Comparative Performance Analysis of Inverse Phase Active Vibration Cancellation Using Macro Fiber Composite (MFC) and Vibration Absorption of Silicone Gel for Vibration Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
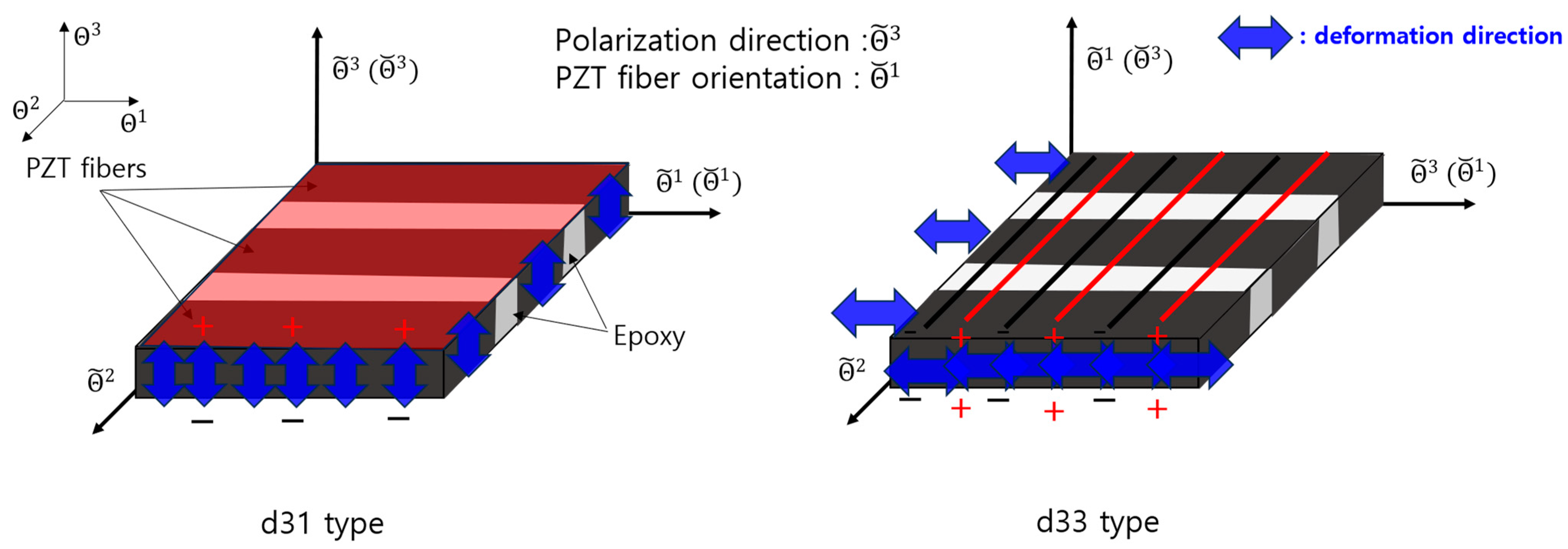
2.1. MFC d31 Type and d33 Type
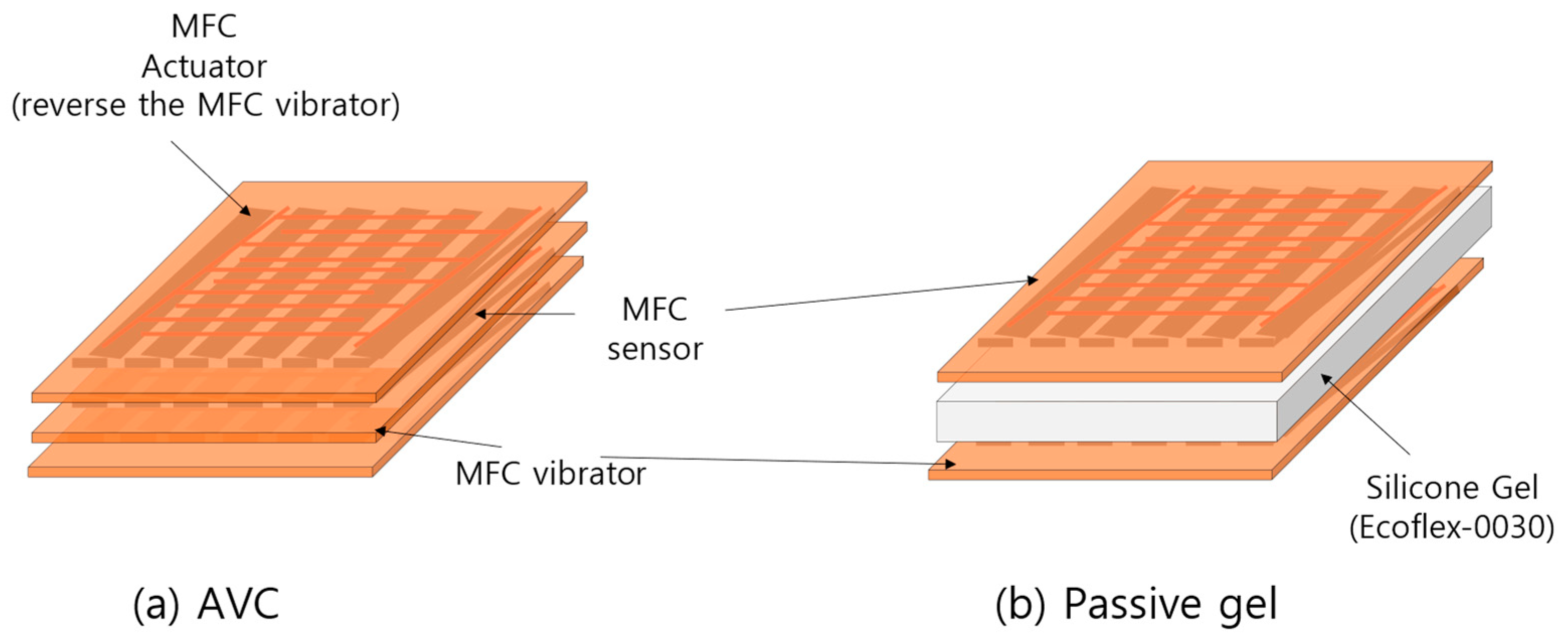
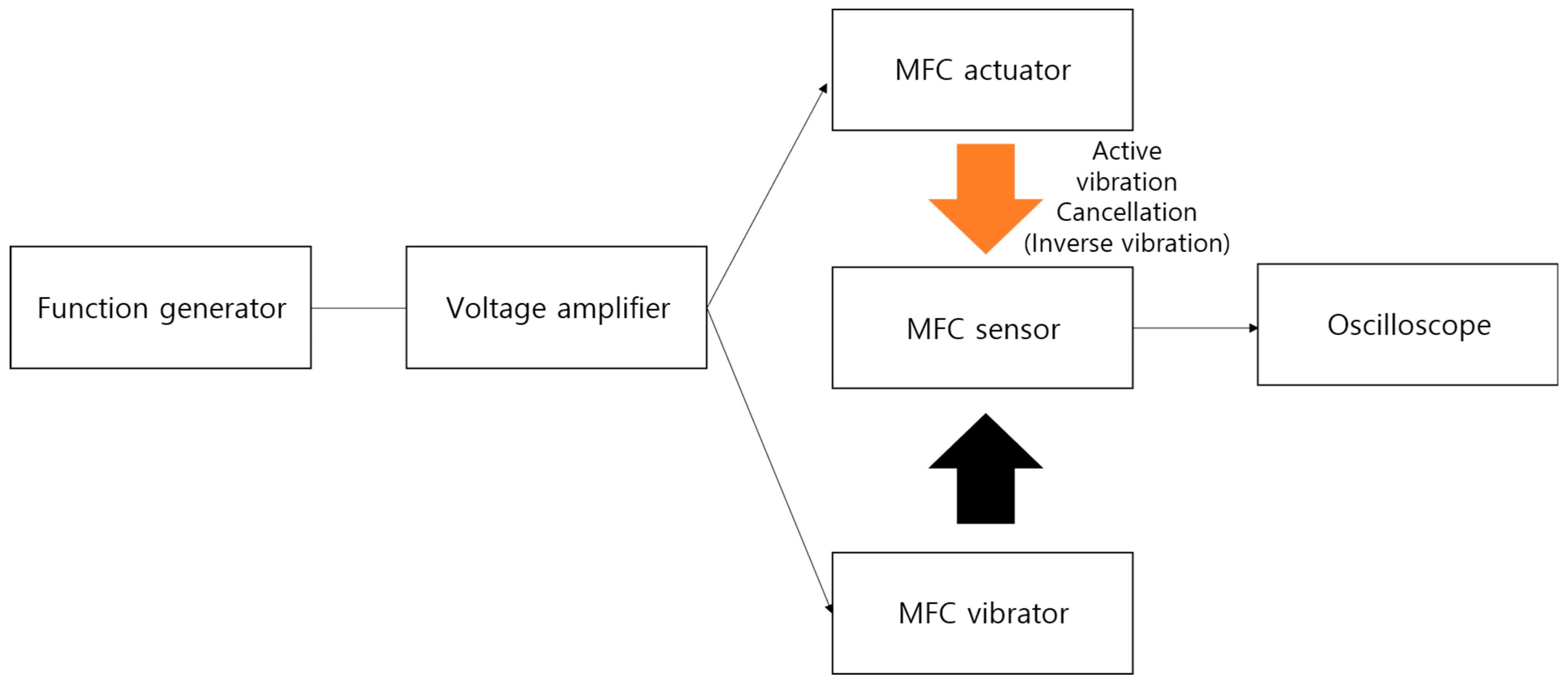
2.2. Active Vibration Cancellation (AVC)
3. Results
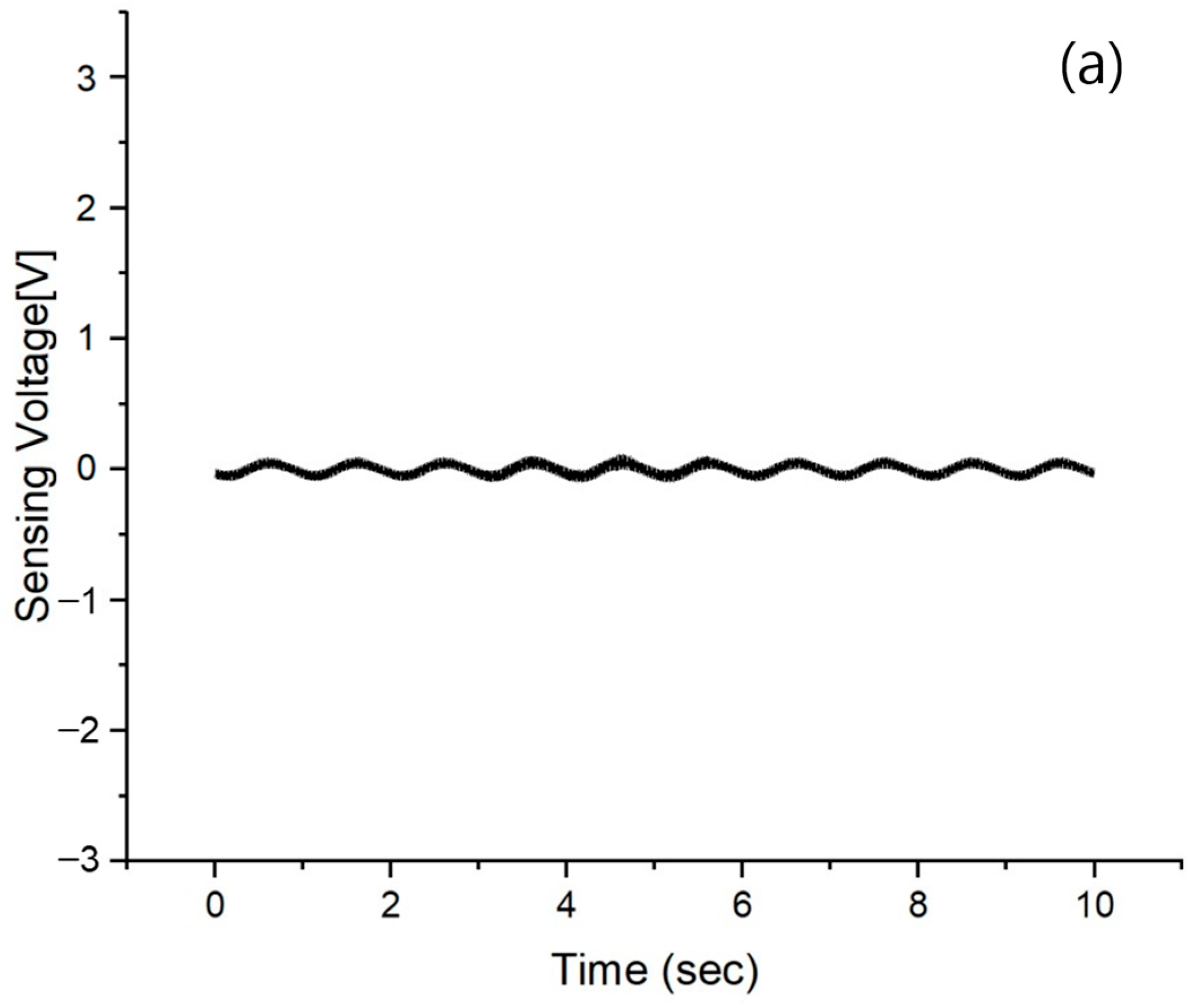
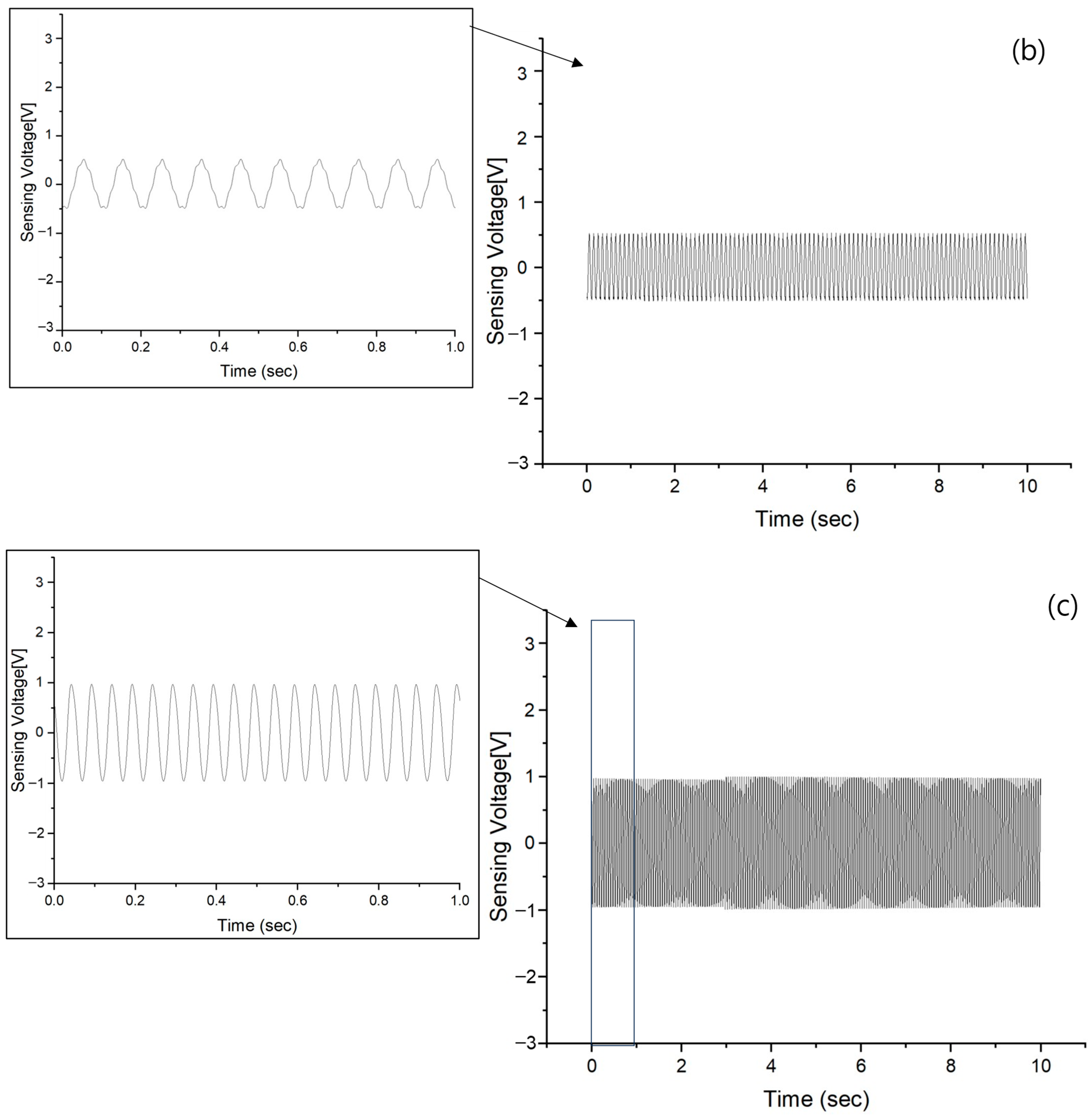
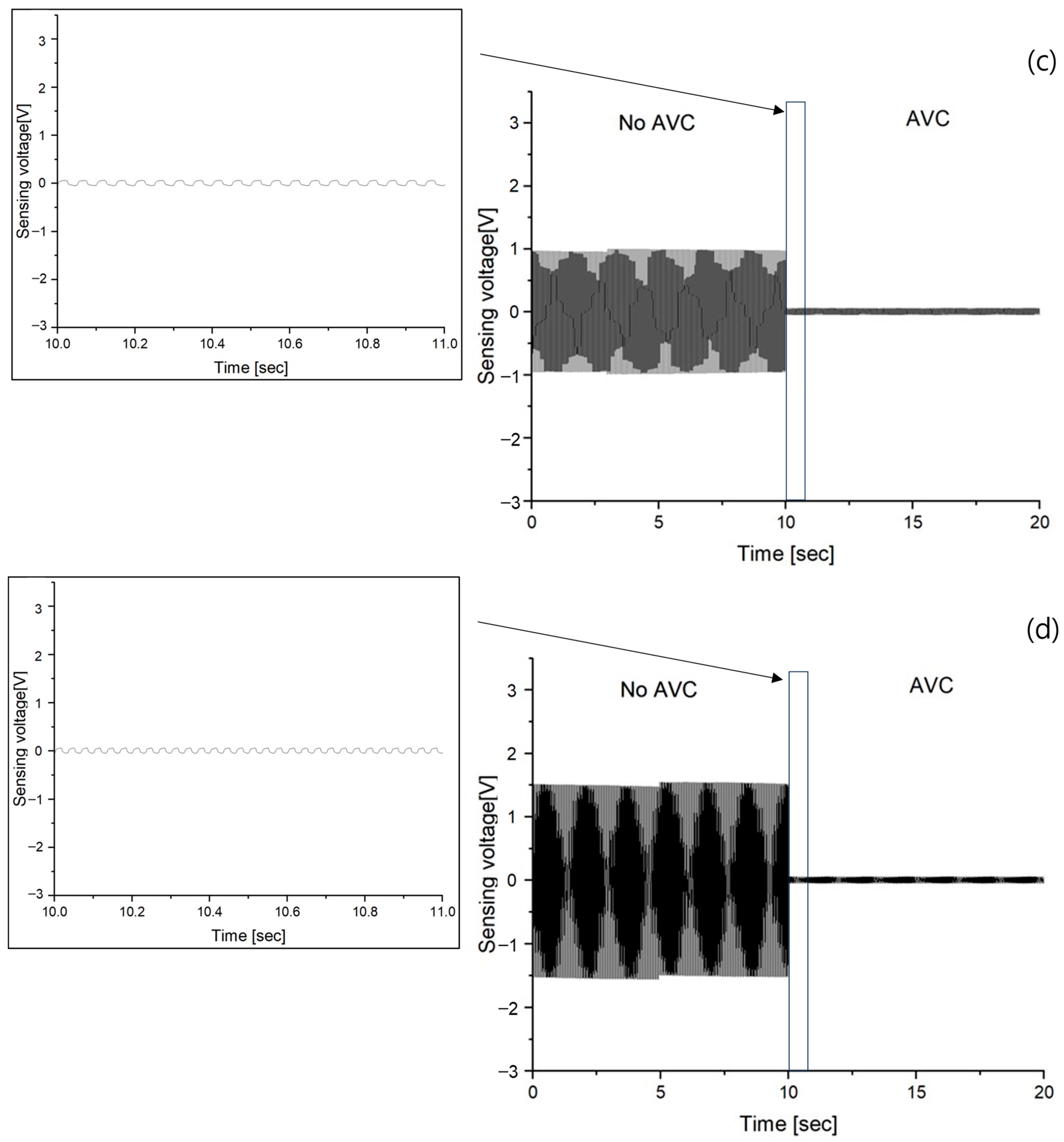
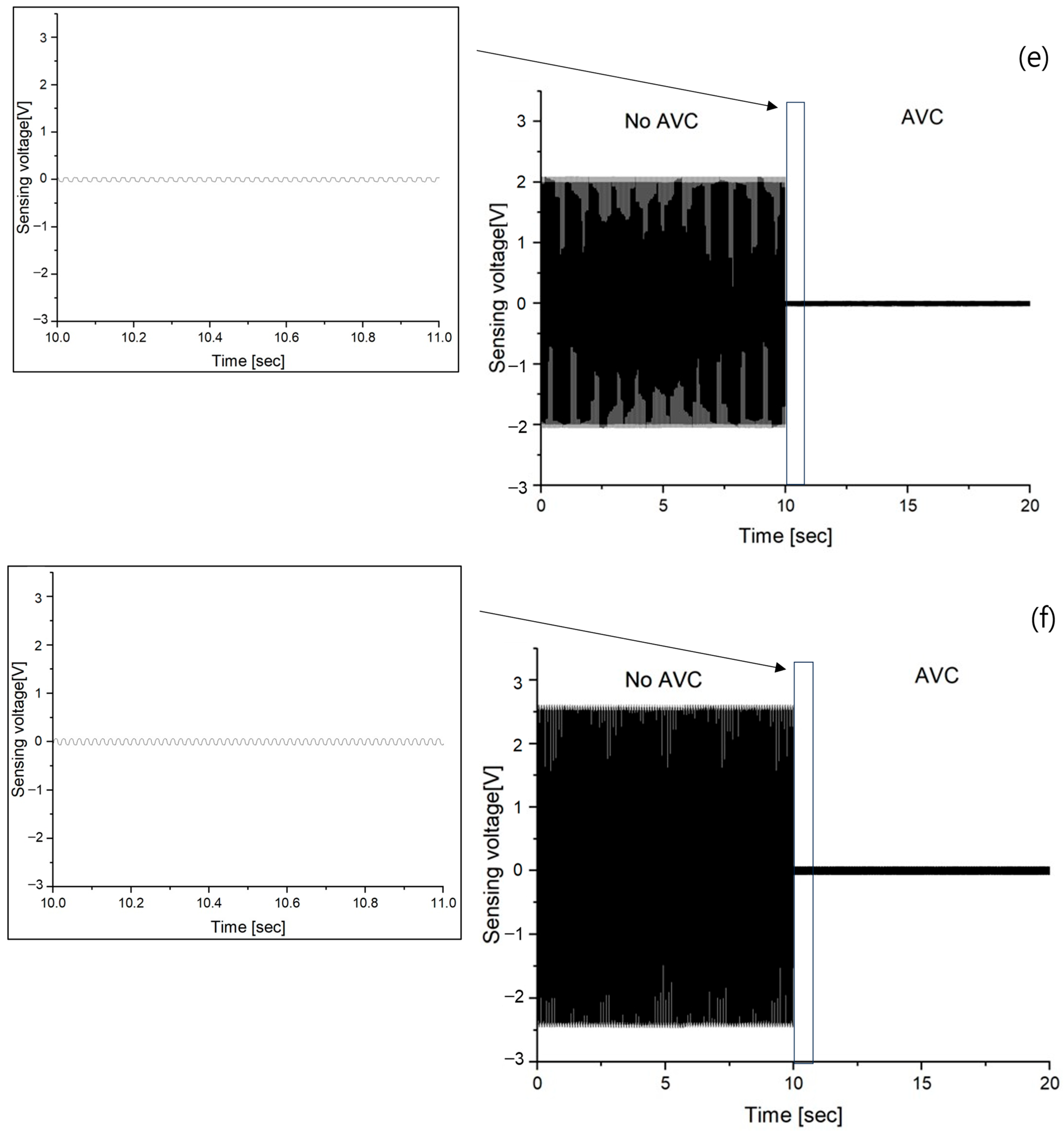
3.1. Vibration Sensing of no AVC
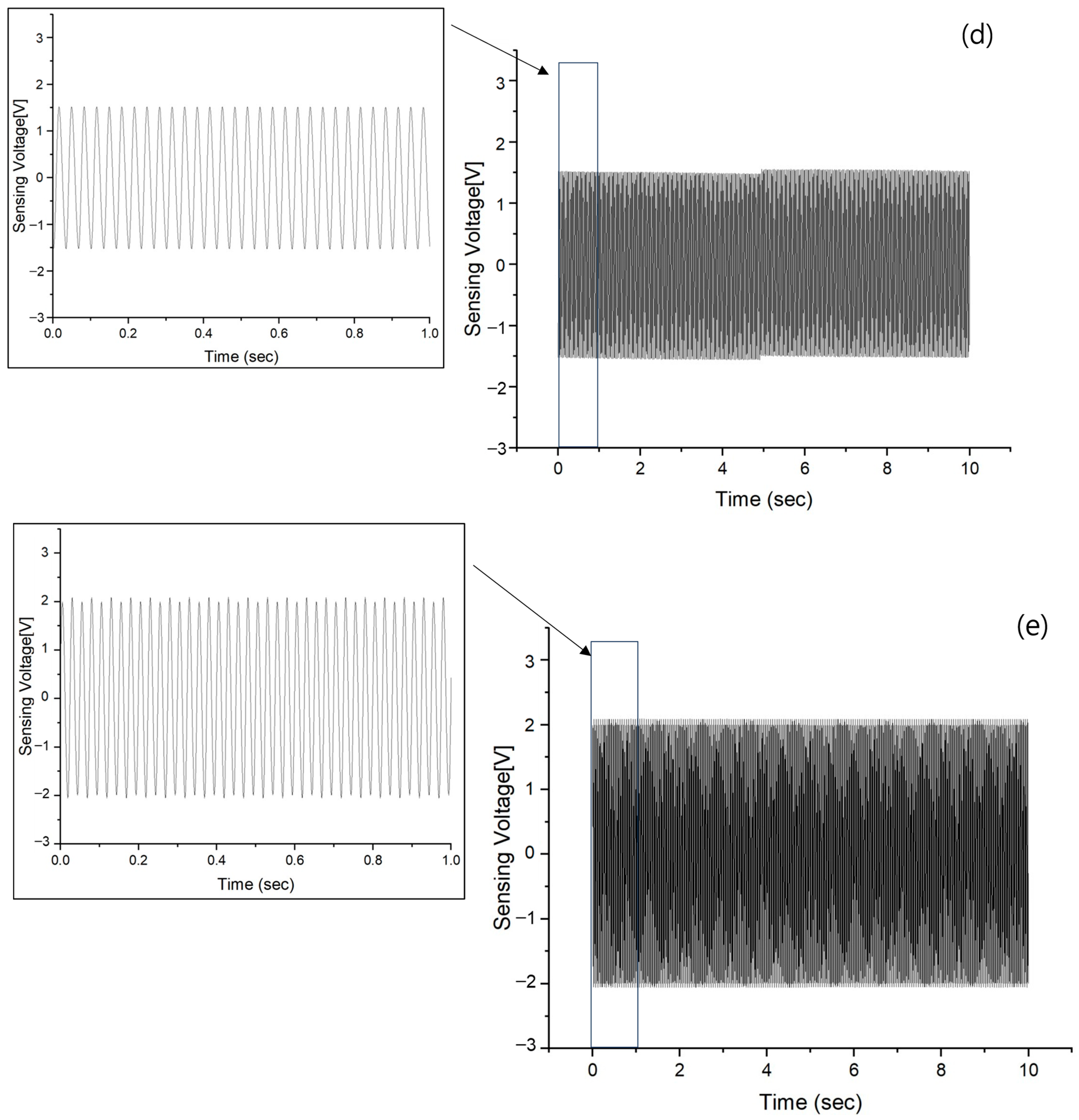
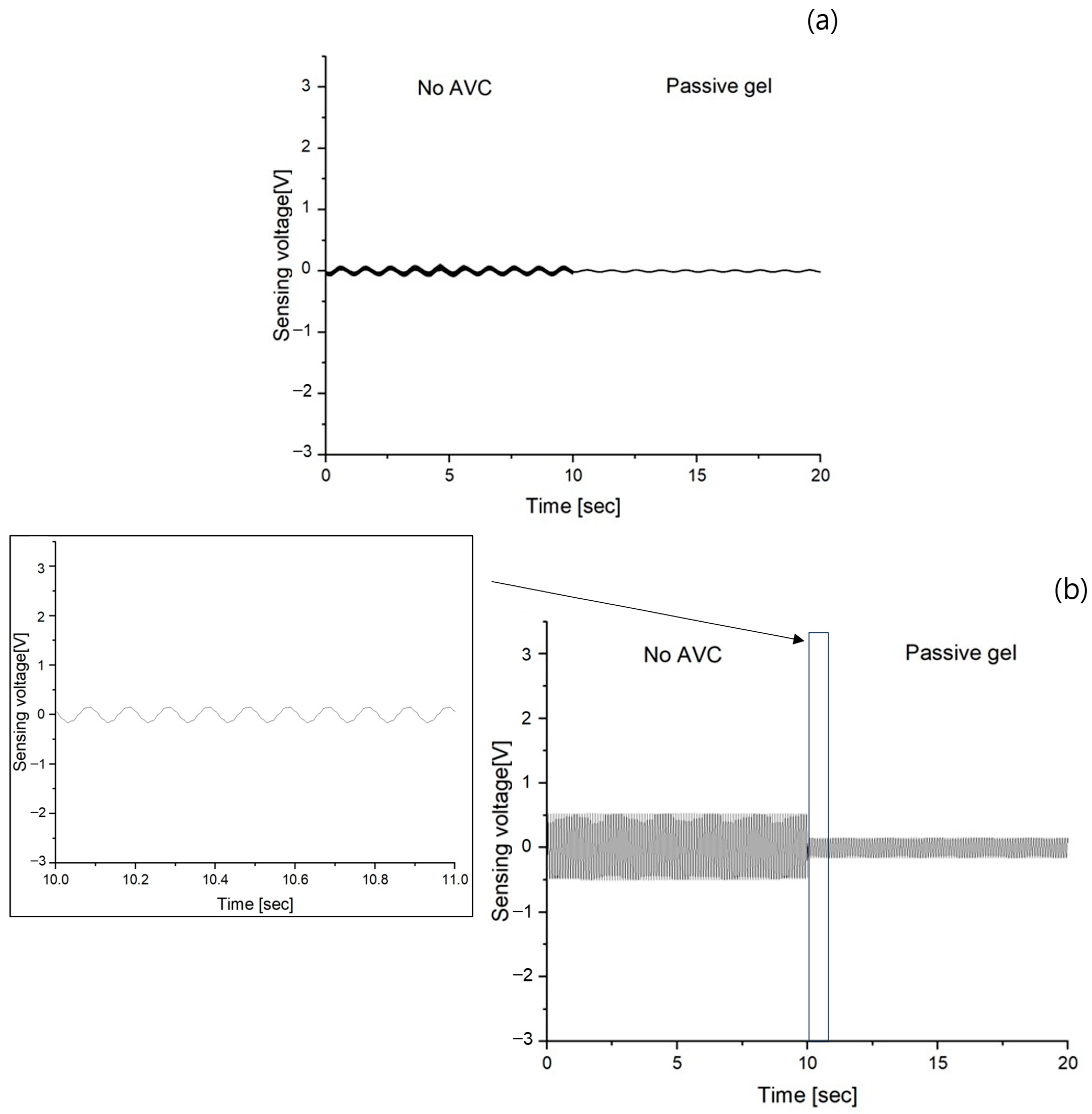
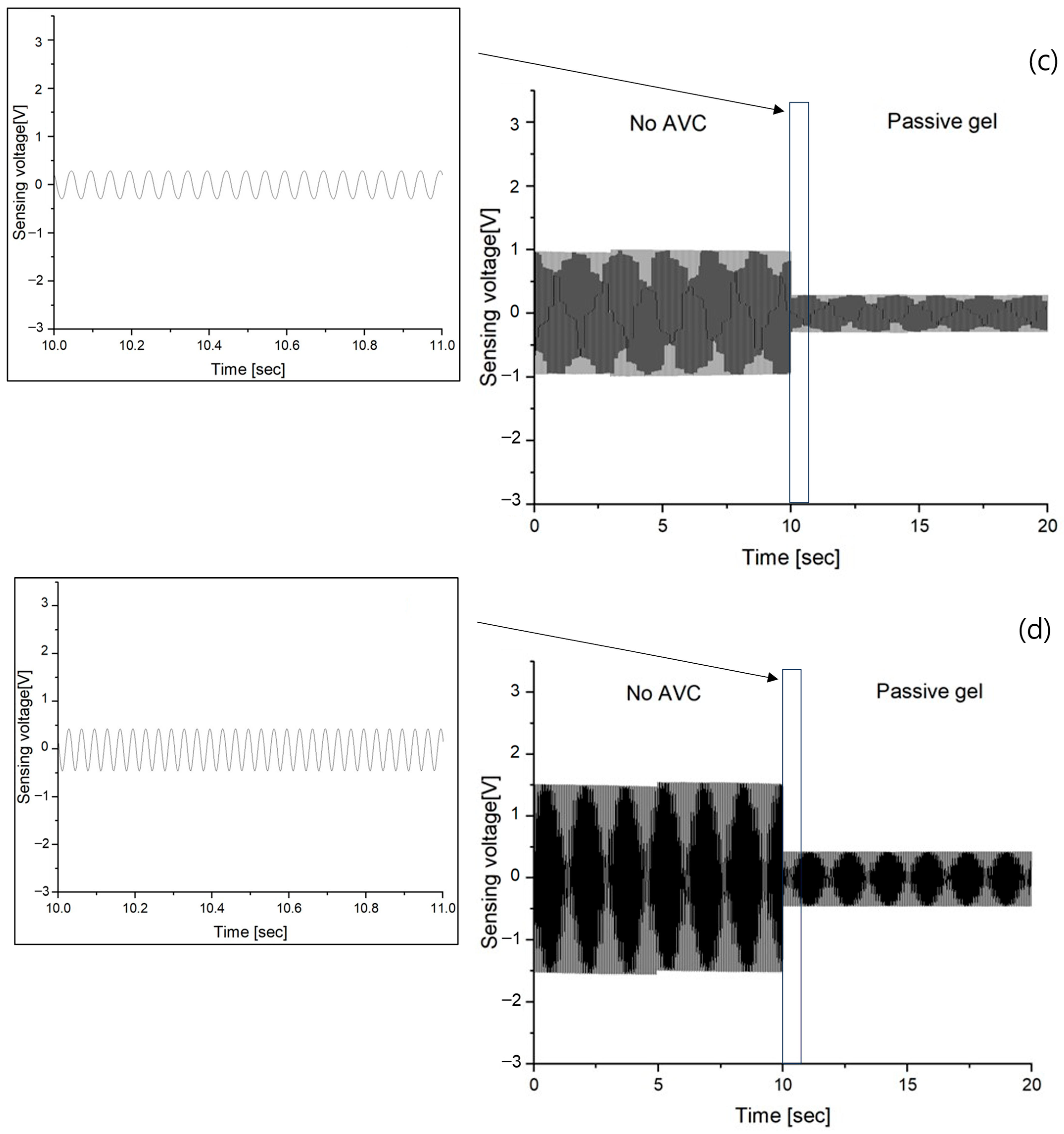
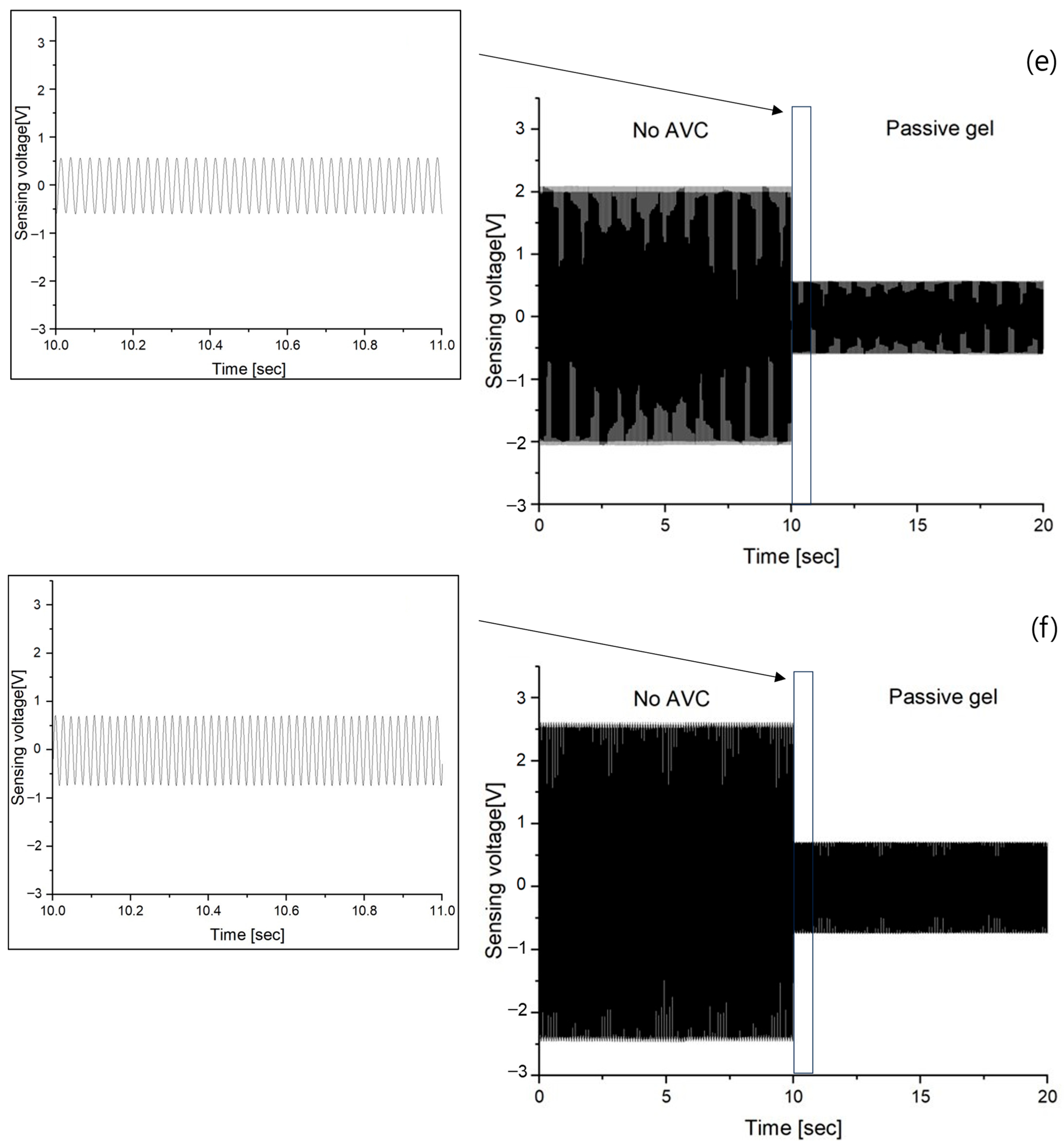
3.2. Vibration Sensing of Passive Gel
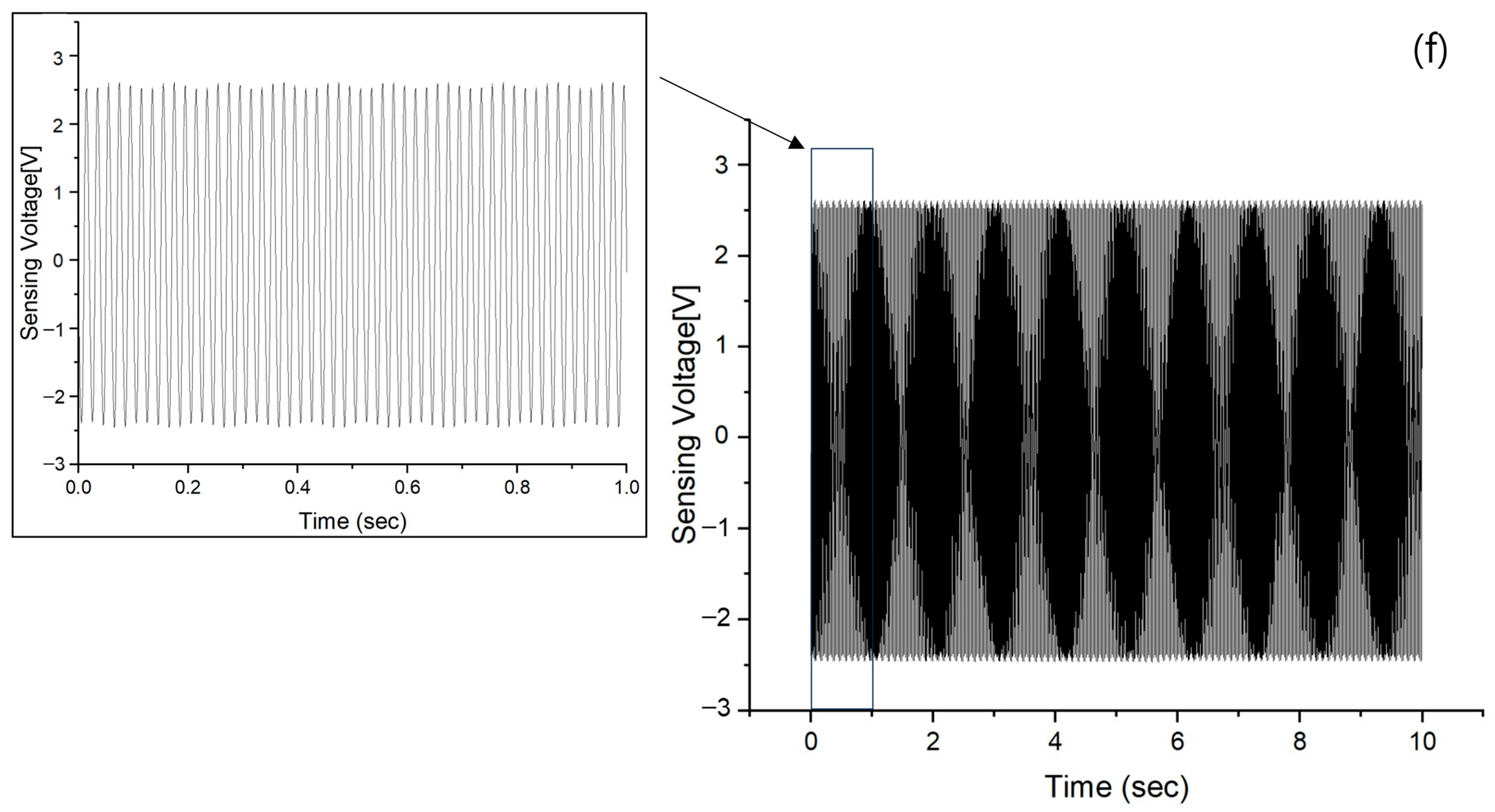
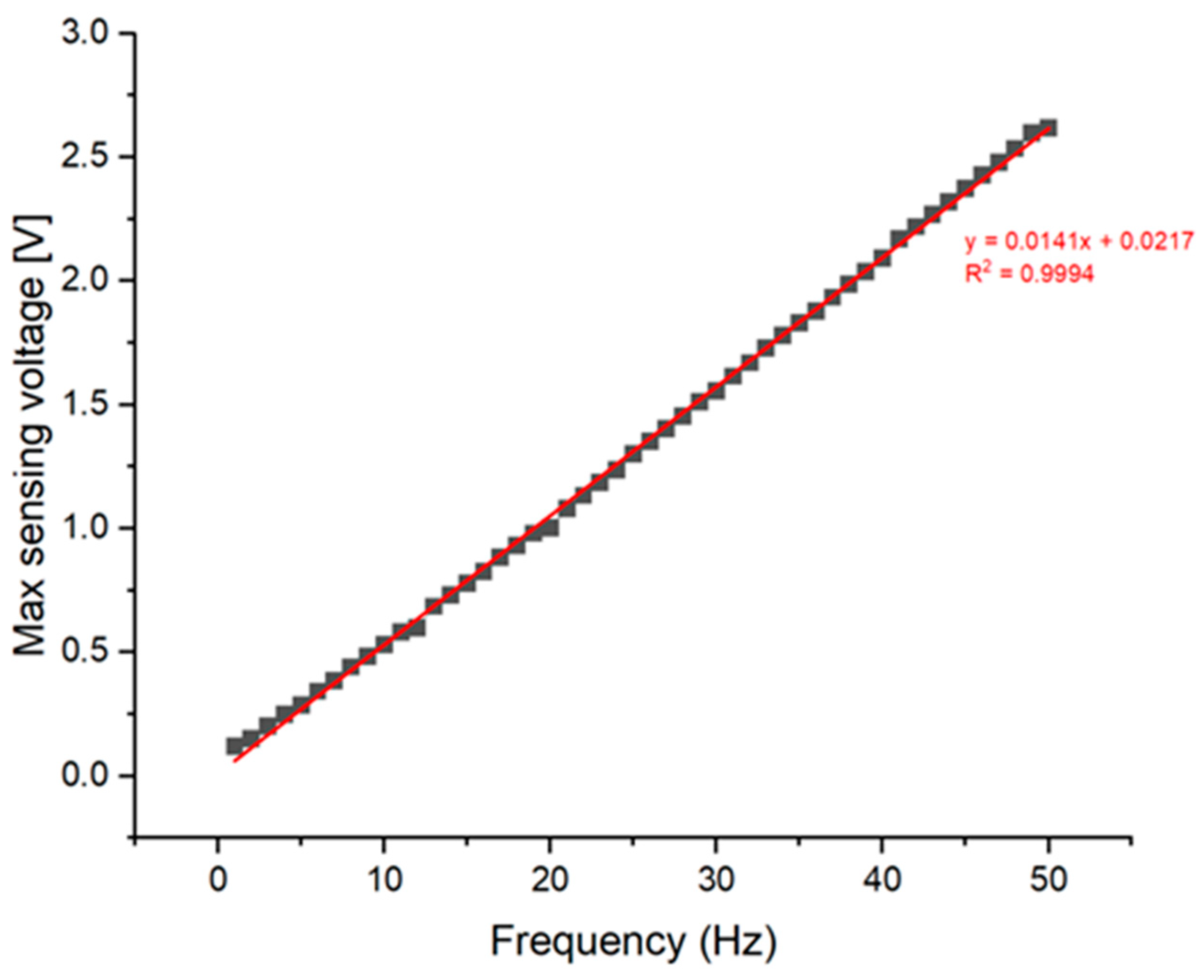
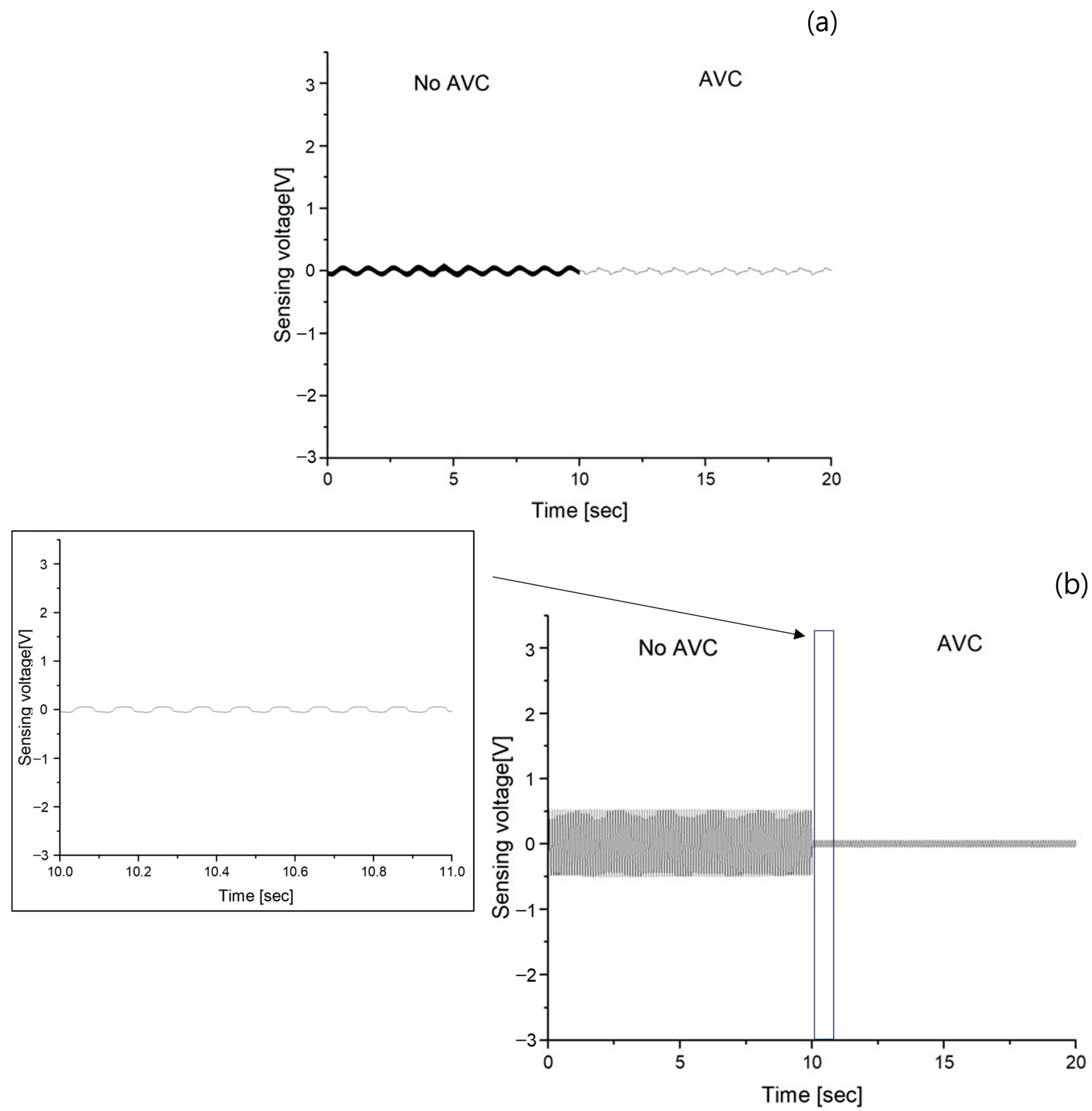
3.3. Vibration Sensing of AVC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkie, W.K.; Bryant, R.G.; High, J.W.; Fox, R.L.; Hellbaum, R.F.; Jalink, A., Jr.; Little, B.D.; Mirick, P.H. Low-cost piezocomposite actuator for structural control applications. In Proceedings of the Smart Structures and Materials 2000: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 12 June 2000; pp. 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.smart-materials.com (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- Choi, S.; Sohn, J. Chattering alleviation in vibration control of smart beam structures using piezofilm actuators: Experimental verification. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 294, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.B.; Park, G.; Inman, D.J.; Wilkie, W.K. An overview of composite actuators with piezoceramic fibers. Proc. IMAC XX 2002, 47, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.-m.; Li, H. Large deformation mechanical modeling with bilinear stiffness for Macro-Fiber Composite bimorph based on extending mixing rules. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2021, 32, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ji, H.; Qiu, J. Prediction and optimization of poling condition for PZT based-macro fiber composites with interdigitated electrodes. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 896, 163020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ji, H.; Qiu, J. The synergism of peak to peak value, frequency and superimposed DC bias voltage on electric-field-induced strain of PZT based-macro fiber composites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22067–22077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konka, H.P.; Wahab, M.A.; Lian, K. Piezoelectric fiber composite transducers for health monitoring in composite structures. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 194, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröck, J.; Meurer, T.; Kugi, A. Control of a flexible beam actuated by macro-fiber composite patches: II. Hysteresis and creep compensation, experimental results. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Jia, H.; Liu, P.; Xin, C. Fabrication and property of flexible macro fiber composites for vibration-based energy harvesting. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 14291–14301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgen, O.; Kochersberger, K.; Diggs, E.; Kurdila, A.; Inman, D. Morphing wing micro-air-vehicles via macro-fiber-composite tactuators. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2007; p. 1785. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgen, O.; Kochersberger, K.; Inman, D.J. Macro-fiber composite actuators for a swept wing unmanned aircraft. Aeronaut. J. 2009, 113, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalovs, A.; Barkanov, E.; Gluhihs, S. Active control of structures using macro-fiber composite (MFC). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 93, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, T.T.; Costantinou, M.C. Passive and Active Structural Vibration Control in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 345. [Google Scholar]
- Park, G.; Ruggiero, E.; Inman, D.J. Dynamic testing of inflatable structures using smart materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R. Recent advances in nonlinear passive vibration isolators. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 314, 371–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y. Recent development of the passive vibration control method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 29, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, S.; Johnson, F.; Pearson, J.; Dixon, R. Active vibration control for marine applications. Control Eng. Pract. 2004, 12, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.; Hubbard, J.E., Jr. Distributed piezoelectric-polymer active vibration control of a cantilever beam. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1985, 8, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, N. A comparative study and analysis of semi-active vibration-control systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 2002, 124, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.; Gupta, S. Thermal resistivity, sound absorption and vibration damping of concrete composite doped with waste tire Rubber: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, V.; Nagarajan, L.; Thomas, M.R. Evaluation of vibration damping behavior of different sizes of waste tyre rubber in natural rubber composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Liao, R.; Yuan, Y. A novel aging characterization method for silicone rubber based on terahertz absorption spectroscopy. Polym. Test. 2022, 115, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xie, Y.; Yang, J.; Kong, J. Tunable sound absorption of silicone rubber materials via mesoporous silica. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 15171–15179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-h.; Dong, Y.; Lee, M.G. Passive vibration reduction with silicone springs and dynamic absorber. Phys. Procedia 2011, 19, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhao, P.; Cheng, H.; He, Q.; Du, L. Improved low-frequency sound absorption of porous silicone rubber resonance sheet with periodic cavities. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2022, 41, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujon, M.A.S.; Islam, A.; Nadimpalli, V.K. Damping and sound absorption properties of polymer matrix composites: A review. Polym. Test. 2021, 104, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.C.; Srinivasan, P. Vibration Damping by Polymers. In Smart Polymers: Basics and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Gürgen, S.; Sofuoğlu, M.A. Smart polymer integrated cork composites for enhanced vibration damping properties. Compos. Struct. 2021, 258, 113200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, A.; Liao, J.; Han, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Guan, L. Physiological Sensing System Integrated with Vibration Sensor and Frequency Gel Dampers Inspired by Spider. Mater. Horiz. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kari, L. Are single polymer network hydrogels with chemical and physical cross-links a promising dynamic vibration absorber material? a simulation model inquiry. Materials 2020, 13, 5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodano, H.A.; Park, G.; Inman, D.J. An investigation into the performance of macro-fiber composites for sensing and structural vibration applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2004, 18, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Q.; Li, Y.-X.; Schmidt, R. Modeling and simulation of macro-fiber composite layered smart structures. Compos. Struct. 2015, 126, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Ouyang, H. Design and experimental investigation of ultra-low frequency vibration isolation during neonatal transport. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 139, 106633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouze, J.; Cheng, L. A feasibility study of active vibration isolation using THUNDER actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sohn, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, S. Active vibration control of smart hull structures using piezoelectric actuators. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2006, 220, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröck, J.; Meurer, T.; Kugi, A. Control of a flexible beam actuated by macro-fiber composite patches: I. Modeling and feedforward trajectory control. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 20, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Engineering Properties | Symbol | MFC d31 Type [2] |
|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus [GPa] | Y11 (fiber direction) | 30.3 |
| Y33 (electrode direction) | 15.9 | |
| Shear modulus [GPa] | G12 | 5.5 |
| Piezoelectric constant [pC/N or pm/V] | d31 | −0.017 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.31 | |
| 0.16 | ||
| Density [g/] | 0.544 |
| Frequency [Hz] | Vibration Ratio [V/V] | |
|---|---|---|
| AVC | Passive Gel | |
| 1 | 0.41 | 0.24 |
| 10 | 0.11 | 0.3 |
| 20 | 0.06 | 0.3 |
| 30 | 0.04 | 0.27 |
| 40 | 0.02 | 0.28 |
| 50 | 0.02 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-U.; Kim, J.-Y. Comparative Performance Analysis of Inverse Phase Active Vibration Cancellation Using Macro Fiber Composite (MFC) and Vibration Absorption of Silicone Gel for Vibration Reduction. Polymers 2023, 15, 4672. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244672
Kim S-U, Kim J-Y. Comparative Performance Analysis of Inverse Phase Active Vibration Cancellation Using Macro Fiber Composite (MFC) and Vibration Absorption of Silicone Gel for Vibration Reduction. Polymers. 2023; 15(24):4672. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244672
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sang-Un, and Joo-Yong Kim. 2023. "Comparative Performance Analysis of Inverse Phase Active Vibration Cancellation Using Macro Fiber Composite (MFC) and Vibration Absorption of Silicone Gel for Vibration Reduction" Polymers 15, no. 24: 4672. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244672
APA StyleKim, S.-U., & Kim, J.-Y. (2023). Comparative Performance Analysis of Inverse Phase Active Vibration Cancellation Using Macro Fiber Composite (MFC) and Vibration Absorption of Silicone Gel for Vibration Reduction. Polymers, 15(24), 4672. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244672







