Paving the Way for Synthetic Intrinsically Disordered Polymers for Soft Robotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthetic Intrinsically Disordered Polymers
2.1. Soft Robots
2.2. Synthesis of Intrinsically Disordered Polymers
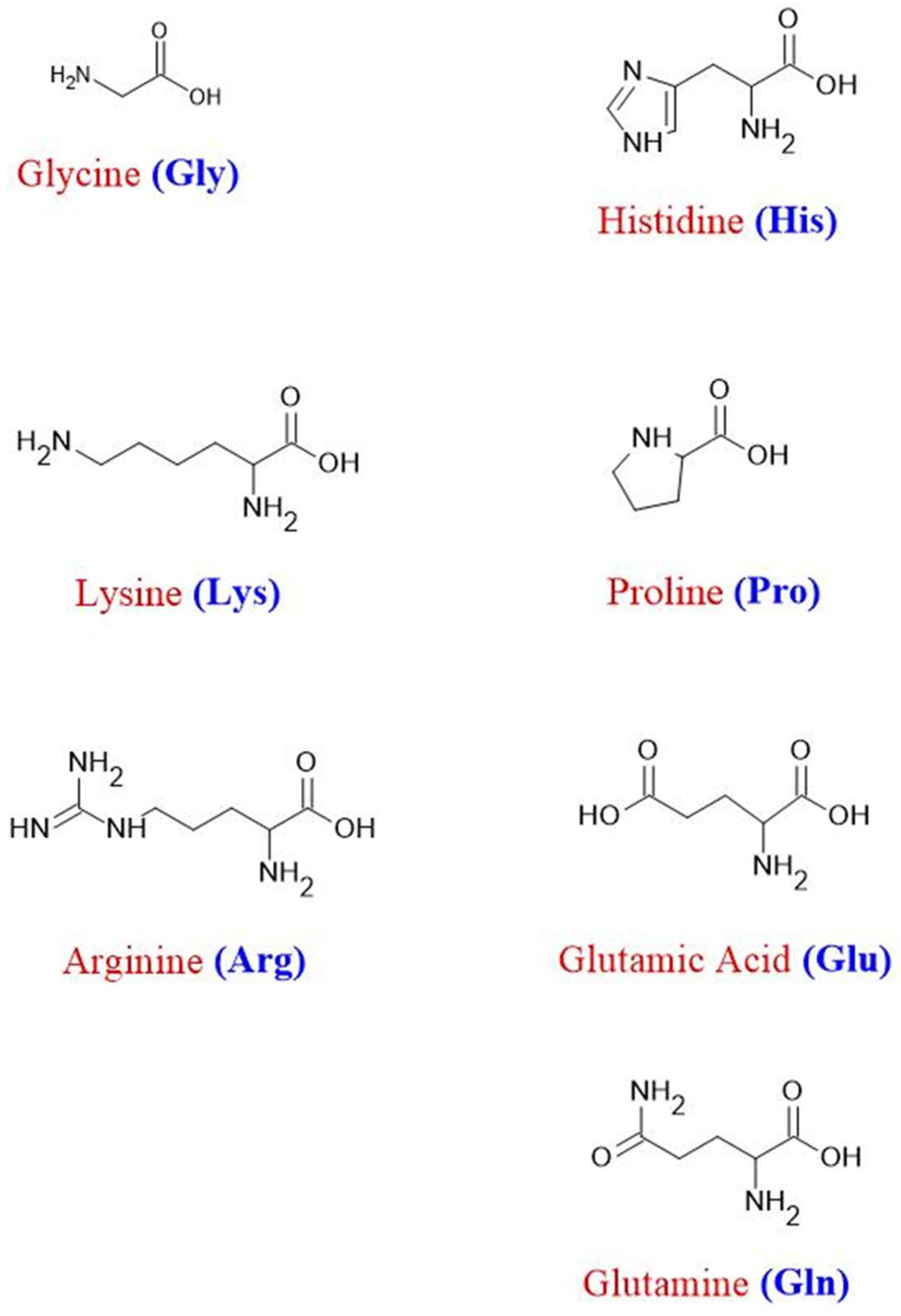
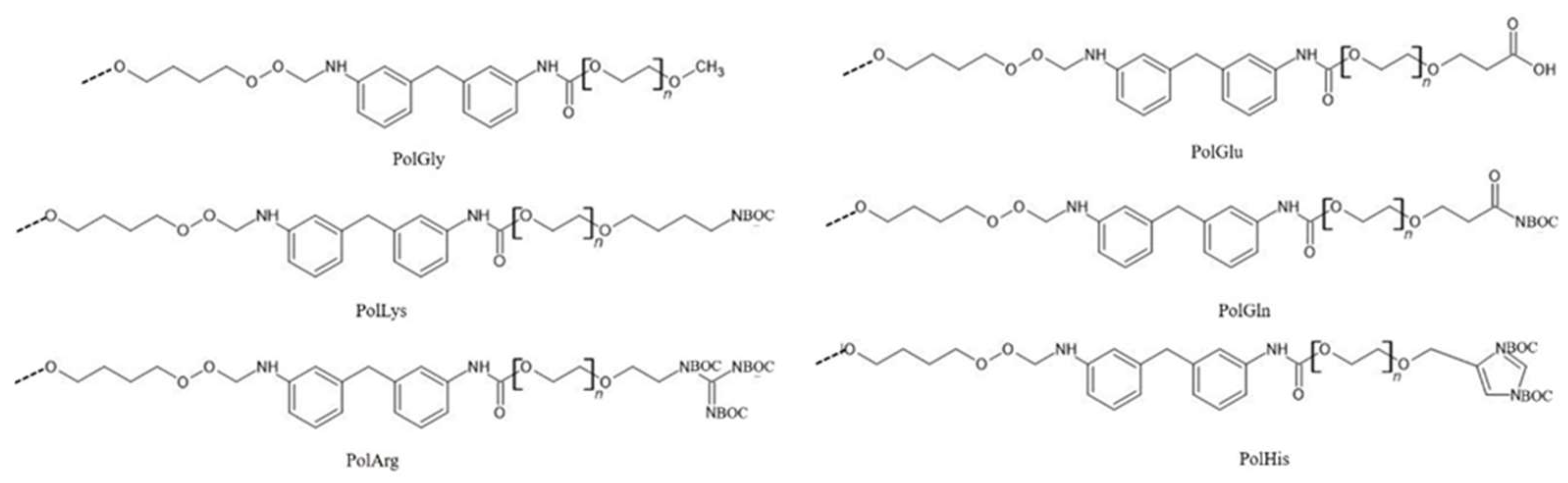
2.2.1. Addition of Structure-Breaking Amino Acid Functional Groups to the Chain Extender
2.2.2. Synthesis of New Bio-Inspired Intrinsically Disordered Polyurethanes
2.2.3. Preparation of Bio-Inspired Intrinsically Disordered Polyurethane Composites
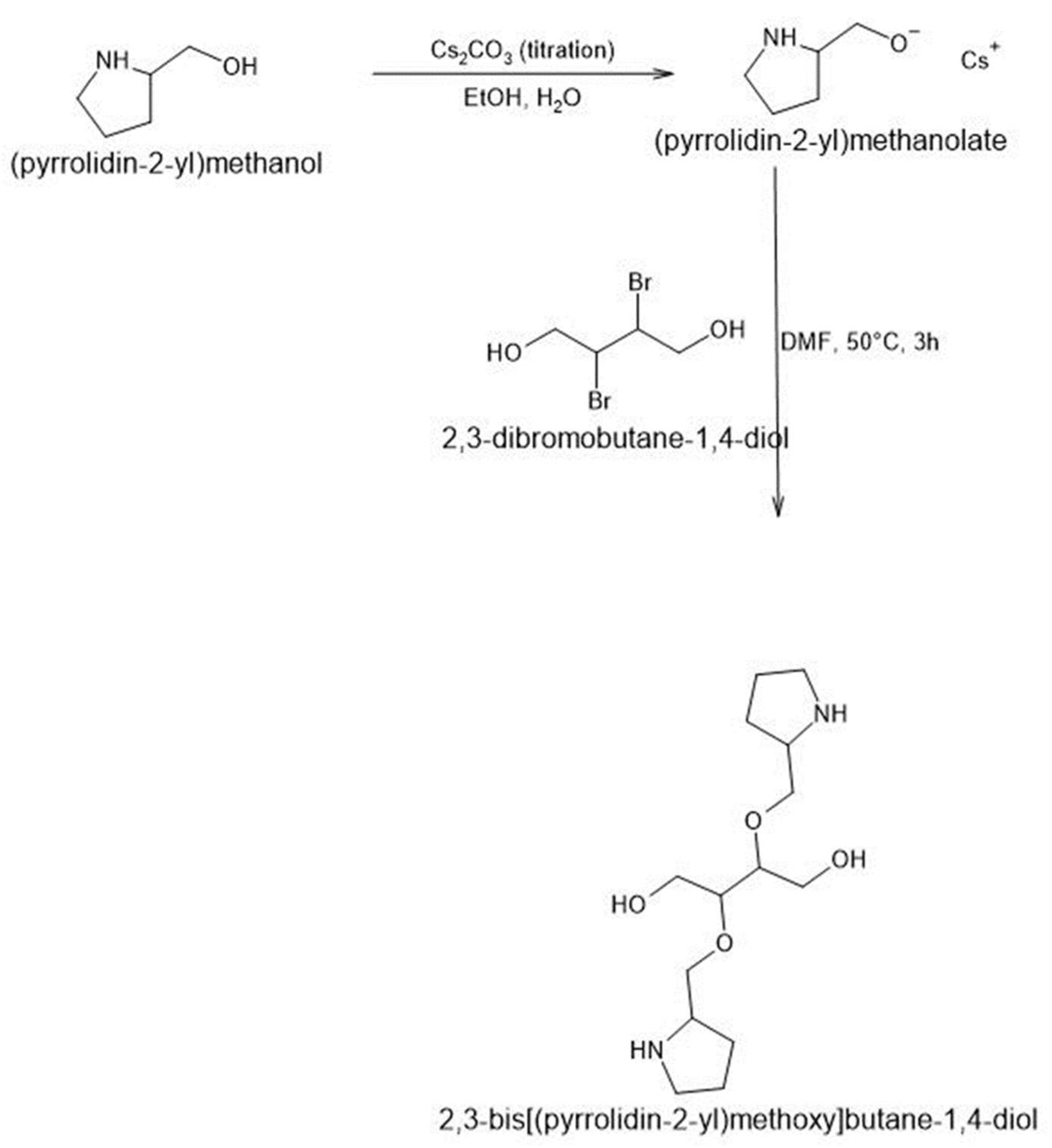
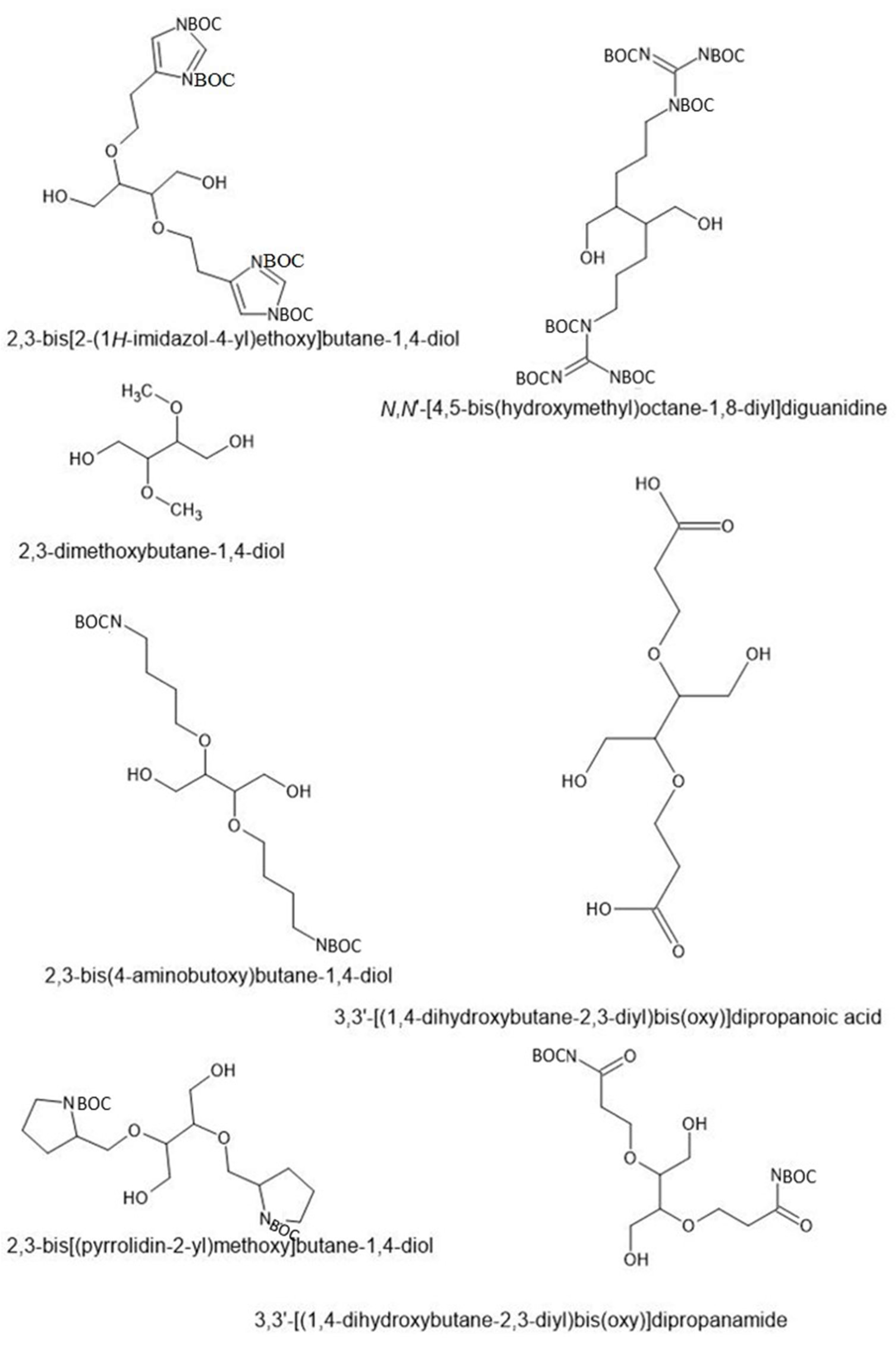
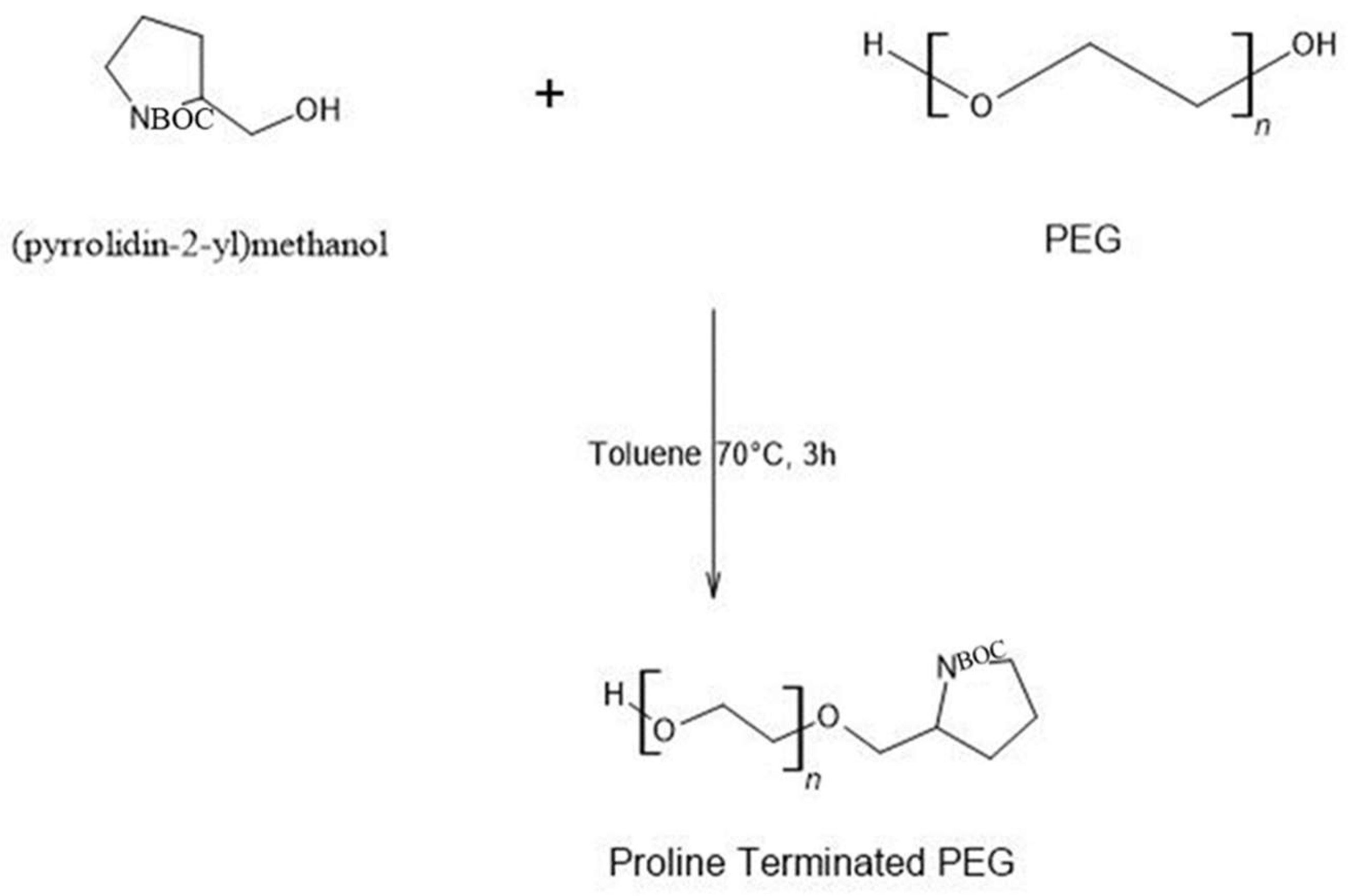
2.2.4. Functionalization of Polyols with Functional Groups of Structure-Breaking Amino Acids
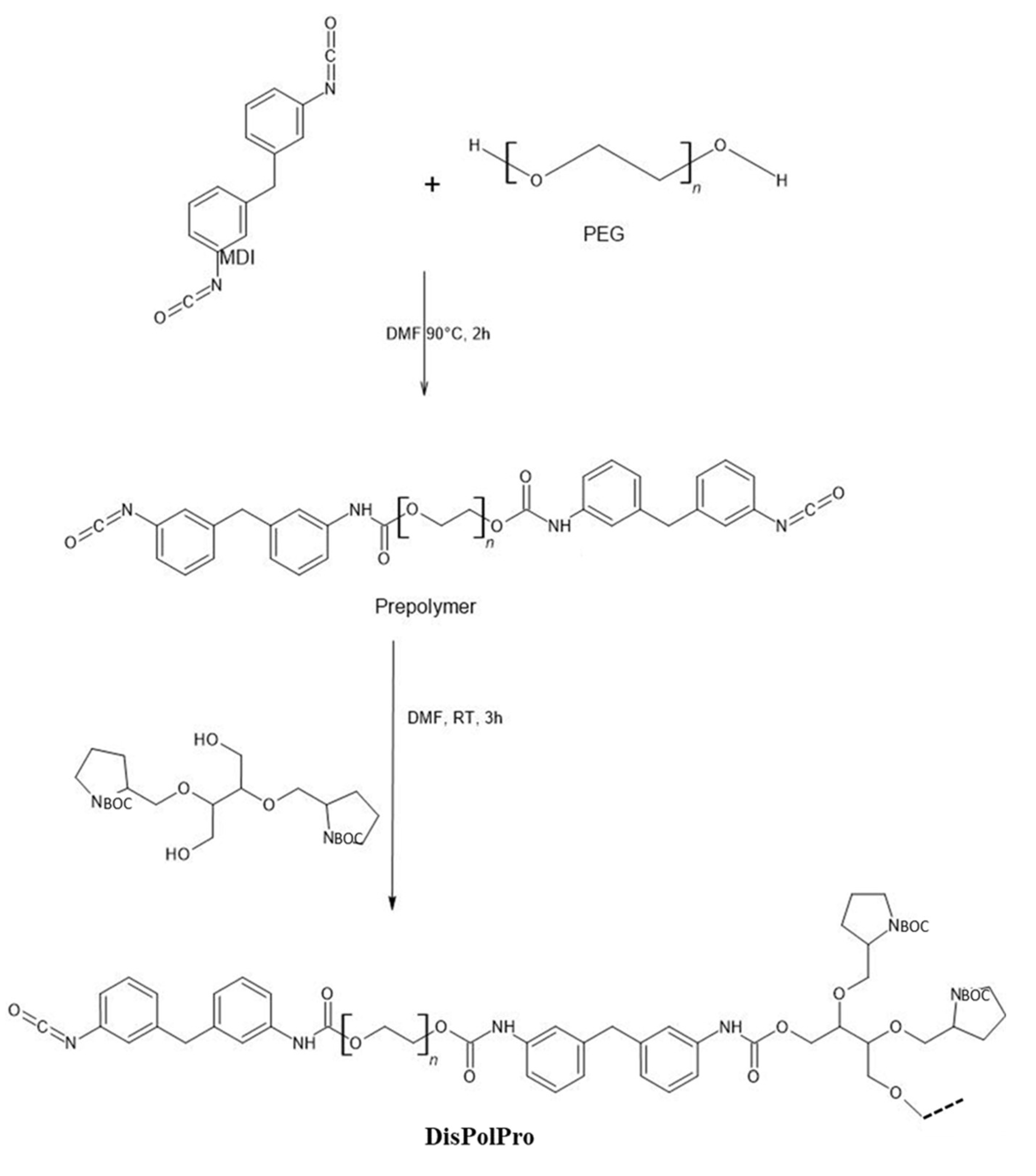
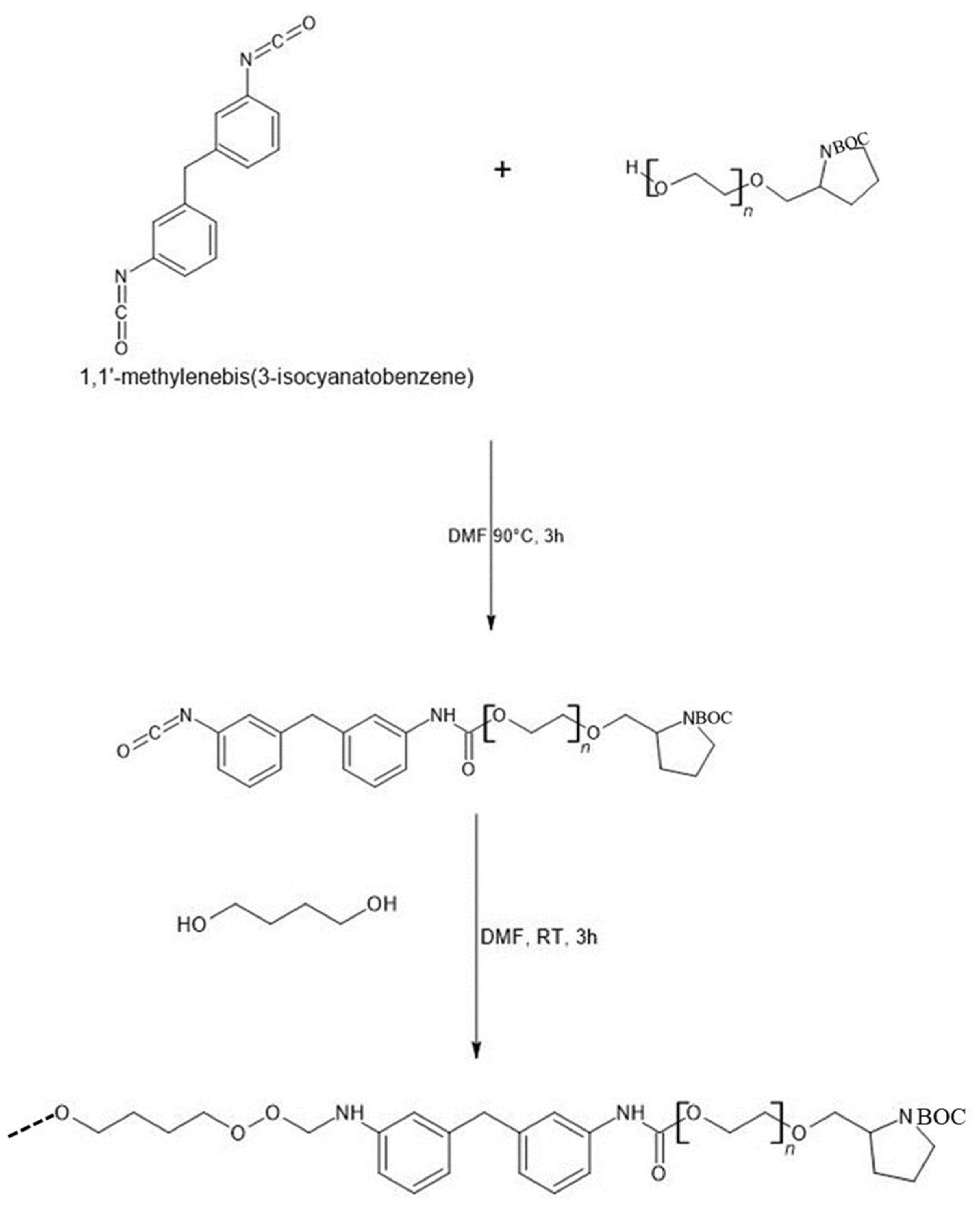
2.2.5. Polymerization Reaction of Functional Group Terminated PEGs with Isocyanate
2.3. Characterization of New Class of Bio-Inspired Intrinsically Disordered Polymers
2.4. Machining of Bulk Polymer Structures into Filaments for 3D Printing Purposes
2.5. Mechanical Characterization of 3D-Printed Polymers
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, N.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S. Soft robot review. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Rahn, C.D.; Kier, W.M.; Walker, I.D. Soft robotics: Biological inspiration, state of the art, and future research. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2008, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Dong, E.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Alici, G.; Jie, Y. Soft and smart modular structures actuated by shape memory alloy (SMA) wires as tentacles of soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 085026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, W.; Cai, S.; Xiong, X.; Guo, J. Pneumatic Soft Robots: Challenges and Benefits. Actuators 2022, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyraz, P.; Runge, G.; Raatz, A. An Overview of Novel Actuators for Soft Robotics. Actuators 2018, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, R.A.; Kramer, R.K. Self-Healing and Damage Resilience for Soft Robotics: A Review. Front. Robot. AI 2017, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, J. Pneumatically Actuated Self-Healing Bionic Crawling Soft Robot. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 100, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Chung, Y.S.; Rodrigue, H. Long Shape Memory Alloy Tendon-based Soft Robotic Actuators and Implementation as a Soft Gripper. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlke, J.; Zechel, S.; Hager, M.D.; Schubert, U.S. How to Design a Self-Healing Polymer: General Concepts of Dynamic Covalent Bonds and Their Application for Intrinsic Healable Materials. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.A.; Becker, K.P.; Wood, R.J. Injection Molding of Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, B. Research on the cast molding process for high quality PDMS molds. Microelectron. Eng. 2009, 86, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terryn, S.; Langenbach, J.; Roels, E.; Brancart, J.; Bakkali-Hassani, C.; Poutrel, Q.-A.; Georgopoulou, A.; George Thuruthel, T.; Safaei, A.; Ferrentino, P.; et al. A review on self-healing polymers for soft robotics. Mater. Today 2021, 47, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Courchesne, N.-M.D.; Duraj-Thatte, A.; Praveschotinunt, P.; Joshi, N.S. Engineered Living Materials: Prospects and Challenges for Using Biological Systems to Direct the Assembly of Smart Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D. What has de novo protein design taught us about protein folding and biophysics? Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-C.; Zuckermann, R.N.; Dill, K.A. Folding a Nonbiological Polymer into a Compact Multihelical Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10999–11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, A.D.; Craig, C.J.; Harker, E.A.; Schepartz, A. Sophistication of foldamer form and function in vitro and in vivo. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasco, M.; Dolain, C.; Guichard, G. Foldamers in Medicinal Chemistry. In Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry II.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 89–125. ISBN 978-0-12-803199-5. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Hecht, S. Remote control over folding by light. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6639–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collie, G.W.; Pulka-Ziach, K.; Lombardo, C.M.; Fremaux, J.; Rosu, F.; Decossas, M.; Mauran, L.; Lambert, O.; Gabelica, V.; Mackereth, C.D.; et al. Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, A.K.; Lawson, J.D.; Brown, C.J.; Williams, R.M.; Romero, P.; Oh, J.S.; Oldfield, C.J.; Campen, A.M.; Ratliff, C.M.; Hipps, K.W.; et al. Intrinsically disordered protein. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2001, 19, 26–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Introduction to Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs). Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6557–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.E.; Dyson, H.J. Intrinsically disordered proteins in cellular signalling and regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y. Advantages of proteins being disordered: Advantages of IDPs. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Lee, R.; Buljan, M.; Lang, B.; Weatheritt, R.J.; Daughdrill, G.W.; Dunker, A.K.; Fuxreiter, M.; Gough, J.; Gsponer, J.; Jones, D.T.; et al. Classification of intrinsically disordered regions and proteins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6589–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner, O.; Uversky, V.N. Tyrosine Regulates β-Sheet Structure Formation in Amyloid-β 42: A New Clustering Algorithm for Disordered Proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1342–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner, O.; Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically disordered proteins in various hypotheses on the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 166, pp. 145–223. ISBN 978-0-12-816851-6. [Google Scholar]
- Coskuner, O.; Wise-Scira, O. Arginine and Disordered Amyloid-β Peptide Structures: Molecular Level Insights into the Toxicity in Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskuner-Weber, O.; Uversky, V. Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases with Molecular Simulations: Understanding the Roles of Artificial and Pathological Missense Mutations in Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Related to Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner-Weber, O.; Uversky, V.N. Alanine Scanning Effects on the Biochemical and Biophysical Properties of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: A Case Study of the Histidine to Alanine Mutations in Amyloid-β42. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskuner, O. Divalent copper ion bound amyloid-β(40) and amyloid-β(42) alloforms are less preferred than divalent zinc ion bound amyloid-β(40) and amyloid-β(42) alloforms. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 21, 957–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, O.; Coskuner, O. New force field parameters for metalloproteins I: Divalent copper ion centers including three histidine residues and an oxygen-ligated amino acid residue. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner-Weber, O. Revisiting Cu(II) Bound Amyloid-β40 and Amyloid-β42 Peptides: Varying Coordination Chemistries. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. Chem. 2018, 981–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise-Scira, O.; Dunn, A.; Aloglu, A.K.; Sakallioglu, I.T.; Coskuner, O. Structures of the E46K Mutant-Type α-Synuclein Protein and Impact of E46K Mutation on the Structures of the Wild-Type α-Synuclein Protein. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise-Scira, O.; Aloglu, A.K.; Dunn, A.; Sakallioglu, I.T.; Coskuner, O. Structures and Free Energy Landscapes of the Wild-Type and A30P Mutant-Type α-Synuclein Proteins with Dynamics. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roels, E.; Terryn, S.; Iida, F.; Bosman, A.W.; Norvez, S.; Clemens, F.; Van Assche, G.; Vanderborght, B.; Brancart, J. Processing of Self-Healing Polymers for Soft Robotics. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, W.H. (Ed.) Self-Healing Polymers: From Principles to Applications, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-3-527-33439-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bode, S.; Enke, M.; Hernandez, M.; Bose, R.K.; Grande, A.M.; van der Zwaag, S.; Schubert, U.S.; Garcia, S.J.; Hager, M.D. Characterization of Self-Healing Polymers: From Macroscopic Healing Tests to the Molecular Mechanism. In Self-Healing Materials; Hager, M.D., van der Zwaag, S., Schubert, U.S., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 273, pp. 113–142. ISBN 978-3-319-32776-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.-P.; Wang, J.-K.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, T.; Li, G.L. Self-healing polymers with tunable mechanical strengths via combined hydrogen bonding and zinc-imidazole interactions. Polymer 2019, 174, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Yadav, B.C.; Kudaibergenov, S.E.; Uflyand, I.E. Basic Approaches to the Design of Intrinsic Self-Healing Polymers for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Polymers 2020, 12, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.J.; Fischer, H.R. Self-healing polymer systems: Properties, synthesis and applications. In Smart Polymers and Their Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 271–298. ISBN 978-0-85709-695-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nik Md Noordin Kahar, N.N.F.; Osman, A.F.; Alosime, E.; Arsat, N.; Mohammad Azman, N.A.; Syamsir, A.; Itam, Z.; Abdul Hamid, Z.A. The Versatility of Polymeric Materials as Self-Healing Agents for Various Types of Applications: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enke, M.; Döhler, D.; Bode, S.; Binder, W.H.; Hager, M.D.; Schubert, U.S. Intrinsic Self-Healing Polymers Based on Supramolecular Interactions: State of the Art and Future Directions. In Self-Healing Materials; Hager, M.D., van der Zwaag, S., Schubert, U.S., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 273, pp. 59–112. ISBN 978-3-319-32776-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl, N.; Bode, S.; Hager, M.D.; Schubert, U.S. Self-Healing Polymers Based on Reversible Covalent Bonds. In Self-healing Materials; Hager, M.D., van der Zwaag, S., Schubert, U.S., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 273, pp. 1–58. ISBN 978-3-319-32776-1. [Google Scholar]
- Coyle, S.; Majidi, C.; LeDuc, P.; Hsia, K.J. Bio-inspired soft robotics: Material selection, actuation, and design. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2018, 22, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Jiang, X.; Sun, H.; Shao, Z.; Song, T.; Luo, Z. Recent researches of the bio-inspired nano-carbon reinforced metal matrix composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 131, 105816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coskuner-Weber, O.; Yuce-Erarslan, E.; Uversky, V.N. Paving the Way for Synthetic Intrinsically Disordered Polymers for Soft Robotics. Polymers 2023, 15, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030763
Coskuner-Weber O, Yuce-Erarslan E, Uversky VN. Paving the Way for Synthetic Intrinsically Disordered Polymers for Soft Robotics. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030763
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoskuner-Weber, Orkid, Elif Yuce-Erarslan, and Vladimir N. Uversky. 2023. "Paving the Way for Synthetic Intrinsically Disordered Polymers for Soft Robotics" Polymers 15, no. 3: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030763
APA StyleCoskuner-Weber, O., Yuce-Erarslan, E., & Uversky, V. N. (2023). Paving the Way for Synthetic Intrinsically Disordered Polymers for Soft Robotics. Polymers, 15(3), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030763






