Reinforcing Efficiency of Recycled Carbon Fiber PLA Filament Suitable for Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of PLA/rCF Composites
2.3. Filament Extrusion of PLA and PLA/rCF Composites
2.4. 3D Printing of PLA/rCF Filaments
2.5. Characterization and Analysis of 3D PLA/rCF Composites
3. Results and Discussion
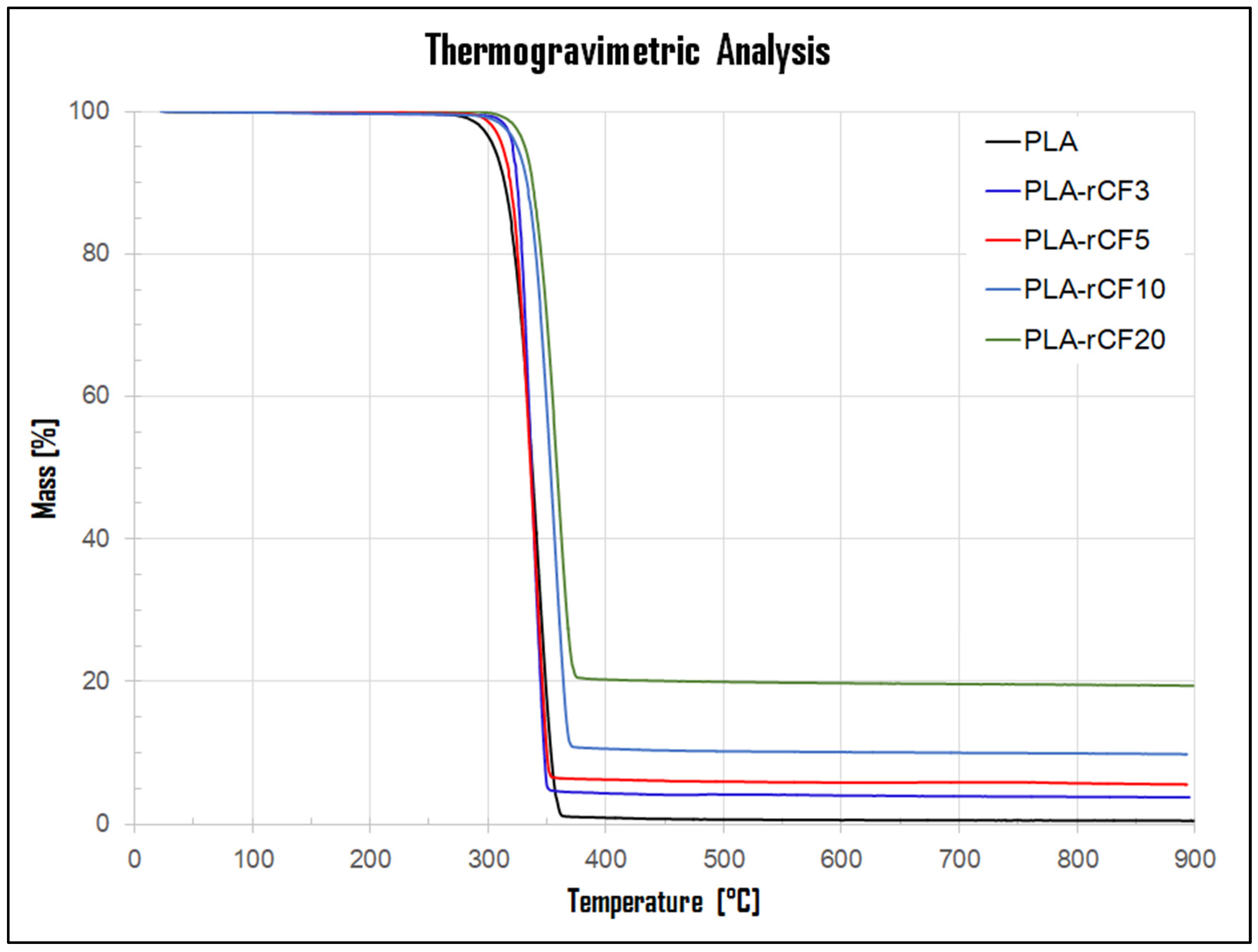
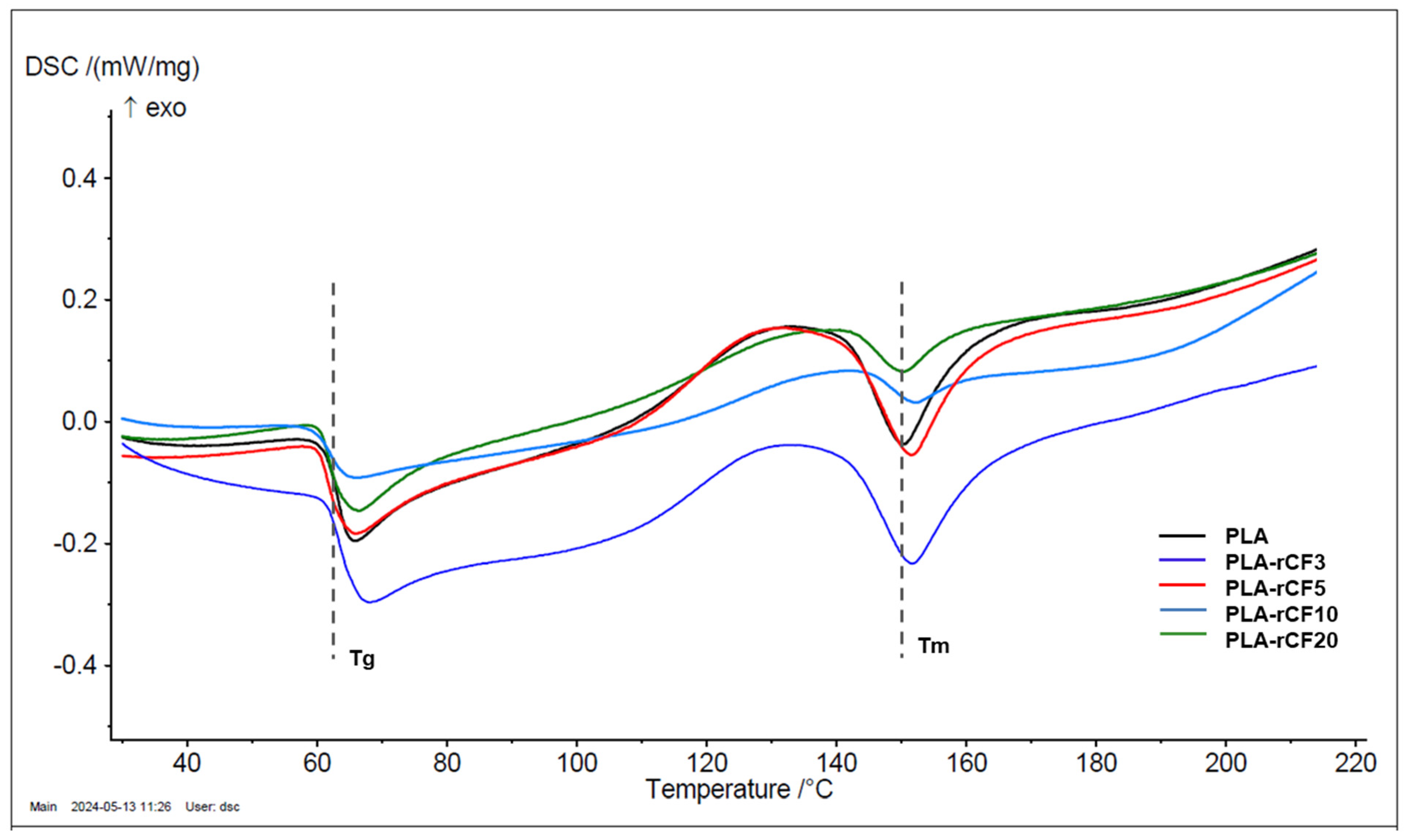
3.1. Thermal Properties
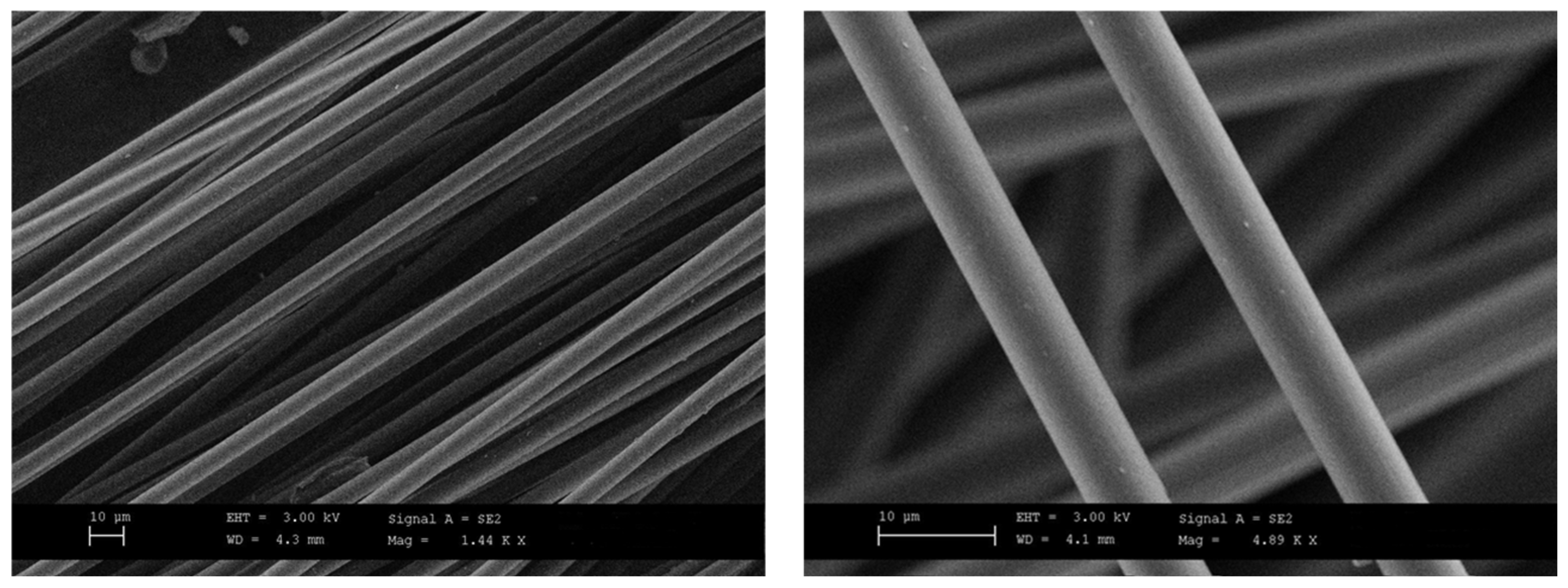
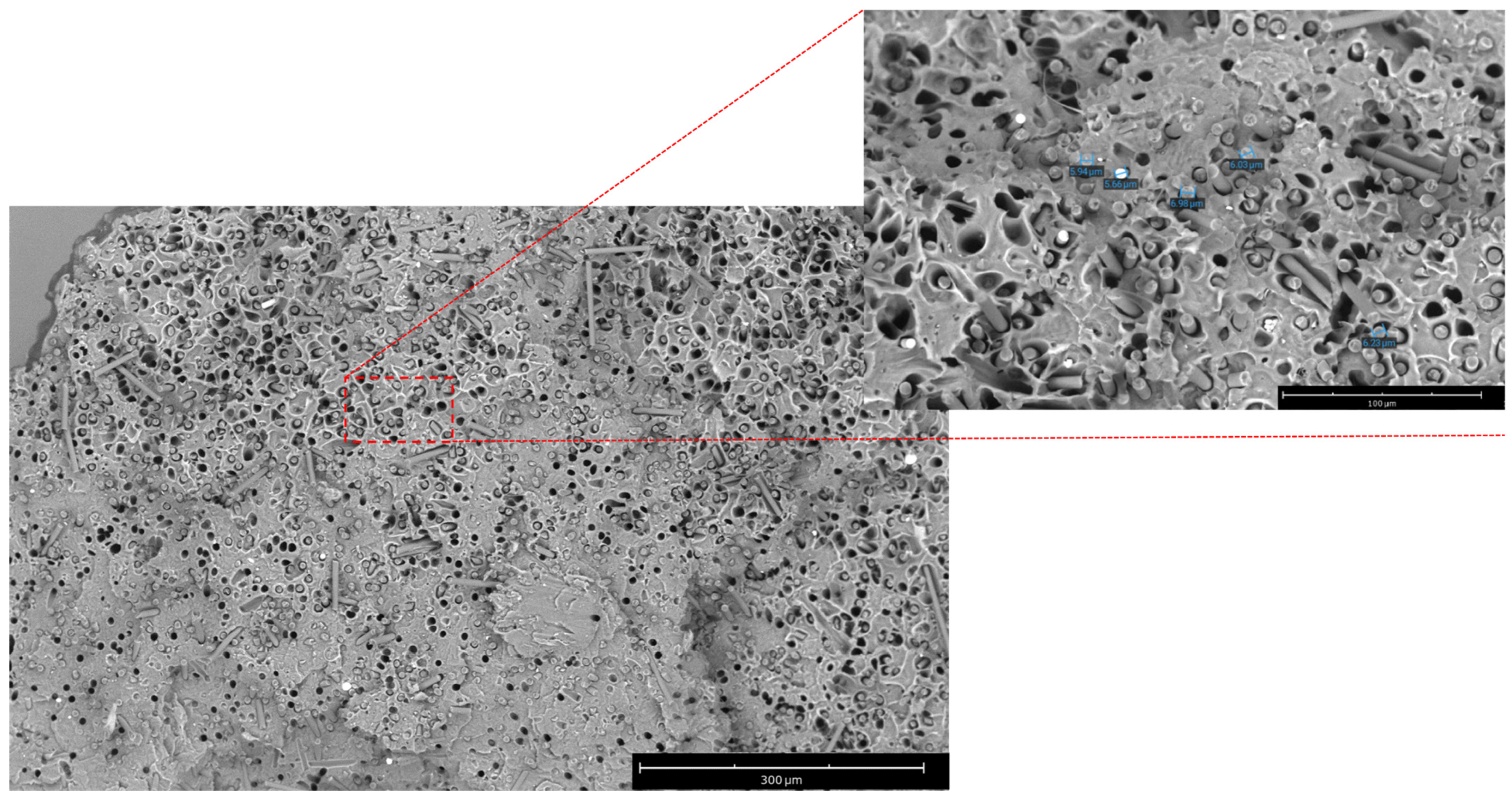
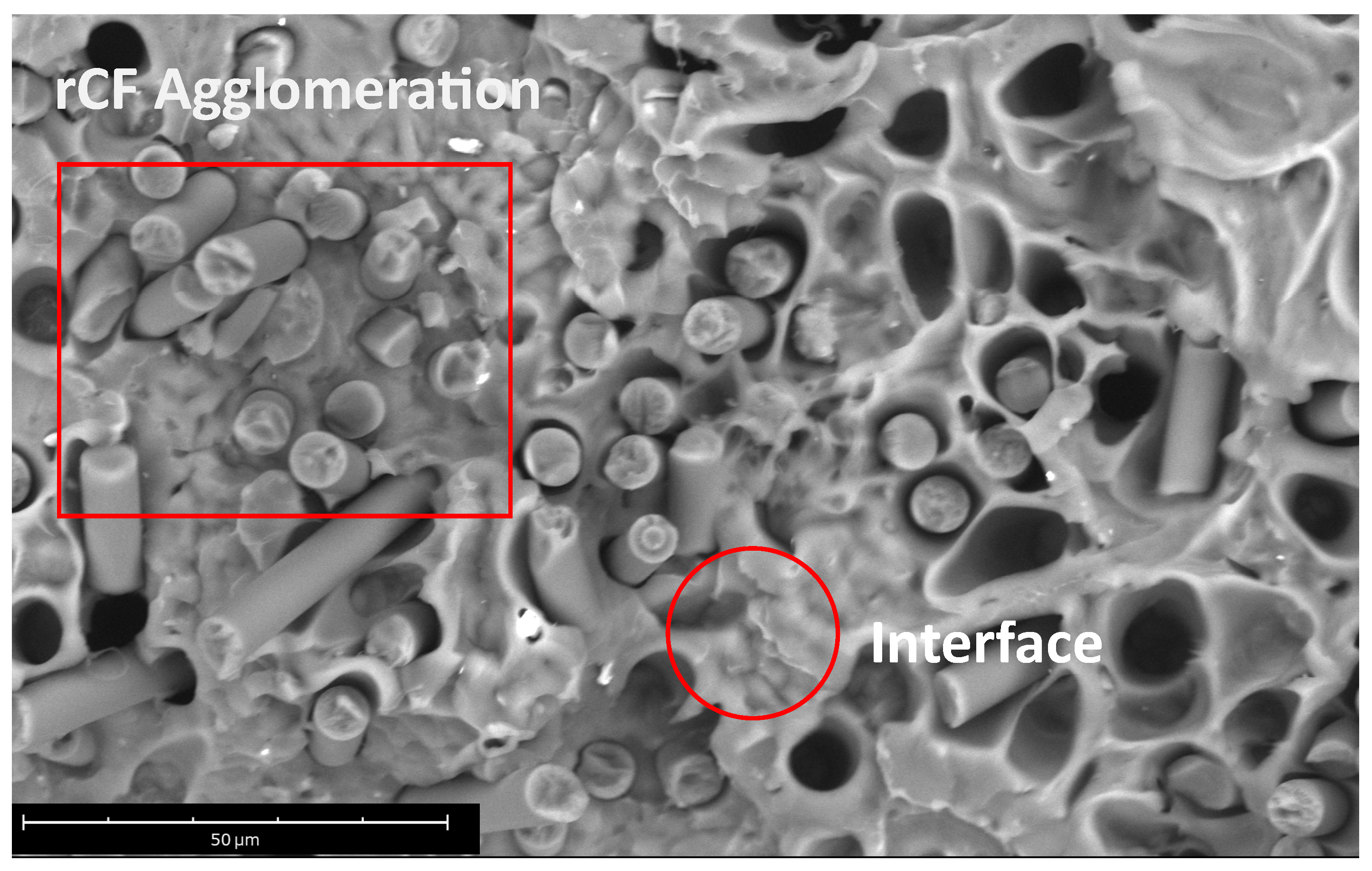
3.2. Morphological Characterization
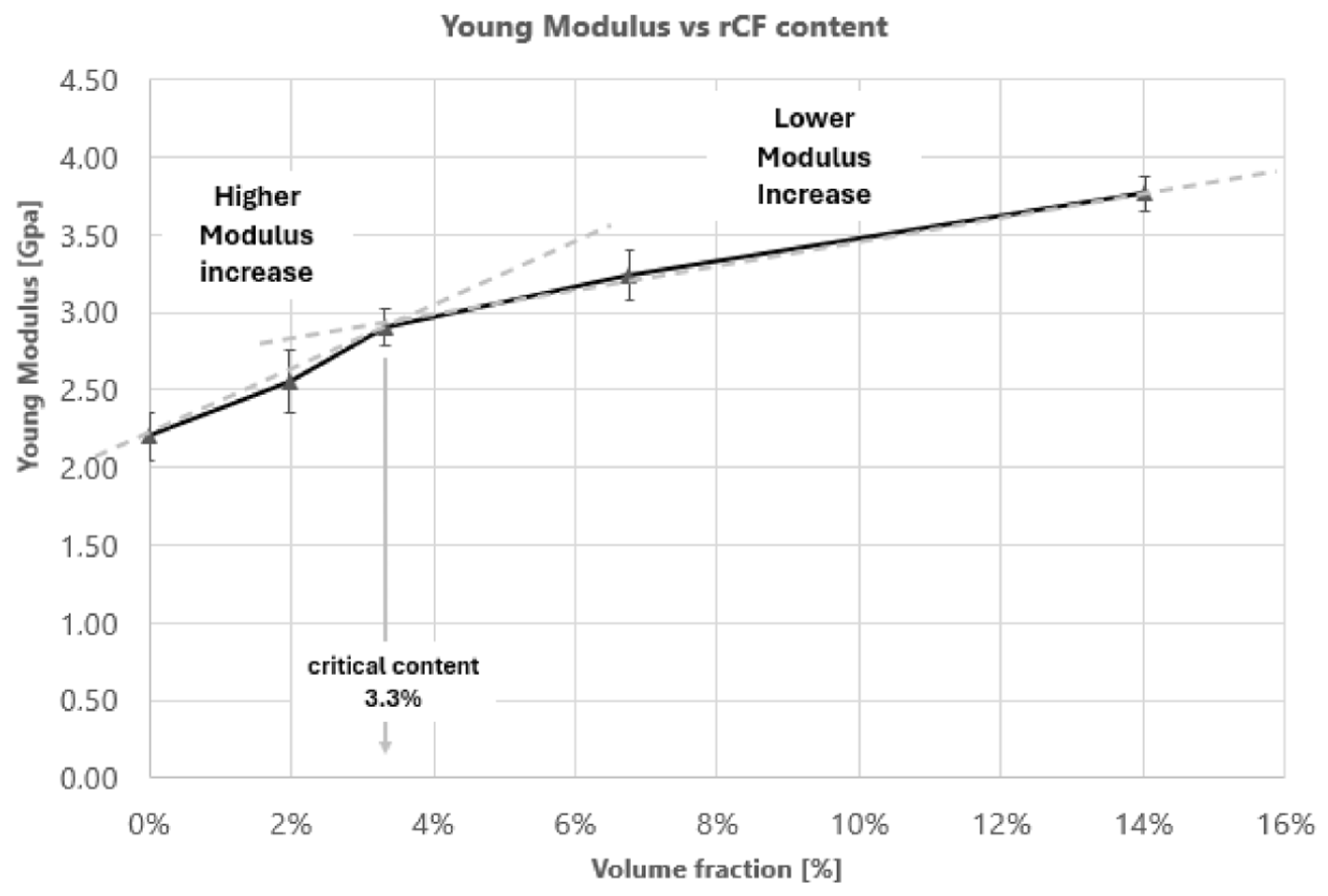
3.3. Filament Mechanical Characterization
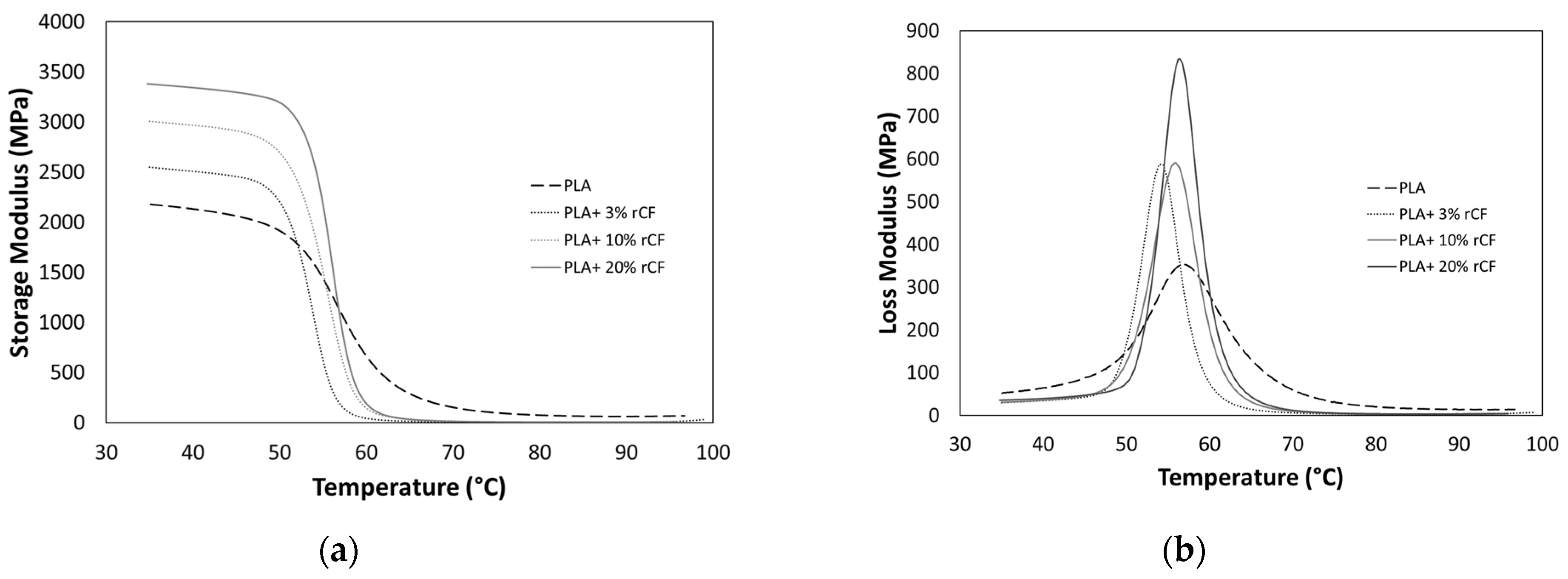
3.4. Viscoelastic Characterization
4. Conclusions
- (A)
- All composite filaments, although there was an absence of additional substances (e.g., stabilizer and/or compatibilizer) and treatment after CF recycling process, showed uniform dispersion of fibers, good extrudability and printability in a commercial FFF printer.
- (B)
- Thermal analysis of extruded filaments showed an improved thermal stability of PLA-rCF filaments with respect to neat PLA filament, more evident at higher rCF content.
- (C)
- The tensile modulus increases as a function of the rCF content (wt%), from 2180 MPa for neat PLA to 3360 MPa for PLA-rCF20 filament.
- (D)
- SEM images showed no agglomerates of fibers at low rCF concentration unlike samples with higher fiber content (PLA-rCF20) for which a strong rCF alignment along with the longitudinal direction of the extrusion flow was detected in the related filament.
- (E)
- Three-dimensional printed specimens from composite filaments were manufactured through a PRUSA 3D printer.
- (F)
- An increase in the storage modulus of about 54% compared to the neat PLA 3D printed sample resulted for samples with higher rCF content (PLA-rCF20).
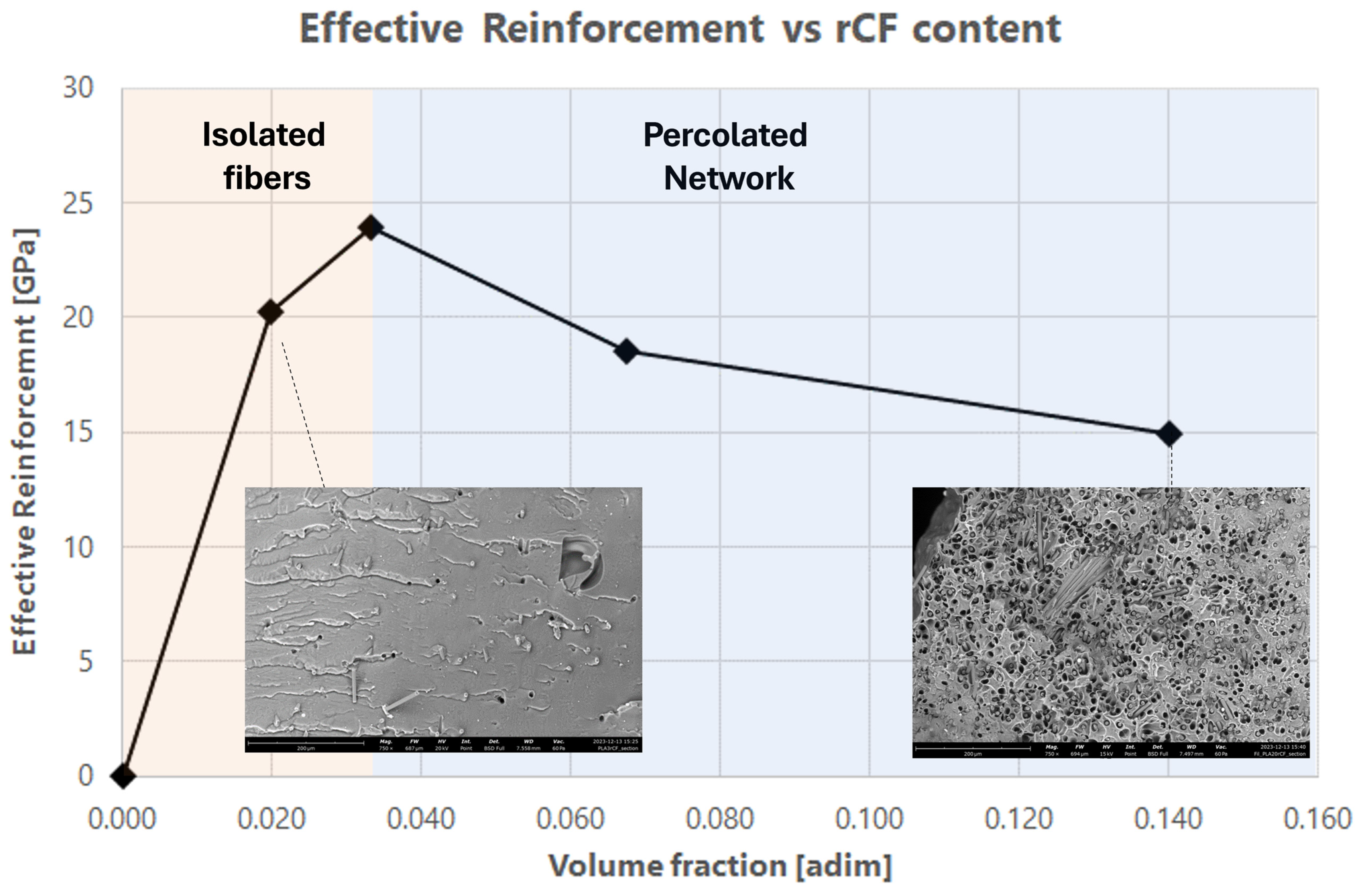
- (G)
- In the 3D printed samples, two different reinforcing regimes were identified, which can be correlated with the percolation behavior related to the 1D reinforcement. In the isolated fiber regime, the reinforcement contributes to increasing the elastic modulus (E′), while in the percolated network the effectiveness of the reinforcement decreases and the dissipative capacity (E″) is improved.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, K.R.; Harrell, T.M.; Skrzypczak, L.; Scherschel, A.; Wu, H.F.; Li, X. Carbon fibers derived from commodity polymers: A review. Carbon 2022, 196, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jia, C.; He, J.; Zhao, F.; Fan, D.; Xing, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, Y. Interfacial characterization, control and modification of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 121, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiruddin, I.; Norlin, N.; Mokhtar, C.I.; Hazizan, M.A.; Wan, F.F.; Wan, A.; Mohd, F.O. A Review on Recycling of Carbon Fibres: Methods to Reinforce and Expected Fibre Composite Degradations. Materials 2022, 15, 4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, C.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, G.; Chen, F.; Ma, P. Mechanical enhancement of carbon fiber-reinforced polymers: From interfacial regulating strategies to advanced processing technologies. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 142, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumoulos, E.P.; Trompeta, A.-F.; Santos, R.-M.; Martins, M.; Santos, C.M.d.; Iglesias, V.; Böhm, R.; Gong, G.; Chiminelli, A.; Verpoest, I.; et al. Research and development in carbon fibers and advanced high-performance composites supply chain in Europe: A roadmap for challenges and the industrial uptake. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, L. Global Carbon Fiber Composites Market Report; ATA CFT Guangzhou Co. Ltd.: Guangzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Hadigheh, S.A. Cost benefit and life cycle analysis of CFRP and GFRP waste treatment methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefeuvre, A.; Garnier, S.; Jacquemin, L.; Pillain, B.; Sonnemann, G. Anticipating in-use stocks of carbon fiber reinforced polymers and related waste flows generated by the commercial aeronautical sector until 2050. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 125, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.R.; Vieira, R.K.; Chain, M.C. Strategy and management for the recycling of carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) in the aircraft industry: A critical review. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2017, 24, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Shi, Q.; Dunn, M.L.; Wang, T.; Qi, H.J. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Thermoset Composite with Near 100% Recyclability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 6098–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, S.; Pinho, S.T. Recycling carbon fibre reinforced polymers for structural applications: Technology review and market outlook. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalraj, S.K.; Karki, T. A review on the recycling of waste carbon fibre/glass fibre-reinforced composites: Fibre recovery, properties and life-cycle analysis. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Feng, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.-H. Recycling and Reutilization of Waste Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics: Current Status and Prospects. Polymers 2023, 15, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3d printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilberoglu, U.M.; Gharehpapagh, B.; Yaman, U.; Dolen, M. The role of additive manufacturing in the era of industry 4.0. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ramanujan, D.; Ramani, K.; Chen, Y.; Williams, C.B.; Wang, C.C.L.; Shin, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Zavattieri, P.D. The status, challenges, and future of additive manufacturing in engineering, CAD. Comput. Aided Des. 2015, 69, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Altassan, A.; Rosen, D.W. Additive manufacturing of fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A technical review and status of design methodologies. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 255, 110603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateeq, M.; Shafique, M.; Azam, A.; Rafiq, M. A review of 3D printing of the recycled carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites: Processing, potential, and perspectives. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 2291–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Ghidini, T.; Cecchini, F.; Brandao, A.; Nanni, F. Additive layer manufacturing of poly (ether ether ketone) via FDM. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 145, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.M.; Kallingal, A.; Suresh, A.M.; Mahapatra, D.K.; Hasanin, M.S.; Haponiuk, J.; Thomas, S. 3D printing of polylactic acid: Recent advances and opportunities. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon, J.M.; Caminero, M.A.; Garcı’a-Plaza, E.; Nunez, P.J. Additive manufacturing of PLA structures using fused deposition modelling: Effect of process parameters on mechanical properties and their optimal selection. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilento, F.; Bassano, A.; Sorrentino, L.; Martone, A.; Giordano, M.; Palmieri, B. PVB Nanocomposites as Energy Directors in Ultrasonic Welding of Epoxy Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.S.; Shah, D.B.; Joshi, S.J.; Patel, K.M. Developments in 3D printing of carbon fiber reinforced polymer containing recycled plastic waste: A review. Clean Prod. 2023, 9, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvagno, S.; Portofino, S.; Lucchesi, A.; Corianò, O.A.; Candelieri, T.; Cornacchia, G. Procedimento per il Recupero Delle Fibre di Carbonio e/o di Vetro da Compositi Delle Stesse in Matrici Polimeriche, e Mezzi per la sua Attuazione. Italian Patent RM 2002 A 000217, 19 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Borriello, C.; Iovane, P.; Portofino, S.; Rametta, G.; Tammaro, L.; Galvagno, S. Recovering of Carbon Fiber from PPS and PEKK Composites and their Valorization by Ceramization Process of their Surface. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 86, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri, B.; Borriello, C.; Rametta, G.; Iovane, P.; Portofino, S.; Tammaro, L.; Galvagno, S.; Giordano, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Martone, A. Investigation on Stress Relaxation of Discontinuous Recycled Carbon Fiber Composites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 3938–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10119:2020; Carbon Fibre—Determination of Density. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ASTM E1131-08; Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM D790-17; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–12. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638-14; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Kopinke, F.-D.; Remmler, M.; Mackenzie, K.; Möder, M.; Wachsen, O. Thermal decomposition of biodegradable polyesters—II. Poly(lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 53, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, P.; Dowdy, K.B.; Kessler, M.R. A comparison of crystallization behavior for melt and cold crystallized poly (l-Lactide) using rapid scanning rate calorimetry. Polymer 2010, 51, 4611–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2584-18; Standard Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced Resins. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Giani, N.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Picchioni, F.; Giorgini, L. Towards sustainability in 3D printing of thermoplastic composites: Evaluation of recycled carbon fibers as reinforcing agent for FDM filament production and 3D printing. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 159, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Lauke, B.; Mäder, E.; Chee-Yoon Yue, C.-H.; Hu, X.; Mai, Y.-W. Hybrid effects on tensile properties of hybrid short-glass-fiber-and short-carbon-fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.N.; Barry, J.N.; McDonnell, K.A.; Dowling, D.P. Fabrication of continuous carbon, glass and Kevlar fibre reinforced polymer composites using additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 16, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayam, A.; Rahman, A.N.M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Smriti, S.A.; Ahmed, F.; Rabbi, M.F.; Hossain, M.; Faruque, M.O. A review on carbon fiber-reinforced hierarchical composites: Mechanical performance, manufacturing process, structural applications and allied challenges. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 1173–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.W.Y.; Shuaib, N.A.; Hadi, M.H.J.A.; Azmi, A.I.; Misbah, M.N. Mechanical and Physical Properties of Recycled-Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polylactide Fused Deposition Modelling Filament. Materials 2022, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starink, M.J.; Syngellakis, S. Shear lag models for discontinuous composites: Fibre end stresses and weak interface layers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 270, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, A.; Faiella, G.; Antonucci, V.; Giordano, M.; Zarrelli, M. The effect of the aspect ratio of carbon nanotubes on their effective reinforcement modulus in an epoxy matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, J.A. On the use of shear-lag methods for analysis of stress transfer in unidirectional composites. Mech. Mater. 1997, 26, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, G.P.; Reifsnider, K.L. Micromechanics of short-fiber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1992, 43, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipse, P. The random contact equation and its implications for (Colloidal) rods in packings, suspensions and anisotropic powders. Langmuir 1996, 12, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Rajeshkumar, L.N.; Srinivasan, N.; Kumar, D.V.; Balaji, D. Influence of filler material on properties of fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review. e-Polymers 2022, 22, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Anwar, S.; AlFaify, A.T.; Al-Ahmari, A.M.; Elgawad, A.E.E.A. Development of PLA/recycled-desized carbon fiber composites for 3D printing: Thermal, mechanical, and morphological analyses. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 2768–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Name | PLA Content (wt%) | rCF Content (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| PLA-rCF3 | 97 | 3 |
| PLA-rCF5 | 95 | 5 |
| PLA-rCF10 | 90 | 10 |
| PLA-rCF20 | 80 | 20 |
| Nozzle Temperature (°C) | Bed Temperature (°C) | Infill Type | Build Orientation (°) | Printing Speed (mm/s) | Layer Thickness (mm) | Infill Density (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220 | 60 | rectangular | 45 | 35 | 0.2 | 100 |
| 35 °C | T Peak (E″) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tg, DMA | E′ | E″ | tanδ | T Peak | E′ | E″ | tanδ | |
| (°C) | (MPa) | (MPa) | (-) | (°C) | (MPa) | (MPa) | (-) | |
| PLA | 56.7 ± 1 | 2180 ± 45 | 52.3 ± 1 | 0.0241 ± 0.0005 | 56.8 ± 1 | 1141 ± 25 | 353.8 ± 10 | 0.3099 ± 0.008 |
| PLA-rCF3 | 53.9 ± 1 | 2547 ± 52 | 29.8 ± 0.6 | 0.0117 ± 0.0002 | 54.3 ± 1 | 923 ± 22 | 588.6 ± 14 | 0.6377 ± 0.016 |
| PLA-rCF10 | 55.5 ± 1 | 3006 ± 60 | 31.2 ± 0.6 | 0.0125 ± 0.0002 | 55.8 ± 1 | 1176 ± 28 | 590.6 ± 15 | 0.6086 ± 0.014 |
| PLA-rCF20 | 56.1 ± 1 | 3360 ± 65 | 37.6 ± 0.7 | 0.0112 ± 0.0002 | 56.4 ± 1 | 1373 ± 32 | 834.0 ± 18 | 0.6073 ± 0.014 |
| Sample | Tonset (°C) | 50% Mass Loss T (°C) | 5% Mass Loss T (°C) | Tendset (°C) | Tvmax (°C) | dW/dT Tvmax (%/°C) | Residual Mass (%) | Vf (%) | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 317.8 | 337.5 | 305.0 | 357.5 | 343.3 | −2.65 | 0.46 | 0 | 63.3 | 150.3 |
| PLA-rCF3 | 322.0 | 336.8 | 321.0 | 349.0 | 344.1 | −4.91 | 3.7 | 2.3 | 63.6 | 151.6 |
| PLA-rCF5 | 319.9 | 336.2 | 312.5 | 350.6 | 341.7 | −3.54 | 5.5 | 3.6 | 61.7 | 151.4 |
| PLA-rCF10 | 332.5 | 353.0 | 324.7 | 371.5 | 344.4 | −3.56 | 9.8 | 6.8 | 62.2 | 152.2 |
| PLA-rCF20 | 339.4 | 358.4 | 331.4 | 370.0 | 355.9 | −3.70 | 19.4 | 14.2 | 61.8 | 150.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tammaro, L.; Martone, A.; Palmieri, B.; Borriello, C.; Portofino, S.; Iovane, P.; Cilento, F.; Giordano, M.; Galvagno, S. Reinforcing Efficiency of Recycled Carbon Fiber PLA Filament Suitable for Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2024, 16, 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152100
Tammaro L, Martone A, Palmieri B, Borriello C, Portofino S, Iovane P, Cilento F, Giordano M, Galvagno S. Reinforcing Efficiency of Recycled Carbon Fiber PLA Filament Suitable for Additive Manufacturing. Polymers. 2024; 16(15):2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152100
Chicago/Turabian StyleTammaro, Loredana, Alfonso Martone, Barbara Palmieri, Carmela Borriello, Sabrina Portofino, Pierpaolo Iovane, Fabrizia Cilento, Michele Giordano, and Sergio Galvagno. 2024. "Reinforcing Efficiency of Recycled Carbon Fiber PLA Filament Suitable for Additive Manufacturing" Polymers 16, no. 15: 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152100
APA StyleTammaro, L., Martone, A., Palmieri, B., Borriello, C., Portofino, S., Iovane, P., Cilento, F., Giordano, M., & Galvagno, S. (2024). Reinforcing Efficiency of Recycled Carbon Fiber PLA Filament Suitable for Additive Manufacturing. Polymers, 16(15), 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152100










