Fabrication of Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Bamboo Cellulose Foam for Oil/Water Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of the Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Bamboo Cellulose Foam
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Setup of Oil Adsorption
3. Results and Discussion
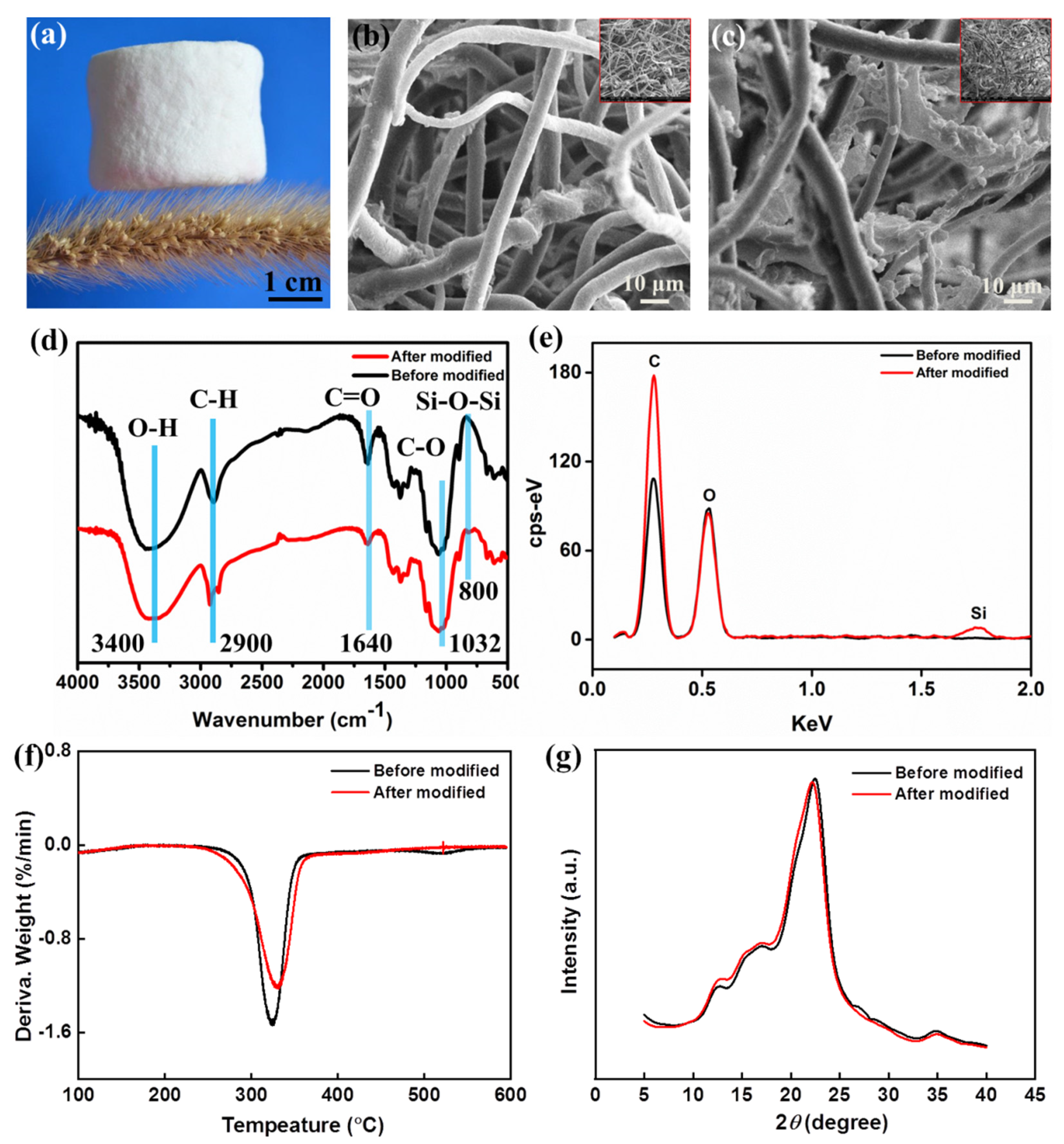
3.1. Surface Micromorphologies and Chemical Compositions
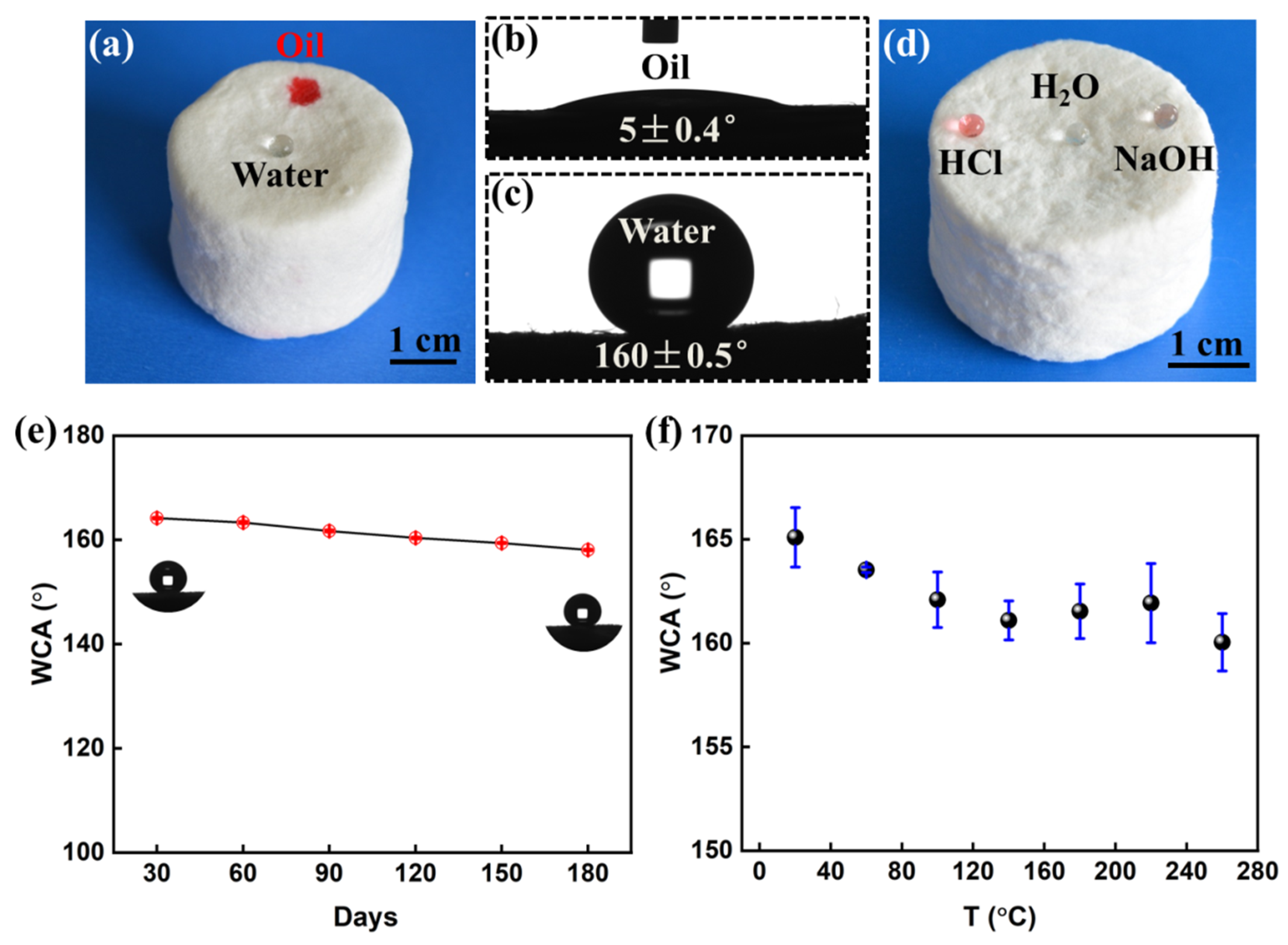
3.2. Wettability and Corrosion Resistance
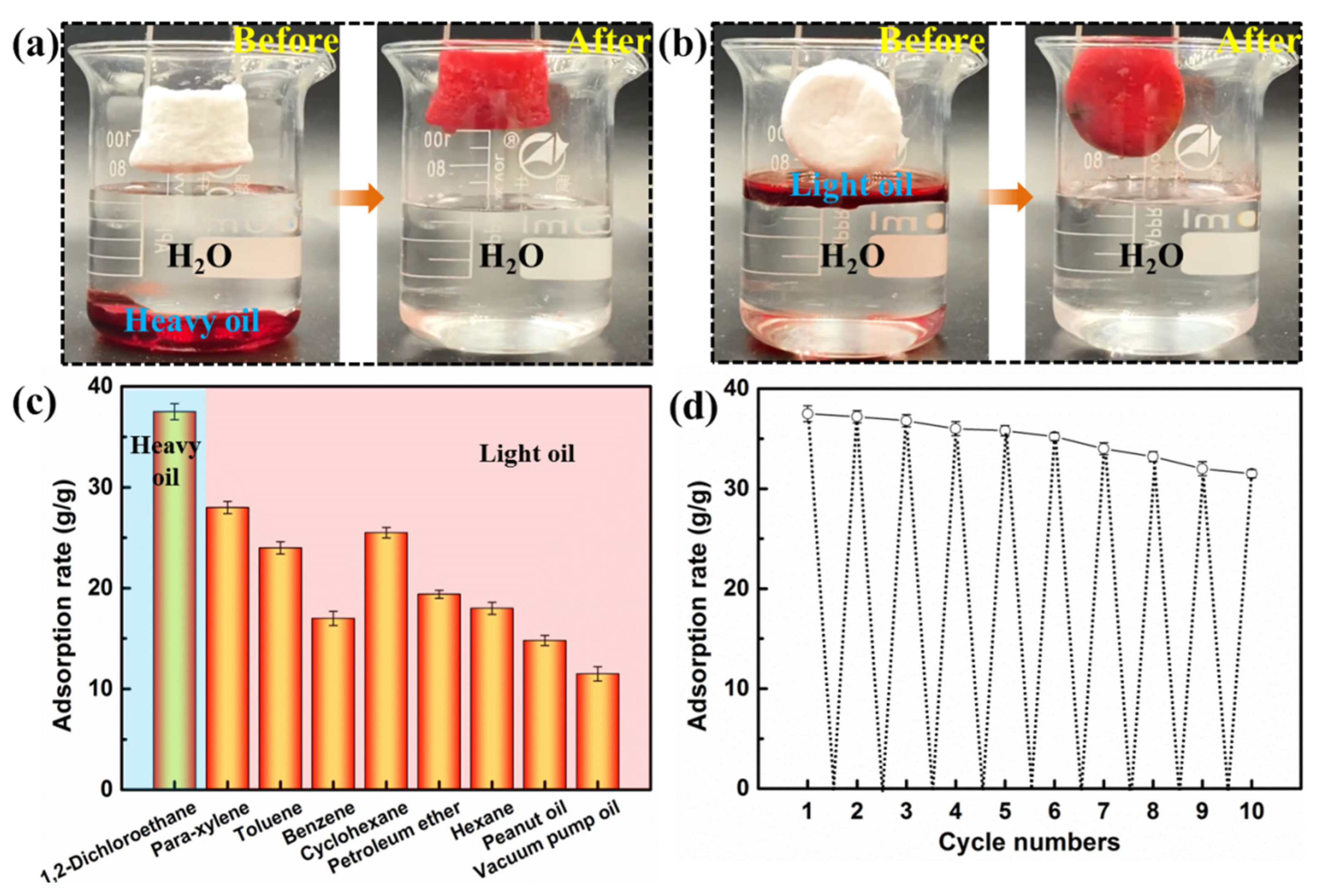
3.3. Performance of Oil Adsorption
3.4. Mechanism of Oil Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Scheres, L.; Xia, H.; Zuilhof, H. Developments and Challenges in Self–Healing Antifouling Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z. Designing novel superwetting surfaces for high–efficiency oil–water separation: Design principles, opportunities, trends and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16831–16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.H.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Hasbullah, H.; Yusof, N.; Aziz, F.; Jaafar, J. Hydrophilic polymer–based membrane for oily wastewater treatment: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 233, 116007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z.; He, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q. Oily sludge treatment in subcritical and supercritical water: A review. J. Hazar. Mater. 2022, 433, 128761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xiao, X.; Au, C.; Mathur, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Kipper, M.J.; Tang, J.; et al. Electrospinning nanofibers and nanomembranes for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 21659–21684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, A. Stainless–steel–net–supported superhydrophobic COF coating for oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 587, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibrous materials: A versatile medium for effective oil/water separation. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, B.; Zhang, K.; Kaya, C.; Stegmaier, T.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. On–demand oil/water separation of 3D Fe foam by controllable wettability. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, W.; Ji, M.; Wang, A.; Gao, S.; Lin, H.; Huang, R.; Jin, J. Double–Defense Design of Super–Anti–Fouling Membranes for Oil/Water Emulsion Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A.; Dong, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, W.; Jin, J. Gradient Adhesive Hydrogel Decorated Superhydrophilic Membranes for Ultra–Stable Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2205990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Unidirectional liquid transportation and selective permeation for oil/water separation on a gradient nanowire structured surface. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, X.; Xu, S.; Cheng, J.; Pi, P. A durable superwetting clusters–inlayed mesh with high efficiency and flux for emulsion separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, M.; Peng, Y.; Jin, X.; Tian, D.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Directional Transport: Bioinspired Continuous and Spontaneous Antigravity Oil Collection and Transportation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1870032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ye, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Bai, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Drioli, E.; Ma, J. Constructing Environmental–Friendly “Oil–Diode” Janus Membrane for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 4684–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Motlhaletsi Moutloali, R.; Mamba, B.B.; Sorokin, P.; Shao, L. Bio–inspired mineral–hydrogel hybrid coating on hydrophobic PVDF membrane boosting oil/water emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentini, R.; Pola, A.; Rizzi, L.G.; Athanassiou, A.; Fragouli, D. A highly porous solvent free PVDF/expanded graphite foam for oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, M.; Mohamed, H.O.; Yasin, A.S.; Yassin, M.A.; Fadali, O.A.; Kim, H.; Barakat, N.A.M. Under–oil superhydrophilic wetted PVDF electrospun modified membrane for continuous gravitational oil/water separation with outstanding flux. Water Res. 2017, 123, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, C.; Jia, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, A.; Cui, Y. Two–Dimensional Fluorinated Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tunable Hydrophobicity for Ultrafast Oil–Water Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113348. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, H.; Otyepková, E.; Schneemann, A.; Zbořil, R.; Otyepka, M.; Fischer, R.A.; Jayaramulu, K. Hierarchical porous metal–organic framework materials for efficient oil–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 2751–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tie, L.; Li, J.; Hou, Y.; Guo, Z. Underoil superhydrophilic surfaces: Water adsorption in metal–organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mähringer, A.; Hennemann, M.; Clark, T.; Bein, T.; Medina, D.D. Energy Efficient Ultrahigh Flux Separation of Oily Pollutants from Water with Superhydrophilic Nanoscale Metal–Organic Framework Architectures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5519–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Li, Z.; Pan, Y.; Feng, X.; Han, L.; Cui, T.; Hu, Y.; Hu, W. A novel approach simultaneously imparting well–hydrophobicity and photothermal conversion effect to polymer materials: Solar–promoted absorption of organic solvents and oils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.; Yue, X.; Hao, B.; Wang, R.; Ma, P.-C. Facile preparation of melamine foam with superhydrophobic performance and its system integration with prototype equipment for the clean–up of oil spills on water surface. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailan, S.M.; Ponnamma, D.; Krupa, I. The Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures by Modified Melamine and Polyurethane Foams: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xie, Y.; Yang, T.; He, X. Melamine Foam with pH–Responsive Wettability for Fast Oil Absorption and Desorption. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2102092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Uwaezuoke, O.J.; Abu Elella, M.H. Superhydrophobic nanohybrid sponges for separation of oil/water mixtures. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Xie, H.; Huang, H.-X.; Turng, L.-S. Magnetically driven superhydrophobic silica sponge decorated with hierarchical cobalt nanoparticles for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, D.; An, P.; Zhang, J.; Feng, S. Highly compression–tolerant and durably hydrophobic macroporous silicone sponges synthesized by a one–pot click reaction for rapid oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18025–18030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanthong, P.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Kongparakul, S.; Samart, C.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Fabrication and evaluation of nanocellulose sponge for oil/water separation. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 190, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.; Peng, S.; Wu, X.; Ren, T.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, Q. A cellulose sponge with robust superhydrophilicity and under–water superoleophobicity for highly effective oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X. Highly Compressible Wood Sponges with a Spring–like Lamellar Structure as Effective and Reusable Oil Absorbents. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10365–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Cao, C.; Pan, Y. Advances of Adsorption and Filtration Techniques in Separating Highly Viscous Crude Oil/Water Mixtures. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.T.; Han, N.; Jang, W.; Jung, W.; Oh, M.; Han, S.W.; Koo, H.Y.; Choi, W.S. Surface Design of Separators for Oil/Water Separation with High Separation Capacity and Mechanical Stability. Langmuir 2017, 33, 8012–8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Qu, W.; Wang, Z. A facile and mild strategy to fabricate an underwater superoleophobic and underoil superhydrophobic mesh with outstanding anti–viscous oil–fouling properties for switchable high viscosity oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 5080–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of Transportation Fuels from Biomass: Chemistry, Catalysts, and Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.-P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating Biopolymer and Sustainable Raw Material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose Nanocrystals: Chemistry, Self–Assembly, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Lee, K.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, U.-J.; You, J. Cellulose nanocrystal–coated TEMPO–oxidized cellulose nanofiber films for high performance all–cellulose nanocomposites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 123100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, L.; Batchelor, W.; Tabor, R.F.; Garnier, G. Gelation mechanism of cellulose nanofibre gels: A colloids and interfacial perspective. J.Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 509, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.J.G.; de Medeiros, A.D.L.M.; de Amorim, J.D.P.; do Nascimento, H.A.; Converti, A.; Costa, A.F.S.; Sarubbo, L.A. Bacterial cellulose biotextiles for the future of sustainable fashion: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2967–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, B.M.; Ibrahim, N.A. Recent developments in sustainable finishing of cellulosic textiles employing biotechnology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Ruan, R.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Tsang, D.C.W. Heterogeneous Diels–Alder tandem catalysis for converting cellulose and polyethylene into BTX. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, C. Photothermally promoted cleavage of β–1,4–glycosidic bonds of cellulosic biomass on Ir/HY catalyst under mild conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 237, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-C.; Yu, H.-Y.; Qi, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Z. Confined Chemical Transitions for Direct Extraction of Conductive Cellulose Nanofibers with Graphitized Carbon Shell at Low Temperature and Pressure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 11620–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Chang, P.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S. Anemone–inspired enzymatic film for cellulose heterogeneous catalysis. Carbohydrate Polymers 2021, 260, 117795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, J. Self–assembled cellulose materials for biomedicine: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 181, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swingler, S.; Gupta, A.; Gibson, H.; Kowalczuk, M.; Heaselgrave, W.; Radecka, I. Recent Advances and Applications of Bacterial Cellulose in Biomedicine. Polymers 2021, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprea, M.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in composites based on cellulose derivatives for biomedical applications. Carbohydrate Polymers 2020, 247, 116683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ngai, T. Recent Advances in Chemically Modified Cellulose and Its Derivatives for Food Packaging Applications: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, R.; Hong, X.; Ni, Y.; Li, Y.; Pang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, Y. Recent trends and applications of cellulose nanocrystals in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Anankanbil, S.; Guo, Z. Applications of nanocellulosic products in food: Manufacturing processes, structural features and multifaceted functionalities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Yao, Z.; Wang, X.; Crombeen, M.; Sweeney, D.G.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose–based materials in wastewater treatment of petroleum industry. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hao, X.; Liu, J. Review on the fate and recovery of cellulose in wastewater treatment. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2022, 184, 106354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, C.; Konwar, A.; Bora, P.; Rajguru, P.; Hazarika, S. Cellulose nanofiber–poly(ethylene terephthalate) nanocomposite membrane from waste materials for treatment of petroleum industry wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 129955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Tiwari, A.; Randhawa, J.K. Electrospun nanofibers of α–hematite/polyacrylonitrile/calcium carbonate/cellulose triacetate as a multifunctional platform in, wastewater treatment and remineralisation. Desalination 2022, 541, 116030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainul Armir, N.A.; Zulkifli, A.; Gunaseelan, S.; Palanivelu, S.D.; Salleh, K.M.; Che Othman, M.H.; Zakaria, S. Regenerated Cellulose Products for Agricultural and Their Potential: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Liyanage, S.; Parajuli, P.; Rumi, S.S.; Shamshina, J.L.; Abidi, N. Utilization of Cellulose to Its Full Potential: A Review on Cellulose Dissolution, Regeneration, and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Adnan, A.S.; Yahya, E.B.; Olaiya, N.G.; Safrida, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Balakrishnan, V.; Gopakumar, D.A.; Abdullah, C.K.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; et al. A Review on Plant Cellulose Nanofibre–Based Aerogels for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Cheng, X.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X. Carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylamide composite hydrogel for cascaded treatment/reuse of heavy metal ions in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, H.; Venkateswaran, S.; Hsiao, B.S. Highly efficient and sustainable carboxylated cellulose filters for removal of cationic dyes/heavy metals ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 123458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdoub, M.; Essamlali, Y.; Amadine, O.; Ganetri, I.; Hafnaoui, A.; Khouloud, M.; Zahouily, M. Octadecylamine as chemical modifier for tuned hydrophobicity of surface modified cellulose: Toward organophilic cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2021, 28, 7717–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, A.; Huang, R.; Penkova, A.; Qi, W.; He, Z.; Su, R. Superhydrophobic, elastic and anisotropic cellulose nanofiber aerogels for highly effective oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, J.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Gao, W.; Xu, J. Rechargeable nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel with excellent biocidal properties for efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhu, K.; Li, X.; Wu, X. Recyclable Bacterial Cellulose Aerogel for Oil and Water Separation. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yu, W. Effects of extraction methods on morphology, structure and properties of bamboo cellulose. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 169, 113640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Correia, V.; Ardanuy, M.; Claramunt, J.; Savastano, H. Assessment of chemical and mechanical behavior of bamboo pulp and nanofibrillated cellulose exposed to alkaline environments. Cellulose 2019, 26, 9269–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L. Preparation and modification of cellulose sponge and application of oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41713–41719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ji, B.; Jiang, R.; Cui, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhou, M.; Li, Z. Polydimethylsiloxane/carbonized bacterial cellulose sponge for oil/water separation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-H.; Shang, J.-P.; Su, X.; Zhao, S.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.-B. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Bamboo Cellulose Foam for Oil/Water Separation. Polymers 2022, 14, 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235162
Liu C-H, Shang J-P, Su X, Zhao S, Peng Y, Li Y-B. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Bamboo Cellulose Foam for Oil/Water Separation. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235162
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chun-Hua, Jiao-Ping Shang, Xing Su, Shuang Zhao, Yun Peng, and Yi-Bao Li. 2022. "Fabrication of Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Bamboo Cellulose Foam for Oil/Water Separation" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235162
APA StyleLiu, C.-H., Shang, J.-P., Su, X., Zhao, S., Peng, Y., & Li, Y.-B. (2022). Fabrication of Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Bamboo Cellulose Foam for Oil/Water Separation. Polymers, 14(23), 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235162





