Enhancing the Properties of Water-Soluble Copolymer Nanocomposites by Controlling the Layer Silicate Load and Exfoliated Nanolayers Adsorbed on Polymer Chains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
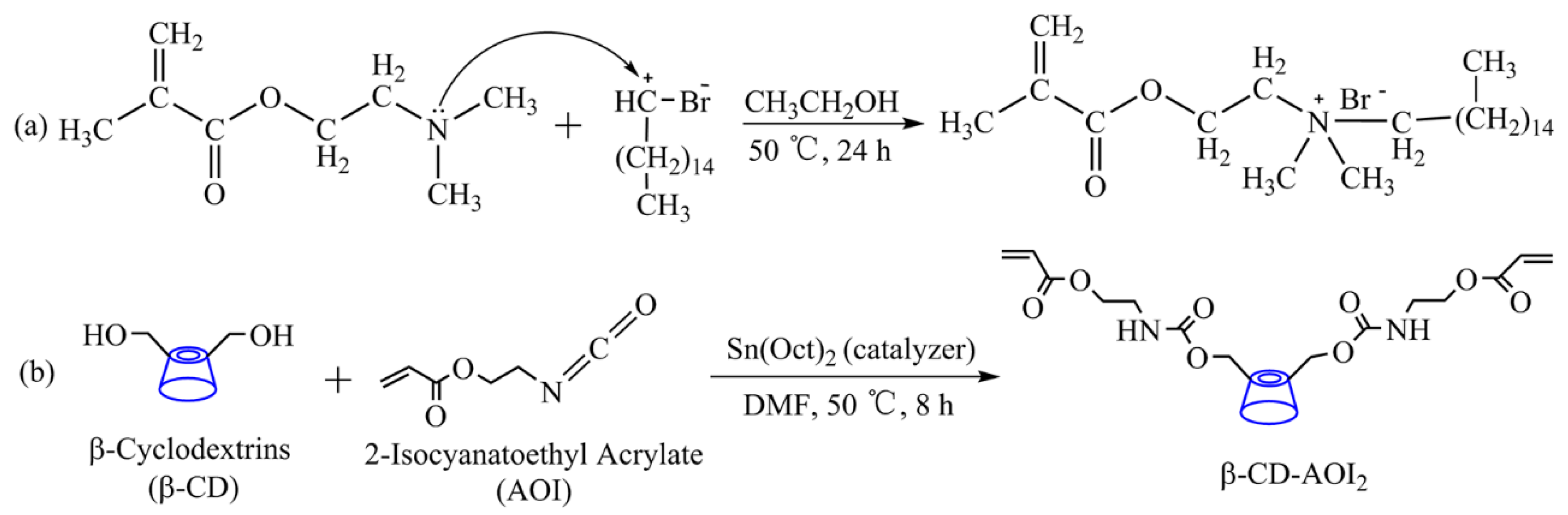
2.2.1. Preparation of DMB and β-CD-AOI2
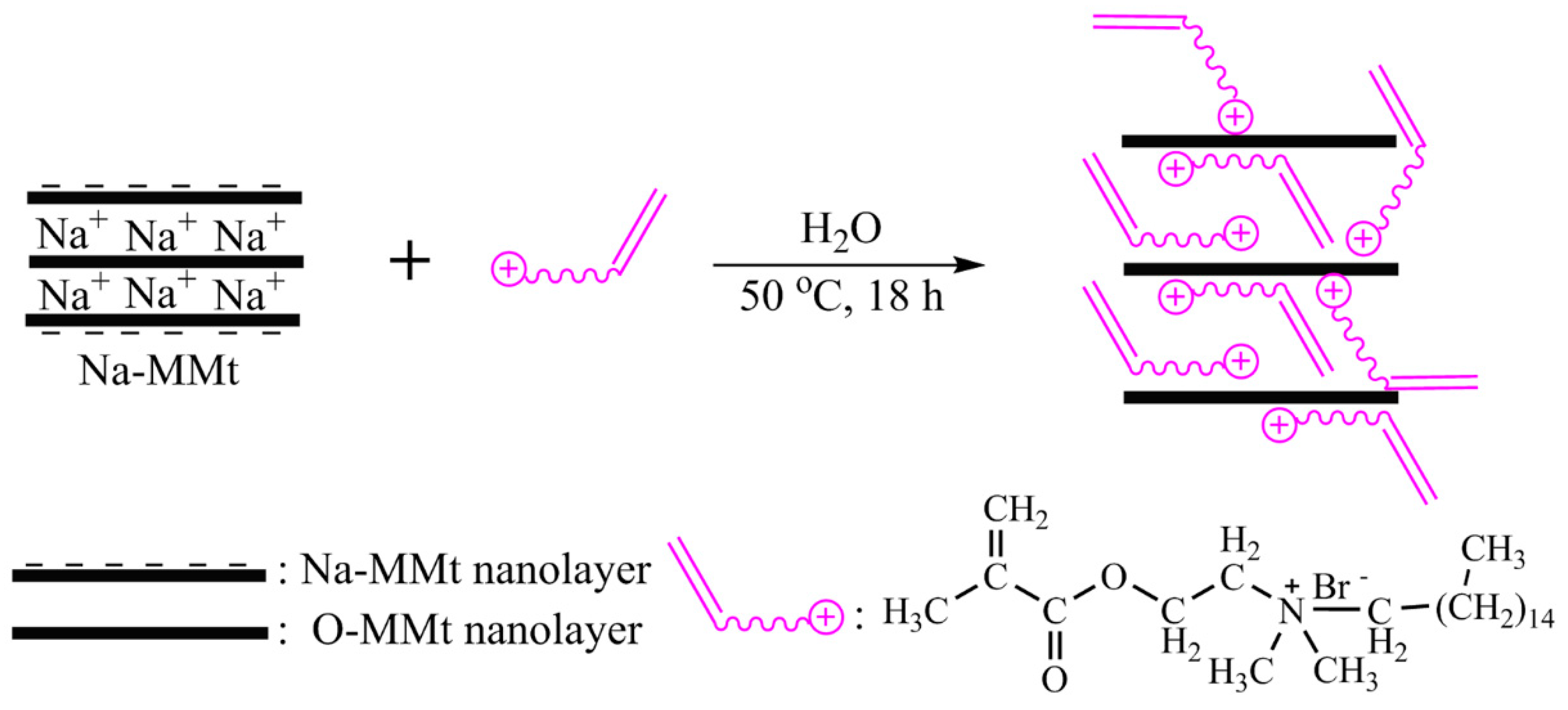
2.2.2. Preparation of the O-MMt Intermediate
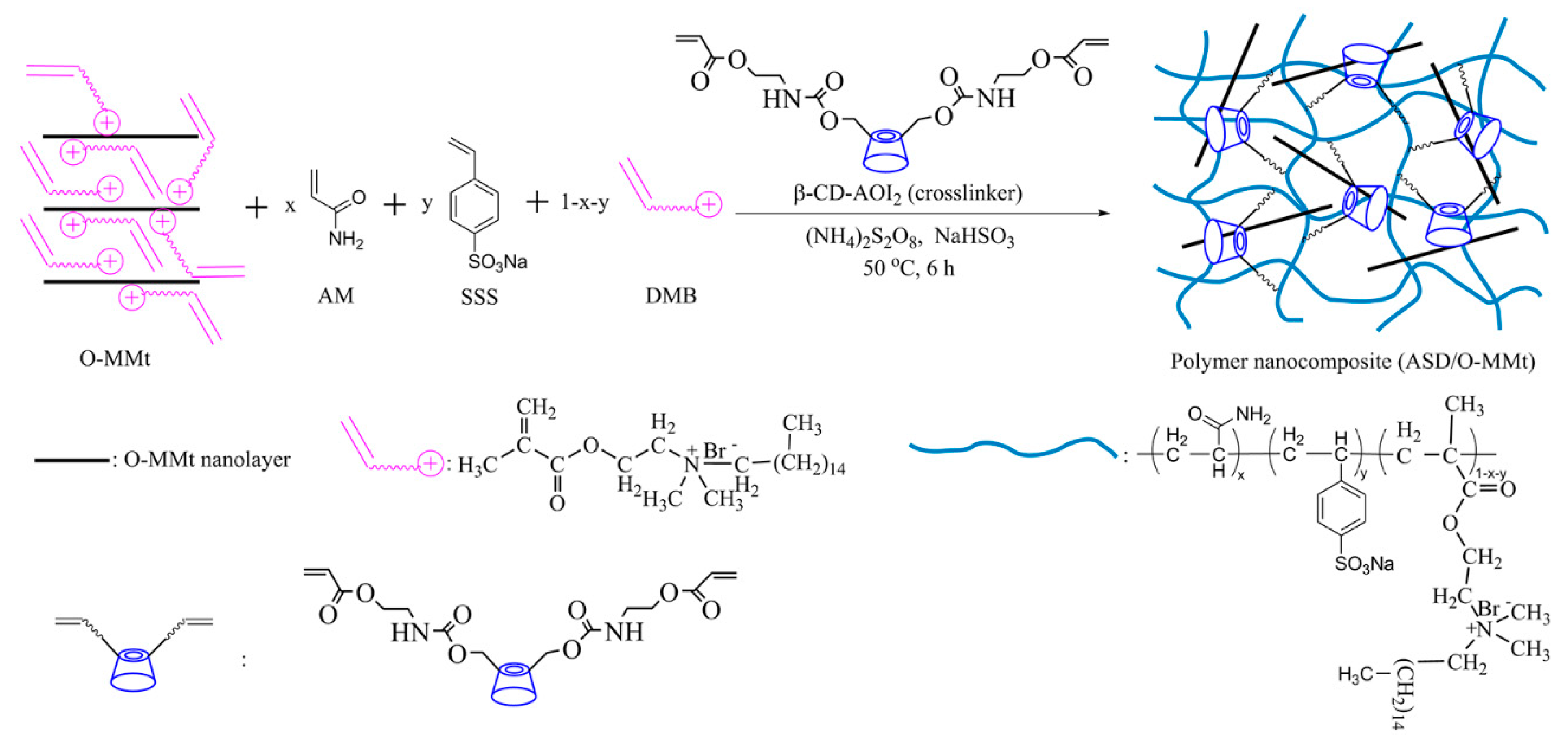
2.2.3. Preparation of the ASD/O-MMt Nanocomposite
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Characterization
2.3.2. Intrinsic Nanocomposite Viscosity
2.3.3. Viscosity
2.3.4. EOR Tests
- (1)
- The core was saturated with synthetic brine (5217 mg/L), after which crude oil was injected into the core until water ceased to flow out from the outlet.
- (2)
- Water flooding was conducted at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min until the water cut reached 98%.
- (3)
- A polymer slug having an injection volume (PV) of 0.3 was injected into the core, and water flooding was continued until the water cut reached 98%.
3. Results and Discussion
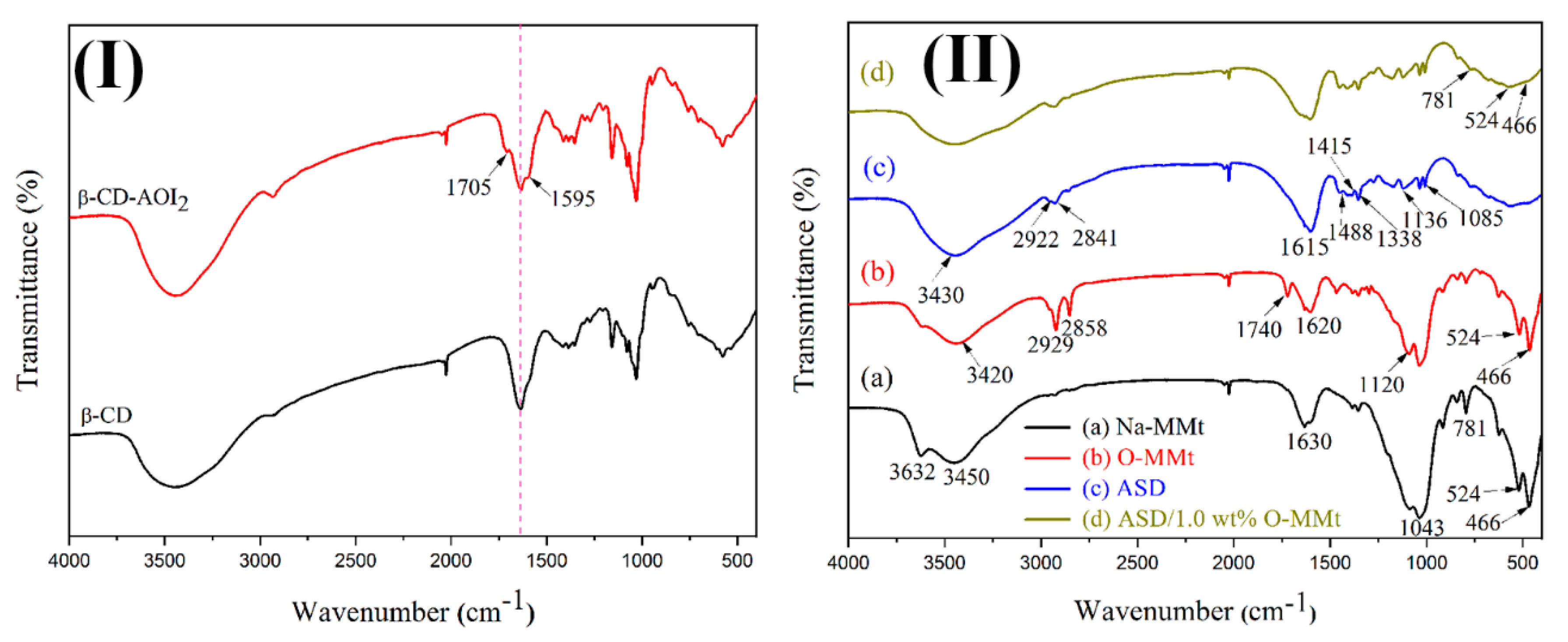
3.1. FTIR Spectroscopy
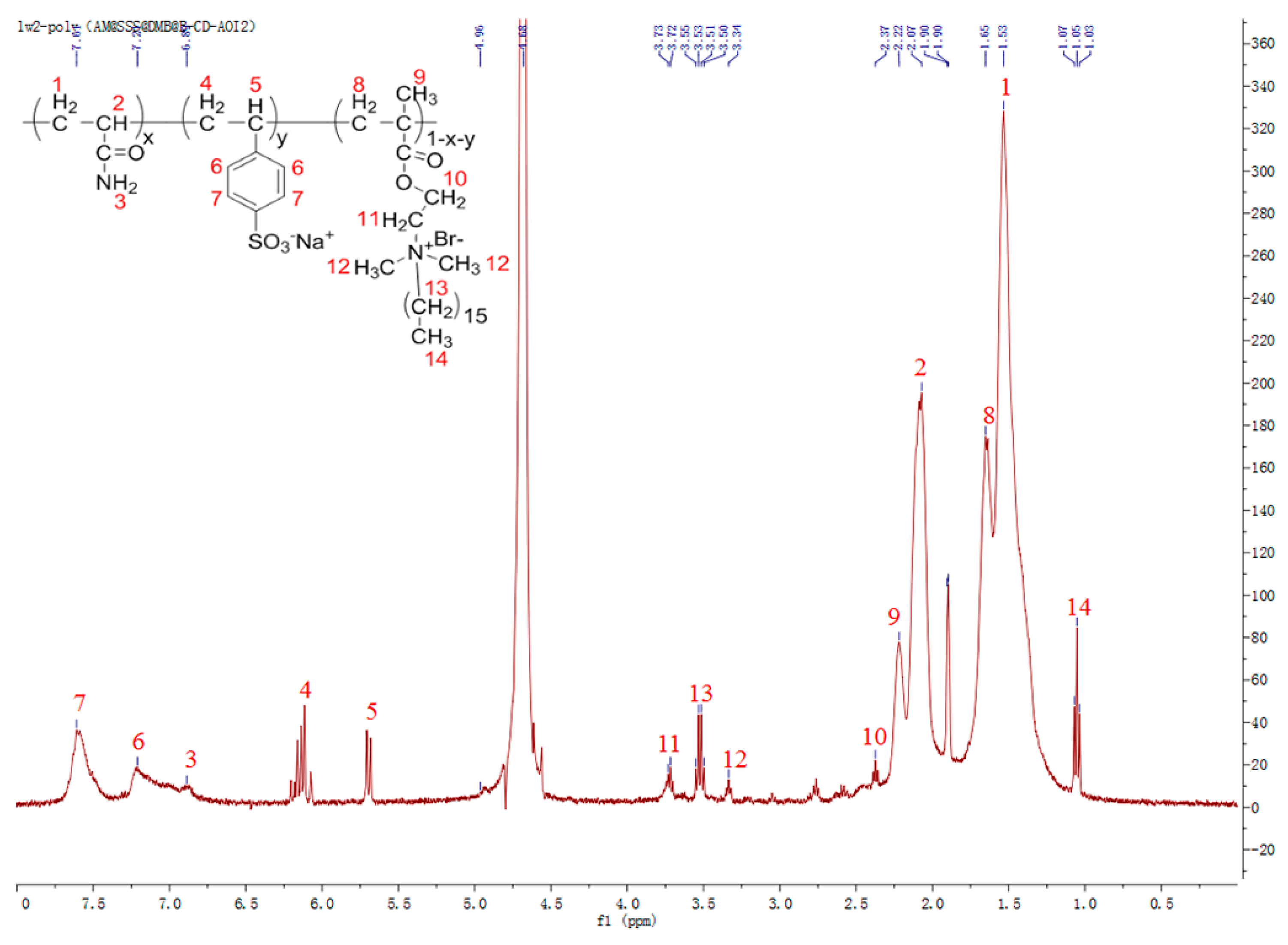
3.2. 1H-NMR Spectroscopy
3.3. XRD
3.4. SEM
3.5. TEM
3.6. TGA
3.7. Intrinsic Viscosity and Viscosity-Average Molecular Weight
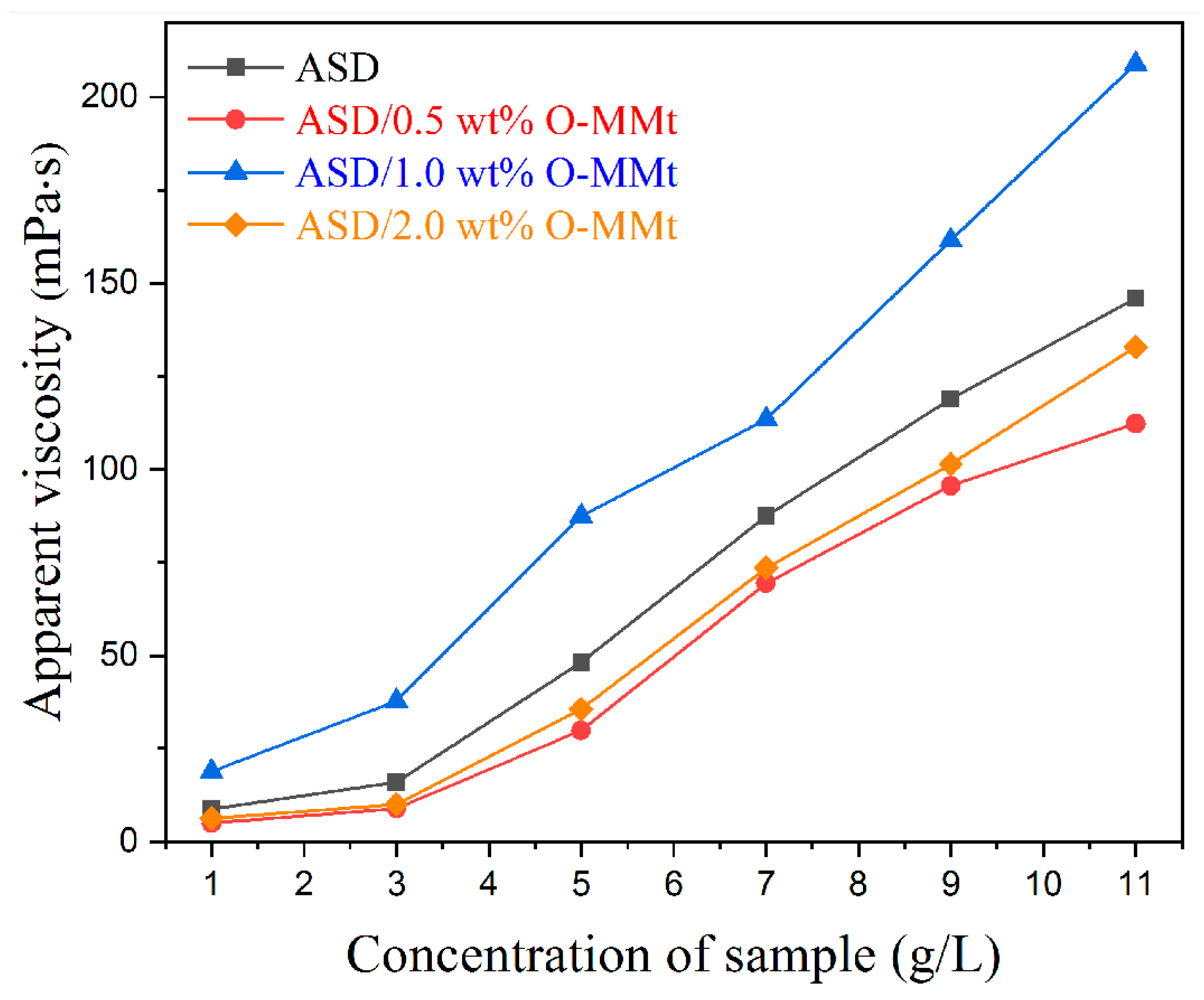
3.8. Viscosity
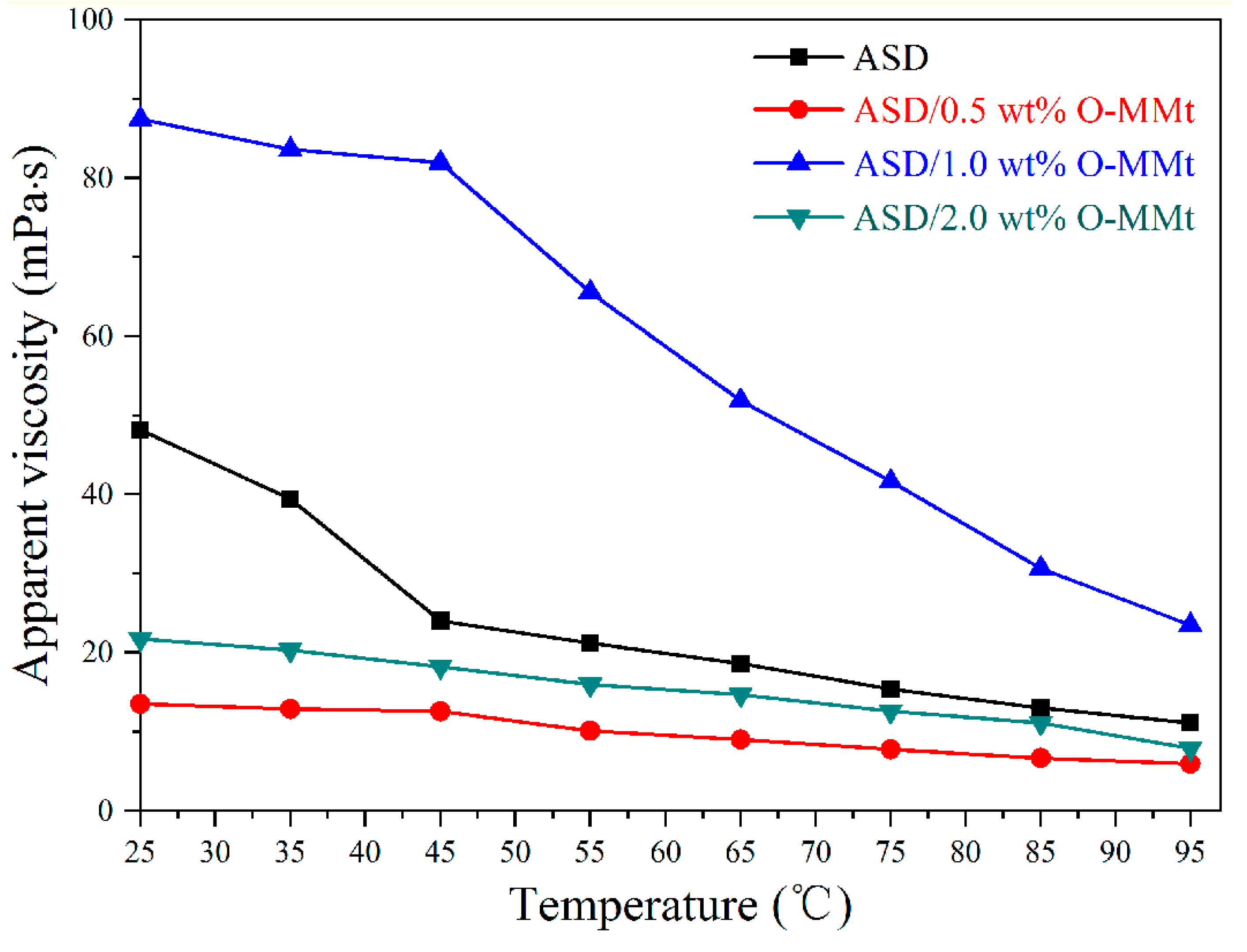
3.9. Temperature Resistance
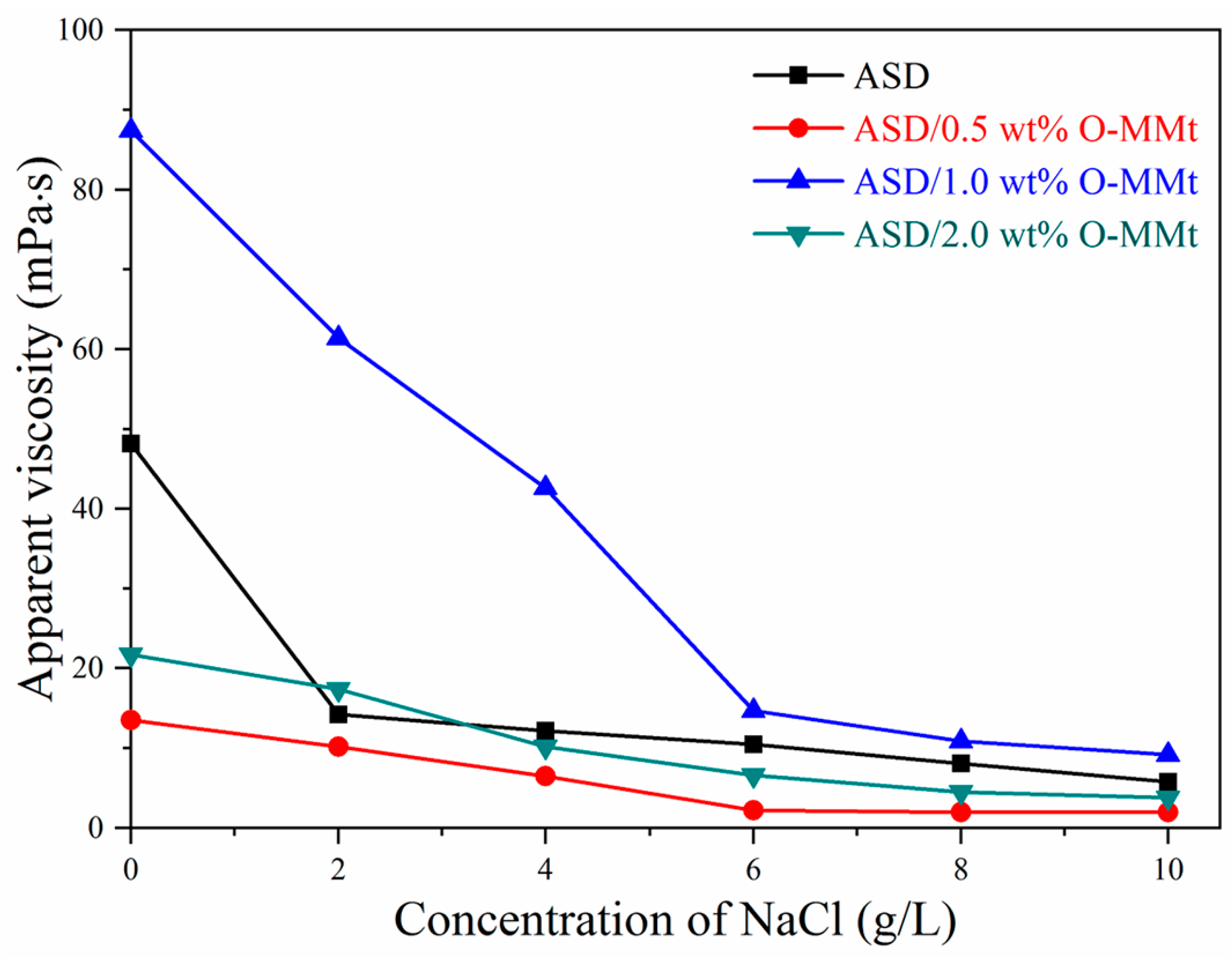
3.10. Salt Resistance
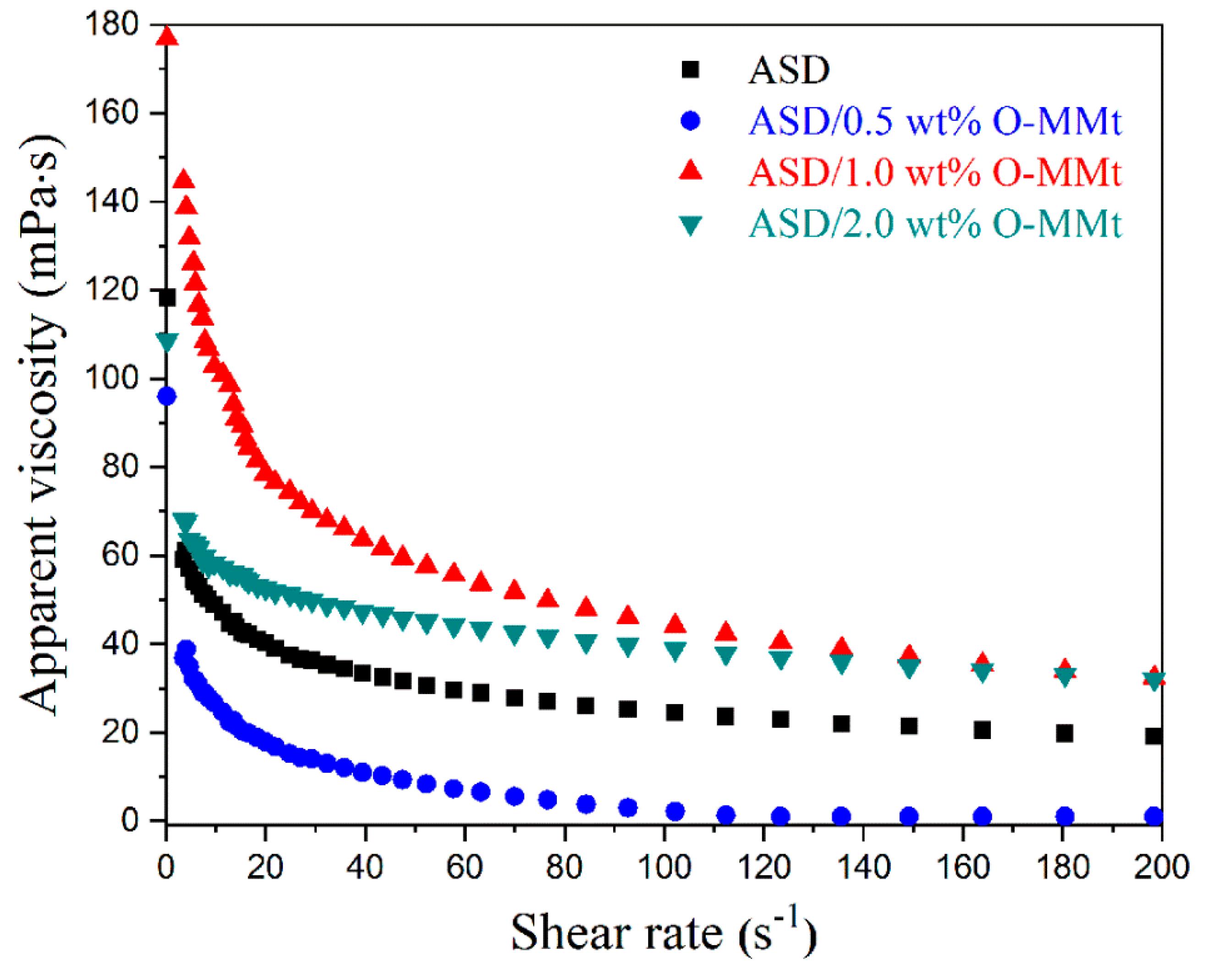
3.11. Shear Resistance
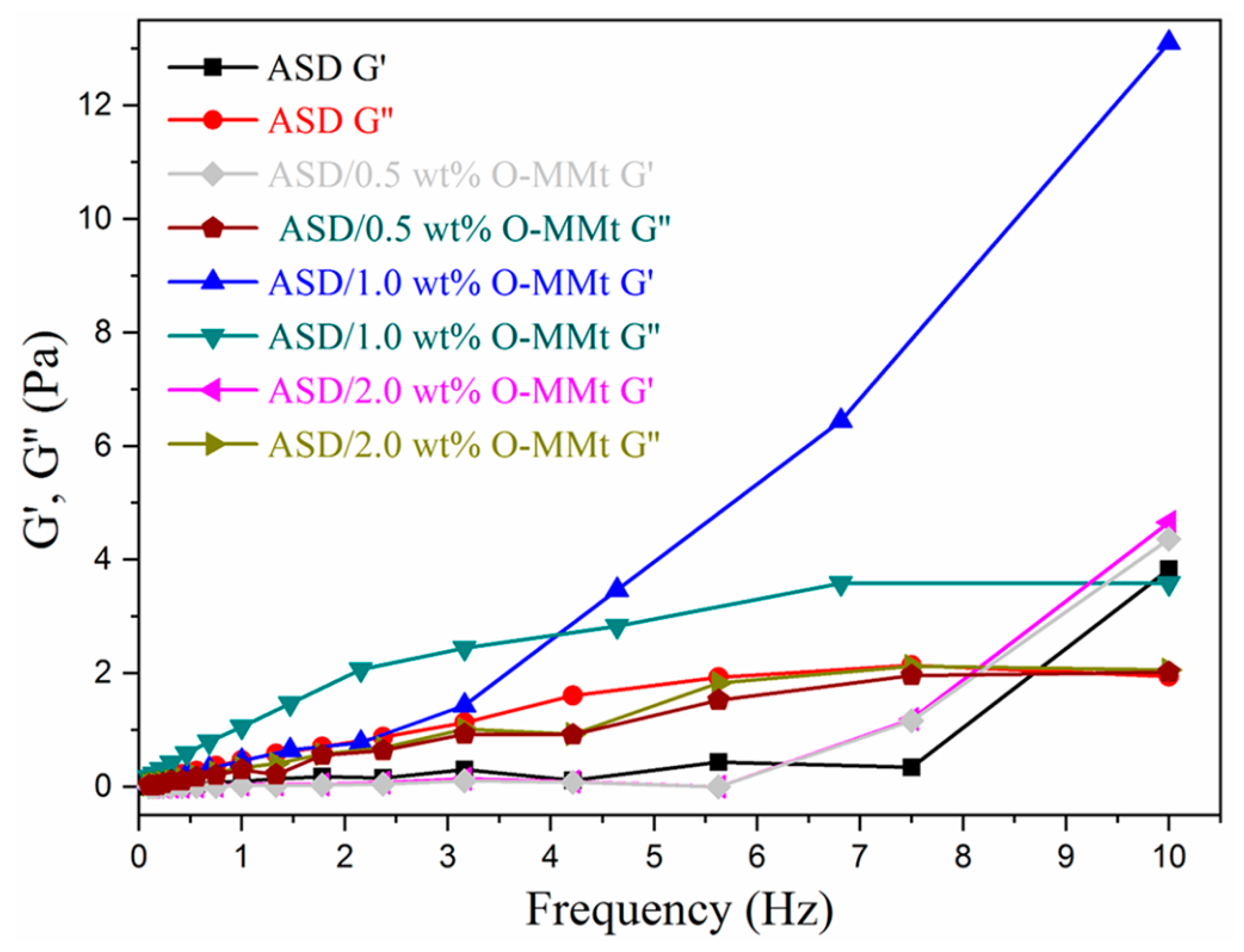
3.12. Viscoelasticity
3.13. EOR Experiments under Laboratory Conditions
3.14. Proposed Adsorption Mechanism of the Exfoliated O-MMt Nanolayers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olajire, A.A. Review of ASP EOR (alkaline surfactant polymer enhanced oil recovery) technology in the petroleum industry: Prospects and challenges. Energy 2014, 77, 963–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboorian-Jooybari, H.; Dejam, M.; Chen, Z. Heavy oil polymer flooding from laboratory core floods to pilot tests and field applications: Half-century studies. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 142, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, K.R.; Sharma, T. Rheological analysis and EOR potential of surfactant treated single-step silica nanofluid at high temperature and salinity. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, A.Z.; Puspasari, T.; Nugroho, W.A. Polymers for Enhanced Oil Recovery Technology. Procedia. Chem. 2012, 4, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Ka, D.; Chung, T.; Jung, J.; Koo, G.; Uhm, T.; Jung, S.H.; Park, S.; Jung, H.T. Evaluation of highly stable ultrahigh-molecular-weight partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide for enhanced oil recovery. Macromol. Res. 2015, 23, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S. Preparation and Characterization of Nanoclay-Based (Na-MMT and Bentonite) Polyacrylamide Hydrogels as Water Shut-Off Agent for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Silicon 2018, 11, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Vishnudas, R. A systematic numerical modeling study of various polymer injection conditions on immiscible and miscible viscous fingering and oil recovery in a five-spot setup. Fuel 2018, 232, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gawad, A.M.; Ramadan, A.R.; Flores, A.; Esawi, A.M.K. Fabrication of Nylon 6-Montmorillonite Clay Nanocomposites with Enhanced Structural and Mechanical Properties by Solution Compounding. Polymers 2022, 14, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Abdi-Khangah, M.; Mohebbi, A.; Tatar, A.; Mohammadi, A.H. Using surface modified clay nanoparticles to improve rheological behavior of Hydrolized Polyacrylamid (HPAM) solution for enhanced oil recovery with polymer flooding. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lv, L.; Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Shao, Q.; Wu, T.; Guo, S.; Sun, K.; Guo, X.; Wujcik, E.K.; et al. Porous lignin based poly (acrylic acid)/organo-montmorillonite nanocomposites: Swelling behaviors and rapid removal of Pb (II) ions. Polymer 2017, 128, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhong, Z.; Lai, X.; Huang, Y. Capture effect of Pb, Zn, Cd and Cr by intercalation-exfoliation modified montmorillonite during coal combustion. Fuel 2021, 290, 119980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth Reddy, O.; Subha, M.C.S.; Jithendra, T.; Madhavi, C.; Chowdoji Rao, K. Curcumin encapsulated dual cross linked sodium alginate/montmorillonite polymeric composite beads for controlled drug delivery. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.K.; Kim, S.; Baljon, J.J.; Wu, B.M.; Aghaloo, T.; Lee, M. Microporous methacrylated glycol chitosan-montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Z.; Wang, J.; Senthil, T.; Wu, L. Mechanical and thermal properties of ABS/montmorillonite nanocomposites for fused deposition modeling 3D printing. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, F.; Batool, R.; Gill, R.; Rehman, Z.U.; Majeed, H.; Ahmad, A.; Shafiq, M.; Dastan, D.; Abbas, G.; Jacob, K. Synthesis and electrochemical investigations of ABPBI grafted montmorillonite based polymer electrolyte membranes for PEMFC applications. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 709–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hu, X.; Lu, S.; Ke, Y.; Luo, J. Preparation of Triple-Functionalized Montmorillonite Layers Promoting Thermal Stability of Polystyrene. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, C.; Ju, F.; Ke, Y. Copolymer nanocomposites with strong adsorption of exfoliated silicate nanosheets and high-temperature stability. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 21672–21683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Yan, K.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, C. Effects of Salinity on Formation Behavior of Methane Hydrate in Montmorillonite. Energies 2020, 13, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; An, J.; Fu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wei, M.; Bai, J.; He, Y. Adsorption of Welan Gum on Montmorillonite and Its Influencing Factors. Polymers 2022, 14, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lv, L.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, H. The Effect of OMMT on the Properties of Vehicle Damping Carbon Black-Natural Rubber Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majka, T.M.; Leszczyńska, A.; Kandola, B.K.; Pornwannachai, W.; Pielichowski, K. Modification of organo-montmorillonite with disodium H-phosphonate to develop flame retarded polyamide 6 nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 139, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrasi, G.; Tortora, M.; Vittoria, V.; Pollet, E.; Lepoittevin, B.; Alexandre, M.; Dubois, P. Vapor barrier properties of polycaprolactone montmorillonite nanocomposites: Effect of clay dispersion. Polymer 2003, 44, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.T.; Zhou, C.H.; Kabwe, F.B.; Wu, Q.Q.; Li, C.S.; Zhang, J.R. Exfoliation of montmorillonite and related properties of clay/polymer nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 169, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, I.J.; Thurn-Albrecht, T.; Kim, H.C.; Russell, T.P.; Wang, J. On exfoliation of montmorillonite in epoxy. Polymer 2001, 42, 5947–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.C.; He, Y.; Qu, J.P. Structure and properties of Polylactide/Poly(butylene succinate)/Organically Modified Montmorillonite nanocomposites with high-efficiency intercalation and exfoliation effect manufactured via volume pulsating elongation flow. Polymer 2019, 180, 121656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hina, M.; Bashir, S.; Kamran, K.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K. Synthesis and characterization of self-healable poly (acrylamide) hydrogel electrolytes and their application in fabrication of aqueous supercapacitors. Polymer 2020, 210, 123020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahanchi, A.; Malloy, R.A.; Sobkowicz, M.J. Extreme shear processing for exfoliating organoclay in nanocomposites with incompatible polymers. Polymer 2018, 145, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Huang, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wei, X.; Huang, W.; Dai, J.; Song, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, D. Synergistic effects of Janus graphene oxide and surfactants on the heavy oil/water interfacial tension and their application to enhance heavy oil recovery. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikiru, S.; Rostami, A.; Soleimani, H.; Yahya, N.; Afeez, Y.; Aliu, O.; Yusuf, J.Y.; Oladosu, T.L. Graphene: Outlook in the enhance oil recovery (EOR). J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha Devi, K.S.; Ponnamma, D.; Causin, V.; Maria, H.J.; Thomas, S. Enhanced morphology and mechanical characteristics of clay/styrene butadiene rubber nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejder Korucu, M.; Gürses, A.; Karaca, S. Poly(ethylene oxide)/clay nanaocomposites: Thermal and mechanical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 378, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Mubarak, C.; Keiegel, R.; Kannan, R.M. Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) dispersion of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/clay nanocomposites: Structural, mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Ke, Y.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, G. Effects of highly exfoliated montmorillonite layers on the properties of clay reinforced terpolymer nanocomposite plugging microspheres. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, D.; Wei, J. Experimental investigation on remaining oil distribution and recovery performances after different flooding methods. Fuel 2022, 322, 124219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadamosi, A.; Patil, S.; Kamal, M.S.; Adewunmi, A.A.; Yusuff, A.S.; Agi, A.; Oseh, J. Application of Polymers for Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaie, F.; Esmaeilnezhad, E.; Choi, H.-J. Effect of Rheological Properties of Polymer Solution on Polymer Flooding Characteristics. Polymers 2022, 14, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riahinezhad, M.; Romero-Zerón, L.; McManus, N.; Penlidis, A. Evaluating the performance of tailor-made water-soluble copolymers for enhanced oil recovery polymer flooding applications. Fuel 2017, 203, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wei, L.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y. Aqueous Hybrids of Silica Nanoparticles and Hydrophobically Associating Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide Used for EOR in High-Temperature and High-Salinity Reservoirs. Energies 2014, 7, 3858–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, M. Synthesis and solution properties of an associative polymer with excellent salt-thickening. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 4049–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Allauddin, S.; Narayan, R.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Raju, K.V.S.N. Characterization of surface-modified montmorillonite nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Sun, S.; Xiao, M.; Liu, T.; Xu, Q.; Dong, H.; Wang, D.; Gong, Y.; Sha, T.; Hou, J.; et al. Microbial Mineralization of Montmorillonite in Low-Permeability Oil Reservoirs for Microbial Enhanced Oil Recovery. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00176-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Ren, J.H.; Yu, Z.Z.; Mai, Y.W. A new approach to polymer/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polymer 2003, 44, 4619–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.H.; Xing, J.Y.; Pu, W.F.; Dong, Z.M.; Yuan, C.D.; Peng, G.F.; Jin, F.Y.; Xia, J.J. Synthesis and property evaluation of a novel polyacrylamide-montmorillonite composite for water shutoff and profile control in high salinity reservoirs. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gou, S.; Zhou, L.; Fei, Y.; Peng, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, L. Modified polyacrylamide containing phenylsulfonamide and betaine sulfonate with excellent viscoelasticity for EOR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Ke, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Deng, Q. Anion amphiphilic random copolymers and their performance as stabilizers for O/W nanoemulsions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14692–14700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Q.; Lin, L.; Zhao, Y. Hyperbranched polyethylenimine modified with silane coupling agent as shale inhibitor for water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 182, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Shen, X.; Li, G. Application of Tea Polyphenols as a Biodegradable Fluid Loss Additive and Study of the Filtration Mechanism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3453–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.-C.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, M.; Bi, T.-F.; Song, S.-X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Synthesis and performance of AM/SSS/THDAB as clay hydration dispersion inhibitor. Polímeros 2019, 29, e2019053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, N.S.; Olayiwola, T.; Elkatatny, S.; Haq, B.; Patil, S. Insights into the application of surfactants and nanomaterials as shale inhibitors for water-based drilling fluid: A review. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 92, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, W.; Gou, S.; Ye, Z.; Luo, C. Synthesis and clay stabilization of a water-soluble copolymer based on acrylamide, modular β-cyclodextrin, and AMPS. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 3398–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ke, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, C.; Lu, S.; Peng, F. Preparation and properties of nanocomposites of β-cyclodextrin-functionalized polyacrylamide and its application for enhancing oil recovery. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 30491–30501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Zhao, P.; Ge, J.; Lei, Y.; Luo, P. β-Cyclodextrin modified anionic and cationic acrylamide polymers for enhancing oil recovery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; An, G.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Mao, C. 3D-printable self-healing and mechanically reinforced hydrogels with host-guest non-covalent interactions integrated into covalently linked networks. Mater Horiz 2019, 6, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y. Polymer Nanocomposites, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.; Zhao, P.; Hu, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, R.; Luo, P. β-Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Hydrophobically Associating Acrylamide Copolymer for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2827–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ke, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, S.; Deng, Q.; Yu, C.; Peng, F. Synthesis, characterization and solution properties of β-cyclodextrin-functionalized polyacrylamide/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Ke, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X. The influence of organically intercalated montmorillonites on the interfacial tension and structure of oil-in-water nanoemulsions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 13378–13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, H.; Tasdelen, M.A.; Prez, F.D.; Yagci, Y. Synthesis and characterization of polymer/clay nanocomposites by intercalated chain transfer agent. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, E.; Avgoustakis, K.; Pšenička, M.; Pospíšil, M.; Papoulis, D. Halloysite nanotubes as carriers for irinotecan: Synthesis and characterization by experimental and molecular simulation methods. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Boutahala, M. Adsorption of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol by organo-montmorillonites from aqueous solutions: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Core | Length (cm) | Diameter (cm) | Porosity (%) | Permeability (mD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 7.76 | 2.53 | 22.13 | 1039 |
| Composition | NaCl | KCl | CaCl2 | MgCl2·5H2O | NaSO4 | NaHCO3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (mg/L) | 2728 | 15 | 55 | 135 | 70 | 2214 | 5217 |
| Sample | O-MMt Load (wt%) | [η] (mL/g) | Mη × 105 (g/mol) | Standard Deviations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASD | 0 | 189.60 | 5.64 | 1.39 |
| ASD/0.5 wt% O-MMt | 0.5 | 109.21 | 2.83 | 1.63 |
| ASD/1.0 wt% O-MMt | 1 | 295.06 | 9.81 | 1.27 |
| ASD/2.0 wt% O-MMt | 2 | 146.32 | 4.08 | 1.98 |
| Sample | Concentration (mg/L) | EW (%) | ET (%) | EOR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASD/1.0 wt% O-MMt | 1000 | 41.9 | 52.4 | 10.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Chen, C.; Hu, X.; Ju, F.; Ke, Y. Enhancing the Properties of Water-Soluble Copolymer Nanocomposites by Controlling the Layer Silicate Load and Exfoliated Nanolayers Adsorbed on Polymer Chains. Polymers 2023, 15, 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061413
Wang D, Chen C, Hu X, Ju F, Ke Y. Enhancing the Properties of Water-Soluble Copolymer Nanocomposites by Controlling the Layer Silicate Load and Exfoliated Nanolayers Adsorbed on Polymer Chains. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061413
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dongyin, Changfeng Chen, Xiaojuan Hu, Fei Ju, and Yangchuan Ke. 2023. "Enhancing the Properties of Water-Soluble Copolymer Nanocomposites by Controlling the Layer Silicate Load and Exfoliated Nanolayers Adsorbed on Polymer Chains" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061413
APA StyleWang, D., Chen, C., Hu, X., Ju, F., & Ke, Y. (2023). Enhancing the Properties of Water-Soluble Copolymer Nanocomposites by Controlling the Layer Silicate Load and Exfoliated Nanolayers Adsorbed on Polymer Chains. Polymers, 15(6), 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061413





