Analysis of the Impact of Electrochemical Properties of Copper-Doped Electrode Membranes on the Output Force of Biomimetic Artificial Muscles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
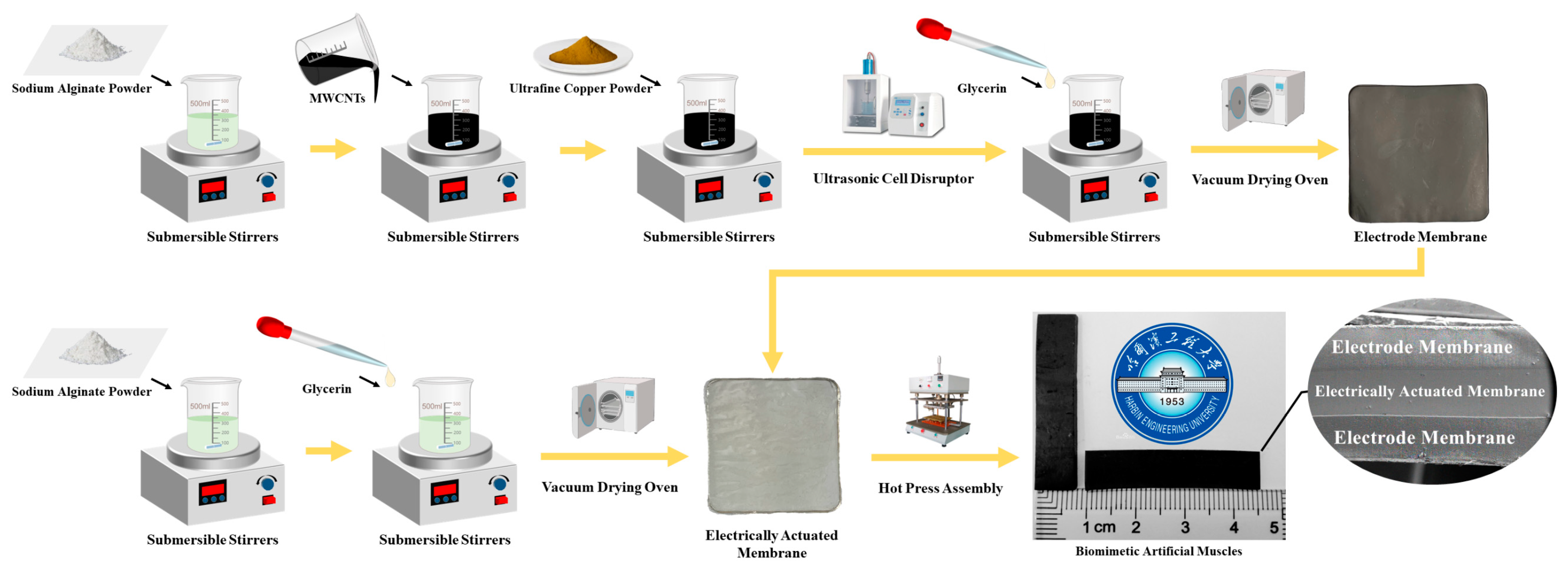
2.2. Preparation of BMAMs
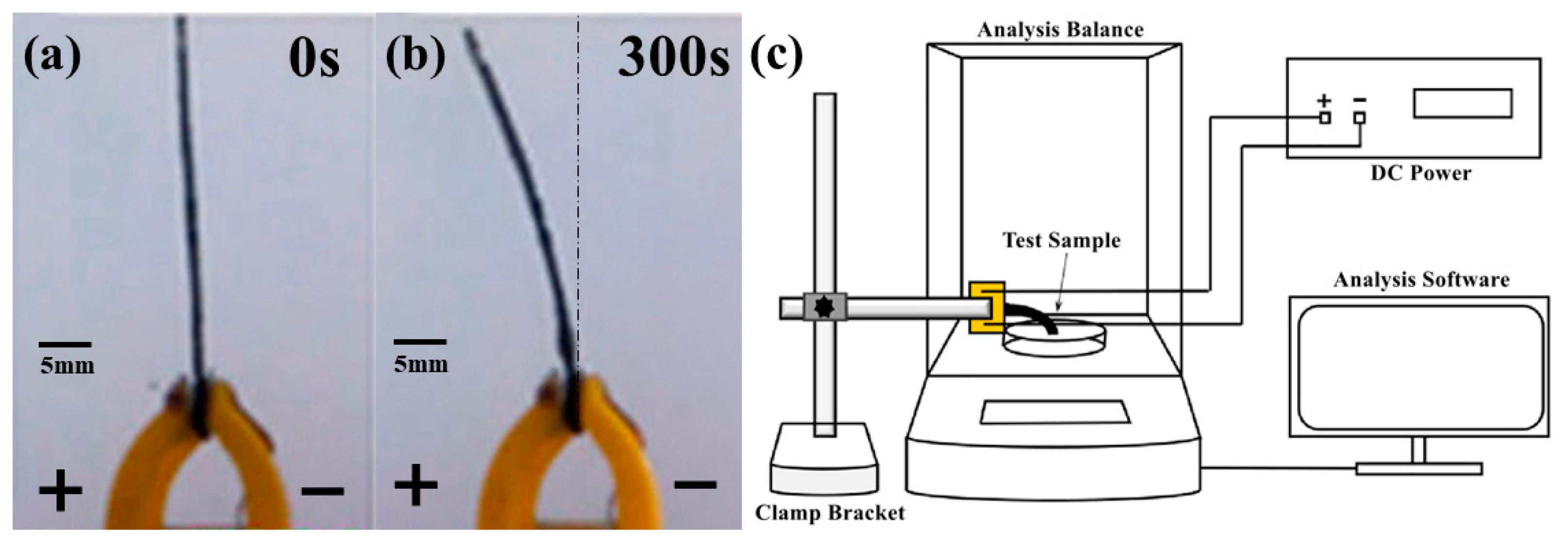
2.3. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
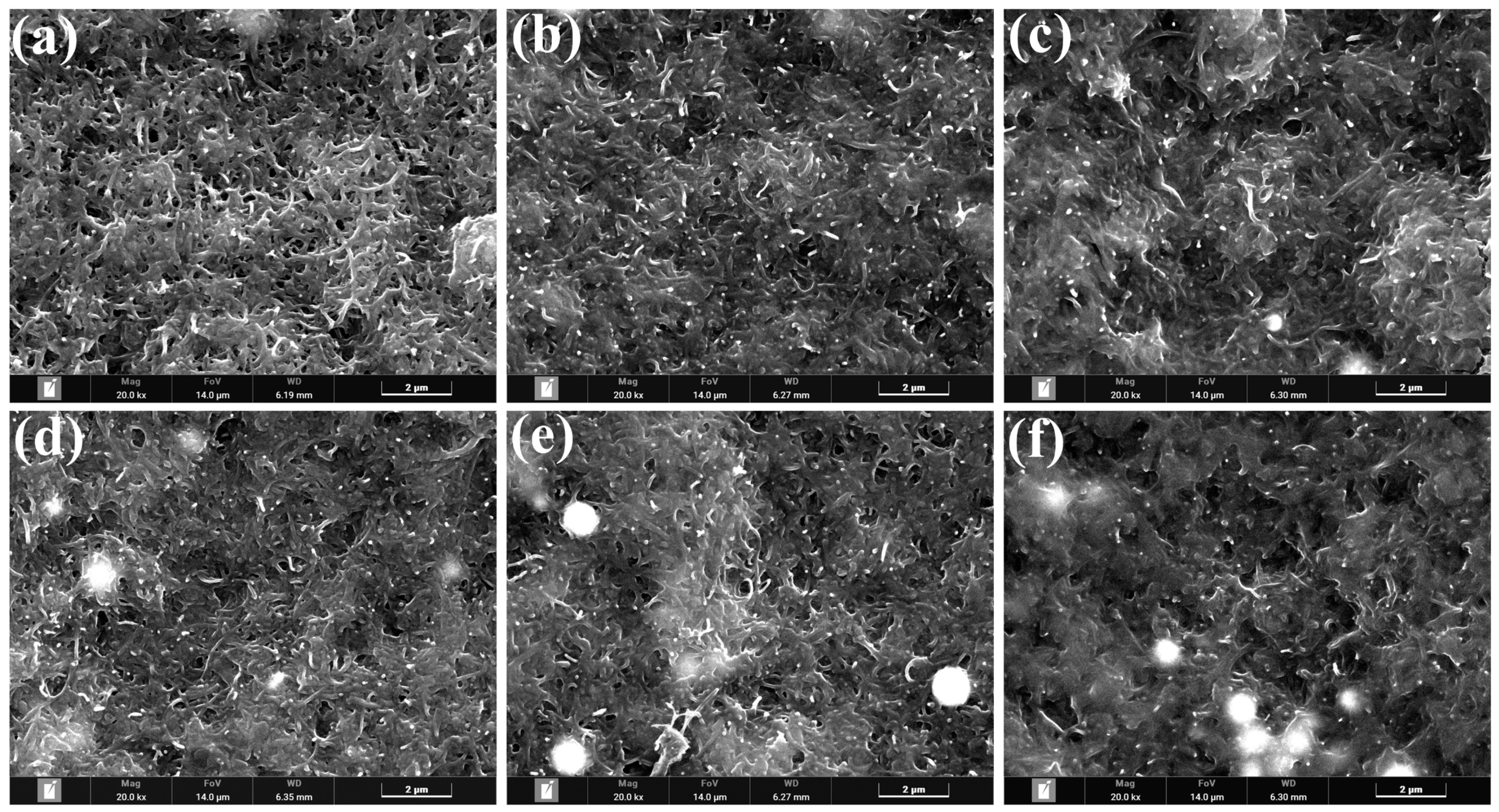
3.1. Analysis of FIB-SEM Results
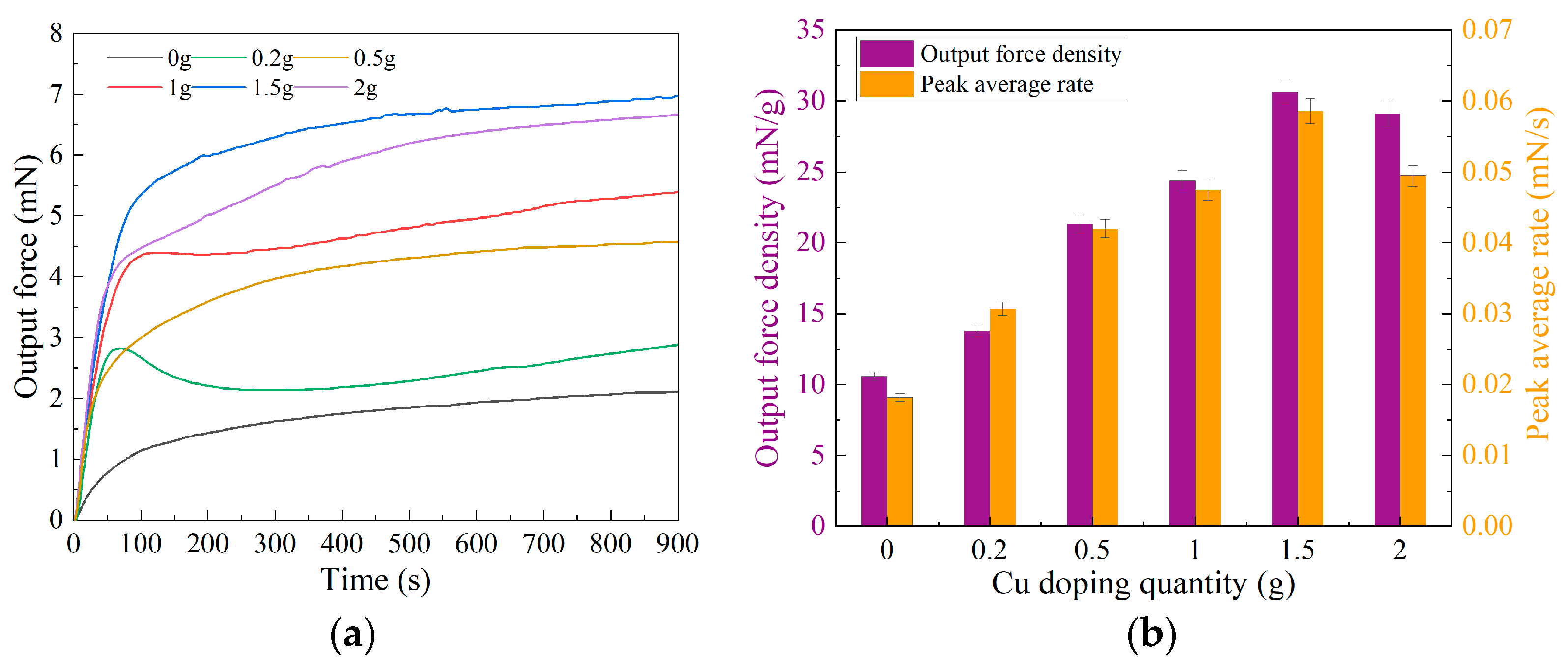
3.2. Analysis of Output Force Testing Results
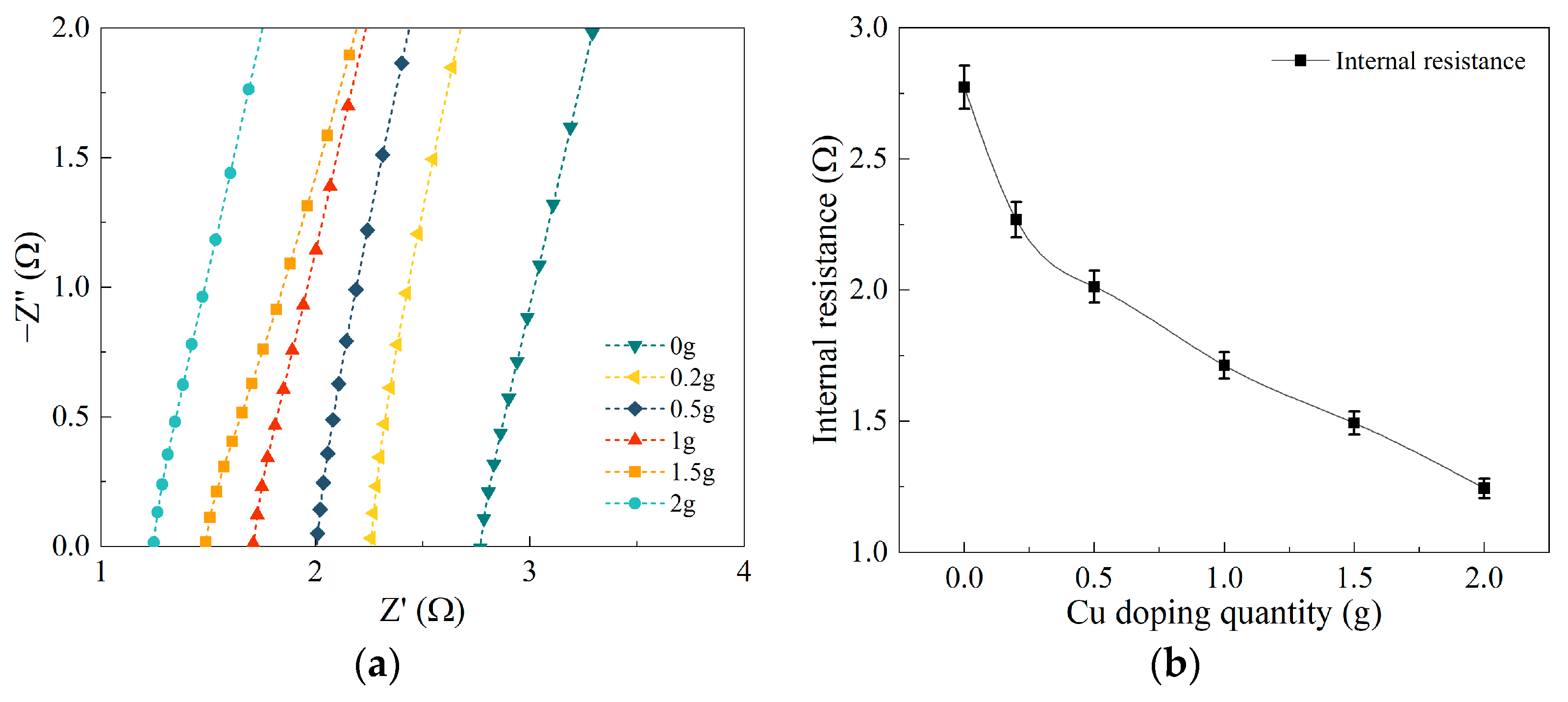
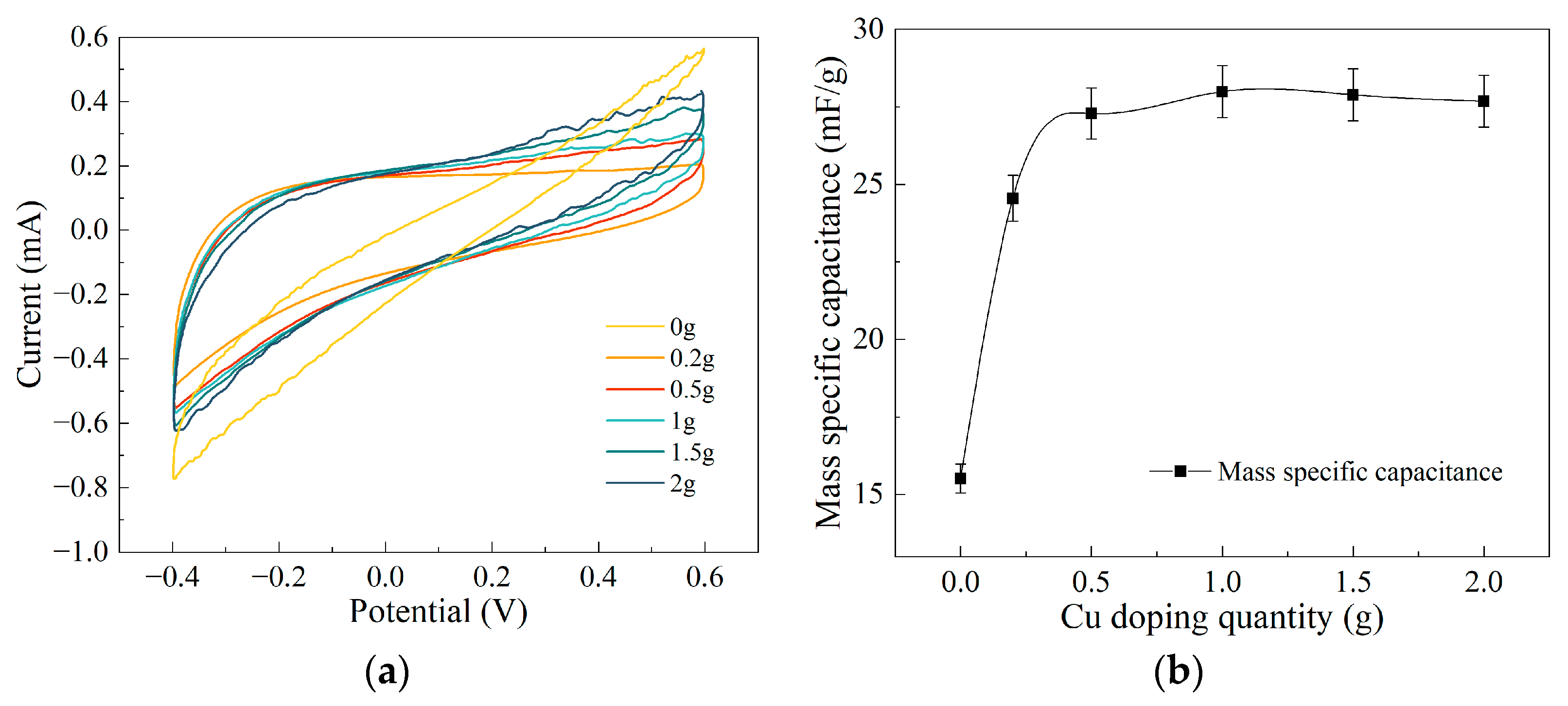
3.3. Analysis of Electrochemical Testing Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bashir, M.; Rajendran, P. A review on electroactive polymers development for aerospace applications. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 3681–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, S. Electromechanical response performance of a reinforced biomass gel artificial muscle based on natural polysaccharide of sodium alginate doped with an ionic liquid for micro-nano regulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liman, M.L.R.; Islam, M.T.; Hossain, M.M. Mapping the Progress in Flexible Electrodes for Wearable Electronic Textiles: Materials, Durability, and Applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 8, 2100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Qian, C.; Liang, Y. A review of shape memory alloy artificial muscles in bionic applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, L.; Cao, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, S.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yuan, N.; Ding, J. Monodomain liquid crystal elastomer bionic muscle fibers with excellent mechanical and actuation properties. iScience 2023, 26, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiang, C.X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhong, W.B.; Li, M.F.; Yan, K.L.; Wang, D. Multistimulus Responsive Actuator with GO and Carbon Nanotube/PDMS Bilayer Structure for Flexible and Smart Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27215–27223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.D.; Shi, Q.; Liang, Y. Electroactive dielectric polymer gels as new-generation soft actuators: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 14943–14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Farajollahi, M.; Choi, Y.S.; Lin, I.T.; Marshall, J.E.; Thompson, N.M.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Madden, J.D.W.; Smoukov, S.K. Electroactive polymers for sensing. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20160026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, A.F.; Pinho, A.C.; Piedade, A.P. Electroactive Polymers Obtained by Conventional and Non-Conventional Technologies. Polymers 2021, 13, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.Q.; Hu, S.T.; Zhou, Y.X.; Ren, X.L.; Huo, X.Q.; Yin, J.X.; Wu, Z.Y. A Magnetically Actuated Miniature Robotic Fish with the Flexible Tail Fin. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 6099–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Han, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z. A highly flexible and stretchable ionic artificial muscle. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, J.; Yu, J. Interpenetrating PAA-PEDOT conductive hydrogels for flexible skin sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 11794–11800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Bosom, S.; Karam, N.; Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Gurke, J.; Casado, N.; Tomé, L.C.; Mecerreyes, D.; Malliaras, G.G. Conducting Polymer-Ionic Liquid Electrode Arrays for High-Density Surface Electromyography. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Li, L.L.; Liu, E.P.; Wang, J.J.; Han, X.; Cao, Y.P.; Lu, C.H. High-Performance Multiresponsive Bilayer Actuators Based on Micro-/Nanostructured Polypyrrole for Robust Smart Devices. Acs Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 5349–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Untethered artificial muscles powered by wearable sweat-based energy generator. Nano Today 2023, 49, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, G.; Pan, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, T.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Soil washing remediation of heavy metal from contaminated soil with EDTMP and PAA: Properties, optimization, and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, J.; Ma, Y. A highly flexible, renewable and green alginate polymer for electroactive biological gel paper actuators reinforced with a double-side casting approach. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3647–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanushali, H.; Amrutkar, S.; Mestry, S.; Mhaske, S.T. Shape memory polymer nanocomposite: A review on structure–property relationship. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 3437–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Rafique, I.; Muhammad, B. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding of Polymer/Nanodiamond, Polymer/Carbon Nanotube, and Polymer/Nanodiamond-Carbon Nanotube Nanobifiller Composite: A Review. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wen, X.; Ma, X.; Cui, Z. Study on the actuation characteristics of a graphene oxide-modified biological gel electroactive actuator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, L.; Azócar, M.; Kogan, M.; Riveros, A.; Páez, M. Copper-polymer nanocomposites: An excellent and cost-effective biocide for use on antibacterial surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, R.M.; Sekiguchi, A.; Sekiya, M.; Yamada, T.; Hata, K. Copper/carbon nanotube composites: Research trends and outlook. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, P.K.; Wan, M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, V.; Yadav, R.R. Enhanced dielectric response and thermal conduction in copper nanoparticles embedded polyaniline nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 249, 114407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.L.; Tay, M.F.; Lee, J.M.; Ho, J.S.; Sim, L.N.; Yeong, W.Y.; Chong, T.H. Potential of Printed Electrodes for Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Toward Membrane Fouling Detection. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, G. Bioinspired Artificial Muscles Based on Sodium Alginate-Wrapped Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Molybdenum Disulfide Composite Electrode Membrane. Polymers 2023, 15, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, J.; Guan, S. Enhanced electroresponsive and electrochemical properties of the biological gel artificial muscle prepared by sodium alginate and carboxylated chitosan. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
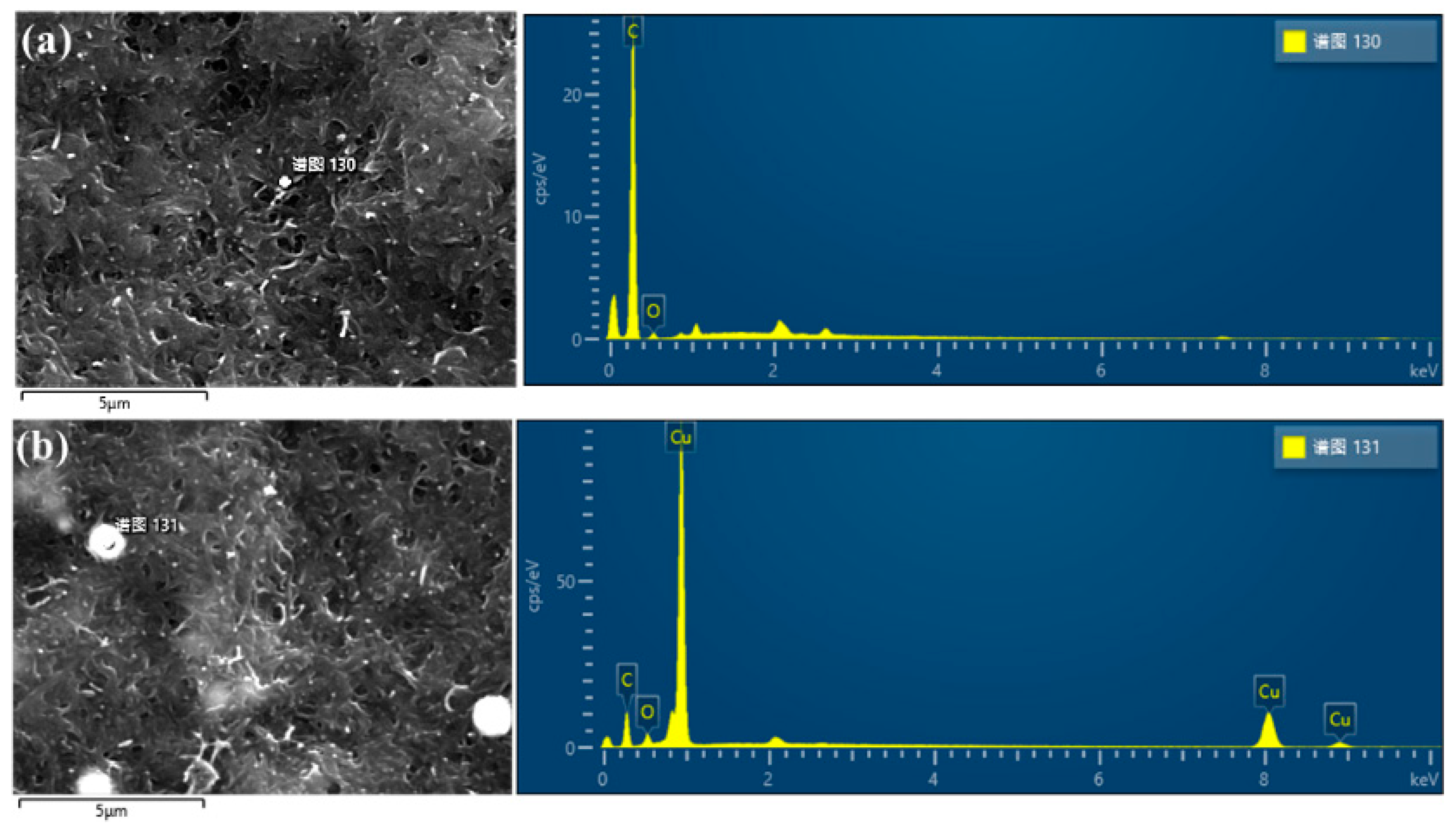
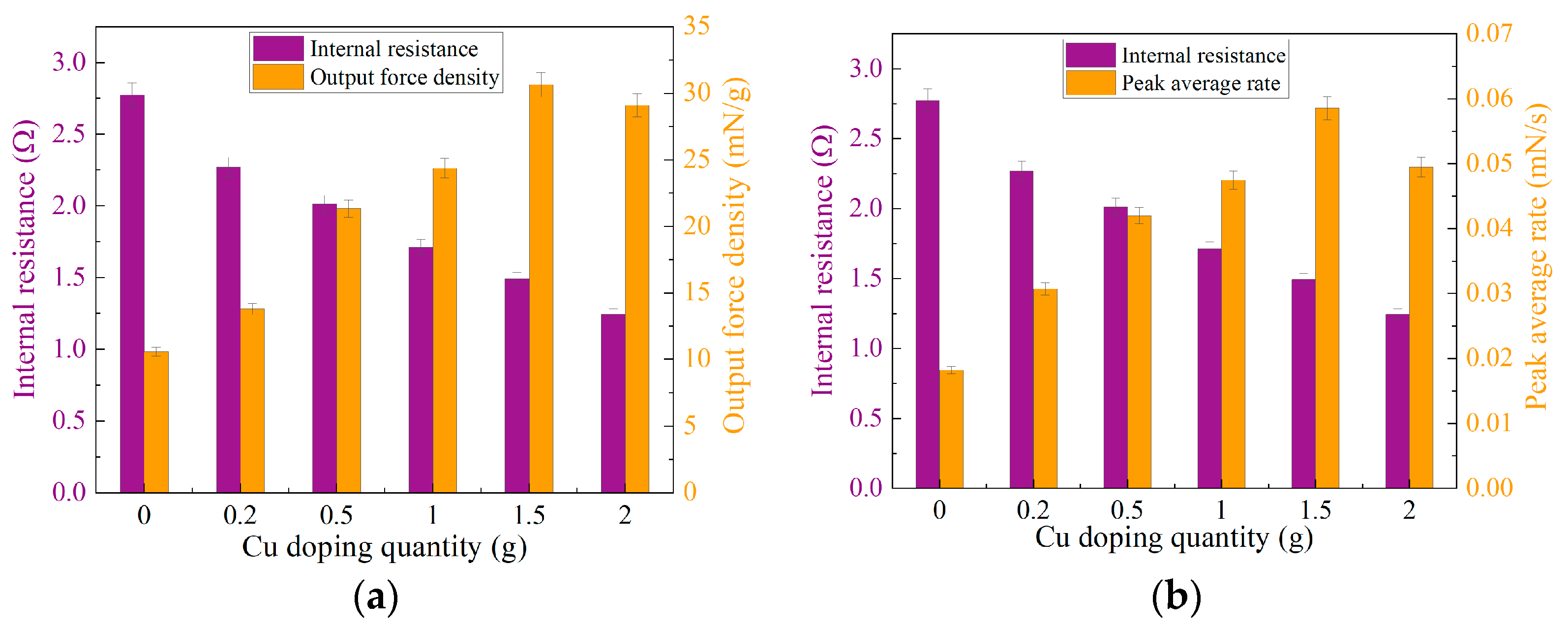
| Element | Position 1 | Position 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass (%) | Atomicity (%) | Mass (%) | Atomicity (%) | |
| C | 96.7 | 97.02 | 40.99 | 75.75 |
| O | 3.93 | 2.98 | 3.51 | 4.86 |
| Cu | 0 | 0 | 55.50 | 19.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, G. Analysis of the Impact of Electrochemical Properties of Copper-Doped Electrode Membranes on the Output Force of Biomimetic Artificial Muscles. Polymers 2023, 15, 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214214
Ji Y, Wang K, Zhao G. Analysis of the Impact of Electrochemical Properties of Copper-Doped Electrode Membranes on the Output Force of Biomimetic Artificial Muscles. Polymers. 2023; 15(21):4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214214
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Yingxin, Keyi Wang, and Gang Zhao. 2023. "Analysis of the Impact of Electrochemical Properties of Copper-Doped Electrode Membranes on the Output Force of Biomimetic Artificial Muscles" Polymers 15, no. 21: 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214214
APA StyleJi, Y., Wang, K., & Zhao, G. (2023). Analysis of the Impact of Electrochemical Properties of Copper-Doped Electrode Membranes on the Output Force of Biomimetic Artificial Muscles. Polymers, 15(21), 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15214214






