An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent Based on Bacterial Cellulose and Vermiculite Composite for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue and Sulfanilamide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. BC Production and Purification
2.3. Preparation of BC/EVMT Composite
2.4. Characterization Methods
2.5. Removal of Sulfanilamide and MB
3. Results and Discussion
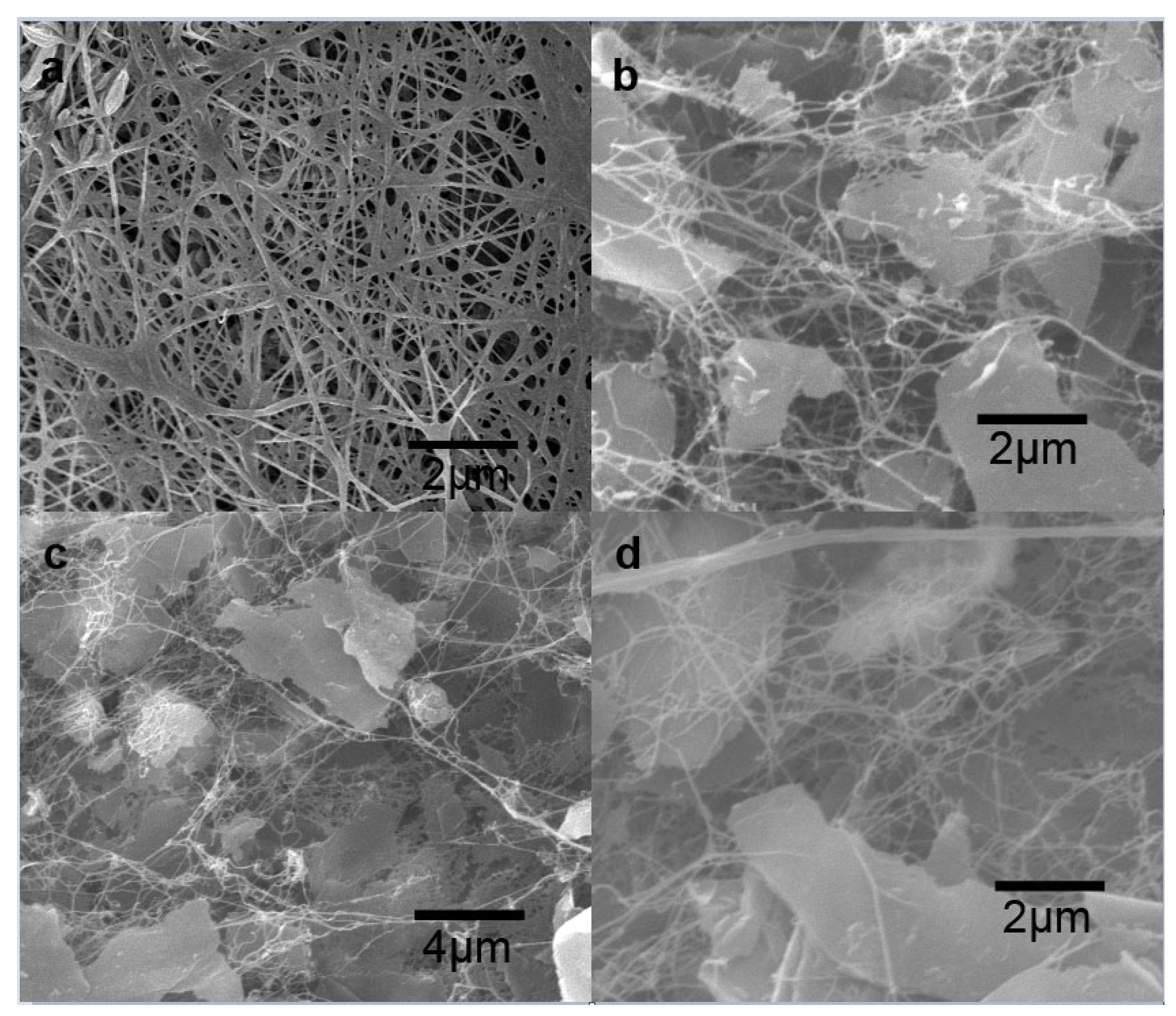
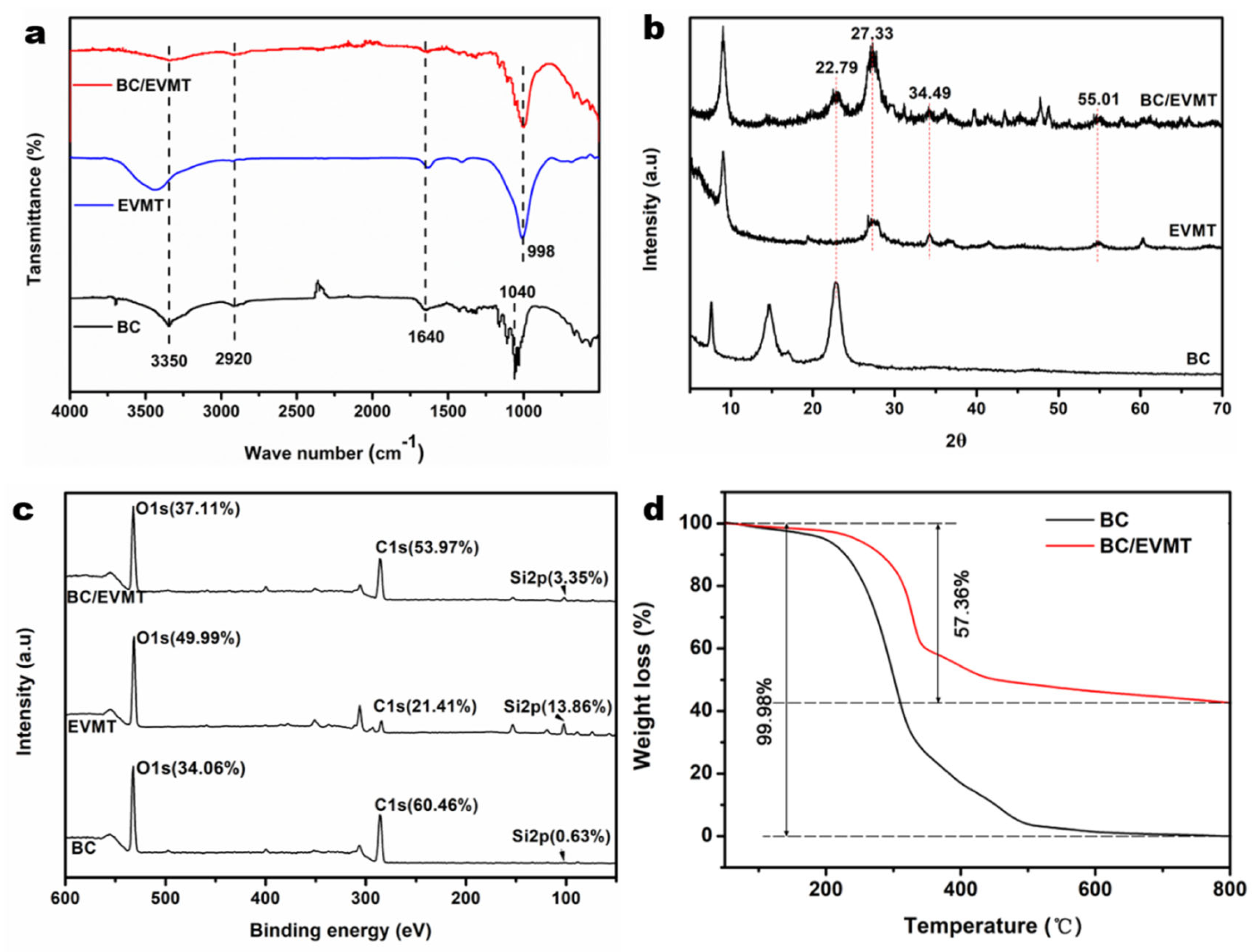
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Adsorption Performance for Dyes and Antibiotics
3.2.1. Effects of Physical and Chemical Parameters on Adsorption Effectiveness
3.2.2. Adsorption Equilibrium Isotherms
3.2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3. Comparison of BC/EVMT with Other Related Adsorbents
3.4. Application to Real Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sayinli, B.; Dong, Y.; Park, Y.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpaa, M. Recent progress and challenges facing ballast water treatment–a review. Chemosphere 2021, 291, 132776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, J.; Cao, D.; Liu, X.; Ma, M.; Zhang, L. Novel magnetic porous biochar derived from degreasing cotton as a multifunctional adsorbent for simultaneous efficient capturing and monitoring of multiple antibiotic residues. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2022, 10, 108377. [Google Scholar]
- Basaleh, A.A.; Al–Malack, M.H.; Saleh, T.A. Methylene blue removal using polyamide–vermiculite nanocomposites: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Li, N.; Hou, Z.; Huang, J.; Yue, C.; Cai, Y.; Song, J. Degradation of sulfonamide antibiotics and a structurally related compound by chlorine dioxide: Efficiency, kinetics, potential products and pathways. Chen. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charradi, K.; Ahmed, Z.; BenMoussa, M.A.; Beji, Z.; Brahmia, A.; Othman, I.; Haija, M.A.; Chtourou, R.; Keshk, S.M.A.S. A facile approach for the synthesis of spinel zinc ferrite/cellulose as an effective photocatalyst for the degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution. Cellulose 2022, 29, 2577–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L. Application of BiVO4-microalgae combined treatment to remove high concentration mixture of sulfamethazine and sulfadiazine. Water 2022, 14, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ao, Z.; Niu, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, H. Facile one-step synthesis of 3D honeycomb-like porous chitosan bead inlaid with Mn-Fe bimetallic oxide nanoparticles for enhanced degradation of dye pollutant. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, K.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L. Adsorption characteristics of sulfonamide antibiotic molecules on carbon nanotube and the effects of environment. J. Mol. Model. 2023, 29, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makofane, A.; Motaung, D.E.; Hintsho–Mbita, N.C. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and sulfisoxazole from water using biosynthesized zinc ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 22615–22626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyet, P.N.; Watari, T.; Hirakata, Y.; Hatamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T. Adsorption and biodegradation removal of methylene blue in a down-flow hanging filter reactor incorporating natural adsorbent. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, Q.; Han, R.; Guo, M.; Shi, J.; Song, C.; Ji, N.; Lu, X.; Ma, D. Potential applications of porous organic polymers as adsorbent for the adsorption of volatile organic compounds. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 105, 184–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gao, M.; Ding, F.; Shen, T. Organo–vermiculites modified by heating and gemini pyridinium surfactants: Preparation, characterization and sulfamethoxazole adsorption. Colloids Surfaces A 2018, 546, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, T.; Xue, B. Highly dispersed molybdenum–embedded polymeric carbon nitride with enhanced photocatalytic activity for degradation of dyes and antibiotics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 528, 146931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Pan, B. Bacterial cellulose derived paper-like purifier with multifunctionality for water decontamination. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.; Tian, G.; Sharma, V.K.; Zhu, Y.; Zong, L.; Wang, A. Mesoporous silicate/carbon composites derived from dye–loaded palygorskite clay waste for efficient removal of organic contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Gu, X.; Gu, C.; Luo, J.; Gao, B. MIL series of metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as novel adsorbents for heavy metals in water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Du, M.; Yin, K.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Y.; Pang, H. Applications of metal-organic frameworks in water treatment: A review. Small 2022, 18, 2105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imessaoudene, A.; Cheikh, S.; Bollinger, J.C.; Belkhiri, L.; Tiri, A.; Bouzaza, A.; Jery, A.E.; Assadi, A.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, L. Zeolite waste characterization and use as low-cost, ecofriendly, and sustainable material for malachite green and methylene blue dyes removal: Box–behnken design, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammar, A.C.; Mouni, L.; Bollinger, J.C.; Belkhiri, L.; Bouzaza, A.; Assadi, A.A.; Belkacemi, H. Modeling and optimization of process parameters in elucidating the adsorption mechanism of Gallic acid on activated carbon prepared from date stones. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchelkia, N.; Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Belkacemi, H.; Bollinger, J.C.; Bouzaza, A.; Zoukel, A.; Zhang, J.; Mouni, L. Jujube stones based highly efficient activated carbon for methylene blue adsorption: Kinetics and isotherms modeling, thermodynamics and mechanism study, optimization via response surface methodology and machine learning approaches. Process Saf. Environ. 2023, 170, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imessaoudene, A.; Cheikh, S.; Hadadi, A.; Hamri, N.; Bollinger, J.C.; Amrane, A.; Tahraoui, H.; Manseri, A.; Mouni, L. Adsorption performance of zeolite for the removal of congo red dye: Factorial design experiments, kinetic, and equilibrium studies. Separations 2023, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Christodoulou, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Basic dye removal with sorption onto low-cost natural textile fibers. Processes 2018, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z. Multifunctional adsorbent based on metal-organic framework modified bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for high efficient removal of heavy metal ion and organic pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F. In-situ fabrication of dynamic and recyclable TiO2 coated bacterial cellulose membranes as an efficient hybrid absorbent for tellurium extraction. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4591–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, W.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Bacterial cellulose nanofibrous ion imprinted aerogel for highly efficient recognition and adsorption of Dy (III). Process Saf. Environ. 2022, 160, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabane, L.; Chahdoura, H.; Mehdaoui, R.; Snoussi, M.; Beyou, E.; Lahcini, M.; Baouab, M.H.V. Functionalization of developed bacterial cellulose with magnetite nanoparticles for nanobiotechnology and nanomedicine applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 247, 116707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, D. Biointerface by cell growth on graphene oxide doped bacterial cellulose/poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 10183–10192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, M.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in composites based on cellulose derivatives for biomedical applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 247, 116683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. Functionalized bacterial cellulose derivatives and nanocomposites. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 101, 1043–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, L.; Cui, J.; Hao, Q.; Sun, D. Handy purifier based on bacterial cellulose and Ca- montmorillonite composites for efficient removal of dyes and antibiotics. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 222, 115017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, V.A.; Pârvulescu, O.C.; Dobre, T. Volatile organic compounds adsorption onto neat and hybrid bacterial cellulose. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 335, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, C.; Ding, L.; Yang, S. Synthesis and adsorption properties of novel bacterial cellulose/graphene oxide/attapulgite materials for Cu and Pb ions in aqueous solutions. Materials 2020, 13, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ai, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, T.; Song, S. Preparation and application of expanded and exfoliated vermiculite: A critical review. Chem. Phys. 2021, 550, 111313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Kim, S.K.; Song, W.; Myung, S.; Lim, J.; Jung, H.K.; An, K.S.; Lee, S.S. An eco-friendly cellulose acetate chemical sorbent for hazardous volatile organic liquid spill: A perfect material to solve the issue of evaporating hazards. Cellulose 2019, 26, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Huang, S.; Liu, B. Enhanced removal of ammonia nitrogen from rare earth wastewater by NaCl modified vermiculite: Performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivadeneira-Mendoza, B.F.; Estrela, O.A.; Fernandez-Andrade, K.J.; Curbelo, F.; Silva, F.F.; Luque, R.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.M. MOF@biomass hybrids: Trends on advanced functional materials for adsorption. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yan, D.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Miao, X. Research progress of graphene for the adsorption, enrichment and analysis of environmental pollutants. B. Mater. Sci. 2023, 46, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Gao, Z.; Zheng, M.; Sun, J. Flame retardant medium-density fiberboard with expanded vermiculite. Bioresources 2016, 11, 6940–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, F.; Cay, V.V. The effect of natural resin on thermo-physical properties of expanded vermiculite-cement composites. Int. J. Thermophys. 2020, 41, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenol, Z.M.; Gürsoy, N.; Şimşek, S.; Özer, A.; Karakuş, N. Removal of food dyes from aqueous solution by chitosan vermiculite beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, L.; Dong, W.; Chen, C.; Sun, D. Bacterial cellulose/attapulgite magnetic composites as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions and dye treatment. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 229, 115512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chang, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, B.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Shi, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, X. Facile synthesis of Vulcan XC-72 nanoparticles-decorated halloysite nanotubes for the highly sensitive electrochemical determination of niclosamide. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhu, G.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, R.; Komarneni, S. 3D interconnected honeycomb-like ginkgo nut-derived porous carbon decorated with β-cyclodextrin for ultrasensitive detection of methyl parathion. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 2023, 380, 133309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, M.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ran, Q.; Nie, F.; Dubovyk, V. Fabrication of gallic acid electrochemical sensor based on interconnected Super-P carbon black@mesoporous silica nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. J Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 2100–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, P.; Su, H.; Qian, H.; Ma, H. One-step fabrication of superhydrophobic sponge with magneticcontrollable and flame-retardancy for oil removing and collecting. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, e49353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-Islam, M.; Khan, T.; Park, J.K. Nanoreinforced bacterial cellulose-montmorillonite composites for biomedical applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 89, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Zong, L.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. Mesoporous polymetallic silicate derived from naturally abundant mixed clay: A potential robust adsorbent for removal of cationic dye and antibiotic. Powder Technol. 2021, 390, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C.S.; Gunjal, D.B.; Naik, V.M.; Jagadale, S.D.; Kadam, A.N.; Patil, P.S.; Kolekar, G.B.; Gore, A.H. Waste tea residue as a low cost adsorbent for removal of hydralazine hydrochloride pharmaceutical pollutant from aqueous media: An environmental remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Ying, Z.; Huo, M.; Yang, W. Effective column adsorption of triclosan from pure water and wastewater treatment plant effluent by using magnetic porous reduced graphene oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Wu, P. Individual and simultaneous adsorption of tetracycline and cadmium by dodecyl dimethyl betaine modified vermiculite. Colloid Surface A 2020, 602, 125171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, Y.; Tufan, G.; Kaya, A.U. Immobilisation of cellulase on vermiculite and the effects on enzymatic kinetics and thermodynamics. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2020, 197, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, W.; Khan, T.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khan, R.; Hussain, Z.; Khalid, A. Development of modified montmorillonite- bacterial cellulose nanocomposites as a novel substitute for burn skin and tissue regeneration. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 206, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Moreno, S.; Molina, R. Characterization of vermiculite by XRD and spectroscopic techniques. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2009, 13, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Huang, C.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Chen, X.; Xiong, L.; Chen, X. Bacterial cellulose based superabsorbent production: A promising example for high value-added utilization of clay and biology resources. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 208, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdino, C.J.S.; Maia, A.D.M.; Meira, H.M.; Souza, T.C.; Amorim, J.D.P.; Almeid, F.C.G.; Costa, A.F.S.; Sarubbo, L.A. Use of a bacterial cellulose filter for the removal of oil from wastewater. Process Biochem. 2020, 91, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Ding, J. Adsorption behavior of magnetic amino-functionalized metal-organic framework for cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48884–48895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabkhani, P.; Asfaram, A. Development of a novel three-dimensional magnetic polymer aerogel as an efficientadsorbent for malachite green removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, X.; Wei, X.; Tang, L.; Wei, S. Metal-ion-imprinted thermo-responsive materials obtained from bacterial cellulose: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption evaluation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11742–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, P.; Yu, L.; Li, L.; Gong, B.; Zhu, N.; Dang, Z.; Yang, C. Preparation and characterization of organo- vermiculite based on phosphatidylcholine and adsorption of two typical antibiotics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 137, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Saha, N.; Saha, T.; Saha, P. Gellan gum/bacterial cellulose hydrogel crosslinked with citric acid as an eco-friendly green adsorbent for safranin and crystal violet dye removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, M.M.H.; Jhung, S.H. Pore creation nanoarchitectonics from non-porous metal-organic framework to porous carbon for adsorptive elimination of sulfanilamide and chloroxylenol from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

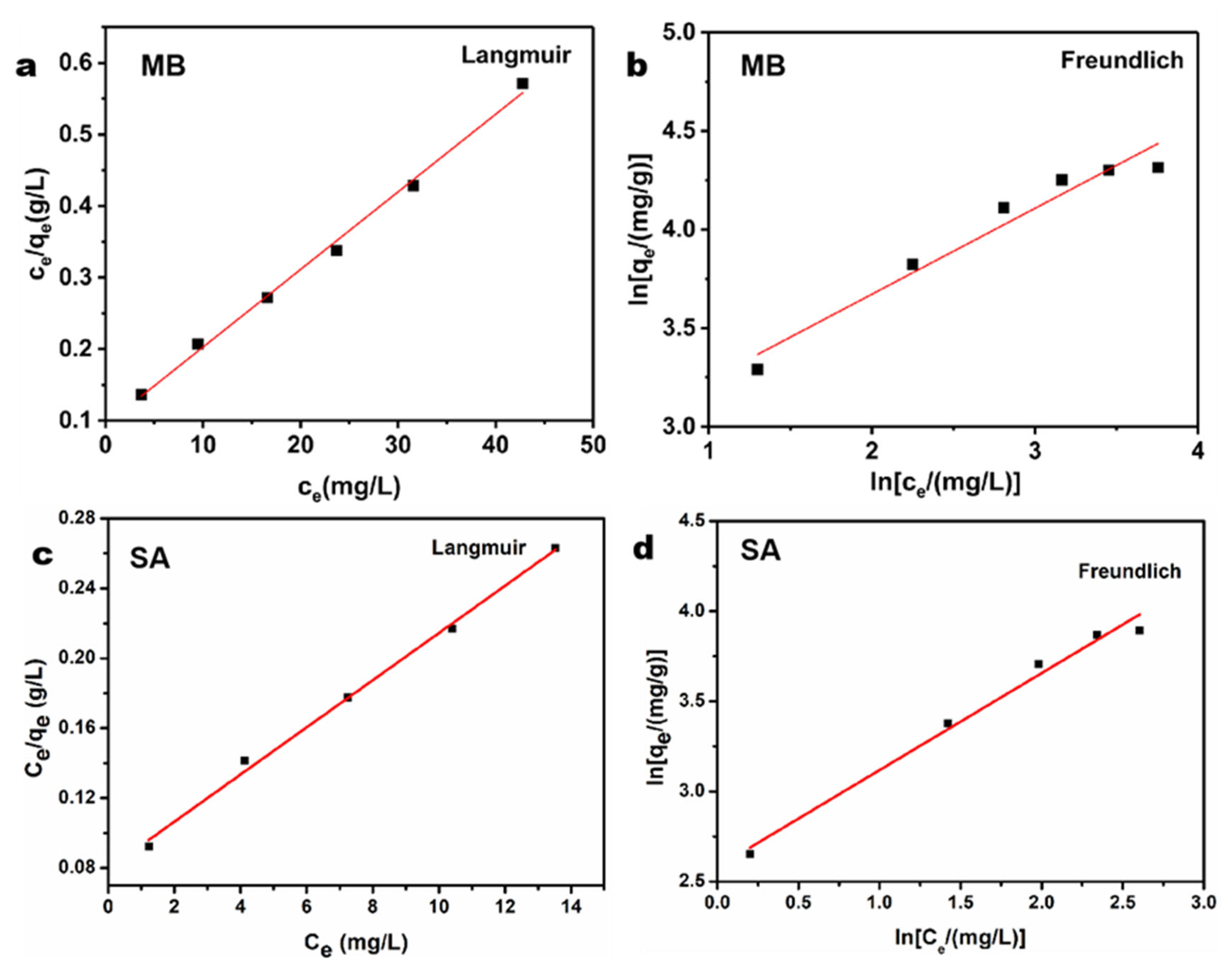

| Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | n | KF (L/g) | R2 | |
| MB | 92.16 | 0.1151 | 0.9945 | 2.29 | 16.46 | 0.9455 |
| SA | 71.53 | 0.1862 | 0.9954 | 1.8437 | 13.17 | 0.9814 |
| C0 (mg/L) | qe,exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe,cal (mg/g) | R2 | k2 × 103 (g/ (mg min)) | qe,cal (mg/g) | R2 | |||
| MB | 60 | 77.65 | 0.06081 | 100.7 | 0.8470 | 1.1244 | 85.03 | 0.9973 |
| SA | 60 | 73.37 | 0.1373 | 25.18 | 0.9738 | 12.8847 | 75.07 | 0.9997 |
| Adsorbents | Adsorbates | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyamide–Vermiculite | MB | 76.42 | 99 | [3] |
| Phosphatidylcholine–Vermiculite | oxytetracycline | 66.40 | 77 | [59] |
| ciprofloxacin | 93.72 | 96 | ||
| Gellan gum/bacterial cellulose | safranin | 17.57 | 66 | [60] |
| crystal violet dye | 13.49 | 28.5 | ||
| MOF-derived carbons | SA | 256 | not calculated | [61] |
| chloroxylenol | 588 | not calculated | ||
| BC/EVMT composite | MB | 92.16 | 72.7 | Present work |
| SA | 71.53 | 68.7 |
| Real Samples | Qe (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| MB | SA | |
| Tap water | 70.25 | 48.33 |
| River water | 68.23 | 47.18 |
| Lake water | 67.45 | 45.77 |
| Mineral water | 65.11 | 47.21 |
| Treatment plant effluent | 60.39 | 41.91 |
| Individual MB or SA in pure water | 71.32 | 50.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Su, T. An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent Based on Bacterial Cellulose and Vermiculite Composite for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue and Sulfanilamide. Polymers 2023, 15, 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102342
Bai X, Liu Z, Liu P, Zhang Y, Hu L, Su T. An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent Based on Bacterial Cellulose and Vermiculite Composite for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue and Sulfanilamide. Polymers. 2023; 15(10):2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102342
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Xiuzhi, Zhongxiang Liu, Pengfei Liu, Yijun Zhang, Linfeng Hu, and Tongchao Su. 2023. "An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent Based on Bacterial Cellulose and Vermiculite Composite for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue and Sulfanilamide" Polymers 15, no. 10: 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102342
APA StyleBai, X., Liu, Z., Liu, P., Zhang, Y., Hu, L., & Su, T. (2023). An Eco-Friendly Adsorbent Based on Bacterial Cellulose and Vermiculite Composite for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue and Sulfanilamide. Polymers, 15(10), 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102342






