Sewage Waste to Alternative Fuel. Fuel 2020, 259, 116262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Svoboda, M.L.; Peart, T.E.; Smyth, S.A. Optimization of a Microwave-Assisted Extraction Procedure for the Determination of Selected Alkyl, Aryl, and Halogenated Phenols in Sewage Sludge and Biosolids. Water Qual. Res. J. Canada 2016, 51, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Antunes, E.; Whelan, A.; Fearon, R.; Sheehan, M.; Reeves, L. Emerging Contaminants in Biosolids: Presence, Fate and Analytical Techniques. Emerg. Contam. 2022, 8, 162–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fonseca, F.G.; Gong, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Hornung, U.; Dahmen, N. Energy Valorization of Integrating Lipid Extraction and Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Lipid-Extracted Sewage Sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathianpour, A.; Taheriyoun, M.; Soleimani, M. Lead and Zinc Stabilization of Soil Using Sewage Sludge Biochar: Optimization through Response Surface Methodology. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne, O.; Mockevičienė, I.; Karčauskienė, D.; Repšienė, R.; Šiaudinis, G.; Barčauskaitė, K.; Žilė, G. Biochar-Assisted Phytoremediation Potential of Sewage Sludge Contaminated Soil. Sustainability 2023, 16, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniowska, E.; Grobelak, A.; Kokot, P.; Kacprzak, M. Sludge Legislation-Comparison between Different Countries. In Industrial and Municipal Sludge Emerging Concerns and Scope for Resource Recovery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos-Delgado, F.D.J.; Reynel-Avila, H.E.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A. Lipid Extraction in the Primary Sludge Generated from Urban Wastewater Treatment: Characteristics and Seasonal Composition Analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 2930–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neha, S.; Vergeynst, L.; Biller, P. Evaluating Hydrothermal Liquefaction Hydrochar from Sewage Sludge as a Phosphorus Resource through Struvite Production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Types of Sewage Sludge | Ref. | Polymer Flocculant | pH | Moisture Content, MC (%) | Total Solid, TS (wt.%) | Volatile Solid, VS (%) | Total Chemical Oxygen Demand, TCOD (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated primary | [20] | No | 5.0–8.0 | - | 2.0–8.0 | a 60–80 | - |
| Digested primary | [20] | No | 6.5–7.5 | - | 6.0–12.0 | a 30–60 | - |
| Secondary | [20] | No | 6.5–8.0 | - | 0.8–1.2 | a 59–88 | - |
| Waste-activated | [21] | No | 6.9 ± 0.1 | - | b 2.8 | b 2.05 | b 33.17 ± 0.72 |
| Dewatered | [28] | Yes | - | - | 20.2 ± 0.3 | 14.6 ± 0.1 | 275.3 ± 7.0 |
| Dewatered | [29] | Yes | - | 66.68 ± 1.67 | - | 35.98 ± 7.95 | - |
| Dewatered | [30] | Yes | 7.7 ± 0.1 | - | 17.1 ± 0.2 | a 60.5 ± 0.5 | - |
| Biocompounds | Units | WAS [31] | DS [30] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-EPS | LB-EPS | TB-EPS | |||
| Polysaccharides | mg/L | a 506.3–3234 | 524.30 | 258.94 | 1132.06 |
| Proteins | mg/L | 2656–13,530 | 1259.76 | 1532.24 | 3708.62 |
| Lipids | mg/L | 166–3960 | - | - | - |
| Humic acids | mg/L | 196.71–5849 | - | - | - |
| Method | Type of Sludge | Solvent | Lipids Yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Bligh and Dyer | Secondary | Chloroform–methanol | 12.6 | [46] |
| Acid hydrolysis | Dewatered | Bromopropane | 7.5 ± 0.55 | [7] |
| Water bath shaking | Dewatered | Hexane–ethanol | 7.5 ± 0.06 | [7] |
| Boiling extraction (reflux) | Scum Primary Secondary | Methanol–hexane–acetone | 33.3 27.0 16.9 | [47] |
| Accelerated solvent extraction system | Secondary | Hexane, methanol | 1.94 − 27.43 | [48] |
| Subcritical fluid extraction system | Stabilized (digested) | Liquefied dimethyl ether | 2.24 | [36] |
| SFE-CO2 | Secondary | Carbon dioxide | 3.55 − 13.56 | [48] |
| SFE-CO2 | Sludge cake | Carbon dioxide | 0.65 | [29] |
| SFE-CO2 | Primary | Carbon dioxide H2O, C2H5OH, H2O2 | 20.34 − 21.35 | [49] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Dewatered | Hexane–ethanol | 10.3 ± 0.20 | [7] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Primary Secondary | Chloroform–methanol | 15.6 4.6 | [42] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Primary | Methanol | 40.21 | [32] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Sludge cake | Methanol Ethanol | 4.05 5.16 | [29] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Primary Secondary Blended Stabilized | Hexane | 25.3 9.1 13.9 1 | [43,50] |
| Soxhlet extraction | Dewatered | Methanol | 11.05 | [51] |
| Parameters | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture content (MC) | % | 80.82 ± 0.94 |
| Total solid (TS) | % | 19.18 ± 0.94 |
| Volatile solid (VS) | % of TS | 46.75 ± 0.74 |
| Particle Size (mm) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| <0.5 | 13.70 ± 5.87 |
| 0.5–1.0 | 13.58 ± 1.56 |
| 1.0–2.0 | 30.88 ± 4.22 |
| 2.0–4.0 | 25.56 ± 2.70 |
| >4.0 | 16.29 ± 3.07 |
| Element | Composition (wt.%) | Difference (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | RDS | Reduce | Increase | |
| O | 45.41 | 36.69 | −8.72 | |
| C | 23.88 | 30.79 | +6.91 | |
| Fe | 15.75 | 18.22 | +2.47 | |
| P | 7.21 | 4.89 | −2.32 | |
| Al | 1.90 | 1.80 | −0.10 | |
| Mg | 1.35 | 1.19 | −0.16 | |
| S | 1.19 | 1.49 | +0.30 | |
| Ca | 0.98 | 1.57 | +0.59 | |
| Si | 0.92 | 2.00 | +1.08 | |
| Na | 0.90 | 0.62 | −0.28 | |
| Cl | 0.31 | 0.41 | +0.10 | |
| K | 0.21 | 0.32 | +0.11 | |
| Sample | Mass Loss at Temperature (%) | Residue at 950 °C (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 °C | 202 °C | 210 °C | 450 °C | 491 °C | ||
| WAS | 5.27 | 6.09 | 6.24 | 29.92 | 34.06 | 35.34 |
| Polymer flocculant | 12.18 | 15.72 | 16.18 | 71.21 | 72.53 | 1.66 |
| DS | 3.52 | 6.09 | 6.44 | 31.63 | 34.06 | 48.40 |
| RDS | 0.23 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 22.41 | 24.95 | 55.51 |
| Sludge | Temperature of Mass Loss (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 20% | 30% | 40% | |
| DS | 252.83 | 330.50 | 428.17 | 683.50 |
| RDS | 323.00 | 418.17 | 638.00 | 840.17 |
| Technology | Objectives | Process | Product/Emission |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gasification | Conversion of organic materials and inert material Energy recovery (heat) | 800–900 °C with limited oxygen Gasifying media | Syngas (H2, CO, CO2 and hydrocarbons) Gasification ash |
| Combustion | Burning organic materials Nutrient recovery Energy recovery (heat) | Burning organic materials in the presence of excess air | Gases (CO2, CO, H2O, NOx, SOx, VOCs) Fly ash Particulate matter |
| Incineration | Volume reduction Harmful substances destruction Energy recovery (heat) | >760 °C in the presence of excess air | Gases (CO2, CO, H2O, NOx, SOx, VOCs) Incinerator ash Particulate matter |
| Pyrolysis | Thermal decomposition of organic material Energy recovery (heat and materials) | 300–700 °C in absence of oxygen | Liquid pyrolytic oil (bio-oil) Solid biochar Non-condensable gas |
| No | Keyword | Cluster | Occurrences | TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sewage sludge | 3 | 712 | 1363 |
| 2 | Heavy metals | 4 | 223 | 498 |
| 3 | Sludge | 2 | 132 | 258 |
| 4 | Sequential extraction | 1 | 114 | 261 |
| 5 | Extraction | 5 | 64 | 143 |
| 6 | Soil | 2 | 61 | 157 |
| 7 | Heavy metal | 4 | 61 | 142 |
| 8 | Bioavailability | 2 | 56 | 160 |
| 9 | Phosphorus | 5 | 50 | 129 |
| 10 | Compost | 2 | 46 | 116 |
| 11 | Anaerobic digestion | 2 | 42 | 66 |
| 12 | Wastewater | 3 | 42 | 97 |
| 13 | Phosphorus recovery | 5 | 42 | 68 |
| 14 | Speciation | 2 | 40 | 118 |
| 15 | Pyrolysis | 4 | 40 | 86 |
| 16 | Biosolids | 3 | 38 | 77 |
| 17 | Metals | 1 | 36 | 75 |
| 18 | Cadmium | 1 | 35 | 91 |
| 19 | Biochar | 4 | 35 | 88 |
| 20 | Composting | 2 | 33 | 83 |
| 21 | Zinc | 1 | 29 | 97 |
| 22 | Sewage sludge ash | 5 | 26 | 50 |
| 23 | Copper | 1 | 25 | 79 |
| 24 | Pressurized liquid extraction | 3 | 24 | 57 |
| 25 | Biodiesel | 3 | 24 | 35 |
| 26 | Leaching | 1 | 23 | 56 |
| 27 | Pharmaceuticals | 3 | 23 | 48 |
| 28 | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon | 3 | 22 | 52 |
| 29 | Sediment | 2 | 20 | 44 |
| 30 | Microwave-assisted extraction | 3 | 19 | 49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalil, N.A.; Lajulliadi, A.F.; Abedin, F.N.J.; Fizal, A.N.S.; Safie, S.I.; Zulkifli, M.; Taweepreda, W.; Hossain, M.S.; Ahmad Yahaya, A.N. Multifaceted Impact of Lipid Extraction on the Characteristics of Polymer-Based Sewage Sludge towards Sustainable Sludge Management. Polymers 2024, 16, 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182646
Khalil NA, Lajulliadi AF, Abedin FNJ, Fizal ANS, Safie SI, Zulkifli M, Taweepreda W, Hossain MS, Ahmad Yahaya AN. Multifaceted Impact of Lipid Extraction on the Characteristics of Polymer-Based Sewage Sludge towards Sustainable Sludge Management. Polymers. 2024; 16(18):2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182646
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalil, Nor Afifah, Ahmad Fiqhri Lajulliadi, Fatin Najwa Joynal Abedin, Ahmad Noor Syimir Fizal, Sairul Izwan Safie, Muzafar Zulkifli, Wirach Taweepreda, Md Sohrab Hossain, and Ahmad Naim Ahmad Yahaya. 2024. "Multifaceted Impact of Lipid Extraction on the Characteristics of Polymer-Based Sewage Sludge towards Sustainable Sludge Management" Polymers 16, no. 18: 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182646
APA StyleKhalil, N. A., Lajulliadi, A. F., Abedin, F. N. J., Fizal, A. N. S., Safie, S. I., Zulkifli, M., Taweepreda, W., Hossain, M. S., & Ahmad Yahaya, A. N. (2024). Multifaceted Impact of Lipid Extraction on the Characteristics of Polymer-Based Sewage Sludge towards Sustainable Sludge Management. Polymers, 16(18), 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182646










