pH-Induced 3D Printable Chitosan Hydrogels for Soft Actuation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
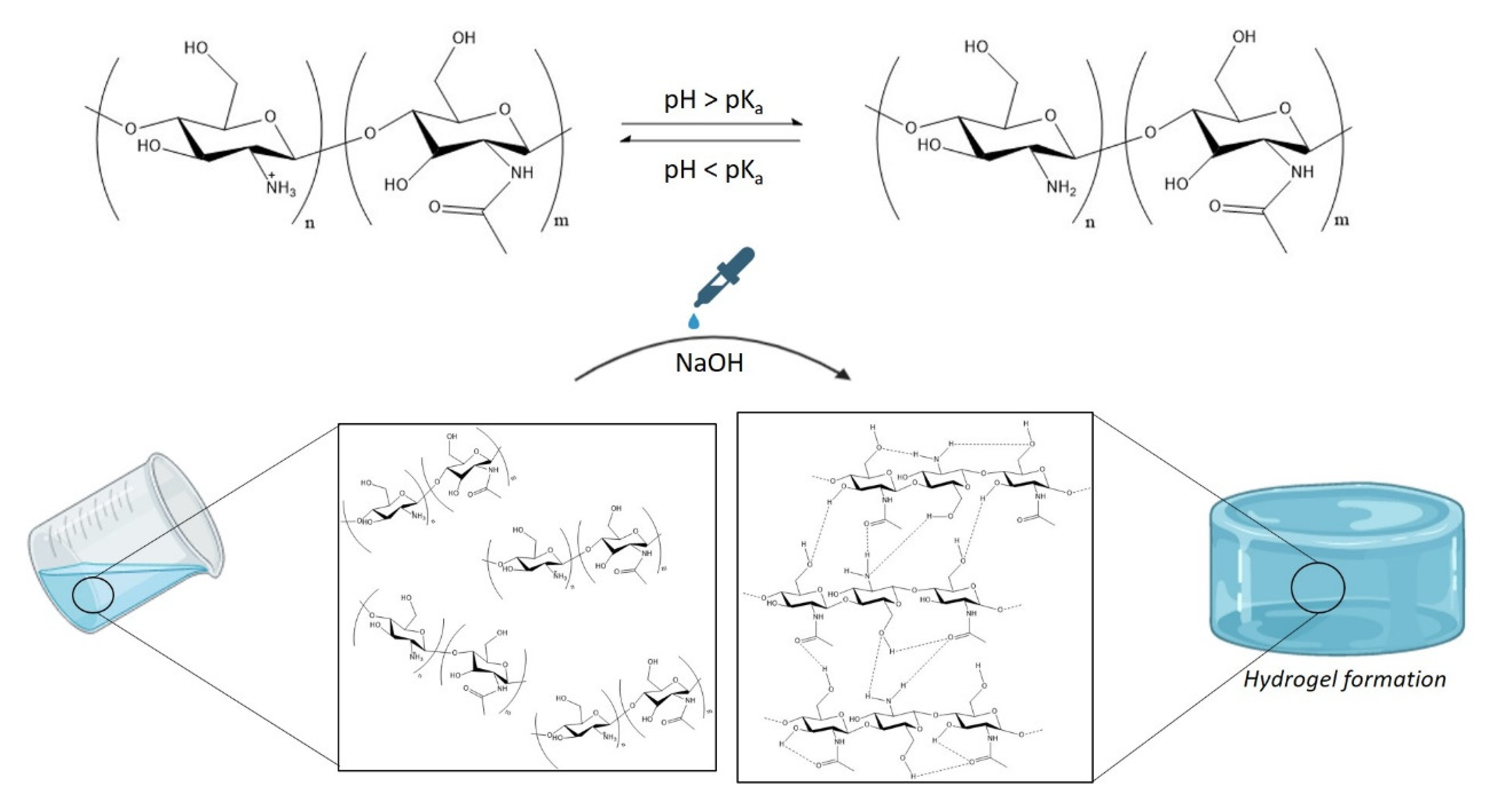
2.2.1. Hydrogel Synthesis and Printability
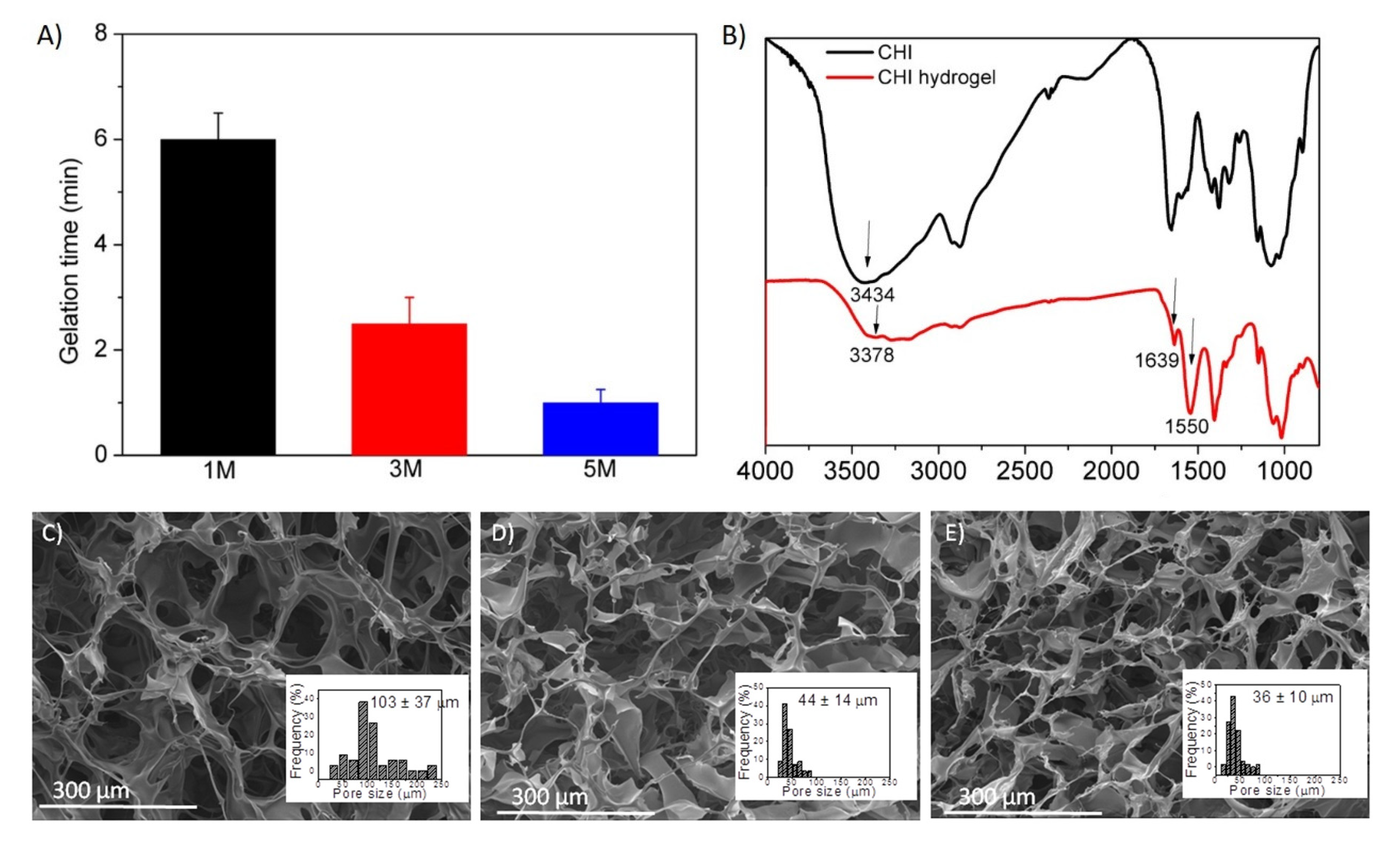
Gelation Time
2.2.2. Physico-Chemical Characterization
Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Morphological Characterization
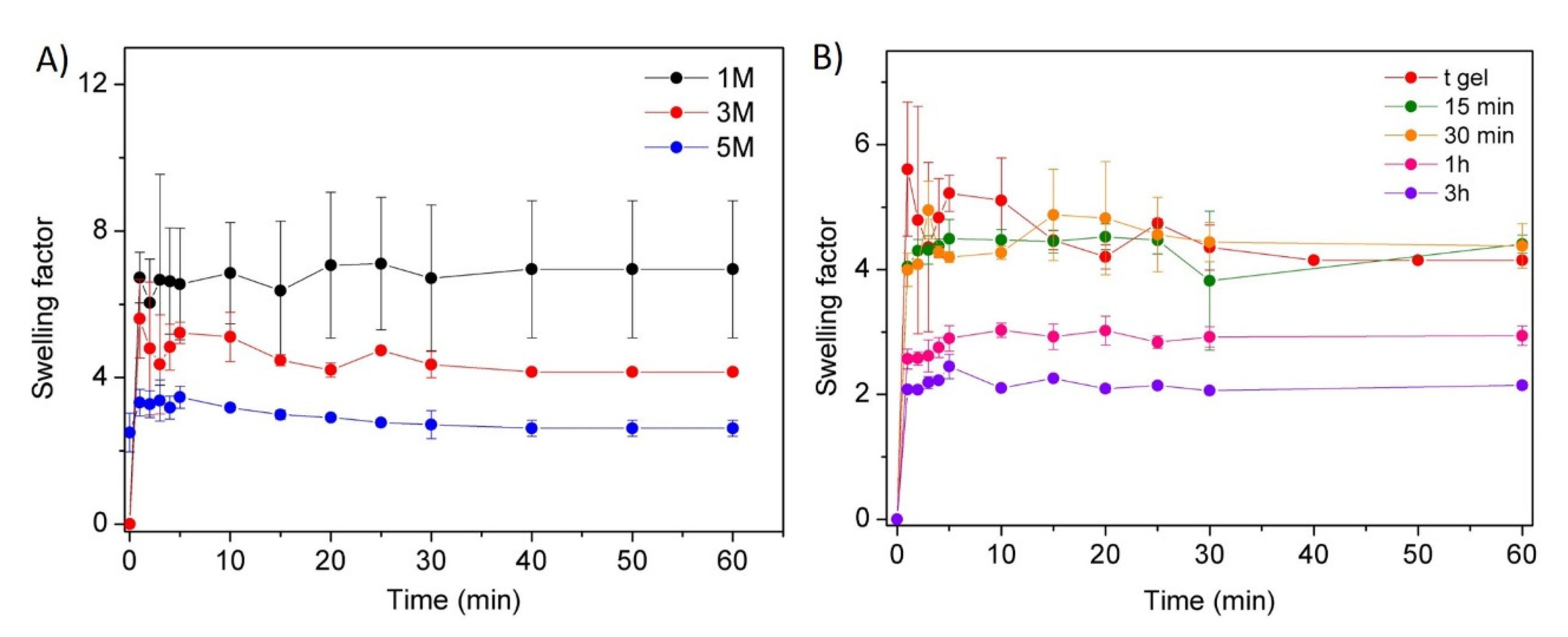
In Vitro Swelling
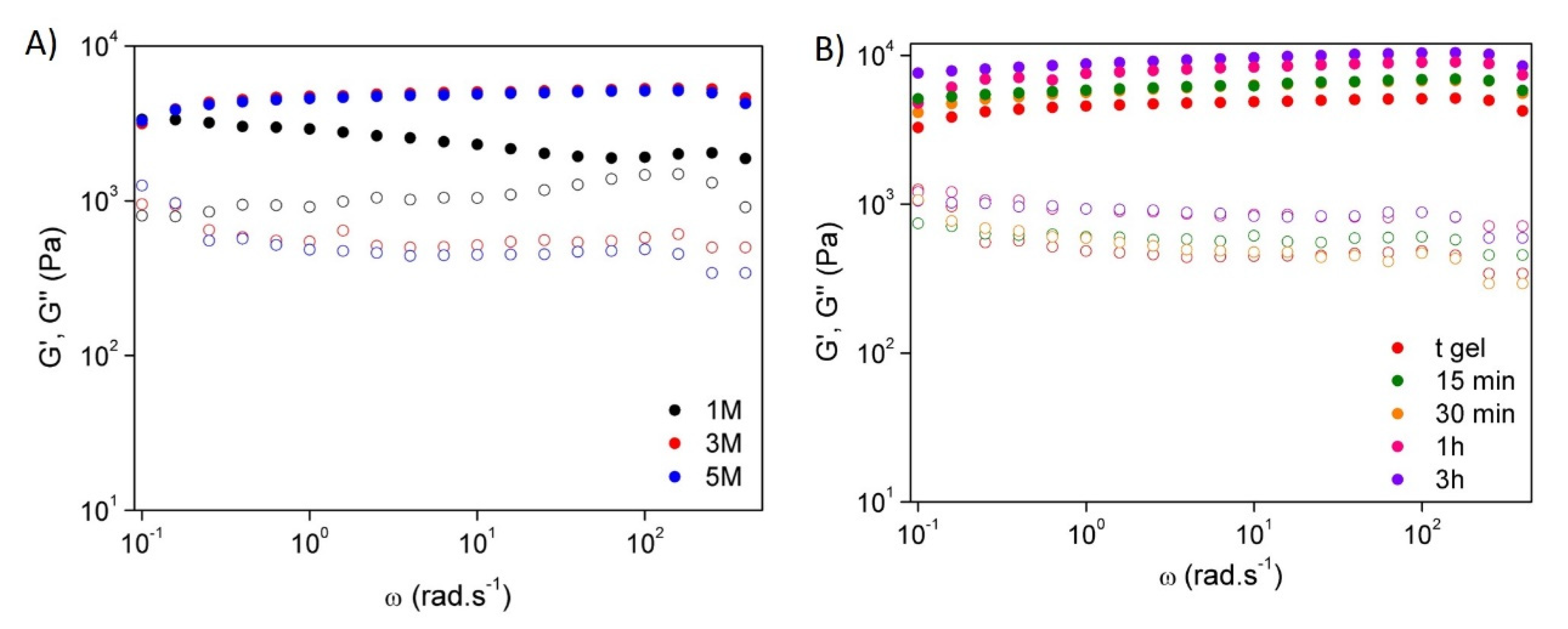
Rheology
Compressive Stress–Strain Tests
2.2.3. Functional Characterization
In Vitro Hydrolytic and Enzymatic Biodegradation
In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
Actuator Bending Response
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Swelling of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
3.2. Mechanical and Rheological Properties
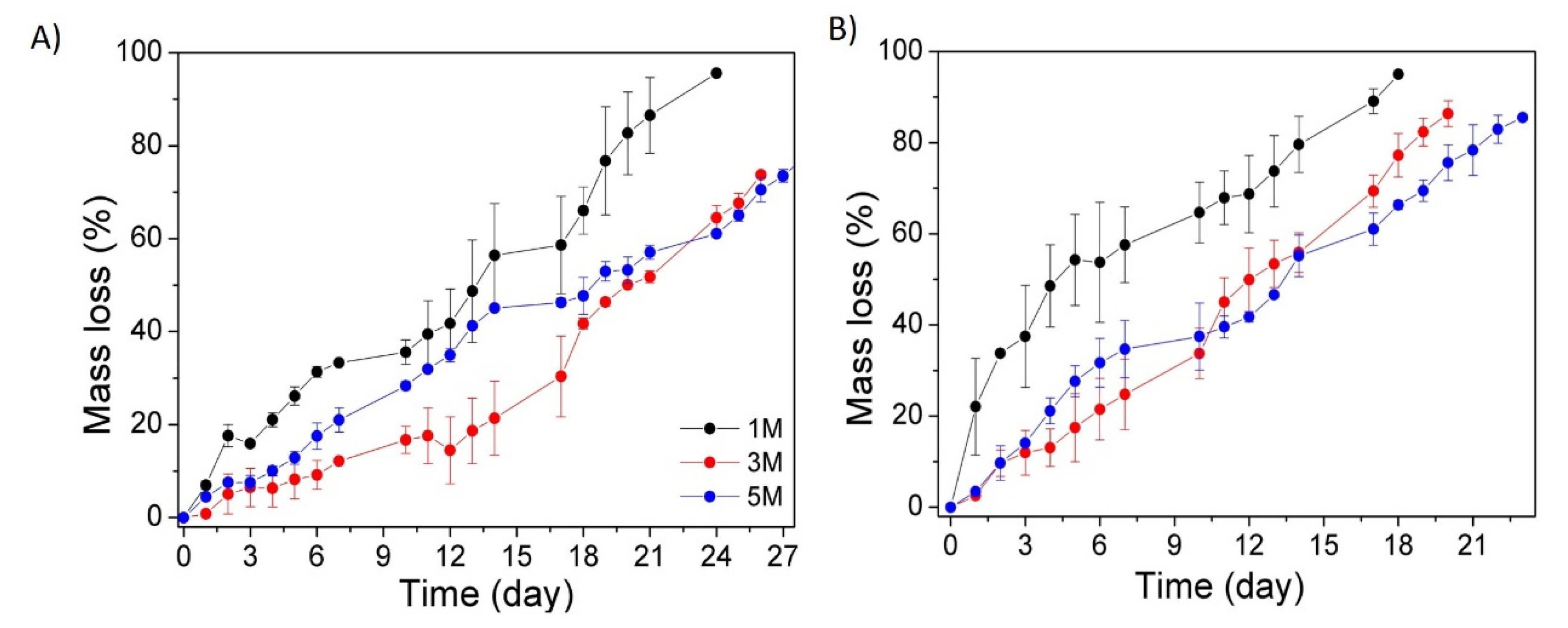
3.3. In Vitro Hydrolytic and Enzymatic Biodegradation
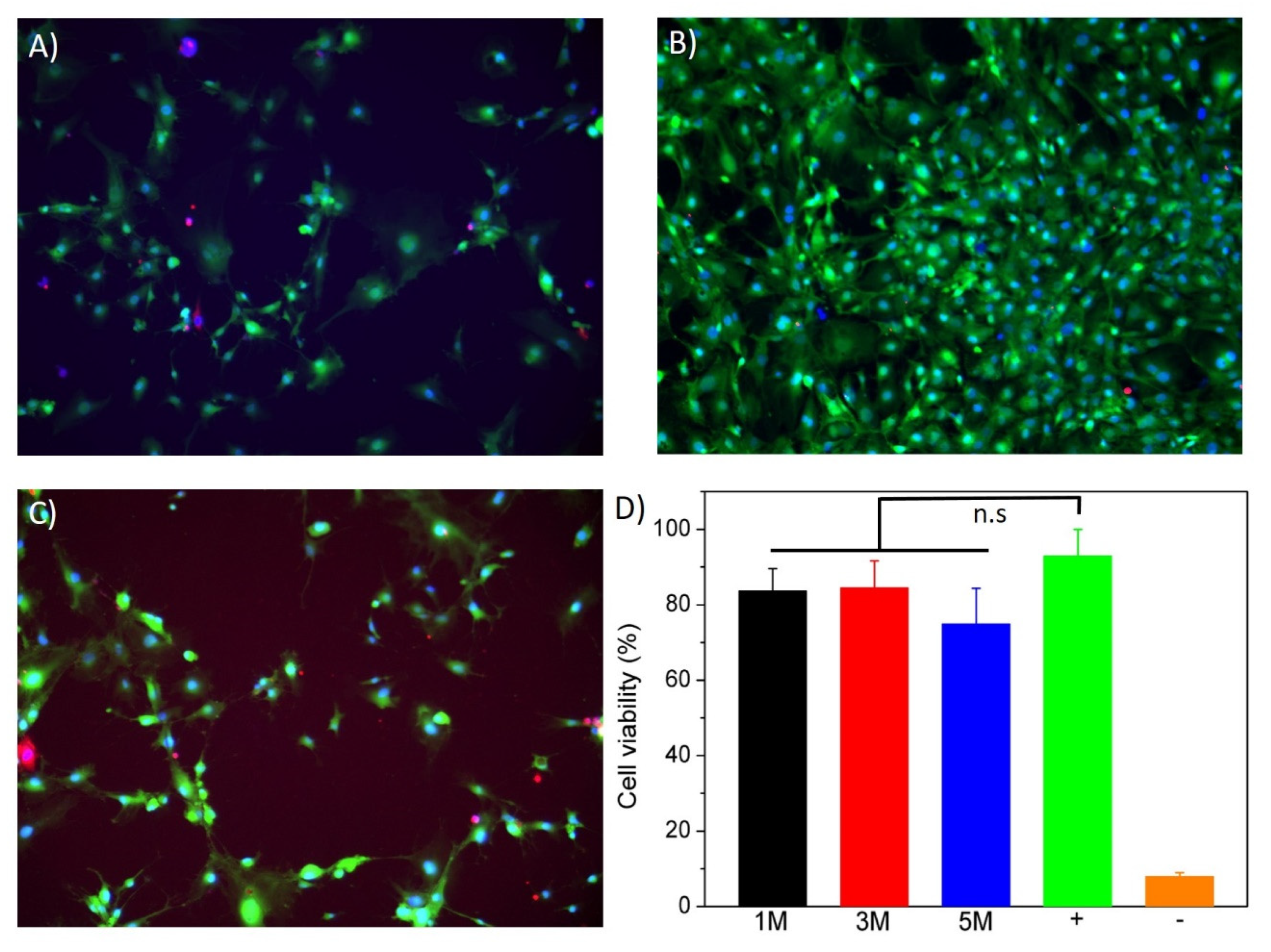
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
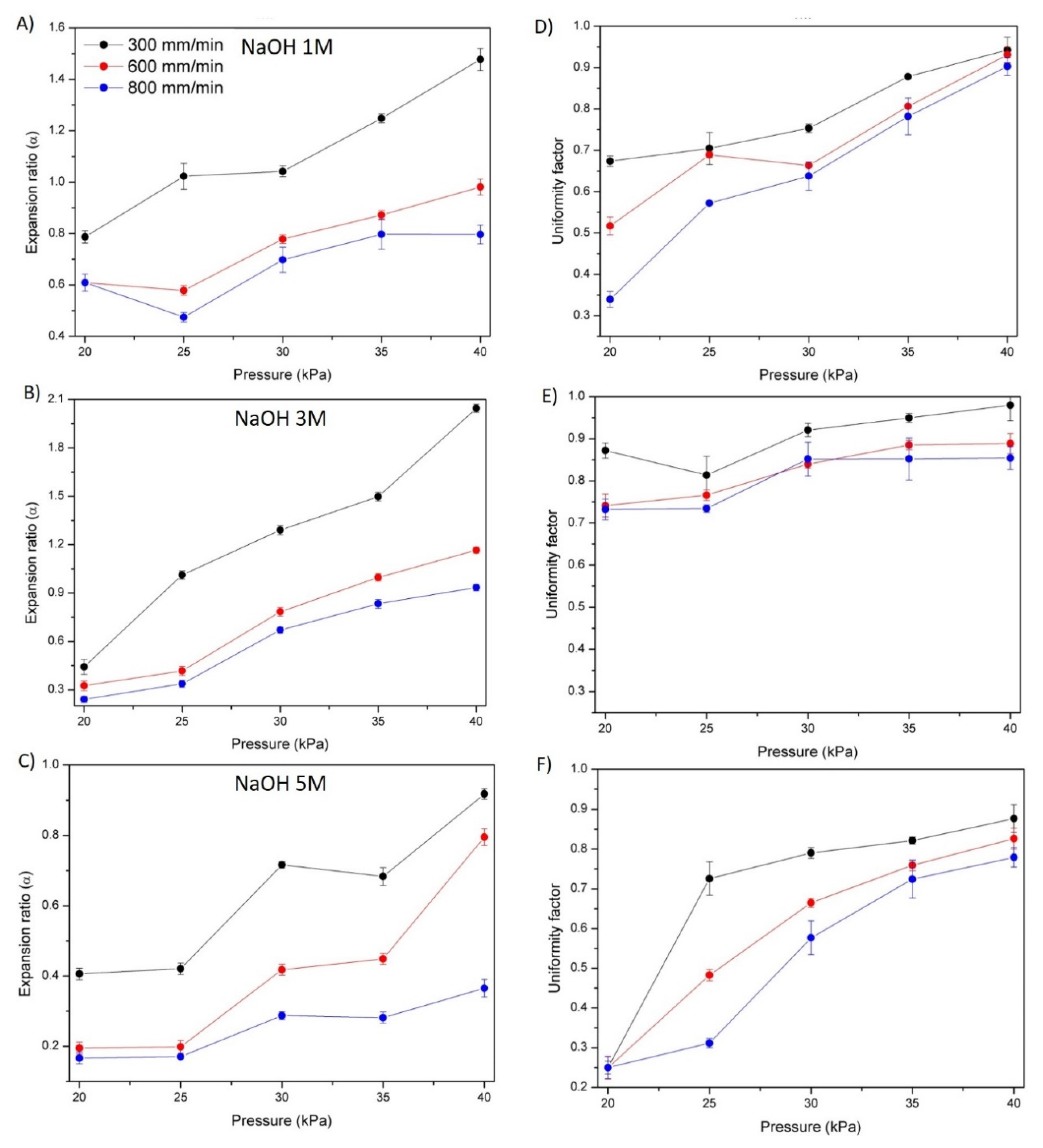
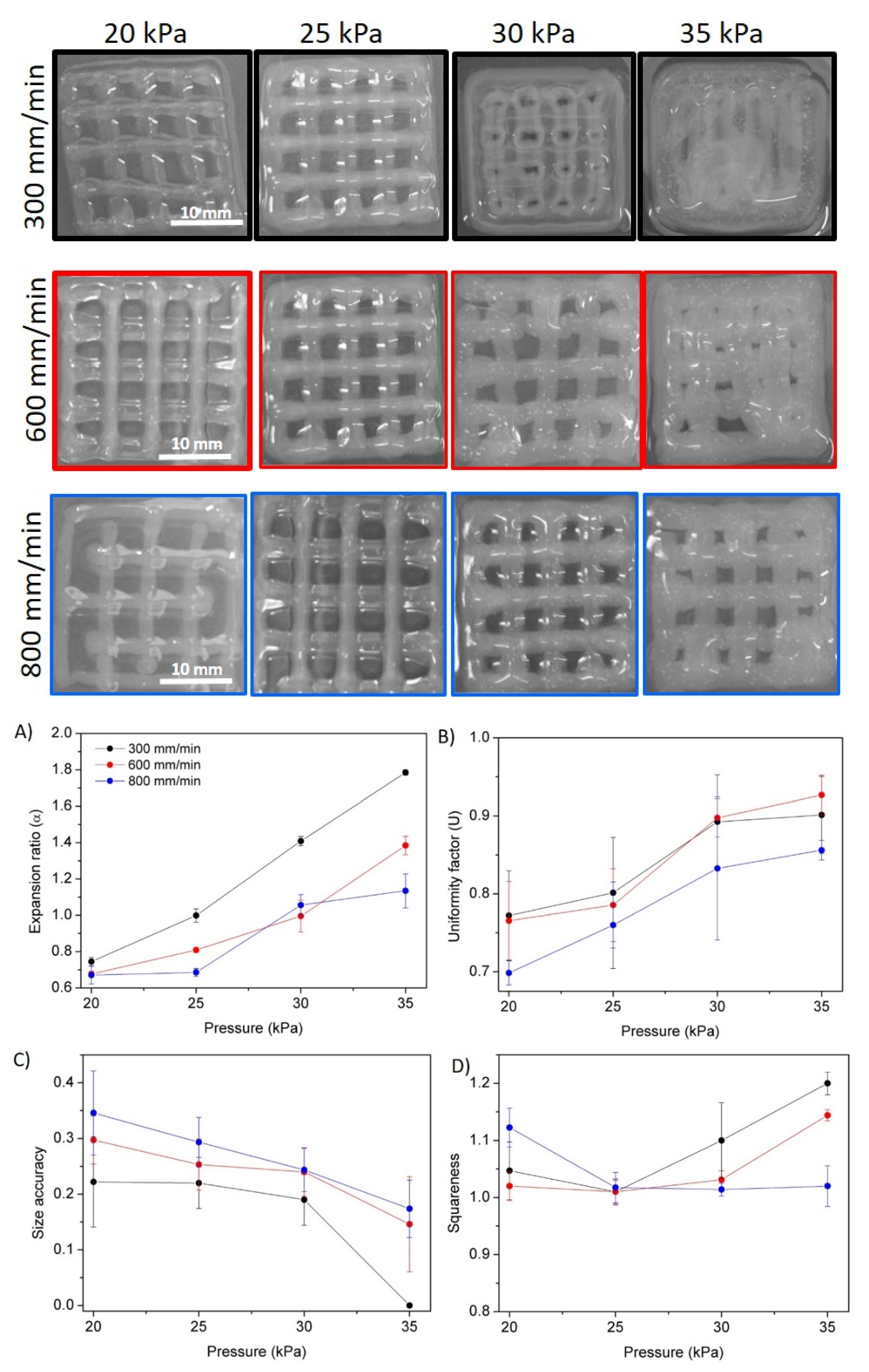
3.5. Hydrogel Printability
3.6. Bending Actuator
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Cao, B.; Jiang, L.; Hou, Y.; Chang, J. Fabrication of Multiple-Layered Hydrogel Scaffolds with Elaborate Structure and Good Mechanical Properties via 3D Printing and Ionic Reinforcement. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18338–18350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, A.V.; Khorsand, B.; Geary, S.M.; Salem, A.K. 3D Printing of Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1742–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Q.; Dong, H.; Su, J.; Han, J.; Song, B.; Wei, Q.; Shi, Y. A Review of 3D Printing Technology for Medical Applications. Engineering 2018, 4, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowska, A.; Jeong, B.; Jasionowski, M. Injectable gels for tissue engineering. Anat. Rec. 2001, 263, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Schacht, E. Biopolymer-Based Hydrogels as Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1387–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, S.; Layland, S.L.; Schenke-Layland, K. ECM and ECM-like materials—Biomaterials for applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Romain, C.; Williams, C.K. Sustainable polymers from renewable resources. Nature 2016, 540, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champeau, M.; Heinze, D.A.; Viana, T.N.; de Souza, E.R.; Chinellato, A.C.; Titotto, S. 4D Printing of Hydrogels: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinathan, J.; Noh, I. Recent trends in bioinks for 3D printing. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collado-González, M.; Espinosa, Y.G.; Goycoolea, F.M. Interaction between Chitosan and Mucin: Fundamentals and applications. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Strand, S.P.; Vårum, K.M.; Draget, K.I.; Nordgård, C.T. Chitosan: Gels and interfacial properties. Polymers 2015, 7, 552–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergonzi, C.; Di Natale, A.; Zimetti, F.; Marchi, C.; Bianchera, A.; Bernini, F.; Silvestri, M.; Bettini, R.; Elviri, L. Study of 3D-printed chitosan scaffold features after different post-printing gelation processes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kean, T.J.; Thanou, M. Utility of Chitosan for 3D Printing and Bioprinting. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews, 1st ed.; Crini, G., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 154–196. ISBN 9783319267760. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabi, M.; McConnell, M.; Cabral, J.; Ali, M.A. Chitosan hydrogels in 3D printing for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.Z.; Zhu, K.J. The influence of multivalent phosphate structure on the properties of ionically cross-linked chitosan films for controlled drug release. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 54, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiz-Fernández, S.; Barroso, N.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Silván, U.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. 3D printable self-healing hyaluronic acid/chitosan polycomplex hydrogels with drug release capability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, H.N.; Wu, B.M. Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials. J. Biol. Eng. 2015, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, C.R.; Serra, T.; Oliveira, M.I.; Planell, J.A.; Barbosa, M.A.; Navarro, M. Impact of 3-D printed PLA- and chitosan-based scaffolds on human monocyte/macrophage responses: Unraveling the effect of 3-D structures on inflammation. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Therriault, D.; Heuzey, M.C. Processing and Properties of Chitosan Inks for 3D Printing of Hydrogel Microstructures. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Allardyce, B.J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Zhao, Y.; Dilley, R.J.; Redmond, S.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. 3D Printing of Silk Particle-Reinforced Chitosan Hydrogel Structures and Their Properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3036–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharian, A.; Kaynak, A.; Khoo, S.Y.; Kouzani, A.Z. Polyelectrolyte Soft Actuators: 3D Printed Chitosan and Cast Gelatin. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 5, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, M.; Law, N.; Webb, B.; Macrae, R.A.; Liew, L.J.; Sercombe, T.B.; Dilley, R.J.; Doyle, B.J. Mechanical behaviour of alginate-gelatin hydrogels for 3D bioprinting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 79, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Yao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W. Effect of bioink properties on printability and cell viability for 3D bioplotting of embryonic stem cells. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 035020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.M.; Simmons, K.L.; Gutowska, A.; Jeong, B. Sol-Gel transition temperature of PLGA-g-PEG aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Verena Kaynig, E.F.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; Cardona, A. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An overview of chitosan nanoparticles and its application in non-parenteral drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora Boza, A.; Wlodarczyk-Biegun, M.K.; Del Campo, A.; Vázquez-Lasal, B.; San Román, J. Chitosan-based inks: 3D printing and bioprinting strategies to improve shape fidelity, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility of 3D scaffolds. Biomecánica 2019, 27, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Peppas, N.A.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.K.; Anderson, H.E.; Lamas, J.; Barret, S.; Cantu, T.; Zauscher, S.; Brittain, W.J.; Betancourt, T. Enhanced Release of Molecules upon Ultraviolet (UV) Light Irradiation from Photoresponsive Hydrogels Prepared from Bifunctional Azobenzene and Four-Arm Poly(ethylene glycol). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30071–30080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gan, H.; Meng, Z.; Gu, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Sun, W.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Effects of genipin cross-linking of chitosan hydrogels on cellular adhesion and viability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalevée, G.; Sudre, G.; Montembault, A.; Meadows, J.; Malaise, S.; Crépet, A.; David, L.; Delair, T. Polyelectrolyte complexes via desalting mixtures of hyaluronic acid and chitosan—Physicochemical study and structural analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, F.; Abdekhodaie, M.J.; Ramazani, S.A.A. Gelation time and degradation rate of chitosan-based injectable hydrogel. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.D.; Hexiu, J.; Patel, D.K.; Ganguly, K.; Lim, K.T. 3D-printed bioactive and biodegradable hydrogel scaffolds of alginate/gelatin/cellulose nanocrystals for tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z. The chitosan hydrogels: From structure to function. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 17162–17180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Shin, S.R.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.I. Electrical response characterization of chitosan/polyacrylonitrile hydrogel in NaCl solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Chitosan-based electroactive hydrogel. Polymer 2008, 49, 5520–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Du, X. Intelligent Polymer-Based Bioinspired Actuators: From Monofunction to Multifunction. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maiz-Fernández, S.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Silván, U.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. pH-Induced 3D Printable Chitosan Hydrogels for Soft Actuation. Polymers 2022, 14, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030650
Maiz-Fernández S, Pérez-Álvarez L, Silván U, Vilas-Vilela JL, Lanceros-Méndez S. pH-Induced 3D Printable Chitosan Hydrogels for Soft Actuation. Polymers. 2022; 14(3):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030650
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaiz-Fernández, Sheila, Leyre Pérez-Álvarez, Unai Silván, José Luis Vilas-Vilela, and Senentxu Lanceros-Méndez. 2022. "pH-Induced 3D Printable Chitosan Hydrogels for Soft Actuation" Polymers 14, no. 3: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030650
APA StyleMaiz-Fernández, S., Pérez-Álvarez, L., Silván, U., Vilas-Vilela, J. L., & Lanceros-Méndez, S. (2022). pH-Induced 3D Printable Chitosan Hydrogels for Soft Actuation. Polymers, 14(3), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030650







