Effects of Filler Anisometry on the Mechanical Response of a Magnetoactive Elastomer Cell: A Single-Inclusion Modeling Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Modeling Process
2.1. General Outline
2.2. Elastic Energy
3. Model Verification
3.1. Elastic Modulus of Polymer Composites with a Small Fraction of Spherical Particulate
3.2. Displacements of a Rod in a Polymer Matrix
4. Mechanical Modeling Results
4.1. Inclusion Rotation
4.2. Translational Motion of the Inclusion
4.3. Uniaxial Extension of the Cell
5. Inclusion Rotation in External Magnetic Field
6. Conclusions
- For a given degree of filling, increasing the anisometry of the filler particles increases the modulus of the cell;
- At fixed anisometry, the effect of the particles on the elastic modulus of the cell is maximized when the orientation of the major axis of the inclusion is parallel to the applied mechanical force;
- The higher the anisometry of the inclusion, the greater the force required to rotate it; however, for the same anisometry, oblate particles rotate more easily than prolate particles;
- The effect of the external magnetic field on the rotation of the inclusion increases with the magnetic anisotropy of the inclusion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- 1.
- Pure rotation
- 2.
- Pure translation
- 3.
- Pure deformation
References
- Filipcsei, G.; Csetneki, I.; Szilágyi, A.; Zrínyi, M. Magnetic Field-Responsive Smart Polymer Composites. In Oligomers—Polymer Composites—Molecular Imprinting; Gong, B., Sanford, A.R., Ferguson, J.S., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 137–189. ISBN 9783540468301. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Du, H. A State-of-the-Art Review on Magnetorheological Elastomer Devices. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, A.M. Tuned, Driven, and Active Soft Matter. Phys. Rep. 2015, 554, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaidillah; Sutrisno, J.; Purwanto, A.; Mazlan, S.A. Recent Progress on Magnetorheological Solids: Materials, Fabrication, Testing, and Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 563–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbach, S. Microstructure and Rheology of Magnetic Hybrid Materials. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2016, 86, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, M.; Durán, J.; Iskakova, L.; Zubarev, A. Mechanics of Magnetopolymer Composites: A Review. J. Nanofluids 2016, 5, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantera, M.A.; Behrooz, M.; Gibson, R.F.; Gordaninejad, F. Modeling of Magneto-Mechanical Response of Magnetorheological Elastomers (MRE) and MRE-Based Systems: A Review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamonin, M.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Highly Responsive Magnetoactive Elastomers. In Novel Magnetic Nanostructures; Domracheva, N., Caporali, M., Rentschler, E., Eds.; Advanced Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 7; pp. 221–245. ISBN 9780128135945. [Google Scholar]
- Kramarenko, E.Y.; Stepanov, G.V.; Khokhlov, A.R. Magnetically Active Silicone Elastomers: Twenty Years of Development. Ineos Open 2020, 2, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbach, S. (Ed.) Magnetic Hybrid-Materials: Multi-Scale Modelling, Synthesis, and Applications; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2021; ISBN 9783110569636. [Google Scholar]
- Nadzharyan, T.A.; Shamonin, M.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Theoretical Modeling of Magnetoactive Elastomers on Different Scales: A State-of-the-Art Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, L.A.; Alekhina, Y.A.; Rusakova, T.S.; Perov, N.S. Tunable Properties of Magnetoactive Elastomers for Biomedical Applications. Phys. Procedia 2016, 82, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Lum, G.Z.; Mastrangeli, M.; Sitti, M. Small-Scale Soft-Bodied Robot with Multimodal Locomotion. Nature 2018, 554, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bira, N.; Dhagat, P.; Davidson, J.R. A Review of Magnetic Elastomers and Their Role in Soft Robotics. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 588391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshiar, A.; Payami, A.; Dargahi, J.; Najarian, S. Magnetostriction-Based Force Feedback for Robot-Assisted Cardiovascular Surgery Using Smart Magnetorheological Elastomers. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 161, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekhina, I.; Kramarenko, E.; Makarova, L.; Perov, N. Magnetorheological Composites for Biomedical Applications. In Magnetic Materials and Technologies for Medical Applications; Tishin, A.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; Chapter 17; pp. 501–526. ISBN 9780128225325. [Google Scholar]
- Makarova, L.A.; Alekhina, Y.A.; Isaev, D.A.; Khairullin, M.F.; Perov, N.S. Tunable Layered Composites Based on Magnetoactive Elastomers and Piezopolymer for Sensors and Energy Harvesting Devices. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2020, 54, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Salehizadeh, M.; Onaizah, O.; Diller, E. Millimeter-Scale Flexible Robots with Programmable Three-Dimensional Magnetization and Motions. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaav4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, H.; Azukizawa, S.; Maeda, K.; Tsumori, F. Bio-Mimic Motion of 3D-Printed Gel Structures Dispersed with Magnetic Particles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B3235–B3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Hu, W.; Dong, X.; Sitti, M. Multi-Functional Soft-Bodied Jellyfish-like Swimming. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Zoumhani, O.; Boutry, C.M. Recent Advances in Magnetic Polymer Composites for BioMEMS: A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.K.; Paudel, M.; Li, L.; Li, W. Recent Progress of Magnetorheological Elastomers: A Review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.K.; Hossain, M. A Review on Magneto-Mechanical Characterizations of Magnetorheological Elastomers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, S.; Hossain, M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D. Recent Advances in Hard-Magnetic Soft Composites: Synthesis, Characterisation, Computational Modelling, and Applications. Compos. Struct. 2022, 279, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, J.M.; Nichols, M.E.; Elie, L.D.; Tardiff, J.L. Magnetorheological Elastomers: Properties and Applications. In Smart Structures and Materials 1999: Smart Materials Technologies; SPIE: Cergy Pontoise, France, 1999; Volume 3675, pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Deng, H.; Yang, J.; Li, W.; Du, H.; Alici, G. Performance Evaluation and Comparison of Magnetorheological Elastomer Absorbers Working in Shear and Squeeze Modes. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.B.; Komatsuzaki, T.; Iwata, Y.; Asanuma, H. Fuzzy Semiactive Vibration Control of Structures Using Magnetorheological Elastomer. Shock Vib. 2017, 2017, e3651057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guell Izard, A.; Valdevit, L. Magnetoelastic Metamaterials for Energy Dissipation and Wave Filtering. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenggana, B.W.; Ubaidillah, U.; Imaduddin, F.; Choi, S.-B.; Purwana, Y.M.; Harjana, H. Review of Magnetorheological Damping Systems on a Seismic Building. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.T.; Wereley, N.M. Adaptively Tunable Magnetorheological Elastomer-Based Vibration Absorber for a Propeller Aircraft Seat. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 035332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Sedaghati, R. Analysis of an Adaptive Periodic Low-Frequency Wave Filter Featuring Magnetorheological Elastomers. Polymers 2023, 15, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Hu, R.; Xie, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Han, X.; Cao, Q.; Li, L. Reconfigurable Magnetic Soft Robots with Multimodal Locomotion. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-J.; Parsons, A.M.; Zheng, L. Magnetically Controlled Soft Robotics Utilizing Elastomers and Gels in Actuation: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yin, J. Bistable and Multistable Actuators for Soft Robots: Structures, Materials, and Functionalities. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.-K.; Yoon, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-W.; Choi, S.-B. Field-Dependent Stiffness of a Soft Structure Fabricated from Magnetic-Responsive Materials: Magnetorheological Elastomer and Fluid. Materials 2020, 13, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, S.; Shepherd, R.F. Elastomeric Haptic Devices for Virtual and Augmented Reality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costrell, S.; Alam, M.; Klatzky, R.L.; McHenry, M.E.; Walker, L.M.; Martinez, M.O. A Magnetic Soft Device for Tactile Haptic Actuation of the Fingertip. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE World Haptics Conference (WHC), Delft, The Netherlands, 10–13 July 2023; pp. 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Stanier, D.C.; Ciambella, J.; Rahatekar, S.S. Fabrication and Characterisation of Short Fibre Reinforced Elastomer Composites for Bending and Twisting Magnetic Actuation. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 91, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, L.A.; Nadzharyan, T.A.; Alekhina, Y.A.; Stepanov, G.V.; Kazimirova, E.G.; Perov, N.S.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Magnetoactive Elastomer as an Element of a Magnetic Retina Fixator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapan, Y.; Karacakol, A.C.; Guzelhan, S.N.; Isik, I.; Sitti, M. Reprogrammable Shape Morphing of Magnetic Soft Machines. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, W.; Soon, R.H.; Davidson, Z.S.; Sitti, M. Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Magnetic Composite Films for Reconfigurable Shape-Morphing Soft Miniature Machines. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Puranam, V.R.; Misra, S.; Venkiteswaran, V.K. A Snake-Inspired Multi-Segmented Magnetic Soft Robot towards Medical Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F. Electromagnetic Properties and Mechanical Properties of Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4/Polyolefin Elastomer Composites for High-Frequency Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3510–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, I.E.; Kolesov, V.V.; Fionov, A.S.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Stepanov, G.V.; Mikheev, M.G.; Verona, E.; Solodov, I. Magnetoactive Elastomers with Controllable Radio-Absorbing Properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 21, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavan, G.; Belyaeva, I.A.; Shamonin, M. Multiferroic Cantilevers Containing a Magnetoactive Elastomer: Magnetoelectric Response to Low-Frequency Magnetic Fields of Triangular and Sinusoidal Waveform. Sensors 2022, 22, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigal, D.; Bergmann, G. Multi-Pole Magnetic Encoders for Active Speed-Measurement Systems. SAE Trans. 1999, 108, 3398–3403. [Google Scholar]
- Mateev, V.; Marinova, I. Magnetic Elastomer Sensor for Dynamic Torque and Speed Measurements. Electronics 2021, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P. Experimental Study on Rolling Friction Coefficient Controllability of Magnetorheological Elastomer. J. Tribol. 2021, 143, 124501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Sokolov, B.O.; Stepanov, G.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Controllable Hydrophobicity of Magnetoactive Elastomer Coatings. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 459, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavan, G.; Salamon, P.; Belyaeva, I.A.; Shamonin, M.; Drevenšek-Olenik, I. Tunable Surface Roughness and Wettability of a Soft Magnetoactive Elastomer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Murakami, D.; Tanaka, M.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Optimal Plasticizer Content for Magnetic Elastomers Used for Cell Culture Substrate. Chem. Lett. 2020, 49, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, X. Magnetic-Responsive Superhydrophobic Surface of Magnetorheological Elastomers Mimicking from Lotus Leaves to Rose Petals. Langmuir 2021, 37, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, P.A.; Minina, E.S.; Kantorovich, S.S.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Surface Relief of Magnetoactive Elastomeric Films in a Homogeneous Magnetic Field: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, D.; Yang, P.; Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, X. Improved Magneto-Sensitive Adhesion Property of Magnetorheological Elastomers Modified Using Graphene Nanoplatelets. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 9143–9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, A.; Belyaeva, I.A.; von Hofen, C.; Gorb, S.; Shamonin, M. Magnetically Switchable Adhesion and Friction of Soft Magnetoactive Elastomers. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2200372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Liao, C.; Yang, P.; Ruan, H.; Shou, M.; Luo, J.; Wang, X. Study on Sliding Friction Characteristics of Magnetorheological Elastomer—Copper Pair Affected by Magnetic-Controlled Surface Roughness and Elastic Modulus. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 31, 015030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.C.; Tran, H.D.; O’Brien, M.J.; Rabinovich, E.; Lopez, G.P. Rapid Prototyping of Active Microfluidic Components Based on Magnetically Modified Elastomeric Materials. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2001, 19, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Sheng, P.; Wen, W. Design and Fabrication of Microfluidic Mixer from Carbonyl Iron–PDMS Composite Membrane. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 10, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.L. A Review of Magnetic Composite Polymers Applied to Microfluidic Devices. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, S.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, S.; Deng, L.; Yun, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Versatile Microfluidic Platforms Enabled by Novel Magnetorheological Elastomer Microactuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolteau, B.; Gelebart, F.; Teisseire, J.; Barthel, E.; Fresnais, J. Digital Microfluidics—How Magnetically Driven Orientation of Pillars Influences Droplet Positioning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 35674–35683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Tian, D. External-Field-Induced Gradient Wetting for Controllable Liquid Transport: From Movement on the Surface to Penetration into the Surface. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyeva, M.A. Equipment for Generating Running Magnetic Fields for Peristaltic Transport of Heavy Oil. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Applications and Manufacturing (ICIEAM), St. Petersburg, Russia, 16–19 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; Tian, X. Magnetoresponsive Surfaces for Manipulation of Nonmagnetic Liquids: Design and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, J.; Han, G.; Guo, Z. A Facile Approach to Achieve Bioinspired PDMS@Fe3O4 Fabric with Switchable Wettability for Liquid Transport and Water Collection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 22741–22748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, B.; Xu, Q. Design of a Magnetic Soft Inchworm Millirobot Based on Pre-Strained Elastomer with Micropillars. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, Z. Recent Progress on the Development of Magnetically-Responsive Micropillars: Actuation, Fabrication, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaidillah, U.; Lenggana, B.W.; Choi, S.-B. Bibliometric Review of Magnetorheological Materials. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, A.M.; Stolbov, O.V.; Raikher, Y.L. Modeling of Particle Interactions in Magnetorheological Elastomers. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 114904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolbov, O.V.; Raikher, Y.L. Magnetostriction Effect in Soft Magnetic Elastomers. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2019, 89, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolbov, O.V.; Raikher, Y.L. Mesostructural Origin of the Field-Induced Pseudo-Plasticity Effect in a Soft Magnetic Elastomer. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 581, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaganov, M.V.; Borin, D.Y.; Odenbach, S.; Raikher, Y.L. Mesomagnetomechanics of Hybrid Elastomer Composites: Magnetization of Elastically Trapped Particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 499, 166249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, V.; Danas, K.; Lopez-Pamies, O. A General Result for the Magnetoelastic Response of Isotropic Suspensions of Iron and Ferrofluid Particles in Rubber, with Applications to Spherical and Cylindrical Specimens. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 107, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, V.; Danas, K.; Lopez-Pamies, O. Two Families of Explicit Models Constructed from a Homogenization Solution for the Magnetoelastic Response of MREs Containing Iron and Ferrofluid Particles. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2020, 119, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaneyko, D.; Toshchevikov, V.; Saphiannikova, M.; Heinrich, G. Mechanical Properties of Magneto-Sensitive Elastomers: Unification of the Continuum-Mechanics and Microscopic Theoretical Approaches. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, D.; Metsch, P.; Kästner, M.; Saphiannikova, M. Theoretical Models for Magneto-Sensitive Elastomers: A Comparison between Continuum and Dipole Approaches. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 042501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, D.; Toshchevikov, V.; Saphiannikova, M. Effects of Local Rearrangement of Magnetic Particles on Deformation in Magneto-Sensitive Elastomers. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3552–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, D.; Saphiannikova, M. A Cascading Mean-Field Approach to the Calculation of Magnetization Fields in Magnetoactive Elastomers. Polymers 2021, 13, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsch, P.; Romeis, D.; Kalina, K.A.; Raßloff, A.; Saphiannikova, M.; Kästner, M. Magneto-Mechanical Coupling in Magneto-Active Elastomers. Materials 2021, 14, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramarenko, E.Y.; Chertovich, A.V.; Stepanov, G.V.; Semisalova, A.S.; Makarova, L.A.; Perov, N.S.; Khokhlov, A.R. Magnetic and Viscoelastic Response of Elastomers with Hard Magnetic Filler. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, J.; Roitsch, S.; Schmidt, A.M. Covalent Hybrid Elastomers Based on Anisotropic Magnetic Nanoparticles and Elastic Polymers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, J.; Günzing, D.; Webers, S.; Dulle, M.; Kruteva, M.; Landers, J.; Wende, H.; Schmidt, A.M. Strain- and Field-Induced Anisotropy in Hybrid Elastomers with Elongated Filler Nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 7565–7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Kirichenko, S.I.; Makhaeva, E.E.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Mechanical Properties of Anisotropic Magnetic Elastomers. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2023, 65, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, L.; Bender, P.; Tschöpe, A.; Birringer, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Shear Modulus Determination in Model Hydrogels by Means of Elongated Magnetic Nanoprobes. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, E. Theory of Filler Reinforcement. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1945, 18, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. Eine Neue Bestimmung Der Moleküldimensionen. Ann. Phys. 1906, 324, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapp, R.L.; Guth, E. Elastic Modulus and Swelling of Butyl Vulcanizates. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1951, 43, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippada, U.; Langrana, N.; Yurke, B. Complete Mechanical Characterization of Soft Media Using Nonspherical Rods. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 063528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, R.M.; Libanori, R.; Rothfuchs, N.; Studart, A.R. Composites Reinforced in Three Dimensions by Using Low Magnetic Fields. Science 2012, 335, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 9780521816144. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vilsteren, S.J.M.; Yarmand, H.; Ghodrat, S. Review of Magnetic Shape Memory Polymers and Magnetic Soft Materials. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorth, R.M. Ferromagnetism; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993; ISBN 9780780310322. [Google Scholar]
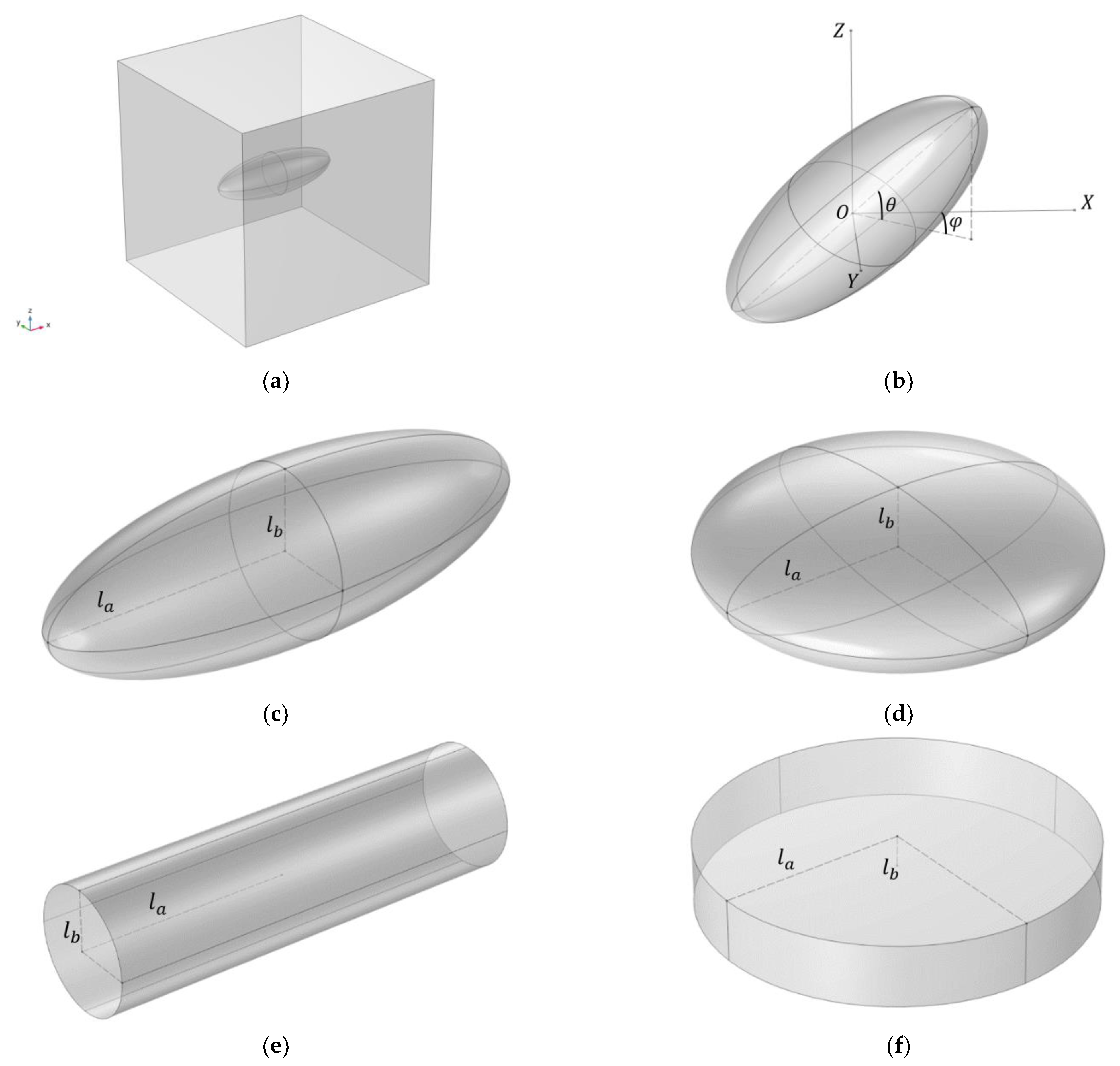
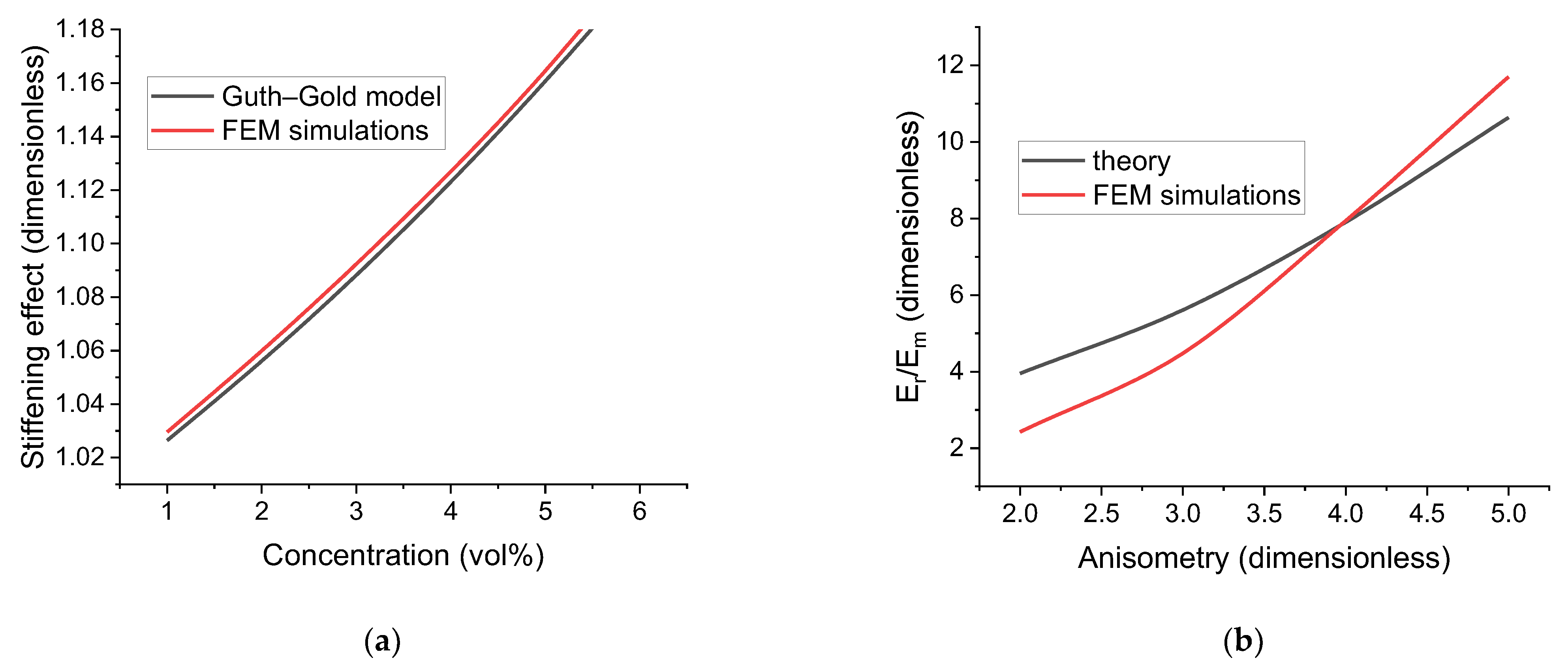
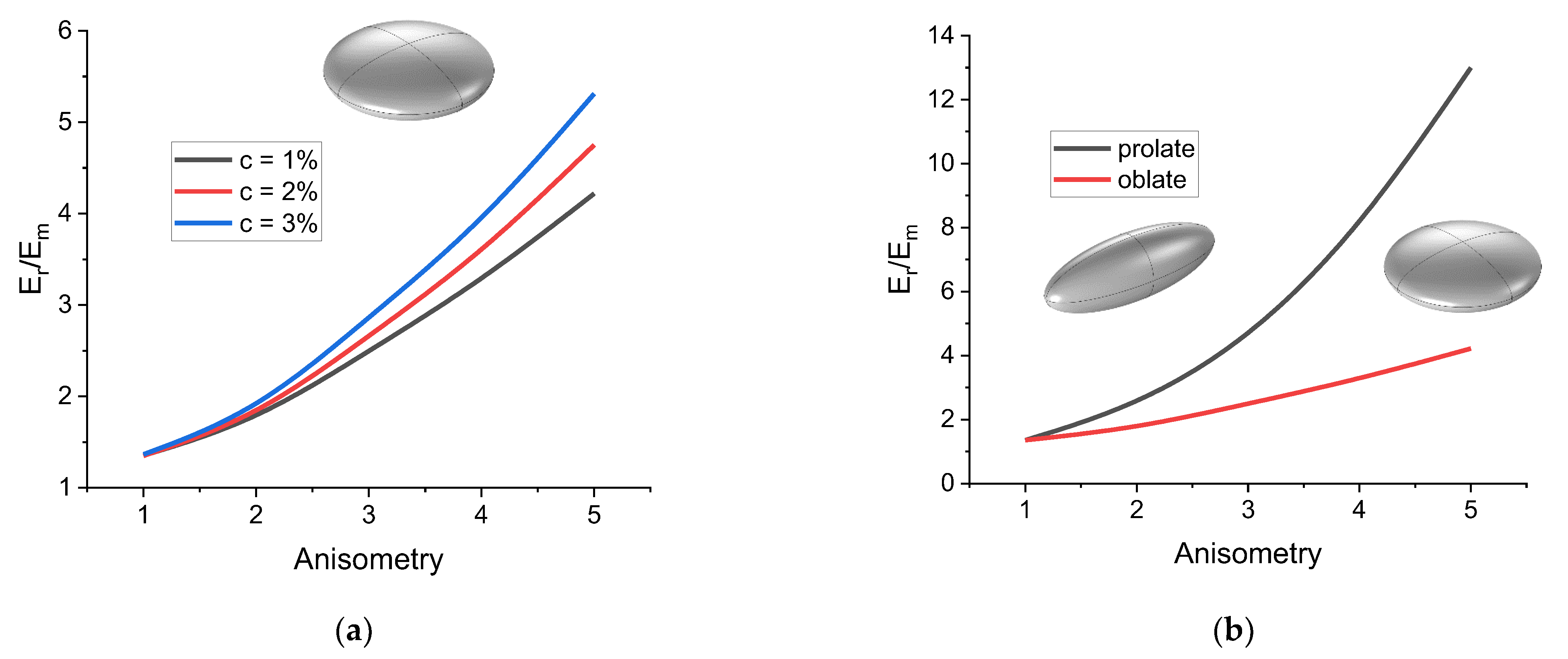
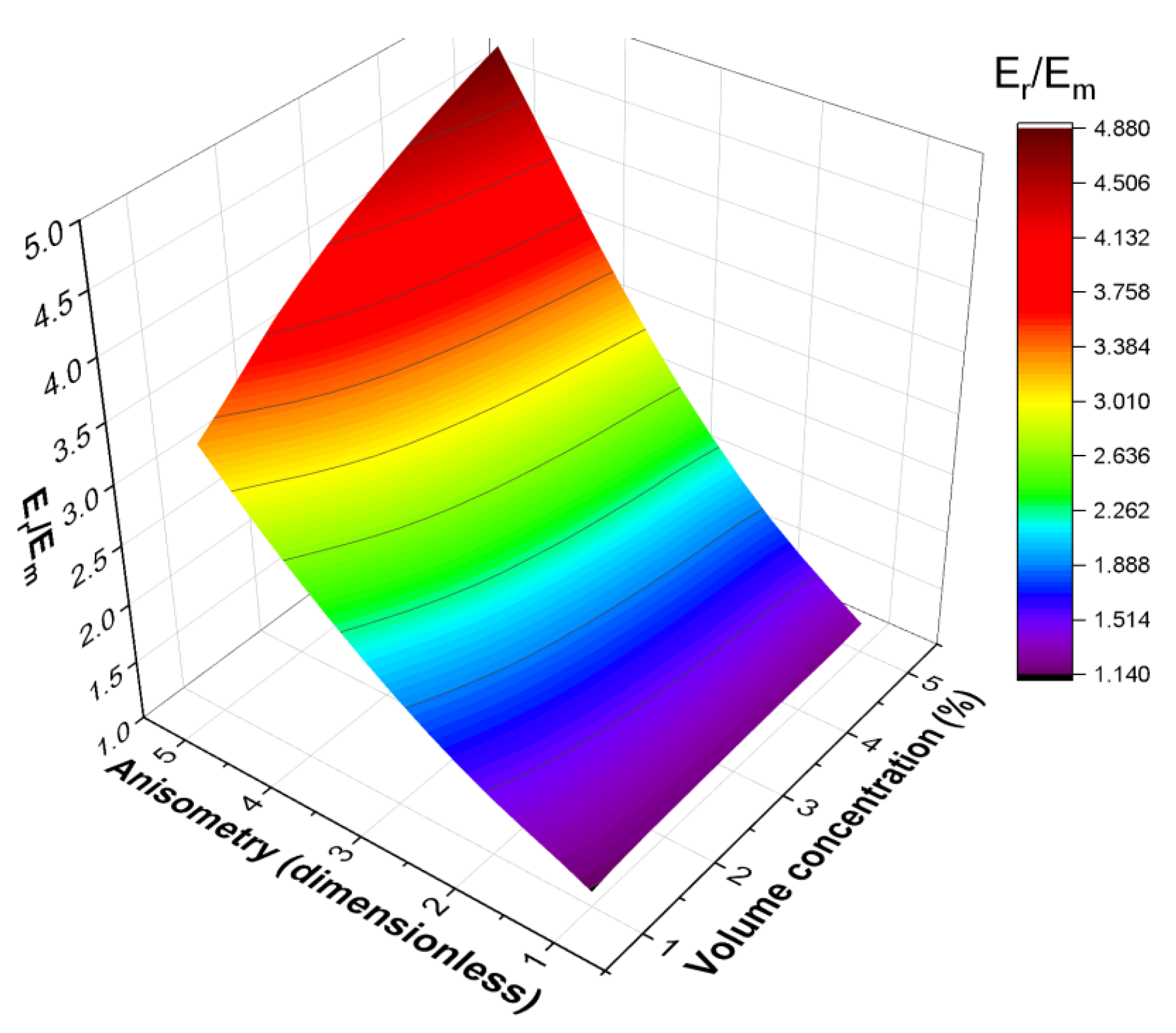
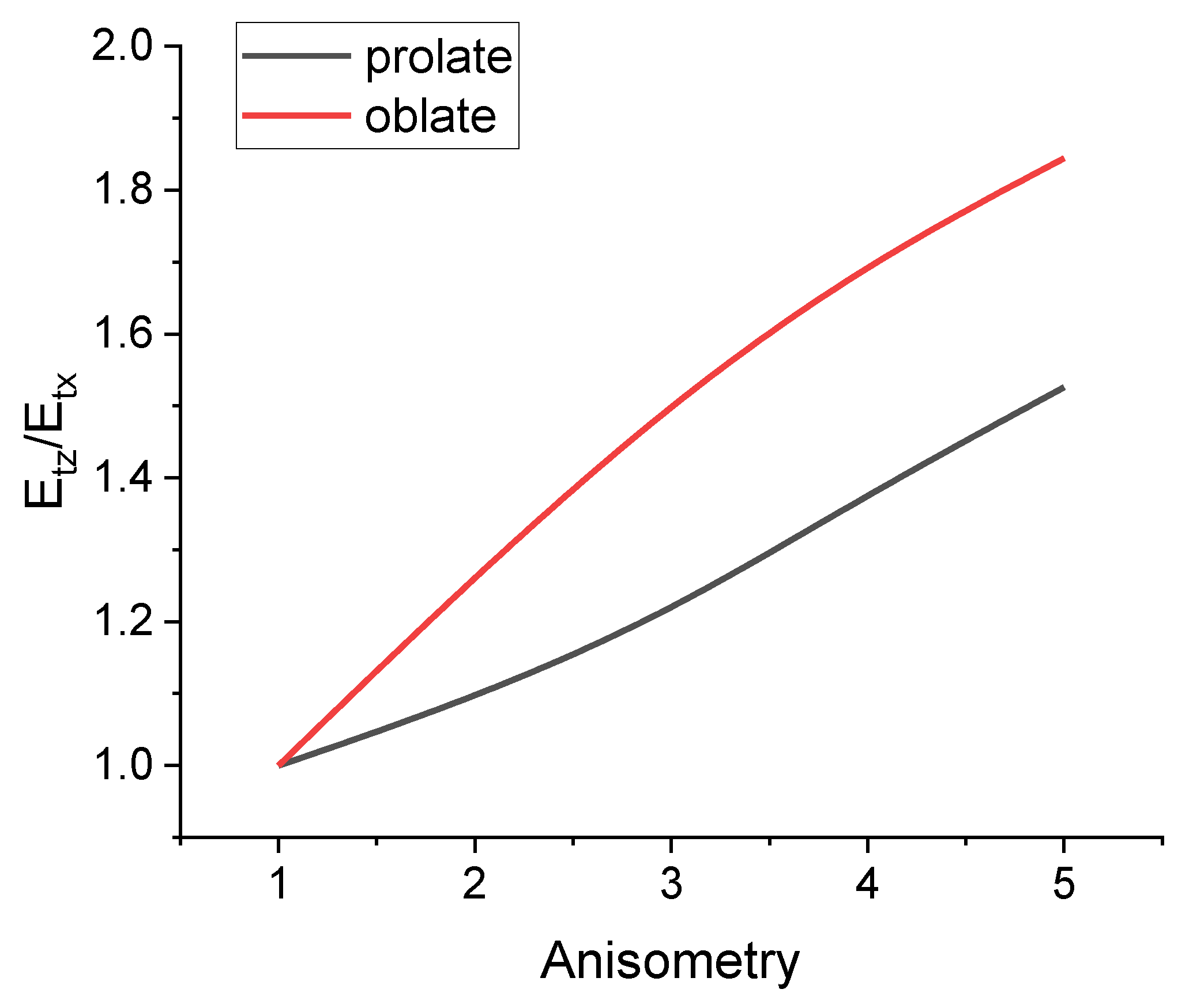
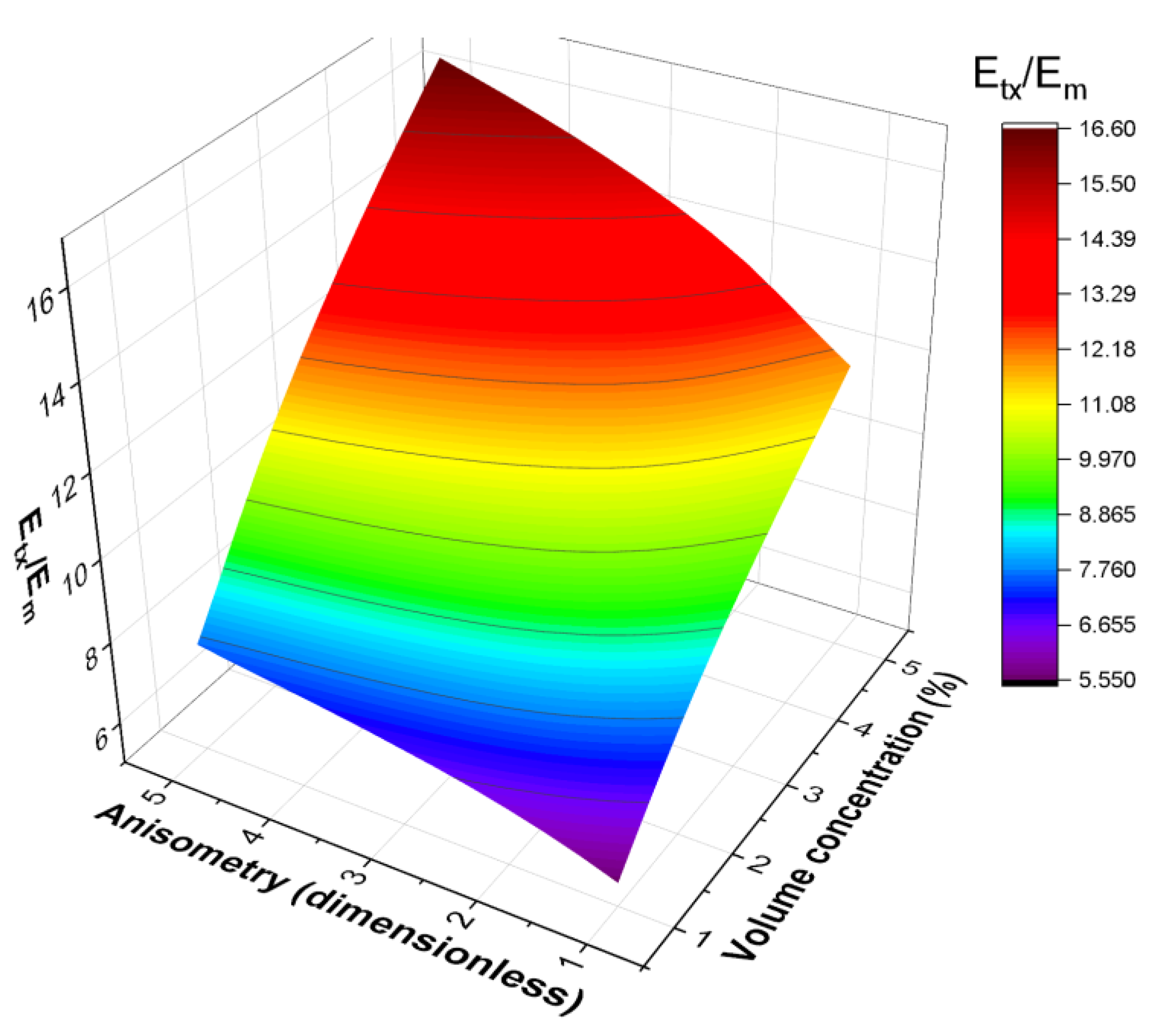
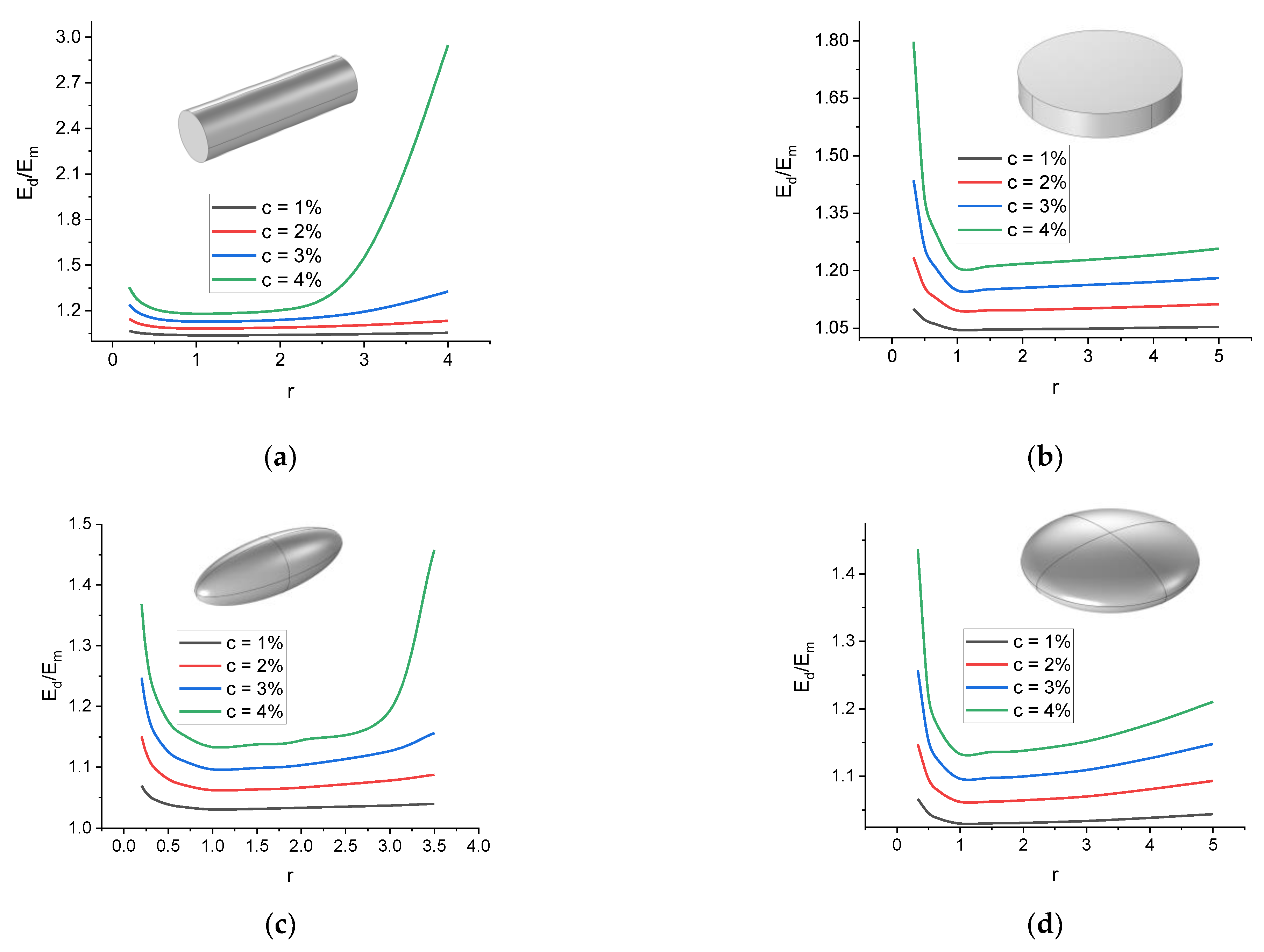
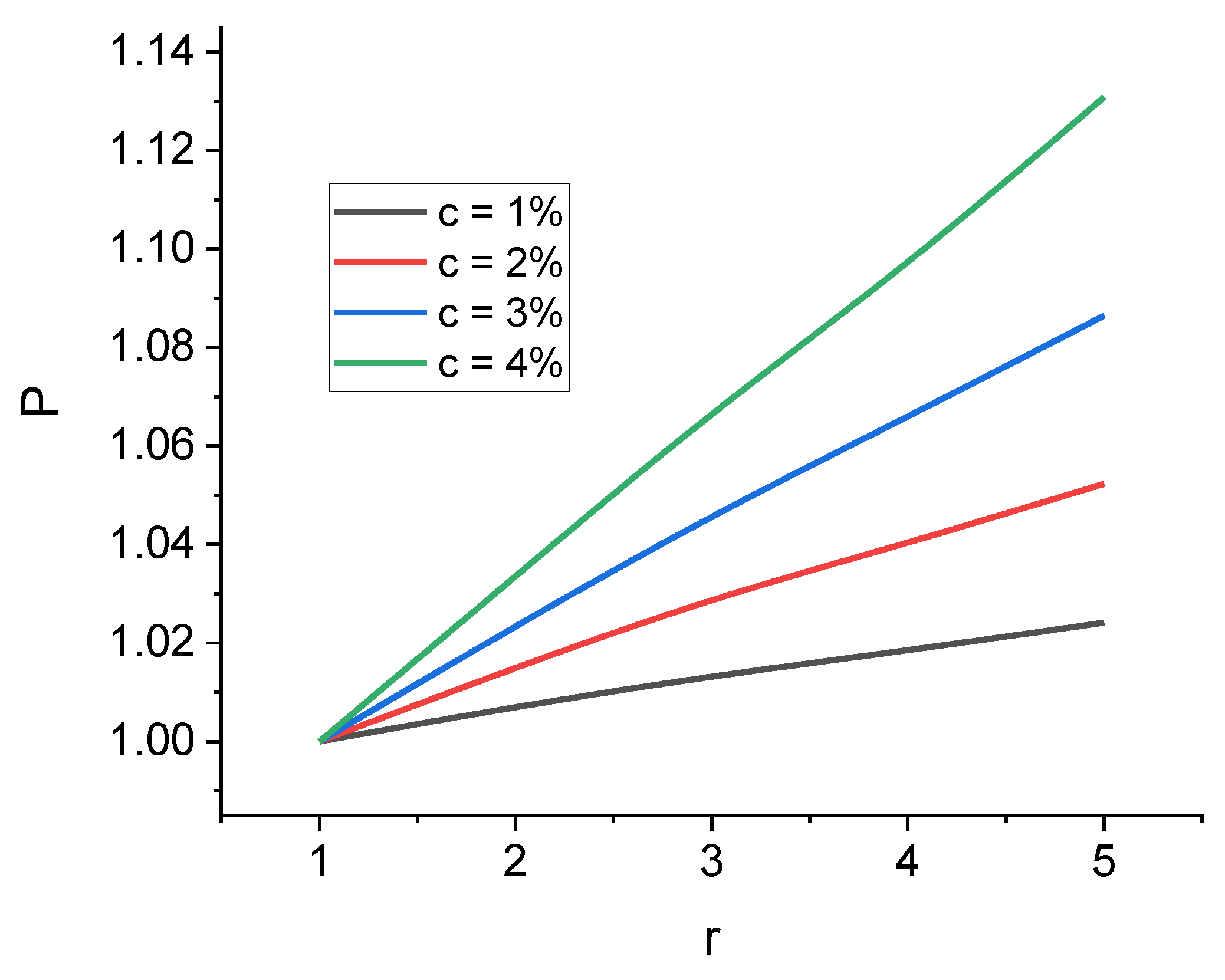
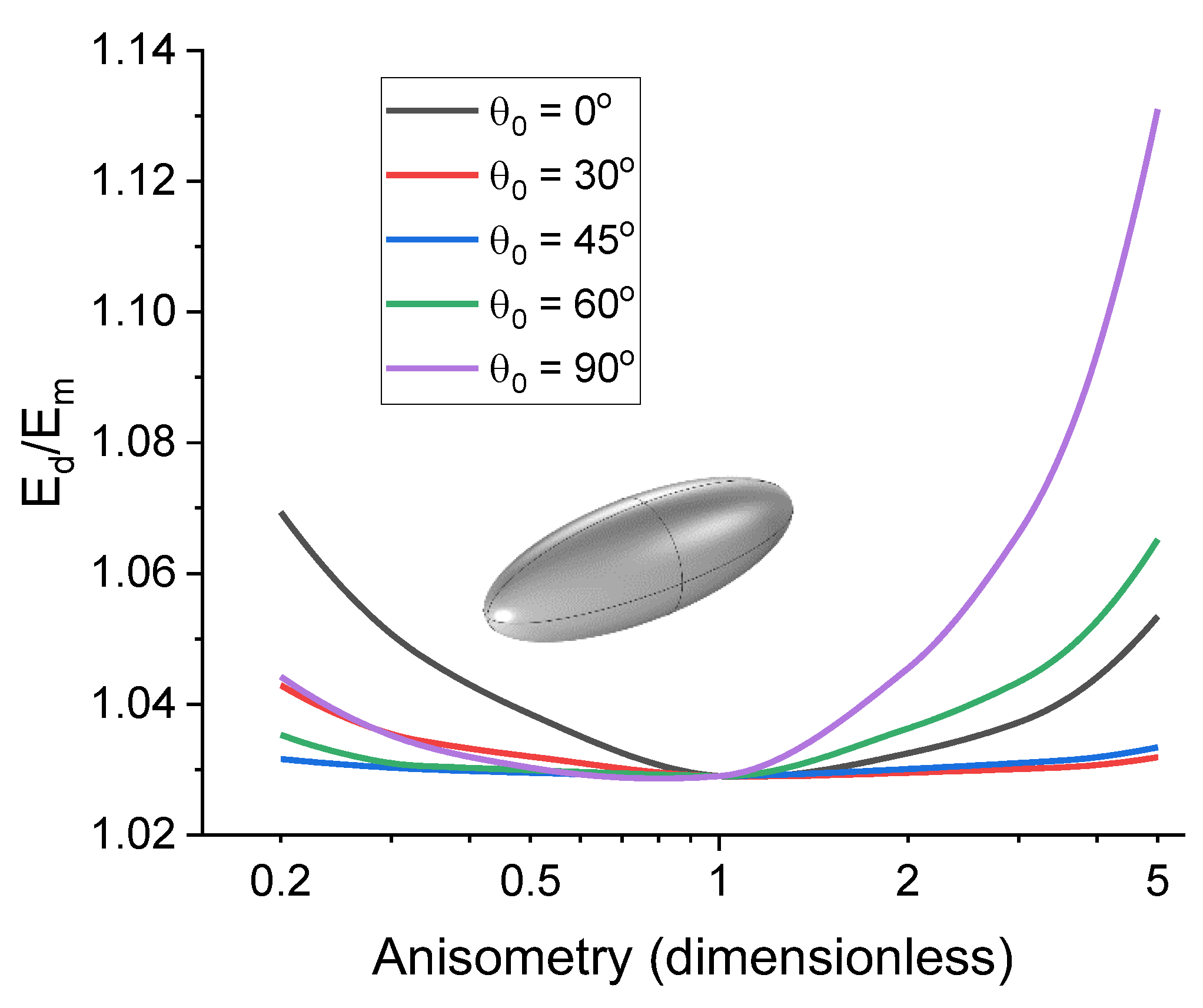

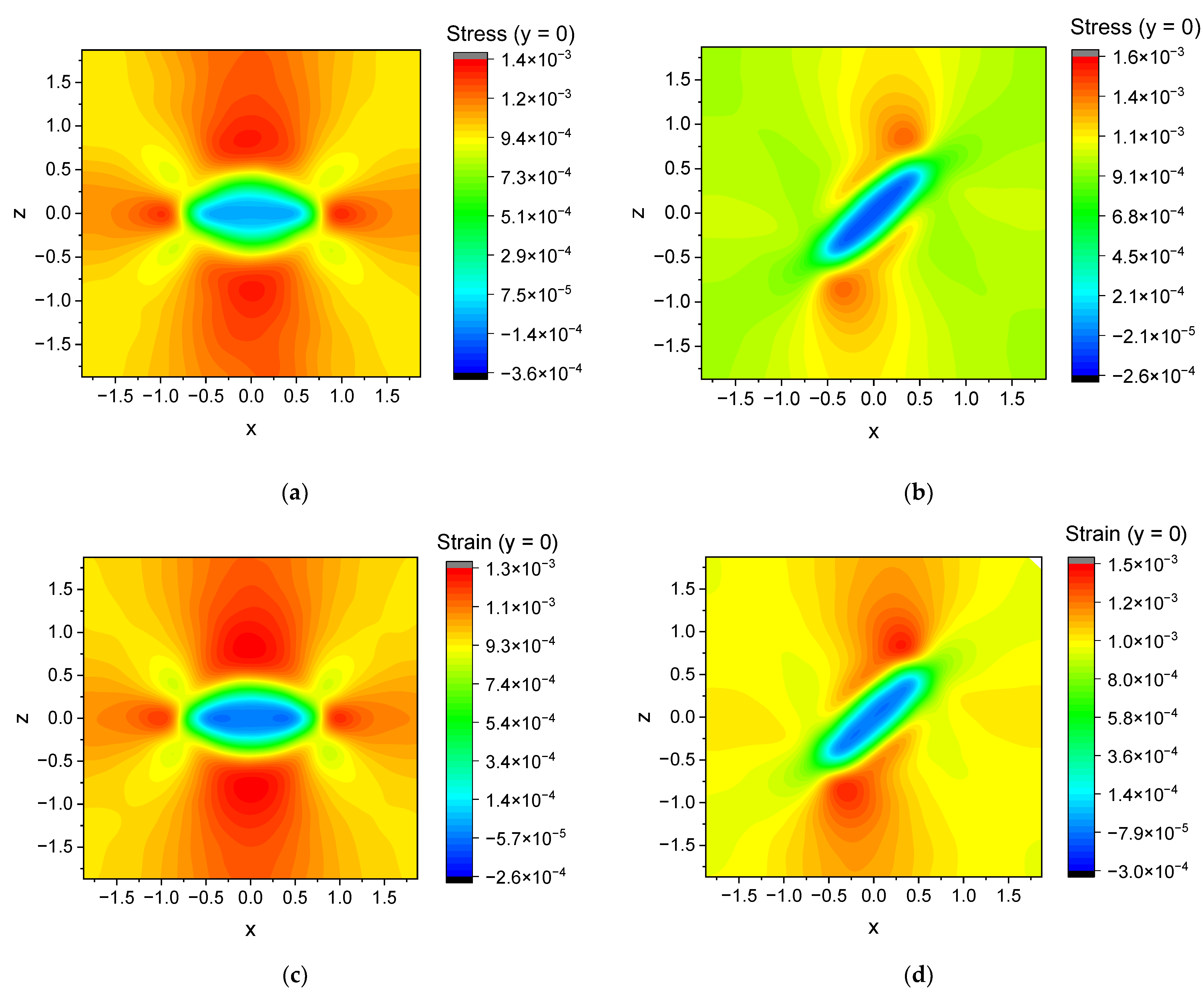

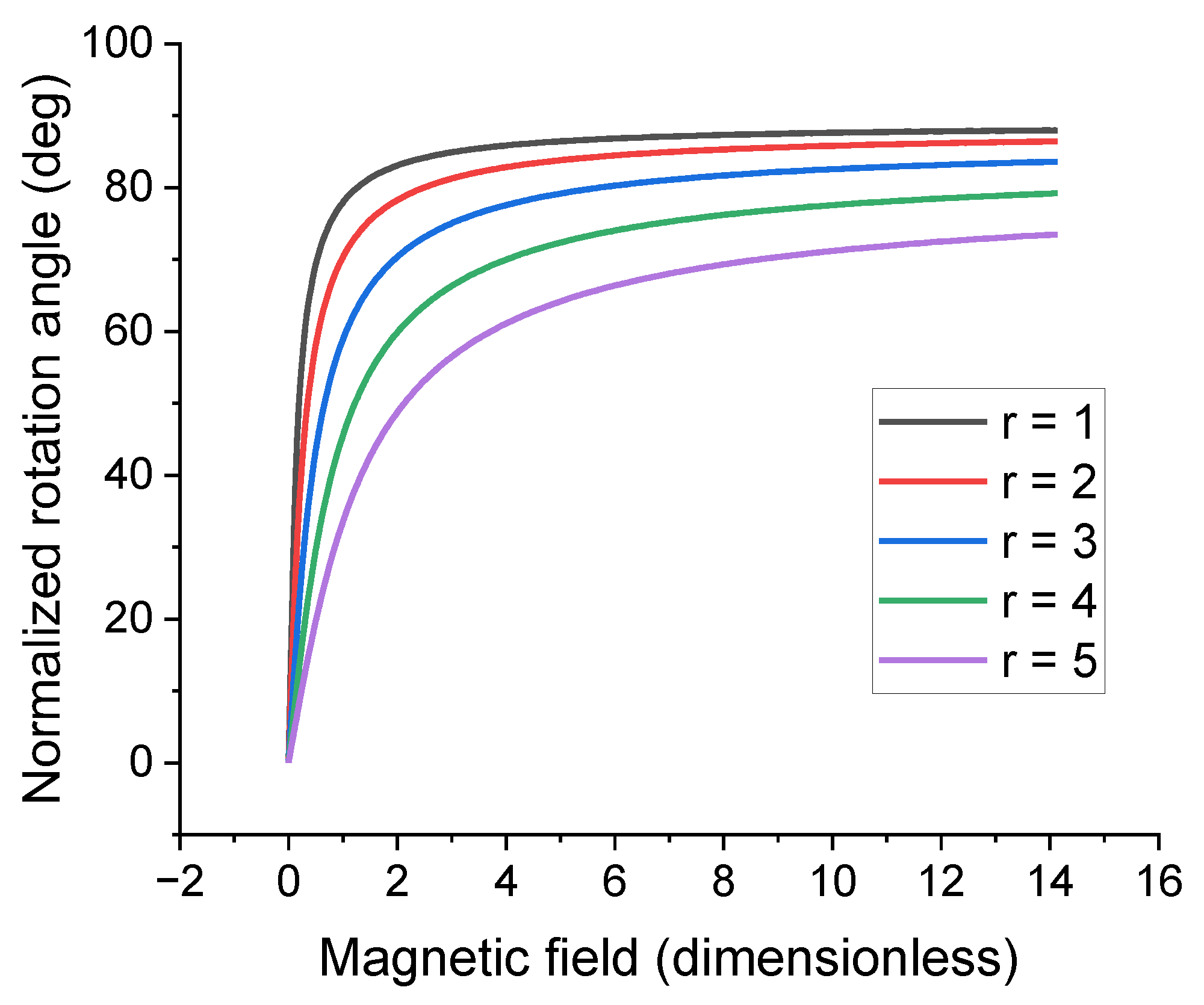

| Parameter | Prolate Spheroid | Oblate Spheroid | Rod-like Cylinder | Disk-like Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | ||||
| μ |
| Parameter | Prolate Spheroid | Oblate Spheroid | Rod-like Cylinder | Disk-like Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | ||||
| μ | 2.2644 | 1.6628 | 1.2759 | 0.631 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nadzharyan, T.A.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Effects of Filler Anisometry on the Mechanical Response of a Magnetoactive Elastomer Cell: A Single-Inclusion Modeling Approach. Polymers 2024, 16, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010118
Nadzharyan TA, Kramarenko EY. Effects of Filler Anisometry on the Mechanical Response of a Magnetoactive Elastomer Cell: A Single-Inclusion Modeling Approach. Polymers. 2024; 16(1):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010118
Chicago/Turabian StyleNadzharyan, Timur A., and Elena Yu. Kramarenko. 2024. "Effects of Filler Anisometry on the Mechanical Response of a Magnetoactive Elastomer Cell: A Single-Inclusion Modeling Approach" Polymers 16, no. 1: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010118
APA StyleNadzharyan, T. A., & Kramarenko, E. Y. (2024). Effects of Filler Anisometry on the Mechanical Response of a Magnetoactive Elastomer Cell: A Single-Inclusion Modeling Approach. Polymers, 16(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010118









