A Brief Overview on Epoxies in Electronics: Properties, Applications, and Modifications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Properties of Epoxy Resins
- Excellent dielectric/electrical insulating properties;
- Ultra-high water resistance;
- Chemical resistance (resistance to a number of aggressive chemicals, alkalis, acids, salts, solvents);
- High mechanical properties (ideal tensile strength, wear resistance, hardness, impact resistance);
- The highest adhesion (high-quality glue connection);
- Low shrinkage during curing (minor deformations);
- High stability;
- Increased heat resistance (withstands temperatures up to 150–200 °C. High coefficient of thermal conductivity);
- The absence of volatile products and the release of side substances during curing;
- A low coefficient of shrinkage in the course of hardening;
- Minimum creep under load;
- Low odor;
- Ease of production and versatility of processing processes;
- Small weight of the finished product;
- Durability and shelf life;
- Environmental friendliness;
- Safety.
1.2. Applications of Epoxy Resins
- Radio, electrical industry, electronics, and microelectronics (chip assembly and printed circuit board assembly, which is an epoxy–fiberglass composite);
- The rocket and space industry;
- The energy industry;
- The engineering industry (production of components);
- Construction (paints and varnishes for interior and exterior decoration of buildings; polishes; the production of durable impregnations and structural materials (PCM); sealants; adhesives; the waterproofing of floors, walls of basements, and swimming pools; the impregnation of concrete, brick, wood, and mortar; the successful replacement of bitumen—bitumen–epoxy composition);
- The textile and leather industries;
- The furniture industry (designer furniture);
- Arts and crafts (the production of unique costume jewelry; the production of artificial amber; models; crafts; dioramas; and in bench modeling);
- The domestic sphere and household (home decor; bar counters).
- Printed circuit boards (PCBs): epoxy resin is used as a substrate material for printed circuit boards, providing insulation between board layers and protecting components from environmental influences;
- Sealing: epoxy resin is used to seal electronic components, protecting them from environmental influences such as moisture and dust;
- Adhesives: epoxy resin is used as an adhesive in the production of electronic components, and is a sensitive strong bond between components and substrates;
- Coatings: epoxy resin is used as a coating material for electronic components, providing protection against moisture, chemical compounds, and abrasion.
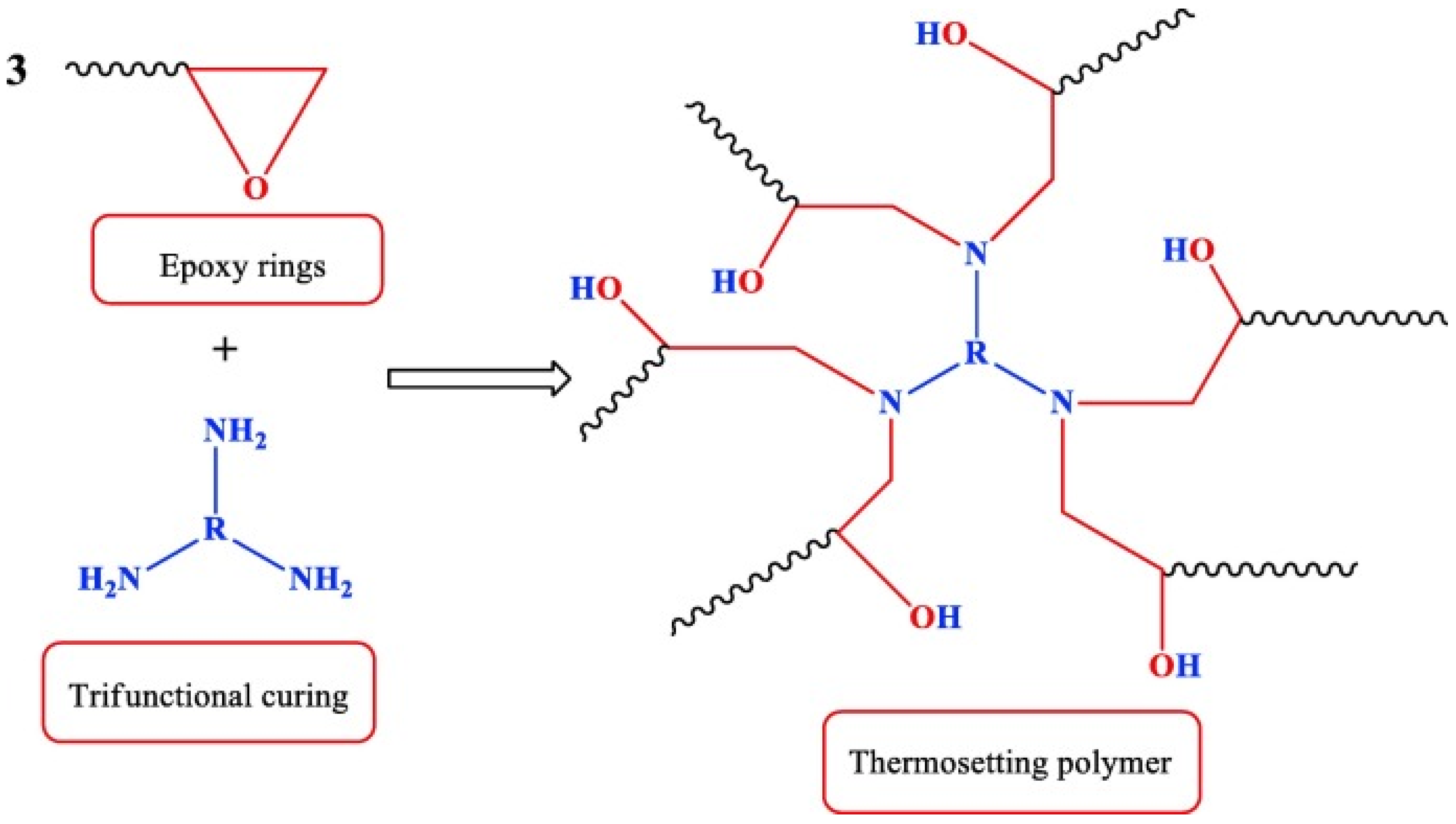
1.3. Curing and Modification of Epoxy Resins
- Vacuum impregnation: this involves placing the electronic component within a vacuum chamber, where epoxy resin is drawn into the component under vacuum pressure;
- Pouring: in this method, an electronic component is situated in a mold and epoxy resin is poured over it, effectively sealing the component;
- Dispensing: epoxy is administered onto an electronic component using a dispensing machine;
- Spray coating: here, epoxy resin is applied onto an electronic component via a spray gun.
- High adhesion to the surface of the material on which they harden;
- High dielectric properties;
- High mechanical strength;
- Good chemical resistance and water resistance;
- Hardening does not emit volatile products and are characterized by low shrinkage (2–2.5%) [40].
1.4. Dielectric Analysis
2. Experimental Data on Modified ERs and Their Properties
2.1. Dielectric Strength Distribution in Modified ER
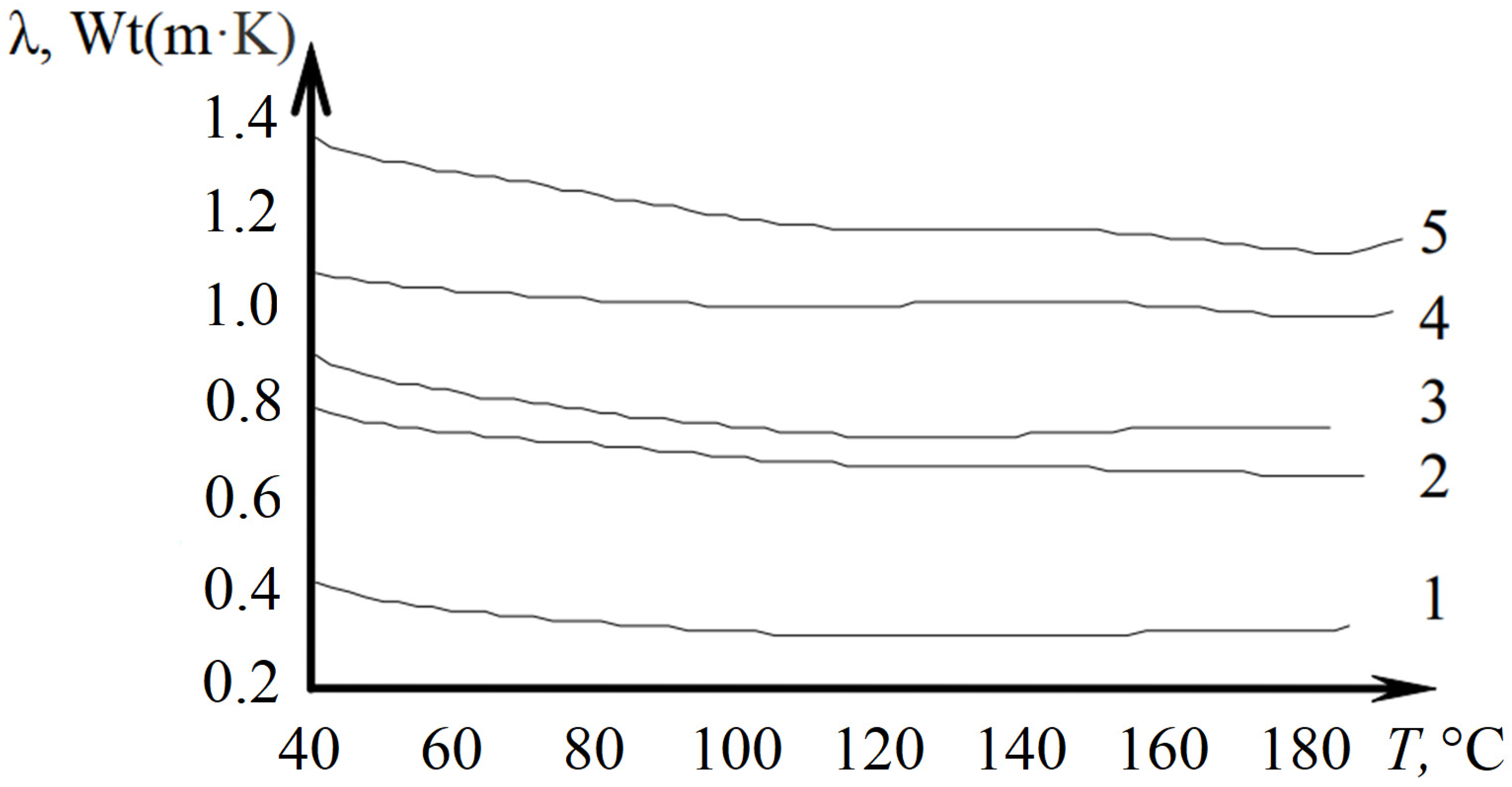
2.2. Thermal Conductivity
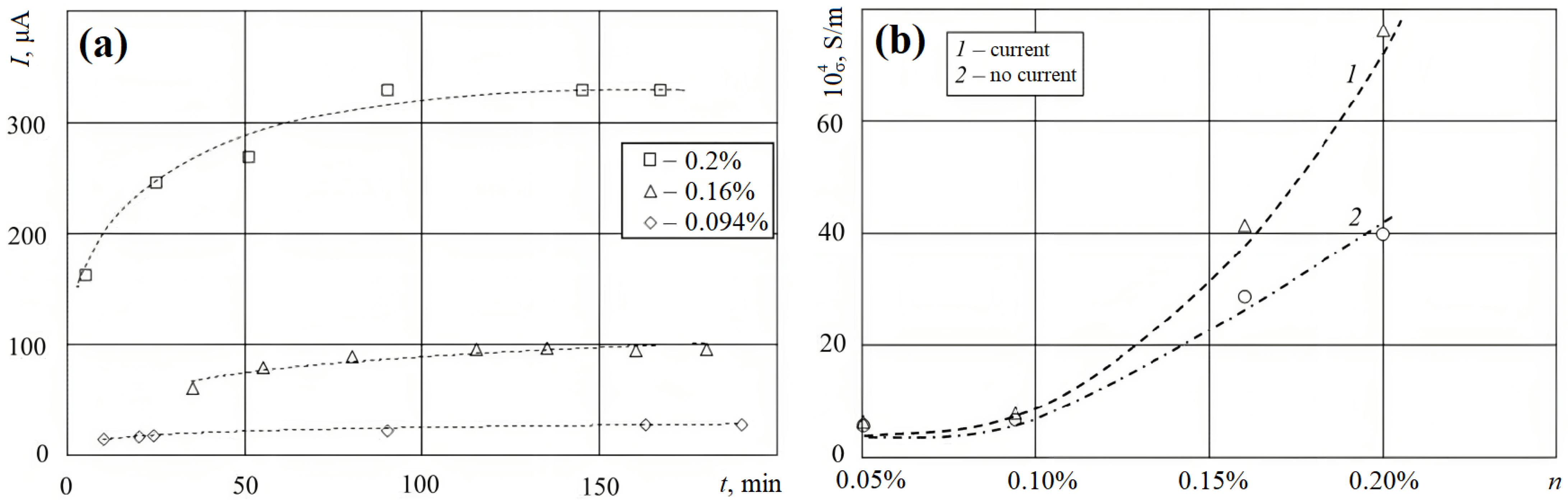
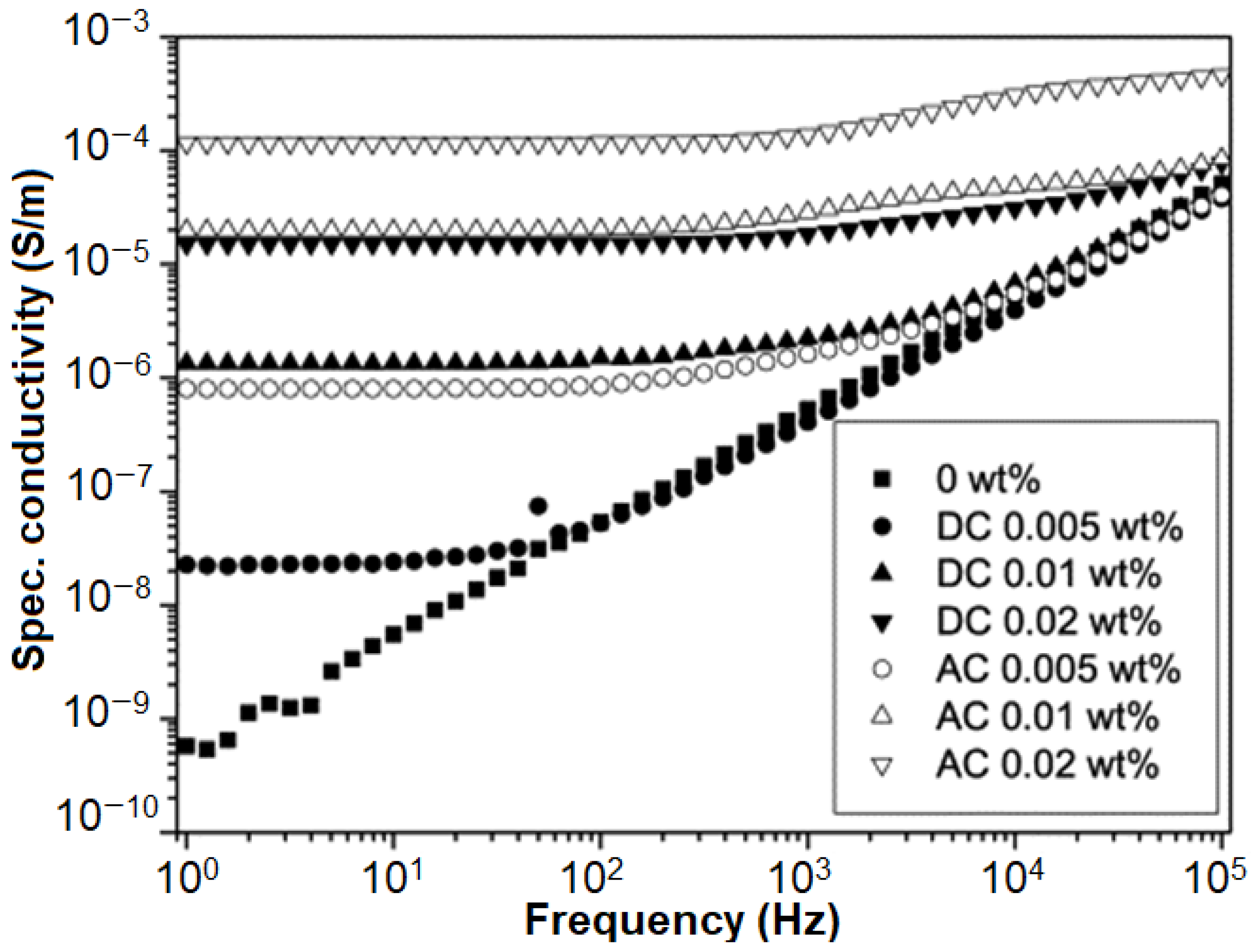
2.3. Specific Conductivity
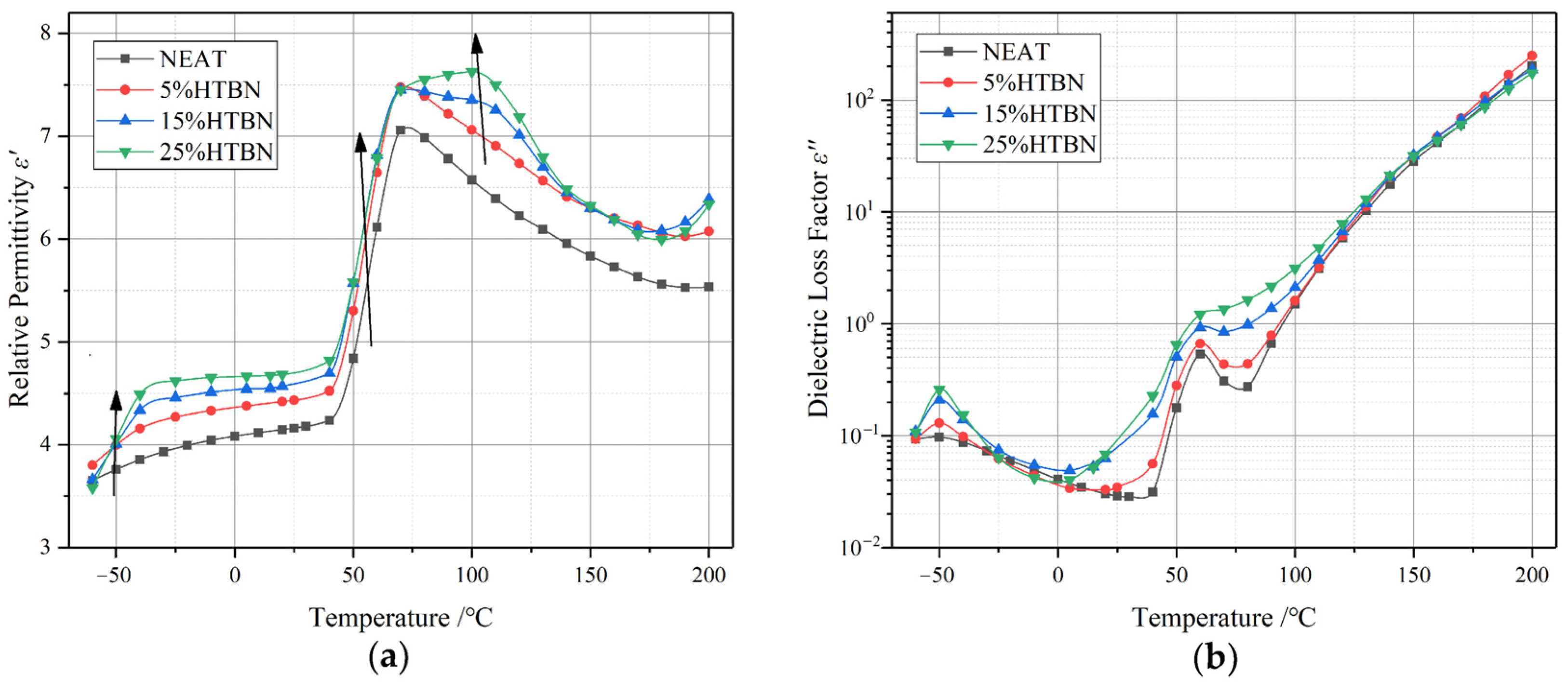
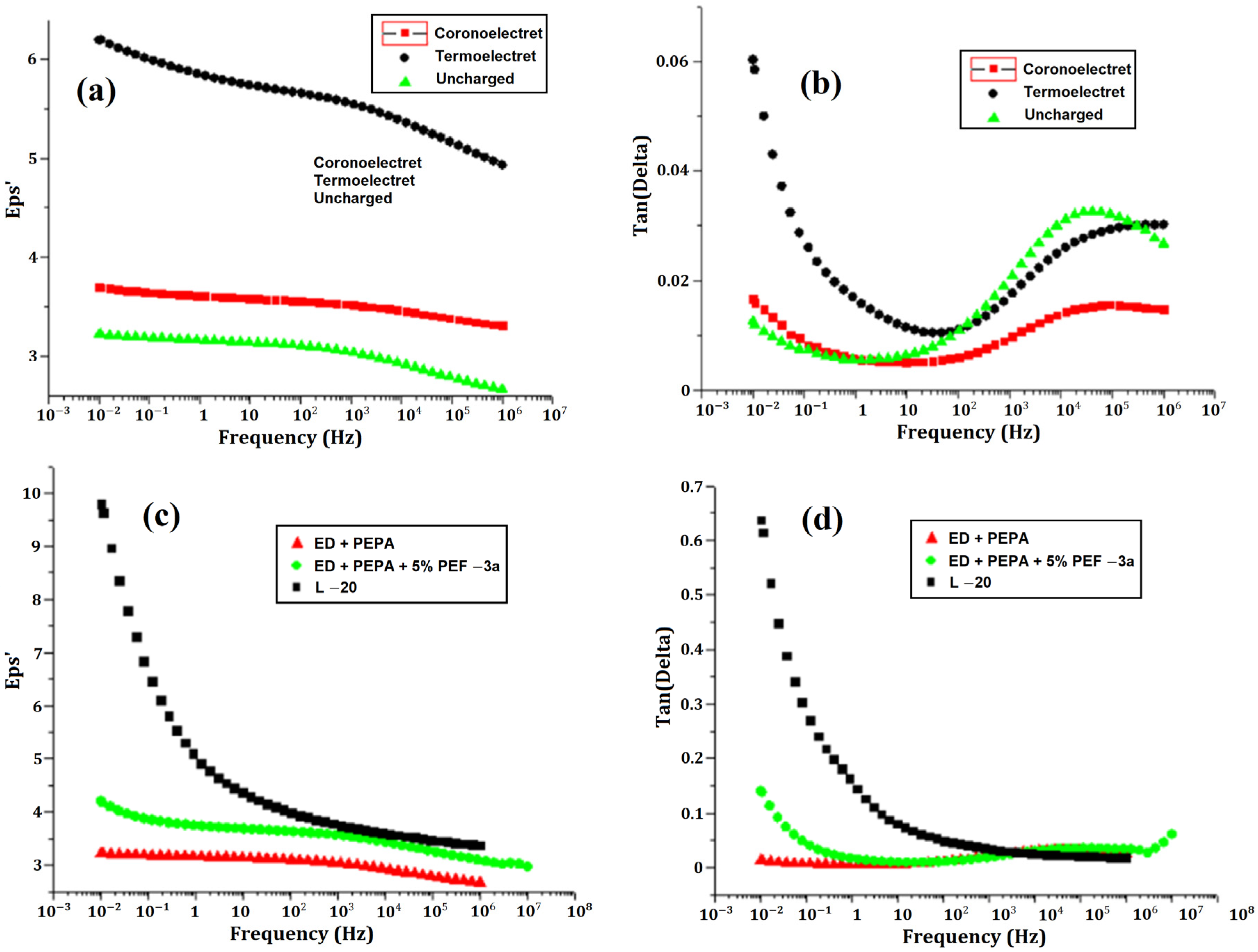
2.4. Dependence of Dielectric Constant on Frequency
2.5. Transmittance of Modified ERs
2.6. Electrical Conductivity of Modified ERs
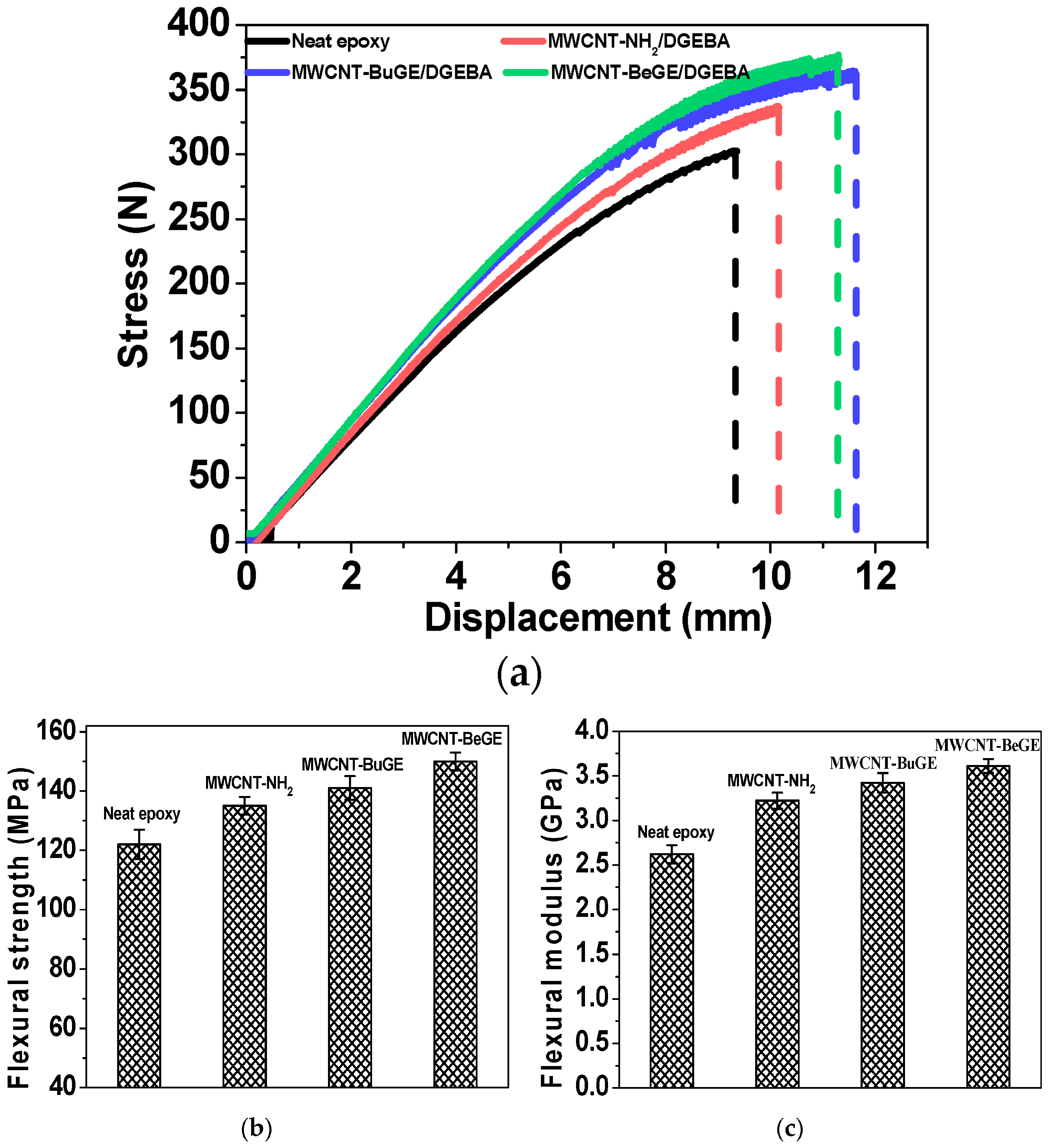
2.7. Bending Strength of Modified ERs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmadi, Z. Epoxy in nanotechnology: A short review. Prog. Org. Coatings 2019, 132, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Xiao, F. Applications of epoxy materials in pavement engineering. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Elhakeem, A.; Kaytbay, S.; Ahmed, A. A Comprehensive Review on the Thermal, Electrical, and Mechanical Properties of Graphene-Based Multi-Functional Epoxy Composites; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 5, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.-S.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Hou, X.-L. Review of chemical recycling and reuse of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites. New Carbon Mater. 2022, 37, 1021–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, L.D.; Capricho, J.C.; Peerzada, M.; Salim, N.V.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Hameed, N. Recent progress and multifunctional applications of fire-retardant epoxy resins. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, C.; Feghali, E.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; Triantafyllidis, K.S. Recent advances in epoxy resins and composites derived from lignin and related bio-oils. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 38, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.-L.; Li, X.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Xia, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L.; Hussain, G.; Li, Q.; Ostrikov, K.K. Adhesion and cohesion of epoxy-based industrial composite coatings. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 193, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkovich, V.P.; Kudryavtseva, A.V. Protection from Ionizing Radiation: A Handbook, 4th ed.; Elektroatomizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1995; 496p. [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sato, K.; Imai, Y. Improvement of interfacial adhesion between oxide ceramic nanoparticles and epoxy resin by wet-jet milling. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 31658–31665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zhou, S.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Gamma ray attenuation behaviors and mechanism of boron rich slag/epoxy resin shielding composites. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Ueshima, M.; Haga, M.; Suganuma, K. Influence of interfacial interaction on the reliability of the bond between encapsulation epoxy and copper substrate. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Electronics Packaging (ICEP), Kumamoto, Japan, 19–22 April 2023; pp. 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y. Experimental investigation on immersion liquid cooled battery thermal management system with phase change epoxy sealant. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 264, 118089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Akpan, E.D.; Quraishi, M.; Dagdag, O.; El Gouri, M.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Ebenso, E.E. Epoxy resins as anticorrosive polymeric materials: A review. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 156, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Pan, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.; Song, P.; He, J.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yang, R. Metal–Organic Frameworks–Based Flame-Retardant System for Epoxy Resin: A Review and Prospect. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, M.; Yang, X.; Fan, R.; Yue, S.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Q.; He, Y. A comprehensive review of reactive flame-retardant epoxy resin: Fundamentals, recent developments, and perspectives. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 201, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.R.; Estaji, S.; Kiaei, H.; Mansourian-Tabaei, M.; Nouranian, S.; Jafari, S.H.; Ruckdäschel, H.; Arjmand, M.; Khonakdar, H.A. A review of electrical and thermal conductivities of epoxy resin systems reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene-based nanoparticles. Polym. Test. 2022, 112, 107645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Wong, C.P. Materials for Advanced Packaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–723. ISBN 978-0-387-78218-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, P.L.; Mariatti, M.; Akil, H.M.; Seetharamu, K.N.; Wagiman, A.N.R.; Beh, K.S. High Filled Epoxy Composites for Electronic Packaging Application. In Proceedings of the 2006 Thirty-First IEEE/CPMT International Electronics Manufacturing Technology Symposium, Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 8–10 November 2006; pp. 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shundo, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Tanaka, K. Network Formation and Physical Properties of Epoxy Resins for Future Practical Applications. JACS Au 2022, 2, 1522–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estridge, C.E. The effects of competitive primary and secondary amine reactivity on the structural evolution and properties of an epoxy thermoset resin during cure: A molecular dynamics study. Polymer 2018, 141, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, B.A. Advance in Polymer Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kinjo, N.; Ogata, M.; Nishi, K.; Kaneda, A. Epoxy Molding Compounds as Encapsulation Materials for Microelectronic Devices. In Speciality Polymers/Polymer Physics; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsissou, R. Review on epoxy polymers and its composites as a potential anticorrosive coatings for carbon steel in 3.5% NaCl solution: Computational approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipchik, V.S.; Smotrova, S.A.; Tomilchik, Y.A. Study of the properties of modified epoxy-containing oligomers. Plast. Masses 2011, 2, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Galikhanov, M.; Mochalova, E.; Gabdrakhmanov, I.; Galikhanov, E.; Lounev, I.; Gusev, Y. Study of Electret State in Epoxyamine Polymers by Dielectric Spectroscopy. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 4473–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagonravova, A.A. Lacquer Epoxy Resins; Blagonravova, A.A., Nepomniachtchi , A.I., Eds.; Chemistry: Moscow, Russia, 1970; 248p. [Google Scholar]
- Electronic Source. Available online: https://www.nkj.ru/archive/articles/32969/?ysclid=lhke7yzvk8640784726 (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Voronkov, A.G.; Yartsev, V.P. Epoxy Polymer Solutions for the Repair and Protection of Building Products and Structures: Tutorial; Tambov Publishing House: Tambov, Russia, 2006; 92p, ISBN 5-8265-0519-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Rogalski, M.; Kessler, M.R. Zirconium Tungstate/Epoxy Nanocomposites: Effect of Nanoparticle Morphology and Negative Thermal Expansivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9478–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, R.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, B.; Cui, J.; Jiang, N.; et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity of epoxy composites filled with tetrapod-shaped ZnO. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12337–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Li, X.-F.; Bai, H.; Xu, W.-W.; Yang, S.-Y.; Lu, Y.; Han, J.-J.; Wang, C.-P.; Liu, X.-J.; Li, W.-B. Influence of microstructural features on thermal expansion coefficient in graphene/epoxy composites. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kislyakov, P.A.; Nizina, T.A. Nanomodified epoxy composites for building purposes. Perspekt. Mater. 2010, 9, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Tarrío-Saavedra, J.; López-Beceiro, J.; Naya, S.; Artiaga, R. Effect of silica content on thermal stability of fumed silica/epoxy composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 2133–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoman, T.S.; Džunuzović, J.V.; Jeremić, K.B.; Grgur, B.N.; Miličević, D.S.; Popović, I.G.; Džunuzović, E.S. Improvement of epoxy resin properties by incorporation of TiO2 nanoparticles surface modified with gallic acid esters. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoikovich, N.; Smilkovich, S.; Tsurkina, S.K.; Laketich, A. Influence of Moisture on Adhesive Joints. Science and Innovations in Construction (to the 45th Anniversary of the Department of Construction and Municipal Economy): Sat. Report International Scientific-practical. Conf., Belgorod, April 21, 2017; Belgorod State Technological University. V.G. Shukhova: Belgorod, Russia, 2017; pp. 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Plakunova, E.V.; Tatarintseva, E.A.; Mostovoy, A.S.; Panova, L.G. Structure and properties of epoxy thermosets. Perspekt. Mater. 2013, 3, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Galeev, R.R.; Maisuradze, N.V.; Abdrakhmanova, L.A. Structure of polymer composites on the basis of epoxy resin and organic and inorganic dispersed industrial wastes. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 871, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyarova, I.A.; Stepina, I.V.; Ilyushkin, D.A.; Tsvetkov, I.S. Assessment of influence of disperse filler polarity on structure and water absorption of epoxy compositions. Vestnik MGSU 2019, 6, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Yap, M.; Chern, W.K.; Oh, J.T.; Chen, Z. Degradation and Lifetime Prediction of Epoxy Composite Insulation Materials under High Relative Humidity. Polymers 2023, 15, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antipova, E.A.; Korotkova, N.P.; Lebedev, V.S. Modern polyurethane, epoxy, PU-acrylate and epoxyacrylate binders for industrial paintwork materials produced by LLC NPP Makromer. Paint. Varn. Mater. Their Appl. 2012, 9, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Modeev, S.A.; Ladinin, M.E.; Kurbatov, V.G. Influence of active diluents on the properties of unfilled epoxy compositions. In Proceedings of the Sixty-sixth All-Russian Scientific and Technical Conference of Students, Undergraduates and Postgraduates of Higher Educational Institutions with International Participation, Yaroslavl, Russia, 23 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Potapochkina, I.I.; Korotkova, N.P.; Loginova, S.E.; Lebedev, V.S. Epoxy and polyurethane adhesive materials of elad, aquapol, and acrolat brands and their components. Glues Seal. Mater. 2011, 4, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanyan, E.A. Influence of diluents on the physical and mechanical properties of 128 epoxy binders and composites based on them. High-Mol. Compd. 1994, 36A, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Gojny, F.; Wichmann, M.; Köpke, U.; Fiedler, B.; Schulte, K. Carbon nanotube-reinforced epoxy-composites: Enhanced stiffness and fracture toughness at low nanotube content. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Youn, J.R. Influence of dispersion states of carbon nanotubes on physical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Carbon 2005, 43, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Lam, C. Thermal and mechanical properties of single-walled carbon nanotube bundle-reinforced epoxy nanocomposites: The role of solvent for nanotube dispersion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudawska, A.; Sarna-Boś, K.; Rudawska, A.; Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Frigione, M. Biological Effects and Toxicity of Compounds Based on Cured Epoxy Resins. Polymers 2022, 14, 4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagidullin, A.I.; Efremova, A.A.; Garipov, R.M.; Deberdeev, R.Y. Influence of reactive modifiers on the properties of epoxy compositions. Bull. KSTU 2003, 1, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Danilenko, E.G.; Chesnokov, E.Y.; Telegin, S.V. Influence of Technological Additives on the Effective Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy Resin; Siberian State University of Science and Technology named after Academician M.F. Reshetnev: Krasnoyarsk, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.S.; Hammoud, A.; Kelly, M. Application of Dielectric Thermal Analysis to Screen Electrical Insulation Candidates for High-Voltage Electric Machines. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20004–20013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhaus, J.; Moeginger, B.; Großgarten, M.; Hausnerova, B. Evaluation of dielectric curing monitoring investigating light-curing dental filling composites. Mater. Eng. 2011, 18, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Senturia, S.D.; Sheppard, N.F., Jr. Dielectric Analysis of Thermoset Cure. In Epoxy Resins and Composites IV.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Philippi, F.; Rauber, D.; Eliasen, K.L.; Bouscharain, N.; Niss, K.; Kay, C.W.M.; Welton, T. Pressing matter: Why are ionic liquids so viscous? Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 2735–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Nutt, S. In situ resin age assessment using dielectric analysis and resin cure map for efficient vacuum infusion. Adv. Manuf. Polym. Compos. Sci. 2020, 6, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Regueira, L.; Gracia-Fernández, C.; Gómez-Barreiro, S. Use of rheology, dielectric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry for gel time determination of a thermoset. Polymer 2005, 46, 5979–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenato, A.; Salla, J.M.; Ramis, X.; Morancho, J.M.; Marroyo, L.M.; Martin, J.L. Determination of gel and vitrification times of thermoset curing process by means of TMA, DMTA and DSC techniques. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1997, 49, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Wang, Y.; Mushtaq, R.T.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Chen, X. Preparation, characterization, and curing kinetics of elevated and cryogenic temperature-resistant epoxy resin composites. Polym. Test. 2022, 116, 107783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, B.; Kaiser, J.M.; Becker, K.F.; Braun, T.; Lang, K.D. Evaluation of the Dielectric Cure Monitoring of Epoxy Molding Compound in Transfer Molding Process for Electronic Packages. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Microelectronics Packaging Conference (EMPC), Friedrichshafen, Germany, 14–16 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Protsenko, A.E.; Telesh, V.V. Inhibition and Cathalysis as a Method to Improve the Mechanical Properties of a Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic. Polym. Mech. 2015, 51, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-J.; Shin, S.-S.; Yoon, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, J.-E. Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Micro-sized Alumina Composite and the Effect of Nano-sized Alumina on Those Properties. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2015, 16, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M. Development of High Thermal Conductive Laminates. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials (ISEIM 2005), Kitakyushu, Japan, 5–9 June 2005; pp. 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Su, B.; Qu, J.; Wong, C.P. Effects of nano-sized particles on electrical and thermal conductivities of polymer composites. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Advanced Packaging Materials: Processes, Properties and Interfaces (IEEE Cat. No.04TH8742), 2004 Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 24–26 March 2004; pp. 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Mannanov, E.R. On dielectric materials with high thermal conductivity for electrical insulation systems of high-voltage electrical machines: A review of domestic and foreign literature. Mater. Science. Power Eng. 2021, 27, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, K.; Ning, X. Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Resin Impregnated Nano-SiO2 Modified Insulating Paper. Polymers 2019, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, Q.; Wang, C.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Z. Dielectric Relaxation Characteristics of Epoxy Resin Modified with Hydroxyl-Terminated Nitrile Rubber. Molecules 2020, 25, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huo, R.; Wu, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, G.; Jiang, P. Influence of Interface Structure on Dielectric Properties of Epoxy/Alumina Nanocomposites. Patent CN103525005B, 4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts, G.G.; Lake, M.L.; Strong, K.L.; Rice, B.P. A review of the fabrication and properties of vapor-grown carbon nanofiber/polymer composites. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.A.; Ravich, D.; Lips, D.; Mayer, J.; Wagner, H.D. Distribution and alignment of carbon nanotubes and nanofibrils in a polymer matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimat, Z.M.; Hamideen, M.S.; Schulte, K.I.; Wittich, H.; de la Vega, A.; Wichmann, M.; Buschhorn, S. Dielectric properties of epoxy/short carbon fiber composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5196–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Marakhovsky, P.S.; Malysheva, G.V. Determination of thermophysical properties of epoxy materials during their curing. Proc. VIAM 2018, 9, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, S.L.; Berlin, A.A.; Kulkov, A.A.; Oshmyan, V.G. Polymer Composite Materials; Intelligence: Dolgoprudny, Russia, 2010; 352p. [Google Scholar]
- Baurova, N.I.; Zorin, V.A. The Use of Polymer Composite Materials in the Production and Repair of Machines: Textbook. Allowance; Izd-vo MADI: Moscow, Russia, 2016; 264p. [Google Scholar]
- Mishkin, S.I.; Raskutin, A.E.; Evdokimov, A.A.; Gulyaev, I.N. Technologies and main stages of construction of the first in Russia arch bridge from composite materials. Proc. VIAM Electron. Sci. Tech. Mag. 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marakhovsky, P.S.; Barinov, D.Y.; Pavlovsky, K.A.; Aleksashin, V.M. Curing of multilayer polymeric composite materials. Part 1. Mathematical modeling of heat transfer during the formation of a thick carbon fiber plate. In All Materials. Encyclopedic Reference Book; Federal State Unitary Enterprise “All-Russian Research Institute of Aviation Materials”: Moscow, Russia, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Barinov, D.Y.; Marakhovsky, P.S.; Kutsevich, K.E.; Chutskova, E.Y. Mathematical modeling of temperature fields taking into account the kinetics of solidification of a thick fiberglass plate. Perspekt. Mater. 2017, 5, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zuev, A.V.; Loshchinin, Y.V.; Barinov, D.Y.; Marakhovsky, P.S. Computational and experimental studies of thermophysical properties. Aviat. Mater. Technol. 2017, S, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuba, D.S.; Vasilyev, S.O.; Savelyev, D.N.; Mainikova, N.F. Research of temperature dependences of thermal conductivity of composite materials based on diane resin ED20. Adv. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2012, 3, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Nejad, S.M.; Srivastava, R.; Bellussi, F.M.; Thielemann, H.C.; Asinari, P.; Fasano, M. Nanoscale thermal properties of carbon nanotubes/epoxy composites by atomistic simulations. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 159, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, V.A.; Rusakov, S.V.; Gilev, V.G. About electrical conductivity of the epoxy matrix with carbon nanotubes. PNRPU Mech. Bull. 2019, 3, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Rowland, S.; Carr, J.; Storm, M.; Choy, K.-L.; Clancy, A.J. The importance of particle dispersion in electrical treeing and breakdown in nano-filled epoxy resin. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 129, 106838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Nie, Y. Electric stress and dielectric breakdown characteristics under high-frequency voltages with multi-harmonics in a solid-state transformer. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 129, 106861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limarenko, N.A.; Mochalova, E.N.; Galikhanov, M.F.; Deberdeev, R.Y. Study of the dielectric properties of electrets based on epoxy polymers. Bull. Kazan Technol. Univ. 2013, 2, 178–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gojny, F.H.; Wichmann, M.H.G. Influence of different carbon nanotubes on the mechanical properties of epoxy matrix composites—A comparative study. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2300–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.S.; Lee, S.K.; In, S.J.; Lee, Y.-S. Improved flame retardant properties of epoxy resin by fluorinated MMT/MWCNT additives. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2010, 89, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyuev, I.Y. Electrophysical Properties of Composites Based on Epoxy Resin Modified with Nanosized Carbon Fillers. OD 9 20-5/1157. Moscow, 2020, 23 sElectronic Resource. Available online: https://viewer.rsl.ru/ru/rsl01010251638?page=1&rotate=0&theme=white (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Kuzhir, P.; Paddubskaya, A.; Plyushch, A.; Volynets, N.; Maksimenko, S.; Macutkevic, J.; Kranauskaite, I.; Banys, J.; Ivanov, E.; Kotsilkova, R.; et al. Epoxy composites filled with high surface area-carbon fillers: Optimization of electromagnetic shielding, electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 164304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Sandler, J.; Windle, A.; Schwarz, M.-K.; Bauhofer, W.; Schulte, K.; Shaffer, M. Electric field-induced aligned multi-wall carbon nanotube networks in epoxy composites. Polymer 2005, 46, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanaseva, E.S.; Babkin, A.V. Mechanical properties of epoxy binders modified with single-walled nanotubes for reinforced composite materials. Vestn. VGU 2016, 12, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Marakhovsky, P.S.; Kondrashov, S.V. On the modification of heat-resistant epoxy binders with carbon nanotubes. Vestnik MTGU im. Bauman 2015, 2, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Akatenkov, R.V. Influence of small amounts of functionalized nanotubes on the physical and mechanical properties and structure of epoxy compositions. Deform. Destr. Mater. 2011, 11, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Sui, G.; Yang, X. Surface Sizing Treated MWCNTs and Its Effect on the Wettability, Interfacial Interaction and Flexural Properties of MWCNT/Epoxy Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Bhattacharjee, Y. Lightweight Epoxy-Based Composites for EMI Shielding Applications. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 1702–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, S. Epoxy resin composites with surface-modified silicon dioxide nanoparticles: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, S.M.; Ma, C.C.; Wu, H.H.; Kuan, H.C.; Chen, W.J.; Liao, S.H.; Hsu, C.W.; Wu, H.L. Preparation and thermal, electrical and morphological properties of multiwalled carbon nanotube and epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 61340-5-1:2016; Electrostatics—Part 5-1: Protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena—General requirements. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.M.L.; Martins, S.A.; da Costa Mattos, H.S. Combination of temperature and electrical conductivity on semiconductor graphite/epoxy composites. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisunova, M.O.; Mamunya, Y.P.; Lebovka, N.I.; Melezhyk, A.V. Percolation behavior of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisala, A.; Li, Q.; Kinloch, I.; Windle, A. Thermal and electrical conductivity of single- and multi-walled carbon nanotube-epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Drzal, L.T.; Qin, Y.; Huang, Z. Processing and characterization of high content multilayer grapheme/epoxy composites with high electrical conductivity. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 2897–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaoui, A.; Bai, S.; Cheng, H.M.; Bai, J.B. Mechanical and electrical properties of a MWNT/epoxy composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, A.; Khavandi, A.; Javadpour, J.; Tcharkhtchi, A. Viscoelastic properties of MWNT/epoxy composites using two different using cycles. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3383–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dehghani-Sanij, A.A.; Blackburn, R.S. Carbon based conductive polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3408–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovodok, E.A.; Ivanovskaya, M.I.; Poznyak, S.K.; Maltanova, A.M.; Gaevskaya, T.V.; Kurilo, V.S. Epoxy Composites Filled with Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene. Sviridovsky Readings: Sat. Art./Editorial Board: O. A. Ivashkevich (prev.) [and Others].—Minsk: Krasiko-Print, 2021, Issue. 17, pp. 65–74. Available online: https://elib.bsu.by/handle/123456789/273068 (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, S.K.; Agarwal, A.K. Tribological studies of epoxy composites with solid and liquid fillers. Tribol. Internat. 2017, 105, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Petrova, R.S.; Mitra, S. Effect of carbon nanotube (CNT) functionalization in epoxy-CNT composites. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharitonov, A.P.; Simbirtseva, G.V.; Tkachev, A.G. Reinforcement of epoxy resin composites with fluorinated carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 107, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, A.F.; Kryzhanovsky, V.K.; Burlov, V.V. Technology of Polymeric Materials; Kryzhanovsky, V.K., Ed.; Profession: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2008; 544p. [Google Scholar]
- Tomishko, M.M.; Alekseev, A.M.; Tomishko, A.G. Carbon nanotubes—The basis of materials of the future. Nanotechnics 2004, 1, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ovejero, G.; Sotelo, J.L.; Romero, M.D.; Rodríguez, A.; Ocaña, M.A.; Rodríguez, G.; García, J. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Liquid-Phase Oxidation. Functionalization, Characterization, and Catalytic Activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wong, S.S. Functional covalent chemistry of carbon nanotube surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, T.; Owuor, P.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Wang, C.; Sha, J.; Shen, L.; Yoon, J.; Wang, W.; Salvatierra, R.V.; et al. Ultra-Stiff Graphene Foams as Three-Dimensional Conductive Fillers for Epoxy Resin. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11219–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dallaev, R.; Pisarenko, T.; Papež, N.; Sadovský, P.; Holcman, V. A Brief Overview on Epoxies in Electronics: Properties, Applications, and Modifications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193964
Dallaev R, Pisarenko T, Papež N, Sadovský P, Holcman V. A Brief Overview on Epoxies in Electronics: Properties, Applications, and Modifications. Polymers. 2023; 15(19):3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193964
Chicago/Turabian StyleDallaev, Rashid, Tatiana Pisarenko, Nikola Papež, Petr Sadovský, and Vladimír Holcman. 2023. "A Brief Overview on Epoxies in Electronics: Properties, Applications, and Modifications" Polymers 15, no. 19: 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193964
APA StyleDallaev, R., Pisarenko, T., Papež, N., Sadovský, P., & Holcman, V. (2023). A Brief Overview on Epoxies in Electronics: Properties, Applications, and Modifications. Polymers, 15(19), 3964. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193964





