A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Our Approach
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.M.; Lv, S.; Zhang, W.; Cui, Y. Microfluidic Point-of-Care (POC) Devices in Early Diagnosis: A Review of Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors 2022, 22, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Du, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.M. Efficient Drug Screening and Nephrotoxicity Assessment on Co-culture Microfluidic Kidney Chip. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. A More Biomimetic Cell Migration Assay with High Reliability and Its Applications. Pharm 2022, 15, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Cui, Y. Dielectrophoresis assisted high-throughput detection system for multiplexed immunoassays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Xing, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W. 3D Bioprinting of the Sustained Drug Release Wound Dressing with Double-Crosslinked Hyaluronic-Acid-Based Hydrogels. Polymers 2019, 11, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Xi, Z.; Tang, T.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W. Electrospun PLGA membrane incorporated with andrographolide-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for sustained antibacterial wound dressing. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2881–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Achenbach, S.; Subramanian, V.; Jacobs, M.; Klymyshyn, D.; Iyer, S.; Moazed, B.; Hanson, J.; Shen, C.; Haluzan, D. SyLMAND: A microfabrication beamline with wide spectral and beam power tuning range at the Canadian Light Source. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2019, 26, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Tony, A.; Yin, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W. Tactile and Thermal Sensors Built from Carbon-Polymer Nanocomposites-A Critical Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Xiao, G.; Watts, B.R.; Xu, C. Sealing SU-8 microfluidic channels using PDMS. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 046503–465038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, S.W.; Yang, S.S. The optimization of PDMS-PMMA bonding process using silane primer. Biochip J. 2010, 4, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Wohl, G.R. Plasma enhanced bonding of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) with parylene. In Proceedings of the 2011 16th International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, TRANSDUCERS’11, Beijing, China, 5–9 June 2011; pp. 1340–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Cho, J. Parylene-PDMS Bilayer Coatings for Microelectronic and MEMS Packaging. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2007, 968, 0968-v07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Datta, A.; Berg, J.M.; Gangopadhyay, S. Studies on surface wettability of poly(dimethyl) siloxane (PDMS) and glass under oxygen-plasma treatment and correlation with bond strength. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2005, 14, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borók, A.; Laboda, K.; Bonyár, A. PDMS Bonding Technologies for Microfluidic Applications: A Review. Biosens 2021, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.-W. Chia-Wen Polymer Microfluidics: Simple, Low-Cost Fabrication Process Bridging Academic Lab Research to Commercialized Production. Micromachines 2016, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, A.; Khan, S.; Didar, T.F. Conventional and emerging strategies for the fabrication and functionalization of PDMS-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3053–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B.; Hanson, R.L.; Almughamsi, H.M.; Pang, C.; Fish, T.R.; Woolley, A.T. Microfluidics: Innovations in Materials and Their Fabrication and Functionalization. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.T.; Woolley, A.T. Thermal bonding of polymeric capillary electrophoresis microdevices in water. Anal. Chem. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Kwok, Y.C.; Nguyen, N.T. Low-pressure, high-temperature thermal bonding of polymeric microfluidic devices and their applications for electrophoretic separation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abgrall, P.; Low, L.-N.; Nguyen, N.-T. Fabrication of planar nanofluidic channels in a thermoplastic by hot-embossing and thermal bonding. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lin, J.; Su, R.; Xie, Y. Vacuum-assisted thermal bonding of plastic capillary electrophoresis microchip imprinted with stainless steel template. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1038, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadpour, H.; Soper, S.A. Two-dimensional electrophoretic separation of proteins using poly(methyl methacrylate) microchips. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3519–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, T.H. Disposable integrated microfluidic biochip for blood typing by plastic microinjection moulding. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, D.C.; McDonald, J.C.; Schueller, O.J.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogończyk, D.; Wgrzyn, J.; Jankowski, P.; Dąbrowski, B.; Garstecki, P. Bonding of microfluidic devices fabricated in polycarbonate. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klank, H.; Kutter, J.P.; Geschke, O. CO2-laser micromachining and back-end processing for rapid production of PMMA-based microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2002, 2, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.J.; Geist, J.; Locascio, L.E.; Gaitan, M.; Rao, M.V.; Vreeland, W.N. Surface modification of poly(methyl methacrylate) for improved adsorption of wall coating polymers for microchip electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 3788–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesdjojo, M.T.; Tennico, Y.H.; Remcho, V.T. Fabrication of a Microfluidic System for Capillary Electrophoresis Using a Two-Stage Embossing Technique and Solvent Welding on Poly(methyl methacrylate) with Water as a Sacrificial Layer. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2311–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Koerner, T.; Horton, J.H.; Oleschuk, R.D. Fabrication and characterization of poly(methylmethacrylate) microfluidic devices bonded using surface modifications and solvents. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, D.A.; Rolandi, M.; Snauko, M.; Noroski, R.; Svec, F.; Fréchet, J.M.J. Room-Temperature Bonding for Plastic High-Pressure Microfluidic Chips. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5097–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.J.; Agirregabiria, M.; Garcia, J.; Berganzo, J.; Tijero, M.; Arroyo, M.T.; Ruano, J.M.; Aramburu, I.; Mayora, K. Novel three-dimensional embedded SU-8 microchannels fabricated using a low temperature full wafer adhesive bonding. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.J.; Teixeira, A. Enhancement of the surface free energy of PDMS for reversible and leakage-free bonding of PDMS–PS microfluidic cell-culture systems. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2018, 22, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Pallandre, A.; Miserere, S.; Weber, J.; Viovy, J.-L. Lamination-based rapid prototyping of microfluidic devices using flexible thermoplastic substrates. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; McClelland, A.A.; Chen, Z.; Lahann, J. Solventless Adhesive Bonding Using Reactive Polymer Coatings. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douville, N.J.; Tung, Y.-C.; Li, R.; Wang, J.D.; El-Sayed, M.E.H.; Takayama, S. Fabrication of Two-Layered Channel System with Embedded Electrodes to Measure Resistance Across Epithelial and Endothelial Barriers. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Hromada, L.; Liu, J.; Kumar, P.; DeVoe, D.L. Low temperature bonding of PMMA and COC microfluidic substrates using UV/ozone surface treatment. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubert, K.; Drier, T.; Beebe, D. PDMS bonding by means of a portable, low-cost corona system. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1548–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillborg, H.; Sandelin, M.; Gedde, U.W. Hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane after exposure to partial discharges as a function of crosslink density. Polymer 2001, 42, 7349–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chaudhury, M.K. Corona-discharge-induced hydrophobicity loss and recovery of silicones. In Proceedings of the 1999 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (Cat. No.99CH36319), Austin, TX, USA, 17–20 October 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Xiao, K.; Wen, W. A simple method for fabricating multi-layer PDMS structures for 3D microfluidic chips. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-A.; Batista, C.; Sarpeshkar, R.; Han, J. Rapid fabrication of microfluidic polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell in PDMS by surface patterning of perfluorinated ion-exchange resin. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, H.I. Hydrophilic Surface Modification of PDMS Using Atmospheric RF Plasma. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 34, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ellis, A.V.; Voelcker, N.H. Recent developments in PDMS surface modification for microfluidic devices. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Khodakov, D.A.; Ellis, A.V.; Voelcker, N.H. Surface modification for PDMS-based microfluidic devices. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechene, J. Surface Modifications of Poly(dimethylsiloxane) for Biological Application of Microfluidic Devices. Electron. Ph.D. Thesis Diss. Repos, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2010; pp. 1–194. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, K.S.; Chin, J.; Chia, J.; Chiang, C.L. Quantitative Studies on PDMS-PDMS Interface Bonding with Piranha Solution and its Swelling Effect. Micromachines 2012, 3, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroma, L.S.; Piazzetta, M.H.O.; Duarte-Junior, G.F.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Carrilho, E.; Gobbi, A.L.; Lima, R.S. Self-regenerating and hybrid irreversible/reversible PDMS microfluidic devices. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.; Gruner, D.; Richter, A.; Loskill, P. Membrane integration into PDMS-free microfluidic platforms for organ-on-chip and analytical chemistry applications. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 1866–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent Compatibility of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Based Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Duong, L.H. Novel solvent bonding method for thermoplastic microfluidic chips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumens, C.V.; Ziai, M.A.; Belsey, K.E.; Batchelor, J.C.; Holder, S.J. Swelling of PDMS networks in solvent vapours; applications for passive RFID wireless sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10091–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangla, R.; Gallaire, F.; Baroud, C.N. Microchannel deformations due to solvent-induced PDMS swelling. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes Atayde, C.; Doi, I. Highly stable hydrophilic surfaces of PDMS thin layer obtained by UV radiation and oxygen plasma treatments. Phys. Status Solidi 2010, 7, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckert, E.P.; Miller, C.J.; Fisher, E.R. The Effect of Ar/O2 and H2O Plasma Treatment of SnO2 Nanoparticles and Nanowires on Carbon Monoxide and Benzene Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15733–15743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Snoeckx, R.; Zhang, X.; Cha, M.S.; Bogaerts, A. Modeling Plasma-based CO2 and CH4 Conversion in Mixtures with N2, O2, and H2O: The Bigger Plasma Chemistry Picture. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8704–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Reis, R.; Chen, Z.; Milne, N.; Winther-Jensen, B.; Kong, L.; Dumée, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Plasma Modification and Synthesis of Membrane Materials—A Mechanistic Review. Membranes 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, S. Polydimethylsioxane Fluidic Interconnects for Microfluidic Systems. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2003, 26, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yuan, Y.J. Investigation on the mechanism of nitrogen plasma modified PDMS bonding with SU-8. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddings, M.A.; Johnson, M.A.; Gale, B.K. Determining the optimal PDMS-PDMS bonding technique for microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 067001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Wu, J.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.; Jin, M.; Shui, L. Large-Area and High-Throughput PDMS Microfluidic Chip Fabrication Assisted by Vacuum Airbag Laminator. Micromachines 2017, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Wohl, G.R. Plasma enhanced bonding of polydimethylsiloxane with parylene and its optimization. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 065024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrito, N.; McLachlan, J.M.; Faria, S.N.; Chan, J.; Norton, P.R. A novel metal-protected plasma treatment for the robust bonding of polydimethylsiloxane. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Chen, P.; Zhou, Q. Adhesion promotion between PDMS and glass by oxygen plasma pre-treatment. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.C.; Liao, E.; Ong, W.L.; Wong, J.D.S.; Agarwal, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Yobas, L. Evaluation of bonding between oxygen plasma treated polydimethyl siloxane and passivated silicon. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 34, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.J.; Akin, D.; Sedlak, M.; Ladisch, M.R.; Bashir, R. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) and silicon hybrid biochip for bacterial culture. Biomed. Microdevices 2003, 5, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Peng, S.; Liu, L.; Wen, W.; Sheng, P. Characterizing and patterning of PDMS-based conducting composites. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-W.; DeVoe, D.L. Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2009, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lee, N.Y. A facile route for irreversible bonding of plastic-PDMS hybrid microdevices at room temperature. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lee, N.Y. One-step surface modification for irreversible bonding of various plastics with a poly(dimethylsiloxane) elastomer at room temperature. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Liao, Y.C. Adhesive Stretchable Printed Conductive Thin Film Patterns on PDMS Surface with an Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11868–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Song, K.Y.; Yin, R.; Zhang, W. Effects of Hydrophilicity, Adhesion Work, and Fluid Flow on Biofilm Formation of PDMS in Microfluidic Systems. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 8386–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.; Kang, Y.; Park, W.; Jo, E.; Kim, J. Fabrication of fine-pored polydimethylsiloxane using an isopropyl alcohol and water mixture for adjustable mechanical, optical, and thermal properties. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18061–18067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plecis, A.; Chen, Y. Fabrication of microfluidic devices based on glass-PDMS-glass technology. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.-H.; Beebe, D.J. Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Microfluidic Systems by Stacking Molded Polydimethylsiloxane(PDMS) Layers. Spie 1999, 3877, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Chua, Y.C.; Kang, T.G. Oxygen plasma treatment for reducing hydrophobicity of a sealed polydimethylsiloxane microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 032204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberti, A.; Marasso, S.L.; Cocuzza, M. PDMS membranes with tunable gas permeability for microfluidic applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61415–61419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldorsson, S.; Lucumi, E.; Gómez-Sjöberg, R.; Fleming, R.M.T. Advantages and challenges of microfluidic cell culture in polydimethylsiloxane devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehling, M. Microfluidic cell culture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 25, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Uchil, A.; Kalsang, T.; Chakrabarty, S.; Ali, M.A.; Srisungsitthisunti, P.; Mahato, K.K.; Surdo, S.; Mazumder, N. The revolution of PDMS microfluidics in cellular biology. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z. Nanofabrication: Principles, Capabilities and Limits, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 9783319393612. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.Y.; Loke, W.K.; Nguyen, N.T. A reliable method for bonding polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and its application in micropumps. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 151, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meer, B.J.; de Vries, H.; Firth, K.S.A.; van Weerd, J.; Tertoolen, L.G.J.; Karperien, H.B.J.; Jonkheijm, P.; Denning, C.; IJzerman, A.P.; Mummery, C.L. Small molecule absorption by PDMS in the context of drug response bioassays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toepke, M.W.; Beebe, D.J. PDMS absorption of small molecules and consequences in microfluidic applications. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1484–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Schwartz, M.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C. PDMS Compound Adsorption in Context. J. Biomol. Screen. 2009, 14.2, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facility, M. Procedure for Silanization of Su-8/Silicon Master Microfabrication Core Facility, Harvard Medical School. 2015, 3–4. Available online: https://hms.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/Departments/Microfluidics and Microfabrication Facility/files/Silanization of Photoresist Master Protocol.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Galliano, A.; Bistac, S.; Schultz, J. Adhesion and friction of PDMS networks: Molecular weight effects. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 265, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Dai, Z.; Lin, B. Multilayer poly(vinyl alcohol)-adsorbed coating on poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic chips for biopolymer separation. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.Y.; Zurawsky, W.; Ulman, A. Molecular Weight Effects in Adhesion. Langmuir 1999, 15, 8447–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, A.; Rasouli, A.; Farahinia, A.; Wells, G.; Zhang, H.; Achenbach, S.; Yang, S.M.; Sun, W.; Zhang, W. Toward a Soft Microfluidic System: Concept and Preliminary Developments. In Proceedings of the IEEE 27th International Conference on Mechatronics Machine Vision Practice (M2VIP 2021), Shanghai, China, 26–28 November 2021; pp. 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour-Tamrin, S.; Sanati-Nezhad, A.; Sen, A. A simple and low-cost approach for irreversible bonding of polymethylmethacrylate and polydimethylsiloxane at room temperature for high-pressure hybrid microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, P.; Selvaganapathy, P.; Wohl, G.; Byun, I. Irreversible bonding of polyimide and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) based on a thiol-epoxy click reaction. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Greco, G.; Cecchini, M. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) irreversible bonding to untreated plastics and metals for microfluidics applications. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 081108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
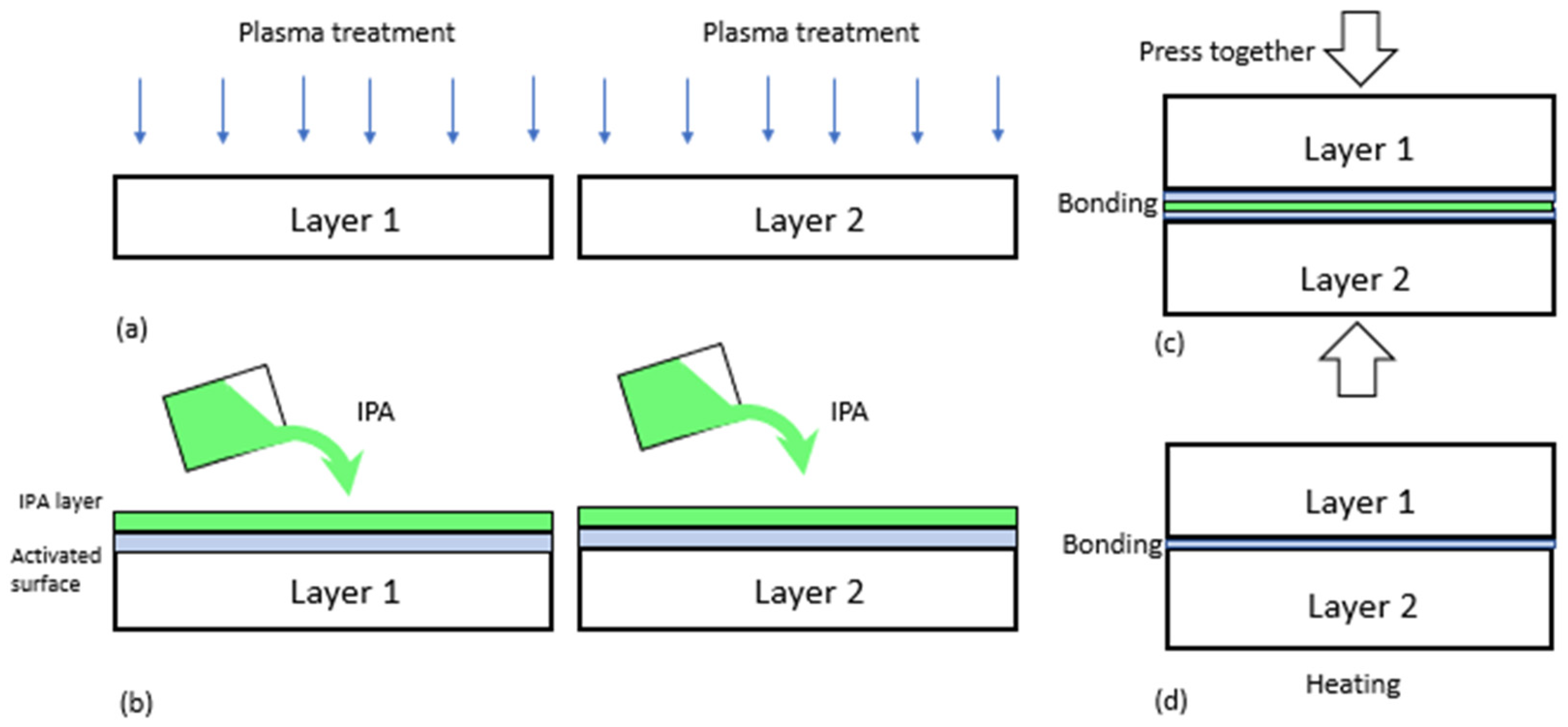
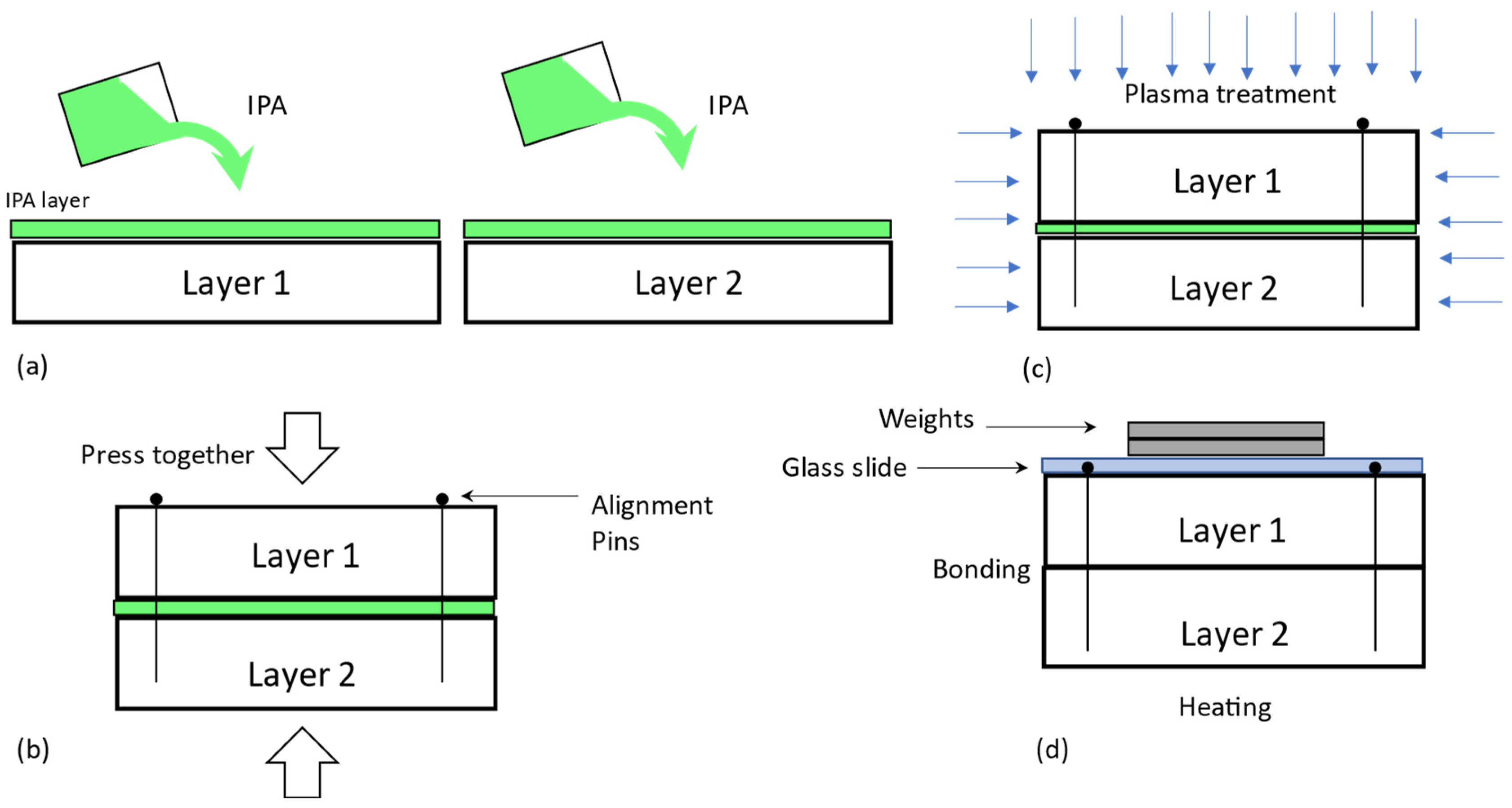

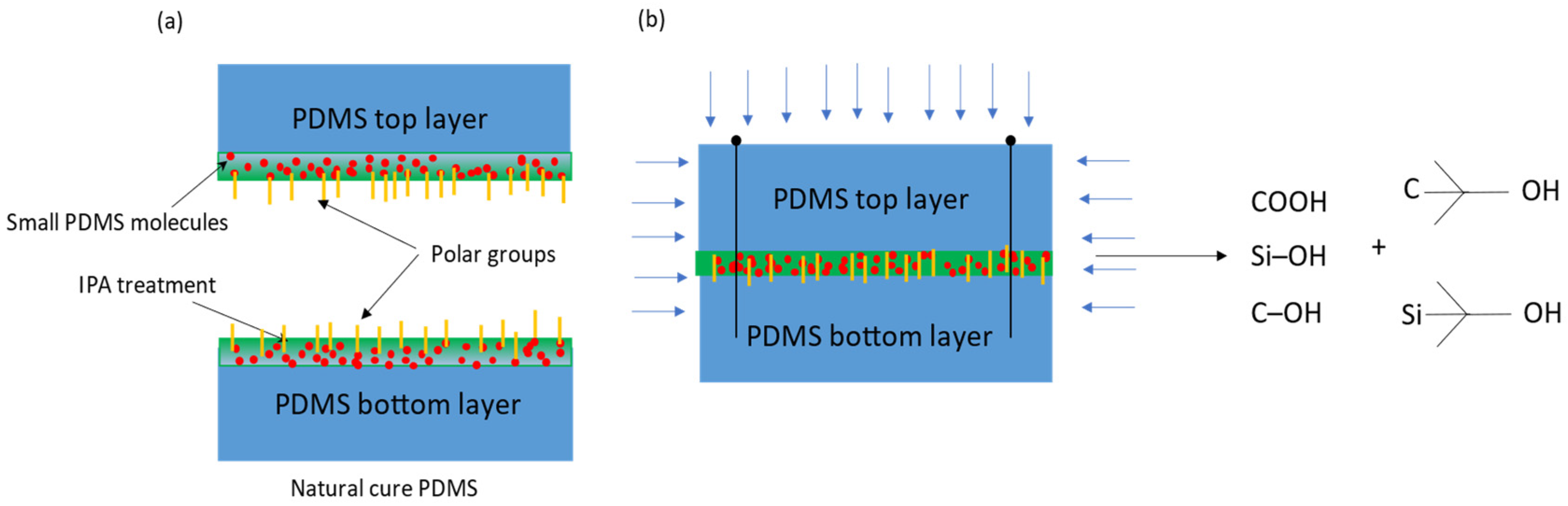
| Method | Substrate | Maximum Bond Strength | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Plasma | PDMS–PDMS | 0.510 MPa | [57] |
| Nitrogen Plasma | PDMS-SU8 | 0.428 MPa | [58] |
| Corona Discharge | PDMS–PDMS | 0.290 MPa | [59] |
| Partial Curing of PDMS | PDMS–PDMS | 0.651 MPa | [59] |
| Vacuum Airbag Lamination (VAL) | PDMS-Glass | 0.739 MPa | [60] |
| Plasma Enhanced | PDMS-PARYLENE | 1.4 MPa | [61] |
| Argon Plasma | PDMS–PDMS | 1.9 MPa | [62] |
| Type of Treatment | Type of Curing | Load (MPa) | Failure Mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | With IPA | Natural | 2.821 | PDMS–PDMS |
| Oven | 1.373 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.392 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.235 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Sample 2 | With IPA | Natural | 2.668 | Glue Failure |
| Oven | 0.686 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.372 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.247 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Sample 3 | With IPA | Natural | 2.786 | Glue Failure |
| Oven | 0.941 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.239 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.215 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Sample 4 | With IPA | Natural | 3.060 | PDMS–PDMS |
| Oven | 1.020 | PDMS–PDMS | ||
| Without IPA | Natural | 0.353 | PDMS–PDMS | |
| Oven | 0.400 | PDMS–PDMS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tony, A.; Badea, I.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, S.-M.; Zhang, W. A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol. Polymers 2023, 15, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006
Tony A, Badea I, Yang C, Liu Y, Wang K, Yang S-M, Zhang W. A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol. Polymers. 2023; 15(4):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006
Chicago/Turabian StyleTony, Anthony, Ildiko Badea, Chun Yang, Yuyi Liu, Kemin Wang, Shih-Mo Yang, and Wenjun Zhang. 2023. "A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol" Polymers 15, no. 4: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006
APA StyleTony, A., Badea, I., Yang, C., Liu, Y., Wang, K., Yang, S.-M., & Zhang, W. (2023). A Preliminary Experimental Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-To-PDMS Bonding Using Oxygen Plasma Treatment Incorporating Isopropyl Alcohol. Polymers, 15(4), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15041006








