Colour Parameters and Changes of Tea-Stained Resin Composite Exposed to Whitening Pen (In Vitro Study)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
- Group 1: Stored in artificial saliva (control)
- Group 2: Stored in artificial saliva followed by whitening pen application
- Group 3: Stored in tea followed by whitening pen application
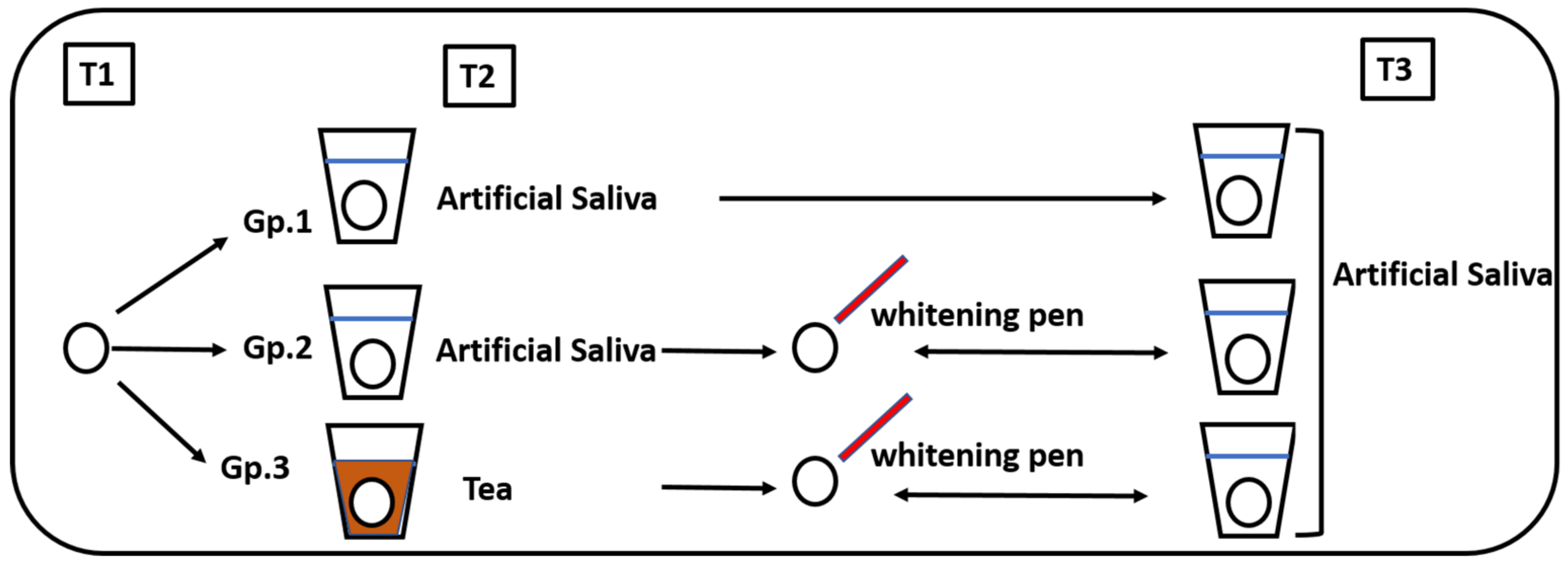
- T1: Before storage (baseline)
- T2: After storage in either artificial saliva or tea for 6 days
- T3: After the whitening pen application for one week in groups 2 and 3
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Specimen Preparation
2.4. Specimen Grouping, Storage, and Bleaching
- Group 1: specimens were incubated in 10 mL of artificial saliva (Sigma-Aldrich CO, St. Louis, MO, USA) at 37 °C for 11 days.
- Group 3: specimens were incubated in 10 mL of tea at 37 °C for 6 days and then subjected to a whitening pen application for 7 days. The tea was prepared by steeping one tea bag (Lipton Yellow Label, Unilever, UK) for 5 min in 200 mL of boiling water.
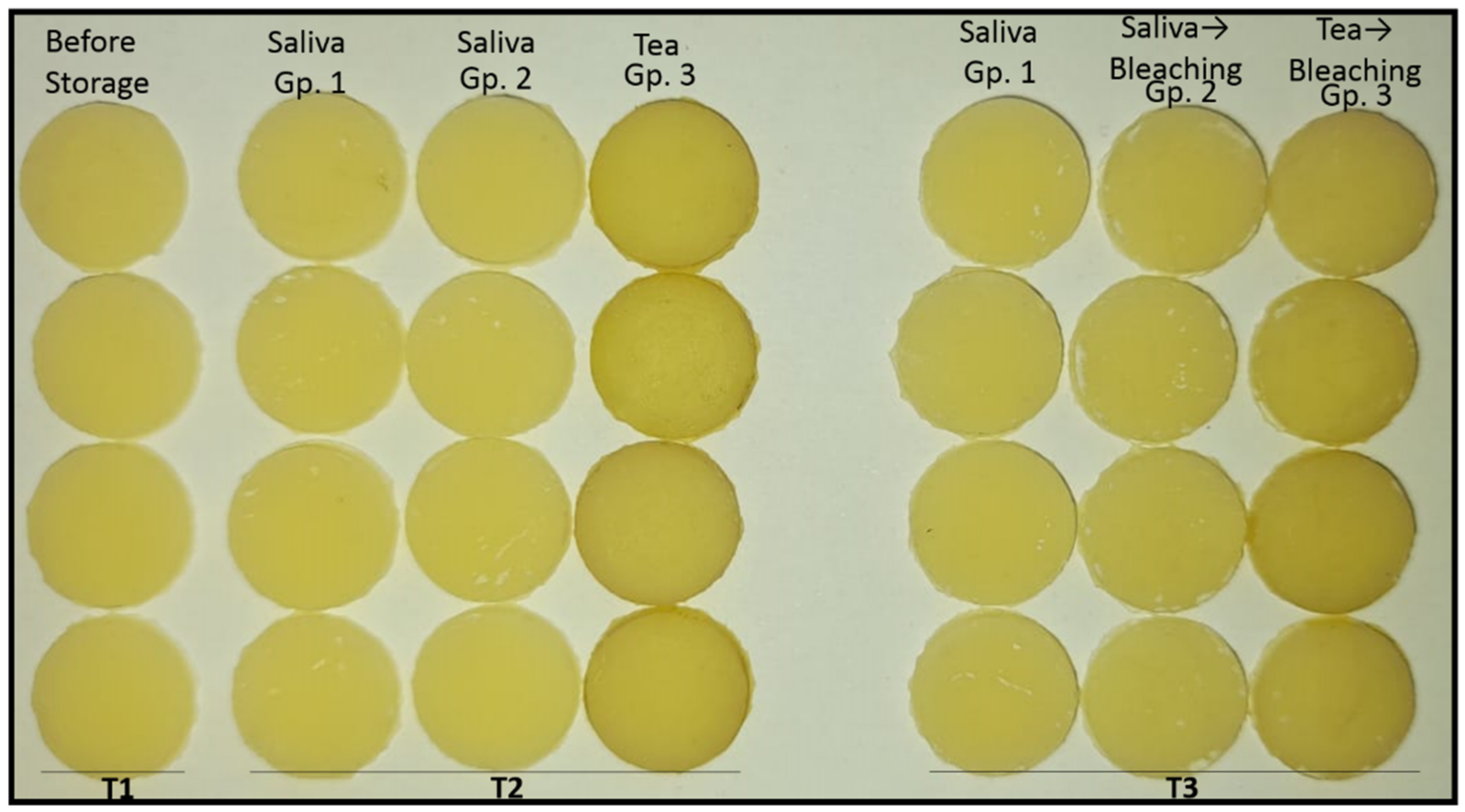
2.5. Colour Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analyses
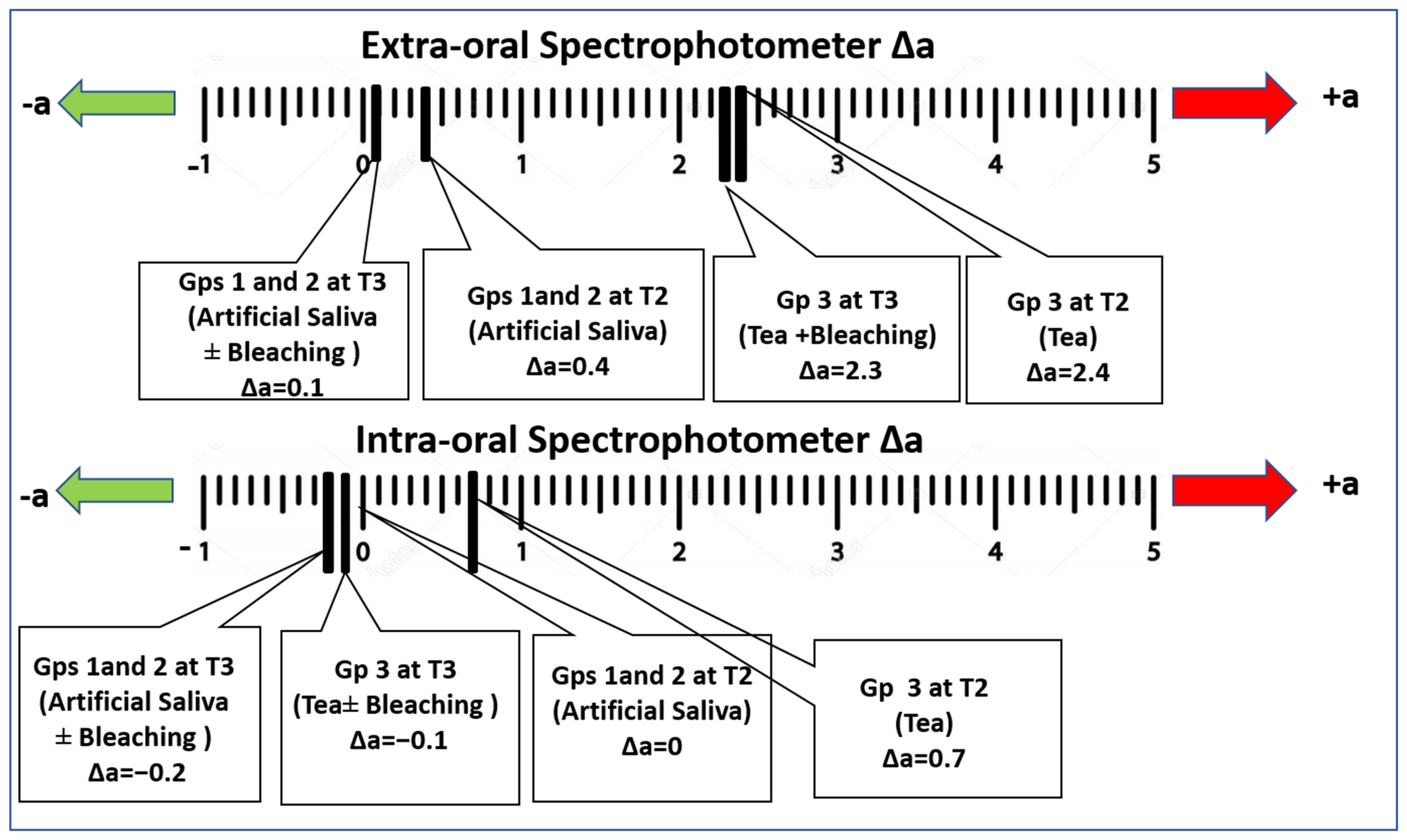
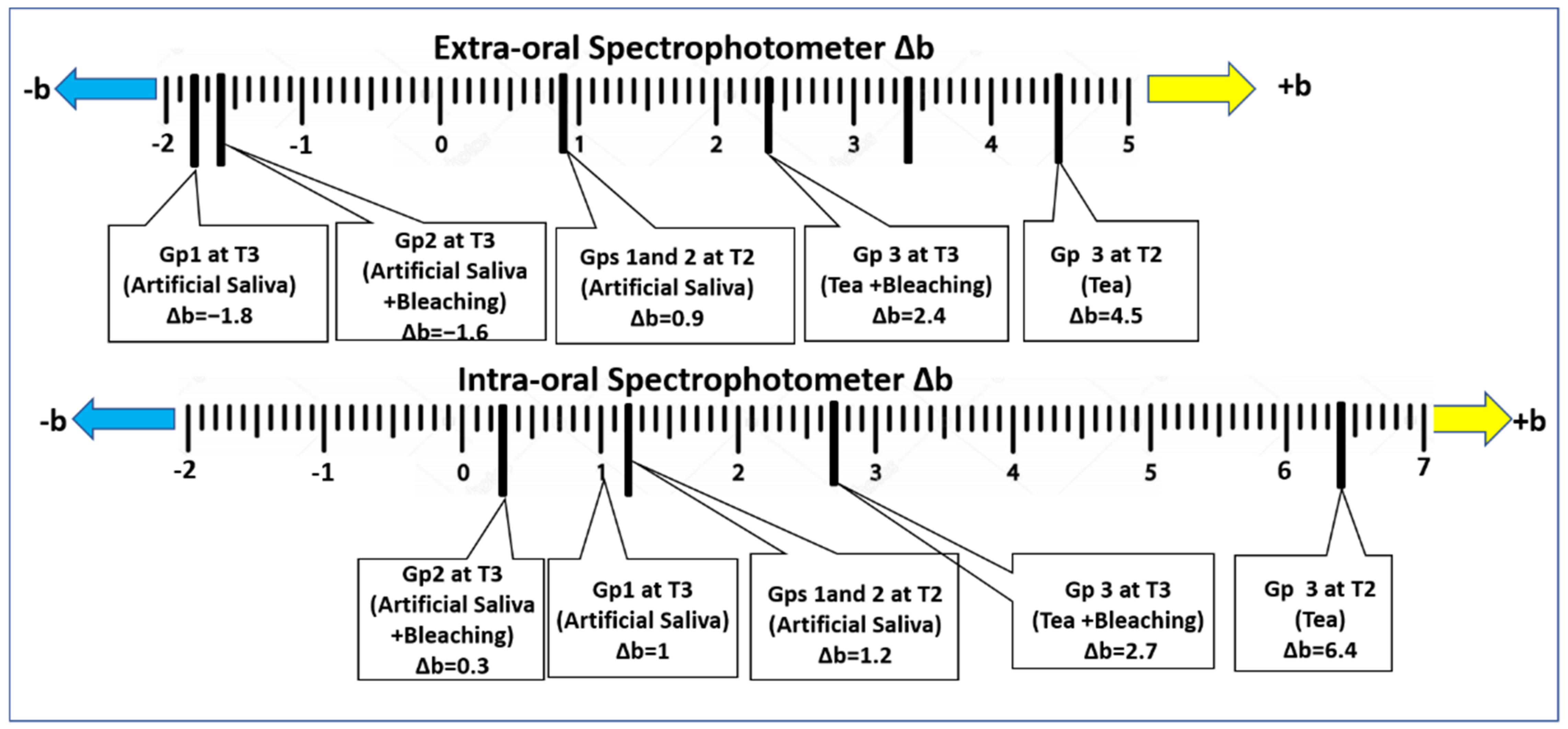
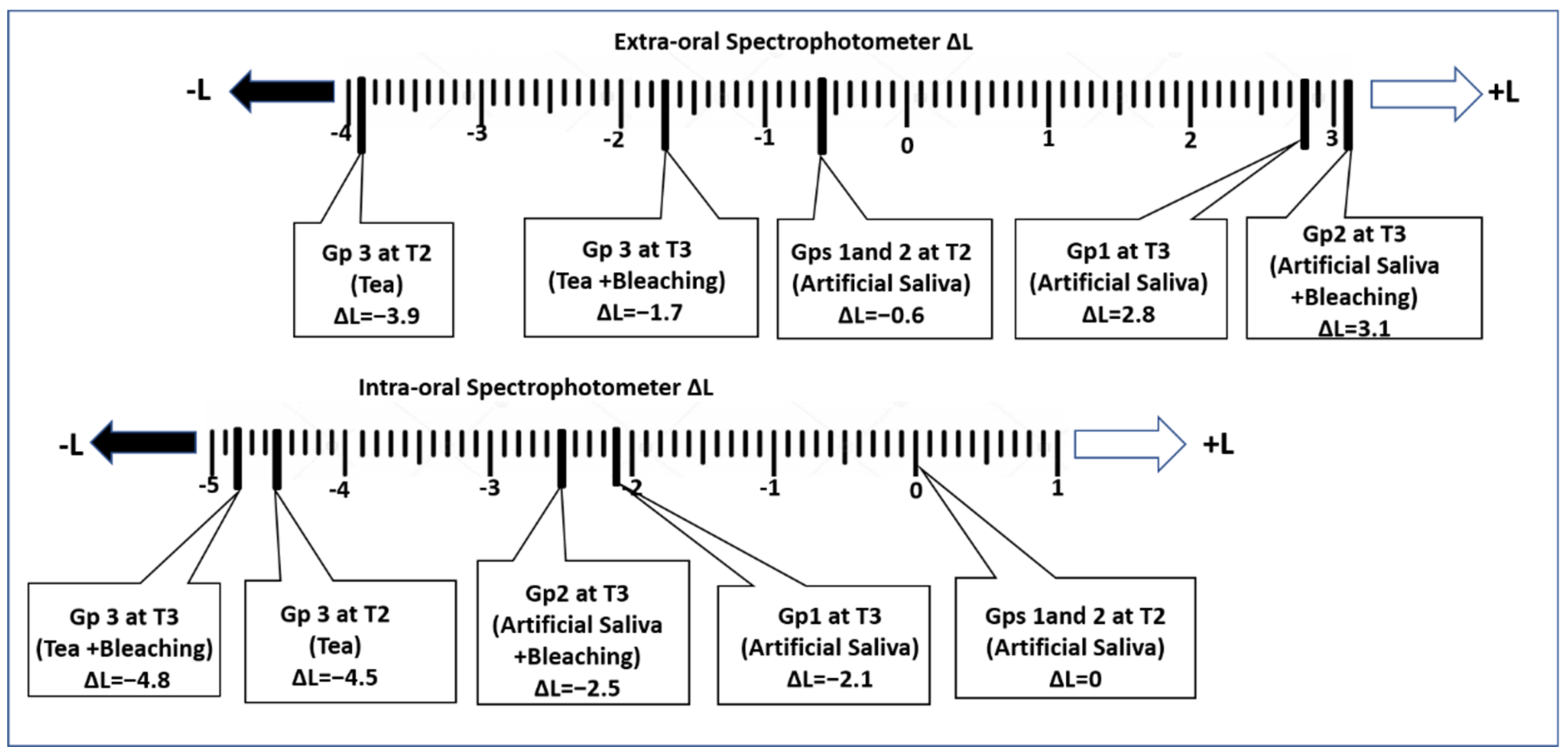
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbel, M.; Mattle, C.; Scheel, M.; Diaz, A.; Jerjen, I.; Lominski, R.; Sterchi, R.; Schulz, G.; Izquierdo, A.; Sigron, G.; et al. Dental Composites for Wide Color Matching. In Proceedings of the Bioinspiration, Biomimetics, and Bioreplication XII, Long Beach, CA, USA, 6 March–11 April 2022; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelraouf, R.M.; Habib, N.A. Color-Matching and Blending-Effect of Universal Shade Bulk-Fill-Resin-Composite in Resin-Composite-Models and Natural Teeth. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4183432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, T.M. Interfacial Microscopic Examination and Chemical Analysis of Resin-Dentin Interface of Self-Adhering Flowable Resin Composite. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, Y.; Jain, V. Tooth Staining: A Review of Etiology and Treatment Modalities. Acta Sci. Dent. Sci. 2018, 2, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdy, T.M.; Abdelnabi, A.; Othman, M.S.; Bayoumi, R.E.; Abdelraouf, R.M. Effect of Different Mouthwashes on the Surface Microhardness and Color Stability of Dental Nanohybrid Resin Composite. Polymers 2023, 15, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardu, S.; Duc, O.; Di Bella, E.; Krejci, I.; Daher, R. Color Stability of Different Composite Resins after Polishing. Odontology 2018, 106, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasoohi, N.; Hadian, M.; Hoorizad, M.; Hashemi, S.; Naziri saeed, S. In-vitro Effect of Alcohol and Non-Alcohol Mouthwash on Color Change of Two Types of Bleach Shade Composite. J. Res. Dent. Maxillofac. Sci. 2019, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydro-Herrero, M.; Montiel-Company, J.M.; Labaig-Rueda, C.; Solá-Ruiz, M.F.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Amengual-Lorenzo, J. Clinical Efficacy of Four In-Office Vital Tooth Bleaching Products with Different Concentrations of Hydrogen Peroxide: A Randomized, Quadruple-Blind Clinical Trial. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shamy, H.; Alyousif, S.; Al-Harbi, M. EFFECT OF VARIOUS BLEACHING METHODS ON COLOR CHANGE AND SURFACE ROUGHNESS OF HUMAN ENAMEL. Egypt. Dent. J. 2018, 64, 2635–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samadani, K.H. The Effect of Preventive Agents (Mouthwashes/Gels) on the Color Stability of Dental Resin-Based Composite Materials. Dent. J. 2017, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturk-Avunduk, A.T.; Cengiz-Yanardag, E.; Karakaya, I. The Effect of Bleaching Applications on Stained Bulk-Fill Resin Composites. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Féliz-Matos, L.; Hernández, L.M.; Abreu, N. Dental Bleaching Techniques; Hydrogen-Carbamide Peroxides and Light Sources for Activation, an Update. Mini Review Article. Open Dent. J. 2015, 8, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Rodrigues, C.; Mozzaquatro, L.R.; Dala Nora, B.; Jacques, L.B.; Mallmann, A. Effect of Bleaching on Color Stability and Roughness of Composite Resins Aged in Staining Beverage. Gen. Dent. 2017, 65, e5–e10. [Google Scholar]
- Llena, C.; Martínez-Galdón, O.; Forner, L.; Gimeno-Mallench, L.; Rodríguez-Lozano, F.J.; Gambini, J. Hydrogen Peroxide Diffusion through Enamel and Dentin. Materials 2018, 11, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soveral, M.; Machado, V.; Botelho, J.; Mendes, J.J.; Manso, C. Effect of Resin Infiltration on Enamel: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElAziz, R.H.A.; Gadallah, L.K.; Saleh, R.S. Evaluation of Charcoal and Sea Salt–Lemon-Based Whitening Toothpastes on Color Change and Surface Roughness of Stained Teeth. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2022, 23, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, C.; Abou Samra, P.; Nahas, P. Discoloration of Resin Composites Induced by Coffee and Tomato Sauce and Subjected to Surface Polishing: An In Vitro Study. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2020, 26, e923279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.W.; Huang, C.F.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chen, A.; Ng, H.H.; Cheng, M.S.; Tsay, S.; Lai, J.Y.; Yang, T.S.; Lee, W.F. Color Stability and Staining Susceptibility of Direct Resin-Based Composites after Light-Activated in-Office Bleaching. Polymers 2021, 13, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertaş, E.; Güler, A.U.; Yücel, A.Ç.; Köprülü, H.; Güler, E. Color Stability of Resin Composites after Immersion in Different Drinks. Dent. Mater. J. 2006, 25, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özyurt, E.; Kurt, A. Effect of Different Beverages on Color Stability and Surface Properties of Composite Resin Materials. Color Res. Appl. 2021, 46, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Wu, W.; Dalal, E.N. The CIEDE2000 Color-Difference Formula: Implementation Notes, Supplementary Test Data, and Mathematical Observations. Color Res. Appl. 2005, 30, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Sapkota, J.; Qin, J.; Siraleartmukul, K.; Siriwongrungson, V. Polymeric Materials and Films in Dentistry: An Overview. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 14, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelraouf, R.M. Chemical Analysis and Microstructure Examination of Extended-Pour Alginate Impression versus Conventional One (Characterization of Dental Extended-Pour Alginate). Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraouf, R.M.; Bayoumi, R.E.; Hamdy, T.M. Effect of Powder/Water Ratio Variation on Viscosity, Tear Strength and Detail Reproduction of Dental Alginate Impression Material (in vitro and Clinical Study). Polymers 2021, 13, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudaev, P.; Chuev, V.; Klyukin, B.; Kuskov, A.; Mezhuev, Y.; Chistyakov, E. Polymeric Dental Nanomaterials: Antimicrobial Action. Polymers 2022, 14, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraouf, R.M.; Bayoumi, R.E.; Hamdy, T.M. Influence of Incorporating 5% Weight Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles on Flexural Strength, Micro-Hardness, Surface Roughness and Water Sorption of Dental Self-Cured Acrylic Resin. Polymers 2022, 14, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolone, G.; Mandurino, M.; De Palma, F.; Mazzitelli, C.; Scotti, N.; Breschi, L.; Gherlone, E.; Cantatore, G.; Vichi, A. Color Stability of Polymer-Based Composite CAD/CAM Blocks: A Systematic Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 464. [Google Scholar]
- Hariprasath, T.K.; Balaji Ganesh, S.; Devi, R.G. Colour Stability of Composite Resins-a Review. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2020, 14, 4673–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavani, C.C.; Sundfeld, D.; Schott, T.C.; Bertoz, A.P.M.; Bigliazzi, R.; Sundfeld, R.H. Home Dental Bleaching Monitored with Microelectronic Sensors to Record the Wearing Times of an Acetate Tray/Bleaching Product. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rashidy, A.A.; Abdelraouf, R.M.; Habib, N.A. Effect of Two Artificial Aging Protocols on Color and Gloss of Single-Shade versus Multi-Shade Resin Composites. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-H.; Hur, B.; Kim, H.-C.; Park, J.-K. Management of White Spots: Resin Infiltration Technique and Microabrasion. J. Korean Acad. Conserv. Dent. 2011, 36, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, A.; Padmanabhan, S. Comparative Evaluation of Icon® Resin Infiltration and ClinproTM XT Varnish on Colour and Fluorescence Changes of White Spot Lesions: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Prog. Orthod. 2019, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, N.; Davis, P.K.; Zielinski, J.M.; Danner, R.P.; Duda, J.L. Application of Free-Volume Theory to Self Diffusion of Solvents in Polymers below the Glass Transition Temperature: A Review. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1629–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Palandi, S.; Kury, M.; Picolo, M.Z.D.; Florez, F.L.E.; Cavalli, V. Effects of Black Tea Tooth Staining Previously to 35% Hydrogen Peroxide Bleaching. Braz. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 22, e238082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarembe, S.; Kiesow, A.; Pratten, J.; Webster, C. The Impact on Dental Staining Caused by Beverages in Combination with Chlorhexidine Digluconate. Eur. J. Dent. 2022, 16, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Vargas, G.G.; Mendoza, J.E.M.Y.; Aliaga-Mariñas, A.S.; Ladera-Castañeda, M.I.; Cervantes-Ganoza, L.A.; Cayo-Rojas, C.F. Effect of Polishing on the Surface Microhardness of Nanohybrid Composite Resins Subjected to 35% Hydrogen Peroxide: An in Vitro Study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2021, 11, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, S.; Colombo, M.; Poggio, C.; Scribante, A.; Saracino, M.; Beltrami, R. Bleaching Effect of Ozonized Substances on Resin Composite: A New Potentiality for Ozone Therapy in Dentistry. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, T.M. Polymerization Shrinkage in Contemporary Resin-Based Dental Composites: A Review Article. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 3087–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Material | Commercial Product | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Resin composite | Luna (Anterior/Posterior Nano- Hybrid Composite, Shade A2), SDI, Victoria, Australia | 22.5 wt.% (39 vol.%) multifunctional methacrylic ester, 77.5 wt.% (61 vol.%) inorganic fillers (40 nm–1.5 μm). |
| Whitening pen | Colgate Optic White Overnight Teeth Whitening Pen, Colgate, NY, USA | 3% Hydrogen peroxide, acrylates/octylacrylamide copolymer, alcohol, water. |
| Device | Group 1 and Group 2 (Artificial Saliva) | Group 3 (Tea) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extra-oral spectrophotometer | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 5.8 ± 0.04 | p = 0.0001 * |
| Intra-oral spectrophotometer | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | |
| p-value | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * |
| Device | Group 1 (Artificial Saliva) | Group 2 (Saliva → Whitening) | Group 3 (Tea → Whitening) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra-oral Spectrophotometer | 2.8 a ± 0.1 | 2.8 a ± 0.1 | 4 b ± 0.3 | p = 0.01 * |
| Intra-oral Spectrophotometer | 1.3 a ± 0.2 | 1.5 a ± 0.3 | 2.9 b ± 0.4 | |
| p-value | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.001 * |
| Device | L | a | b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extra-oral Spectrophotometer | 68.1 ± 0.2 | −1.8 ± 0.06 | 5.1 ± 0.2 |
| Intra-oral Spectrophotometer | 93.9 ± 0.4 | −1.1 ± 0.1 | 39.8 ± 0.2 |
| p-value | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.003 * | p = 0.0001 * |
| Device | L Artificial Saliva | L Tea | a Artificial Saliva | a Tea | b Artificial Saliva | b Tea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra-oral Spectrophotometer | 67.5 ± 0.1 | 64.2 ± 0.1 | −1.4 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.08 | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 9.6 ± 0.1 |
| Intra-oral Spectrophotometer | 93.9 ± 0.4 | 89.4 ± 0.4 | −1.1 ± 0.1 | −0.4 ± 0.2 | 41.0 ± 0.5 | 46.2 ± 1.4 |
| p-value | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.003 * | p = 0.003 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * |
| Device | L Group 1 | L Group 2 | L Group 3 | a Group 1 | a Group 2 | a Group 3 | b Group 1 | b Group 2 | b Group 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra-oral Spectrophotometer | 70.9 ± 0.1 | 71.2 ± 0.1 | 66.4 ± 0.10 | −1. 7± 0.1 | −1.7 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 7.5 ± 0.1 |
| Intra-oral Spectrophotometer | 91.8 ± 1.0 | 91.4 ± 0.6 | 89.1 ± 1.5 | −1.3 ± 0.3 | −1.3 ± 0.2 | −1.2 ± 0.2 | 40.8 ± 0.5 | 40.1 ± 0.5 | 42.5 ± 0.9 |
| p value | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * | p = 0.0001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhotan, A.; Abdelraouf, R.M.; Alhijji, S.; De Vera, M.A.T.; Sufyan, A.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Hamdy, T.M. Colour Parameters and Changes of Tea-Stained Resin Composite Exposed to Whitening Pen (In Vitro Study). Polymers 2023, 15, 3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143068
Alhotan A, Abdelraouf RM, Alhijji S, De Vera MAT, Sufyan A, Matinlinna JP, Hamdy TM. Colour Parameters and Changes of Tea-Stained Resin Composite Exposed to Whitening Pen (In Vitro Study). Polymers. 2023; 15(14):3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143068
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhotan, Abdulaziz, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Saleh Alhijji, Merry Angelyn Tan De Vera, Aref Sufyan, Jukka P. Matinlinna, and Tamer M. Hamdy. 2023. "Colour Parameters and Changes of Tea-Stained Resin Composite Exposed to Whitening Pen (In Vitro Study)" Polymers 15, no. 14: 3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143068
APA StyleAlhotan, A., Abdelraouf, R. M., Alhijji, S., De Vera, M. A. T., Sufyan, A., Matinlinna, J. P., & Hamdy, T. M. (2023). Colour Parameters and Changes of Tea-Stained Resin Composite Exposed to Whitening Pen (In Vitro Study). Polymers, 15(14), 3068. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15143068







