Analysis of the Impact of Cooling Lubricants on the Tensile Properties of FDM 3D Printed PLA and PLA+CF Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PLA and PLA+CF Materials Specification and Mechanical Parameters
| Parameters | Test Method | Material Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | PLA+CF | ||
| Density (g/cm3) | ISO 1183 [58] | 1.24 | ~1.29 |
| Young’s modulus (MPa) | ISO 527 [59] | 1000–1100 | 1100–1300 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | ISO 527 | 45–49 | 40–45 |
| Elongation at break (%) | ISO 527 | 13.5–15.5 | 11.5–13.5 |
| Heat deflection temperature (°C) | ISO 75 [60] | 53 | 60 |
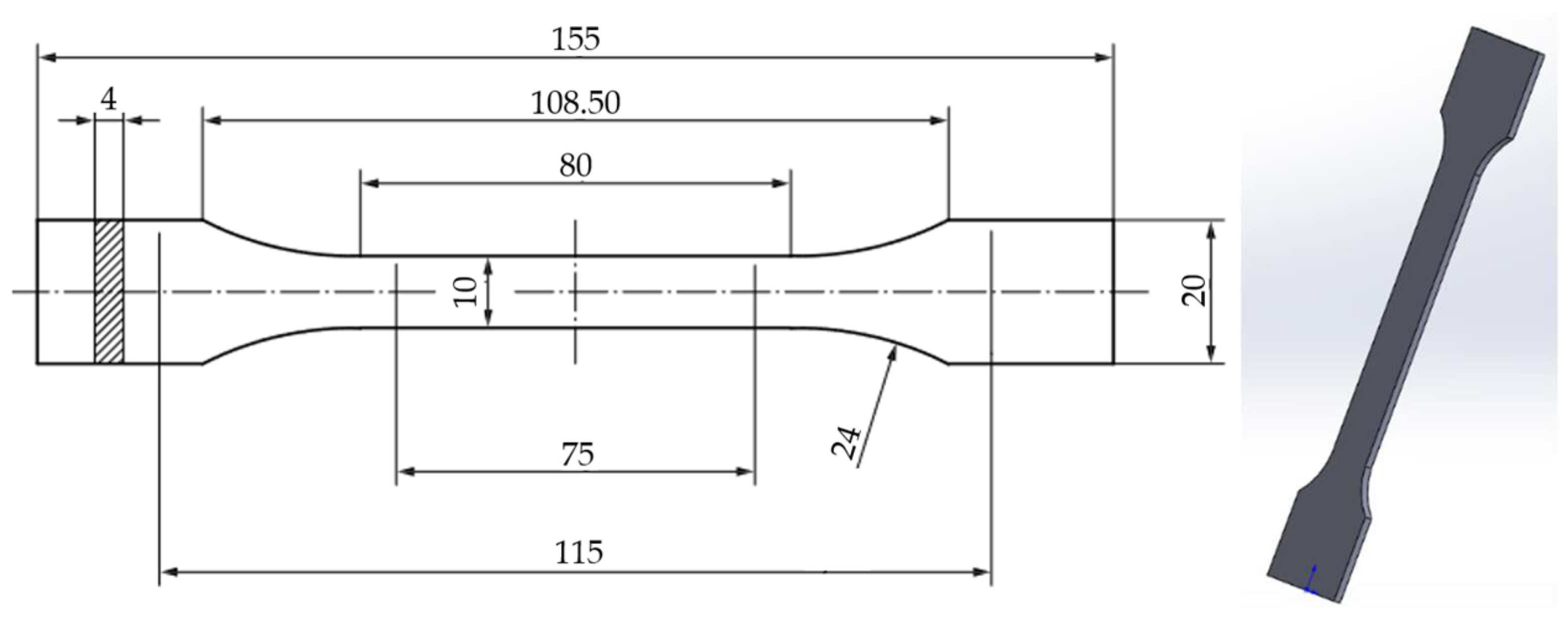
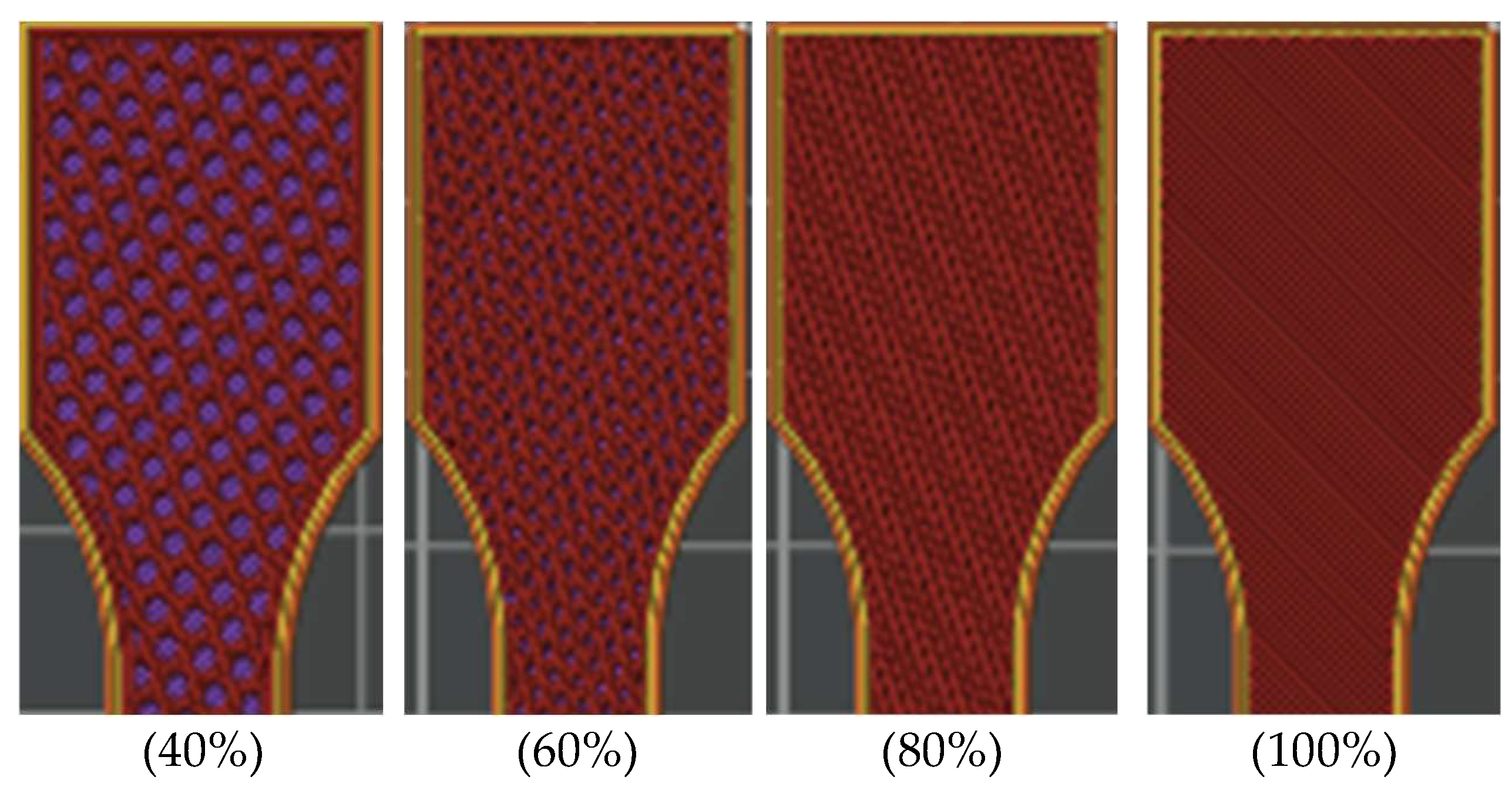
2.2. Preparation and 3D Printing of Tensile Test Specimens
2.3. Tensile Testing for 3D-Printed Specimens
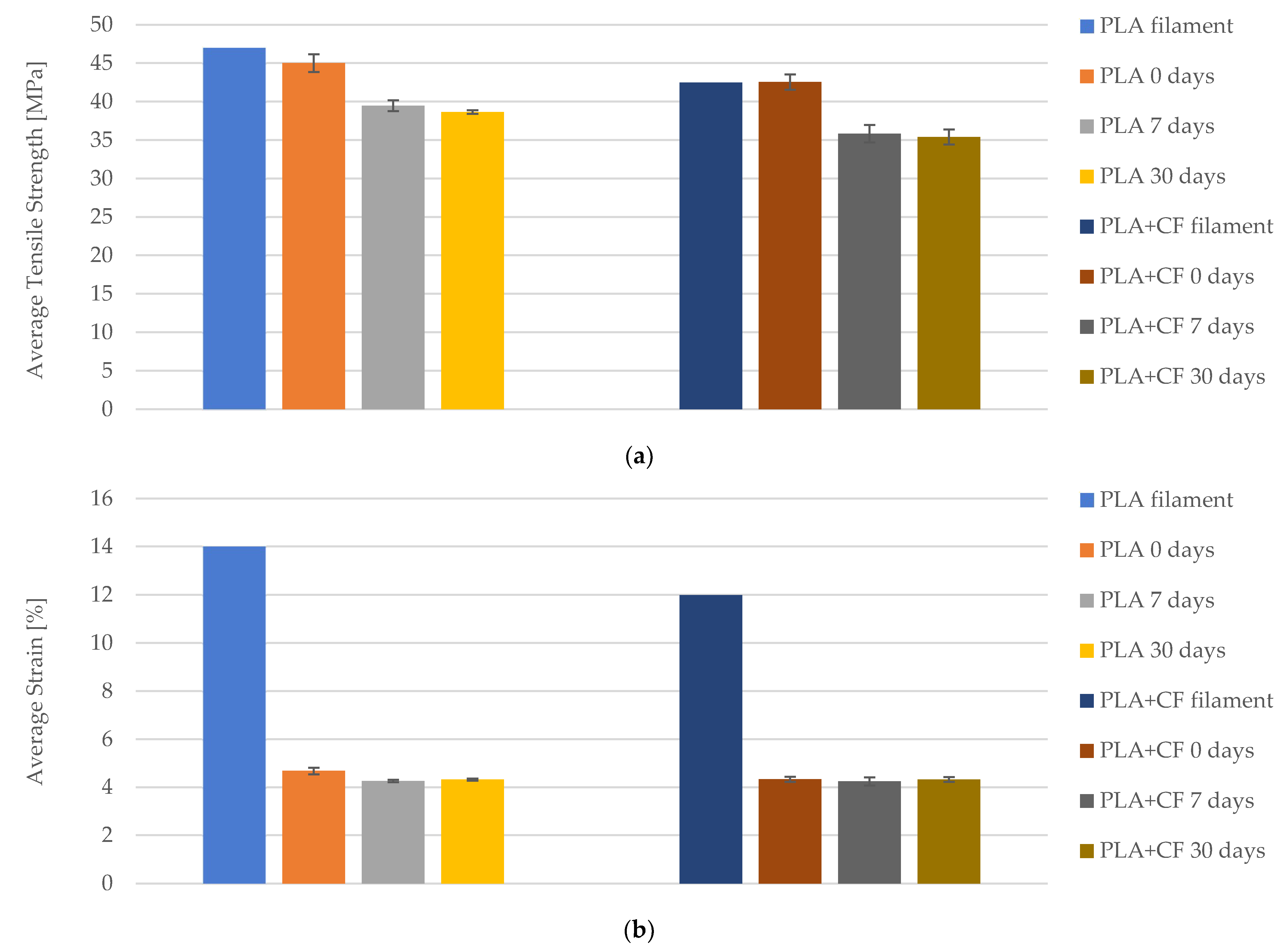
3. Results
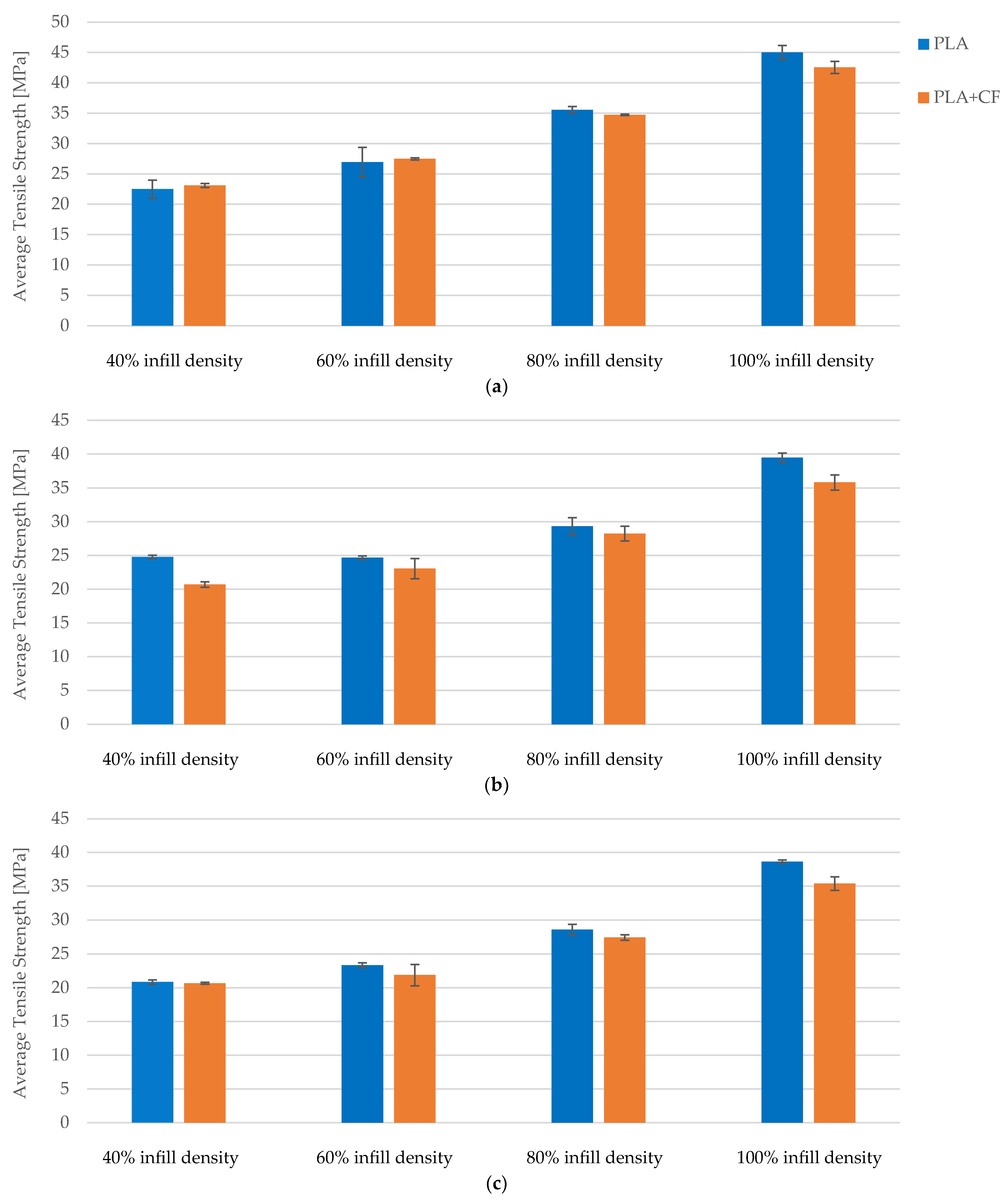
3.1. Tensile Properties of the FDM 3D-Printed PLA Specimens
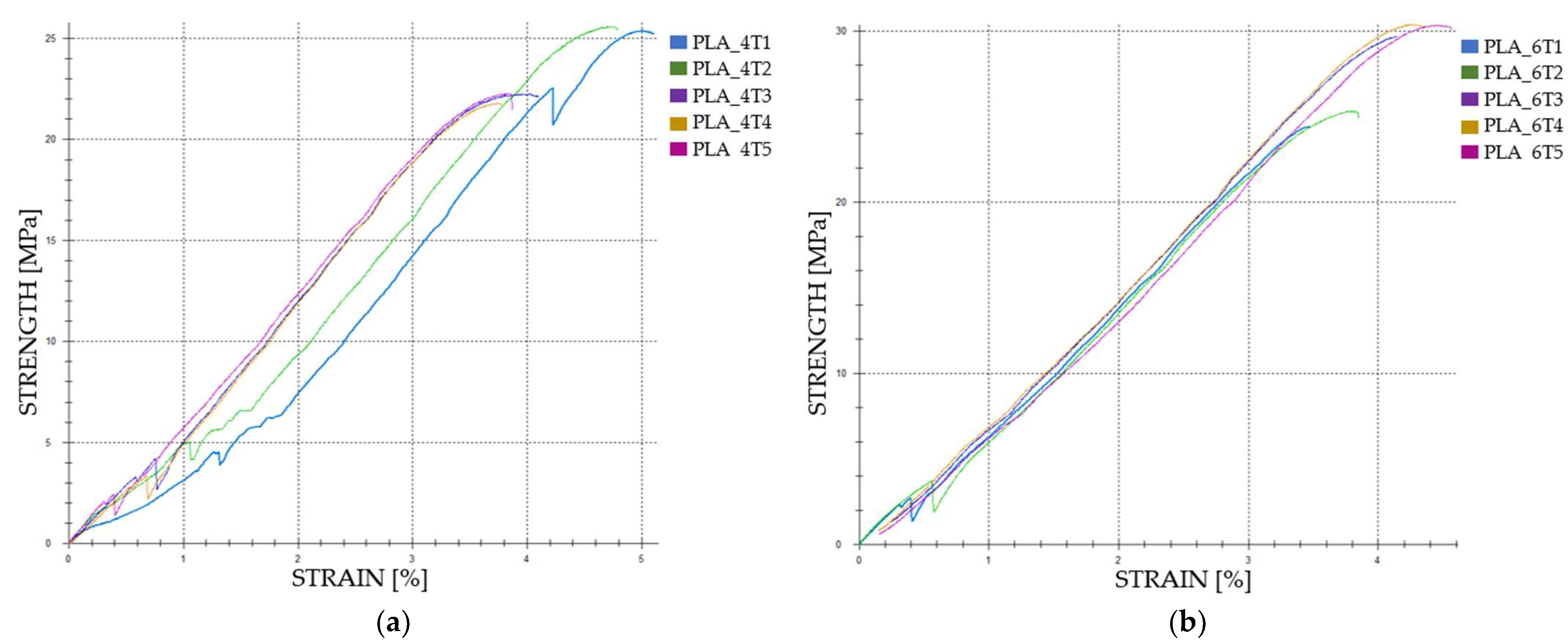
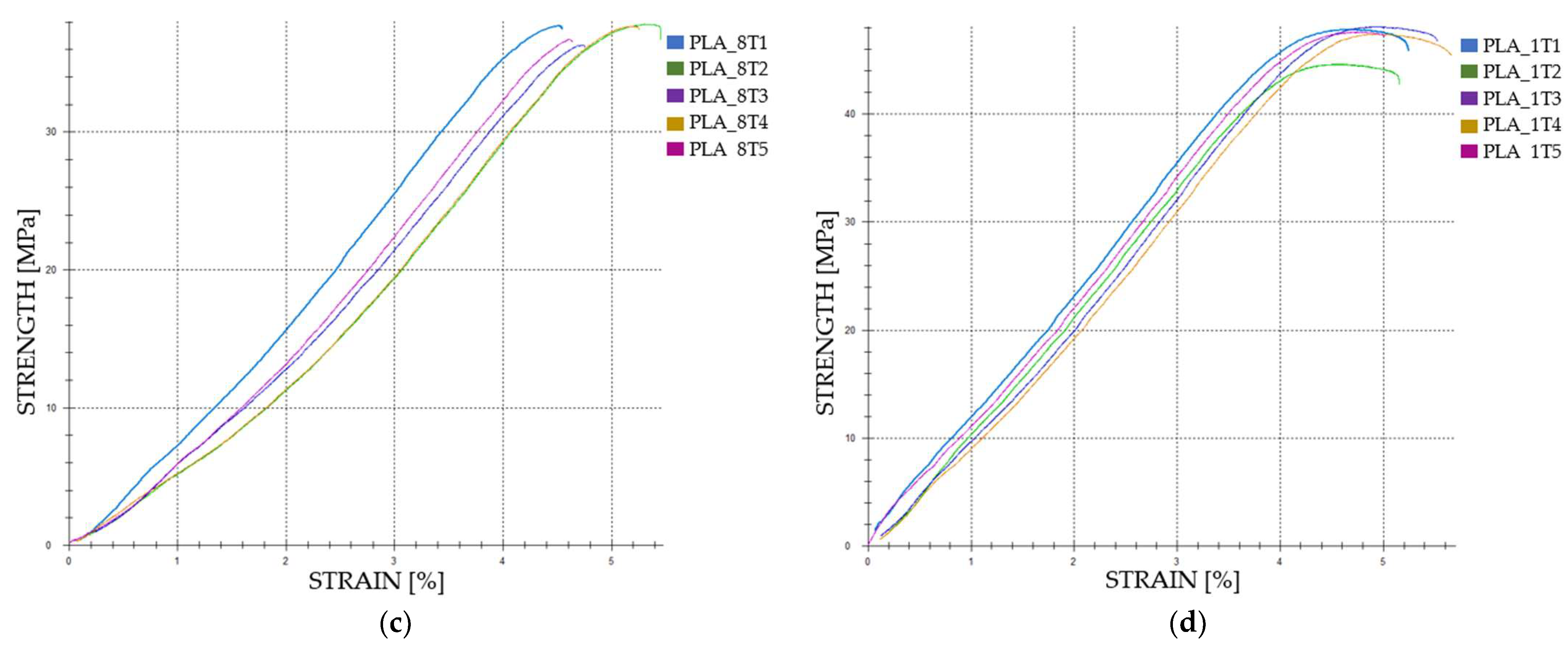
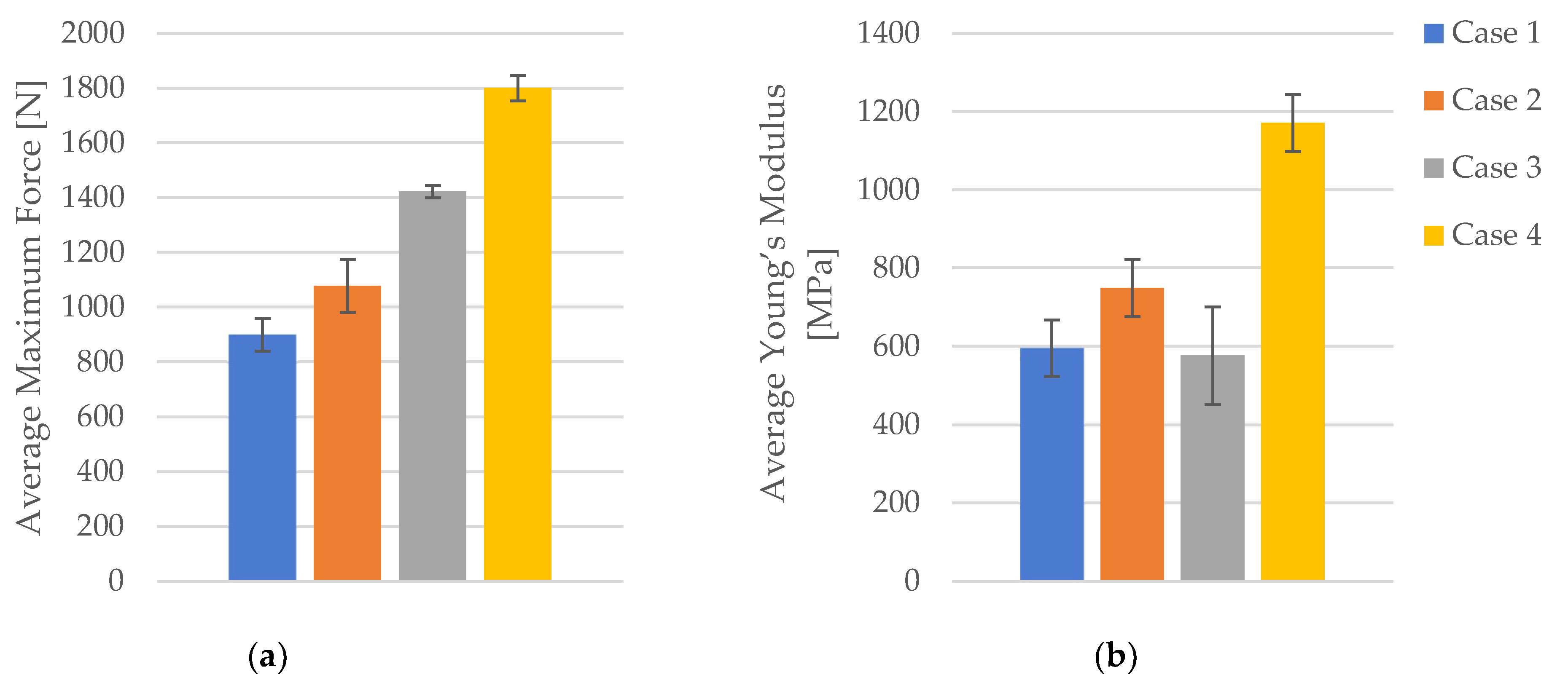
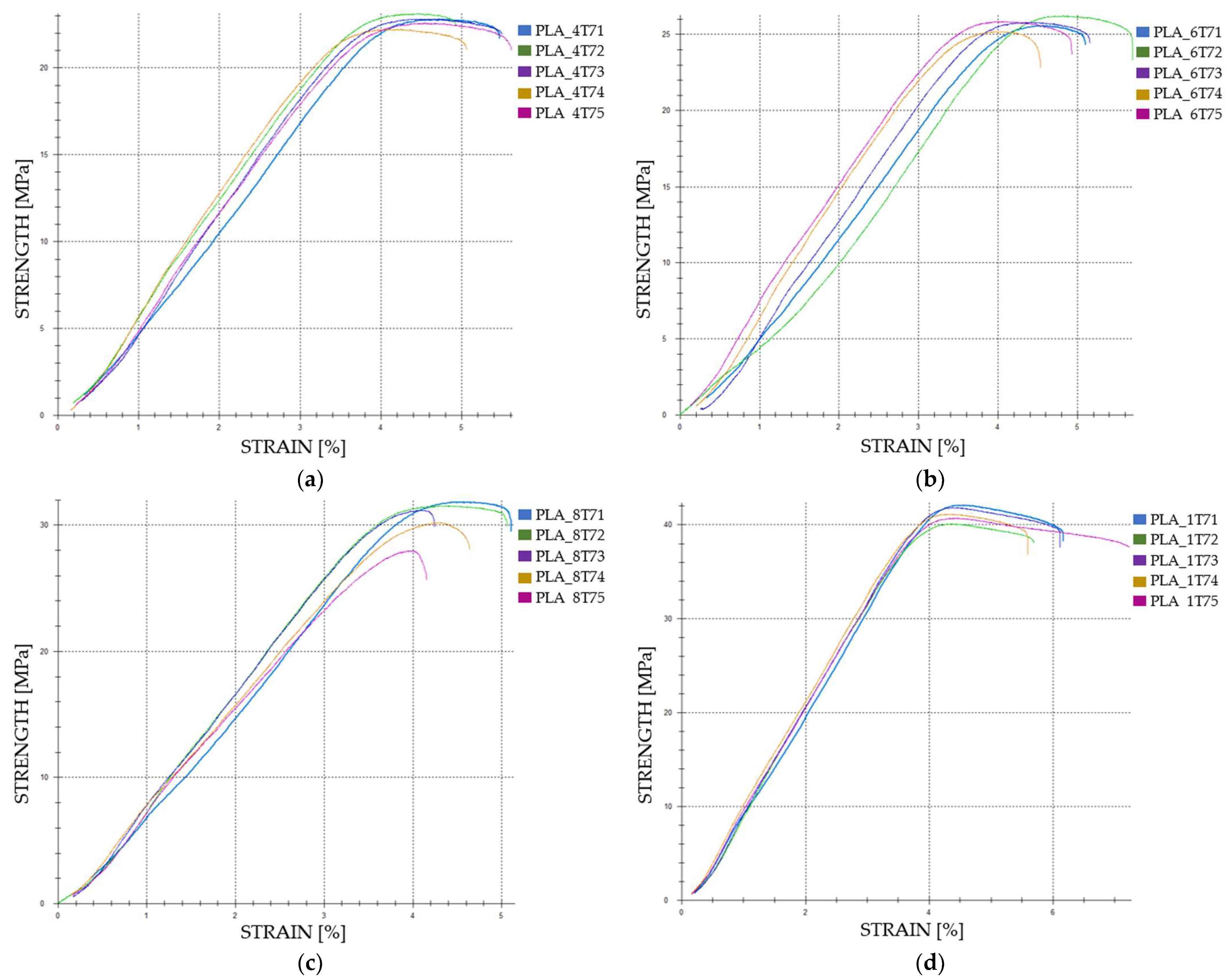
3.1.1. Tensile Properties of FDM 3D-Printed PLA Specimens Not Exposed to Cooling Lubricant
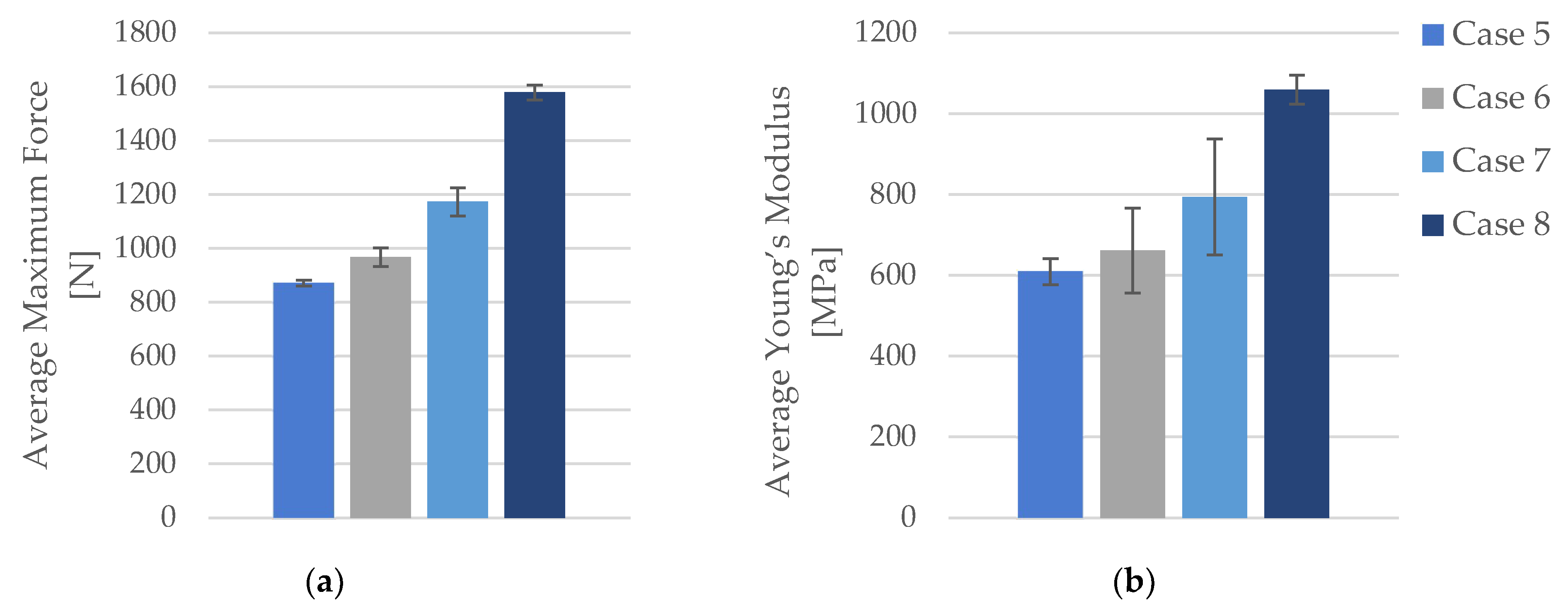
3.1.2. Tensile Properties of FDM 3D-Printed PLA Specimens Exposed to Cooling Lubricant for 7 Days
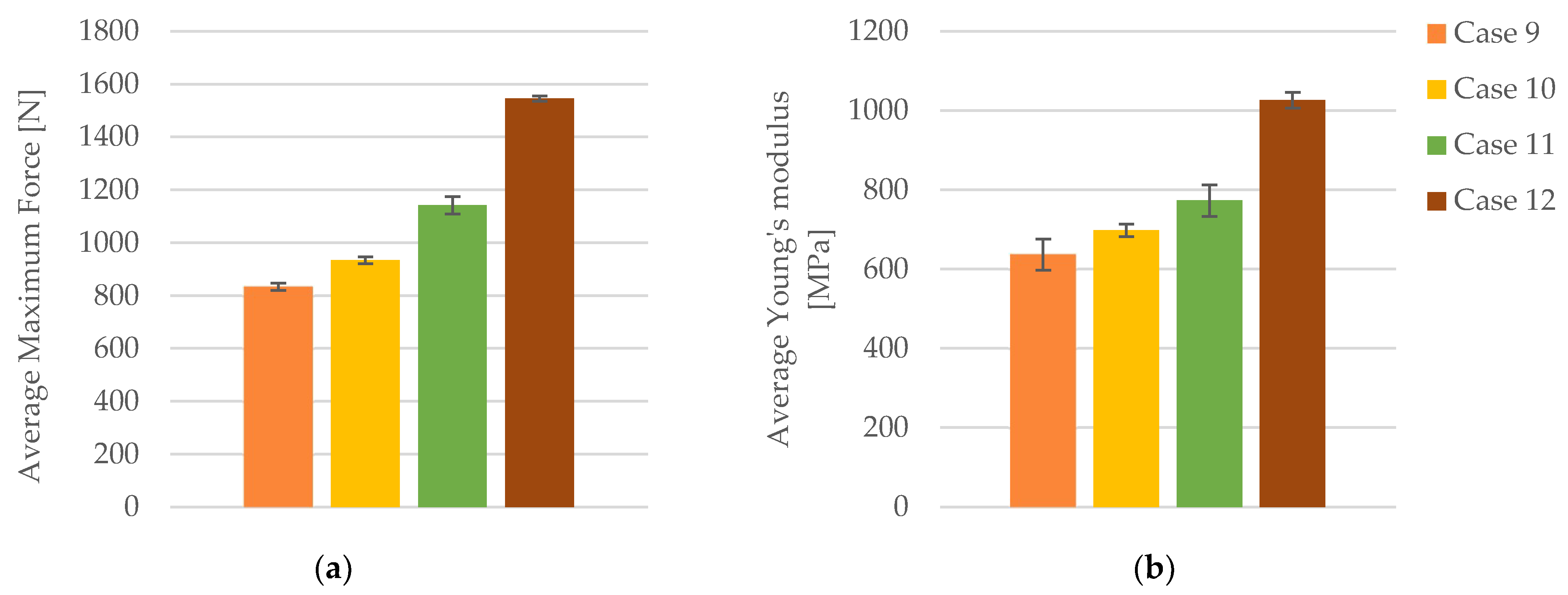
3.1.3. Tensile Properties of FDM 3D-Printed PLA Specimens Exposed to Cooling Lubricant for 30 Days
3.2. Tensile Properties of the FDM 3D-Printed PLA+CF Specimens
3.2.1. Tensile Properties of the FDM 3D-Printed PLA+CF Specimens Not Exposed to Cooling Lubricant
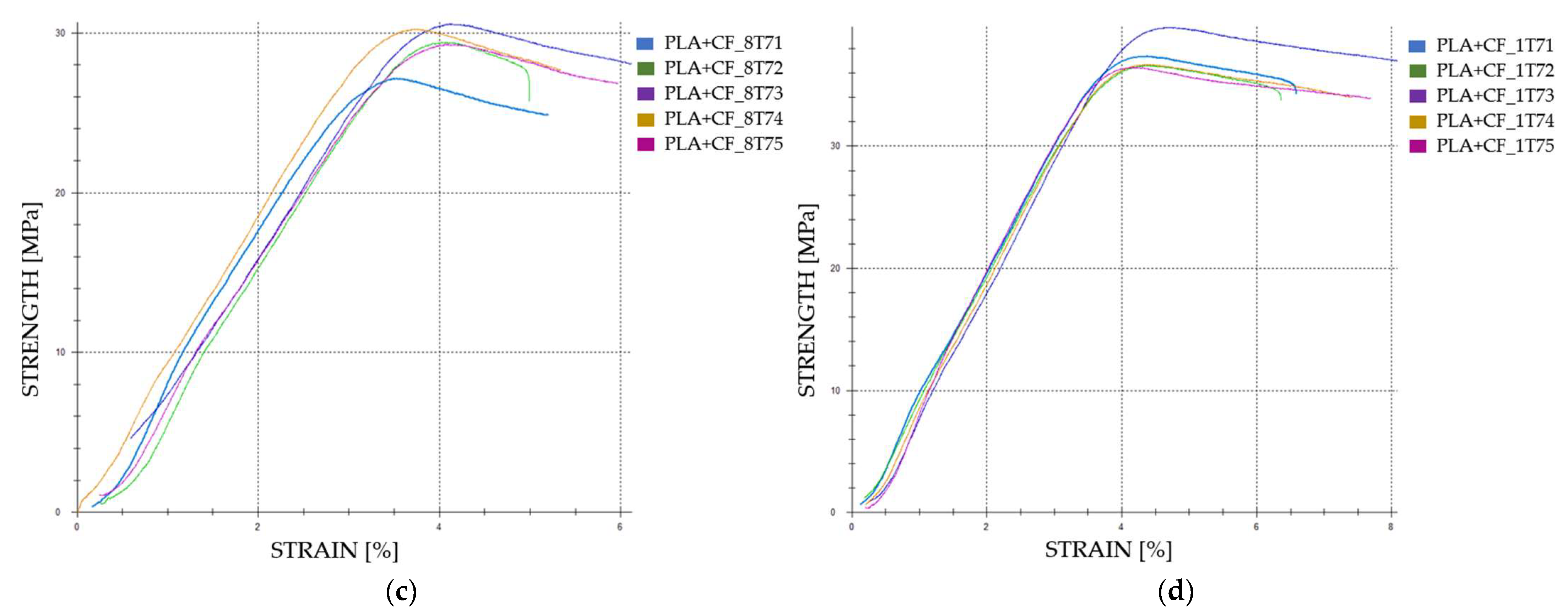
3.2.2. Tensile Properties of the FDM 3D-Printed PLA+CF Specimens Exposed to Cooling Lubricant for 7 Days
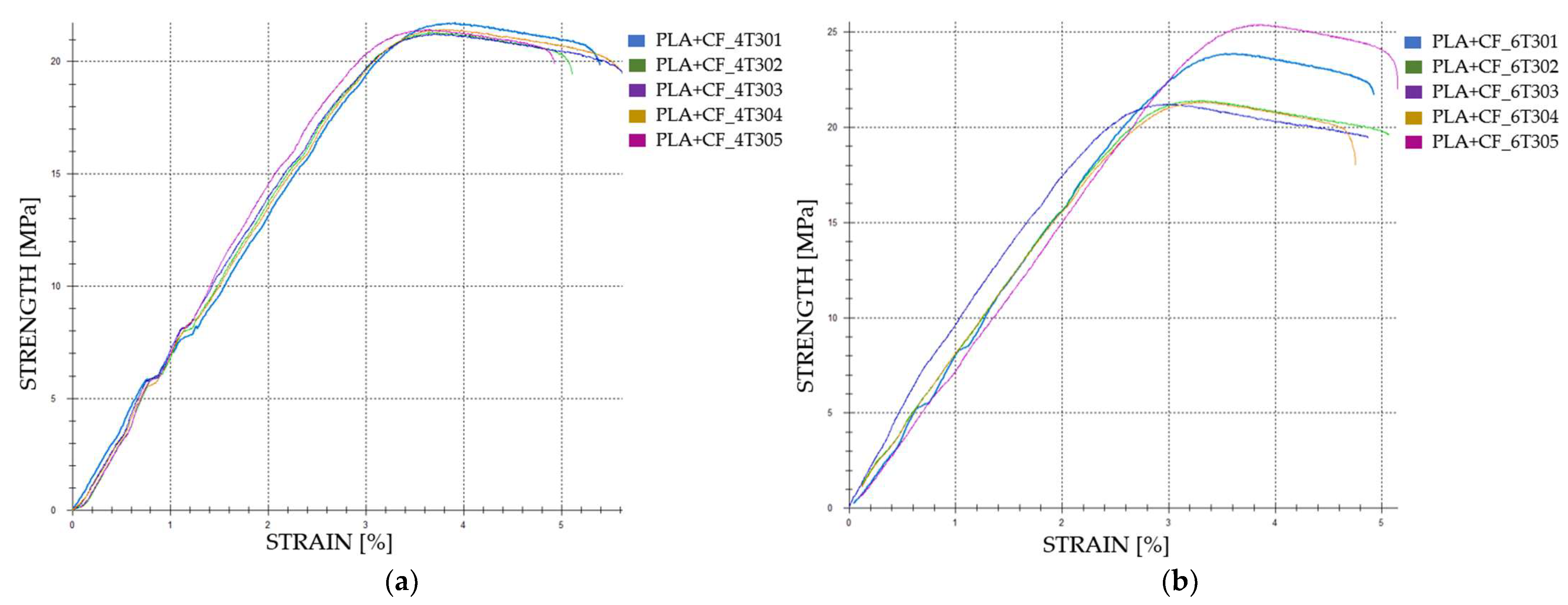
3.2.3. Tensile Properties of the FDM 3D-Printed PLA+CF Specimens Exposed to Cooling Lubricant for 30 Days
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B.; Khorasani, M. Introduction and basic principles. In Additive Manufacturing Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tofail, S.A.M.; Koumoulos, E.P.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S.; O’Donoghue, L.; Charitidis, C. Additive manufacturing: Scientific and technological challenges, market uptake and opportunities. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, R.D.; Tuck, C.J.; Hague, R.J.M. Laser sintering of polyamides and other polymers. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 229–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Simonelli, M.; Parry, L.; Ashcroft, I.; Tuck, C.; Hague, R. 3D printing of Aluminium alloys: Additive Manufacturing of Aluminium alloys using selective laser melting. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, J.M.; Caminero, M.A.; García-Plaza, E.; Núñez, P.J. Additive manufacturing of PLA structures using fused deposition modelling: Effect of process parameters on mechanical properties and their optimal selection. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminero, M.A.; Chacón, J.M.; García-Plaza, E.; Núñez, P.J.; Reverte, J.M. Interlaminar bonding performance of 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites using fused deposition modelling. Polymers 2018, 10, 976. [Google Scholar]
- Aliheidari, N.; Tripuraneni, R.; Nadimpalli, S.; Hossain, M.S. Fracture resistance of FDM 3D printed materials: Impact of layer thickness, raster angle, and feed rate. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 13, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Garzon-Hernandez, S.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D.; Jérusalem, A.; Arias, A. Design of FDM 3D printed polymers: An experimental-modelling methodology for the prediction of mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2020, 188, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Montal, J.; Valero-Vidal, C.; Poblet-Castell, C.; de Frutos, J.M.; Gámez-Pérez, J. Comparative study of the mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed parts using different photopolymer resins. Polymers 2021, 13, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePalma, M.T.; Ghita, O.; Farris, S.; Coles, S.R. Comparative analysis of sustainable 3D printing materials for fused deposition modelling and selective laser sintering. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101396. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Panes, A.; Claver, J.; Camacho, A.M. The Influence of Manufacturing Parameters on the Mechanical Behaviour of PLA and ABS Pieces Manufactured by FDM: A Comparative Analysis. Materials 2018, 11, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozdić, E.; Hozdić, E. Comparative Analysis of the Influence of Mineral Engine Oil on the Mechanical Parameters of FDM 3D-Printed PLA, PLA+CF, PETG, and PETG+CF. Materials 2023, 16, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, I.J.; Sevvel, P.; Gunasekaran, J. A review on the various processing parameters in FDM. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 37, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.J.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, K. Recent progress on polymer materials for additive manufacturing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh Alghamdi, S.; John, S.; Roy Choudhury, N.; Dutta, N.K. Additive Manufacturing of Polymer Materials: Progress, Promise and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, M.; Jäger, H. Current Status in the Utilization of Biobased Polymers for 3D Printing Process: A Systematic Review of the Materials, Processes, and Challenges. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 325–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadagi, B.; Lekurwale, R. A review on advances in 3D metal printing. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.; Gardner, L. Metal 3D printing in construction: A review of methods, research, applications, opportunities and challenges. Eng. Struct. 2019, 180, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, V.; Taylor, R.M. A review of geometric sensitivities in laser metal 3D printing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2020, 15, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, L.E. A Metallographic Review of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing of Metal and Alloy Products and Components. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2018, 7, 103–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Lao, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; He, Y. 3D printing of ceramics: A review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 661–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, L.C.; Rajoo, S.; Noor, A.M.; Ahmad, N.; Uday, M.B. Recent advances in 3D printing of porous ceramics: A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Shang, Y.; Xiong, K.; Xu, Z.; Guo, R.; Cai, S.; Zheng, C. Dense ceramics with complex shape fabricated by 3D printing: A review. J. Adv. Ceram. 2021, 10, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.W.D.; Panda, B.; Paul, S.C.; Noor Mohamed, N.A.; Tan, M.J.; Leong, K.F. 3D printing trends in building and construction industry: A review. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2017, 12, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, S.L.; Yeong, W.Y.; Wiria, F.E.; Tay, B.Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tian, Z.; Yang, S. Direct selective laser sintering and melting of ceramics: A review. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2017, 23, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.K.; Leong, K.F.; Lim, C.S. Rapid Prototyping: Principles and Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, D.; Zapciu, A.; Amza, C.; Baciu, F.; Marinescu, R. FDM process parameters influence over the mechanical properties of polymer specimens: A review. Polym. Test. 2018, 69, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, S.; Do, T.; Tran, P. FDM-Based 3D printing of polymer and associated composite: A review on mechanical properties, defects and treatments. Polymers 2020, 12, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Cui, C.; Guo, Y.; Yan, C. A critical review of fused deposition modeling 3D printing technology in manufacturing polylactic acid parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 2877–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Roan Eagle, I.N.; Yodo, N. A Review on Filament Materials for Fused Filament Fabrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourell, D.; Kruth, J.P.; Leu, M.; Levy, G.; Rosen, D.; Beese, A.M.; Clare, A. Materials for additive manufacturing. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedrtnam, A.; Ghabezi, P.; Gunwant, D.; Jiang, Y.; Sam-Daliri, O.; Harrison, N.; Goggins, J.; Finnegan, W. Mechanical performance of 3D-printed continuous fibre Onyx composites for drone applications: An experimental and numerical analysis. Compos. Part C Open Access 2023, 12, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, R.; Armoni, D.; Dul, S.; Alessandro, P. From nautical waste to additive manufacturing: Sustainable recycling of high-density polyethylene for 3D printing applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabezi, P.; Sam-Daliri, O.; Flanagan, T.; Walls, M.; Harrison, N.M. Circular economy innovation: A deep investigation on 3D printing of industrial waste polypropylene and carbon fibre composites. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 206, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozdić, E. Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Mechanical Parameters of FDM- and SLA-Printed ABS Materials. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, N. Investigating the Material Properties and Microstructural Changes of Fused Filament Fabricated PLA and Tough-PLA Parts. Polymers 2021, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yrlybayev, D.; Zharylkassyn, B.; Seisekulova, A.; Akhmetov, M.; Perveen, A.; Talamona, D. Optimisation of Strength Properties of FDM Printed Parts—A Critical Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, M.; Ghazali, S. Comparative Study of the Sensitivity of PLA, ABS, PEEK, and PETG’s Mechanical Properties to FDM Printing Process Parameters. Crystals 2021, 11, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiendl, J.; Gao, C. Controlling toughness and strength of FDM 3D-printed PLA components through the raster layup. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 180, 107562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qattawi, A.; Alrawi, B.; Guzman, A. Experimental optimization of fused deposition modelling processing parameters: A design-for-manufacturing approach. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 10, 791–803. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzotti, A.; Grasso, M.; Staiano, G.; Martorelli, M. The impact of process parameters on mechanical properties of parts fabricated in PLA with an open-source 3-D printer. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Cole, M.; Owji, A.; DeMastry, Z.; Gordon, A.P. An approach for mechanical property optimization of fused deposition modeling with polylactic acid via design of experiments. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2016, 22, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizon, J.R.C.; Gache, C.C.L.; Cascolan, H.M.S.; Cancino, L.T.; Advincula, R.C. Post-Processing of 3D-Printed Polymers. Technologies 2021, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cai, J. Effects of fused deposition modeling process parameters on tensile, dynamic mechanical properties of 3D printed polylactic acid materials. Polym. Test. 2020, 86, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Geng, P.; Li, G.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Influence of layer thickness and raster angle on the mechanical properties of 3D-printed PEEK and a comparative mechanical study between PEEK and ABS. Materials 2015, 8, 5834–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrose, M.F.; Masood, S.H.; Iovenitti, P.; Nikzad, M.; Sbarski, I. Effects of part build orientations on fatigue behaviour of FDM-processed PLA material. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 1, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.N.; Strong, R.; Gold, S.A. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: II. Materials, dimensional accuracy, and surface roughness. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankouhi, B.; Javadpour, S.; Delfanian, F.; Letcher, T. Failure analysis and mechanical characterization of 3D printed ABS with respect to layer thickness and orientation. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2016, 16, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Magri, A.; El Mabrouk, K.; Vaudreuil, S.; Touhami, M.E. Mechanical properties of CF-reinforced PLA parts manufactured by fused deposition modeling. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 20, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, D.; Papageorgiou, C.; Tsamasphyros, G. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of PLA Reinforced with Carbon Fibers. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y. The effect of carbon fiber reinforcement on the mechanical properties of polylactic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Tymrak, B.M.; Kreiger, M.; Pearce, J.M. Mechanical properties of components fabricated with open-source 3-D printers under realistic environmental conditions. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniran, O.; Cong, W.; Bediako, E.; Adu, S.P. Environmental affected mechanical performance of additively manufactured carbon fiber–reinforced plastic composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FASHFORGE. Comparison between Flashforge PLA, PLA Pro, PLA+CF, ABS, ABS Pro, PETG, PETG Pro, PETG+CF. Available online: https://flashforge.com/collections/filament?sort_by=price-ascending (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- Ogaili, A.A.F.; Basem, A.; Kadhim, M.S.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Jaber, A.A.; Njim, E.K.; Al-Haddad, L.A.; Hamzah, M.N.; Al-Ameen, E.S. The Effect of Chopped Carbon Fibers on the Mechanical Properties and Fracture Toughness of 3D-Printed PLA Parts: An Experimental and Simulation Study. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, S.; Senthilvelan, T. Characterization of PLA-CF Composites Fabricated by Fused Filament Fabrication Technique. Trans. Indian Inst. Mater. 2022, 75, 2607–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 1183-1:2019; Plastics—Methods for Determining the Density of Non-Cellular plastics—Part 1: Immersion Method, Liquid Pyknometer Method and Titration Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 527-2:2012; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 75-1:2020; Plastics—Determination of Temperature of Deflection under Load—Part 1: General Test Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Available online: https://github.com/bambulab/BambuStudio/releases/download/v01.09.03.50/Bambu_Studio_win_public-v01.09.03.50-20240621095059.exe (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- Available online: https://bambulab.com (accessed on 28 July 2024).


| Material Type | PLA | PLA+CF |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | 1.75 | 1.75 |
| Net filament weight (g) | 1000 | 1000 |
| Water absorption (equilibrium in water, 23 °C) | <0.3 | 0.5 |
| Printing speed (mm/s) | 40–60 | 60–90 |
| Layer height (mm) | 0.1–0.2 | 0.1–0.2 |
| Extrusion temperature (°C) | 190–220 | 200–230 |
| Bed platform temperature (°C) | 50–55 | 40–50 |
| 3D Printing Parameter | PLA | PLA+CF |
|---|---|---|
| Filament diameter (mm) | 1.75 | 1.75 |
| Infill pattern | Honeycomb | Honeycomb |
| Infill density (%) | 40, 60, 80, 100 | 40, 60, 80, 100 |
| Nozzle diameter (mm) | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Base print speed (mm/s) | 60 | 60 |
| Travel speed (mm/s) | 100 | 100 |
| First layer maximum (mm/s) | 10 | 10 |
| Top solid layers | 4 | 4 |
| Bottom solid layers | 3 | 3 |
| Layer height (mm) | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| First layer height (mm) | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Extrusion temperature (°C) | 210 | 225 |
| Bed temperature (°C) | 50 | 50 |
| Case | Specimen Code | Max. Force [N] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Strain [%] | Young’s Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | PLA_4T1 | 966.79 | 24.17 | 5.00 | 493 |
| PLA_4T2 | 977.09 | 24.41 | 4.73 | 662 | |
| PLA_4T3 | 855.98 | 21.40 | 3.88 | 595 | |
| PLA_4T4 | 840.13 | 21.00 | 3.72 | 541 | |
| PLA_4T5 | 858.06 | 21.45 | 3.84 | 685 | |
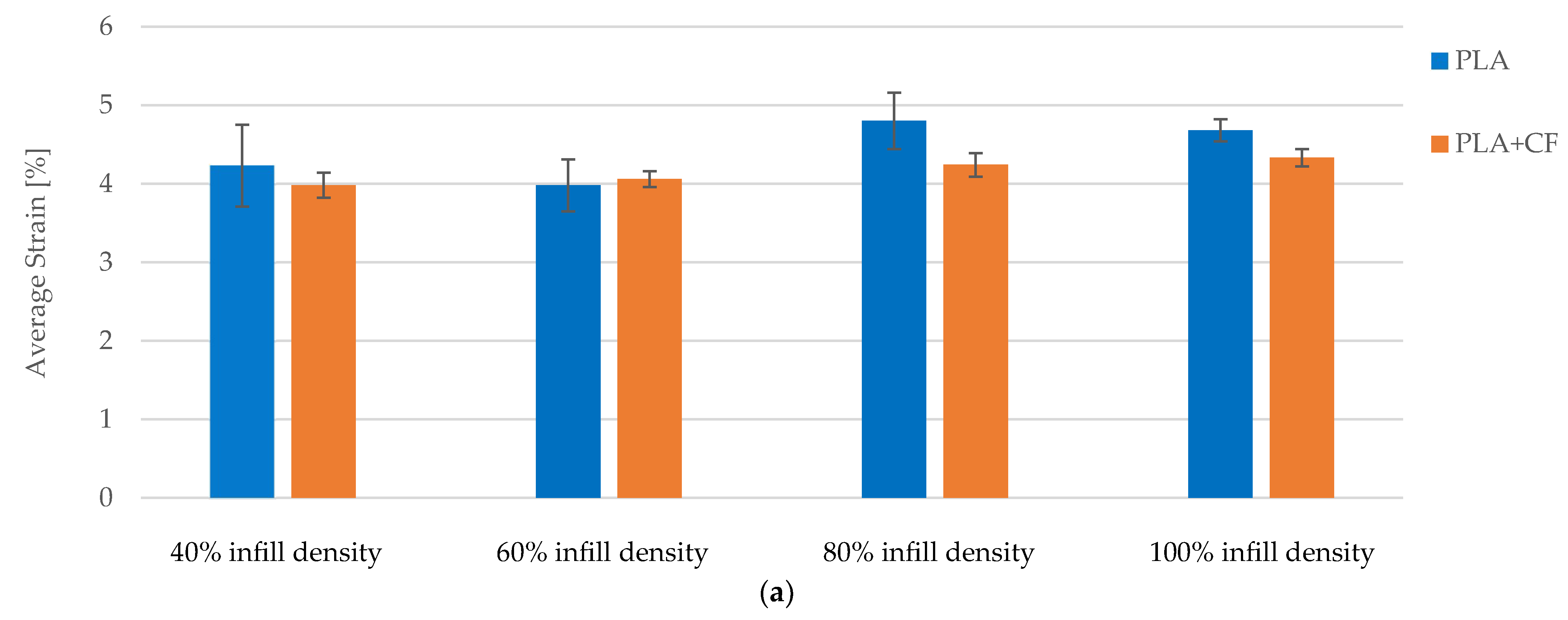
| Average | 899.61 | 22.49 | 4.23 | 595.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 59.47 | 1.48 | 0.52 | 71.98 | |
| PLA_6T1 | 943.49 | 23.59 | 3.46 | 779 | |
| PLA_6T2 | 976.50 | 24.41 | 3.77 | 871 | |
| Case 2 | PLA_6T3 | 1140.88 | 28.52 | 4.06 | 733 |
| PLA_6T4 | 1166.76 | 29.17 | 4.21 | 709 | |
| PLA_6T5 | 1162.77 | 29.07 | 4.38 | 653 | |
| Average | 1078.08 | 26.95 | 3.98 | 749.00 | |
| St. Dev. | 97.38 | 2.43 | 0.33 | 73.29 | |
| PLA_8T1 | 1444.58 | 36.11 | 4.45 | 771 | |
| PLA_8T2 | 1438.17 | 35.95 | 5.28 | 529 | |
| Case 3 | PLA_8T3 | 1387.41 | 34.69 | 4.64 | 654 |
| PLA_8T4 | 1434.09 | 35.85 | 5.19 | 521 | |
| PLA_8T5 | 1404.10 | 35.10 | 4.46 | 408 | |
| Average | 1421.67 | 35.54 | 4.80 | 576.60 | |
| St. Dev. | 22.06 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 124.55 | |
| Case 4 | PLA_1T1 | 1828.56 | 45.71 | 4.67 | 1115 |
| PLA_1T2 | 1709.83 | 42.75 | 4.42 | 1095 | |
| PLA_1T3 | 1834.72 | 45.87 | 4.81 | 977 | |
| PLA_1T4 | 1809.31 | 45.23 | 4.81 | 950 | |
| PLA_1T5 | 1818.39 | 45.46 | 4.70 | 1119 | |
| Average | 1800.16 | 45.00 | 4.68 | 1051.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 45.99 | 1.15 | 0.14 | 72.57 |
| Case | Specimen code | Max. Force [N] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Strain [%] | Young’s Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 5 | PLA_4T71 | 872.57 | 21.81 | 4.47 | 557 |
| PLA_4T72 | 886.77 | 22.17 | 4.37 | 625 | |
| PLA_4T73 | 875.14 | 21.88 | 4.26 | 609 | |
| PLA_4T74 | 855.21 | 21.38 | 3.95 | 655 | |
| PLA_4T75 | 865.55 | 21.64 | 4.42 | 600 | |
| Average | 871.05 | 21.78 | 4.29 | 609.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 10.46 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 32.11 | |
| PLA_6T71 | 980.39 | 24.51 | 4.36 | 629 | |
| PLA_6T72 | 901.35 | 25.03 | 4.70 | 473 | |
| Case 6 | PLA_6T73 | 990.86 | 24.77 | 4.03 | 695 |
| PLA_6T74 | 970.49 | 24.26 | 3.82 | 754 | |
| PLA_6T75 | 995.09 | 24.88 | 3.94 | 756 | |
| Average | 967.64 | 24.69 | 4.17 | 661.40 | |
| St. Dev. | 34.23 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 105.07 | |
| PLA_8T71 | 1219.89 | 30.50 | 4.40 | 784 | |
| PLA_8T72 | 1208.87 | 30.22 | 4.33 | 754 | |
| Case 7 | PLA_8T73 | 1199.87 | 30.00 | 3.94 | 861 |
| PLA_8T74 | 1158.67 | 28.97 | 4.24 | 793 | |
| PLA_8T75 | 1076.91 | 26.92 | 3.88 | 780 | |
| Average | 1172.84 | 29.32 | 4.16 | 794.40 | |
| St. Dev. | 52.24 | 1.31 | 0.21 | 35.74 | |
| Case 8 | PLA_1T71 | 1612.36 | 40.31 | 4.35 | 1030 |
| PLA_1T72 | 1538.22 | 38.46 | 4.23 | 1060 | |
| PLA_1T73 | 1604.78 | 40.12 | 4.26 | 1070 | |
| PLA_1T74 | 1578.05 | 39.45 | 4.22 | 1081 | |
| PLA_1T75 | 1560.62 | 39.02 | 4.24 | 1055 | |
| Average | 1578.81 | 39.47 | 4.26 | 1059.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 27.49 | 0.69 | 0.05 | 17.10 |
| Case | Specimen Code | Max. Force [N] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Strain [%] | Young’s Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 9 | PLA_4T301 | 810.72 | 20.27 | 4.14 | 579 |
| PLA_4T302 | 849.30 | 21.23 | 3.97 | 684 | |
| PLA_4T303 | 831.12 | 20.78 | 4.02 | 639 | |
| PLA_4T304 | 845.33 | 21.13 | 3.76 | 675 | |
| PLA_4T305 | 832.08 | 20.80 | 4.04 | 608 | |
| Average | 833.71 | 20.84 | 3.99 | 637.00 | |
| St. Dev. | 13.53 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 39.65 | |
| PLA_6T301 | 925.61 | 23.14 | 3.77 | 727 | |
| PLA_6T302 | 929.01 | 23.23 | 4.04 | 685 | |
| Case 10 | PLA_6T303 | 960.20 | 24.01 | 4.00 | 705 |
| PLA_6T304 | 923.99 | 23.10 | 3.97 | 687 | |
| PLA_6T305 | 930.85 | 23.27 | 4.01 | 688 | |
| Average | 933.93 | 23.35 | 3.96 | 698.40 | |
| St. Dev. | 13.36 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 15.99 | |
| PLA_8T301 | 1158.34 | 28.96 | 3.99 | 842 | |
| PLA_8T302 | 1159.91 | 29.00 | 4.19 | 787 | |
| Case 11 | PLA_8T303 | 1150.01 | 28.75 | 4.40 | 733 |
| PLA_8T304 | 1166.66 | 29.17 | 4.28 | 769 | |
| PLA_8T305 | 1077.42 | 26.94 | 3.86 | 735 | |
| Average | 1142.47 | 28.56 | 4.14 | 773.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 32.95 | 0.82 | 0.20 | 40.04 | |
| Case 12 | PLA_1T301 | 1540.82 | 38.52 | 4.27 | 1018 |
| PLA_1T302 | 1538.58 | 38.46 | 4.36 | 1015 | |
| PLA_1T303 | 1563.66 | 39.09 | 4.31 | 1052 | |
| PLA_1T304 | 1547.40 | 38.68 | 4.29 | 1046 | |
| PLA_1T305 | 1539.02 | 38.48 | 4.36 | 1000 | |
| Average | 1545.90 | 38.65 | 4.32 | 1026.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 9.43 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 19.98 |
| Case | Specimen Code | Max. Force [N] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Strain [%] | Young’s Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
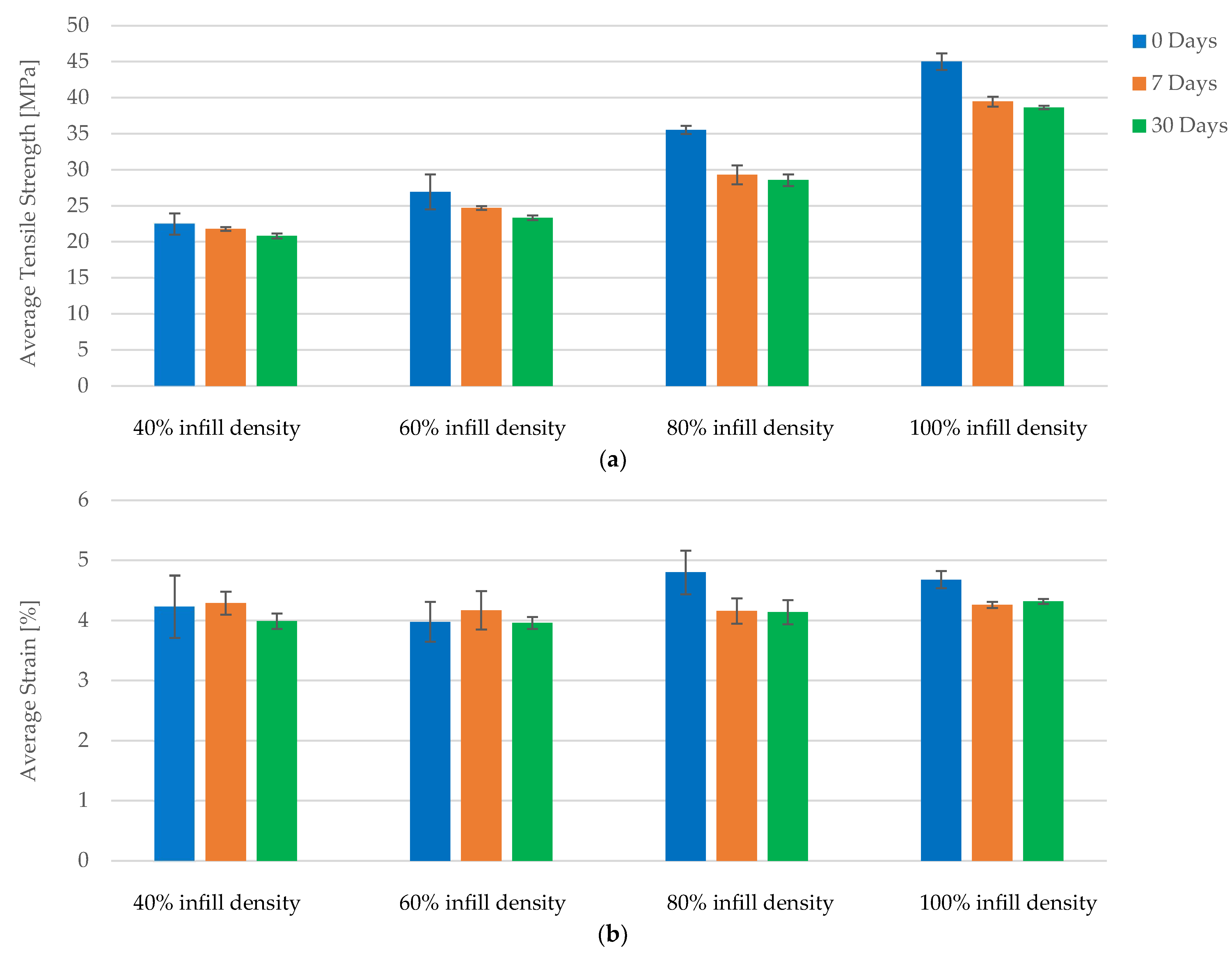
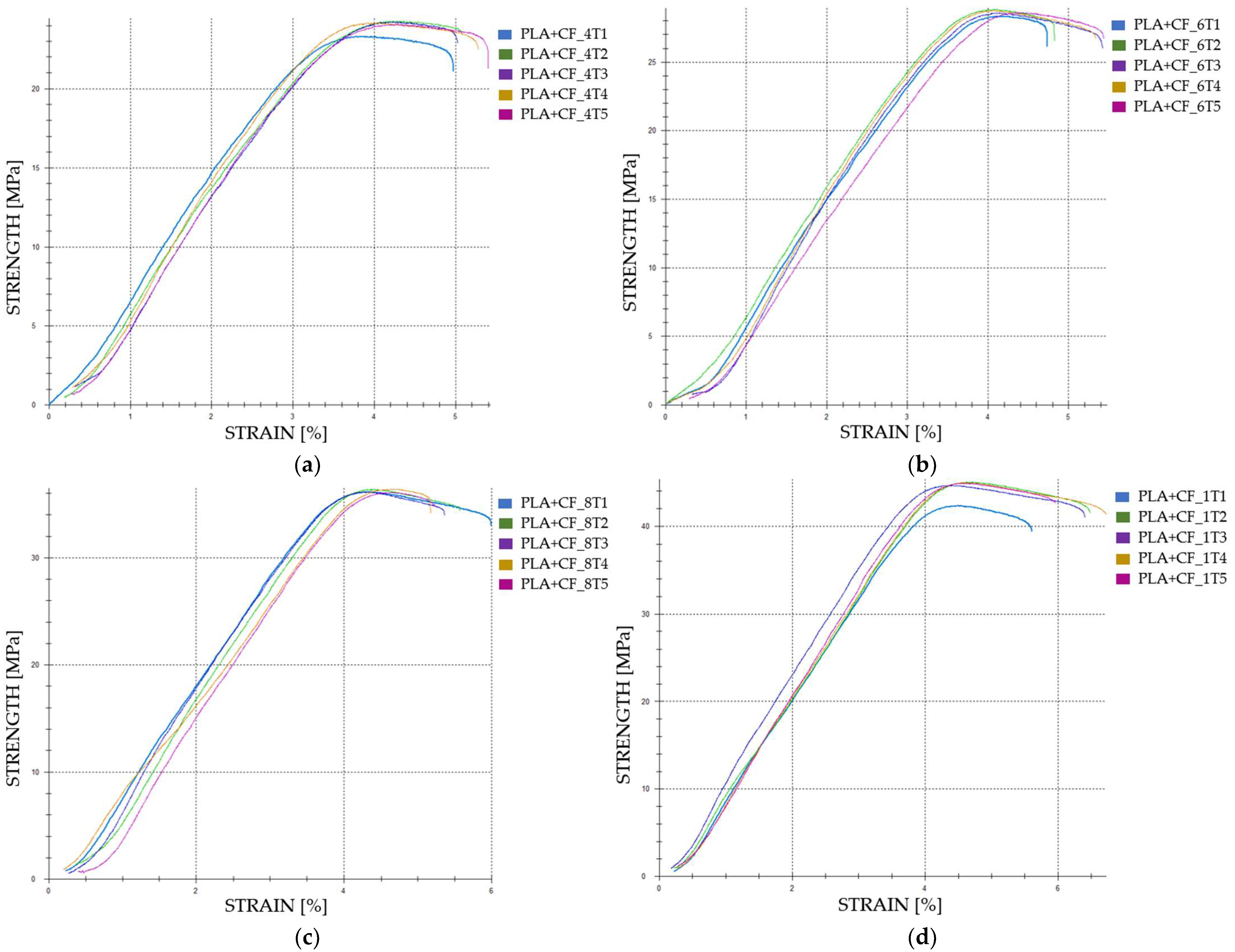
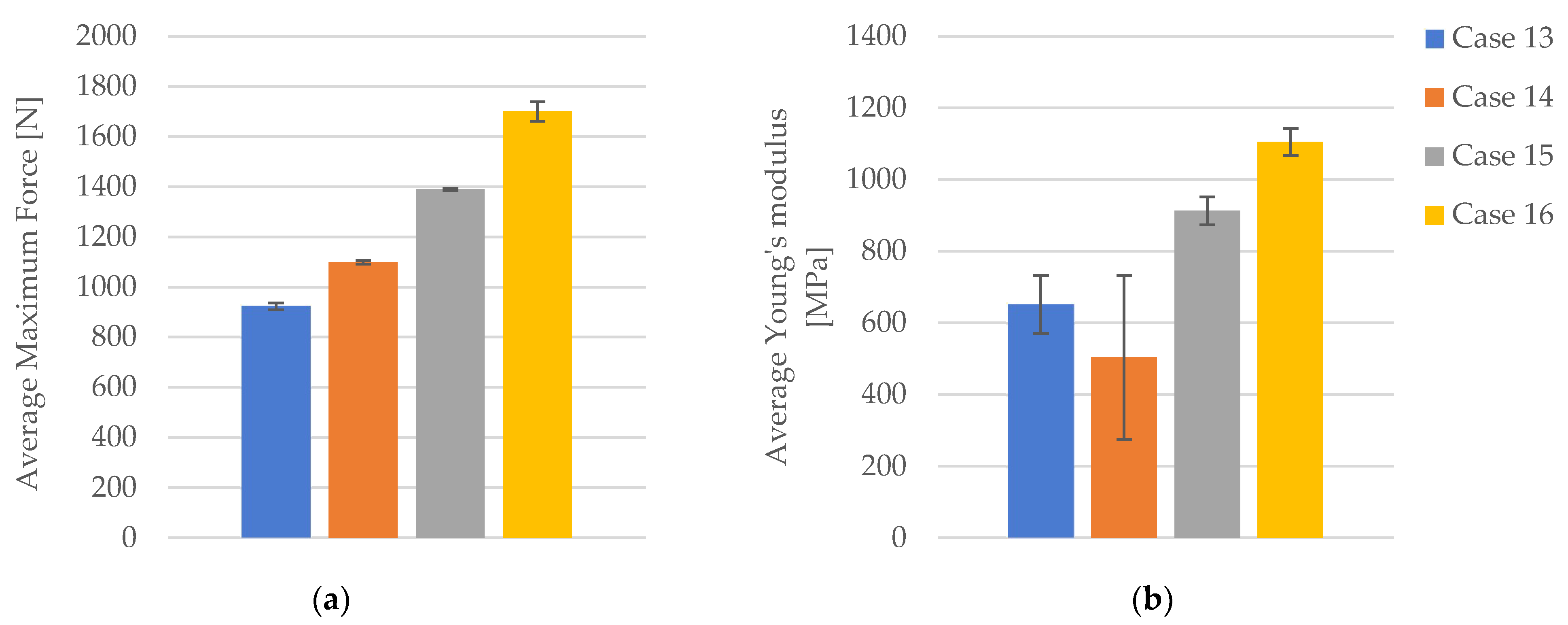
| Case 13 | PLA+CF_4T1 | 897.76 | 22.44 | 3.78 | 493 |
| PLA+CF_4T2 | 933.16 | 23.33 | 4.09 | 693 | |
| PLA+CF_4T3 | 931.15 | 23.28 | 4.13 | 675 | |
| PLA+CF_4T4 | 931.31 | 23.28 | 3.79 | 715 | |
| PLA+CF_4T5 | 925.44 | 23.14 | 4.11 | 684 | |
| Average | 923.76 | 23.09 | 3.98 | 652.00 | |
| St. Dev. | 13.26 | 0.33 | 0.16 | 80.60 | |
| PLA+CF_6T1 | 1088.01 | 27.20 | 4.13 | 279 | |
| PLA+CF_6T2 | 1108.25 | 27.71 | 4.12 | 447 | |
| Case 14 | PLA+CF_6T3 | 1099.72 | 27.49 | 3.86 | 803 |
| PLA+CF_6T4 | 1104.18 | 27.60 | 4.09 | 252 | |
| PLA+CF_6T5 | 1097.97 | 27.45 | 4.10 | 740 | |
| Average | 1099.63 | 27.49 | 4.06 | 504.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 6.82 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 229.12 | |
| PLA+CF_8T1 | 1387.45 | 34.69 | 4.15 | 947 | |
| PLA+CF_8T2 | 1396.61 | 34.92 | 4.18 | 920 | |
| Case 15 | PLA+CF_8T3 | 1387.98 | 34.70 | 4.10 | 959 |
| PLA+CF_8T4 | 1392.13 | 34.80 | 4.53 | 852 | |
| PLA+CF_8T5 | 1383.80 | 34.59 | 4.24 | 887 | |
| Average | 1389.59 | 34.74 | 4.24 | 913.00 | |
| St. Dev. | 4.39 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 39.29 | |
| Case 16 | PLA+CF_1T1 | 1623.84 | 40.60 | 4.31 | 1074 |
| PLA+CF_1T2 | 1724.62 | 43.12 | 4.49 | 1075 | |
| PLA+CF_1T3 | 1713.50 | 42.84 | 4.15 | 1176 | |
| PLA+CF_1T4 | 1723.88 | 43.10 | 4.39 | 1091 | |
| PLA+CF_1T5 | 1721.71 | 43.04 | 4.33 | 1113 | |
| Average | 1701.51 | 42.54 | 4.33 | 1105.80 | |
| St. Dev. | 39.04 | 0.98 | 0.11 | 37.84 |
| Case | Specimen Code | Max. Force [N] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Strain [%] | Young’s Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
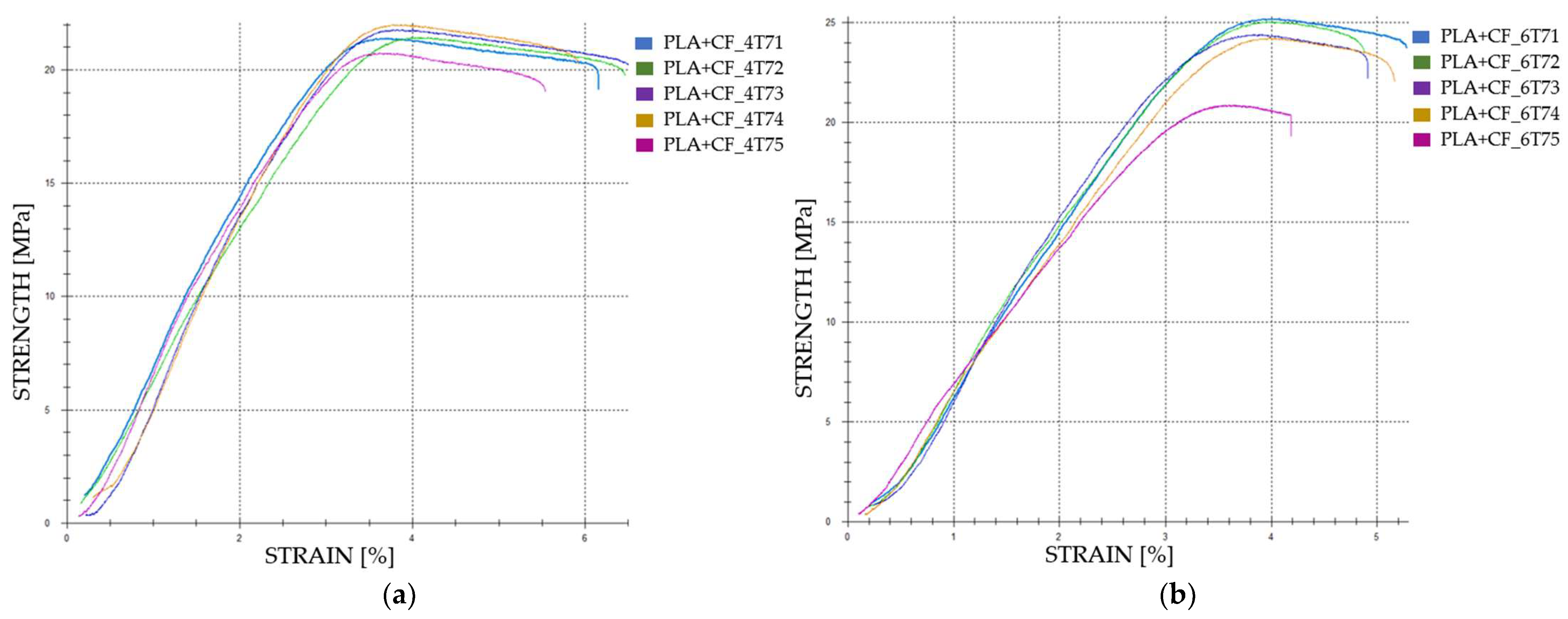
| Case 17 | PLA+CF_4T71 | 825.13 | 20.63 | 3.60 | 714 |
| PLA+CF_4T72 | 824.42 | 20.61 | 3.96 | 640 | |
| PLA+CF_4T73 | 840.55 | 21.01 | 3.62 | 690 | |
| PLA+CF_4T74 | 848.97 | 21.22 | 3.65 | 681 | |
| PLA+CF_4T75 | 801.33 | 20.03 | 3.53 | 704 | |
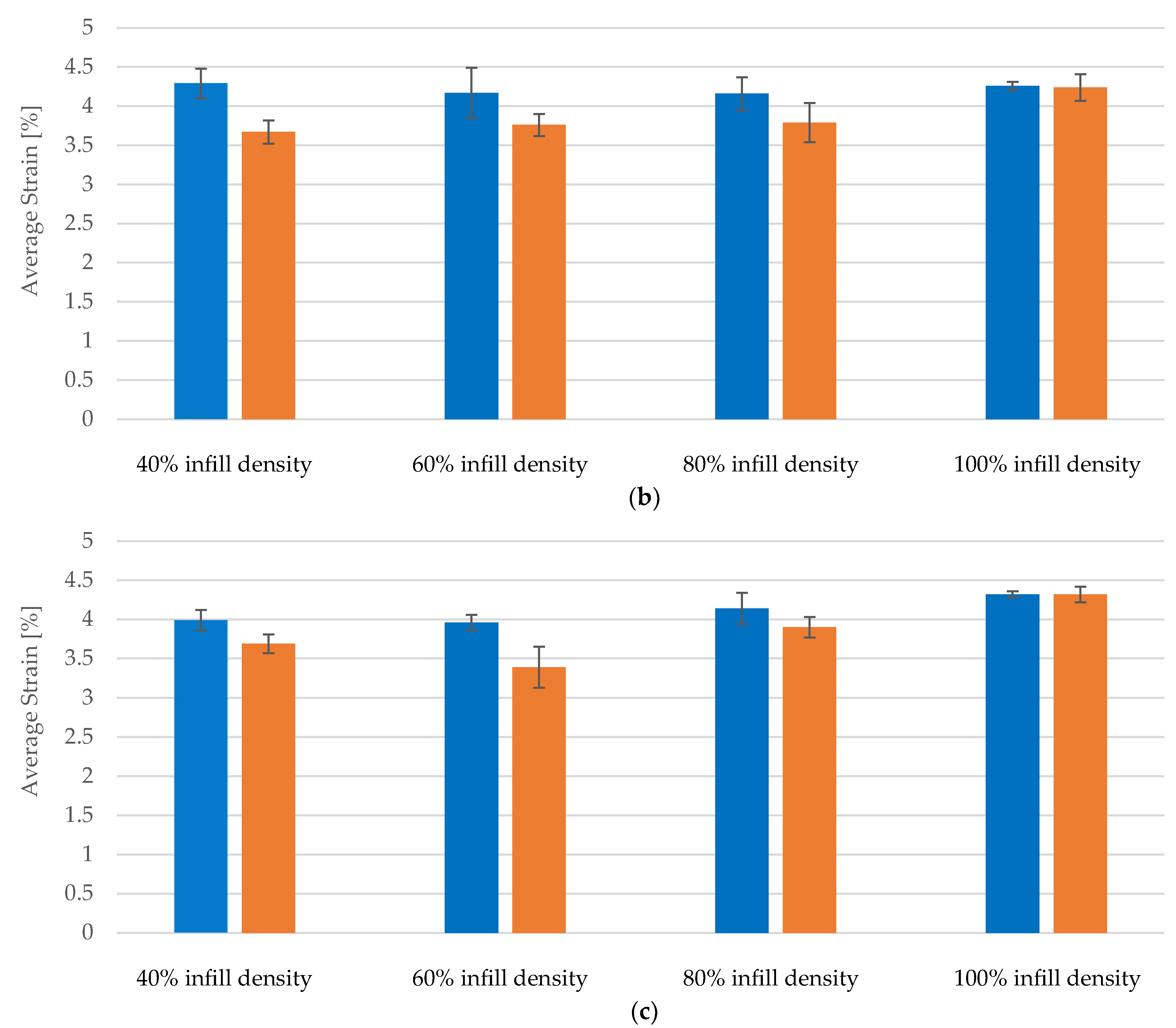
| Average | 828.08 | 20.70 | 3.67 | 685.80 | |
| St. Dev. | 16.31 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 25.55 | |
| PLA+CF_6T71 | 969.74 | 24.24 | 3.81 | 736 | |
| PLA+CF_6T72 | 964.35 | 24.11 | 3.88 | 744 | |
| Case 18 | PLA+CF_6T73 | 940.71 | 23.52 | 3.74 | 770 |
| PLA+CF_6T74 | 933.16 | 23.33 | 3.87 | 711 | |
| PLA+CF_6T75 | 806.35 | 20.16 | 3.50 | 690 | |
| Average | 922.86 | 23.07 | 3.76 | 730.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 59.86 | 1.50 | 0.14 | 27.54 | |
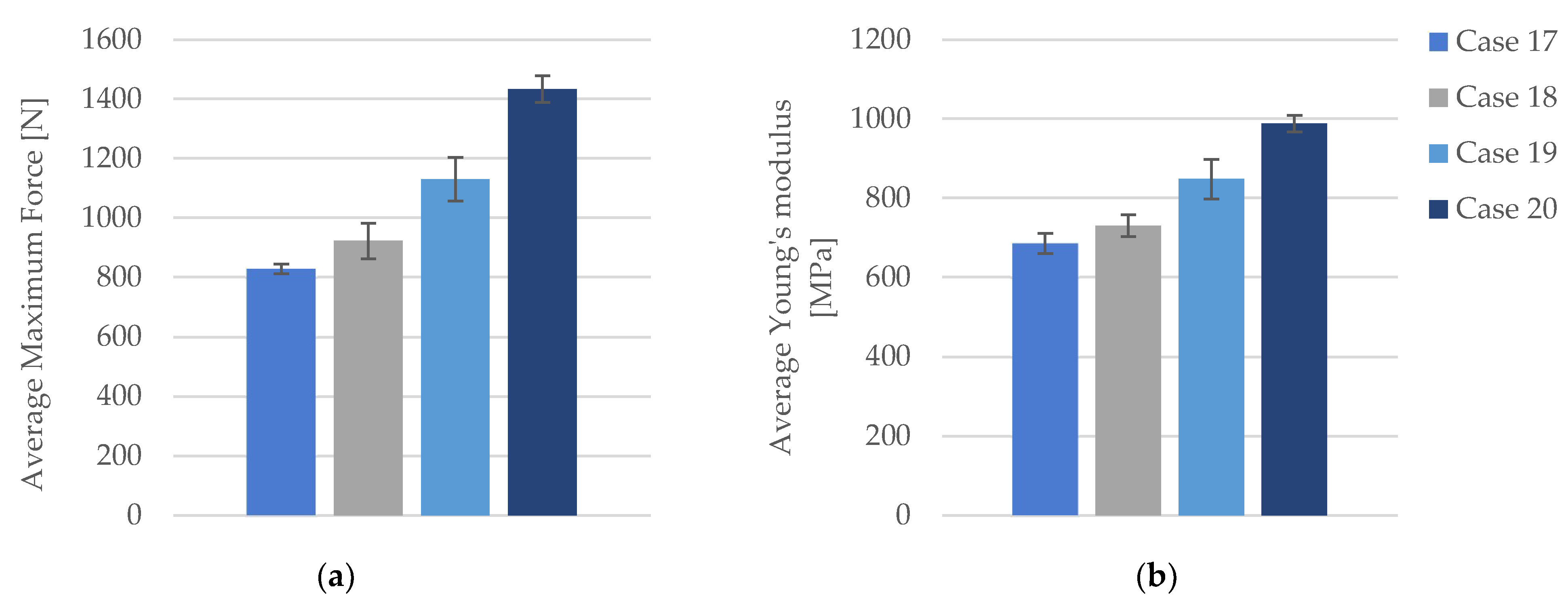
| PLA+CF_8T71 | 1050.72 | 26.27 | 3.37 | 905 | |
| PLA+CF_8T72 | 1132.51 | 28.31 | 3.84 | 818 | |
| Case 19 | PLA+CF_8T73 | 1174.76 | 29.37 | 4.10 | 792 |
| PLA+CF_8T74 | 1166.20 | 29.15 | 3.71 | 912 | |
| PLA+CF_8T75 | 1126.73 | 28.17 | 3.95 | 812 | |
| Average | 1130.18 | 28.25 | 3.79 | 847.80 | |
| St. Dev. | 73.85 | 1.09 | 0.25 | 50.35 | |
| Case 20 | PLA+CF_1T71 | 1433.15 | 35.83 | 4.19 | 992 |
| PLA+CF_1T72 | 1403.24 | 35.08 | 4.26 | 974 | |
| PLA+CF_1T73 | 1520.31 | 38.01 | 4.53 | 969 | |
| PLA+CF_1T74 | 1407.82 | 35.20 | 4.23 | 979 | |
| PLA+CF_1T75 | 1401.42 | 35.04 | 3.99 | 1026 | |
| Average | 1433.19 | 35.83 | 4.24 | 988.00 | |
| St. Dev. | 45.03 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 20.48 |
| Case | Specimen Code | Max. Force [N] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Strain [%] | Young s Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
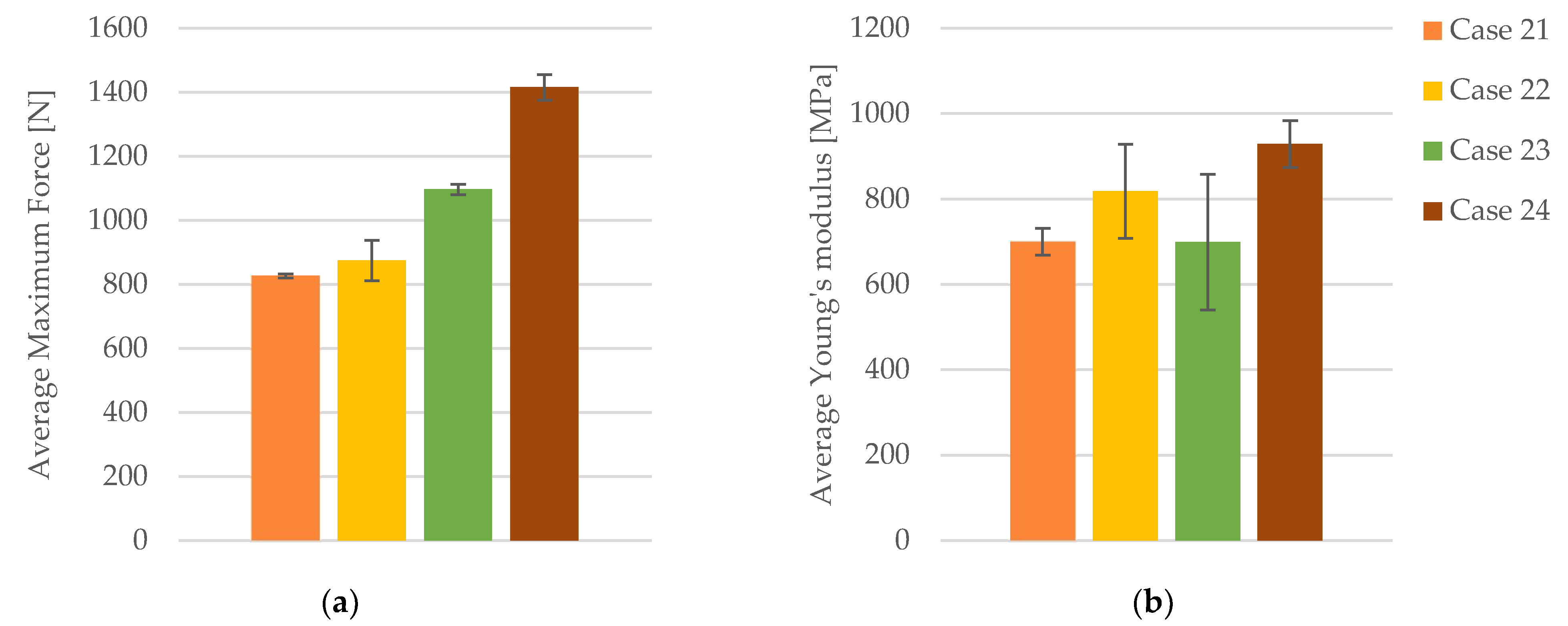
| Case 21 | PLA+CF_4T301 | 837.09 | 20.93 | 3.91 | 737 |
| PLA+CF_4T302 | 822.78 | 20.57 | 3.62 | 677 | |
| PLA+CF_4T303 | 819.94 | 20.50 | 3.68 | 694 | |
| PLA+CF_4T304 | 826.53 | 20.66 | 3.65 | 658 | |
| PLA+CF_4T305 | 828.33 | 20.71 | 3.58 | 735 | |
| Average | 826.93 | 20.67 | 3.69 | 700.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 5.86 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 31.38 | |
| PLA+CF_6T301 | 921.01 | 23.03 | 3.52 | 778 | |
| PLA+CF_6T302 | 828.11 | 20.70 | 3.25 | 765 | |
| Case 22 | PLA+CF_6T303 | 823.74 | 20.59 | 3.01 | 1037 |
| PLA+CF_6T304 | 825.22 | 20.63 | 3.37 | 771 | |
| PLA+CF_6T305 | 978.38 | 24.46 | 3.78 | 741 | |
| Average | 875.29 | 21.88 | 3.39 | 818.40 | |
| St. Dev. | 63.42 | 1.59 | 0.26 | 110.01 | |
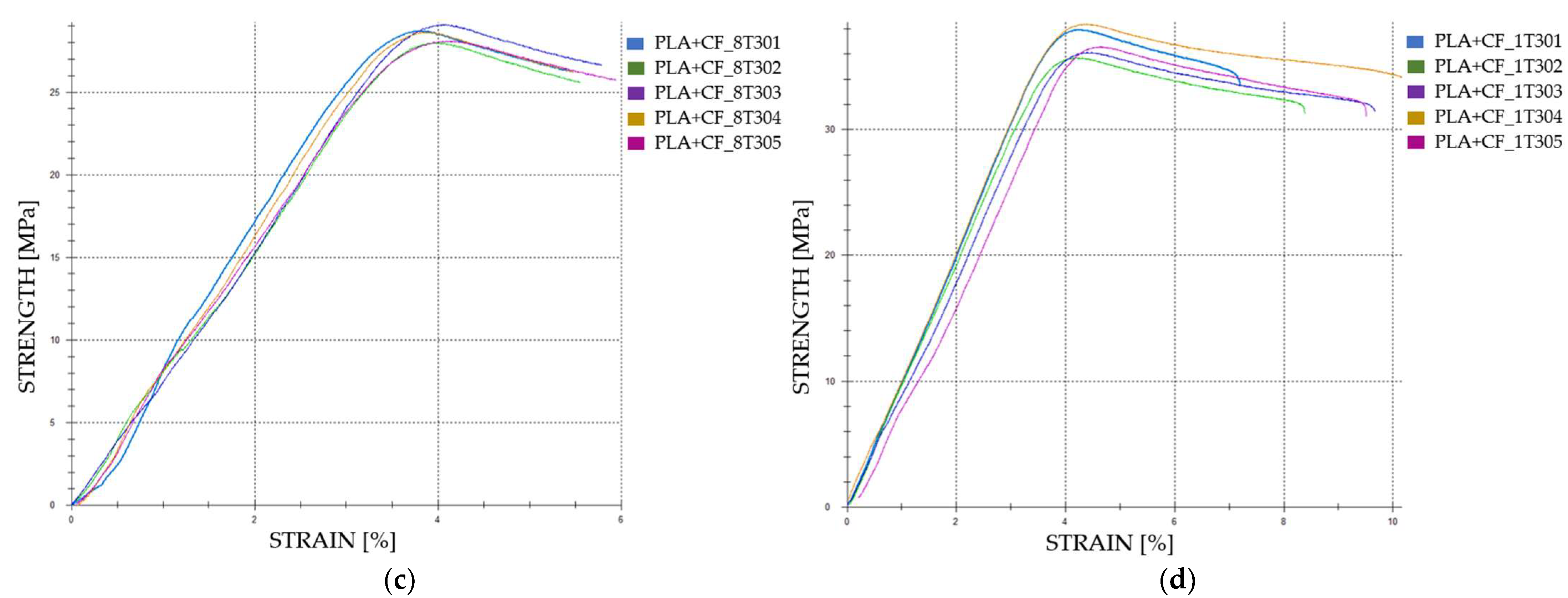
| PLA+CF_8T301 | 1106.40 | 27.66 | 3.74 | 387 | |
| PLA+CF_8T302 | 1076.76 | 26.92 | 3.90 | 758 | |
| Case 23 | PLA+CF_8T303 | 1117.87 | 27.95 | 4.04 | 737 |
| PLA+CF_8T304 | 1104.13 | 27.60 | 3.76 | 829 | |
| PLA+CF_8T305 | 1080.09 | 27.00 | 4.06 | 785 | |
| Average | 1097.05 | 27.43 | 3.90 | 699.20 | |
| St. Dev. | 15.94 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 159.10 | |
| Case 24 | PLA+CF_1T301 | 1455.55 | 36.39 | 4.22 | 987 |
| PLA+CF_1T302 | 1370.33 | 34.26 | 4.19 | 958 | |
| PLA+CF_1T303 | 1383.95 | 34.60 | 4.34 | 865 | |
| PLA+CF_1T304 | 1470.31 | 36.76 | 4.38 | 974 | |
| PLA+CF_1T305 | 1399.56 | 34.99 | 4.46 | 861 | |
| Average | 1415.94 | 35.40 | 4.32 | 929.00 | |
| St. Dev. | 39.74 | 0.99 | 0.10 | 54.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hozdić, E.; Hasanagić, R. Analysis of the Impact of Cooling Lubricants on the Tensile Properties of FDM 3D Printed PLA and PLA+CF Materials. Polymers 2024, 16, 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152228
Hozdić E, Hasanagić R. Analysis of the Impact of Cooling Lubricants on the Tensile Properties of FDM 3D Printed PLA and PLA+CF Materials. Polymers. 2024; 16(15):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152228
Chicago/Turabian StyleHozdić, Elvis, and Redžo Hasanagić. 2024. "Analysis of the Impact of Cooling Lubricants on the Tensile Properties of FDM 3D Printed PLA and PLA+CF Materials" Polymers 16, no. 15: 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152228
APA StyleHozdić, E., & Hasanagić, R. (2024). Analysis of the Impact of Cooling Lubricants on the Tensile Properties of FDM 3D Printed PLA and PLA+CF Materials. Polymers, 16(15), 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152228








