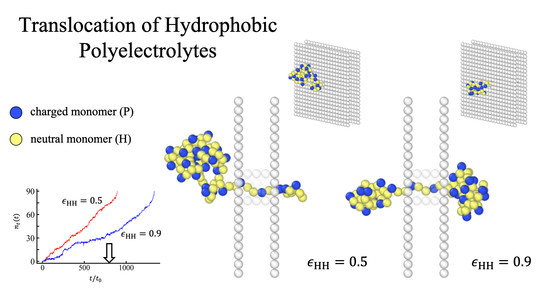
Translocation of Hydrophobic Polyelectrolytes under Electrical Field: Molecular Dynamics Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
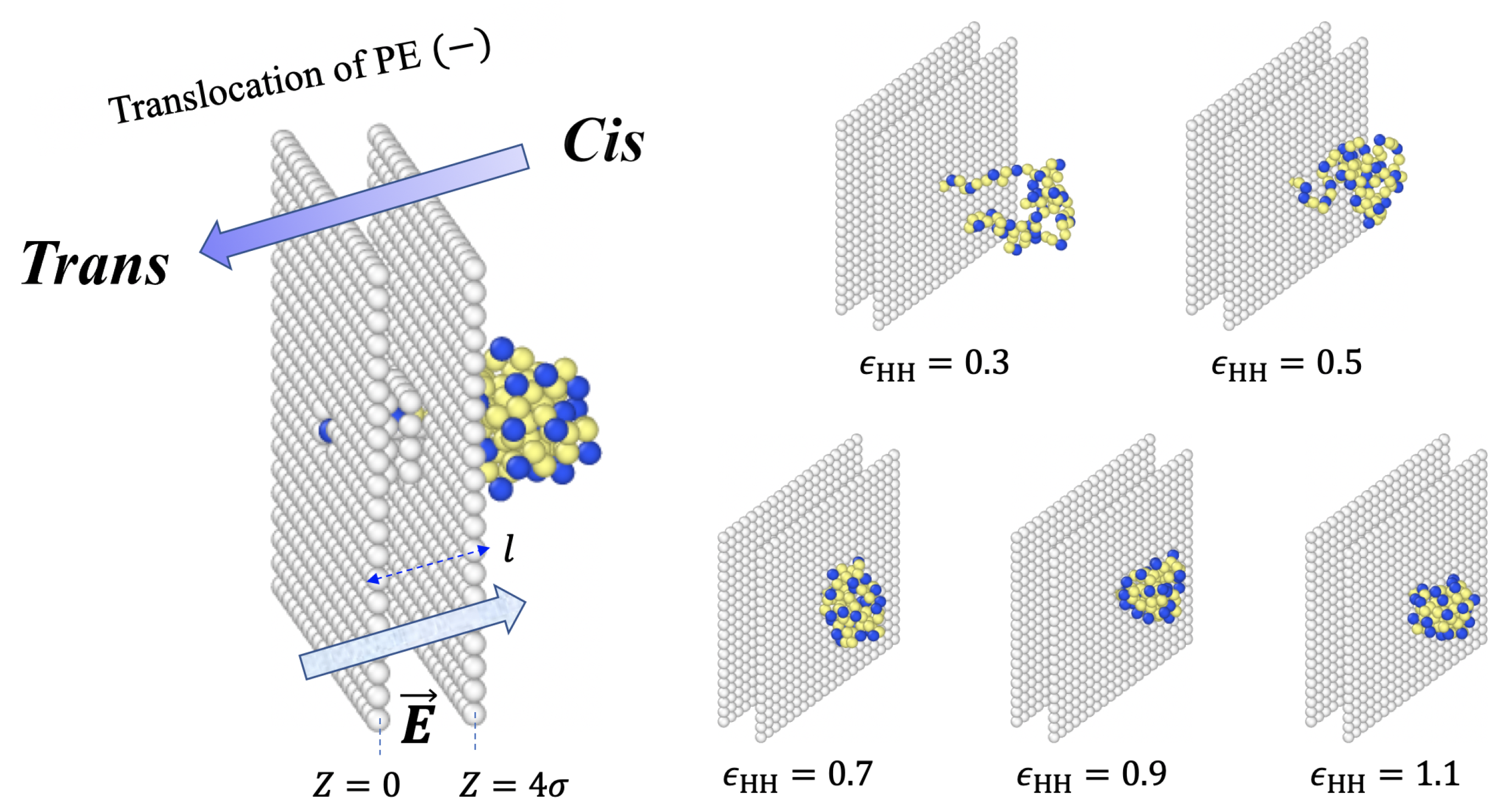
Simulation Model
3. Results
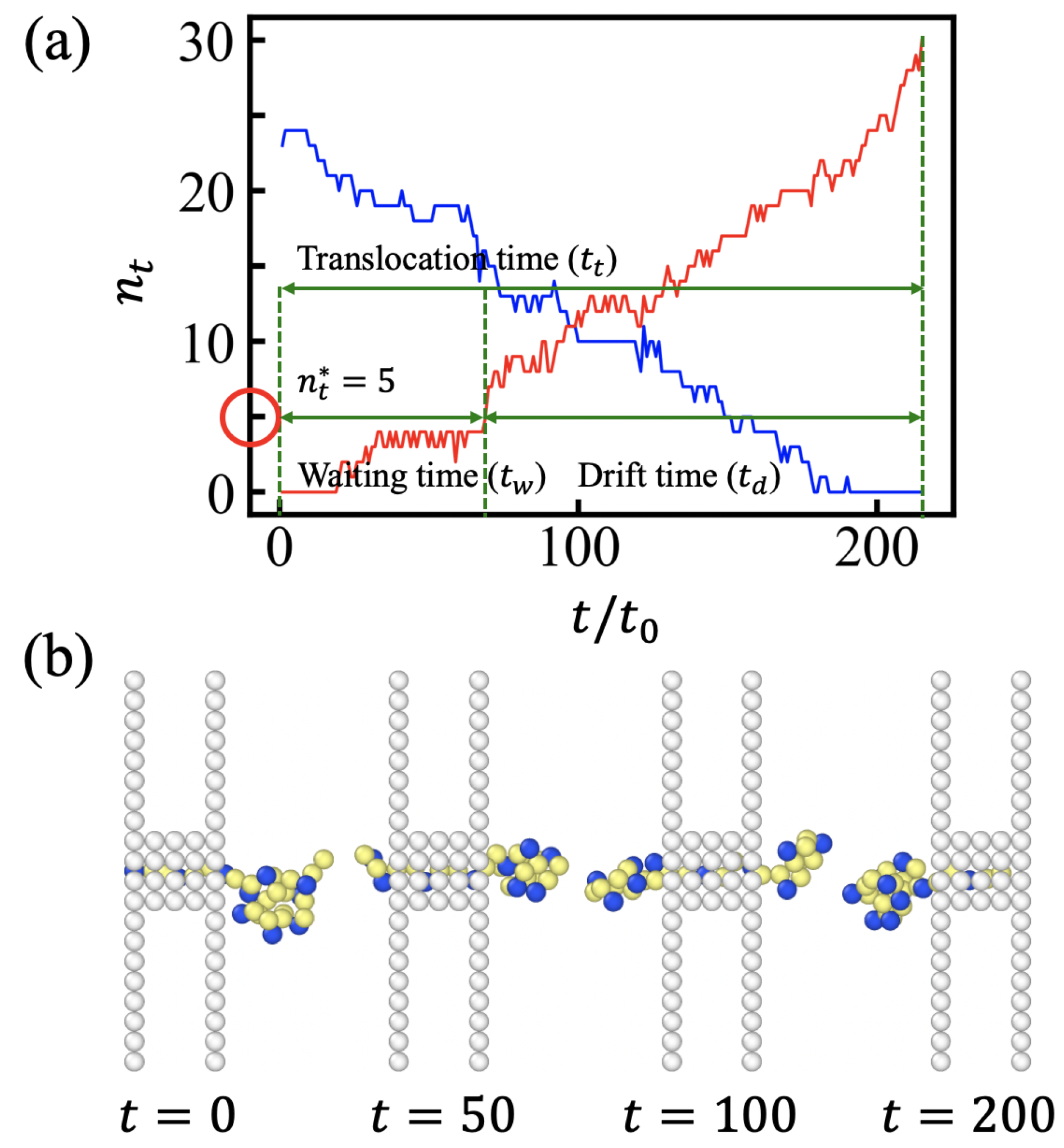
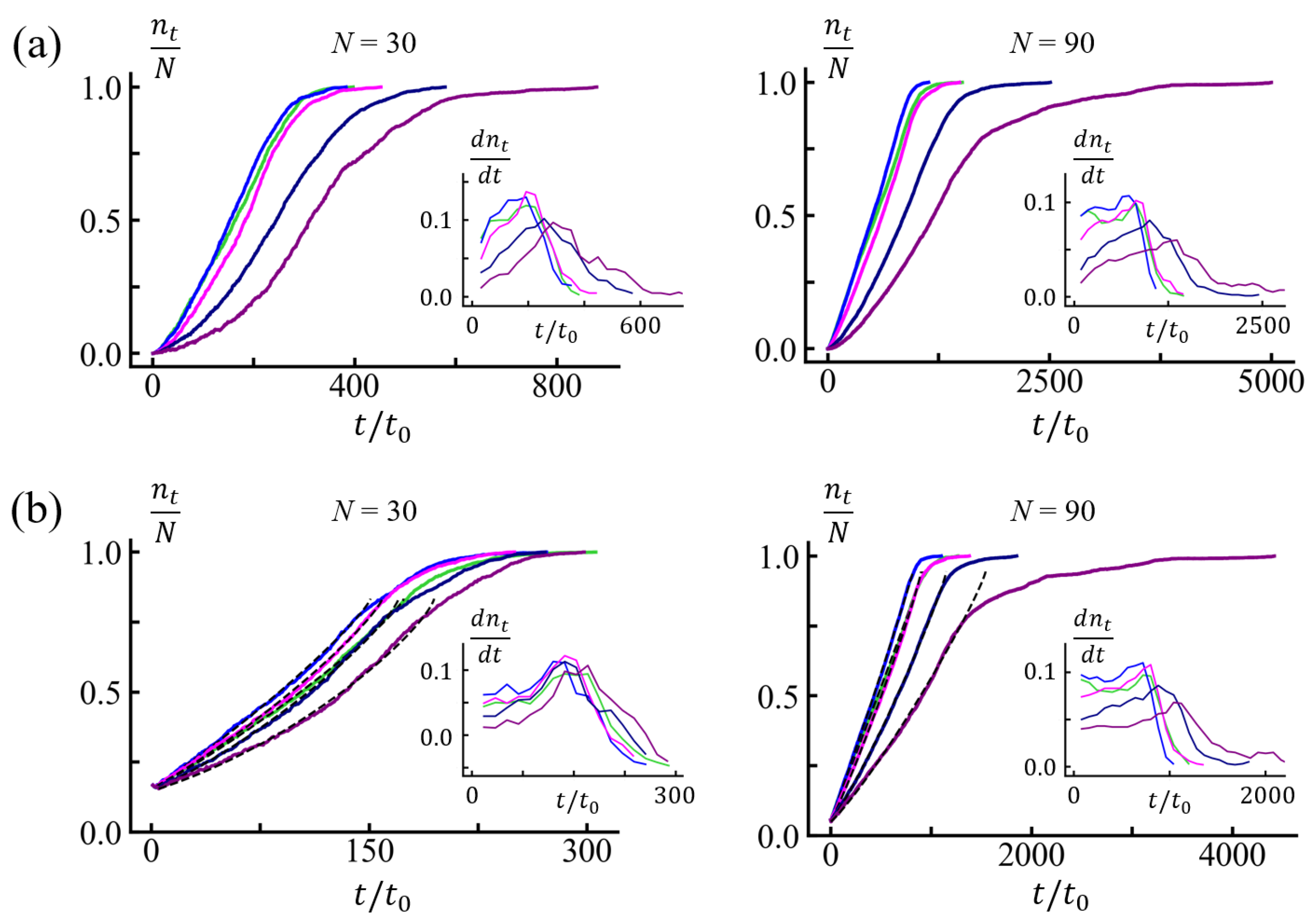
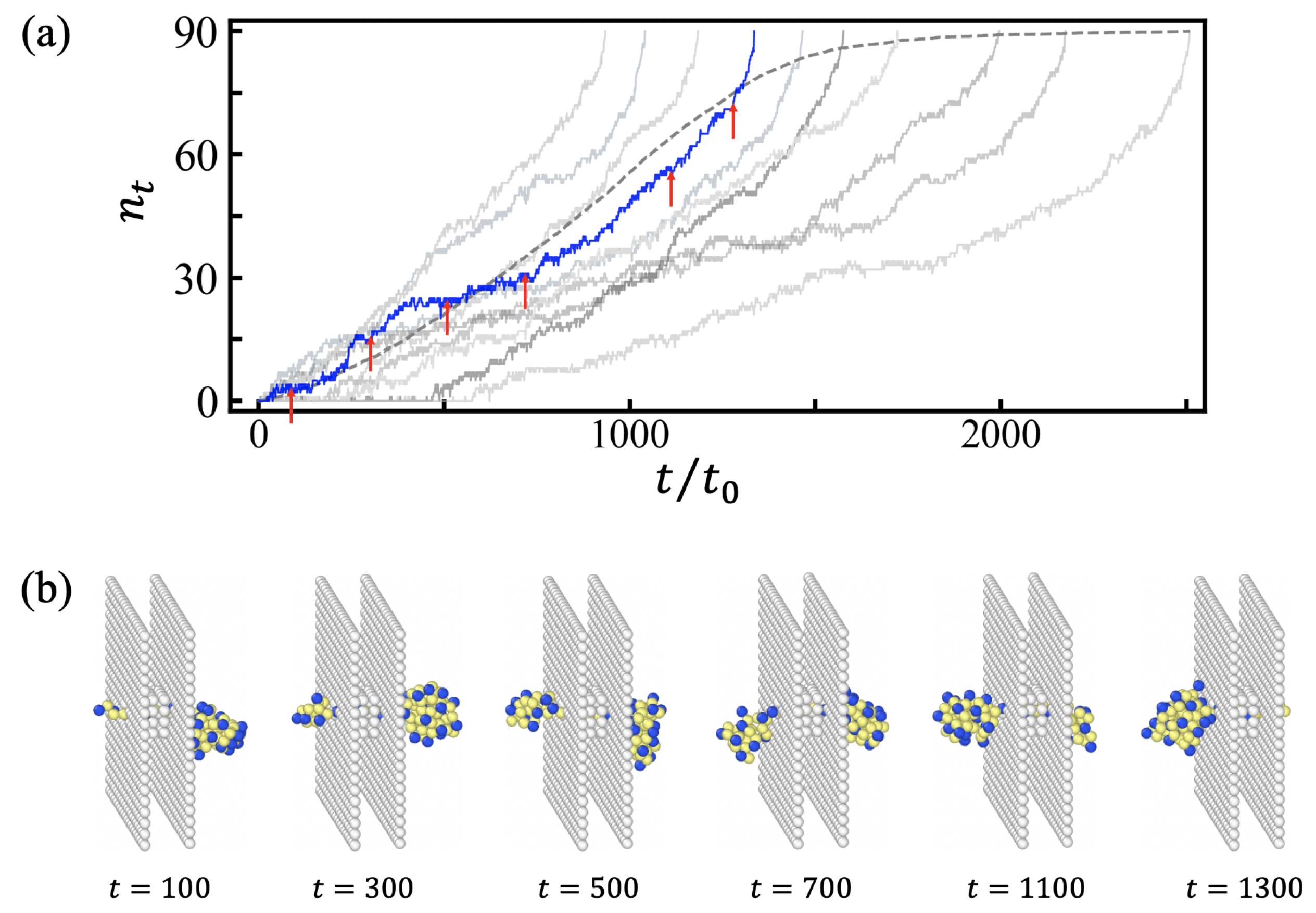
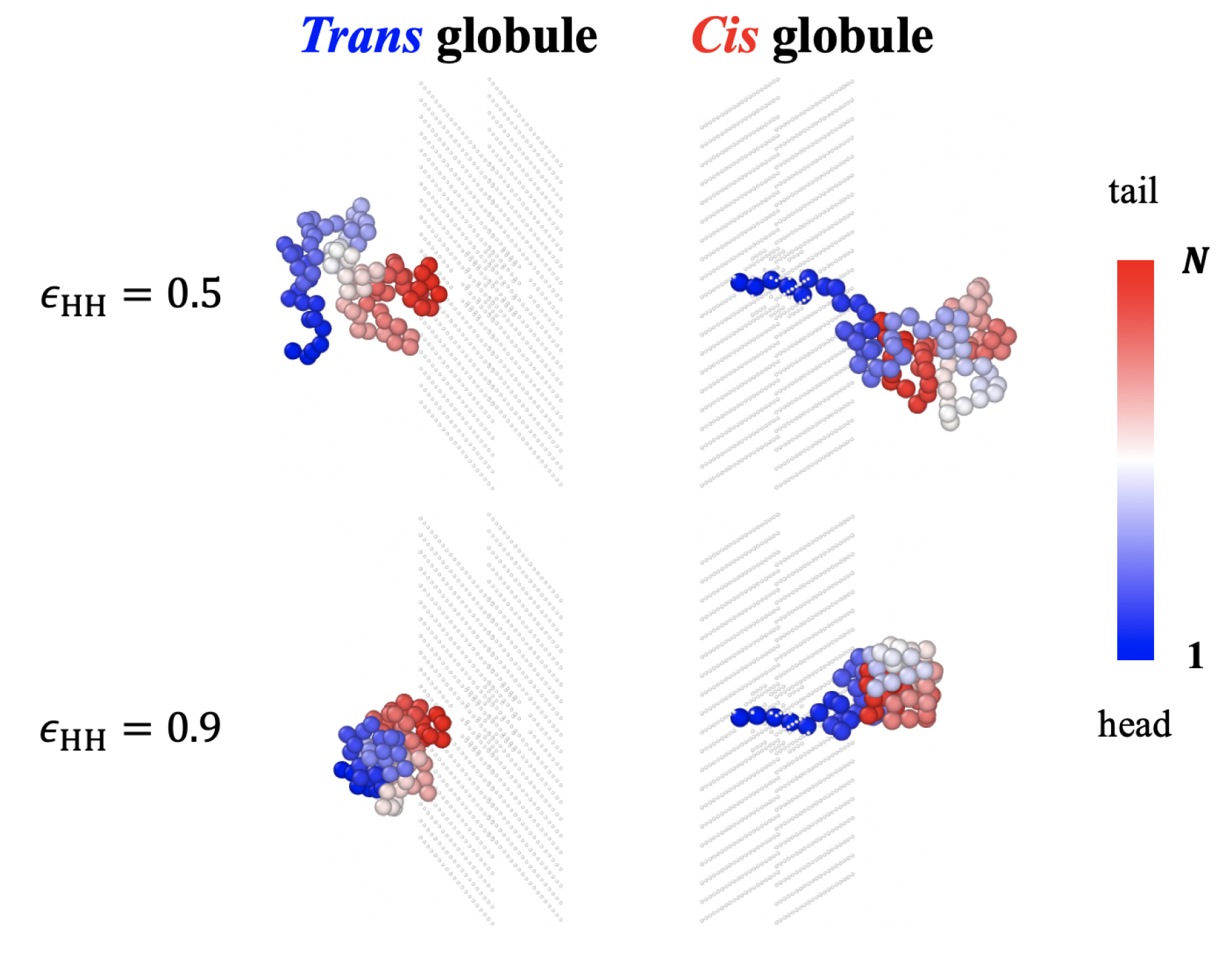
3.1. Translocation Times and Their Dispersions: (100) Sequences
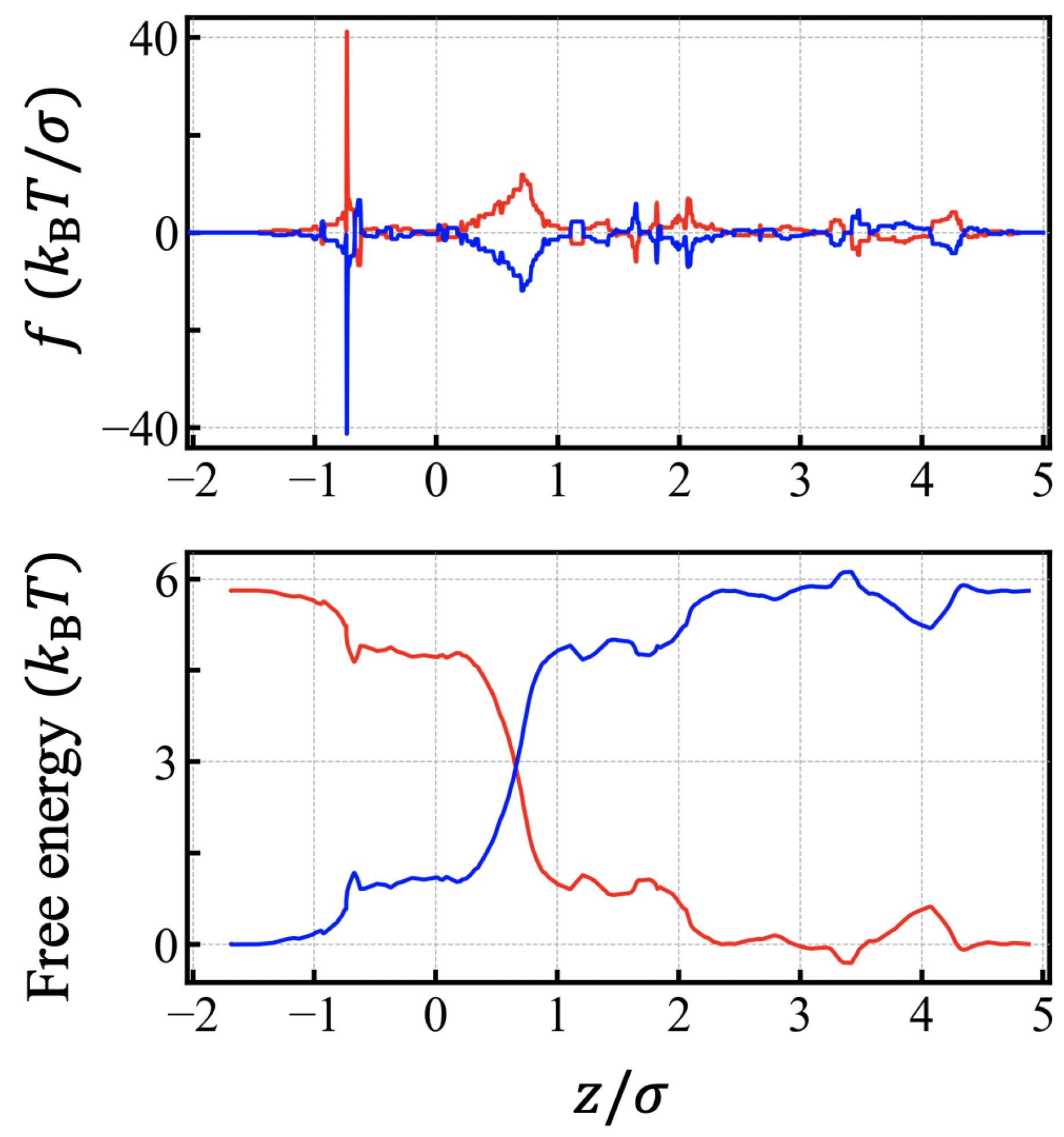
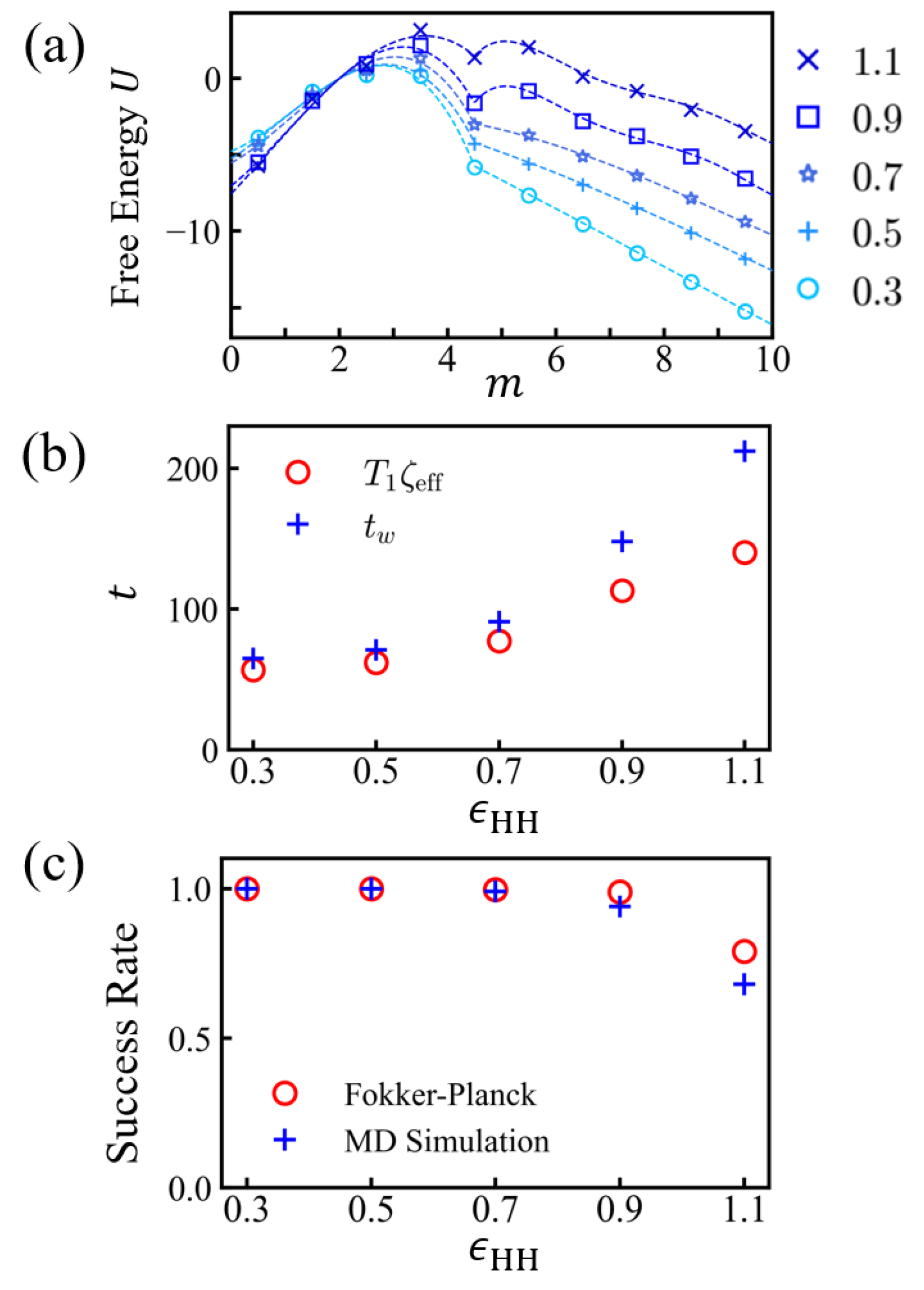
3.2. Free Energy Profiles and the Solution of Fokker-Planck Equation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
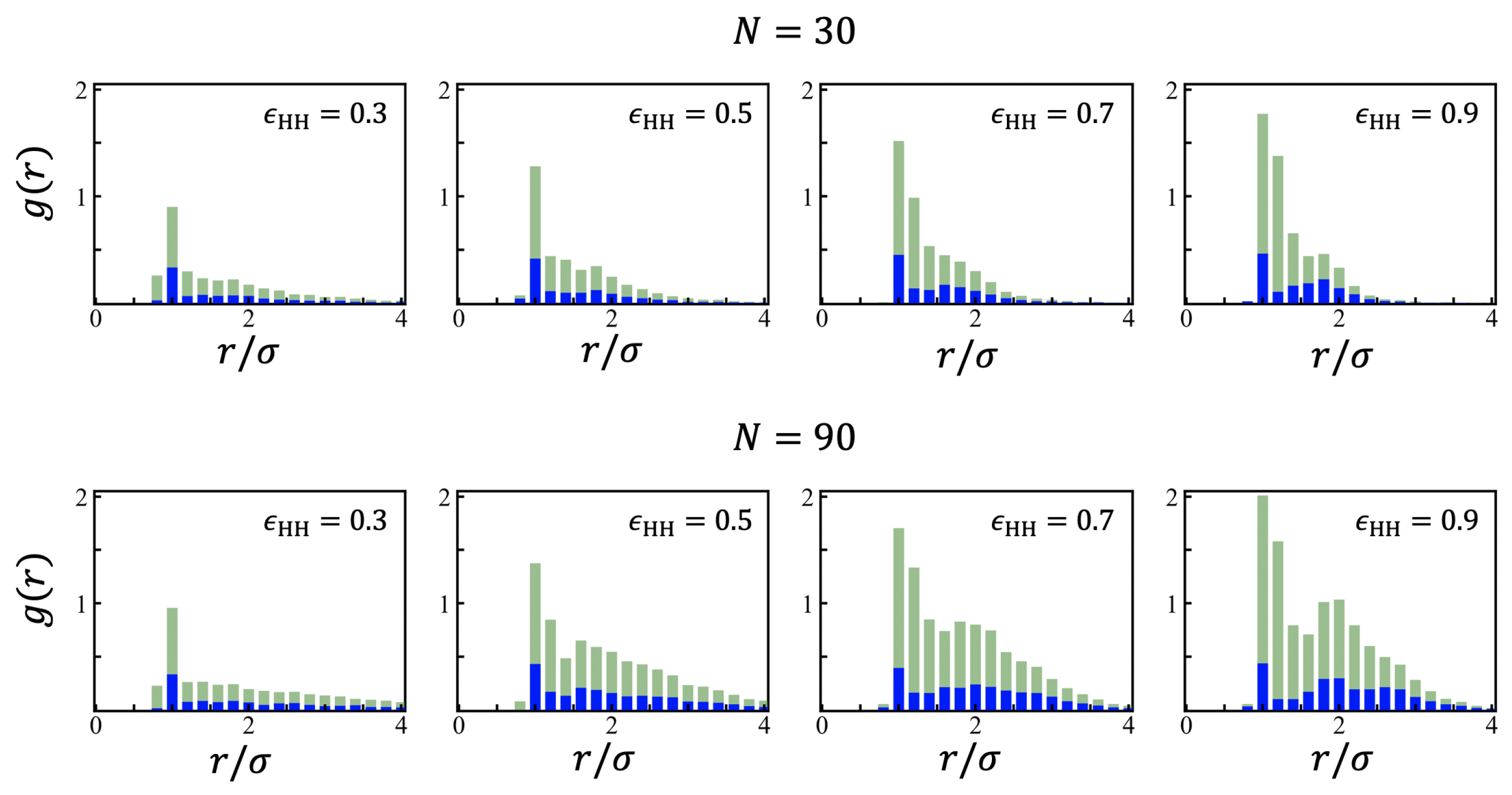
Appendix A. Density Correlations

Appendix B. Fokker–Planck Equation for the Translocation
References
- Song, L.; Hobaugh, M.R.; Shustak, C.; Cheley, S.; Bayley, H.; Gouaux, J.E. Structure of staphylococcal α-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore. Science 1996, 274, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payet, L.; Martinho, M.; Merstorf, C.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Pelta, J.; Viasnoff, V.; Auvray, L.; Muthukumar, M.; Mathé, J. Temperature effect on ionic current and ssDNA transport through nanopores. Biophys. J. 2015, 109, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumar, M. Polymer Translocation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Palyulin, V.V.; Ala-Nissila, T.; Metzler, R. Polymer translocation: The first two decades and the recent diversification. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9016–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, P.-Y. Polyelectrolyte threading through a nanopore. Polymers 2016, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowghanian, P.; Grosberg, A.-Y. Electrophoretic capture of a DNA chain into a nanopore. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 042722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrynin, A.V.; Rubinstein, M.; Obukhov, S.P. Cascade of transitions of polyelectrolytes in poor solvents. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 2974–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, M.-K.; Lee, N.-K.; Jung, Y.; Joanny, J.F.; Johner, A. Structure of a hydrophobic polyelectrolyte chain with a random sequence. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 6275–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Jung, Y.; Johner, A.; Joanny, J.F. Globular Polyampholytes: Structure and Translocation. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 2394–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarkova, E.; Vlugt, T.J.; Lee, N.-K. Stretching a heteropolymer. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 114904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, K. Theory for the folding and stability of globular proteins. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-Y.; Yuan, J.M.; Mou, C.-Y. Mechanical unfolding and refolding of proteins: An off-lattice model study. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 021905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeycutt, J.; Thirumalai, D. Metastability of the folded states of globular proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3526–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, S.Y.; Im, W.; Roux, B. Ion Permeation through the α-Hemolysin Channel: Theoretical Studies Based on Brownian Dynamics and Poisson-Nernst-Plank Electrodiffusion Theory. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-B.; Chae, M.-K.; Park, J.-M.; Johner, A.; Lee, N.-K. Translocation, rejection and trapping of polyampholytes. Polymers 2022, 14, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.T.A.; Muthukumar, M. Polymer translocation through α-hemolysin pore with tunable polymer-pore electrostatic interaction. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 07B607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.-J.; Muthukumar, M. Electrostatic control of polymer translocation speed through α-hemolysin protein pore. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9132–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, I.; Muthukumar, M. Effects of nanopore charge decorations on the translocation dynamics of DNA. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, P.-Y. Conformation change, tension propagation and drift-diffusion properties of polyelectrolyte in nanopore translocation. Polymers 2016, 8, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Sung, B.J. Effects of solvent quality and non-equilibrium conformations on polymer translocation. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 244907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Yang, W.; Jin, X.; Liao, Q. Unforced translocation of a polymer chain through a nanopore: The solvent effect. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 05B610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.N.; Uversky, V.N. Pre-molten, wet, and dry molten globules En Route Funct. State Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Dobrynin, A.V. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Polyelectrolyte- Polyampholyte Complexes. Effect of Solvent Quality and Salt Concentration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24652–24665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, P.-Y.; Chen, W.-Y. A general theory of polymer ejection tested in a quasi two-dimensional space. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-C.; Hsiao, P.-Y. Scaling behaviors of a polymer ejected from a cavity through a small pore. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 267801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-K.; Abrams, C.F.; Johner, A.; Obukhov, S. Arrested swelling of highly entangled polymer globules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 225504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-K.; Abrams, C.F.; Johner, A.; Obukhov, S. Swelling dynamics of collapsed polymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, P.-Y. Translocation of Charged Polymers through a Nanopore in Monovalent and Divalent Salt Solutions: A Scaling Study Exploring over the Entire Driving Force Regimes. Polymeres 2018, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, P.-Y. Translocation of a Polyelectrolyte through a Nanopore in the Presence of Trivalent Counterions: A Comparison with the Cases in Monovalent and Divalent Salt Solutions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 19805–19819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosberg, A.Y.; Nechaev, S.K.; Shakhnovich, E.I. The role of topological constraints in the kinetics of collapse of macromolecules. J. Phys. 1988, 49, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosberg, A.Y.; Nechaev, S.; Tamm, M.; Vasilyev, O. How long does it take to pull an ideal polymer into a small hole? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 228105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.; Weysser, F.; Meyer, H.; Farago, J.; Fuchs, M.; Baschnagel, J. Simulated glass-forming polymer melts: Dynamic scattering functions, chain length effects, and mode-coupling theory analysis. Eur. Phys. J. E 2015, 38, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschnagel, J.; Kriuchevskyi, I.; Helfferich, J.; Ruscher, C.; Meyer, H.; Benzerara, O.; Farago, J.; Wittmer, J. Polymer Glasses; Roth, C.B., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, R.; Klafter, J. When translocation dynamics becomes anomalous. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 2776–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbeldam, J.; Rostiashvili, V.; Milchev, A.; Vilgis, T.A. Forced translocation of a polymer: Dynamical scaling versus molecular dynamics simulation. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 041801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C. Stochastic Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Lianwei, L. Flow-induced translocation and conformational transition of polymer chains through nanochannels: Recent advances and future perspectives. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 9773–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, K.; Chen, S.B. Flow-Induced Translocation of Star Polymers through a Nanopore. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 7919–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
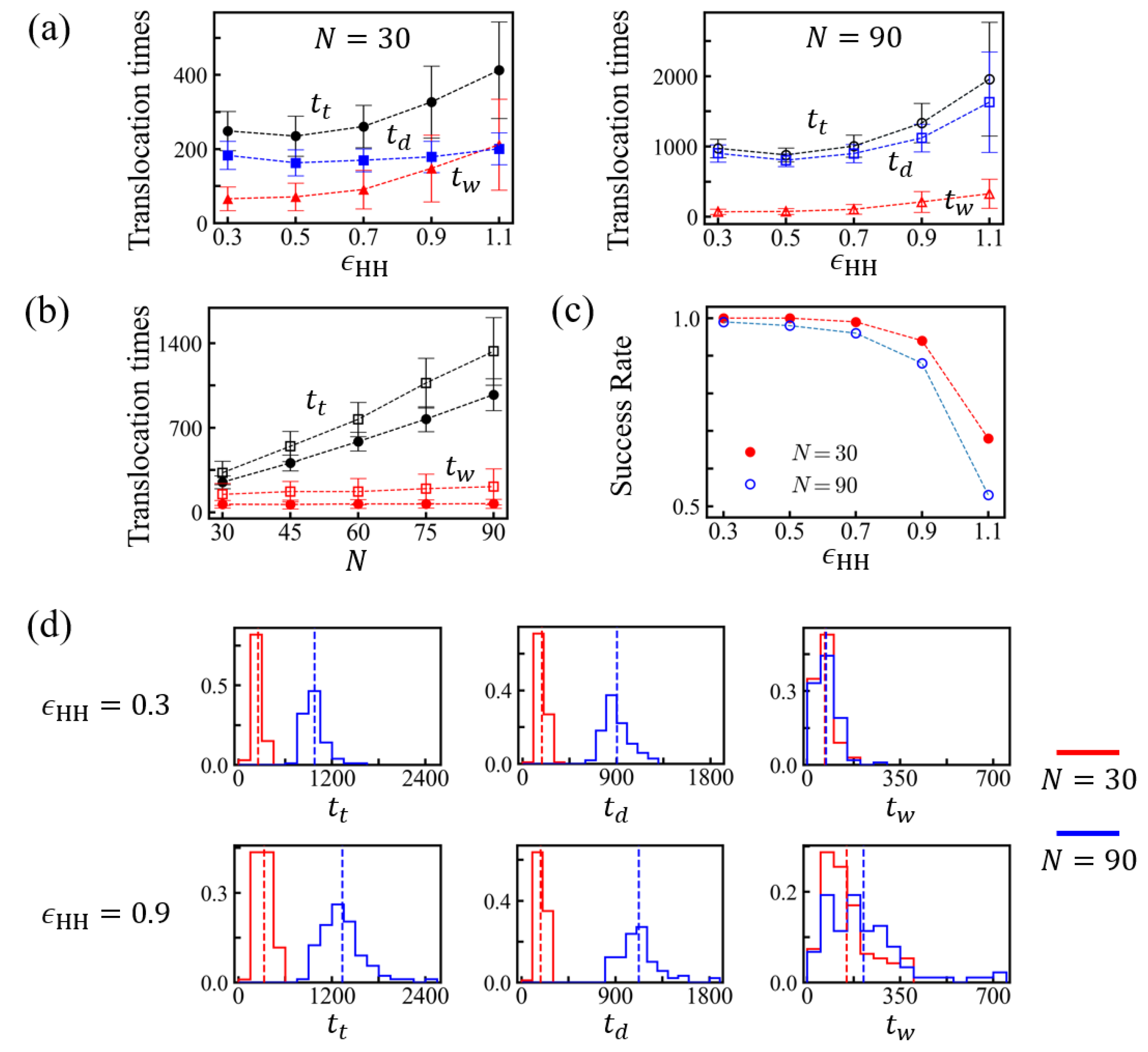
| (a) N = 30 | ||||
| success rate | ||||
| 0.1 | 1.00 | 260 ± 50 | 71 ± 29 | 189 ± 39 |
| 0.3 | 1.00 | 251 ± 41 | 65 ± 28 | 187 ± 39 |
| 0.5 | 1.00 | 235 ± 54 | 71 ± 37 | 163 ± 35 |
| 0.7 | 0.99 | 261 ± 57 | 91 ± 52 | 170 ± 31 |
| 0.9 | 0.94 | 327 ± 97 | 148 ± 90 | 179 ± 42 |
| 1.1 | 0.68 | 413 ± 130 | 212 ± 123 | 201 ± 43 |
| (b) N = 90 | ||||
| success rate | ||||
| 0.1 | 1.00 | 1035 ± 144 | 69 ± 35 | 966 ± 134 |
| 0.3 | 0.99 | 974 ± 132 | 71 ± 38 | 903 ± 124 |
| 0.5 | 0.98 | 881 ± 100 | 76 ± 42 | 805 ± 91 |
| 0.7 | 0.96 | 1006 ± 157 | 106 ± 69 | 900 ± 130 |
| 0.9 | 0.88 | 1333 ± 280 | 212 ± 149 | 1121 ± 195 |
| 1.1 | 0.53 | 1959 ± 810 | 328 ± 207 | 1631 ± 714 |
| N = 30 | N = 90 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 20.0 (21.6) | 2.00 | 18.1 | 23.6 (24.1) | 0.2 | 23.0 |
| 0.5 | 17.4 (20.3) | 1.90 | 15.8 | 21.4 (22.4) | 0.5 | 20.5 |
| 0.7 | 18.8 (24.3) | 2.50 | 16.7 | 25.2 (27.2) | 1.7 | 22.5 |
| 0.9 | 20.6 (32.6) | 3.20 | 17.5 | 32.8 (38.3) | 2.1 | 28.5 |
| 1.1 | 24.9 (41.3) | 4.40 | 19.6 | 45.1 (53.0) | 2.2 | 38.0 |
| N | Success Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.94 | 327 ± 97 | 148 ± 90 | 179 ± 42 |
| 45 | 0.96 | 546 ±125 | 171 ± 84 | 376 ± 89 |
| 60 | 0.85 | 769 ± 142 | 171 ± 110 | 598 ± 111 |
| 75 | 0.83 | 1070 ± 205 | 195 ± 121 | 876 ± 168 |
| 90 | 0.88 | 1333 ± 280 | 212 ± 149 | 1121 ± 195 |
| 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (100) | 252 | 235 | 261 | 327 | 413 |
| (1) | (1) | (0.99) | (0.94) | (0.68) | |
| (010) | 232 | 225 | 244 | 263 | 338 |
| (0.88) | (0.89) | (0.78) | (0.79) | (0.57) | |
| (001) | 241 | 241 | 220 | 210 | 375 |
| (0.29) | (0.29) | (0.18) | (0.03) | (0.02) |
| 0.3 | −0.336 | 1.143 | 1.437 | −4.758 | 0 | 0 | 0.0022 | −0.025 | −1.819 | −5.742 |
| 0.5 | −0.251 | 0.676 | 2.275 | −5,246 | 0 | 0 | 0.003 | −0.070 | −1.232 | −4.194 |
| 0.7 | −0.287 | 0.986 | 1.939 | −5.526 | 0 | 0 | 0.011 | −0.174 | −0.705 | −2.959 |
| 0.9 | −0.282 | 0.908 | 2.831 | −7.038 | 0.0202 | −0.3336 | 1.9913 | −5.1950 | 4.2521 | −1.565 |
| 1.1 | −0.160 | 0.333 | 3.753 | −7.558 | 0.0196 | −0.3228 | 1.9213 | −4.9750 | 3.9750 | 1.479 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Lee, N.-K.; Chae, M.-K.; Johner, A.; Park, J.-M. Translocation of Hydrophobic Polyelectrolytes under Electrical Field: Molecular Dynamics Study. Polymers 2023, 15, 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112550
Kim S, Lee N-K, Chae M-K, Johner A, Park J-M. Translocation of Hydrophobic Polyelectrolytes under Electrical Field: Molecular Dynamics Study. Polymers. 2023; 15(11):2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112550
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seowon, Nam-Kyung Lee, Min-Kyung Chae, Albert Johner, and Jeong-Man Park. 2023. "Translocation of Hydrophobic Polyelectrolytes under Electrical Field: Molecular Dynamics Study" Polymers 15, no. 11: 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112550
APA StyleKim, S., Lee, N.-K., Chae, M.-K., Johner, A., & Park, J.-M. (2023). Translocation of Hydrophobic Polyelectrolytes under Electrical Field: Molecular Dynamics Study. Polymers, 15(11), 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112550